More About Quadrilaterals
|
|
|
- Rosamond Maria Rogers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
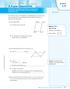
1 More About Quadrilaterals A 4-gon Conclusion Lesson 16-1 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Parallelogram Learning Targets: Develop criteria for showing that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. Prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. SUGGSTD LARNING STRATGIS: Think-Pair-Share, Group Presentation, Discussion Groups, Visualization In a previous activity, the definition of a parallelogram was used to verify that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram by showing that both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. 1. Given quadrilateral CHIA: a. Find the slope of each side. H (2, 5) I (6, 5) b. Use the slopes to explain how you know quadrilateral CHIA is a parallelogram. C (0, 0) A (4, 0) ACTIVITY 16 MATH TIP Slope Formula Given A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) Slope of AB: m = ( y2 y1 ) ( x x ) Given quadrilateral SKIP with SK = IP and KI = SP. a. PSI. xplain. S K MATH TIP Once a theorem has been proven, it can be used to justify other steps or statements in proofs. P I b. SIP and PSI. xplain. c. SK IP and KI SP because. d. Complete the theorem. Theorem If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are congruent, then the quadrilateral is a. 3. Given quadrilateral WALK with coordinates W(8, 7), A(11, 3), L(4, 1), and K(1, 5). Use the theorem in Item 2 to show that WALK is a parallelogram. Activity 16 More About Quadrilaterals 223
2 ACTIVITY 16 Lesson 16-1 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Parallelogram W Z X Y 4. Given WXYZ with WX ZY and WX ZY. a. WZX. xplain. b. Construct viable arguments. xplain why WZ XY. c. Complete the theorem. Theorem If one pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are congruent and parallel, then the quadrilateral is a. 5. Given GOLD with coordinates G( 1, 0), O(5, 4), L(9, 2), and D(3, 2). Use the theorem in Item 4 to show that GOLD is a parallelogram. Now you can prove a theorem that can be used to show that a given quadrilateral is a parallelogram. xample A Theorem If both pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral are congruent, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. P Given: POLY with P L and O Y Prove: POLY is a parallelogram. Statements 1. POLY with P L and O Y 2. m P = m L and m O = m Y 3. m P + m O + m L + m Y = m P + m O + m P + m O = 360 Reasons 1. Given 2. Def. of congruent angles 3. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is Substitution Property 5. 2m P + 2m O = Simplify. 6. m P + m O = Division Property of quality 7. m P + m Y + m P + 7. Substitution Property m Y = m P + 2m Y = Simplify. Y L O 224 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals
3 Lesson 16-1 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Parallelogram ACTIVITY 16 Statements Reasons 9. m P + m Y = Division Property of quality 10. PY OL and PO YL 10. If two lines are intersected by a transversal and a pair of consecutive interior angles are supplementary, then the lines are parallel. 11. POLY is a parallelogram. 11. Def. of a parallelogram Try These A Write a proof using the theorem in xample 1 as the last reason. Given: RT RK RKT U 1 2 Prove: TRUC 1 R T K C 2 U 6. Given PLAN whose diagonals, PA and LN, bisect each other. Complete the statements. a. LP and LA. xplain. L A P N b. AL and LP. xplain. c. xplain how the information in part b can be used to prove that PLAN is a parallelogram. d. Complete the theorem. Theorem If the diagonals of a quadrilateral, then the quadrilateral is a. 7. Given THIN with coordinates T(3, 3), H(5, 9), I(6, 5), and N(4, 1). a. Find the coordinates for the midpoint of each diagonal. b. Do the diagonals bisect each other? xplain. c. The best name for this quadrilateral is: A. quadrilateral B. kite C. trapezoid D. parallelogram Activity 16 More About Quadrilaterals 225
4 ACTIVITY 16 Lesson 16-1 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Parallelogram 8. Summarize this part of the activity by making a list of the five ways to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. Check Your Understanding 9. xplain why showing that only one pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are parallel is not sufficient for proving it is a parallelogram. 10. Three of the interior angle measures of a quadrilateral are 48, 130, and 48. Is the quadrilateral a parallelogram? xplain. LSSON 16-1 PRACTIC Make use of structure. Tell what theorem can be used to prove the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. If there is not enough information to prove it is a parallelogram, write not enough information Three vertices of a parallelogram are given. Find the coordinates of the fourth vertex. 15. (1, 5), (3, 3), (8, 3) 16. ( 5, 0), ( 2, 4), (3, 0) Find the values of x and y that make the quadrilateral a parallelogram x 18. (2x + 1) y x 4x 15 (2x - 5) 226 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals
5 Lesson 16-2 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Rectangle ACTIVITY 16 Learning Targets: Develop criteria for showing that a quadrilateral is a rectangle. Prove that a quadrilateral is a rectangle. SUGGSTD LARNING STRATGIS: Think-Pair-Share, Create Representations, Group Presentation, Discussion Groups 1. Complete the following definition. A rectangle is a parallelogram with. 2. a. Complete the theorem. Theorem If a parallelogram has one right angle, then it has right angles, and it is a. b. Use one or more properties of a parallelogram and the definition of a rectangle to explain why the theorem in Item 1 is true. 3. Given WXYZ. a. If WXYZ is equiangular, then find the measure of each angle. b. Complete the theorem. Theorem If a quadrilateral is equiangular, then it is a. X Y W Z 4. Make sense of problems. Identify the hypothesis and the conclusion of the theorem in Item 3. Use the figure in Item 3. Hypothesis: Conclusion: 5. Write a proof for the theorem in Item 3. Activity 16 More About Quadrilaterals 227
6 ACTIVITY 16 Lesson 16-2 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Rectangle 6. Given OKAY with congruent diagonals, OA and KY. O K Y A a. List the three triangles that are congruent to OYA, and the reason for the congruence. b. List the three angles that are corresponding parts of congruent triangles and congruent to OYA. c. Find the measure of each of the angles in part b. d. Complete the theorem. Theorem If the diagonals of a parallelogram are, then the parallelogram is a. 7. Given ABCD with coordinates A(1, 0), B(0, 3), C(6, 5), and D(7, 2). a. Show that ABCD is a parallelogram. b. Use the theorem in Item 6 to show that ABCD is a rectangle. 8. Write a two-column proof using the theorem in Item 6 as the last reason. G Given: GRAM GRM RGA Prove: GRAM is a rectangle. M 9. Summarize this part of the activity by making a list of the ways to prove that a quadrilateral (or parallelogram) is a rectangle. R A 228 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals
