Year 6 Science Unit 6F - How we see things
|
|
|
- Camron Goodwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Year 6 Science Unit 6F - How we see things ABOUT THE UNIT In this unit children learn that mirrors and shiny surfaces alter the direction in which light travels and that when they see objects, light enters the eye. Children contrast reflection and shadow formation. Experimental and investigative work focuses on: planning and carrying out a fair test making observations and measurements recognising when to repeat measurements presenting results in line graphs identifying patterns in data. Work in this unit also offers opportunities for children to relate their understanding of light, reflection and shadow formation to everyday phenomena. Visually impaired children will need particular support in this unit. They will be able to take part through careful use of residual vision, through their awareness that many light sources are also heat sources and through their sense of touch. It is important for teachers to help children to be sensitive to those who are visually impaired. This unit takes approximately 6 hours. WHERE THE UNIT FITS IN VOCABULARY RESOURCES Builds on Unit 3F Light and shadows and Unit 5E Earth, Sun and Moon Children need to: know that when light is blocked by some materials, shadows are formed be familiar with representing data in line graphs know how to make careful measurements of length. Links to Unit 3C and art. In this unit children will have opportunities to use: words and phrases related to shadow formation and reflection eg opaque, reflect, reflection, light beam, mirror, light travelling expressions making generalisations about patterns in results descriptions and explanations involving a sequence of ideas. torches with powerful beams white card small mirrors selection of shiny/polished and unpolished/dull materials opaque objects for shadow formation metre sticks or tape measures EXPECTATIONS at the end of this unit most children will: some children will not have made so much progress and will: some children will have progressed further and will also: recognise that light travels from a source, that when it is blocked, a shadow is formed and when it hits a shiny surface, it is reflected; that light sources are seen when light from them enters the eyes; make careful measurements of shadows and represent these in a line graph recognise that when light is blocked, a shadow is formed, and that reflections can be seen in shiny surfaces; make measurements and present these in a table explain the difference between shadow formation and reflection in terms of the path of light QCA 1998 adapted AAC GJ 2005/2006 Ref: QCA/98/210W
2 Sc 4.3 a, b 1 Introductory activities Review children s understanding of light and shadows by asking them to draw and annotate a diagram to show how a shadow is formed. Suggest children use terms eg light source, opaque, travel, block. Discuss children s diagrams with them, drawing attention to the idea of light travelling. This activity is intended to help teachers find out what children know and understand about light and shadows. Teachers will need to take this into account in their short-term planning of later activities in this unit. 1. that light travels from a source 2. to use their knowledge about light to explain observations Sc 4.3 a, b 2 Light travels If appropriate, demonstrate to children or ask children to demonstrate to others that light travels eg by shining a torch onto a wall and blocking the light half way using a piece of card. Ask children to draw a diagram to explain what is happening. Belair Lesson 1 Developing Science 6: p 49 Letts Science Activity Book p 124 explain eg by drawing a diagram that light travels from the torch to the wall and may be blocked by an opaque object QCA Ref: QCA/98/210W
3 3. that we see light sources because light from the source enters our eyes 3a that we see objects that are not light sources only if light reflected or scattered from them enters our eyes 3 How we see things Ask children to explain how they see the light from the torch. Prompt by showing small light sources in dark areas and asking eg Why we can see them more clearly when they are switched on? Help children to draw diagrams to show and explain what is happening. explain eg by drawing a diagram that they see the torch light when light from it enters their eyes Children may need help in recognising that they see things when light enters their eyes rather than thinking they see things because light travels from their eyes. Sc 4.3 d Belair Lesson 2 Developing Science 6: p 50 Letts Science Activity Book p that light from an object can be reflected by a mirror, the reflected light enters our eyes and we see the object 5. that the direction of a beam or ray of light travelling from a light source can be indicated by a straight line with an arrow Sc 1.2 e, h Sc 4.3 c, d 4 Reflections (1) Ask children to explore what they can see with a mirror by posing questions eg Can you see behind you? Can you make a beam of light move round the classroom? Ask children to think of other questions to explore and to record and explain their observations in drawing and writing. Help children to represent the direction of a light beam using straight lines with arrows. Belair Lesson 3 Developing Science 6: p 51 Letts Science Activity Book p explain eg using drawings how mirrors can change the direction of a light beam, representing the direction in which the light beam travels by an arrow QCA Ref: QCA/98/210W
4 6. that when a beam of light is reflected from a surface, its direction changes 7. to make careful observations and comparisons Sc 4.3 c 5 Reflections (2) Demonstrate to children, in a relatively dark area, what happens when a torch with a powerful beam is placed on a piece of white paper and shone at a mirror. Ask children to trace the path of the beam and of the reflected beam and to explore what happens when the light hits the mirror at different angles. trace the path of the torch beam and explain that it is reflected from the mirror recognise eg in drawings that when the angle at which the light hits the mirror is changed, the path of the reflected light also alters At this stage children do not need to know formally that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. With the children sitting in a semi-circle, use a table on its side, a tennis ball and a large mirror to demonstrate the angle of reflection from a mirror, and that it can be compared to the way a ball bounces off a wall. Belair Lesson 3 Developing Science 6: p that shiny surfaces reflect light better than dull surfaces 9. to make and record comparisons of how different surfaces reflect light and to draw conclusions from the comparisons Sc 1.2 e - j 6 Reflectivity of different materials Present children with a collection of shiny and dull surfaces eg mirrors, polished metals, perspex, paper, gloss and matt painted surfaces, polished wood. Ask children to find out which ones they can see themselves in and which ones reflect a torch beam, to record their results and to draw conclusions from their results. Ask children to use their own knowledge and secondary sources to identify everyday uses of mirrors. Additional whole class activity: set up slide projector as constant light source shining into a black box at the end of which different samples can be placed. Record the reflected light reading from different materials using a light meter. produce a table of observations showing that shiny materials both reflect a torch beam and allow children to see themselves make a generalisation about shiny surfaces and reflection eg polished surfaces reflect light better than other surfaces, shiny surfaces can be used as mirrors, dull surfaces cannot SAFETY Make sure that mirrors etc do not have sharp edges. Belair Lesson 4 QCA Ref: QCA/98/210W
