Introduction to VPython for E&M This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython
|
|
|
- Evelyn Barnett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to VPython for E&M This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython VPython is a programming language that allows you to easily make 3-D graphics and animations. We will use it extensively in this course to model physical systems. First we will introduce how to create simple 3-D objects. Then we will use VPython to explore vectors and vector operations in 3-D. On the screen desktop there should be an icon called VPython Starter (icon with a snake). Click on the icon. This starts IDLE, which is the editing environment for VPython. 1. Starting a program Enter the following line of code in the IDLE editor window from visual import * Every VPython program begins with this line. This line tells the program to use the 3D module (called visual ). Before we write any more, let s save the program: In the IDLE editor, from the File menu, select Save. Browse to a location where you can save the file, and give it the name vectors.py. YOU MUST TYPE the.py file extension --IDLE will NOT automatically add it. 2. Creating a sphere Now let s tell VPython to make a sphere. On the next line, type: sphere() This line tells the computer to create a sphere object. Run the program by pressing F5 on the keyboard (fn-f5). Two new windows appear in addition to the editing window. One of them is the 3-D graphics window, which now contains a sphere. 3. The 3-D graphics scene By default the sphere is at the center of the scene, and the camera (that is, your point of view) is looking directly at the center. Hold down the option key and mouse button and move the mouse up and down to make the camera move closer or farther away from the center of the scene. Hold down the apply key and mouse button alone and move the mouse to make the camera revolve around the scene, while always looking at the center. When you first run the program, the coordinate system has the positive x direction to the right, the positive y direction pointing up, and the positive z direction coming out of the screen toward you. You can then rotate the camera view to make these axes point in other directions. 4. The Python Shell window The second new window that opened when you ran the program is the Python Shell window. If you include lines in the program that tell the computer to print text, the text will appear in this window. Use the mouse to make the Python Shell window smaller, and move it to the lower part of the screen. Keep it open when you are writing and running programs so you can easily spot error messages, which appear in this window. Make your edit window small enough that you can see both the edit window and the Python Shell window at all times. Do not expand the edit window to fill the whole screen. You will lose important information if you do! To kill the program, close the graphics window. Do not close the Python Shell window. To see an example of an error message, let s try making a spelling mistake:
2 Change the first line of the program to the following: from bisual import * Notice you get a message in red text in the Python Shell window. The message gives the filename, the line where the error occurred, and a description of the error (in this case ImportError: No module named bisual ). Correct the error in the first line. Whenever your program fails to run properly, look for a red error message in the Python Shell window. Even if you don t understand the error message, it is important to be able to see it, in order to find out that there is an error in your code. This helps you distinguish between a typing or coding mistake, and a program that runs correctly but does something other than what you intended. 5. Attributes Now let s give the sphere a different position in space and a radius. Change the last line of the program to the following: sphere(pos=vector(-5,2,-3), radius=0.40, color=color.red) The sphere-creation statement gives the sphere object three attributes : 1.) pos: the position vector of the center of the sphere, relative to the origin at the center of the screen 2.) radius: the sphere s radius 3.) color: the sphere s color. Color values are written as color.xxx, where xxx could be red, blue, green, cyan, magenta, yellow, orange, black, or white. Change the last line to read: sphere(pos=vector(2,4,0), radius=0.20, color=color.white) Note the changes in the sphere s position, radius, and color. Experiment with different values for the attributes of the sphere. Try giving the sphere other position vectors. Try giving it different values for radius. Run the program each time you make a change to see the results. When you are done, reset the line to how it appears above (that is, pos=vector(2,4,0), and radius=0.20). 6. Autoscaling and units VPython automatically zooms the camera in or out so that all objects appear in the window. Because of this autoscaling, the numbers for the pos and radius could be in any consistent set of units, like meters, centimeters, inches, etc. For example, this could represent a sphere with a radius 0.20 m and a position vector of < 2, 4, 0 > m. In this course we will always use SI units in our programs ( Systeme International, the system of units based on meters, kilograms, and seconds). 7. Creating a second object We can tell the program to create additional objects. Type the following on a new line, then run the program: sphere(pos=vector(-3,-1,0), radius=0.15, color=color.green) You should now see the original white sphere and a new green sphere. In later exercises, the white sphere will represent a baseball and the green sphere will represent a tennis ball. (The radii are exaggerated for visibility.) 8. Arrows We often use arrow objects in VPython to depict vector quantities. We next add arrows to our programs.
