Distributed Computing Group
|
|
|
- Vanessa Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Distributed Computing Group HS 2009 Prof. Dr. Roger Wattenhofer, Thomas Locher, Remo Meier, Benjamin Sigg Assigned: December 11, 2009 Discussion: none Distributed Systems Theory exercise 6 1 ALock2 Have a look at the source code below. It is a modified version of the ALock (slides 8/42 ff). public c l a s s ALock2 implements Lock { int [ ] f l a g s = {true, true, false,..., f a l s e ; AtomicInteger next = new AtomicInteger ( 0 ) ; ThreadLocal<Integer > myslot ; public void l o c k ( ) { myslot = next. getandincrement ( ) ; while (! f l a g s [ myslot % n ] ) { f l a g s [ myslot % n ] = f a l s e ; public void unlock ( ) { f l a g s [ ( myslot+2) % n ] = true ; a) What was the intention of the author of ALock2? b) Will ALock2 work properly? Why (not)? c) Give an idea how to repair ALock2. Hint: don t bother about performance. Solution a) The author wants that two processes can acquire the lock simultaneously. 1
2 b) The lock is seriously flawed. An example shows how the lock will fail: Assume there are n processes, all processes try to acquire the lock. The first two processes (p 1, p 2 ) get the lock, the others have to wait. Process p 1 keeps the lock a very long time, while p 2 releases the lock almost immediately. Afterwards every second process (p 4, p 6,...) acquires and releases the lock. One half of all process are waiting on the lock (p 3, p 5,...), the others continues to work (p 4, p 6,...). If the working process now start to acquire the lock again, then they wait in slots that are already in use. c) A solution would be to increase the size of the array to 2 n. With this size there are simply not enough processes to wrap around too early. Or we mark any occupied slot. If a process tries to obtain an occupied slot, it just tries again with the next slot. Unfortunately one process could still block all the other processes, and FIFO (first in, first out) is still not guaranteed. In a second step one could make the unlock method more intelligent: instead of jumping two slots, the next slot is first checked. If there is a process waiting there, then this process gets the lock. If the process there already acquired the lock, the next but one slot gets the lock. We can use a lock to protect the unlock method against race conditions. // some simple lock, e. g. a spin l o c k Lock somelock =... void unlock ( ) { somelock. l o c k ( ) ; i f ( f l a g s [ ( myslot+1) % n ] ){ // the next s l o t a l r e a d y has a c q uired the l o c k f l a g s [ ( myslot+2) % n ] = true ; // the next s l o t did not a l r e a d y a c q u i r e the l o c k f l a g s [ ( myslot+1) % n ] = true ; somelock. unlock ( ) ; 2 MCS Queue Lock See slides 8/56 ff. a) A developer suggests to add an abort flag to each node: if a process no longer wants to wait it sets this abort flag to true. If a process unlocks the lock, it may see the abort flag of the next node, jump over the aborted node, and check the successor s successor node. Modify the basic algorithm to support aborts. Optional: sketch a proof for your answer. Hint: Be aware of race-conditions! 2
3 b) Assuming many processes may abort concurrently, does your answer from a) still work? Explain why. If it does not work: modify your algorithm to allow concurrent aborts. Optional: sketch a proof for your answer. c) Instead of a locked and an aborted flag one could use an integer, and modify the integer with the CAS operation. What do you think about this idea? How is the algorithm affected? How is performance affected? d) The CLH lock (slide 8/49) is basically the same as an MCS lock. Conceptually the only difference is, that a process spins on the locked field of the predecessor node, not on its own node. What could be an advantage of CLH over MCS and what could be a disadvantage? Solution a) There is more than one solution, but we can solve this problem without using RMW registers or other locks. It is important to set and read the flags in the right order: The unlock method first sets locked, then reads aborted. The abort method on the other hand first sets aborted, then reads locked. This way if unlock and abort run in parallel, one of them must already have written its flag before the other can read it. In the worst case unlock is called twice for some process, but that is not a problem. Unlocking an already unlocked lock results in no action. public void unlock ( ) { i f (... missing s u c c e s s o r... )... wait for missing s u c c e s s o r qnode. next. locked = f a l s e ; i f ( qnode. next. aborted ){ i f (... qnode. next misses s u c c e s s o r... ){ i f (... r e a l l y no s u c c e s s o r... ) return ;... wait for missing s u c c e s s o r... qnode. next. next. locked = f a l s e ; public void abort ( ) { qnode. aborted = true ; i f (! qnode. locked ){ unlock ( ) ; 3
4 b) The solution of a) does not yet work for concurrent aborts. Making the unlock method recursive will help. public void unlock ( ) { unlock ( qnode ) ; private void unlock ( QNode qnode ){ // as b e f o r e... i f (... missing s u c c e s s o r... )... wait for missing s u c c e s s o r qnode. next. locked = f a l s e ; i f ( qnode. next. aborted ){ // wait f o r s u c c e s s o r o f qnode. next i f (... ){ unlock ( qnode. next ) ; c) There are four combinations of values the locked and aborted flag can have. We can easily encode these combinations in an integer. We would not need too worry about the order in which we read and write to the flags, as we could do this atomically. So the algorithm would get easier. We could also ensure that unlock is called only once. Depending on the benchmark this could increase the performance. On the other hand, a CAS operation is quite expensive and could decrease performance. d) - There could be problems with caches: spinning on a value that belongs to another process can introduce additional load on the bus, and thus slow down the entire application. + The implementation is much easier: when releasing the lock one has only to set its own locked flag to false. + Also aborting is easier: a blocked process could read the state of its predecessor. If the predecessor is aborted, then the successor can just remove the node from the queue, and continue reading values from its predecessor s predecessor. 3 Linked-Lists a) Write a proof for: a linked-list using fine-grained locking (as described on slide 8/76 ff) does not deadlock. b) Lazy synchronization: can the contains method return a false answer when searching for x because processes concurrently try to add and remove x? Make a reasonable assumption how add works. c) Optimistic synchronization: describe a scenario where a process is forever attempting to delete a node. 4