5 QCA Ref: QCA/98/210W
6 10. to identify factors which might affect the size and position of the shadow of an object 11. to investigate how changing one factor causes a shadow to change 12. to consider trends in results and to decide whether there are results which do not fit the pattern 13. to check measurements by repeating them Sc 1 most elements Sc 4.3 b 7 Shadow investigations Remind children of shadow formation using an opaque object eg a cardboard figure. Ask them to explore ways in which the shadow of the figure can be made to change. Ask children to suggest questions they could investigate eg What happens to the size of the shadow when you move the figure nearer the light? Help children to decide how to carry out the investigation, including deciding on the measurements they are going to take. Ask children to record results and help them to present them in a line graph. Talk with children about patterns in the results and, if necessary, encourage them to repeat measurements to check them. Belair Lesson 5 Developing Science 6: p 53 Letts Science Activity Book p suggest questions which might be investigated eg distance of object from screen, distance of object from light source, angle at which light source shines on object show, in the investigation, that they changed one factor while keeping others the same identify results which do not seem to fit the pattern and check these by repeating measurements make a generalisation from the results eg the nearer the figure was to the torch, the bigger the shadow This activity offers children the opportunity to carry out a whole investigation. It may be helpful to concentrate on the aspects of investigation highlighted in the learning objectives. This type of investigation needs a point source of light to work well. Using a bare 1.5 V bulb overdriven at 3 V produces a bright light approximating to a point source. QCA Ref: QCA/98/210W
7 14. to recognise differences between shadows and reflections Sc 4.3 a - d 8 Review and assessment Review work in this unit by asking children to suggest differences between shadows and images (reflections) seen in shiny surfaces. Belair Lesson 6 Developing Science 6: p 54 Letts Science Activity Book p Belair Test 6F for school records identify observable differences eg my shadow is dark and I can only see my shape, when I look at myself in a mirror I can see my face, or opaque objects make shadows and you can see yourself in shiny surfaces explain differences between shadows and reflections in terms of light eg shadows are made when light is blocked, when light is reflected it changes direction when it hits a shiny surface Children sometimes confuse shadows and reflections. It is important to clarify that children understand that reflection occurs when a light beam changes direction on hitting a surface. A shadow is formed when a light beam is blocked by an opaque object. QCA Ref: QCA/98/210W
Light. Teacher Resource
 Watch the film: You might find it useful to watch the light film before you read through the resources. bbc.com/teach/terrificscientific/ks2/zv9qf4j Introduction We need light to be able to see things.
Watch the film: You might find it useful to watch the light film before you read through the resources. bbc.com/teach/terrificscientific/ks2/zv9qf4j Introduction We need light to be able to see things.
learning outcomes 10 min.
 Reflecting light Light H 49 time 60 minutes Tip. In this lesson every child makes their own periscope. If you prefer they can also work in pairs or small groups. learning outcomes To: know that light always
Reflecting light Light H 49 time 60 minutes Tip. In this lesson every child makes their own periscope. If you prefer they can also work in pairs or small groups. learning outcomes To: know that light always
Lesson Plan Outline for Rainbow Science
 Lesson Plan Outline for Rainbow Science Lesson Title: Rainbow Science Target Grades: Middle and High School Time Required: 120 minutes Background Information for Teachers and Students Rainbows are fascinating
Lesson Plan Outline for Rainbow Science Lesson Title: Rainbow Science Target Grades: Middle and High School Time Required: 120 minutes Background Information for Teachers and Students Rainbows are fascinating
2 Reflection and Mirrors
 2 Reflection and Mirrors Section 2 Reflection and Mirrors Reading Preview Key Concepts What are the kinds of reflection? What types of images are produced by plane, concave, and convex mirrors? Key Terms
2 Reflection and Mirrors Section 2 Reflection and Mirrors Reading Preview Key Concepts What are the kinds of reflection? What types of images are produced by plane, concave, and convex mirrors? Key Terms
3 Interactions of Light Waves
 CHAPTER 22 3 Interactions of Light Waves SECTION The Nature of Light BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does reflection affect the way we see
CHAPTER 22 3 Interactions of Light Waves SECTION The Nature of Light BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does reflection affect the way we see
3. Confirm Does the law of reflection apply to rough surfaces? Explain. Diffuse Reflection
 Light Key Concepts How does light reflect from smooth surfaces and rough surfaces? What happens to light when it strikes a concave mirror? Which types of mirrors can produce a virtual image? Reflection
Light Key Concepts How does light reflect from smooth surfaces and rough surfaces? What happens to light when it strikes a concave mirror? Which types of mirrors can produce a virtual image? Reflection
Light Energy. Name: Key
 Light Energy Name: Key What is Light? Make a list of things that give us light. How many can you think of? Answers will vary Count the items on your list. How many did you write? Light: Light is a form
Light Energy Name: Key What is Light? Make a list of things that give us light. How many can you think of? Answers will vary Count the items on your list. How many did you write? Light: Light is a form
How does light energy travel? transparent transmit mediums media medium
 Have you ever observed a solar eclipse like the one in this photograph? During a solar eclipse, it can become very dark in the middle of a sunny day. This may seem amazing to us, but it was terrifying
Have you ever observed a solar eclipse like the one in this photograph? During a solar eclipse, it can become very dark in the middle of a sunny day. This may seem amazing to us, but it was terrifying
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
Shedding Light on Reflection Question Sheet Name: Part A: Light Reflection 1. What is a luminous object? Give three examples.