7 Lesson 16-2 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Rectangle ACTIVITY 16 Check Your Understanding 10. Jamie says a quadrilateral with one right angle is a rectangle. Find a counterexample to show that Jamie is incorrect. 11. Do the diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other? Justify your answer. LSSON 16-2 PRACTIC Three vertices of a rectangle are given. Find the coordinates of the fourth vertex. 12. ( 3, 2), ( 3, 1), (3, 1) 13. ( 12, 2), ( 6, 6), (4, 2) 14. (4, 5), ( 3, 4), (6, 1) Find the value of x that makes the parallelogram a rectangle (2x + 4) (5x + 15) 4x 17. Model with mathematics. Jill is building a new gate for her yard as shown. How can she use the diagonals of the gate to determine if the gate is a rectangle? Activity 16 More About Quadrilaterals 229
8 ACTIVITY 16 Lesson 16-3 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Rhombus Learning Targets: Develop criteria for showing that a quadrilateral is a rhombus. Prove that a quadrilateral is a rhombus. SUGGSTD LARNING STRATGIS: Think-Pair-Share, Create Representations, Group Presentation, Discussion Groups 1. Complete the following definition. A rhombus is a parallelogram with. 2. a. Complete the theorem. Theorem If a parallelogram has two consecutive congruent sides, then it has congruent sides, and it is a. b. Use one or more properties of a parallelogram and the definition of a rhombus to explain why the theorem in Item 2a is true. 3. Complete the theorem. Theorem If a quadrilateral is equilateral, then it is a. 4. Write a paragraph proof to explain why the theorem in Item 3 is true. 5. Given KIND with KN ID. D N a. List the three triangles that are congruent to KXD, and give the reason for the congruence. K X I b. List all segments congruent to KD and explain why. c. Complete the theorem. Theorem If the diagonals of a parallelogram are, then the parallelogram is a. 230 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals
9 Lesson 16-3 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Rhombus ACTIVITY Given BIRD with coordinates B( 2, 3), I(1, 1), R(6, 1), and D(3, 3). a. Show that BIRD is a parallelogram. b. Use the theorem in Item 5 to show BIRD is a rhombus. 7. Given WST with T that bisects WS and WTS. W T S a. List all angles congruent to 1 and explain why. b. In WT, WT. In ST, ST. xplain. c. Complete the theorem. Theorem If a diagonal bisects in a parallelogram, then the parallelogram is a. 8. Construct viable arguments. Write a proof that uses the theorem in Item 7 as the last reason. Given: BLU BL UL B Prove: BLU is a rhombus. L U Activity 16 More About Quadrilaterals 231
10 ACTIVITY 16 Lesson 16-3 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Rhombus 9. Summarize this part of the activity by making a list of the ways to prove that a quadrilateral is a rhombus. Check Your Understanding 10. Can a rectangle ever be classified as a rhombus as well? xplain. LSSON 16-3 PRACTIC Three vertices of a rhombus are given. Find the coordinates of the fourth vertex. 11. ( 2, 8), (3, 3), ( 9, 7) 12. ( 1, 2), ( 1, 1), (2, 1) 13. (1, 1), ( 1, 2), (1, 5) 14. Find the value of x that makes the parallelogram a rhombus. a. (2x 2 ) b. 3x + 1 (3x + 5) 10x Reason quantitatively. LaToya is using a coordinate plane to design a new pendant for a necklace. She wants the pendant to be a rhombus. Three of the vertices of the rhombus are (3, 1), ( 1, 1), and (1, 2). Assuming each unit of the coordinate plane represents one centimeter, what is the perimeter of the pendant? Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 232 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals
11 Lesson 16-4 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Square ACTIVITY 16 Learning Targets: Develop criteria for showing that a quadrilateral is a square. Prove that a quadrilateral is a square. SUGGSTD LARNING STRATGIS: Think-Pair-Share, Create Representations, Group Presentation, Discussion Groups 1. Given JKLM. a. What information is needed to prove that JKLM is a square? J K O M L b. What additional information is needed to prove that JKLM is a square? xplain. c. What additional information is needed to prove that rectangle JKLM is a square? xplain. d. What additional information is needed to prove that rhombus JKLM is a square? xplain. 2. Given DAV with coordinates D( 1, 1), A(0, 7), V(6, 6), and (5, 0). Show that DAV is a square. Activity 16 More About Quadrilaterals 233
12 ACTIVITY 16 Lesson 16-4 Proving a Quadrilateral Is a Square 3. Critique the reasoning of others. Several students in a class made the following statements. Decide whether you agree with each statement. If you disagree, change the statement to make it correct. a. A quadrilateral with congruent diagonals must be a rectangle. b. A parallelogram with two right angles must be a square. c. A quadrilateral with a pair of opposite parallel sides is always a parallelogram. d. A rhombus with four congruent angles is a square. Check Your Understanding 4. lena has a garden with congruent sides, as shown below. Describe two different ways to show the garden is square. LSSON 16-4 PRACTIC The coordinates of a parallelogram are given. Determine whether the figure is a square. 5. ( 2, 3), (3, 3), (3, 0), ( 2, 0) 6. (0, 1), ( 1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 2) 7. (3, 6), (6, 2), ( 2, 3), ( 5, 7) 8. (3, 8), ( 1, 6), (1, 2), (5, 4) 9. xpress regularity in repeated reasoning. Find the length of the diagonal of a square with three of its vertices at (1, 0), (0, 0), and (0, 1). Then find the length of the diagonal of a square with three of its vertices at (2, 0), (0, 0), and (0, 2). Finally, find the length of the diagonal of a square with three of its vertices at (3, 0), (0, 0), and (0, 3). Use your findings to make a conjecture about the length of the diagonal of a square with three of its vertices at (s, 0), (0, 0), and (0, s). 234 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals
13 More About Quadrilaterals A 4-gon Conclusion ACTIVITY 16 ACTIVITY 16 PRACTIC Write your answers on notebook paper. Show your work. Lesson Given RSTU with coordinates R(0, 0), S( 2, 2), T(6, 6), and U(8, 4). a. Show that RSTU is a parallelogram by finding the slope of each side. b. Show that RSTU is a parallelogram by finding the length of each side. c. Show that RSTU is a parallelogram by showing that the diagonals bisect each other. 2. Write a proof using the theorem in Item 2 of Lesson 16-1 as the last reason. Given: ABC FD CD CG CG AF Prove: ACDF A B C 6. Which of the following additional pieces of information would allow you to prove that ABCD is a parallelogram? A D C A. AD BC B. AD BC C. AB DC D. AB DC Lesson ach of the following sets of given information is sufficient to prove that SPAR is a rectangle except: S P K B F 3. Write a proof using the theorem in Item 4 of Lesson 16-1 as the last reason. Given: JKLM X is midpt of JK. Y is midpt of ML. Prove: JXLY D J X K G M Y L 4. Which of the following is not a sufficient condition to prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram? A. The diagonals bisect each other. B. One pair of opposite sides are parallel. C. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. D. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. 5. Show that the quadrilateral with vertices ( 2, 3), ( 2, 1), (1, 1), and (1, 5) is a parallelogram. R A A. SPAR and SPA PAR B. SK = KA = RK = KP C. SPAR and SKP PKA D. RSP SPA PAR ARS 8. Given FOUR with coordinates F(0, 6), O(10, 8), U(13, 3), and R(3, 0). Show that FOUR is not a rectangle. 9. Write an indirect proof. Given: C DF Prove: CDF is not a rectangle. C D F 10. What is the best name for a quadrilateral if the diagonals are congruent and bisect each other? A. parallelogram B. rectangle C. kite D. trapezoid 11. Three vertices of a rectangle are ( 4, 3), (8, 3), and (5, 6). Show that the diagonals are congruent. Activity 16 More About Quadrilaterals 235