5 d) CAS: think about how to implement the add method. Write the interesting parts as pseudo-code. Solution a) We assign a number p to each node, according to their location in the list. The first node gets p = 1.0, the second node gets p = 2.0, etc... A new node gets the mean of its successor and predecessor, e.g. a new node between the first and second node would get the number p = ( )/2 = 1.5. We observe: the first lock a process acquires never causes problems. cannot acquire its first lock, then it cannot block any other process. If the process We further observer: if a process wants to acquire the lock of node n a with p a, then the process has not yet acquired the lock of a node n b width p b > p a. Assume a process locked n a and wants to lock n b, then p a < p b. If another process locked n b and wants to lock n a, then p a > p b. This is a contradiction, hence a deadlock never occurs. This argument can be repeated for any number and combination of locks and processes. b) The add method will lock the future predecessor and successor nodes as well. If add and remove work with the same item, they will never modify the list at the same time. As a result it is always clear whether an item is in the list or not, and contains will never fail. c) In order to delete a node, the validate method must return true. If we prevent validate from being true, the process will spin forever. For example we could have some process(es) which insert nodes between pred and curr. Since validate traverses the whole list, there is enough time to do the damage. d) A solution could be to remove marked nodes on the fly when encountered. The pseudo code below is such an example. // Node node : node i s a p o i n t e r to a Node o b j e c t. Node p o i n t e r ( Node node ){ return node & 1 ; boolean marked ( Node node ){ return ( node & 1) == 1 ; boolean add ( Item item ){ int key = item. hashcode ( ) ; r e t r y : while ( true ){ 5
6 // t r a v e r s e to p r e d e c e s s o r Node pred = head ; Node curr = p o i n t e r ( pred >next ) ; while ( curr >key < key ){ Node succ = curr >next ; // I f curr >next (== succ ) c o n t a i n s the marked f l a g, // curr i s marked as being removed. // We r e p l a c e i t on the f l y i f ( marked ( succ ) ) { // t r y to r e p l a c e pred. next. I f pred i s marked, // then t h i s CAS f a i l s. i f ( pred >next.cas( curr FALSE, succ FALSE ) ) { curr = succ ; succ = p o i n t e r ( curr ) >next ; // on f a i l u r e : j u s t s t a r t over continue : r e t r y ; pred = curr ; curr = succ ; // add item i f ( curr >key == key ){ return f a l s e ; Node node = new Node ( item ) ; node >next = c u r r FALSE; // t r y to i n s e r t the new node. I f CAS f a i l s, // the loop s t a r t s again. i f ( pred >next.cas( curr FALSE, node FALSE ) ) { return true ; 6
Computer Engineering II Solution to Exercise Sheet Chapter 10
 Distributed Computing FS 2017 Prof. R. Wattenhofer Computer Engineering II Solution to Exercise Sheet Chapter 10 Quiz 1 Quiz a) The AtomicBoolean utilizes an atomic version of getandset() implemented in
Distributed Computing FS 2017 Prof. R. Wattenhofer Computer Engineering II Solution to Exercise Sheet Chapter 10 Quiz 1 Quiz a) The AtomicBoolean utilizes an atomic version of getandset() implemented in
Locks Chapter 4. Overview. Introduction Spin Locks. Queue locks. Roger Wattenhofer. Test-and-Set & Test-and-Test-and-Set Backoff lock
 Locks Chapter 4 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test-and-Set & Test-and-Test-and-Set Backoff lock Queue locks 4/2 1 Introduction: From
Locks Chapter 4 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test-and-Set & Test-and-Test-and-Set Backoff lock Queue locks 4/2 1 Introduction: From
Locking. Part 2, Chapter 11. Roger Wattenhofer. ETH Zurich Distributed Computing
 Locking Part 2, Chapter 11 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test-and-Set & Test-and-Test-and-Set Backoff lock Queue locks 11/2 Introduction:
Locking Part 2, Chapter 11 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test-and-Set & Test-and-Test-and-Set Backoff lock Queue locks 11/2 Introduction:
Spin Locks and Contention. Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit
 Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Real world concurrency Understanding hardware architecture What is contention How to
Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Real world concurrency Understanding hardware architecture What is contention How to
Exam Distributed Systems
 Exam Distributed Systems 5 February 2010, 9:00am 12:00pm Part 2 Prof. R. Wattenhofer Family Name, First Name:..................................................... ETH Student ID Number:.....................................................
Exam Distributed Systems 5 February 2010, 9:00am 12:00pm Part 2 Prof. R. Wattenhofer Family Name, First Name:..................................................... ETH Student ID Number:.....................................................
Spin Locks and Contention. Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit
 Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Focus so far: Correctness and Progress Models Accurate (we never lied to you) But idealized
Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Focus so far: Correctness and Progress Models Accurate (we never lied to you) But idealized
Linked Lists: The Role of Locking. Erez Petrank Technion
 Linked Lists: The Role of Locking Erez Petrank Technion Why Data Structures? Concurrent Data Structures are building blocks Used as libraries Construction principles apply broadly This Lecture Designing
Linked Lists: The Role of Locking Erez Petrank Technion Why Data Structures? Concurrent Data Structures are building blocks Used as libraries Construction principles apply broadly This Lecture Designing
Spin Locks and Contention
 Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Modified for Software1 students by Lior Wolf and Mati Shomrat Kinds of Architectures
Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Modified for Software1 students by Lior Wolf and Mati Shomrat Kinds of Architectures
Transactional Memory: Architectural Support for Lock-Free Data Structures Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss ISCA 93
 Transactional Memory: Architectural Support for Lock-Free Data Structures Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss ISCA 93 What are lock-free data structures A shared data structure is lock-free if its operations
Transactional Memory: Architectural Support for Lock-Free Data Structures Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss ISCA 93 What are lock-free data structures A shared data structure is lock-free if its operations
Spin Locks and Contention. Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit
 Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Focus so far: Correctness and Progress Models Accurate (we never lied to you) But idealized
Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Focus so far: Correctness and Progress Models Accurate (we never lied to you) But idealized
Spin Locks and Contention. Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit
 Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Focus so far: Correctness Models Accurate (we never lied to you) But idealized (so we forgot to mention a
Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Focus so far: Correctness Models Accurate (we never lied to you) But idealized (so we forgot to mention a
Spin Locks and Contention. Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit
 Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit MIMD Architectures memory Shared Bus Memory Contention Communication Contention Communication
Spin Locks and Contention Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit MIMD Architectures memory Shared Bus Memory Contention Communication Contention Communication
Lecture 9: Multiprocessor OSs & Synchronization. CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown
 Lecture 9: Multiprocessor OSs & Synchronization CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown The Problem Coordinated management of shared resources Resources may be accessed by multiple threads Need to control
Lecture 9: Multiprocessor OSs & Synchronization CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown The Problem Coordinated management of shared resources Resources may be accessed by multiple threads Need to control
Lecture 21: Transactional Memory. Topics: consistency model recap, introduction to transactional memory
 Lecture 21: Transactional Memory Topics: consistency model recap, introduction to transactional memory 1 Example Programs Initially, A = B = 0 P1 P2 A = 1 B = 1 if (B == 0) if (A == 0) critical section