 Shedding Light on Reflection Question Sheet Name: Part A: Light Reflection 1. What is a luminous object? Give three examples. 2. How is it possible that we can see non-luminous objects if they re not actually
Shedding Light on Reflection Question Sheet Name: Part A: Light Reflection 1. What is a luminous object? Give three examples. 2. How is it possible that we can see non-luminous objects if they re not actually
Reflection of Light. 1)Students will discover how light interacts with certain types of surfaces
 Reflection of Light 1)Students will discover how light interacts with certain types of surfaces 2) Students will understand the laws governing the phenomenon of reflection 3) Discover how images are formed,
Reflection of Light 1)Students will discover how light interacts with certain types of surfaces 2) Students will understand the laws governing the phenomenon of reflection 3) Discover how images are formed,
 S2 Science EM Spectrum Revision Notes --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- What is light? Light is a form of
S2 Science EM Spectrum Revision Notes --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- What is light? Light is a form of
6 th Grade Reflection and Transmission of Light Lab
 6 th Grade Reflection and Transmission of Light Lab Summary: Opaque, translucent, and transparent materials are explored by using a flashlight and 10 different shields. Reflection in mirrors is studied
6 th Grade Reflection and Transmission of Light Lab Summary: Opaque, translucent, and transparent materials are explored by using a flashlight and 10 different shields. Reflection in mirrors is studied
The Question. What are the 4 types of interactions that waves can have when they encounter an object?
 The Question What are the 4 types of interactions that waves can have when they encounter an object? Waves, Wave fronts and Rays Wave Front: Crests of the waves. Rays: Lines that are perpendicular to the
The Question What are the 4 types of interactions that waves can have when they encounter an object? Waves, Wave fronts and Rays Wave Front: Crests of the waves. Rays: Lines that are perpendicular to the
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P ) Light Rays & Reflection. The Ray Model of Light
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
Lesson Plan: Refraction of light at boundaries OVERVIEW
 Lesson Plan: Refraction of light at boundaries OVERVIEW This lesson is broken up into several small units. The focus is on observations of optical phenomena resulting from the refraction of light and the
Lesson Plan: Refraction of light at boundaries OVERVIEW This lesson is broken up into several small units. The focus is on observations of optical phenomena resulting from the refraction of light and the
Optics Test Science What are some devices that you use in everyday life that require optics?
 Optics Test Science 8 Introduction to Optics 1. What are some devices that you use in everyday life that require optics? Light Energy and Its Sources 308-8 identify and describe properties of visible light
Optics Test Science 8 Introduction to Optics 1. What are some devices that you use in everyday life that require optics? Light Energy and Its Sources 308-8 identify and describe properties of visible light
ACTIVITY 2: Reflection of Light
 UNIT L Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 2: Reflection of Light Purpose Most people realize that light is necessary to see things, like images in mirrors, and various kinds of objects. But how does that happen?
UNIT L Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 2: Reflection of Light Purpose Most people realize that light is necessary to see things, like images in mirrors, and various kinds of objects. But how does that happen?
UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 1 UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 LIGHT BEHAVES IN PREDICTABLE WAYS. Section 2.0 1 3 LIGHT TRAVELS IN RAYS AND INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS Topic 2.1 RAY DIAGRAMS Scientists use ray diagrams
1 UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 LIGHT BEHAVES IN PREDICTABLE WAYS. Section 2.0 1 3 LIGHT TRAVELS IN RAYS AND INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS Topic 2.1 RAY DIAGRAMS Scientists use ray diagrams
Light, Reflection and Mirrors. Light Reflection
 Name: Light Reflection Read from Lesson 1 of the Reflection chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/u13l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/u13l1b.html
Name: Light Reflection Read from Lesson 1 of the Reflection chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/u13l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/u13l1b.html
Light and Sound. Wave Behavior and Interactions
 Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
CAUTION: Direct eye exposure to lasers can damage your sight. Do not shine laser pointers near anyone s face, or look directly into the beam.