14 ACTIVITY 16 More About Quadrilaterals A 4-gon Conclusion Lesson ach of the following sets of given information is sufficient to prove that HOP is a rhombus except: H O X Lesson Write a proof. Given: PAR, P A; P A Prove: PAR is a square. P P A. HX = XP = X = XO B. OH = OP = P = H C. HOP and HXO OXP D. HOP and H = P 13. Given DRUM with coordinates D( 2, 2), R( 3, 3), U(2, 5), and M(3, 0). Show that DRUM is not a rhombus. 14. Write a proof using the theorem in Item 5 of Lesson 16-3 as the last reason. Given: NIGH NTI NTH Prove: NIGH is a rhombus. N H T I G R 16. Given SOPH with coordinates S( 8, 0), O(0, 6), P(10, 6), and H(2, 0). What is the best name for this quadrilateral? A. parallelogram B. rectangle C. rhombus D. square 17. What is the best name for an equilateral quadrilateral whose diagonals are congruent? A. parallelogram B. rectangle C. rhombus D. square MATHMATICAL PRACTICS Look For and Make Use of Structure 18. Why is every rhombus a parallelogram but not every parallelogram a rhombus? Why is every square a rectangle but not every rectangle a square? Why is every square a rhombus but not every rhombus a square? L A 236 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals
H (2, 5) I (6, 5) C (0, 0) A (4, 0) SP because.
 More bout Quadrilaterals SUGGSTD LRNING STRTGIS: ctivating rior Knowledge, Think/air/Share, Group resentation, In a previous activity, the definition of a parallelogram was used to verify that a quadrilateral
More bout Quadrilaterals SUGGSTD LRNING STRTGIS: ctivating rior Knowledge, Think/air/Share, Group resentation, In a previous activity, the definition of a parallelogram was used to verify that a quadrilateral
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review
 Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 5: Polygon Notes Period:
 Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 5: Polygon Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 270 271 #8 14 Even, #15 20, #27-32 (2) Page 276 1 10, #11 25 Odd (3) Page 276 277 #12 30 Even (4) Page 283 #1-14 All (5) Page
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 5: Polygon Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 270 271 #8 14 Even, #15 20, #27-32 (2) Page 276 1 10, #11 25 Odd (3) Page 276 277 #12 30 Even (4) Page 283 #1-14 All (5) Page
Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets
 Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of the way along each median
Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of the way along each median
Period: Date Lesson 13: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means
 : Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
Unit 5: Polygons and Quadrilaterals
 Unit 5: Polygons and Quadrilaterals Scale for Unit 5 4 Through independent work beyond what was taught in class, students could (examples include, but are not limited to): - Research a unique building
Unit 5: Polygons and Quadrilaterals Scale for Unit 5 4 Through independent work beyond what was taught in class, students could (examples include, but are not limited to): - Research a unique building
Examples: Identify the following as equilateral, equiangular or regular. Using Variables: S = 180(n 2)
 Ch. 6 Notes 6.1: Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems Examples: Identify the following as equilateral, equiangular or regular. 1) 2) 3) S = 180(n 2) Using Variables: and Examples: Find the sum of the interior angles
Ch. 6 Notes 6.1: Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems Examples: Identify the following as equilateral, equiangular or regular. 1) 2) 3) S = 180(n 2) Using Variables: and Examples: Find the sum of the interior angles
Chapter 6: Quadrilaterals. of a polygon is a segment that connects any two nonconsecutive. Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon
 Lesson 6-1: Angles of Polygons A vertices. Example: Date: of a polygon is a segment that connects any two nonconsecutive Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon Since the sum of the angle measures of a
Lesson 6-1: Angles of Polygons A vertices. Example: Date: of a polygon is a segment that connects any two nonconsecutive Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon Since the sum of the angle measures of a
Geometry Unit 6 Note Sheets Date Name of Lesson. 6.2 Parallelograms. 6.3 Tests for Parallelograms. 6.4 Rectangles. 6.5 Rhombi and Squares
 Date Name of Lesson 6.2 Parallelograms 6.3 Tests for Parallelograms 6.4 Rectangles 6.5 Rhombi and Squares 6.6 Trapezoids and Kites 1 Quadrilaterals Properties Property Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square
Date Name of Lesson 6.2 Parallelograms 6.3 Tests for Parallelograms 6.4 Rectangles 6.5 Rhombi and Squares 6.6 Trapezoids and Kites 1 Quadrilaterals Properties Property Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square
Over Lesson 6 2??? Over Lesson 6 2? A. B. C. 2
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 2) CCSS Then/Now Theorems: Conditions for Parallelograms Proof: Theorem 6.9 Example 1: Identify Parallelograms Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Parallelograms to Prove
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 2) CCSS Then/Now Theorems: Conditions for Parallelograms Proof: Theorem 6.9 Example 1: Identify Parallelograms Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Parallelograms to Prove
Geometry Review for Test 3 January 13, 2016
 Homework #7 Due Thursday, 14 January Ch 7 Review, pp. 292 295 #1 53 Test #3 Thurs, 14 Jan Emphasis on Ch 7 except Midsegment Theorem, plus review Betweenness of Rays Theorem Whole is Greater than Part
Homework #7 Due Thursday, 14 January Ch 7 Review, pp. 292 295 #1 53 Test #3 Thurs, 14 Jan Emphasis on Ch 7 except Midsegment Theorem, plus review Betweenness of Rays Theorem Whole is Greater than Part
Geo, Chap 6 Practice Test, EV Ver 1
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Geo, Chap 6 Practice Test, EV Ver 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. (6-1) Which statement is true? a. All rectangles
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Geo, Chap 6 Practice Test, EV Ver 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. (6-1) Which statement is true? a. All rectangles
Student Name: Teacher: Date: Miami-Dade County Public Schools. Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 2