3 Type the following on a new line, then run the program: arrow(pos=vector(2,-3,0), axis=vector(3,4,0), color=color.cyan) This line tells VPython to create an arrow object with 3 attributes: 1.) pos: the position vector of the tail of the arrow. In this case, the tail of the arrow is at the position < 2, -3,0 > m. 2.) axis: the components of the arrow vector; that is, the vector measured from the tail to the tip of the arrow. In this case, the arrow vector is < 3, 4, 0 > m. 3.) color: the arrow s color. To demonstrate the difference between pos and axis, let s make a second arrow with a different pos but same axis. Type the following on a new line, then run the program: arrow(pos=vector(3,2,0), axis=vector(3,4,0), color=color.red) Note the red arrow starts at a different point than the cyan arrow, but has the same magnitude and direction. This is because they have the same axis, but different values of pos. Question: What position would you give a sphere so that it would appear at the tip of the red arrow? Discuss this with your partners. Then check the answer at the end of this tutorial. 9. Scaling an arrow s axis Since the axis of an arrow is a vector, we can perform scalar multiplication on it. Modify the axis of the red arrow by changing the last line of the program to the following: arrow(pos=vector(3,2,0), axis=-0.5*vector(3,4,0), color=color.red) Run the program. The axis of the red arrow is now equal to -0.5 times the axis of the cyan arrow. This means that the red arrow now points in the opposite direction of the cyan arrow and is half as long. Multiplying an axis vector by a scalar will change the length of the arrow, because it changes the magnitude of the axis vector. The arrow will point in the same direction if the scalar is positive, and in the opposite direction if the scalar is negative. 10. Comments (lines ignored by the computer) For the next section, we will only need one arrow. Let s make VPython ignore one of the arrow lines in the program. Change the second to last line (the cyan arrow) to the following: #arrow(pos=vector(2,-3,0), axis=vector(3,4,0), color=color.cyan) Note the pound sign at the beginning of the line. The pound sign lets VPython know that anything after it is just a comment, not actual instructions. The line will be skipped when the program is run. There should now only be one arrow on the screen. 11. Arrows and position vectors We can use arrows to represent position vectors and relative position vectors. Remember that a relative position vector that starts at a position A and ends at a position B can be found by final minus initial, or B - A. Do the following exercise: We want to make an arrow represent the relative position vector of the tennis ball with respect to the baseball. That is, the arrow s tail should be at the position of the baseball (the white sphere), and the tip should be at the position of the tennis ball (the green sphere). What would be the pos of this arrow, whose tail is on the baseball (the white sphere)? What would be the axis of this arrow, so that the tip is on the tennis ball (the green sphere)? Using these values of pos and axis, change the last line of the program to make the red arrow
4 point from the white baseball to the green tennis ball. Self check: Examine the 3D display carefully. If the red arrow does not point from the white baseball to the green tennis ball, correct your program. 12. Naming objects and using object attributes Now change the position of the tennis ball (the second, green sphere in the program)--imagine it now has a z-component, so that the line would now be: sphere(pos=vector(-3,-1,3.5), radius=0.15, color=color.green) Note that the relative position arrow still points in its original direction. We want this arrow to always point towards the tennis ball, no matter what position we give the tennis ball. To do this, we will have to refer to the tennis ball s position symbolically. But first, since there is more than one sphere and we need to tell them apart, we need to give the objects names. Give names to the spheres by changing the sphere lines of the program to the following: baseball = sphere(pos=vector(2,4,0), radius=0.20, color=color.white) tennisball = sphere(pos=vector(-3,-1,3.5), radius=0.15, color=color.green) We ve now given names to the spheres. We can use these names later in the program to refer to each sphere individually. Furthermore, we can specifically refer to the attributes of each object by writing, for example, tennisball.pos to refer to the tennis ball s position attribute, or baseball.color to refer to the baseball s color attribute. To see how this works, do the following exercise. Start a new line at the end of your program and type: print tennisball.pos Look at the text output window. The printed vector should be the same as the tennis ball s position. Let s also give a name to the arrow. Edit the last line of the program ( the red arrow) to the following, to give the arrow a name: bt = arrow(pos=vector(3,2,0), axis=-0.5*vector(3,4,0), color=color.red) Since we can refer to the attributes of objects symbolically, we want to write symbolic expressions for the axis and pos of the arrow bt. The expressions should use general attribute names in symbolic form, like tennisball.pos and baseball.pos, not specific numerical vector values such as vector(-3,-1,0). This way, if the positions of the tennis ball or baseball are changed, the arrow will still point from baseball to tennis ball. In symbols (letters, not numbers), what should be the pos of the red arrow that points from the baseball to the tennis ball? Make sure that your expression doesn t contain any numbers. In symbols (letters, not numbers), what should be the axis of the red arrow that points from the baseball to the tennis ball? (Remember that a relative position vector that starts at position A and ends at position B can be found by final minus initial, or B - A.). Make sure that your expression doesn t contain any numbers. Change the last line of the program so that the arrow statement uses these symbolic expressions for pos and axis. Examine the 3D display closely to make sure that the red arrow still points from the baseball to the tennis ball. If it doesn t, correct your program, still using no numbers. Change the pos of the baseball to (-4, -2, 5). Change the pos of the tennis ball to (3, 1, -2). Run the program. Examine the 3D display closely to make sure that the red arrow still points from the baseball to the tennis ball. If it doesn t, correct your program, still using no numbers.
5 13. Loops Another programming concept we will use in the course is a loop. A loop is a set of instructions in a program that are repeated over and over until some condition is met. There are several ways to create a loop, but usually in this course we will use the while statement to make loops. Let s try using a loop to repeatedly add to a quantity and print out the current value of the quantity. Start a new line at the end of your program and type: t = 0 This tells the program to create a variable called t and assign it the value of 0. On the next line, type: while t<10: Press the Enter key. Notice that the cursor is now indented on the next line. (If it s not indented, check to see if you typed the colon at the end of the while line. If not, go back and add the colon, then press Enter again.) The while statement tells the computer to repeat certain instructions while a certain condition is true. The lines that will be repeated are the ones that are indented after the while statement. In this case, the loop will continue as long as the variable t is less than 10. On the next (indented) line, type: t = t+0.5 In algebra, t = t+0.5 would be an incorrect statement, but in VPython as in most programming languages, the equals sign means something different than it does in algebra. In VPython, the equals sign is used for assignment, not equality. That is, the line assigns the variable t a new value, which is the current value of t plus 0.5. This means that the first time through the loop, the computer adds the current value of t, which is 0, to 0.5, giving 0.5, and then assigns t this new value of 0.5. The next time through the loop, the computer again adds 0.5 to t, making t equal to 1.0, and so on. To show this, on the next line (still indented), type: print t The last four lines you typed should now look like this: t = 0 while t<10: t = t+0.5 print t In the text output window, you should see a list of numbers from 0.5 to 10.0 in increments of 0.5. The first number, 0.5, is the value of t after the first time through the loop. Before each execution of the loop, the computer compares the current value of t to 10, and if it is less than 10, it executes the loop again. After the 20th time, the value of t is now When the computer goes back to the while statement for the next repetition, it finds the statement t<10 is now false, since 10.0 is not less than itself. Because the condition is false, the computer does not do any more executions of the loop. To go back to writing statements that are not repeated in a loop, simply unindent by pressing the Backspace key. Type the following on a new, unindented, line:
6 print "End of program" Now the last five lines should look like this: t = 0 while t<10: t = t+0.5 print t print "End of program" You ll now see the sequence of numbers printed, followed by the text End of program. The line that prints this text is not in the loop, so the text prints only after the loop is done executing. 14. A second loop At the end of the program, add a new loop. This loop should print out the value of angles in radians, starting at 0 and ending at 2*pi, in steps of pi/5. ('pi' is already defined as a constant in VPython). Use the name "theta" for the variable. 15. A new program (to be turned in in WebAssign): Start a new program by pulling down the File menu in IDLE and choosing New Window. The first line of the program should be: from visual import * Save your program, making sure to give it a name ending in '.py'. 16. Spheres at the corners of a cube Create 8 spheres, of any color, located at the corners of a cube. Make the spheres small enough, or the cube large enough, that the spheres are separated by a distance at least 5 times as large as the diameter of a single sphere (that is, the spheres should not be too close together). Create 4 arrows, placed tip to tail in such a way that they form a rectangle, with each vertex being the center of one of the spheres at the corners of the cube. For example, the arrows could go around one face of the cube, or they could form a rectangle that cuts diagonally through the cube. The arrows should be a color other than white. 17. A circle of spheres At the end of your program, write a loop to place 12 spheres in a circle surrounding the cube. To do this, you will need a loop like the one you wrote in section 14. Instead of printing the value of the angle, however, you will use the angle to position a sphere. It will probably be easiest to place the spheres in either the xy plane, the yz plane, or the xz plane. Remember that in this case only two of the coordinates vary. Also remember that the radius of the circle and the sine or cosine of the angle are needed to determine the coordinates of each sphere. In VPython, sin(θ) is written sin(theta), and cos(θ) is written cos(theta). Angles are in radians. 18. Turn in your program in WebAssign There is a WebAssign assignment where you will turn in the program you just finished (cube of spheres, etc.). One person from each group must upload the program. Answer to question in tutorial: The tip of the red arrow is located at pos + axis = < 3, 2, 0 > + < 3, 4, 0 > = < 6, 6, 0 >.