 Name: Date: Partners: Purpose: To understand the basic properties of light and how it interacts with matter to reflect, refract, disperse or diffract. Part 1A: Reflection Materials: 1. mirror 2. ruler
Name: Date: Partners: Purpose: To understand the basic properties of light and how it interacts with matter to reflect, refract, disperse or diffract. Part 1A: Reflection Materials: 1. mirror 2. ruler
4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb?
 1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11)
 Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11) Introduction In this lab you will investigate the reflection and refraction of light. Reflection of light from a surface is
Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11) Introduction In this lab you will investigate the reflection and refraction of light. Reflection of light from a surface is
Reflection 16/03/2016 cgrahamphysics.com 2016
 Reflection What happens to light when it hits a mirror? Reflection Starter: We use our eyes to see. Who s eye am I? Starter Use a mirror to draw a mirror image of your name. When something is reflected
Reflection What happens to light when it hits a mirror? Reflection Starter: We use our eyes to see. Who s eye am I? Starter Use a mirror to draw a mirror image of your name. When something is reflected
Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version
 Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version In this lab, you will explore the behavior of light. You will observe reflection and refraction of a laser beam in jello, and use a diffraction pattern
Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version In this lab, you will explore the behavior of light. You will observe reflection and refraction of a laser beam in jello, and use a diffraction pattern
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
When light strikes an object there are different ways it can be affected. Light can be
 When light strikes an object there are different ways it can be affected. Light can be transmitted, reflected, refracted, and absorbed, It depends on the type of matter that it strikes. For example light
When light strikes an object there are different ways it can be affected. Light can be transmitted, reflected, refracted, and absorbed, It depends on the type of matter that it strikes. For example light
REFLECTION & REFRACTION
 REFLECTION & REFRACTION OBJECTIVE: To study and verify the laws of reflection and refraction using a plane mirror and a glass block. To see the virtual images that can be formed by the reflection and refraction
REFLECTION & REFRACTION OBJECTIVE: To study and verify the laws of reflection and refraction using a plane mirror and a glass block. To see the virtual images that can be formed by the reflection and refraction
Photo-realism Fundamentals
 1-(800) 877-2745 www.ashlar-vellum.com Photo-realism Fundamentals Using Cobalt, Xenon, Argon Copyright 2008 Ashlar Incorporated. All rights reserved. Photo-realism Fundamentals Photo-realistic rendering
1-(800) 877-2745 www.ashlar-vellum.com Photo-realism Fundamentals Using Cobalt, Xenon, Argon Copyright 2008 Ashlar Incorporated. All rights reserved. Photo-realism Fundamentals Photo-realistic rendering
Common terminology of reflection of light on a plane mirror. Normal : A line at right angles to the mirror s surface.
 LESSON 5.1 Understanding reflection of light Introduction : Light is a form energy that enables us to see. Light is emitted or given by hot objects, like a candle flame, or the glowing filament of light
LESSON 5.1 Understanding reflection of light Introduction : Light is a form energy that enables us to see. Light is emitted or given by hot objects, like a candle flame, or the glowing filament of light
LAB REFLECTION FROM A PLANE MIRROR
 Name (printed) LAB REFLECTION FROM A PLANE MIRROR INTRODUCTION It s true that plane mirrors produce simpler images than curved mirrors, but they certainly aren t trivial. Ask a group of people who have
Name (printed) LAB REFLECTION FROM A PLANE MIRROR INTRODUCTION It s true that plane mirrors produce simpler images than curved mirrors, but they certainly aren t trivial. Ask a group of people who have
Light Energy and Matter
 Light Energy and Matter UNIT 9 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 9 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a library s bookshelves that are illuminated by a
Light Energy and Matter UNIT 9 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 9 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a library s bookshelves that are illuminated by a
1 -- Light. Lesson at a Glance
 1 -- Light Lesson at a Glance We can see an object only when light from an object enters our eyes. The light may have been emitted by the object or may have been reflected by the object. A mirror changes
1 -- Light Lesson at a Glance We can see an object only when light from an object enters our eyes. The light may have been emitted by the object or may have been reflected by the object. A mirror changes
Official Documentation of Investigation. Completed By. (Student Name) Pre-Read
 Official Documentation of Investigation Completed By (Student Name) Pre-Read When light waves hit a material, they cause the atoms (specifically, the electrons in metals) to oscillate (move back and forth).
Official Documentation of Investigation Completed By (Student Name) Pre-Read When light waves hit a material, they cause the atoms (specifically, the electrons in metals) to oscillate (move back and forth).
What is Light? What is Electromagnetic Radiation?
