AGDC Per-Pixel Shading. Sim Dietrich
|
|
|
- Angelica May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AGDC Per-Pixel Shading Sim Dietrich
2 Goal Of This Talk The new features of Dx8 and the next generation of HW make huge strides in the area of Per-Pixel Shading Most developers have yet to adopt Per-Pixel Shading techniques, and rely on simple multitexturing The goal of this talk is to introduce you to Per- Pixel Shading concepts necessary to understand and implement these techniques in your app
3 What is Per-Pixel Shading? Dynamic Shading computed on a per-pixel basis Per Pixel shading includes a variety of dynamic shading techniques Bump Mapping Per-Pixel Directional Lights Per-Pixel Spot Lights Per-Pixel Point Lights
4 A Single Quad Lit Per-Pixel
5 What this Talk will Cover Bump Mapping Overview EMBM, Embossing, DOT3 Bump Mapping as Per-Pixel Shading Texture Space A Vertex-Local Coordinate System Animation And Per-Pixel Shading Per-Pixel Directional Lights Point Lights Distance Attenuation Spot Lights
6 What This Talk Will Cover DX8 Pixel Shaders How they improve upon Dx7-Style Per-Pixel Shading Integrating Pixel Shaders
7 Bump Mapping Overview Bump Mapping is a subset of Per-Pixel Lighting Bump Mapping examples such as Embossing simulate diffuse directional lighting Dx6 Environmental Bump Mapping ( EMBM ) simulates planar specular reflections However, DOT3 Per Pixel Lighting can be used to achieve diffuse and/or specular point lights, spotlights and volumetric lights as well
8 DOT3 Overview This talk will primarily cover D3DTOP_DOTPRODUCT3, or DOT3 effects DOT3 is more generally useful for per-pixel lighting than either Embossing or EMBM DOT3 is a texture blending operation that performs a dot product between two vectors It yields a value from 0 to 1
9 Performing a Per-Pixel Dot Product Directional Diffuse Lighting is computed by LightColor * ( LightVector DOT SurfaceNormal ) Directional Specular Lighting is computed via LightColor * ( HalfAngle DOT SurfaceNormal ) The DOT3 per-pixel operation allows us to perform L dot N or H dot N on a per-pixel basis
10 Per-Pixel Dot Products To perform a per-pixel dot product, we require three things A Light Vector L A Surface Normal N A Common Coordinate System for L and N
11 The Light Vector L We can store the Light Vector L on a per-vertex basis in an iterated color We can use either the Diffuse or Specular iterated color This allows the L vector to be interpolated across a triangle, just like a color perspective correction is important for this
12 The Surface Normal N We also want a per-pixel surface normal N This is stored in a Normal Map which is typically derived from a Height Map Height Map Normal Map
13 Normal Maps Normal Maps are just an array of normalized surface vectors encoded as RGB colors They are defined such that : X maps to Red Y maps to Green Z maps to Blue Alpha is available for gloss or other scalar values
14 Screenshot of BumpMaker Tool
15 Single Quad Lit With Per-Pixel Directional and Point Lights
16 What About a Common Coordinate System? The Surface Normals are expressed in their own coordinate system, such that +X points to the Right +Y points Up +Z points Out of the screen The Light Vector is expressed in World Space Either N must be transformed into World Space with L, or we must transform L into this Normal Map coordinate system
17 Normals In World Space? We can generate Normal Maps in World Space, but then our world needs to be more or less uniquely textured, wasting texture memory This also only works for static geometry what would happen if the geometry rotated? Here is the underlying problem : Texels Don t Rotate
18 Help, My Texel Won t Rotate! When we rotate Bump-Mapped geometry, the texels within the Normal Map don t rotate along with the geometry Even if we could rotate each texel, it would be an expensive proposition to perform a per-texel rotation matrix This implies we need a way to move a light vector L from World Space into the Normal Map s coordinate Space
19 Enter Texture Space Texture Space is a per-vertex coordinate system that expresses how to go from Model Space into the Normal Map Coordinate System, where : +X Axis points to the Right +Y Axis points Up +Z Axis points Out of the screen
20 Texture Space Diagram SxT T Normal Map A flat plane in S,T direction S L and N are expressed in different coordinate systems Solution = Rotate Light position into S,T,SxT space. Result: New light position for each vertex.
21 How to Author for Texture Space The best method for generating Texture Space for your geometry is as follows : Have the artist apply bump maps in their authoring tool or just use the same mapping as the decal Don t let them use texture mirroring Don t use degenerate projections ( ie stretched textures ) When loading in a model, create an extra set of 3 3D vectors per vertex These will store the axes of the Texture Space basis Generate the Texture Space vectors from the vertex positions and bump map texture coordinates
22 How to Generate Texture Space? For each triangle in the model : Use the x,y,z position and the s,t bump map texture coordinates Create plane equations of the form : Ax + Bs + Ct + D = 0 Ay + Bs + Ct + D = 0 Az + Bs + Ct + D = 0 Solve for the texture gradients dsdx, dsdy, dsdz, etc.