Lecture 21: Transactional Memory Topics: consistency model recap, introduction to transactional memory 1 Example Programs Initially, A = B = 0 P1 P2 A = 1 B = 1 if (B == 0) if (A == 0) critical section
Locking. Part 2, Chapter 7. Roger Wattenhofer. ETH Zurich Distributed Computing
 Locking Part 2, Chapter 7 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test-and-Set & Test-and-Test-and-Set Backoff lock Queue locks Concurrent
Locking Part 2, Chapter 7 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test-and-Set & Test-and-Test-and-Set Backoff lock Queue locks Concurrent
Linked Lists: Locking, Lock-Free, and Beyond. Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit
 Linked Lists: Locking, Lock-Free, and Beyond Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Concurrent Objects Adding threads should not lower throughput Contention
Linked Lists: Locking, Lock-Free, and Beyond Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Concurrent Objects Adding threads should not lower throughput Contention
Practice: Small Systems Part 2, Chapter 3
 Practice: Small Systems Part 2, Chapter 3 Roger Wattenhofer Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test and Set & Test and Test and Set Backoff lock Queue locks Concurrent Linked List Fine grained synchronization
Practice: Small Systems Part 2, Chapter 3 Roger Wattenhofer Overview Introduction Spin Locks Test and Set & Test and Test and Set Backoff lock Queue locks Concurrent Linked List Fine grained synchronization
Mutual Exclusion Algorithms with Constant RMR Complexity and Wait-Free Exit Code
 Mutual Exclusion Algorithms with Constant RMR Complexity and Wait-Free Exit Code Rotem Dvir 1 and Gadi Taubenfeld 2 1 The Interdisciplinary Center, P.O.Box 167, Herzliya 46150, Israel rotem.dvir@gmail.com
Mutual Exclusion Algorithms with Constant RMR Complexity and Wait-Free Exit Code Rotem Dvir 1 and Gadi Taubenfeld 2 1 The Interdisciplinary Center, P.O.Box 167, Herzliya 46150, Israel rotem.dvir@gmail.com
Lecture: Consistency Models, TM
 Lecture: Consistency Models, TM Topics: consistency models, TM intro (Section 5.6) No class on Monday (please watch TM videos) Wednesday: TM wrap-up, interconnection networks 1 Coherence Vs. Consistency
Lecture: Consistency Models, TM Topics: consistency models, TM intro (Section 5.6) No class on Monday (please watch TM videos) Wednesday: TM wrap-up, interconnection networks 1 Coherence Vs. Consistency
Lecture 21: Transactional Memory. Topics: Hardware TM basics, different implementations
 Lecture 21: Transactional Memory Topics: Hardware TM basics, different implementations 1 Transactions New paradigm to simplify programming instead of lock-unlock, use transaction begin-end locks are blocking,
Lecture 21: Transactional Memory Topics: Hardware TM basics, different implementations 1 Transactions New paradigm to simplify programming instead of lock-unlock, use transaction begin-end locks are blocking,
Implementing Locks. Nima Honarmand (Based on slides by Prof. Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau)
 Implementing Locks Nima Honarmand (Based on slides by Prof. Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau) Lock Implementation Goals We evaluate lock implementations along following lines Correctness Mutual exclusion: only one
Implementing Locks Nima Honarmand (Based on slides by Prof. Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau) Lock Implementation Goals We evaluate lock implementations along following lines Correctness Mutual exclusion: only one
Lecture 7: Transactional Memory Intro. Topics: introduction to transactional memory, lazy implementation
 Lecture 7: Transactional Memory Intro Topics: introduction to transactional memory, lazy implementation 1 Transactions New paradigm to simplify programming instead of lock-unlock, use transaction begin-end
Lecture 7: Transactional Memory Intro Topics: introduction to transactional memory, lazy implementation 1 Transactions New paradigm to simplify programming instead of lock-unlock, use transaction begin-end
Lecture: Consistency Models, TM. Topics: consistency models, TM intro (Section 5.6)
 Lecture: Consistency Models, TM Topics: consistency models, TM intro (Section 5.6) 1 Coherence Vs. Consistency Recall that coherence guarantees (i) that a write will eventually be seen by other processors,
Lecture: Consistency Models, TM Topics: consistency models, TM intro (Section 5.6) 1 Coherence Vs. Consistency Recall that coherence guarantees (i) that a write will eventually be seen by other processors,
Modern High-Performance Locking
 Modern High-Performance Locking Nir Shavit Slides based in part on The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Locks (Mutual Exclusion) public interface Lock { public void lock();
Modern High-Performance Locking Nir Shavit Slides based in part on The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Locks (Mutual Exclusion) public interface Lock { public void lock();
Concurrent programming: From theory to practice. Concurrent Algorithms 2015 Vasileios Trigonakis
 oncurrent programming: From theory to practice oncurrent Algorithms 2015 Vasileios Trigonakis From theory to practice Theoretical (design) Practical (design) Practical (implementation) 2 From theory to
oncurrent programming: From theory to practice oncurrent Algorithms 2015 Vasileios Trigonakis From theory to practice Theoretical (design) Practical (design) Practical (implementation) 2 From theory to
Concurrency. Part 2, Chapter 10. Roger Wattenhofer. ETH Zurich Distributed Computing
 Concurrency Part 2, Chapter 10 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Concurrent Linked List Fine-grained synchronization Optimistic synchronization Lazy synchronization
Concurrency Part 2, Chapter 10 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Concurrent Linked List Fine-grained synchronization Optimistic synchronization Lazy synchronization
Concurrent Data Structures
 Concurrent Data Structures Chapter 8 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Concurrent Linked List Fine-grained synchronization Optimistic synchronization Lazy synchronization
Concurrent Data Structures Chapter 8 Roger Wattenhofer ETH Zurich Distributed Computing www.disco.ethz.ch Overview Concurrent Linked List Fine-grained synchronization Optimistic synchronization Lazy synchronization
Hardware: BBN Butterfly
 Algorithms for Scalable Synchronization on Shared-Memory Multiprocessors John M. Mellor-Crummey and Michael L. Scott Presented by Charles Lehner and Matt Graichen Hardware: BBN Butterfly shared-memory
Algorithms for Scalable Synchronization on Shared-Memory Multiprocessors John M. Mellor-Crummey and Michael L. Scott Presented by Charles Lehner and Matt Graichen Hardware: BBN Butterfly shared-memory
Concurrent Skip Lists. Companion slides for The Art of Multiprocessor Programming by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit
 Concurrent Skip Lists Companion slides for The by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Set Object Interface Collection of elements No duplicates Methods add() a new element remove() an element contains() if element
Concurrent Skip Lists Companion slides for The by Maurice Herlihy & Nir Shavit Set Object Interface Collection of elements No duplicates Methods add() a new element remove() an element contains() if element
CS 31: Introduction to Computer Systems : Threads & Synchronization April 16-18, 2019
 CS 31: Introduction to Computer Systems 22-23: Threads & Synchronization April 16-18, 2019 Making Programs Run Faster We all like how fast computers are In the old days (1980 s - 2005): Algorithm too slow?