 What is Light? Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that can be seen by the eye. What is Electromagnetic Radiation? Electromagnetic radiation is a term used to describe waves that are created by
What is Light? Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that can be seen by the eye. What is Electromagnetic Radiation? Electromagnetic radiation is a term used to describe waves that are created by
FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign
 Name: Book: Period: Due Date: Lab Partners: FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign Purpose: The theme in this lab is the interaction between light and matter. Matter and light seem very different
Name: Book: Period: Due Date: Lab Partners: FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign Purpose: The theme in this lab is the interaction between light and matter. Matter and light seem very different
4. Refraction. glass, air, Perspex and water.
 Mr. C. Grima 11 1. Rays and Beams A ray of light is a narrow beam of parallel light, which can be represented by a line with an arrow on it, in diagrams. A group of rays makes up a beam of light. In laboratory
Mr. C. Grima 11 1. Rays and Beams A ray of light is a narrow beam of parallel light, which can be represented by a line with an arrow on it, in diagrams. A group of rays makes up a beam of light. In laboratory
Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Ray Model of Light (pp. 172-187) Models of Light wave model of light: a model in which light is a type of wave that travels through space and transfers energy from one
Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Ray Model of Light (pp. 172-187) Models of Light wave model of light: a model in which light is a type of wave that travels through space and transfers energy from one
2D Shapes, Scaling, and Tessellations
 2D Shapes, Scaling, and Tessellations Name(s): Sarah Hunter Title of lesson: How do different shapes fit together? Date of lesson: Week 2, Day 5 Length of lesson: 50 Minutes (1 Class Period) Description
2D Shapes, Scaling, and Tessellations Name(s): Sarah Hunter Title of lesson: How do different shapes fit together? Date of lesson: Week 2, Day 5 Length of lesson: 50 Minutes (1 Class Period) Description
Geometry Sixth Grade
 Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK. Chapter 5 Light Optics (Section 1) Ms. Jamieson This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 5 Light Optics (Section 1) Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 5.1 - The Ray Model
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 5 Light Optics (Section 1) Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 5.1 - The Ray Model
CHAPTER 29: REFLECTION
 CHAPTER 29: REFLECTION 29.1 REFLECTION The return of a wave back to its original medium is called reflection. Fasten a spring to a wall and send a pulse along the spring s length. The wall is a very rigid
CHAPTER 29: REFLECTION 29.1 REFLECTION The return of a wave back to its original medium is called reflection. Fasten a spring to a wall and send a pulse along the spring s length. The wall is a very rigid
P03 ray drawing with plane mirrors. November 06, Worlds Best Optical Illusion. Owls. Ray Diagrams.
 Worlds Best Optical Illusion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=haxm0diuyug Owls http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hoc42xegvt8 Ray Diagrams http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ed4jexpdwuo&feature=related 1 Locate
Worlds Best Optical Illusion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=haxm0diuyug Owls http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hoc42xegvt8 Ray Diagrams http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ed4jexpdwuo&feature=related 1 Locate
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics
 Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Light. Reflection of light. Types of reflection
 Light Reflection of light Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the
Light Reflection of light Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the
Turn on the Lights: Reflectance
 Turn on the Lights: Reflectance Part 2: Shading Tuesday, October 15 2012 Lecture #14 Goal of Shading Model simple light sources Point light sources Extended light sources Ambient lighting Model lighting
Turn on the Lights: Reflectance Part 2: Shading Tuesday, October 15 2012 Lecture #14 Goal of Shading Model simple light sources Point light sources Extended light sources Ambient lighting Model lighting
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics Regular and Diffuse Reflection Sections 23-1 to 23-2. How We See Weseebecauselightreachesoureyes. There are two ways, therefore, in which we see: (1) light from a luminous object
Light: Geometric Optics Regular and Diffuse Reflection Sections 23-1 to 23-2. How We See Weseebecauselightreachesoureyes. There are two ways, therefore, in which we see: (1) light from a luminous object
Experiment 3: Reflection
 Model No. OS-8515C Experiment 3: Reflection Experiment 3: Reflection Required Equipment from Basic Optics System Light Source Mirror from Ray Optics Kit Other Required Equipment Drawing compass Protractor
Model No. OS-8515C Experiment 3: Reflection Experiment 3: Reflection Required Equipment from Basic Optics System Light Source Mirror from Ray Optics Kit Other Required Equipment Drawing compass Protractor
The Role of Light to Sight
 Reflection The Role of Light to Sight The visual ability of humans and other animals is the result of the complex interaction of light, eyes and brain. Absence of Light Darkness. Luminous objects are objects
Reflection The Role of Light to Sight The visual ability of humans and other animals is the result of the complex interaction of light, eyes and brain. Absence of Light Darkness. Luminous objects are objects
SketchUp Quick Start For Surveyors
 SketchUp Quick Start For Surveyors Reason why we are doing this SketchUp allows surveyors to draw buildings very quickly. It allows you to locate them in a plan of the area. It allows you to show the relationship
SketchUp Quick Start For Surveyors Reason why we are doing this SketchUp allows surveyors to draw buildings very quickly. It allows you to locate them in a plan of the area. It allows you to show the relationship
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Lecture 11. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134. Review for Exam. Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves
 PHY 92 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when
PHY 92 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when
PHY 222 Lab 11 Interference and Diffraction Patterns Investigating interference and diffraction of light waves
 PHY 222 Lab 11 Interference and Diffraction Patterns Investigating interference and diffraction of light waves Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names Instructions April 17, 2015 Before lab, read the
PHY 222 Lab 11 Interference and Diffraction Patterns Investigating interference and diffraction of light waves Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names Instructions April 17, 2015 Before lab, read the
Light, Photons, and MRI
 Light, Photons, and MRI When light hits an object, some of it will be reflected. The reflected light can form an image. We usually want to be able to characterize the image given what we know about the
Light, Photons, and MRI When light hits an object, some of it will be reflected. The reflected light can form an image. We usually want to be able to characterize the image given what we know about the
Decimals should be spoken digit by digit eg 0.34 is Zero (or nought) point three four (NOT thirty four).