23 Generating Texture Space Now treat the dsdx, dsdy, and dsdz as a 3D vector representing the S axis < dsdx, dsdy, dsdz > Do the same to generate the T axis Now cross the two to generate the SxT axis this is the Z or up axis of Texture Space, and is typically close to parallel with the triangle s normal If your SxT and the triangle normal point in opposite directions, the artist applied the texture backwards have the artist fix this, or negate the SxT axis
24 Generating Texture Space These 3 Axes together make up a 3x3 rotation/scale matrix dsdx dtdx SxTx dsdy dtdy SxTy dsdz dtdz SxTz Putting an XYZ model-space vector through this 3x3 matrix produces a vector expressed in local Texture Space
25 Per-Triangle Bases T SxT T SxT S S S T
26 Per-Triangle Bases We now have a coordinate basis for each triangle We need them on a per-vertex basis so they can vary smoothly across our geometry The solution : For each vertex, sum up the S vectors from each face that shares this vertex Do the same for all T and SxT vectors Normalize each sum vector Optionally scale by the average original magnitude of S,T or SxT if your texture map is applied anisotropically The result is per-vertex Texture Space This is analogous to calculating vertex normals for lighting
27 Per-Vertex Texture Space Now we have what we need to move a light into a local space defined at each vertex via the Texture Space Basis Matrix For each per-pixel light, we move it s L or H vector into local Texture Space On the CPU with C code Or on the GPU with a vertex program
28 The Resulting Per-Vertex Texture Space Per Vertex Texture Space is derived From Shared Faces T SxT T SxT T S S S SxT T SxT T S S
29 Texture Space In Practice The L or H vector is linearly interpolated across the polygon in Texture Space : In the diffuse or specular color It must be normalized before storing in the iterated color It will get de-normalized across large polygons Doesn t handle anisotropy well Or in a set of 3D texture coordinates Use a Cube Map to renormalize the vector Able to support scaling on textures Can avoid CPU or GPU work The L or H vector can be renormalized per-pixel via a texture, such as a Cube Map, Volume Map or Projected Texture
30 What about Animation? When triangles distort, so do their texture gradients, invalidating the Model Space->Texture Space matrix When triangles rotate relative to Model Space, the Model Space->Texture Space matrix is invalid Therefore, the Texture Space will need to be updated or recomputed during animation The obvious approach, and one practical for simple models, is to simply go through the previous steps for each animation frame Regenerate Texture Space for each triangle, then each vertex
31 A Better Way Update the Bases The two most popular animation techniques both work with Texture Space bump mapping WITHOUT requiring recalculating the entire basis Bone-Based Skinning ( Indexed or Not ) Keyframe Interpolation
32 Bone-Based Skinning For each axis of the Texture Space S, T and SxT, skin the axis by putting it through the same matrix as the vertex normals Alternatively, skip the SxT axis and perform S cross T instead can be cheaper if you have many bones
33 Keyframe Interpolation Create keyframes for the S, T and SxT axes as well Linearly interpolate between the S(0) and S(1) using the keyframe weight from 0 to 1 ( 1 Weight ) S0 + ( Weight ) * S1 Now Normalize the result To handle scaled or stretched textures Rescale by the linearly interpolated length of the two keyframe vectors NormalizedVector *= ( 1 Weight ) LengthOf(S0 ) + ( Weight ) * LengthOf(S1)
34 Keyframe Interpolation The normalizing of the vector approximates a spherical interpolation, or SLERP The rescaling ensures that any stretching or scaling in the textures is preserved especially important if morphing
35 Texture Space Calculations These calculations are a prerequisite for practical Per-Pixel Lighting The cost of computing and updating Texture Space for moving models can seem large Keep it in perspective : For a certain amount of per-vertex work, you are getting tremendous per-pixel detail All of the previous techniques for moving lights into Texture Space and updating the Texture Space vectors for moving objects can be handled with Dx8 Vertex Shaders
36 Texture Space Overview Texture Space is necessary to handle arbitrary, animating bump mapped geometry correctly It allows us to setup the per-pixel dot product For each vertex, we rotate the L or H vector into local Texture Space, where it is interpolated across the polygon as a color Now, we can perform L dot N or H dot N per pixel and achieve per-pixel lighting
37 Implementing Per-Pixel Light Types Directional Lights Spot Lights Attenuation Point Lights Attenuation
38 Directional Lights Directional Lights are the simplest just perform L dot N or H dot N, then multiply by the light color LightColor * ( L dot N ) or LightColor * ( H dot N )
39 Spot Lights Spot lights are a little harder We need to use a projective texture to represent the spotlight s cosine attenuation from the umbra and penumbra This is pre-generated as a circular texture map, like so :
40 Spot Light Directional Falloff Penumbra penumbra Umbra Direction of light (-L)
41 Spot Light Texture The interior should hold the cosine falloff term from 1 ( everywhere in the umbra ) ramping down to 0 ( at the edge of the penumbra ) Ensure that the edges of the texture are black Set up a Light Plane at the spotlight, pointing in the same direction as the light Set up texture coordinate generation and the texture matrix to so that the vertex positions are projected onto the Light Plane
42 Getting Clever Since it is a scalar value, one can place the cosine falloff term in the texture alpha only That frees up the RGB values to hold the L vector This has two benefits : Per Pixel Spotlights with a single 2D texture Handles self-shadowing automatically Put the distance attenuation in the diffuse color or alpha ( SpotLight.RGB DOT3 Normal.RGB ) * ( SpotLight.Alpha * Diffuse.RGB )
43 Point Lights Point Lights are similar to SpotLights in complexity They require a per-pixel distance attenuation value There are four basic ways to achieve this
44 Four Attenuation Techniques 3D Texture holds Attenuation function + Can be an arbitrary function - Not all cards have 3D Textures - Lots of Texture Memory Use 2 2D Textures to compute 1 d*d [ 1 x * x y * y ] [ z * z ] Or Use 1 texture, and compute z*z in texture blender via Diffuse or Specular + Works on all cards - Not very flexible for attenuation