CS 31: Introduction to Computer Systems 22-23: Threads & Synchronization April 16-18, 2019 Making Programs Run Faster We all like how fast computers are In the old days (1980 s - 2005): Algorithm too slow?
6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, Class 15
 6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, 2009 Class 15 Today s plan z z z z z Pragmatic issues for shared-memory multiprocessors Practical mutual exclusion algorithms Test-and-set locks Ticket locks Queue locks
6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, 2009 Class 15 Today s plan z z z z z Pragmatic issues for shared-memory multiprocessors Practical mutual exclusion algorithms Test-and-set locks Ticket locks Queue locks
The University of Texas at Arlington
 The University of Texas at Arlington Lecture 6: Threading and Parallel Programming Constraints CSE 5343/4342 Embedded Systems II Based heavily on slides by Dr. Roger Walker More Task Decomposition: Dependence
The University of Texas at Arlington Lecture 6: Threading and Parallel Programming Constraints CSE 5343/4342 Embedded Systems II Based heavily on slides by Dr. Roger Walker More Task Decomposition: Dependence
Non-Blocking Synchronization
 Herlihy Ch 9. Linked Lists: The Role of Locking Non-Blocking Synchronization BJÖRN A. JOHNSSON Overview? So far: Coarse- and fine-grained synchronization Optimistic synchronization Lazy synchronization
Herlihy Ch 9. Linked Lists: The Role of Locking Non-Blocking Synchronization BJÖRN A. JOHNSSON Overview? So far: Coarse- and fine-grained synchronization Optimistic synchronization Lazy synchronization
Parallel linked lists
 Parallel linked lists Lecture 10 of TDA384/DIT391 (Principles of Conent Programming) Carlo A. Furia Chalmers University of Technology University of Gothenburg SP3 2017/2018 Today s menu The burden of locking
Parallel linked lists Lecture 10 of TDA384/DIT391 (Principles of Conent Programming) Carlo A. Furia Chalmers University of Technology University of Gothenburg SP3 2017/2018 Today s menu The burden of locking
Mutual Exclusion: Classical Algorithms for Locks
 Mutual Exclusion: Classical Algorithms for Locks John Mellor-Crummey Department of Computer Science Rice University johnmc@cs.rice.edu COMP 422 Lecture 18 21 March 2006 Motivation Ensure that a block of
Mutual Exclusion: Classical Algorithms for Locks John Mellor-Crummey Department of Computer Science Rice University johnmc@cs.rice.edu COMP 422 Lecture 18 21 March 2006 Motivation Ensure that a block of
CPSC/ECE 3220 Summer 2018 Exam 2 No Electronics.
 CPSC/ECE 3220 Summer 2018 Exam 2 No Electronics. Name: Write one of the words or terms from the following list into the blank appearing to the left of the appropriate definition. Note that there are more
CPSC/ECE 3220 Summer 2018 Exam 2 No Electronics. Name: Write one of the words or terms from the following list into the blank appearing to the left of the appropriate definition. Note that there are more
Combining Techniques Application for Tree Search Structures
 RAYMOND AND BEVERLY SACKLER FACULTY OF EXACT SCIENCES BLAVATNIK SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Combining Techniques Application for Tree Search Structures Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of requirements
RAYMOND AND BEVERLY SACKLER FACULTY OF EXACT SCIENCES BLAVATNIK SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Combining Techniques Application for Tree Search Structures Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of requirements
Atomicity CS 2110 Fall 2017
 Atomicity CS 2110 Fall 2017 Parallel Programming Thus Far Parallel programs can be faster and more efficient Problem: race conditions Solution: synchronization Are there more efficient ways to ensure the
Atomicity CS 2110 Fall 2017 Parallel Programming Thus Far Parallel programs can be faster and more efficient Problem: race conditions Solution: synchronization Are there more efficient ways to ensure the
Thread-Local. Lecture 27: Concurrency 3. Dealing with the Rest. Immutable. Whenever possible, don t share resources
 Thread-Local Lecture 27: Concurrency 3 CS 62 Fall 2016 Kim Bruce & Peter Mawhorter Some slides based on those from Dan Grossman, U. of Washington Whenever possible, don t share resources Easier to have
Thread-Local Lecture 27: Concurrency 3 CS 62 Fall 2016 Kim Bruce & Peter Mawhorter Some slides based on those from Dan Grossman, U. of Washington Whenever possible, don t share resources Easier to have
Scalable Locking. Adam Belay
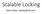 Scalable Locking Adam Belay Problem: Locks can ruin performance 12 finds/sec 9 6 Locking overhead dominates 3 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 Cores Problem: Locks can ruin performance the locks
Scalable Locking Adam Belay Problem: Locks can ruin performance 12 finds/sec 9 6 Locking overhead dominates 3 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 Cores Problem: Locks can ruin performance the locks
Marwan Burelle. Parallel and Concurrent Programming
 marwan.burelle@lse.epita.fr http://wiki-prog.infoprepa.epita.fr Outline 1 2 Solutions Overview 1 Sharing Data First, always try to apply the following mantra: Don t share data! When non-scalar data are
marwan.burelle@lse.epita.fr http://wiki-prog.infoprepa.epita.fr Outline 1 2 Solutions Overview 1 Sharing Data First, always try to apply the following mantra: Don t share data! When non-scalar data are
Advance Operating Systems (CS202) Locks Discussion
 Advance Operating Systems (CS202) Locks Discussion Threads Locks Spin Locks Array-based Locks MCS Locks Sequential Locks Road Map Threads Global variables and static objects are shared Stored in the static
Advance Operating Systems (CS202) Locks Discussion Threads Locks Spin Locks Array-based Locks MCS Locks Sequential Locks Road Map Threads Global variables and static objects are shared Stored in the static
CS 450 Exam 2 Mon. 4/11/2016
 CS 450 Exam 2 Mon. 4/11/2016 Name: Rules and Hints You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only additional resource you may consult during this exam. No calculators.