 Numeracy Essentials Section 1 Number Skills Reading and writing numbers All numbers should be written correctly. Most pupils are able to read, write and say numbers up to a thousand, but often have difficulty
Numeracy Essentials Section 1 Number Skills Reading and writing numbers All numbers should be written correctly. Most pupils are able to read, write and say numbers up to a thousand, but often have difficulty
Understanding Visual Performance A Pacific Energy Center Factsheet
 Understanding Visual Performance A Pacific Energy Center Factsheet Factors Affecting Visual Performance Our ability to perform a visual task depends on how well our eyes perceive the details of the task.
Understanding Visual Performance A Pacific Energy Center Factsheet Factors Affecting Visual Performance Our ability to perform a visual task depends on how well our eyes perceive the details of the task.
Assignment 1 Due September 6, 2011
 Assignment 1 Due September 6, 2011 Text readings A brief history of optics [Pages 1-9] Reflection and refraction [Pages 95-104] Huygen's principle [pages 104-106] Fermat's principle [Pages 106-111] Total
Assignment 1 Due September 6, 2011 Text readings A brief history of optics [Pages 1-9] Reflection and refraction [Pages 95-104] Huygen's principle [pages 104-106] Fermat's principle [Pages 106-111] Total
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Diffraction: Taking Light Apart
 Diffraction: Taking Light Apart Engage Student Guide A. Waves Let s first consider diffraction. It s part of everyday life, in which waves of energy don t seem to move in straight lines. Do the activity
Diffraction: Taking Light Apart Engage Student Guide A. Waves Let s first consider diffraction. It s part of everyday life, in which waves of energy don t seem to move in straight lines. Do the activity
/Core Components: Content essential to nurture national identity ST.XAVIER S INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION MUMBAI LESSON PLAN
 ST.XAVIER S INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION MUMBAI LESSON PLAN CONTEXT Name of the Student Teacher: Cardoza Adalbert Roll No: 5 Name of the topic: Reflection of light Internship School: St. Andrew's High School
ST.XAVIER S INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION MUMBAI LESSON PLAN CONTEXT Name of the Student Teacher: Cardoza Adalbert Roll No: 5 Name of the topic: Reflection of light Internship School: St. Andrew's High School
Early Years Typical Progression Chart with additional guidance for practitioners. Shape and Space
 Early Years Typical Progression Chart with additional guidance for practitioners Shape and Space Mathematically, the areas of shape and space are about developing visualising skills and understanding relationships,
Early Years Typical Progression Chart with additional guidance for practitioners Shape and Space Mathematically, the areas of shape and space are about developing visualising skills and understanding relationships,
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE
 VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs Properties of Waves Fall 2018 Goal: To investigate properties waves by studying reflection, diffraction and refraction of
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs Properties of Waves Fall 2018 Goal: To investigate properties waves by studying reflection, diffraction and refraction of
INTERFERENCE. Interf - 1
 INTERFERENCE This laboratory will investigate the phenomenon of interference. The interference and diffraction of light waves will be studied. Specifically, the interference patterns of a single slit,
INTERFERENCE This laboratory will investigate the phenomenon of interference. The interference and diffraction of light waves will be studied. Specifically, the interference patterns of a single slit,
LIGHT Measuring Angles
 1. Using a protractor LIGHT Measuring Angles This angle is 33 Put vertex (corner) of angle where lines cross One arm of angle goes through middle of 0 This angle is 45 Measure these angles: 66 Light an
1. Using a protractor LIGHT Measuring Angles This angle is 33 Put vertex (corner) of angle where lines cross One arm of angle goes through middle of 0 This angle is 45 Measure these angles: 66 Light an
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT
 PHYSICS LAB REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision Spring 2002 REF 45 blank page REF 46
PHYSICS LAB REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision Spring 2002 REF 45 blank page REF 46
Unit 9 Light & Optics
 Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
Lines of Symmetry. Grade 3. Amy Hahn. Education 334: MW 8 9:20 a.m.
 Lines of Symmetry Grade 3 Amy Hahn Education 334: MW 8 9:20 a.m. GRADE 3 V. SPATIAL SENSE, GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT A. Spatial Sense Understand the concept of reflection symmetry as applied to geometric
Lines of Symmetry Grade 3 Amy Hahn Education 334: MW 8 9:20 a.m. GRADE 3 V. SPATIAL SENSE, GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT A. Spatial Sense Understand the concept of reflection symmetry as applied to geometric
MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Pacing Guide GEOMETRY HONORS Course Code:
 Topic II: Transformations in the Plane Pacing Date(s) Traditional 14 09/15/14-10/03/14 Block 07 09/15/14-10/03/14 MATHEMATICS FLORIDA STANDARDS & MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE (MP) MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE (MP) ESSENTIAL
Topic II: Transformations in the Plane Pacing Date(s) Traditional 14 09/15/14-10/03/14 Block 07 09/15/14-10/03/14 MATHEMATICS FLORIDA STANDARDS & MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE (MP) MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE (MP) ESSENTIAL
Lab 12 - Interference-Diffraction of Light Waves
 Lab 12 - Interference-Diffraction of Light Waves Equipment and Safety: No special safety equipment is required for this lab. Do not look directly into the laser. Do not point the laser at other people.