45 Alternate 2 Texture Attenuation Use 2 2D Textures to compute e ^ - d*d [ e ^ ( - x*x y*y ) ] * [ e ^ ( - z * z ) ] + Works on All Cards + Smoother Attenuation Function + Can use other factors other than e - Must use 2 Textures
46 Last Attenuation Technique 3D Texture - Store 3D L vector in RGB of texture, put Attenuation Function in Alpha only + Less Textures used, easier to reduce passes - Not all cards have 3D Textures - Lots of Texture Memory - May have to Point Sample if close to the Light
47 Attenuation Tips Always keep the edge of the Attenuation textures black if using scalars, or use the zero vector if encoding vectors, and use CLAMP mode Use Alpha Test to eliminate pixels that map to the border of the Attenuation Map Set up the texture coordinate generation / texture matrix to offset to the light s position and scale by 1 / LightRange You can use Destination Alpha to hold Attenuation for multi-pass effects
48 1-d*d e^(-d*d)
49 Bringing It All Together At Author Time Apply Bump Maps ( Actually Normal Maps ) to your models NEVER Pre-Light Textures You can t combine pre-lit and real-time lights Storing global ambient light / shadows in a *separate* light map is OK At Load Time Per Triangle Generate Per-Triangle Texture Space Per Vertex Generate Texture Space Matrices from Per Triangle Bases
50 Bringing It All Together - Runtime Per Vertex Move L or H into Local Texture Space Per Pixel Perform Dot Product Apply Attenuation Apply Light Color
51 Multiple Per-Pixel Point Lights
52 What About Dx8 / Pixel Shaders? All of the preceding material applies directly to Dx8 and more advanced Pixel Shading Understanding the preceding sections is extremely helpful when investigating Dx8-Level Pixel Shading Dx8 Pixel Shaders are mostly extensions of the same ideas behind DOT3
53 What s New With Dx8 Pixel Shaders? Math is performed in floating point instead of fixed point Can perform dependent textures Texture1.S = ( Texture0.AR ) Texture1.T = ( Texture1.GB ) Can perform a per-pixel reflection vector lookup into a CubeMap True per-pixel bumpy reflections
54 Pixel Shaders Allow Per-Pixel Bumpy Reflections
55 Further Topics Using Cube Maps To Normalize Light Vectors + Keeps Vectors Normalized - Takes up a Texture See my GDC 2000 presentation on Cube Maps Creating Normal Maps from Height Values or Other Textures See my GDC 2000 presentation on Per-Pixel Lighting Both of these are employed in the Bump Maker tool on NVIDIA s public developer website
56 Credits : Where I First Learned of These Techniques Texture Space Generation Idea Sim Dietrich Texture Space Generation Details Sim Dietrich and Doug Rogers 3D Texture Attenuation John Carmack SpotLight Attenuation w/ Normals Sim Dietrich 1 d*d Attenuation w/ 1 or 2 Textures Sim Dietrich e ^ ( -d*d ) Attenuation w/ 2 Textures Cass Everitt 3D Texture w/ Normals & Attenuation Sim Dietrich
Shadow Techniques. Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation
 Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
CS 354R: Computer Game Technology
 CS 354R: Computer Game Technology Texture and Environment Maps Fall 2018 Texture Mapping Problem: colors, normals, etc. are only specified at vertices How do we add detail between vertices without incurring
CS 354R: Computer Game Technology Texture and Environment Maps Fall 2018 Texture Mapping Problem: colors, normals, etc. are only specified at vertices How do we add detail between vertices without incurring
Canonical Shaders for Optimal Performance. Sébastien Dominé Manager of Developer Technology Tools
 Canonical Shaders for Optimal Performance Sébastien Dominé Manager of Developer Technology Tools Agenda Introduction FX Composer 1.0 High Performance Shaders Basics Vertex versus Pixel Talk to your compiler
Canonical Shaders for Optimal Performance Sébastien Dominé Manager of Developer Technology Tools Agenda Introduction FX Composer 1.0 High Performance Shaders Basics Vertex versus Pixel Talk to your compiler
Render-To-Texture Caching. D. Sim Dietrich Jr.
 Render-To-Texture Caching D. Sim Dietrich Jr. What is Render-To-Texture Caching? Pixel shaders are becoming more complex and expensive Per-pixel shadows Dynamic Normal Maps Bullet holes Water simulation
Render-To-Texture Caching D. Sim Dietrich Jr. What is Render-To-Texture Caching? Pixel shaders are becoming more complex and expensive Per-pixel shadows Dynamic Normal Maps Bullet holes Water simulation
CS 130 Final. Fall 2015
 CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Shadow Buffer Theory Observation:
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Shadow Buffer Theory Observation:
Projective Shadows. D. Sim Dietrich Jr.
 Projective Shadows D. Sim Dietrich Jr. Topics Projective Shadow Types Implementation on DirectX 7 HW Implementation on DirectX8 HW Integrating Shadows into an engine Types of Projective Shadows Static
Projective Shadows D. Sim Dietrich Jr. Topics Projective Shadow Types Implementation on DirectX 7 HW Implementation on DirectX8 HW Integrating Shadows into an engine Types of Projective Shadows Static
All the Polygons You Can Eat. Doug Rogers Developer Relations
 All the Polygons You Can Eat Doug Rogers Developer Relations doug@nvidia.com Future of Games Very high resolution models 20,000 triangles per model Lots of them Complex Lighting Equations Floating point
All the Polygons You Can Eat Doug Rogers Developer Relations doug@nvidia.com Future of Games Very high resolution models 20,000 triangles per model Lots of them Complex Lighting Equations Floating point
Per-Pixel Lighting and Bump Mapping with the NVIDIA Shading Rasterizer
 Per-Pixel Lighting and Bump Mapping with the NVIDIA Shading Rasterizer Executive Summary The NVIDIA Quadro2 line of workstation graphics solutions is the first of its kind to feature hardware support for
Per-Pixel Lighting and Bump Mapping with the NVIDIA Shading Rasterizer Executive Summary The NVIDIA Quadro2 line of workstation graphics solutions is the first of its kind to feature hardware support for
Texturing Theory. Overview. All it takes is for the rendered image to look right. -Jim Blinn 11/10/2018
 References: Real-Time Rendering 3 rd Edition Chapter 6 Texturing Theory All it takes is for the rendered image to look right. -Jim Blinn Overview Introduction The Texturing Pipeline Example The Projector
References: Real-Time Rendering 3 rd Edition Chapter 6 Texturing Theory All it takes is for the rendered image to look right. -Jim Blinn Overview Introduction The Texturing Pipeline Example The Projector
Optimal Shaders Using High-Level Languages