Introduction to VPython This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython.
 1 Introduction to VPython This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython. VPython is a programming language that allows you to easily make 3-D graphics and animations. We will
1 Introduction to VPython This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython. VPython is a programming language that allows you to easily make 3-D graphics and animations. We will
Introduction to VPython This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython.
 Introduction to VPython This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython. VPython is a programming language that allows you to easily make 3-D graphics and animations. We will
Introduction to VPython This tutorial will guide you through the basics of programming in VPython. VPython is a programming language that allows you to easily make 3-D graphics and animations. We will
Introduction to VPython and 3D Computer Modeling
 Introduction to VPython and 3D Computer Modeling OBJECTIVES In this course you will construct computer models to: Visualize motion in 3D Visualize vector quantities like position, momentum, and force in
Introduction to VPython and 3D Computer Modeling OBJECTIVES In this course you will construct computer models to: Visualize motion in 3D Visualize vector quantities like position, momentum, and force in
Introduction to 3D computer modeling
 OBJECTIVES In this course you will construct computer models to: Introduction to 3D computer modeling Visualize motion in 3D Visualize vector quantities like position, momentum, and force in 3D Do calculations
OBJECTIVES In this course you will construct computer models to: Introduction to 3D computer modeling Visualize motion in 3D Visualize vector quantities like position, momentum, and force in 3D Do calculations
Adding Fillet, Shell, and Draft Features
 Learn how to: Adding Fillet, Shell, and Draft Features I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills add draft features add fillet features use the Ball Corner Fillet option add shell features Before you begin...
Learn how to: Adding Fillet, Shell, and Draft Features I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills add draft features add fillet features use the Ball Corner Fillet option add shell features Before you begin...
Transforming Objects and Components
 4 Transforming Objects and Components Arrow selection Lasso selection Paint selection Move Rotate Scale Universal Manipulator Soft Modification Show Manipulator Last tool used Figure 4.1 Maya s manipulation
4 Transforming Objects and Components Arrow selection Lasso selection Paint selection Move Rotate Scale Universal Manipulator Soft Modification Show Manipulator Last tool used Figure 4.1 Maya s manipulation
L E S S O N 2 Background
 Flight, Naperville Central High School, Naperville, Ill. No hard hat needed in the InDesign work area Once you learn the concepts of good page design, and you learn how to use InDesign, you are limited
Flight, Naperville Central High School, Naperville, Ill. No hard hat needed in the InDesign work area Once you learn the concepts of good page design, and you learn how to use InDesign, you are limited
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b
 SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
SolidWorks 2½D Parts
 SolidWorks 2½D Parts IDeATe Laser Micro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part In this lab, you ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select
SolidWorks 2½D Parts IDeATe Laser Micro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part In this lab, you ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select
This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space.
 3D Modeling with Blender: 01. Blender Basics Overview This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space. Concepts Covered Blender s
3D Modeling with Blender: 01. Blender Basics Overview This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space. Concepts Covered Blender s
First Animated Model Yellow Submarine
 Course: 3D Design Title: First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (May 2012) First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Most of you are perhaps too young
Course: 3D Design Title: First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (May 2012) First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Most of you are perhaps too young
Lesson 1: Creating T- Spline Forms. In Samples section of your Data Panel, browse to: Fusion 101 Training > 03 Sculpt > 03_Sculpting_Introduction.
 3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
PLAY VIDEO. Fences can be any shape from a simple rectangle to a multisided polygon, even a circle.