Lab 12 - Interference-Diffraction of Light Waves Equipment and Safety: No special safety equipment is required for this lab. Do not look directly into the laser. Do not point the laser at other people.
WORKBOOK 10 ACTION GEOMETRY SQUARE AND PENTAGON
 UCL/CAS Training for Teachers Algorithms and Programming Module 1 WORKBOOK 10 ACTION GEOMETRY SQUARE AND PENTAGON Action Geometry Unplugged: starting with the square, we explore the properties of simple
UCL/CAS Training for Teachers Algorithms and Programming Module 1 WORKBOOK 10 ACTION GEOMETRY SQUARE AND PENTAGON Action Geometry Unplugged: starting with the square, we explore the properties of simple
Reflections. I feel pretty, oh so pretty
 Reflections I feel pretty, oh so pretty Objectives By the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Draw an accurate reflective angle Determine the focal length of a spherical mirror Light Review Light
Reflections I feel pretty, oh so pretty Objectives By the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Draw an accurate reflective angle Determine the focal length of a spherical mirror Light Review Light
Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 3: Properties of Shapes. Released March 2018
 Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Introduction. Experiment A: Snell s Law. Physics 1CL REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT Summer Session II 2010
 Introduction This laboratory is a quantitative investigation of the reflection and refraction of light off optical interfaces. An optical interface is a boundary between two transparent media of different
Introduction This laboratory is a quantitative investigation of the reflection and refraction of light off optical interfaces. An optical interface is a boundary between two transparent media of different
Unit 3: Chapter 5. Reflection
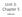 Unit 3: Chapter 5 Reflection The Law of Reflection To show how light is reflected from a solid surface, we can use ray diagrams. A ray diagram has 5 main components: this is the incoming ray that will
Unit 3: Chapter 5 Reflection The Law of Reflection To show how light is reflected from a solid surface, we can use ray diagrams. A ray diagram has 5 main components: this is the incoming ray that will
Guidance note Geometry geometrical reasoning
 1 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Guidance note Geometry geometrical reasoning This material has been written to support a mathematics teacher in a mainstream classroom. The context is a geometry
1 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Guidance note Geometry geometrical reasoning This material has been written to support a mathematics teacher in a mainstream classroom. The context is a geometry
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
this is the incoming ray that will hit the solid surface/barrier (e.g. a mirror)
 To show how light is reflected from a solid surface, we can use ray diagrams. A ray diagram has 5 main components: this is the incoming ray that will hit the solid surface/barrier (e.g. a mirror) barrier.
To show how light is reflected from a solid surface, we can use ray diagrams. A ray diagram has 5 main components: this is the incoming ray that will hit the solid surface/barrier (e.g. a mirror) barrier.
LECTURE 15 REFLECTION & REFRACTION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 15 REFLECTION & REFRACTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 15 2 18.1 The ray model of light Source of light rays Ray diagrams Seeing objects Shadows 18.2 Reflection Diffuse reflection The plane
LECTURE 15 REFLECTION & REFRACTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 15 2 18.1 The ray model of light Source of light rays Ray diagrams Seeing objects Shadows 18.2 Reflection Diffuse reflection The plane
Intermediate Physics PHYS102
 Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION LIGHT Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object. Its speed is 3 10 8 m/s in vacuum. Light always travel in straight line. Reflection: The
CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION LIGHT Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object. Its speed is 3 10 8 m/s in vacuum. Light always travel in straight line. Reflection: The
Lab in a Box 4 OPTICS
 Lab in a Box 4 OPTICS 1 Inventory Sl.No. Material Quantity Models 1 Optic kit 1 2 Smoke box 1 3 Shadow kit 1 4 Kaleidoscope 1 5 Periscope 1 Equipment s 6 Assembly of concave lens 1 7 Assembly of convex
Lab in a Box 4 OPTICS 1 Inventory Sl.No. Material Quantity Models 1 Optic kit 1 2 Smoke box 1 3 Shadow kit 1 4 Kaleidoscope 1 5 Periscope 1 Equipment s 6 Assembly of concave lens 1 7 Assembly of convex
Lighting & 3D Graphics. Images from 3D Creative Magazine
 Lighting & 3D Graphics Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions 3D Lighting Basics 3D Light Sources Lighting Controls & Effects Brightness & Colour Shadows Hotspot And Falloff
Lighting & 3D Graphics Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions 3D Lighting Basics 3D Light Sources Lighting Controls & Effects Brightness & Colour Shadows Hotspot And Falloff
Today s Topic: The Law of Reflection
 Today s Topic: The Law of Reflection Learning Goal: Students will be able to explain the laws that govern the reflection of light. Do Now: Jackie wears a green shirt. White light hits her shirt from the
Today s Topic: The Law of Reflection Learning Goal: Students will be able to explain the laws that govern the reflection of light. Do Now: Jackie wears a green shirt. White light hits her shirt from the
PHYSICS 116 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION
 Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE: PARTS OF THIS LAB INVOLVE THE USE OF HELIUM-NEON LASERS. THESE LASERS WILL NOT BURN YOUR SKIN BUT CAN CAUSE EYE
Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE: PARTS OF THIS LAB INVOLVE THE USE OF HELIUM-NEON LASERS. THESE LASERS WILL NOT BURN YOUR SKIN BUT CAN CAUSE EYE
MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
Visual Perception. Visual contrast
 TEXTURE Visual Perception Our perception of the visual shape, size, color, and texture of things is affected by the optical environment in which we see them and the relationships we can discern between
TEXTURE Visual Perception Our perception of the visual shape, size, color, and texture of things is affected by the optical environment in which we see them and the relationships we can discern between
En light ening Geometry
 En light ening Geometry for Middle School Students by Julie LaConte Many science topics can naturally be integrated with a variety of mathematical concepts, including the study of light and optics. Working
En light ening Geometry for Middle School Students by Julie LaConte Many science topics can naturally be integrated with a variety of mathematical concepts, including the study of light and optics. Working
Key Terms write the definitions of the boldface terms on your own paper, definitions are available at theteterszone.net
 On-level Physics Optics This unit will allow each student to: a. gain a better understanding of the behavior and characteristics of light as it is reflected and refracted by s and lenses b. continue making
On-level Physics Optics This unit will allow each student to: a. gain a better understanding of the behavior and characteristics of light as it is reflected and refracted by s and lenses b. continue making
Lesson Plan Lesson 8: Foundations of Similarity Mathematics High School Math II
 Lesson Plan Lesson 8: Foundations of Similarity Mathematics High School Math II Unit Name: Unit 5: Similarity, Right Triangle Trigonometry, and Proof Lesson Plan Number & Title: Lesson 8: Foundations of
Lesson Plan Lesson 8: Foundations of Similarity Mathematics High School Math II Unit Name: Unit 5: Similarity, Right Triangle Trigonometry, and Proof Lesson Plan Number & Title: Lesson 8: Foundations of
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4
 Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 History of Light https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j1yiapztlos History of Light Early philosophers (Pythagoras) believed light was made up of tiny particles Later scientist found
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 History of Light https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j1yiapztlos History of Light Early philosophers (Pythagoras) believed light was made up of tiny particles Later scientist found
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Geometric Optics Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 36! The study of light divides itself into three fields geometric optics wave optics quantum optics! In the previous chapter,
Geometric Optics Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 36! The study of light divides itself into three fields geometric optics wave optics quantum optics! In the previous chapter,
Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2. Sources of light
 We are here Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2 Some history of technology How vision works What is light Wavelength and Frequency: c = f λ Scientific notation and metric units Electromagnetic spectrum Transmission
We are here Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2 Some history of technology How vision works What is light Wavelength and Frequency: c = f λ Scientific notation and metric units Electromagnetic spectrum Transmission
Can light bend? REFRACTION
 Can light bend? REFRACTION Have you ever wondered Disappearing Coin Trick Can you explain what happens? Refraction Starter: Why does the pencil appear bent in the water? The pencil appears bent because
Can light bend? REFRACTION Have you ever wondered Disappearing Coin Trick Can you explain what happens? Refraction Starter: Why does the pencil appear bent in the water? The pencil appears bent because
Images in Plane Mirrors. Monday, May 23, 16
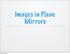 Images in Plane Mirrors Reflection: Light bouncing off of an object and entering our eye. You can use light rays and the laws of reflection to show how a plane mirror produces a virtual image and where
Images in Plane Mirrors Reflection: Light bouncing off of an object and entering our eye. You can use light rays and the laws of reflection to show how a plane mirror produces a virtual image and where
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
ACTIVITY OVERVIEW NGSS CONNECTIONS NGSS CORRELATION
 8 Wave Reflection l a b o r at o r y 2 c l a s s sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW NGSS CONNECTIONS Students investigate the reflection of sound and light waves. They find that some surfaces are good reflectors
8 Wave Reflection l a b o r at o r y 2 c l a s s sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW NGSS CONNECTIONS Students investigate the reflection of sound and light waves. They find that some surfaces are good reflectors
Reflection AB5 Concave Mirror. Teacher s Notes
 Reflection: Concave Mirror Teacher s Notes Main Topic Subtopic Learning Level Technology Level Activity Type Required Equipment Optional Equipment & Color Reflection Middle Low Student and Optical Set
Reflection: Concave Mirror Teacher s Notes Main Topic Subtopic Learning Level Technology Level Activity Type Required Equipment Optional Equipment & Color Reflection Middle Low Student and Optical Set
Physics 1CL WAVE OPTICS: INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION Fall 2009
 Introduction An important property of waves is interference. You are familiar with some simple examples of interference of sound waves. This interference effect produces positions having large amplitude
Introduction An important property of waves is interference. You are familiar with some simple examples of interference of sound waves. This interference effect produces positions having large amplitude