 Optimal Shaders Using High-Level Languages The Good, The Bad, The Ugly All high level languages provide significant power and flexibility that: Make writing shaders easy Make writing slow shaders easy
Optimal Shaders Using High-Level Languages The Good, The Bad, The Ugly All high level languages provide significant power and flexibility that: Make writing shaders easy Make writing slow shaders easy
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods. Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CPSC / Texture Mapping
 CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Introduction and Motivation so far: detail through polygons & materials example: brick wall problem: many polygons & materials needed for detailed structures inefficient for memory
CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Introduction and Motivation so far: detail through polygons & materials example: brick wall problem: many polygons & materials needed for detailed structures inefficient for memory
CS 450: COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEXTURE MAPPING SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE
 CS 450: COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEXTURE MAPPING SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION Texturing = process that takes a surface and modifies its appearance at each location using some image, function,
CS 450: COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEXTURE MAPPING SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION Texturing = process that takes a surface and modifies its appearance at each location using some image, function,
Homework 3: Programmable Shaders
 Homework 3: Programmable Shaders Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging (Summer 2012), Stanford University Due Monday, July 23, 11:59pm Warning: The coding portion of this homework involves features
Homework 3: Programmable Shaders Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging (Summer 2012), Stanford University Due Monday, July 23, 11:59pm Warning: The coding portion of this homework involves features
Mattan Erez. The University of Texas at Austin
 EE382V: Principles in Computer Architecture Parallelism and Locality Fall 2008 Lecture 10 The Graphics Processing Unit Mattan Erez The University of Texas at Austin Outline What is a GPU? Why should we
EE382V: Principles in Computer Architecture Parallelism and Locality Fall 2008 Lecture 10 The Graphics Processing Unit Mattan Erez The University of Texas at Austin Outline What is a GPU? Why should we
The Illusion of Motion Making magic with textures in the vertex shader. Mario Palmero Lead Programmer at Tequila Works
 The Illusion of Motion Making magic with textures in the vertex shader Mario Palmero Lead Programmer at Tequila Works Dark Ages before Textures in the Vertex Shader What is the Vertex Shader? A programmable
The Illusion of Motion Making magic with textures in the vertex shader Mario Palmero Lead Programmer at Tequila Works Dark Ages before Textures in the Vertex Shader What is the Vertex Shader? A programmable
GUERRILLA DEVELOP CONFERENCE JULY 07 BRIGHTON
 Deferred Rendering in Killzone 2 Michal Valient Senior Programmer, Guerrilla Talk Outline Forward & Deferred Rendering Overview G-Buffer Layout Shader Creation Deferred Rendering in Detail Rendering Passes
Deferred Rendering in Killzone 2 Michal Valient Senior Programmer, Guerrilla Talk Outline Forward & Deferred Rendering Overview G-Buffer Layout Shader Creation Deferred Rendering in Detail Rendering Passes
Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural
 1 Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural to consider using it in video games too. 2 I hope that
1 Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural to consider using it in video games too. 2 I hope that
Interactive Cloth Simulation. Matthias Wloka NVIDIA Corporation
 Interactive Cloth Simulation Matthias Wloka NVIDIA Corporation MWloka@nvidia.com Overview Higher-order surfaces Vertex-shader deformations Lighting modes Per-vertex diffuse Per-pixel diffuse with bump-map
Interactive Cloth Simulation Matthias Wloka NVIDIA Corporation MWloka@nvidia.com Overview Higher-order surfaces Vertex-shader deformations Lighting modes Per-vertex diffuse Per-pixel diffuse with bump-map
Bringing Hollywood to Real Time. Abe Wiley 3D Artist 3-D Application Research Group
 Bringing Hollywood to Real Time Abe Wiley 3D Artist 3-D Application Research Group Overview > Film Pipeline Overview and compare with Games > The RhinoFX/ATI Relationship > Ruby 1 and 2 The Movies > Breakdown
Bringing Hollywood to Real Time Abe Wiley 3D Artist 3-D Application Research Group Overview > Film Pipeline Overview and compare with Games > The RhinoFX/ATI Relationship > Ruby 1 and 2 The Movies > Breakdown
Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm
 CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
Announcements. Written Assignment 2 is out see the web page. Computer Graphics
 Announcements Written Assignment 2 is out see the web page 1 Texture and other Mappings Shadows Texture Mapping Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Watt Chapter 8 COMPUTER GRAPHICS 15-462
Announcements Written Assignment 2 is out see the web page 1 Texture and other Mappings Shadows Texture Mapping Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Watt Chapter 8 COMPUTER GRAPHICS 15-462
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications
 CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook University) Stony Brook, New York 11794--4400 Tel: (631)632-8450; Fax: (631)632-8334
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook University) Stony Brook, New York 11794--4400 Tel: (631)632-8450; Fax: (631)632-8334
Texture. Texture Mapping. Texture Mapping. CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics. Lecture 11 : Texture
 Texture CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. Lecture 11 : Texture http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
Texture CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. Lecture 11 : Texture http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics. Lecture 11 : Texture
 CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Lecture 11 : Texture Texture Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
CS 475 / CS 675 Computer Graphics Lecture 11 : Texture Texture Add surface detail Paste a photograph over a surface to provide detail. Texture can change surface colour or modulate surface colour. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/uv_mapping
In-Game Special Effects and Lighting