 Chapter Eight Groups PLAY VIDEO INTRODUCTION There will be times when you need to perform the same operation on several elements. Although this can be done by repeating the operation for each individual
Chapter Eight Groups PLAY VIDEO INTRODUCTION There will be times when you need to perform the same operation on several elements. Although this can be done by repeating the operation for each individual
OrbBasic Lesson 1 Goto and Variables: Student Guide
 OrbBasic Lesson 1 Goto and Variables: Student Guide Sphero MacroLab is a really cool app to give the Sphero commands, but it s limited in what it can do. You give it a list of commands and it starts at
OrbBasic Lesson 1 Goto and Variables: Student Guide Sphero MacroLab is a really cool app to give the Sphero commands, but it s limited in what it can do. You give it a list of commands and it starts at
Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1
 Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1 Launch Inventor Professional 2015 1. Start a New part. Depending on how Inventor was installed, using this icon may get you an Inch or Metric file. To be
Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1 Launch Inventor Professional 2015 1. Start a New part. Depending on how Inventor was installed, using this icon may get you an Inch or Metric file. To be
Digitizer Leapfrogging
 Digitizer Leapfrogging Leapfrogging lets you digitize objects that are larger than your digitizing arm. You start with one section of the object, then leapfrog around by creating leapfrog stations in both
Digitizer Leapfrogging Leapfrogging lets you digitize objects that are larger than your digitizing arm. You start with one section of the object, then leapfrog around by creating leapfrog stations in both
OrbBasic 1: Student Guide
 OrbBasic 1: Student Guide Sphero MacroLab is a really cool app to give the Sphero commands, but it s limited in what it can do. You give it a list of commands and it starts at the top and goes to the bottom,
OrbBasic 1: Student Guide Sphero MacroLab is a really cool app to give the Sphero commands, but it s limited in what it can do. You give it a list of commands and it starts at the top and goes to the bottom,
Drawing a Circle. 78 Chapter 5. geometry.pyde. def setup(): size(600,600) def draw(): ellipse(200,100,20,20) Listing 5-1: Drawing a circle
 5 Transforming Shapes with Geometry In the teahouse one day Nasrudin announced he was selling his house. When the other patrons asked him to describe it, he brought out a brick. It s just a collection
5 Transforming Shapes with Geometry In the teahouse one day Nasrudin announced he was selling his house. When the other patrons asked him to describe it, he brought out a brick. It s just a collection
Creating T-Spline Forms
 1 / 28 Goals 1. Create a T-Spline Primitive Form 2. Create a T-Spline Revolve Form 3. Create a T-Spline Sweep Form 4. Create a T-Spline Loft Form 2 / 28 Instructions Step 1: Go to the Sculpt workspace
1 / 28 Goals 1. Create a T-Spline Primitive Form 2. Create a T-Spline Revolve Form 3. Create a T-Spline Sweep Form 4. Create a T-Spline Loft Form 2 / 28 Instructions Step 1: Go to the Sculpt workspace
Part II: Creating Visio Drawings
 128 Part II: Creating Visio Drawings Figure 5-3: Use any of five alignment styles where appropriate. Figure 5-4: Vertical alignment places your text at the top, bottom, or middle of a text block. You could
128 Part II: Creating Visio Drawings Figure 5-3: Use any of five alignment styles where appropriate. Figure 5-4: Vertical alignment places your text at the top, bottom, or middle of a text block. You could
BobCAD-CAM FAQ #50: How do I use a rotary 4th axis on a mill?
 BobCAD-CAM FAQ #50: How do I use a rotary 4th axis on a mill? Q: I ve read FAQ #46 on how to set up my milling machine. How do I enable 4th axis to actually use it? A: Enabling 4th axis in the machine
BobCAD-CAM FAQ #50: How do I use a rotary 4th axis on a mill? Q: I ve read FAQ #46 on how to set up my milling machine. How do I enable 4th axis to actually use it? A: Enabling 4th axis in the machine
AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body
 AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body Abstract This project explores how to use the sculpting tools available in Autodesk Fusion 360 Ultimate to design the body of a RC car. John Helfen john.helfen@autodesk.com
AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body Abstract This project explores how to use the sculpting tools available in Autodesk Fusion 360 Ultimate to design the body of a RC car. John Helfen john.helfen@autodesk.com
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25
 Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
Quick Guide. Choose It Maker 2. Overview/Introduction. ChooseIt!Maker2 is a motivating program at first because of the visual and musical
 Choose It Maker 2 Quick Guide Created 09/06 Updated SM Overview/Introduction This is a simple to use piece of software that can be tailored for use by children as an alternative to a pencil and paper worksheet,
Choose It Maker 2 Quick Guide Created 09/06 Updated SM Overview/Introduction This is a simple to use piece of software that can be tailored for use by children as an alternative to a pencil and paper worksheet,
3D Modeler Creating Custom myhouse Symbols
 3D Modeler Creating Custom myhouse Symbols myhouse includes a large number of predrawn symbols. For most designs and floorplans, these should be sufficient. For plans that require that special table, bed,
3D Modeler Creating Custom myhouse Symbols myhouse includes a large number of predrawn symbols. For most designs and floorplans, these should be sufficient. For plans that require that special table, bed,
Working with the Dope Sheet Editor to speed up animation and reverse time.
 Bouncing a Ball Page 1 of 2 Tutorial Bouncing a Ball A bouncing ball is a common first project for new animators. This classic example is an excellent tool for explaining basic animation processes in 3ds
Bouncing a Ball Page 1 of 2 Tutorial Bouncing a Ball A bouncing ball is a common first project for new animators. This classic example is an excellent tool for explaining basic animation processes in 3ds
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS This tutorial is essential pre-requisite material for anyone studying mechanical engineering. This tutorial uses the principle of learning by example.
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS This tutorial is essential pre-requisite material for anyone studying mechanical engineering. This tutorial uses the principle of learning by example.
4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb?