CS 450 Exam 2 Mon. 4/11/2016 Name: Rules and Hints You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only additional resource you may consult during this exam. No calculators.
Synchronization. CSCI 3753 Operating Systems Spring 2005 Prof. Rick Han
 Synchronization CSCI 3753 Operating Systems Spring 2005 Prof. Rick Han Announcements HW #3 is coming, due Friday Feb. 25, a week+ from now PA #2 is coming, assigned about next Tuesday Midterm is tentatively
Synchronization CSCI 3753 Operating Systems Spring 2005 Prof. Rick Han Announcements HW #3 is coming, due Friday Feb. 25, a week+ from now PA #2 is coming, assigned about next Tuesday Midterm is tentatively
6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, Class 20
 6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, 2009 Class 20 Today s plan z z z Transactional Memory Reading: Herlihy-Shavit, Chapter 18 Guerraoui, Kapalka, Chapters 1-4 Next: z z z Asynchronous networks vs asynchronous
6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, 2009 Class 20 Today s plan z z z Transactional Memory Reading: Herlihy-Shavit, Chapter 18 Guerraoui, Kapalka, Chapters 1-4 Next: z z z Asynchronous networks vs asynchronous
Spin Locks and Contention Management
 Chapter 7 Spin Locks and Contention Management 7.1 Introduction We now turn our attention to the performance of mutual exclusion protocols on realistic architectures. Any mutual exclusion protocol poses
Chapter 7 Spin Locks and Contention Management 7.1 Introduction We now turn our attention to the performance of mutual exclusion protocols on realistic architectures. Any mutual exclusion protocol poses
A Concurrent Skip List Implementation with RTM and HLE
 A Concurrent Skip List Implementation with RTM and HLE Fan Gao May 14, 2014 1 Background Semester Performed: Spring, 2014 Instructor: Maurice Herlihy The main idea of my project is to implement a skip
A Concurrent Skip List Implementation with RTM and HLE Fan Gao May 14, 2014 1 Background Semester Performed: Spring, 2014 Instructor: Maurice Herlihy The main idea of my project is to implement a skip
Multiprocessors II: CC-NUMA DSM. CC-NUMA for Large Systems
 Multiprocessors II: CC-NUMA DSM DSM cache coherence the hardware stuff Today s topics: what happens when we lose snooping new issues: global vs. local cache line state enter the directory issues of increasing
Multiprocessors II: CC-NUMA DSM DSM cache coherence the hardware stuff Today s topics: what happens when we lose snooping new issues: global vs. local cache line state enter the directory issues of increasing
! Why is synchronization needed? ! Synchronization Language/Definitions: ! How are locks implemented? Maria Hybinette, UGA
 Chapter 6: Process [& Thread] Synchronization CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems Synchronization Part 1 : The Basics! Why is synchronization needed?! Synchronization Language/Definitions:» What are race
Chapter 6: Process [& Thread] Synchronization CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems Synchronization Part 1 : The Basics! Why is synchronization needed?! Synchronization Language/Definitions:» What are race
PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION
 PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION Process Synchronization Background The Critical-Section Problem Peterson s Solution Synchronization Hardware Semaphores Classic Problems of Synchronization Monitors Synchronization
PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION Process Synchronization Background The Critical-Section Problem Peterson s Solution Synchronization Hardware Semaphores Classic Problems of Synchronization Monitors Synchronization
Section I Section Real Time Systems. Processes. 1.4 Inter-Processes Communication (part 1)
 EE206: Software Engineering IV 1.4 Inter-Processes Communication 1 page 1 of 16 Section I Section Real Time Systems. Processes 1.4 Inter-Processes Communication (part 1) Process interaction Processes often
EE206: Software Engineering IV 1.4 Inter-Processes Communication 1 page 1 of 16 Section I Section Real Time Systems. Processes 1.4 Inter-Processes Communication (part 1) Process interaction Processes often
Adaptive Lock. Madhav Iyengar < >, Nathaniel Jeffries < >
 Adaptive Lock Madhav Iyengar < miyengar@andrew.cmu.edu >, Nathaniel Jeffries < njeffrie@andrew.cmu.edu > ABSTRACT Busy wait synchronization, the spinlock, is the primitive at the core of all other synchronization
Adaptive Lock Madhav Iyengar < miyengar@andrew.cmu.edu >, Nathaniel Jeffries < njeffrie@andrew.cmu.edu > ABSTRACT Busy wait synchronization, the spinlock, is the primitive at the core of all other synchronization
Database Systems CSE 414
 Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 27: Transaction Implementations 1 Announcements Final exam will be on Dec. 14 (next Thursday) 14:30-16:20 in class Note the time difference, the exam will last ~2 hours
Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 27: Transaction Implementations 1 Announcements Final exam will be on Dec. 14 (next Thursday) 14:30-16:20 in class Note the time difference, the exam will last ~2 hours
Multi-Core Computing with Transactional Memory. Johannes Schneider and Prof. Roger Wattenhofer
 Multi-Core Computing with Transactional Memory Johannes Schneider and Prof. Roger Wattenhofer 1 Overview Introduction Difficulties with parallel (multi-core) programming A (partial) solution: Transactional
Multi-Core Computing with Transactional Memory Johannes Schneider and Prof. Roger Wattenhofer 1 Overview Introduction Difficulties with parallel (multi-core) programming A (partial) solution: Transactional
CPSC/ECE 3220 Fall 2017 Exam Give the definition (note: not the roles) for an operating system as stated in the textbook. (2 pts.
 CPSC/ECE 3220 Fall 2017 Exam 1 Name: 1. Give the definition (note: not the roles) for an operating system as stated in the textbook. (2 pts.) Referee / Illusionist / Glue. Circle only one of R, I, or G.
CPSC/ECE 3220 Fall 2017 Exam 1 Name: 1. Give the definition (note: not the roles) for an operating system as stated in the textbook. (2 pts.) Referee / Illusionist / Glue. Circle only one of R, I, or G.