 In-Game Special Effects and Lighting Introduction! Tomas Arce! Special Thanks! Matthias Wloka! Craig Galley! Stephen Broumley! Cryrus Lum! Sumie Arce! Inevitable! nvidia! Bungy What Is Per-Pixel Pixel
In-Game Special Effects and Lighting Introduction! Tomas Arce! Special Thanks! Matthias Wloka! Craig Galley! Stephen Broumley! Cryrus Lum! Sumie Arce! Inevitable! nvidia! Bungy What Is Per-Pixel Pixel
Whiz-Bang Graphics and Media Performance for Java Platform, Micro Edition (JavaME)
 Whiz-Bang Graphics and Media Performance for Java Platform, Micro Edition (JavaME) Pavel Petroshenko, Sun Microsystems, Inc. Ashmi Bhanushali, NVIDIA Corporation Jerry Evans, Sun Microsystems, Inc. Nandini
Whiz-Bang Graphics and Media Performance for Java Platform, Micro Edition (JavaME) Pavel Petroshenko, Sun Microsystems, Inc. Ashmi Bhanushali, NVIDIA Corporation Jerry Evans, Sun Microsystems, Inc. Nandini
Texture mapping. Computer Graphics CSE 167 Lecture 9
 Texture mapping Computer Graphics CSE 167 Lecture 9 CSE 167: Computer Graphics Texture Mapping Overview Interpolation Wrapping Texture coordinates Anti aliasing Mipmaps Other mappings Including bump mapping
Texture mapping Computer Graphics CSE 167 Lecture 9 CSE 167: Computer Graphics Texture Mapping Overview Interpolation Wrapping Texture coordinates Anti aliasing Mipmaps Other mappings Including bump mapping
Today. Texture mapping in OpenGL. Texture mapping. Basic shaders for texturing. Today. Computergrafik
 Computergrafik Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Texture mapping Glue textures (images) onto
Computergrafik Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Texture mapping Glue textures (images) onto
CS5620 Intro to Computer Graphics
 So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
Introduction to 3D Graphics
 Graphics Without Polygons Volume Rendering May 11, 2010 So Far Volumetric Rendering Techniques Misc. So Far Extended the Fixed Function Pipeline with a Programmable Pipeline Programming the pipeline is
Graphics Without Polygons Volume Rendering May 11, 2010 So Far Volumetric Rendering Techniques Misc. So Far Extended the Fixed Function Pipeline with a Programmable Pipeline Programming the pipeline is
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Advanced Lighting Techniques Due: Monday November 2 at 10pm
 CMSC 23700 Autumn 2015 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 3 October 20, 2015 Advanced Lighting Techniques Due: Monday November 2 at 10pm 1 Introduction This assignment is the third and final part
CMSC 23700 Autumn 2015 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 3 October 20, 2015 Advanced Lighting Techniques Due: Monday November 2 at 10pm 1 Introduction This assignment is the third and final part
Hardware-Assisted Relief Texture Mapping
 EUROGRAPHICS 0x / N.N. and N.N. Short Presentations Hardware-Assisted Relief Texture Mapping Masahiro Fujita and Takashi Kanai Keio University Shonan-Fujisawa Campus, Fujisawa, Kanagawa, Japan Abstract
EUROGRAPHICS 0x / N.N. and N.N. Short Presentations Hardware-Assisted Relief Texture Mapping Masahiro Fujita and Takashi Kanai Keio University Shonan-Fujisawa Campus, Fujisawa, Kanagawa, Japan Abstract
Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows
 Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows Tom Thorne Slides courtesy of Taku Komura www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/cg Overview Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow textures Shadow volume Shadow map Soft
Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows Tom Thorne Slides courtesy of Taku Komura www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/cg Overview Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow textures Shadow volume Shadow map Soft
CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3
 ?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
Computer Graphics. Shadows
 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
#Short presentation of the guys
 1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on a PC/XBOX360/PS3 game. For
1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on a PC/XBOX360/PS3 game. For
Computergrafik. Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016 2 Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures 3 Texture mapping Glue textures (images)
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016 2 Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures 3 Texture mapping Glue textures (images)
Textures and normals in ray tracing
 Textures and normals in ray tracing CS 4620 Lecture 7 1 Texture mapping Objects have properties that vary across the surface 2 Texture Mapping So we make the shading parameters vary across the surface
Textures and normals in ray tracing CS 4620 Lecture 7 1 Texture mapping Objects have properties that vary across the surface 2 Texture Mapping So we make the shading parameters vary across the surface
Normal Maps and Cube Maps. What are they and what do they mean?
 Normal Maps and Cube Maps What are they and what do they mean? What s the Point of All This? Q: What re we doing? What s the Point of All This? Q: What re we doing? A: Making a game that looks good What
Normal Maps and Cube Maps What are they and what do they mean? What s the Point of All This? Q: What re we doing? What s the Point of All This? Q: What re we doing? A: Making a game that looks good What
Building scalable 3D applications. Ville Miettinen Hybrid Graphics
 Building scalable 3D applications Ville Miettinen Hybrid Graphics What s going to happen... (1/2) Mass market: 3D apps will become a huge success on low-end and mid-tier cell phones Retro-gaming New game
Building scalable 3D applications Ville Miettinen Hybrid Graphics What s going to happen... (1/2) Mass market: 3D apps will become a huge success on low-end and mid-tier cell phones Retro-gaming New game
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline
 CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
Lecture 21: Shading. put your trust in my shadow. Judges 9:15
 Lecture 21: Shading put your trust in my shadow. Judges 9:15 1. Polygonal Models Polygonal models are one of the most common representations for geometry in Computer Graphics. Polygonal models are popular
Lecture 21: Shading put your trust in my shadow. Judges 9:15 1. Polygonal Models Polygonal models are one of the most common representations for geometry in Computer Graphics. Polygonal models are popular
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Textures can Alias. Schedule. Questions? Quiz 1: Tuesday October 26 th, in class (1 week from today!