 1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
Using IDLE for
 Using IDLE for 15-110 Step 1: Installing Python Download and install Python using the Resources page of the 15-110 website. Be sure to install version 3.3.2 and the correct version depending on whether
Using IDLE for 15-110 Step 1: Installing Python Download and install Python using the Resources page of the 15-110 website. Be sure to install version 3.3.2 and the correct version depending on whether
CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and graphs
 Ch 5. Trigonometry 6. Angles 6. Right triangles 6. Trig funs for general angles 5.: Trigonometric functions and graphs 5.5 Inverse functions CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and
Ch 5. Trigonometry 6. Angles 6. Right triangles 6. Trig funs for general angles 5.: Trigonometric functions and graphs 5.5 Inverse functions CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and
Physics 212E Classical and Modern Physics Spring VPython Class 6: Phasors and Interference
 Physics 212E Classical and Modern Physics Spring 2017 VPython Class 6: Phasors and Interference 1 Introduction We re going to set up a VPython program that will take three inputs: the number of slits,
Physics 212E Classical and Modern Physics Spring 2017 VPython Class 6: Phasors and Interference 1 Introduction We re going to set up a VPython program that will take three inputs: the number of slits,
Activity A 1-D Free-Fall with v i = 0
 Physics 151 Practical 3 Python Programming Freefall Kinematics Department of Physics 60 St. George St. NOTE: Today's activities must be done in teams of one or two. There are now twice as many computers
Physics 151 Practical 3 Python Programming Freefall Kinematics Department of Physics 60 St. George St. NOTE: Today's activities must be done in teams of one or two. There are now twice as many computers
Google SketchUp. and SketchUp Pro 7. The book you need to succeed! CD-ROM Included! Kelly L. Murdock. Master SketchUp Pro 7 s tools and features
 CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
Using Google SketchUp
 Using Google SketchUp Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu http://cs.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/sketchup What is Google SketchUp? Google SketchUp is a program which lets you sketch in 3D. It is excellent for creating
Using Google SketchUp Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu http://cs.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/sketchup What is Google SketchUp? Google SketchUp is a program which lets you sketch in 3D. It is excellent for creating
SketchUp Quick Start For Surveyors
 SketchUp Quick Start For Surveyors Reason why we are doing this SketchUp allows surveyors to draw buildings very quickly. It allows you to locate them in a plan of the area. It allows you to show the relationship
SketchUp Quick Start For Surveyors Reason why we are doing this SketchUp allows surveyors to draw buildings very quickly. It allows you to locate them in a plan of the area. It allows you to show the relationship
Getting Started. Chapter 1. How to Get Matlab. 1.1 Before We Begin Matlab to Accompany Lay s Linear Algebra Text
 Chapter 1 Getting Started How to Get Matlab Matlab physically resides on each of the computers in the Olin Hall labs. See your instructor if you need an account on these machines. If you are going to go
Chapter 1 Getting Started How to Get Matlab Matlab physically resides on each of the computers in the Olin Hall labs. See your instructor if you need an account on these machines. If you are going to go
Scale Rate by Object Size: Only available when the current Emitter Type is Surface, Curve, or Volume. If you turn on this attribute, the
 Basic Emitter Attributes Emitter Name: The name helps you identify the emitter object in the Outliner. If you don t enter a name, the emitter object receives a default name such as emitter1. Solver: (For
Basic Emitter Attributes Emitter Name: The name helps you identify the emitter object in the Outliner. If you don t enter a name, the emitter object receives a default name such as emitter1. Solver: (For
This is the opening view of blender.
 This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
 University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
Selective Space Structures Manual
 Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Blender Lesson Ceramic Bowl
 Blender Lesson Ceramic Bowl This lesson is going to show you how to create a ceramic looking bowl using the free program Blender. You will learn how to change the view, add, delete, scale and edit objects
Blender Lesson Ceramic Bowl This lesson is going to show you how to create a ceramic looking bowl using the free program Blender. You will learn how to change the view, add, delete, scale and edit objects
Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry
 Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry Review of Triangles Recall that the sum of all angles in any triangle is 180. Let s look at what this means for a right triangle: A right angle is an angle which
Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry Review of Triangles Recall that the sum of all angles in any triangle is 180. Let s look at what this means for a right triangle: A right angle is an angle which
WAYLAND FREE PUBLIC LIBRARY 3D Design and Printing Tutorial: Create a Keychain
 WAYLAND FREE PUBLIC LIBRARY 3D Design and Printing Tutorial: Create a Keychain Welcome! In this tutorial we will be creating a 3D printed keychain. You will personalize this name tag with text to make
WAYLAND FREE PUBLIC LIBRARY 3D Design and Printing Tutorial: Create a Keychain Welcome! In this tutorial we will be creating a 3D printed keychain. You will personalize this name tag with text to make
Plotting Points. By Francine Wolfe Professor Susan Rodger Duke University June 2010
 Plotting Points By Francine Wolfe Professor Susan Rodger Duke University June 2010 Description This tutorial will show you how to create a game where the player has to plot points on a graph. The method
Plotting Points By Francine Wolfe Professor Susan Rodger Duke University June 2010 Description This tutorial will show you how to create a game where the player has to plot points on a graph. The method
CREATING DESMOS ETOOLS
 CREATING DESMOS ETOOLS Table of Contents Using Desmos... 3 Creating & Using a Desmos Account (Top Black Bar)... 4 Domain/Range & Axis Labels & Zoom: (Right side Icons)... 6 Adding Items in the List Tray:
CREATING DESMOS ETOOLS Table of Contents Using Desmos... 3 Creating & Using a Desmos Account (Top Black Bar)... 4 Domain/Range & Axis Labels & Zoom: (Right side Icons)... 6 Adding Items in the List Tray:
An Approach to Content Creation for Trainz
 An Approach to Content Creation for Trainz Paul Hobbs Part 6 GMax Basics (Updates and sample files available from http://www.44090digitalmodels.de) Page 1 of 18 Version 3 Index Foreward... 3 The Interface...
An Approach to Content Creation for Trainz Paul Hobbs Part 6 GMax Basics (Updates and sample files available from http://www.44090digitalmodels.de) Page 1 of 18 Version 3 Index Foreward... 3 The Interface...
5. Introduction to Procedures
 5. Introduction to Procedures Topics: The module SimpleGraphics Creating and Showing figures Drawing Rectangles, Disks, and Stars Optional arguments Application Scripts Procedures We continue our introduction
5. Introduction to Procedures Topics: The module SimpleGraphics Creating and Showing figures Drawing Rectangles, Disks, and Stars Optional arguments Application Scripts Procedures We continue our introduction
Using Google SketchUp
 Using Google SketchUp Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu http://cs.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/sketchup What is Google SketchUp? Google SketchUp is a program which lets you sketch in 3D. It is excellent for creating
Using Google SketchUp Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu http://cs.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/sketchup What is Google SketchUp? Google SketchUp is a program which lets you sketch in 3D. It is excellent for creating
LIGHT: Two-slit Interference
 LIGHT: Two-slit Interference Objective: To study interference of light waves and verify the wave nature of light. Apparatus: Two red lasers (wavelength, λ = 633 nm); two orange lasers (λ = 612 nm); two
LIGHT: Two-slit Interference Objective: To study interference of light waves and verify the wave nature of light. Apparatus: Two red lasers (wavelength, λ = 633 nm); two orange lasers (λ = 612 nm); two
SETTING UP A. chapter
 1-4283-1960-3_03_Rev2.qxd 5/18/07 8:24 PM Page 1 chapter 3 SETTING UP A DOCUMENT 1. Create a new document. 2. Create master pages. 3. Apply master pages to document pages. 4. Place text and thread text.