Operating Systems. Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy
 Operating Systems Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy Dept. of Systems & Computer Eng.. AL-AZHAR University Website : eaymanelshenawy.wordpress.com Email : eaymanelshenawy@yahoo.com Reference
Operating Systems Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy Dept. of Systems & Computer Eng.. AL-AZHAR University Website : eaymanelshenawy.wordpress.com Email : eaymanelshenawy@yahoo.com Reference
Concurrent Preliminaries
 Concurrent Preliminaries Sagi Katorza Tel Aviv University 09/12/2014 1 Outline Hardware infrastructure Hardware primitives Mutual exclusion Work sharing and termination detection Concurrent data structures
Concurrent Preliminaries Sagi Katorza Tel Aviv University 09/12/2014 1 Outline Hardware infrastructure Hardware primitives Mutual exclusion Work sharing and termination detection Concurrent data structures
Lecture 6: Lazy Transactional Memory. Topics: TM semantics and implementation details of lazy TM
 Lecture 6: Lazy Transactional Memory Topics: TM semantics and implementation details of lazy TM 1 Transactions Access to shared variables is encapsulated within transactions the system gives the illusion
Lecture 6: Lazy Transactional Memory Topics: TM semantics and implementation details of lazy TM 1 Transactions Access to shared variables is encapsulated within transactions the system gives the illusion
Coarse-grained and fine-grained locking Niklas Fors
 Coarse-grained and fine-grained locking Niklas Fors 2013-12-05 Slides borrowed from: http://cs.brown.edu/courses/cs176course_information.shtml Art of Multiprocessor Programming 1 Topics discussed Coarse-grained
Coarse-grained and fine-grained locking Niklas Fors 2013-12-05 Slides borrowed from: http://cs.brown.edu/courses/cs176course_information.shtml Art of Multiprocessor Programming 1 Topics discussed Coarse-grained
CPSC/ECE 3220 Summer 2017 Exam 2
 CPSC/ECE 3220 Summer 2017 Exam 2 Name: Part 1: Word Bank Write one of the words or terms from the following list into the blank appearing to the left of the appropriate definition. Note that there are
CPSC/ECE 3220 Summer 2017 Exam 2 Name: Part 1: Word Bank Write one of the words or terms from the following list into the blank appearing to the left of the appropriate definition. Note that there are
CSE 332: Locks and Deadlocks. Richard Anderson, Steve Seitz Winter 2014
 CSE 332: Locks and Deadlocks Richard Anderson, Steve Seitz Winter 2014 1 Recall Bank Account Problem class BankAccount { private int balance = 0; synchronized int getbalance() { return balance; } synchronized
CSE 332: Locks and Deadlocks Richard Anderson, Steve Seitz Winter 2014 1 Recall Bank Account Problem class BankAccount { private int balance = 0; synchronized int getbalance() { return balance; } synchronized
Pre- and post- CS protocols. CS 361 Concurrent programming Drexel University Fall 2004 Lecture 7. Other requirements for a mutual exclusion algorithm
 CS 361 Concurrent programming Drexel University Fall 2004 Lecture 7 Bruce Char and Vera Zaychik. All rights reserved by the author. Permission is given to students enrolled in CS361 Fall 2004 to reproduce
CS 361 Concurrent programming Drexel University Fall 2004 Lecture 7 Bruce Char and Vera Zaychik. All rights reserved by the author. Permission is given to students enrolled in CS361 Fall 2004 to reproduce
TEST CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING. code: date: 19 June 2015 time:
 TEST CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING code: 01400537 date: 19 June 015 time: 13.45 16.45 - This is an open book examination. You are allowed to have a copy of Java Concurrency in Practice, and a copy of the (unannotated)
TEST CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING code: 01400537 date: 19 June 015 time: 13.45 16.45 - This is an open book examination. You are allowed to have a copy of Java Concurrency in Practice, and a copy of the (unannotated)
CS510 Advanced Topics in Concurrency. Jonathan Walpole
 CS510 Advanced Topics in Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Threads Cannot Be Implemented as a Library Reasoning About Programs What are the valid outcomes for this program? Is it valid for both r1 and r2 to
CS510 Advanced Topics in Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Threads Cannot Be Implemented as a Library Reasoning About Programs What are the valid outcomes for this program? Is it valid for both r1 and r2 to
Advanced Multiprocessor Programming: Locks
 Advanced Multiprocessor Programming: Locks Martin Wimmer, Jesper Larsson Träff TU Wien 20th April, 2015 Wimmer, Träff AMP SS15 1 / 31 Locks we have seen so far Peterson Lock ilter Lock Bakery Lock These
Advanced Multiprocessor Programming: Locks Martin Wimmer, Jesper Larsson Träff TU Wien 20th April, 2015 Wimmer, Träff AMP SS15 1 / 31 Locks we have seen so far Peterson Lock ilter Lock Bakery Lock These
Portland State University ECE 588/688. Transactional Memory
 Portland State University ECE 588/688 Transactional Memory Copyright by Alaa Alameldeen 2018 Issues with Lock Synchronization Priority Inversion A lower-priority thread is preempted while holding a lock
Portland State University ECE 588/688 Transactional Memory Copyright by Alaa Alameldeen 2018 Issues with Lock Synchronization Priority Inversion A lower-priority thread is preempted while holding a lock
Multiprocessor System. Multiprocessor Systems. Bus Based UMA. Types of Multiprocessors (MPs) Cache Consistency. Bus Based UMA. Chapter 8, 8.
 Multiprocessor System Multiprocessor Systems Chapter 8, 8.1 We will look at shared-memory multiprocessors More than one processor sharing the same memory A single CPU can only go so fast Use more than
Multiprocessor System Multiprocessor Systems Chapter 8, 8.1 We will look at shared-memory multiprocessors More than one processor sharing the same memory A single CPU can only go so fast Use more than
Spinlocks. Spinlocks. Message Systems, Inc. April 8, 2011
 Spinlocks Samy Al Bahra Devon H. O Dell Message Systems, Inc. April 8, 2011 Introduction Mutexes A mutex is an object which implements acquire and relinquish operations such that the execution following
Spinlocks Samy Al Bahra Devon H. O Dell Message Systems, Inc. April 8, 2011 Introduction Mutexes A mutex is an object which implements acquire and relinquish operations such that the execution following
Part III Synchronization Software and Hardware Solutions
 Part III Synchronization Software and Hardware Solutions Spring 2018 Computers are useless. They can only give answers. 1 Pablo Picasso Software Solutions for Two Processes Suppose we have two processes
Part III Synchronization Software and Hardware Solutions Spring 2018 Computers are useless. They can only give answers. 1 Pablo Picasso Software Solutions for Two Processes Suppose we have two processes
1) If a location is initialized to 0, what will the first invocation of TestAndSet on that location return?