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
TEXTURE MAPPING. DVA338 Computer Graphics Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri
 TEXTURE MAPPING DVA338 Computer Graphics Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri OVERVIEW Motivation Texture Mapping Coordinate Mapping (2D, 3D) Perspective Correct Interpolation Texture Filtering Mip-mapping Anisotropic
TEXTURE MAPPING DVA338 Computer Graphics Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri OVERVIEW Motivation Texture Mapping Coordinate Mapping (2D, 3D) Perspective Correct Interpolation Texture Filtering Mip-mapping Anisotropic
LEVEL 1 ANIMATION ACADEMY2010
 1 Textures add more realism to an environment and characters. There are many 2D painting programs that can be used to create textures, such as Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter. Many artists use photographs
1 Textures add more realism to an environment and characters. There are many 2D painting programs that can be used to create textures, such as Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter. Many artists use photographs
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry
 INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Texturing Christopher Dyken Martin Reimers 06.10.2010 Page 1 Texturing Linear interpolation Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5: Visual Appearance Chapter 6:
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Texturing Christopher Dyken Martin Reimers 06.10.2010 Page 1 Texturing Linear interpolation Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5: Visual Appearance Chapter 6:
Complex Shading Algorithms
 Complex Shading Algorithms CPSC 414 Overview So far Rendering Pipeline including recent developments Today Shading algorithms based on the Rendering Pipeline Arbitrary reflection models (BRDFs) Bump mapping
Complex Shading Algorithms CPSC 414 Overview So far Rendering Pipeline including recent developments Today Shading algorithms based on the Rendering Pipeline Arbitrary reflection models (BRDFs) Bump mapping
Soft shadows. Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February
 Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Computergrafik. Matthias Zwicker. Herbst 2010
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
Recall: Indexing into Cube Map
 Recall: Indexing into Cube Map Compute R = 2(N V)N-V Object at origin Use largest magnitude component of R to determine face of cube Other 2 components give texture coordinates V R Cube Map Layout Example
Recall: Indexing into Cube Map Compute R = 2(N V)N-V Object at origin Use largest magnitude component of R to determine face of cube Other 2 components give texture coordinates V R Cube Map Layout Example
C P S C 314 S H A D E R S, O P E N G L, & J S RENDERING PIPELINE. Mikhail Bessmeltsev
 C P S C 314 S H A D E R S, O P E N G L, & J S RENDERING PIPELINE UGRAD.CS.UBC.C A/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev 1 WHAT IS RENDERING? Generating image from a 3D scene 2 WHAT IS RENDERING? Generating image
C P S C 314 S H A D E R S, O P E N G L, & J S RENDERING PIPELINE UGRAD.CS.UBC.C A/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev 1 WHAT IS RENDERING? Generating image from a 3D scene 2 WHAT IS RENDERING? Generating image
Surface Rendering. Surface Rendering
 Surface Rendering Surface Rendering Introduce Mapping Methods - Texture Mapping - Environmental Mapping - Bump Mapping Go over strategies for - Forward vs backward mapping 2 1 The Limits of Geometric Modeling
Surface Rendering Surface Rendering Introduce Mapping Methods - Texture Mapping - Environmental Mapping - Bump Mapping Go over strategies for - Forward vs backward mapping 2 1 The Limits of Geometric Modeling
Texture Mapping and Sampling
 Texture Mapping and Sampling CPSC 314 Wolfgang Heidrich The Rendering Pipeline Geometry Processing Geometry Database Model/View Transform. Lighting Perspective Transform. Clipping Scan Conversion Depth
Texture Mapping and Sampling CPSC 314 Wolfgang Heidrich The Rendering Pipeline Geometry Processing Geometry Database Model/View Transform. Lighting Perspective Transform. Clipping Scan Conversion Depth
Texture Mapping. CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science
 Texture Mapping CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce Mapping Methods - Texture Mapping - Environment Mapping - Bump Mapping Consider
Texture Mapping CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce Mapping Methods - Texture Mapping - Environment Mapping - Bump Mapping Consider
CS GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 11: GPU Texturing 1. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 11: GPU Texturing 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #6 (until Mar. 9) Read (required): Programming Massively Parallel Processors book, Chapter 4 (CUDA
CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 11: GPU Texturing 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #6 (until Mar. 9) Read (required): Programming Massively Parallel Processors book, Chapter 4 (CUDA
Orthogonal Projection Matrices. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING
 CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization
 Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization GPU Volume Raycasting Christof Rezk-Salama University of Siegen, Germany Volume Rendering in a Nutshell Image Plane Eye Data Set Back-to-front iteration
Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization GPU Volume Raycasting Christof Rezk-Salama University of Siegen, Germany Volume Rendering in a Nutshell Image Plane Eye Data Set Back-to-front iteration
Practical Shadows. Outline
 Practical Shadows Out of the demo, into the engine Tom Forsyth RAD Game Tools Outline Shadow volumes (stencil shadows) Fairly brief covered well elsewhere Shadow buffers Scene management of shadow buffers
Practical Shadows Out of the demo, into the engine Tom Forsyth RAD Game Tools Outline Shadow volumes (stencil shadows) Fairly brief covered well elsewhere Shadow buffers Scene management of shadow buffers
Optimizing Direct3D for the GeForce 256 Douglas H. Rogers Please send me your comments/questions/suggestions
 Optimizing Direct3D for the GeForce 256 Douglas H. Rogers Please send me your comments/questions/suggestions drogers@nvidia.com Transform and Lighting (T&L) Acceleration under Direct3D To enable hardware
Optimizing Direct3D for the GeForce 256 Douglas H. Rogers Please send me your comments/questions/suggestions drogers@nvidia.com Transform and Lighting (T&L) Acceleration under Direct3D To enable hardware
Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.