1-4283-1960-3_03_Rev2.qxd 5/18/07 8:24 PM Page 1 chapter 3 SETTING UP A DOCUMENT 1. Create a new document. 2. Create master pages. 3. Apply master pages to document pages. 4. Place text and thread text.
DSP First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials
 DSP First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Lab Report: It is only necessary to turn in a report on Section 5 with graphs and explanations. You are ased to label the axes of your plots and include
DSP First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Lab Report: It is only necessary to turn in a report on Section 5 with graphs and explanations. You are ased to label the axes of your plots and include
QuickTutor. An Introductory SilverScreen Modeling Tutorial. Solid Modeler
 QuickTutor An Introductory SilverScreen Modeling Tutorial Solid Modeler TM Copyright Copyright 2005 by Schroff Development Corporation, Shawnee-Mission, Kansas, United States of America. All rights reserved.
QuickTutor An Introductory SilverScreen Modeling Tutorial Solid Modeler TM Copyright Copyright 2005 by Schroff Development Corporation, Shawnee-Mission, Kansas, United States of America. All rights reserved.
SNOWFLAKES PHOTO BORDER - PHOTOSHOP CS6 / CC
 Photo Effects: Snowflakes Photo Border (Photoshop CS6 / CC) SNOWFLAKES PHOTO BORDER - PHOTOSHOP CS6 / CC In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun snowflakes photo border,
Photo Effects: Snowflakes Photo Border (Photoshop CS6 / CC) SNOWFLAKES PHOTO BORDER - PHOTOSHOP CS6 / CC In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun snowflakes photo border,
CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION COMMANDS
 PROGRAMMING JANUARY 2005 CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION COMMANDS G02 CW CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION MOTION & G03 CCW CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION MOTION *X Circular end point X-axis motion *Y Circular end point Y-axis motion
PROGRAMMING JANUARY 2005 CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION COMMANDS G02 CW CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION MOTION & G03 CCW CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION MOTION *X Circular end point X-axis motion *Y Circular end point Y-axis motion
Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ x + 5y + 7z 9x + 3y + 11z
 Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
Plate 'n' Sheet Development Version 4 Professional Edition. Module 1
 Module 1 1. Introduction and Overview 2. Create a Shape 3. Develop a Pattern 4. Use the Viewing Controls 5. Getting Help Richard Stewart 2007 R & L CAD Services Pty Ltd Mackay QLD AUSTRALIA Page 1 Table
Module 1 1. Introduction and Overview 2. Create a Shape 3. Develop a Pattern 4. Use the Viewing Controls 5. Getting Help Richard Stewart 2007 R & L CAD Services Pty Ltd Mackay QLD AUSTRALIA Page 1 Table
MATLAB Tutorial III Variables, Files, Advanced Plotting
 MATLAB Tutorial III Variables, Files, Advanced Plotting A. Dealing with Variables (Arrays and Matrices) Here's a short tutorial on working with variables, taken from the book, Getting Started in Matlab.
MATLAB Tutorial III Variables, Files, Advanced Plotting A. Dealing with Variables (Arrays and Matrices) Here's a short tutorial on working with variables, taken from the book, Getting Started in Matlab.
PC-MATLAB PRIMER. This is intended as a guided tour through PCMATLAB. Type as you go and watch what happens.
 PC-MATLAB PRIMER This is intended as a guided tour through PCMATLAB. Type as you go and watch what happens. >> 2*3 ans = 6 PCMATLAB uses several lines for the answer, but I ve edited this to save space.
PC-MATLAB PRIMER This is intended as a guided tour through PCMATLAB. Type as you go and watch what happens. >> 2*3 ans = 6 PCMATLAB uses several lines for the answer, but I ve edited this to save space.
HAPPY HOLIDAYS PHOTO BORDER
 HAPPY HOLIDAYS PHOTO BORDER In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun Happy Holidays winter photo border! Photoshop ships with some great snowflake shapes that we can use in
HAPPY HOLIDAYS PHOTO BORDER In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create a simple and fun Happy Holidays winter photo border! Photoshop ships with some great snowflake shapes that we can use in
(Refer Slide Time: 00:04:20)
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 8 Three Dimensional Graphics Welcome back all of you to the lectures in Computer
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 8 Three Dimensional Graphics Welcome back all of you to the lectures in Computer
Adobe Illustrator. Quick Start Guide
 Adobe Illustrator Quick Start Guide 1 In this guide we will cover the basics of setting up an Illustrator file for use with the laser cutter in the InnovationStudio. We will also cover the creation of
Adobe Illustrator Quick Start Guide 1 In this guide we will cover the basics of setting up an Illustrator file for use with the laser cutter in the InnovationStudio. We will also cover the creation of
Technique or Feature Where Introduced
 Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
Using Microsoft Excel
 About Excel Using Microsoft Excel What is a Spreadsheet? Microsoft Excel is a program that s used for creating spreadsheets. So what is a spreadsheet? Before personal computers were common, spreadsheet
About Excel Using Microsoft Excel What is a Spreadsheet? Microsoft Excel is a program that s used for creating spreadsheets. So what is a spreadsheet? Before personal computers were common, spreadsheet
Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11
 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your
Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your
Autodesk Fusion 360: Model. Overview. Modeling techniques in Fusion 360
 Overview Modeling techniques in Fusion 360 Modeling in Fusion 360 is quite a different experience from how you would model in conventional history-based CAD software. Some users have expressed that it
Overview Modeling techniques in Fusion 360 Modeling in Fusion 360 is quite a different experience from how you would model in conventional history-based CAD software. Some users have expressed that it
Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
The Best of SketchUp This amazing 3D design program can make you a better woodworker.