 Synchronization Part 1: Synchronization - Locks Dekker s Algorithm and the Bakery Algorithm provide software-only synchronization. Thanks to advancements in hardware, synchronization approaches have been
Synchronization Part 1: Synchronization - Locks Dekker s Algorithm and the Bakery Algorithm provide software-only synchronization. Thanks to advancements in hardware, synchronization approaches have been
G Programming Languages Spring 2010 Lecture 13. Robert Grimm, New York University
 G22.2110-001 Programming Languages Spring 2010 Lecture 13 Robert Grimm, New York University 1 Review Last week Exceptions 2 Outline Concurrency Discussion of Final Sources for today s lecture: PLP, 12
G22.2110-001 Programming Languages Spring 2010 Lecture 13 Robert Grimm, New York University 1 Review Last week Exceptions 2 Outline Concurrency Discussion of Final Sources for today s lecture: PLP, 12
Multiprocessor Systems. COMP s1
 Multiprocessor Systems 1 Multiprocessor System We will look at shared-memory multiprocessors More than one processor sharing the same memory A single CPU can only go so fast Use more than one CPU to improve
Multiprocessor Systems 1 Multiprocessor System We will look at shared-memory multiprocessors More than one processor sharing the same memory A single CPU can only go so fast Use more than one CPU to improve
Quiz II Solutions MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Fall Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Fall 2014 Quiz II Solutions Mean 62.1 Median 65.0 Standard deviation 14.0 Kurtosis 2.6 20 15 10 5 0
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.828 Fall 2014 Quiz II Solutions Mean 62.1 Median 65.0 Standard deviation 14.0 Kurtosis 2.6 20 15 10 5 0
Learning from Bad Examples. CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 25 11/18/2014
 Learning from Bad Examples CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 25 11/18/2014 1 Goals Demonstrate techniques to design for shared mutability Build on an example where multiple threads
Learning from Bad Examples CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 25 11/18/2014 1 Goals Demonstrate techniques to design for shared mutability Build on an example where multiple threads
A simple correctness proof of the MCS contention-free lock. Theodore Johnson. Krishna Harathi. University of Florida. Abstract
 A simple correctness proof of the MCS contention-free lock Theodore Johnson Krishna Harathi Computer and Information Sciences Department University of Florida Abstract Mellor-Crummey and Scott present
A simple correctness proof of the MCS contention-free lock Theodore Johnson Krishna Harathi Computer and Information Sciences Department University of Florida Abstract Mellor-Crummey and Scott present
Part II Process Management Chapter 6: Process Synchronization
 Part II Process Management Chapter 6: Process Synchronization 1 Process Synchronization Why is synchronization needed? Race Conditions Critical Sections Pure Software Solutions Hardware Support Semaphores
Part II Process Management Chapter 6: Process Synchronization 1 Process Synchronization Why is synchronization needed? Race Conditions Critical Sections Pure Software Solutions Hardware Support Semaphores
What is the Race Condition? And what is its solution? What is a critical section? And what is the critical section problem?
 What is the Race Condition? And what is its solution? Race Condition: Where several processes access and manipulate the same data concurrently and the outcome of the execution depends on the particular
What is the Race Condition? And what is its solution? Race Condition: Where several processes access and manipulate the same data concurrently and the outcome of the execution depends on the particular
Potential violations of Serializability: Example 1
 CSCE 6610:Advanced Computer Architecture Review New Amdahl s law A possible idea for a term project Explore my idea about changing frequency based on serial fraction to maintain fixed energy or keep same
CSCE 6610:Advanced Computer Architecture Review New Amdahl s law A possible idea for a term project Explore my idea about changing frequency based on serial fraction to maintain fixed energy or keep same
Monitors; Software Transactional Memory
 Monitors; Software Transactional Memory Parallel and Distributed Computing Department of Computer Science and Engineering (DEI) Instituto Superior Técnico October 18, 2012 CPD (DEI / IST) Parallel and
Monitors; Software Transactional Memory Parallel and Distributed Computing Department of Computer Science and Engineering (DEI) Instituto Superior Técnico October 18, 2012 CPD (DEI / IST) Parallel and
CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 17: Shared-Memory Concurrency & Mutual Exclusion. Ruth Anderson Winter 2019
 CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 17: Shared-Memory Concurrency & Mutual Exclusion Ruth Anderson Winter 2019 Toward sharing resources (memory) So far, we have been studying parallel algorithms
CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 17: Shared-Memory Concurrency & Mutual Exclusion Ruth Anderson Winter 2019 Toward sharing resources (memory) So far, we have been studying parallel algorithms
Database Systems CSE 414
 Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 22: Transaction Implementations CSE 414 - Spring 2017 1 Announcements WQ7 (last!) due on Sunday HW7: due on Wed, May 24 using JDBC to execute SQL from Java using SQL Server
Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 22: Transaction Implementations CSE 414 - Spring 2017 1 Announcements WQ7 (last!) due on Sunday HW7: due on Wed, May 24 using JDBC to execute SQL from Java using SQL Server
The Art of Multiprocessor Programming Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. October 3, 2007 DRAFT COPY
 The Art of Multiprocessor Programming Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved Maurice Herlihy October 3, 2007 Nir Shavit 2 Contents 1 Introduction 13 1.1 Shared Objects and Synchronization..............
The Art of Multiprocessor Programming Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved Maurice Herlihy October 3, 2007 Nir Shavit 2 Contents 1 Introduction 13 1.1 Shared Objects and Synchronization..............
Multiprocessors and Locking
 Types of Multiprocessors (MPs) Uniform memory-access (UMA) MP Access to all memory occurs at the same speed for all processors. Multiprocessors and Locking COMP9242 2008/S2 Week 12 Part 1 Non-uniform memory-access
Types of Multiprocessors (MPs) Uniform memory-access (UMA) MP Access to all memory occurs at the same speed for all processors. Multiprocessors and Locking COMP9242 2008/S2 Week 12 Part 1 Non-uniform memory-access
Chapter 6: Synchronization. Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition,
 Chapter 6: Synchronization, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Outline Background The Critical-Section Problem Peterson s Solution Synchronization Hardware Semaphores Classic Problems of Synchronization
Chapter 6: Synchronization, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Outline Background The Critical-Section Problem Peterson s Solution Synchronization Hardware Semaphores Classic Problems of Synchronization
CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems. Class 3 Threads & Concurrency. Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University
 CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 3 Threads & Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University 1 The Process Concept 2 The Process Concept Process a program in execution
CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 3 Threads & Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University 1 The Process Concept 2 The Process Concept Process a program in execution
Concurrency: Signaling and Condition Variables
 Concurrency: Signaling and Condition Variables Questions Answered in this Lecture: How do we make fair locks perform better? How do we notify threads of that some condition has been met? Hale CS450 Thanks
Concurrency: Signaling and Condition Variables Questions Answered in this Lecture: How do we make fair locks perform better? How do we notify threads of that some condition has been met? Hale CS450 Thanks
Multiprocessor Systems. Chapter 8, 8.1
 Multiprocessor Systems Chapter 8, 8.1 1 Learning Outcomes An understanding of the structure and limits of multiprocessor hardware. An appreciation of approaches to operating system support for multiprocessor
Multiprocessor Systems Chapter 8, 8.1 1 Learning Outcomes An understanding of the structure and limits of multiprocessor hardware. An appreciation of approaches to operating system support for multiprocessor
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions
 CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
Chapter 6: Process [& Thread] Synchronization. CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems. Why does cooperation require synchronization?
![Chapter 6: Process [& Thread] Synchronization. CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems. Why does cooperation require synchronization? Chapter 6: Process [& Thread] Synchronization. CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems. Why does cooperation require synchronization?](/thumbs/88/114609946.jpg) Chapter 6: Process [& Thread] Synchronization CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems Synchronization Part 1 : The Basics Why is synchronization needed? Synchronization Language/Definitions:» What are race conditions?»
Chapter 6: Process [& Thread] Synchronization CSCI [4 6] 730 Operating Systems Synchronization Part 1 : The Basics Why is synchronization needed? Synchronization Language/Definitions:» What are race conditions?»
CHAPTER 6: PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION
 CHAPTER 6: PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION The slides do not contain all the information and cannot be treated as a study material for Operating System. Please refer the text book for exams. TOPICS Background
CHAPTER 6: PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION The slides do not contain all the information and cannot be treated as a study material for Operating System. Please refer the text book for exams. TOPICS Background
Lock-Free, Wait-Free and Multi-core Programming. Roger Deran boilerbay.com Fast, Efficient Concurrent Maps AirMap
 Lock-Free, Wait-Free and Multi-core Programming Roger Deran boilerbay.com Fast, Efficient Concurrent Maps AirMap Lock-Free and Wait-Free Data Structures Overview The Java Maps that use Lock-Free techniques
Lock-Free, Wait-Free and Multi-core Programming Roger Deran boilerbay.com Fast, Efficient Concurrent Maps AirMap Lock-Free and Wait-Free Data Structures Overview The Java Maps that use Lock-Free techniques
CoSc 450: Programming Paradigms. The Critical Section Problem
 CoSc 450: Programming Paradigms 03 The Critical Section Problem Algorithm 3.1: Critical section problem global variables p q local variables local variables loop forever loop forever non-critical section
CoSc 450: Programming Paradigms 03 The Critical Section Problem Algorithm 3.1: Critical section problem global variables p q local variables local variables loop forever loop forever non-critical section
Promela and SPIN. Mads Dam Dept. Microelectronics and Information Technology Royal Institute of Technology, KTH. Promela and SPIN
 Promela and SPIN Mads Dam Dept. Microelectronics and Information Technology Royal Institute of Technology, KTH Promela and SPIN Promela (Protocol Meta Language): Language for modelling discrete, event-driven
Promela and SPIN Mads Dam Dept. Microelectronics and Information Technology Royal Institute of Technology, KTH Promela and SPIN Promela (Protocol Meta Language): Language for modelling discrete, event-driven
Lecture: Transactional Memory. Topics: TM implementations
 Lecture: Transactional Memory Topics: TM implementations 1 Summary of TM Benefits As easy to program as coarse-grain locks Performance similar to fine-grain locks Avoids deadlock 2 Design Space Data Versioning
Lecture: Transactional Memory Topics: TM implementations 1 Summary of TM Benefits As easy to program as coarse-grain locks Performance similar to fine-grain locks Avoids deadlock 2 Design Space Data Versioning
Lecture Notes on Binary Decision Diagrams
 Lecture Notes on Binary Decision Diagrams 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation William Lovas Notes by Frank Pfenning Lecture 25 April 21, 2011 1 Introduction In this lecture we revisit the important
Lecture Notes on Binary Decision Diagrams 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation William Lovas Notes by Frank Pfenning Lecture 25 April 21, 2011 1 Introduction In this lecture we revisit the important
Concurrent & Distributed Systems Supervision Exercises
 Concurrent & Distributed Systems Supervision Exercises Stephen Kell Stephen.Kell@cl.cam.ac.uk November 9, 2009 These exercises are intended to cover all the main points of understanding in the lecture
Concurrent & Distributed Systems Supervision Exercises Stephen Kell Stephen.Kell@cl.cam.ac.uk November 9, 2009 These exercises are intended to cover all the main points of understanding in the lecture
The New Java Technology Memory Model
 The New Java Technology Memory Model java.sun.com/javaone/sf Jeremy Manson and William Pugh http://www.cs.umd.edu/~pugh 1 Audience Assume you are familiar with basics of Java technology-based threads (
The New Java Technology Memory Model java.sun.com/javaone/sf Jeremy Manson and William Pugh http://www.cs.umd.edu/~pugh 1 Audience Assume you are familiar with basics of Java technology-based threads (
Programmazione di sistemi multicore
 Programmazione di sistemi multicore A.A. 2015-2016 LECTURE 12 IRENE FINOCCHI http://wwwusers.di.uniroma1.it/~finocchi/ Shared-memory concurrency & mutual exclusion TASK PARALLELISM AND OVERLAPPING MEMORY
Programmazione di sistemi multicore A.A. 2015-2016 LECTURE 12 IRENE FINOCCHI http://wwwusers.di.uniroma1.it/~finocchi/ Shared-memory concurrency & mutual exclusion TASK PARALLELISM AND OVERLAPPING MEMORY
Atomic Transac1ons. Atomic Transactions. Q1: What if network fails before deposit? Q2: What if sequence is interrupted by another sequence?
 CPSC-4/6: Operang Systems Atomic Transactions The Transaction Model / Primitives Serializability Implementation Serialization Graphs 2-Phase Locking Optimistic Concurrency Control Transactional Memory
CPSC-4/6: Operang Systems Atomic Transactions The Transaction Model / Primitives Serializability Implementation Serialization Graphs 2-Phase Locking Optimistic Concurrency Control Transactional Memory
Programming in Parallel COMP755
 Programming in Parallel COMP755 All games have morals; and the game of Snakes and Ladders captures, as no other activity can hope to do, the eternal truth that for every ladder you hope to climb, a snake
Programming in Parallel COMP755 All games have morals; and the game of Snakes and Ladders captures, as no other activity can hope to do, the eternal truth that for every ladder you hope to climb, a snake