 Shadows Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.com Practical & Robust Stenciled Shadow Volumes for Hardware-Accelerated
Shadows Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.com Practical & Robust Stenciled Shadow Volumes for Hardware-Accelerated
Advanced Graphics and Animation
 Advanced Graphics and Animation Character Marco Gillies and Dan Jones Goldsmiths Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will be able to describe How 3D characters are animated Skeletal animation
Advanced Graphics and Animation Character Marco Gillies and Dan Jones Goldsmiths Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will be able to describe How 3D characters are animated Skeletal animation
Module Contact: Dr Stephen Laycock, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series PG Examination 2013-14 COMPUTER GAMES DEVELOPMENT CMPSME27 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer any THREE questions. (40 marks each) Notes are
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series PG Examination 2013-14 COMPUTER GAMES DEVELOPMENT CMPSME27 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer any THREE questions. (40 marks each) Notes are
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Ken Joy.! Winter 2014
 ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes. CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan
 Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011
 Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Computer Graphics: Programming, Problem Solving, and Visual Communication
 Computer Graphics: Programming, Problem Solving, and Visual Communication Dr. Steve Cunningham Computer Science Department California State University Stanislaus Turlock, CA 95382 copyright 2002, Steve
Computer Graphics: Programming, Problem Solving, and Visual Communication Dr. Steve Cunningham Computer Science Department California State University Stanislaus Turlock, CA 95382 copyright 2002, Steve
3D Programming. 3D Programming Concepts. Outline. 3D Concepts. 3D Concepts -- Coordinate Systems. 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models
 3D Programming Concepts Outline 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models 3D Programming CS 4390 3D Computer 1 2 3D Concepts 3D Model is a 3D simulation of an object. Coordinate Systems 3D Models 3D Shapes 3D Concepts
3D Programming Concepts Outline 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models 3D Programming CS 4390 3D Computer 1 2 3D Concepts 3D Model is a 3D simulation of an object. Coordinate Systems 3D Models 3D Shapes 3D Concepts
PROFESSIONAL. WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB. Andreas Anyuru WILEY. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
 PROFESSIONAL WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB Andreas Anyuru WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. INTRODUCTION xxl CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING WEBGL 1 The Basics of WebGL 1 So Why Is WebGL So Great?
PROFESSIONAL WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB Andreas Anyuru WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. INTRODUCTION xxl CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING WEBGL 1 The Basics of WebGL 1 So Why Is WebGL So Great?
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2014
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2014 Announcements Project 2 due Friday, Oct. 24 th Midterm Exam
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2014 Announcements Project 2 due Friday, Oct. 24 th Midterm Exam
Hardware Shading: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges
 Hardware Shading: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges Hans-Peter Seidel Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken,, Germany Graphics Hardware Hardware is now fast enough for complex geometry for
Hardware Shading: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges Hans-Peter Seidel Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken,, Germany Graphics Hardware Hardware is now fast enough for complex geometry for
https://ilearn.marist.edu/xsl-portal/tool/d4e4fd3a-a3...
 Assessment Preview - This is an example student view of this assessment done Exam 2 Part 1 of 5 - Modern Graphics Pipeline Question 1 of 27 Match each stage in the graphics pipeline with a description
Assessment Preview - This is an example student view of this assessment done Exam 2 Part 1 of 5 - Modern Graphics Pipeline Question 1 of 27 Match each stage in the graphics pipeline with a description
Drawing a Crowd. David Gosselin Pedro V. Sander Jason L. Mitchell. 3D Application Research Group ATI Research
 Drawing a Crowd David Gosselin Pedro V. Sander Jason L. Mitchell 3D Application Research Group ATI Research Introduction In this chapter, we present a technique for efficiently rendering a large crowd
Drawing a Crowd David Gosselin Pedro V. Sander Jason L. Mitchell 3D Application Research Group ATI Research Introduction In this chapter, we present a technique for efficiently rendering a large crowd
Textures. Texture coordinates. Introduce one more component to geometry
 Texturing & Blending Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides by Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Textures Rendering tiny triangles
Texturing & Blending Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides by Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Textures Rendering tiny triangles
The Rasterization Pipeline
 Lecture 5: The Rasterization Pipeline Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley CS184/284A, Spring 2016 What We ve Covered So Far z x y z x y (0, 0) (w, h) Position objects and the camera in the world
Lecture 5: The Rasterization Pipeline Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley CS184/284A, Spring 2016 What We ve Covered So Far z x y z x y (0, 0) (w, h) Position objects and the camera in the world
Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment. Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment
 Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment Screen-space techniques Deferred rendering Screen-space ambient occlusion Depth of Field
Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment Screen-space techniques Deferred rendering Screen-space ambient occlusion Depth of Field
Surface Detail Maps with Soft Self- Shadowing. Chris Green, VALVE
 Surface Detail Maps with Soft Self- Shadowing Chris Green, VALVE Contribution A replacement format for surface bumpmaps Encodes surface orientation, ambient occlusion, selfshadowing, and albedo modulation
Surface Detail Maps with Soft Self- Shadowing Chris Green, VALVE Contribution A replacement format for surface bumpmaps Encodes surface orientation, ambient occlusion, selfshadowing, and albedo modulation
Lets assume each object has a defined colour. Hence our illumination model is looks unrealistic.
 Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Chapter 17: The Truth about Normals
 Chapter 17: The Truth about Normals What are Normals? When I first started with Blender I read about normals everywhere, but all I knew about them was: If there are weird black spots on your object, go
Chapter 17: The Truth about Normals What are Normals? When I first started with Blender I read about normals everywhere, but all I knew about them was: If there are weird black spots on your object, go
Homework #2 and #3 Due Friday, October 12 th and Friday, October 19 th
 Homework #2 and #3 Due Friday, October 12 th and Friday, October 19 th 1. a. Show that the following sequences commute: i. A rotation and a uniform scaling ii. Two rotations about the same axis iii. Two
Homework #2 and #3 Due Friday, October 12 th and Friday, October 19 th 1. a. Show that the following sequences commute: i. A rotation and a uniform scaling ii. Two rotations about the same axis iii. Two
Advanced 3D Game Programming with DirectX* 10.0
 Advanced 3D Game Programming with DirectX* 10.0 Peter Walsh Wordware Publishing, Inc. Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xv Chapter I Windows I A Word about Windows I Hungarian Notation 3 General Windows
Advanced 3D Game Programming with DirectX* 10.0 Peter Walsh Wordware Publishing, Inc. Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xv Chapter I Windows I A Word about Windows I Hungarian Notation 3 General Windows
Graphics Performance Optimisation. John Spitzer Director of European Developer Technology
 Graphics Performance Optimisation John Spitzer Director of European Developer Technology Overview Understand the stages of the graphics pipeline Cherchez la bottleneck Once found, either eliminate or balance
Graphics Performance Optimisation John Spitzer Director of European Developer Technology Overview Understand the stages of the graphics pipeline Cherchez la bottleneck Once found, either eliminate or balance
Illumination Models & Shading
 Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Programming Graphics Hardware
 Tutorial 5 Programming Graphics Hardware Randy Fernando, Mark Harris, Matthias Wloka, Cyril Zeller Overview of the Tutorial: Morning 8:30 9:30 10:15 10:45 Introduction to the Hardware Graphics Pipeline
Tutorial 5 Programming Graphics Hardware Randy Fernando, Mark Harris, Matthias Wloka, Cyril Zeller Overview of the Tutorial: Morning 8:30 9:30 10:15 10:45 Introduction to the Hardware Graphics Pipeline
Chapter Answers. Appendix A. Chapter 1. This appendix provides answers to all of the book s chapter review questions.
 Appendix A Chapter Answers This appendix provides answers to all of the book s chapter review questions. Chapter 1 1. What was the original name for the first version of DirectX? B. Games SDK 2. Which
Appendix A Chapter Answers This appendix provides answers to all of the book s chapter review questions. Chapter 1 1. What was the original name for the first version of DirectX? B. Games SDK 2. Which
LIGHTING - 1. Note. Lights. Ambient occlusion
 Note LIGHTING - 1 The creation and use of lights varies greatly between the default Blender renderer and the Cycles renderer. This section refers only to simple lighting in the default renderer. Lights
Note LIGHTING - 1 The creation and use of lights varies greatly between the default Blender renderer and the Cycles renderer. This section refers only to simple lighting in the default renderer. Lights
Lighting and Shading
 Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
Methodology for Lecture. Importance of Lighting. Outline. Shading Models. Brief primer on Color. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010) CS 184, Lecture 11: OpenGL 3 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Methodology for Lecture Lecture deals with lighting (teapot shaded as in HW1) Some Nate
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010) CS 184, Lecture 11: OpenGL 3 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Methodology for Lecture Lecture deals with lighting (teapot shaded as in HW1) Some Nate
Texture Mapping. Michael Kazhdan ( /467) HB Ch. 14.8,14.9 FvDFH Ch. 16.3, , 16.6
 Texture Mapping Michael Kazhdan (61.457/467) HB Ch. 14.8,14.9 FvDFH Ch. 16.3, 16.4.5, 16.6 Textures We know how to go from this to this J. Birn Textures But what about this to this? J. Birn Textures How
Texture Mapping Michael Kazhdan (61.457/467) HB Ch. 14.8,14.9 FvDFH Ch. 16.3, 16.4.5, 16.6 Textures We know how to go from this to this J. Birn Textures But what about this to this? J. Birn Textures How
#Short presentation of the guys
 1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on Remember me, the new Capcom
1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on Remember me, the new Capcom
Shading/Texturing. Dr. Scott Schaefer
 Shading/Texturing Dr. Scott Schaefer Problem / Problem / Problem 4/ Problem / Problem / Shading Algorithms Flat Shading Gouraud Shading Phong Shading / Flat Shading Apply same color across entire polygon
Shading/Texturing Dr. Scott Schaefer Problem / Problem / Problem 4/ Problem / Problem / Shading Algorithms Flat Shading Gouraud Shading Phong Shading / Flat Shading Apply same color across entire polygon
Shading 1: basics Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Shading 1: basics Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Picking colors Shading is finding the right color for a pixel This color depends on several factors: The material of the surface itself The color and
Shading 1: basics Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Picking colors Shading is finding the right color for a pixel This color depends on several factors: The material of the surface itself The color and
Shading Shades. Frank Jargstorff. June 1, Abstract
 Shading Shades Frank Jargstorff fjargstorff@nvidia.com June 1, 2004 Abstract Procedural material shaders continue to pop up since the advent of fragment programmability. Most of these shaders concentrate
Shading Shades Frank Jargstorff fjargstorff@nvidia.com June 1, 2004 Abstract Procedural material shaders continue to pop up since the advent of fragment programmability. Most of these shaders concentrate
Life on the Bleeding Edge: More Secrets of the NVIDIA Demo Team Eugene d Eon NVIDIA Corporation.
 Life on the Bleeding Edge: More Secrets of the NVIDIA Demo Team Eugene d Eon Run the Demo Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Skin Shading Skin Shading Same
Life on the Bleeding Edge: More Secrets of the NVIDIA Demo Team Eugene d Eon Run the Demo Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Concept Artwork Skin Shading Skin Shading Same
Abstract. 2 Description of the Effects Used. 1 Introduction Phong Illumination Bump Mapping
 Developing a Real-Time Renderer With Optimized Shadow Volumes Mátyás Premecz (email: pmat@freemail.hu) Department of Control Engineering and Information Technology, Budapest University of Technolgy Hungary
Developing a Real-Time Renderer With Optimized Shadow Volumes Mátyás Premecz (email: pmat@freemail.hu) Department of Control Engineering and Information Technology, Budapest University of Technolgy Hungary
CS 464 Review. Review of Computer Graphics for Final Exam
 CS 464 Review Review of Computer Graphics for Final Exam Goal: Draw 3D Scenes on Display Device 3D Scene Abstract Model Framebuffer Matrix of Screen Pixels In Computer Graphics: If it looks right then
CS 464 Review Review of Computer Graphics for Final Exam Goal: Draw 3D Scenes on Display Device 3D Scene Abstract Model Framebuffer Matrix of Screen Pixels In Computer Graphics: If it looks right then
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
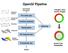 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