 The Best of SketchUp This amazing 3D design program can make you a better woodworker. By David Heim More and more woodworkers have switched from T-square and pencil to the SketchUp 3D program to design
The Best of SketchUp This amazing 3D design program can make you a better woodworker. By David Heim More and more woodworkers have switched from T-square and pencil to the SketchUp 3D program to design
Class #10 Wednesday, November 8, 2017
 Graphics In Excel Before we create a simulation, we need to be able to make a drawing in Excel. The techniques we use here are also used in Mathematica and LabVIEW. Drawings in Excel take place inside
Graphics In Excel Before we create a simulation, we need to be able to make a drawing in Excel. The techniques we use here are also used in Mathematica and LabVIEW. Drawings in Excel take place inside
Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS. Learn about:
 Learn about: Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills windows mouse buttons applications and tasks menus icons part modeling viewing selecting data management using the online tutorials
Learn about: Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills windows mouse buttons applications and tasks menus icons part modeling viewing selecting data management using the online tutorials
TI-89 Calculator Workshop #1 The Basics
 page 1 TI-89 Calculator Workshop #1 The Basics After completing this workshop, students will be able to: 1. find, understand, and manipulate keys on the calculator keyboard 2. perform basic computations
page 1 TI-89 Calculator Workshop #1 The Basics After completing this workshop, students will be able to: 1. find, understand, and manipulate keys on the calculator keyboard 2. perform basic computations
CMPSCI 119 LAB #2 Anime Eyes Professor William T. Verts
 CMPSCI 119 LAB #2 Anime Eyes Professor William T. Verts The goal of this Python programming assignment is to write your own code inside a provided program framework, with some new graphical and mathematical
CMPSCI 119 LAB #2 Anime Eyes Professor William T. Verts The goal of this Python programming assignment is to write your own code inside a provided program framework, with some new graphical and mathematical
ME009 Engineering Graphics and Design CAD 1. 1 Create a new part. Click. New Bar. 2 Click the Tutorial tab. 3 Select the Part icon. 4 Click OK.
 PART A Reference: SolidWorks CAD Student Guide 2014 2 Lesson 2: Basic Functionality Active Learning Exercises Creating a Basic Part Use SolidWorks to create the box shown at the right. The step-by-step
PART A Reference: SolidWorks CAD Student Guide 2014 2 Lesson 2: Basic Functionality Active Learning Exercises Creating a Basic Part Use SolidWorks to create the box shown at the right. The step-by-step
3ds Max Cottage Step 1. Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch.
 3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
Introduction to SolidWorks Basics Materials Tech. Wood
 Introduction to SolidWorks Basics Materials Tech. Wood Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Book End... 2 Introduction... 2 Learning Intentions... 2 Modelling the Base... 3 Modelling the Front... 10
Introduction to SolidWorks Basics Materials Tech. Wood Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Book End... 2 Introduction... 2 Learning Intentions... 2 Modelling the Base... 3 Modelling the Front... 10
Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns
 Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns Make a new Folder inside your Computer Animation Folder and name it: Temple Save using Save As, and select Incremental Save, with 5 Saves. Name: Lesson3Temple YourName.ma
Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns Make a new Folder inside your Computer Animation Folder and name it: Temple Save using Save As, and select Incremental Save, with 5 Saves. Name: Lesson3Temple YourName.ma
Using Microsoft Word. Getting Started With Word. Starting the Program
 Using Microsoft Word Starting the Program There are several ways to start a program in Microsoft Windows and they may include the following: 1. Clicking an icon on the desktop. 2. Clicking an icon in the
Using Microsoft Word Starting the Program There are several ways to start a program in Microsoft Windows and they may include the following: 1. Clicking an icon on the desktop. 2. Clicking an icon in the
SketchUp Tool Basics
 SketchUp Tool Basics Open SketchUp Click the Start Button Click All Programs Open SketchUp Scroll Down to the SketchUp 2013 folder Click on the folder to open. Click on SketchUp. Set Up SketchUp (look
SketchUp Tool Basics Open SketchUp Click the Start Button Click All Programs Open SketchUp Scroll Down to the SketchUp 2013 folder Click on the folder to open. Click on SketchUp. Set Up SketchUp (look
Math 1525 Excel Lab 1 Introduction to Excel Spring, 2001
 Math 1525 Excel Lab 1 Introduction to Excel Spring, 2001 Goal: The goal of Lab 1 is to introduce you to Microsoft Excel, to show you how to graph data and functions, and to practice solving problems with
Math 1525 Excel Lab 1 Introduction to Excel Spring, 2001 Goal: The goal of Lab 1 is to introduce you to Microsoft Excel, to show you how to graph data and functions, and to practice solving problems with
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 162. Slide 2 / 162. Slide 3 / 162. Trigonometric Functions. Trig Functions
 Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Introduction to Matlab to Accompany Linear Algebra. Douglas Hundley Department of Mathematics and Statistics Whitman College
 Introduction to Matlab to Accompany Linear Algebra Douglas Hundley Department of Mathematics and Statistics Whitman College August 27, 2018 2 Contents 1 Getting Started 5 1.1 Before We Begin........................................
Introduction to Matlab to Accompany Linear Algebra Douglas Hundley Department of Mathematics and Statistics Whitman College August 27, 2018 2 Contents 1 Getting Started 5 1.1 Before We Begin........................................
Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder
 Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder 1 2 SketchUp 1. SketchUp is free, and you can download it from the website www.sketchup.com. For some K12 use, see www.sketchup.com/3dfor/k12-education.
Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder 1 2 SketchUp 1. SketchUp is free, and you can download it from the website www.sketchup.com. For some K12 use, see www.sketchup.com/3dfor/k12-education.
DeskCNC setup and operation manual
 DeskCNC setup and operation manual This document explains how to install, setup and cut foam shapes using DeskCNC 4 axis foam cutting software. The document will go through a step by step process of how
DeskCNC setup and operation manual This document explains how to install, setup and cut foam shapes using DeskCNC 4 axis foam cutting software. The document will go through a step by step process of how
Detailed instructions for video analysis using Logger Pro.
 Detailed instructions for video analysis using Logger Pro. 1. Begin by locating or creating a video of a projectile (or any moving object). Save it to your computer. Most video file types are accepted,
Detailed instructions for video analysis using Logger Pro. 1. Begin by locating or creating a video of a projectile (or any moving object). Save it to your computer. Most video file types are accepted,
Prerequisites: This tutorial assumes that you are familiar with the menu structure in FLUENT, and that you have solved Tutorial 1.
 Tutorial 22. Postprocessing Introduction: In this tutorial, the postprocessing capabilities of FLUENT are demonstrated for a 3D laminar flow involving conjugate heat transfer. The flow is over a rectangular
Tutorial 22. Postprocessing Introduction: In this tutorial, the postprocessing capabilities of FLUENT are demonstrated for a 3D laminar flow involving conjugate heat transfer. The flow is over a rectangular
AutoCAD 2009 Tutorial
 AutoCAD 2009 Tutorial Second Level: 3D Modeling Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD 2009
AutoCAD 2009 Tutorial Second Level: 3D Modeling Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD 2009
Randy H. Shih. Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS
 Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS WWW.SDCACAD.COM AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics! " # 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial Introduction Learning
Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS WWW.SDCACAD.COM AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics! " # 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial Introduction Learning
3D printing Workshop Breakdown
 3D printing Workshop Breakdown Opening Lecture/Remarks (20-30 Minutes) -Introduction to 3D modeling software Overview of what 3D modeling software is Introduction to 123D Design Introduction to 123D Design
3D printing Workshop Breakdown Opening Lecture/Remarks (20-30 Minutes) -Introduction to 3D modeling software Overview of what 3D modeling software is Introduction to 123D Design Introduction to 123D Design
My First iphone App (for Xcode version 6.4)
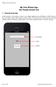 My First iphone App (for Xcode version 6.4) 1. Tutorial Overview In this tutorial, you re going to create a very simple application on the iphone or ipod Touch. It has a text field, a label, and a button
My First iphone App (for Xcode version 6.4) 1. Tutorial Overview In this tutorial, you re going to create a very simple application on the iphone or ipod Touch. It has a text field, a label, and a button
A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015
 A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015 Written by Mitchell Youngerman Table of Contents Layout of Toolbars...pg 1 Creating Objects...pg 2 Selecting & Deselecting Objects...pg 3 Changing Perspective... pg 4 Transforming
A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015 Written by Mitchell Youngerman Table of Contents Layout of Toolbars...pg 1 Creating Objects...pg 2 Selecting & Deselecting Objects...pg 3 Changing Perspective... pg 4 Transforming
SCENE FILE MANIPULATION SCENE FILE MANIPULATION GETTING STARTED MODELING ANIMATION MATERIALS + MAPPING RENDERING. Saving Files. Save.
 SCENE FILE MANIPULATION SCENE FILE MANIPULATION There are several things you can do with a scene file in 3ds Max. You can save a file, save a file temporarily and retrieve it, and combine scene files.
SCENE FILE MANIPULATION SCENE FILE MANIPULATION There are several things you can do with a scene file in 3ds Max. You can save a file, save a file temporarily and retrieve it, and combine scene files.
Drawing Tools. Drawing a Rectangle
 Chapter Microsoft Word provides extensive DRAWING TOOLS that allow you to enhance the appearance of your documents. You can use these tools to assist in the creation of detailed publications, newsletters,
Chapter Microsoft Word provides extensive DRAWING TOOLS that allow you to enhance the appearance of your documents. You can use these tools to assist in the creation of detailed publications, newsletters,
Lab 3: For Loops. Introduction to Programming in Python. Name:
 Introduction to Programming in Python Name: Lab material prepared for Harrison High School Physics courses in collaboration with Purdue University as part of the project Science Education in Computational
Introduction to Programming in Python Name: Lab material prepared for Harrison High School Physics courses in collaboration with Purdue University as part of the project Science Education in Computational
Workshop BOND UNIVERSITY Bachelor of Interactive Multimedia and Design Beginner Game Dev Character Control Building a character animation controller.
 Workshop BOND UNIVERSITY Bachelor of Interactive Multimedia and Design Beginner Game Dev Character Control Building a character animation controller. FACULTY OF SOCIETY AND DESIGN Building a character
Workshop BOND UNIVERSITY Bachelor of Interactive Multimedia and Design Beginner Game Dev Character Control Building a character animation controller. FACULTY OF SOCIETY AND DESIGN Building a character
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson 1 - Basics and Modeling. Introduction to Robotics
 SOLIDWORKS: Lesson 1 - Basics and Modeling Fundamentals Introduction to Robotics SolidWorks SolidWorks is a 3D solid modeling package which allows users to develop full solid models in a simulated environment
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson 1 - Basics and Modeling Fundamentals Introduction to Robotics SolidWorks SolidWorks is a 3D solid modeling package which allows users to develop full solid models in a simulated environment
The original image. Let s get started! The final result.
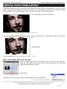 Vertical Photo Panels Effect In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create the illusion that a single photo is being displayed as a series of vertical panels. It may look complicated, but as we
Vertical Photo Panels Effect In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create the illusion that a single photo is being displayed as a series of vertical panels. It may look complicated, but as we
The ProtoTRAK Parasolid Converter Operating Manual
 The ProtoTRAK Parasolid Converter Operating Manual Document: P/N 28070 Version: 042216 Parasolid for Mills Compatible with offline and SMX ProtoTRAK Control models Southwestern Industries, Inc. 2615 Homestead
The ProtoTRAK Parasolid Converter Operating Manual Document: P/N 28070 Version: 042216 Parasolid for Mills Compatible with offline and SMX ProtoTRAK Control models Southwestern Industries, Inc. 2615 Homestead
MS Word Basics. Groups within Tabs
 MS Word Basics Instructor: Bev Alderman L e t s G e t S t a r t e d! Open and close MS Word Open Word from the desktop of your computer by Clicking on the Start>All programs>microsoft Office >Word 2010
MS Word Basics Instructor: Bev Alderman L e t s G e t S t a r t e d! Open and close MS Word Open Word from the desktop of your computer by Clicking on the Start>All programs>microsoft Office >Word 2010
3D Design with 123D Design
 3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
SciGraphica. Tutorial Manual - Tutorials 1and 2 Version 0.8.0
 SciGraphica Tutorial Manual - Tutorials 1and 2 Version 0.8.0 Copyright (c) 2001 the SciGraphica documentation group Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms
SciGraphica Tutorial Manual - Tutorials 1and 2 Version 0.8.0 Copyright (c) 2001 the SciGraphica documentation group Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms