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 2 Description: GEO Topic 5: Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Geometry Form: 201 1. If the quadrilateral
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 2 Description: GEO Topic 5: Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Geometry Form: 201 1. If the quadrilateral
6-5 Rhombi and Squares. ALGEBRA Quadrilateral ABCD is a rhombus. Find each value or measure. 1. If, find. ANSWER: 32
 ALGEBRA Quadrilateral ABCD is a rhombus. Find each value or measure. 4. GAMES The checkerboard below is made up of 64 congruent black and red squares. Use this information to prove that the board itself
ALGEBRA Quadrilateral ABCD is a rhombus. Find each value or measure. 4. GAMES The checkerboard below is made up of 64 congruent black and red squares. Use this information to prove that the board itself
6.1: Date: Geometry. Polygon Number of Triangles Sum of Interior Angles
 6.1: Date: Geometry Polygon Number of Triangles Sum of Interior Angles Triangle: # of sides: # of triangles: Quadrilateral: # of sides: # of triangles: Pentagon: # of sides: # of triangles: Hexagon: #
6.1: Date: Geometry Polygon Number of Triangles Sum of Interior Angles Triangle: # of sides: # of triangles: Quadrilateral: # of sides: # of triangles: Pentagon: # of sides: # of triangles: Hexagon: #
GEOMETRY COORDINATE GEOMETRY Proofs
 GEOMETRY COORDINATE GEOMETRY Proofs Name Period 1 Coordinate Proof Help Page Formulas Slope: Distance: To show segments are congruent: Use the distance formula to find the length of the sides and show
GEOMETRY COORDINATE GEOMETRY Proofs Name Period 1 Coordinate Proof Help Page Formulas Slope: Distance: To show segments are congruent: Use the distance formula to find the length of the sides and show
Unit 6: Quadrilaterals
 Name: Geometry Period Unit 6: Quadrilaterals Part 1 of 2: Coordinate Geometry Proof and Properties! In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please note: Calculator
Name: Geometry Period Unit 6: Quadrilaterals Part 1 of 2: Coordinate Geometry Proof and Properties! In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please note: Calculator
Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises?
 Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises? Here is a question for you. In the diagram on the board, DE is parallel to AC, DB = 4, AB = 9 and BE = 8. What is the length EC? Polygons Definitions:
Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises? Here is a question for you. In the diagram on the board, DE is parallel to AC, DB = 4, AB = 9 and BE = 8. What is the length EC? Polygons Definitions:
Unit 2: Triangles and Quadrilaterals Lesson 2.1 Apply Triangle Sum Properties Lesson 4.1 from textbook
 Unit 2: Triangles and Quadrilaterals Lesson 2.1 pply Triangle Sum Properties Lesson 4.1 from textbook Objectives Classify angles by their sides as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. Classify triangles
Unit 2: Triangles and Quadrilaterals Lesson 2.1 pply Triangle Sum Properties Lesson 4.1 from textbook Objectives Classify angles by their sides as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. Classify triangles
Name Date Class. 6. In JKLM, what is the value of m K? A 15 B 57 A RS QT C QR ST
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 6 Chapter Review #1 Form B Circle the best answer. 1. Which best describes the figure? 6. In JKLM, what is the value of m K? A regular convex heptagon B irregular convex heptagon
Name Date Class CHAPTER 6 Chapter Review #1 Form B Circle the best answer. 1. Which best describes the figure? 6. In JKLM, what is the value of m K? A regular convex heptagon B irregular convex heptagon
Unit 2: Triangles and Polygons
 Unit 2: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about lines and angles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Using the diagram below, answer the following questions. Line
Unit 2: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about lines and angles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Using the diagram below, answer the following questions. Line
Midpoint Quadrilaterals
 Math Objectives Students will explore the parallelogram formed by the midpoints of any quadrilateral. Students will further explore special outer and inner quadrilaterals formed by the connected midpoints.
Math Objectives Students will explore the parallelogram formed by the midpoints of any quadrilateral. Students will further explore special outer and inner quadrilaterals formed by the connected midpoints.
Secondary Math II Honors. Unit 4 Notes. Polygons. Name: Per:
 Secondary Math II Honors Unit 4 Notes Polygons Name: Per: Day 1: Interior and Exterior Angles of a Polygon Unit 4 Notes / Secondary 2 Honors Vocabulary: Polygon: Regular Polygon: Example(s): Discover the
Secondary Math II Honors Unit 4 Notes Polygons Name: Per: Day 1: Interior and Exterior Angles of a Polygon Unit 4 Notes / Secondary 2 Honors Vocabulary: Polygon: Regular Polygon: Example(s): Discover the
Q3 Exam Review Date: Per:
 Geometry Name: Q3 Exam Review Date: Per: Show all your work. Box or circle your final answer. When appropriate, write your answers in simplest radical form, as a simplified improper fraction, AND as a
Geometry Name: Q3 Exam Review Date: Per: Show all your work. Box or circle your final answer. When appropriate, write your answers in simplest radical form, as a simplified improper fraction, AND as a
8-2 Parallelograms. Refer to Page 489. a. If. b. If c. If MQ = 4, what is NP? SOLUTION:
 1 NAVIGATION To chart a course, sailors use a parallel ruler One edge of the ruler is placed along the line representing the direction of the course to be taken Then the other ruler is moved until its
1 NAVIGATION To chart a course, sailors use a parallel ruler One edge of the ruler is placed along the line representing the direction of the course to be taken Then the other ruler is moved until its
Geometry 1 st Semester Exam REVIEW Chapters 1-4, 6. Your exam will cover the following information:
 Geometry 1 st Semester Exam REVIEW Chapters 1-4, 6 Your exam will cover the following information: Chapter 1 Basics of Geometry Chapter 2 Logic and Reasoning Chapter 3 Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Chapter
Geometry 1 st Semester Exam REVIEW Chapters 1-4, 6 Your exam will cover the following information: Chapter 1 Basics of Geometry Chapter 2 Logic and Reasoning Chapter 3 Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Chapter
Pre-AICE 2: Unit 5 Exam - Study Guide
 Pre-AICE 2: Unit 5 Exam - Study Guide 1 Find the value of x. (The figure may not be drawn to scale.) A. 74 B. 108 C. 49 D. 51 2 Find the measure of an interior angle and an exterior angle of a regular
Pre-AICE 2: Unit 5 Exam - Study Guide 1 Find the value of x. (The figure may not be drawn to scale.) A. 74 B. 108 C. 49 D. 51 2 Find the measure of an interior angle and an exterior angle of a regular
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
4.0 independently go beyond the classroom to design a real-world connection with polygons that represents a situation in its context.
 ANDERSON Lesson plans!!! Intro to Polygons 10.17.16 to 11.4.16 Level SCALE Intro to Polygons Evidence 4.0 independently go beyond the classroom to design a real-world connection with polygons that represents
ANDERSON Lesson plans!!! Intro to Polygons 10.17.16 to 11.4.16 Level SCALE Intro to Polygons Evidence 4.0 independently go beyond the classroom to design a real-world connection with polygons that represents
U4 Polygon Notes January 11, 2017 Unit 4: Polygons
 Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Honors Geometry. Worksheet 4.1: Quadrilaterals. Quadrilateral:. (definition) Parallelogram:. (definition)
 Honors Geometry Name: Worksheet 4.1: Quadrilaterals Fill in the blanks using definitions and theorems about quadrilaterals. Quadrilateral:. The midquad of a quadrilateral is a. The sum of the measures
Honors Geometry Name: Worksheet 4.1: Quadrilaterals Fill in the blanks using definitions and theorems about quadrilaterals. Quadrilateral:. The midquad of a quadrilateral is a. The sum of the measures
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Angles of Polygons
 6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Angles of Polygons Polygon Interior Angles Sum The segments that connect the nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon are called diagonals. Drawing all of the diagonals from
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Angles of Polygons Polygon Interior Angles Sum The segments that connect the nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon are called diagonals. Drawing all of the diagonals from
Given the following information about rectangle ABCD what triangle criterion will you use to prove ADC BCD.
 A B D Given the following information about rectangle ABCD what triangle criterion will you use to prove ADC BCD. ADC and BCD are right angles because ABCD is a rectangle ADC BCD because all right angles
A B D Given the following information about rectangle ABCD what triangle criterion will you use to prove ADC BCD. ADC and BCD are right angles because ABCD is a rectangle ADC BCD because all right angles
Unit 7: Quadrilaterals
 Name: Geometry Period Unit 7: Quadrilaterals Part 1 of 2: Coordinate Geometry Proof and Properties! In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please note: Calculator
Name: Geometry Period Unit 7: Quadrilaterals Part 1 of 2: Coordinate Geometry Proof and Properties! In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please note: Calculator
6-4 Rectangles 1. QR ANSWER: 7 ft 2. SQ ANSWER: ANSWER: 33.5 ANSWER: ALGEBRA Quadrilateral DEFG is a rectangle.
 FARMING An X-brace on a rectangular barn door is both decorative and functional It helps to prevent the door from warping over time If feet, PS = 7 feet, and, find each measure 6 If, find 51 7 PROOF If
FARMING An X-brace on a rectangular barn door is both decorative and functional It helps to prevent the door from warping over time If feet, PS = 7 feet, and, find each measure 6 If, find 51 7 PROOF If
Name Date Class. The Polygon Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angle measures of a convex polygon with n sides is (n 2)180.
 Name Date Class 6-1 Properties and Attributes of Polygons continued The Polygon Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angle measures of a convex polygon with n sides is (n 2)180. Convex
Name Date Class 6-1 Properties and Attributes of Polygons continued The Polygon Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angle measures of a convex polygon with n sides is (n 2)180. Convex
5.5 Properties of Parallelogram
 GEOMETRY Q2T6 5.5 Exam View WS Name: Class: Date: 5.5 Properties of Parallelogram True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. In a parallelogram, the consecutive angles are congruent.
GEOMETRY Q2T6 5.5 Exam View WS Name: Class: Date: 5.5 Properties of Parallelogram True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. In a parallelogram, the consecutive angles are congruent.
6-6 Trapezoids and Kites. Find each measure. 1. ANSWER: WT, if ZX = 20 and TY = 15 ANSWER: 5
 Find each measure 1 ANALYZE RELATIONSHIPS If ABCD is a kite, find each measure 6 AB 101 2 WT, if ZX = 20 and TY = 15 5 7 5 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Quadrilateral ABCD has vertices A ( 4, 1), B( 2, 3), C(3,
Find each measure 1 ANALYZE RELATIONSHIPS If ABCD is a kite, find each measure 6 AB 101 2 WT, if ZX = 20 and TY = 15 5 7 5 COORDINATE GEOMETRY Quadrilateral ABCD has vertices A ( 4, 1), B( 2, 3), C(3,
Quadrilaterals and Their Properties
 Quadrilaterals and heir Properties 4-gon Hypothesis Lesson 15-1 Kites and riangle Midsegments IVIY 15 Learning argets: evelop properties of kites. Prove the riangle Midsegment heorem. SUGGS LRNING SRGIS:
Quadrilaterals and heir Properties 4-gon Hypothesis Lesson 15-1 Kites and riangle Midsegments IVIY 15 Learning argets: evelop properties of kites. Prove the riangle Midsegment heorem. SUGGS LRNING SRGIS:
Assumption High School. Bell Work. Academic institution promoting High expectations resulting in Successful students
 Bell Work Geometry 2016 2017 Day 36 Topic: Chapter 4 Congruent Figures Chapter 6 Polygons & Quads Chapter 4 Big Ideas Visualization Visualization can help you connect properties of real objects with two-dimensional
Bell Work Geometry 2016 2017 Day 36 Topic: Chapter 4 Congruent Figures Chapter 6 Polygons & Quads Chapter 4 Big Ideas Visualization Visualization can help you connect properties of real objects with two-dimensional
Unit 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals
 6.1 What is a Polygon? A closed plane figure formed by segments that intersect only at their endpoints Regular Polygon- a polygon that is both equiangular and equilateral Unit 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals
6.1 What is a Polygon? A closed plane figure formed by segments that intersect only at their endpoints Regular Polygon- a polygon that is both equiangular and equilateral Unit 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Unit 9: Quadrilaterals
 Unit 9: Quadrilaterals Topic/Assignment I CAN statement Turned in? Properties of Quadrilaterals HW: Worksheet Properties of all Quadrilaterals Properties of Parallelograms HW: Properties of Parallelograms
Unit 9: Quadrilaterals Topic/Assignment I CAN statement Turned in? Properties of Quadrilaterals HW: Worksheet Properties of all Quadrilaterals Properties of Parallelograms HW: Properties of Parallelograms
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide
 Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
8 Quadrilaterals. Before
 8 Quadrilaterals 8. Find Angle Measures in Polygons 8. Use Properties of Parallelograms 8.3 Show that a Quadrilateral is a Parallelogram 8.4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares 8.5 Use Properties
8 Quadrilaterals 8. Find Angle Measures in Polygons 8. Use Properties of Parallelograms 8.3 Show that a Quadrilateral is a Parallelogram 8.4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares 8.5 Use Properties
Lesson 4.3 Ways of Proving that Quadrilaterals are Parallelograms
 Lesson 4.3 Ways of Proving that Quadrilaterals are Parallelograms Getting Ready: How will you know whether or not a figure is a parallelogram? By definition, a quadrilateral is a parallelogram if it has
Lesson 4.3 Ways of Proving that Quadrilaterals are Parallelograms Getting Ready: How will you know whether or not a figure is a parallelogram? By definition, a quadrilateral is a parallelogram if it has
5.6notes November 13, Based on work from pages , complete In an isosceles triangle, the &
 chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
pd 3notes 5.4 November 09, 2016 Based on work from pages , complete In an isosceles triangle, the &
 chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
chapter 5 Based on work from pages 178-179, complete In an isosceles triangle, the & & & drawn from the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle are the! 5.1 Indirect proof. G: DB AC F is the midpt. of AC
Chapter 6 Practice Test
 Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of each convex polygon. 1. hexagon A hexagon has six sides. Use the Polygon Interior Angles Sum Theorem to find the sum of its interior angle measures.
Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of each convex polygon. 1. hexagon A hexagon has six sides. Use the Polygon Interior Angles Sum Theorem to find the sum of its interior angle measures.
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide
 Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Ch 7 Quadrilaterals January 06, 2016
 Theorem 17: Equal corresponding angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 1: Equal alternate interior angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 2: Supplementary interior angles on the same side
Theorem 17: Equal corresponding angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 1: Equal alternate interior angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 2: Supplementary interior angles on the same side
In this activity, you will learn about quadrilaterals. You will apply these mathematical concepts to real-world situations such as designing logos.
 Quadrilaterals ACTIVITY 5 Previewing the Activity In this activity, you will learn about quadrilaterals. You will apply these mathematical concepts to real-world situations such as designing logos. Activity
Quadrilaterals ACTIVITY 5 Previewing the Activity In this activity, you will learn about quadrilaterals. You will apply these mathematical concepts to real-world situations such as designing logos. Activity
HIGH SCHOOL. Geometry. Soowook Lee
 HIGH SCHOOL Geometry Soowook Lee Chapter 4 Quadrilaterals This chapter will cover basic quadrilaterals, including parallelograms, trapezoids, rhombi, rectangles, squares, kites, and cyclic quadrilaterals.
HIGH SCHOOL Geometry Soowook Lee Chapter 4 Quadrilaterals This chapter will cover basic quadrilaterals, including parallelograms, trapezoids, rhombi, rectangles, squares, kites, and cyclic quadrilaterals.
Geometry. Kites Families of Quadrilaterals Coordinate Proofs Proofs. Click on a topic to
 Geometry Angles of Polygons Properties of Parallelograms Proving Quadrilaterals are Parallelograms Constructing Parallelograms Rhombi, Rectangles and Squares Kites Families of Quadrilaterals Coordinate
Geometry Angles of Polygons Properties of Parallelograms Proving Quadrilaterals are Parallelograms Constructing Parallelograms Rhombi, Rectangles and Squares Kites Families of Quadrilaterals Coordinate
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Polygons are named by the number of sides they have:
 Unit 5 Lesson 1 Polygons and Angle Measures I. What is a polygon? (Page 322) A polygon is a figure that meets the following conditions: It is formed by or more segments called, such that no two sides with
Unit 5 Lesson 1 Polygons and Angle Measures I. What is a polygon? (Page 322) A polygon is a figure that meets the following conditions: It is formed by or more segments called, such that no two sides with
Problems #1. A convex pentagon has interior angles with measures (5x 12), (2x + 100), (4x + 16), (6x + 15), and (3x + 41). Find x.
 1 Pre-AP Geometry Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: G.CO.11/ C.1.i.: I can use properties of special quadrilaterals in a proof. D.2.g.: I can identify and classify quadrilaterals, including parallelograms,
1 Pre-AP Geometry Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: G.CO.11/ C.1.i.: I can use properties of special quadrilaterals in a proof. D.2.g.: I can identify and classify quadrilaterals, including parallelograms,
Chapter 11 Areas of Polygons and Circles
 Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
Math 3 - Lesson Title: Using the Coordinate Plane for Proofs
 Targeted Content Standard(s): Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove
Targeted Content Standard(s): Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove
A closed plane figure with at least 3 sides The sides intersect only at their endpoints. Polygon ABCDEF
 A closed plane figure with at least 3 sides The sides intersect only at their endpoints B C A D F E Polygon ABCDEF The diagonals of a polygon are the segments that connects one vertex of a polygon to another
A closed plane figure with at least 3 sides The sides intersect only at their endpoints B C A D F E Polygon ABCDEF The diagonals of a polygon are the segments that connects one vertex of a polygon to another
8.1 Find Angle Measures in Polygons
 VOCABULARY 8.1 Find Angle Measures in Polygons DIAGONAL Review: EQUILATERAL EQUIANGULAR REGULAR CLASSIFYING POLYGONS Polygon Interior Angle Theorem: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a
VOCABULARY 8.1 Find Angle Measures in Polygons DIAGONAL Review: EQUILATERAL EQUIANGULAR REGULAR CLASSIFYING POLYGONS Polygon Interior Angle Theorem: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a
22. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
 Chapter 4 Quadrilaterals 4.1 Properties of a Parallelogram Definitions 22. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. 23. An altitude of a parallelogram is the
Chapter 4 Quadrilaterals 4.1 Properties of a Parallelogram Definitions 22. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. 23. An altitude of a parallelogram is the
Geometry SIA #2. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Geometry SIA #2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the value of x. a. 4 b. 8 c. 6.6 d. 6 2. Find the length of the midsegment.
Class: Date: Geometry SIA #2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the value of x. a. 4 b. 8 c. 6.6 d. 6 2. Find the length of the midsegment.
Squares and Rectangles
 LESSON.1 Assignment Name Date Squares and Rectangles Properties of Squares and Rectangles 1. In quadrilateral VWXY, segments VX and WY bisect each other, and are perpendicular and congruent. Is this enough
LESSON.1 Assignment Name Date Squares and Rectangles Properties of Squares and Rectangles 1. In quadrilateral VWXY, segments VX and WY bisect each other, and are perpendicular and congruent. Is this enough
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS
 EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
Proving Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane
 Proving Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane Mathematical Goals Prove theorems pertaining to lines and angles. Prove theorems pertaining to triangles. Prove theorems pertaining to parallelograms. STANDARDS
Proving Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane Mathematical Goals Prove theorems pertaining to lines and angles. Prove theorems pertaining to triangles. Prove theorems pertaining to parallelograms. STANDARDS
a) Triangle KJF is scalene. b) Triangle KJF is not isosoceles. c) Triangle KJF is a right triangle. d) Triangle KJF is not equiangular.
 Geometry Unit 2 Exam Review Name: 1. Triangles ABC and PQR are congruent. Which statement about the triangles is true? a) A R b) C R c) AB RQ d) CB PQ 2. Which figure contains two congruent triangles?
Geometry Unit 2 Exam Review Name: 1. Triangles ABC and PQR are congruent. Which statement about the triangles is true? a) A R b) C R c) AB RQ d) CB PQ 2. Which figure contains two congruent triangles?
My Notes. Activity 31 Quadrilaterals and Their Properties 529
 Quadrilaterals and Their Properties 4-gon Hypothesis Learning Targets: Develop properties of kites. Prove the Triangle idsegment Theorem. SUGGSTD LRNING STRTGIS: reate Representations, Think-Pair-Share,
Quadrilaterals and Their Properties 4-gon Hypothesis Learning Targets: Develop properties of kites. Prove the Triangle idsegment Theorem. SUGGSTD LRNING STRTGIS: reate Representations, Think-Pair-Share,
1) Draw line m that contains the points A and B. Name two other ways to name this line.
 1) Draw line m that contains the points A and B. Name two other ways to name this line. 2) Find the next 3 terms in the sequence and describe the pattern in words. 1, 5, 9, 13,,, 3) Find the next 3 terms
1) Draw line m that contains the points A and B. Name two other ways to name this line. 2) Find the next 3 terms in the sequence and describe the pattern in words. 1, 5, 9, 13,,, 3) Find the next 3 terms
Math Geometry FAIM 2015 Form 1-A [ ]
![Math Geometry FAIM 2015 Form 1-A [ ] Math Geometry FAIM 2015 Form 1-A [ ]](/thumbs/80/81205175.jpg) Math Geometry FAIM 2015 Form 1-A [1530458] Student Class Date Instructions Use your Response Document to answer question 13. 1. Given: Trapezoid EFGH with vertices as shown in the diagram below. Trapezoid
Math Geometry FAIM 2015 Form 1-A [1530458] Student Class Date Instructions Use your Response Document to answer question 13. 1. Given: Trapezoid EFGH with vertices as shown in the diagram below. Trapezoid
Geometry Quarter 4 Test Study Guide
 Geometry Quarter 4 Test Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Quarter 4 Test Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
DISTANCE FORMULA: to find length or distance =( ) +( )
 MATHEMATICS ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY DISTANCE FORMULA: to find length or distance =( ) +( ) A. TRIANGLES: Distance formula is used to show PERIMETER: sum of all the sides Scalene triangle: 3 unequal sides Isosceles
MATHEMATICS ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY DISTANCE FORMULA: to find length or distance =( ) +( ) A. TRIANGLES: Distance formula is used to show PERIMETER: sum of all the sides Scalene triangle: 3 unequal sides Isosceles
Geometry Formulas. Area Formulas. Volume Formulas. Other Formulas. Special Right Triangles. d x x y y. 1 p. A bh A(Parallelogram)
 Geometry Formulas Area Formulas Lateral Area of cylinder C h rh Surface Area of prisms and cylinders LA B Lateral Area of prism Lateral Area of cone Lateral Area of pyramid A(Circle) p h Surface Area of
Geometry Formulas Area Formulas Lateral Area of cylinder C h rh Surface Area of prisms and cylinders LA B Lateral Area of prism Lateral Area of cone Lateral Area of pyramid A(Circle) p h Surface Area of
m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 1 m 4 m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ m 6 m 2 1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true?
 1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true? m 1 m 4 m 6 m 2 m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ 2. Look at parallelogram ABCD below. How could you prove that ABCD is a rhombus? Show that
1. In the figure below, p q. Which of the statements is NOT true? m 1 m 4 m 6 m 2 m 6 + m 3 = 180⁰ m 2 m 5 = 180⁰ 2. Look at parallelogram ABCD below. How could you prove that ABCD is a rhombus? Show that
theorems & postulates & stuff (mr. ko)
 theorems & postulates & stuff (mr. ko) postulates 1 ruler postulate The points on a line can be matched one to one with the real numbers. The real number that corresponds to a point is the coordinate of
theorems & postulates & stuff (mr. ko) postulates 1 ruler postulate The points on a line can be matched one to one with the real numbers. The real number that corresponds to a point is the coordinate of
6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms
 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Justify each statement. 1. 2. Reflex Prop. of Conv. of Alt. Int. s Thm. Evaluate each expression for x = 12 and
6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Justify each statement. 1. 2. Reflex Prop. of Conv. of Alt. Int. s Thm. Evaluate each expression for x = 12 and
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles
 Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
Geometry Formulas. Area Formulas. bh A(Regular Polygon) ap. 1 A(Trapezoid) b1 b2. Volume Formulas. 4 3 r Other Formulas.
 Lateral Area of cylinder C h Lateral Area of prism Lateral Area of cone Lateral Area of pyramid A(Circle) Geometry Formulas Area Formulas rh Surface Area of prisms and cylinders LA p h Surface Area of
Lateral Area of cylinder C h Lateral Area of prism Lateral Area of cone Lateral Area of pyramid A(Circle) Geometry Formulas Area Formulas rh Surface Area of prisms and cylinders LA p h Surface Area of
Geometry Module 3 Unit 2 Practice Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Geometry Module 3 Unit 2 Practice Exam Short Answer 1. If BCDE is congruent to OPQR, then BC is congruent to?. 2. NPM? 3. Given QRS TUV, QS 4v 3, and TV 8v 9, find the length of QS and
Name: Class: Date: Geometry Module 3 Unit 2 Practice Exam Short Answer 1. If BCDE is congruent to OPQR, then BC is congruent to?. 2. NPM? 3. Given QRS TUV, QS 4v 3, and TV 8v 9, find the length of QS and
Modeling with Geometry
 Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Unit Goals Stage 1. Number of Days: 14 days 1/29/18-2/16/18
 Number of : 14 1/29/18-2/16/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Drawing on our knowledge of the definitions of special quadrilaterals and a few of their properties, students will now prove those properties
Number of : 14 1/29/18-2/16/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Drawing on our knowledge of the definitions of special quadrilaterals and a few of their properties, students will now prove those properties
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
 Benchmark: MA.912.D.6.2 Find the converse, inverse, and contrapositive of a statement. (Also assesses MA.912.D.6.3 Determine whether two propositions are logically equivalent.) Problem 1: Which of the
Benchmark: MA.912.D.6.2 Find the converse, inverse, and contrapositive of a statement. (Also assesses MA.912.D.6.3 Determine whether two propositions are logically equivalent.) Problem 1: Which of the
Polygon Interior Angles
 Polygons can be named by the number of sides. A regular polygon has All other polygons are irregular. A concave polygon has All other polygons are convex, with all vertices facing outwards. Name each polygon
Polygons can be named by the number of sides. A regular polygon has All other polygons are irregular. A concave polygon has All other polygons are convex, with all vertices facing outwards. Name each polygon
14. How many sides does a regular polygon have, if the measure of an interior angle is 60?
 State whether the figure is a polygon; if it is a polygon, state whether the polygon is convex or concave. HINT: No curves, no gaps, and no overlaps! 1. 2. 3. 4. Find the indicated measures of the polygon.
State whether the figure is a polygon; if it is a polygon, state whether the polygon is convex or concave. HINT: No curves, no gaps, and no overlaps! 1. 2. 3. 4. Find the indicated measures of the polygon.
Unit 3: Triangles and Polygons
 Unit 3: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about triangles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Example 1: Trapezoid on the coordinate plane below has the following
Unit 3: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about triangles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Example 1: Trapezoid on the coordinate plane below has the following
1/8/2016 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Theorem 6.13: Diagonals of a Rectangle Example 1: Real-World Example: Use Pr
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Theorem 6.13: Diagonals of a Rectangle Example 1: Real-World Example: Use Properties of Rectangles Example 2: Use Properties of Rectangles
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Theorem 6.13: Diagonals of a Rectangle Example 1: Real-World Example: Use Properties of Rectangles Example 2: Use Properties of Rectangles
Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
 Chapter 8 Applying Congruent Triangles In the last chapter, we came across a very important concept. That is, corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent - cpctc. In this chapter, we will
Chapter 8 Applying Congruent Triangles In the last chapter, we came across a very important concept. That is, corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent - cpctc. In this chapter, we will
Regents Exam Questions G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2 Page 1 Name:
 Regents Exam Questions G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2 Page 1 G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane: Investigate, justify, and apply the properties of quadrilaterals in the coordinate
Regents Exam Questions G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane 2 Page 1 G.G.69: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane: Investigate, justify, and apply the properties of quadrilaterals in the coordinate
Geometric Concepts. Academic Vocabulary composite
 275-276_SB_MS1_SE_U05_OP.indd Page 275 7/26/13 4:50 AM deepaksharma pjh /103/SB00001_DEL/work/indd/SE/M01_Middile_School/Math_01/Application_files/SE_M1_... Geometric Concepts 5 Unit Overview In this unit
275-276_SB_MS1_SE_U05_OP.indd Page 275 7/26/13 4:50 AM deepaksharma pjh /103/SB00001_DEL/work/indd/SE/M01_Middile_School/Math_01/Application_files/SE_M1_... Geometric Concepts 5 Unit Overview In this unit
Geometry Chapter 5 Review Sheet
 Geometry hapter 5 Review Sheet Name: 1. List the 6 properties of the parallelogram. 2. List the 5 ways to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. 3. Name two properties of the rectangle that are
Geometry hapter 5 Review Sheet Name: 1. List the 6 properties of the parallelogram. 2. List the 5 ways to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. 3. Name two properties of the rectangle that are
1. Write three things you already know about angles. Share your work with a classmate. Does your classmate understand what you wrote?
 LESSON : PAPER FOLDING. Write three things you already know about angles. Share your work with a classmate. Does your classmate understand what you wrote? 2. Write your wonderings about angles. Share your
LESSON : PAPER FOLDING. Write three things you already know about angles. Share your work with a classmate. Does your classmate understand what you wrote? 2. Write your wonderings about angles. Share your
Transformations and Congruence
 Name Date Class UNIT 1 Transformations and Congruence Unit Test: C 1. Draw ST. Construct a segment bisector and label the intersection of segments Y. If SY = a + b, what is ST? Explain your reasoning.
Name Date Class UNIT 1 Transformations and Congruence Unit Test: C 1. Draw ST. Construct a segment bisector and label the intersection of segments Y. If SY = a + b, what is ST? Explain your reasoning.
POLYGON NAME UNIT # ASSIGN # 2.) STATE WHETHER THE POLYGON IS EQUILATERAL, REGULAR OR EQUIANGULAR
 POLYGONS POLYGON CLOSED plane figure that is formed by three or more segments called sides. 2.) STTE WHETHER THE POLYGON IS EQUILTERL, REGULR OR EQUINGULR a.) b.) c.) VERTEXThe endpoint of each side of
POLYGONS POLYGON CLOSED plane figure that is formed by three or more segments called sides. 2.) STTE WHETHER THE POLYGON IS EQUILTERL, REGULR OR EQUINGULR a.) b.) c.) VERTEXThe endpoint of each side of
Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont)
 49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26)
 Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26) Learning Target: At the end of today s lesson we will be able to successfully name and sketch geometric figures.
Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26) Learning Target: At the end of today s lesson we will be able to successfully name and sketch geometric figures.
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
8 sides 17 sides. x = 72
 GEOMETRY Chapter 7 Review Quadrilaterals Name: Hour: Date: SECTION 1: State whether each polygon is equilateral, equiangular, or regular. 1) 2) 3) equilateral regular equiangular SECTION 2: Calculate the
GEOMETRY Chapter 7 Review Quadrilaterals Name: Hour: Date: SECTION 1: State whether each polygon is equilateral, equiangular, or regular. 1) 2) 3) equilateral regular equiangular SECTION 2: Calculate the
6-2 Parallelograms. Refer to Page 407. a. If. b. If. c. If MQ = 4, what is NP? ANSWER: a. 148 b. 125 c. 4
 1. NAVIGATION To chart a course, sailors use a parallel ruler. One edge of the ruler is placed along the line representing the direction of the course to be taken. Then the other ruler is moved until its
1. NAVIGATION To chart a course, sailors use a parallel ruler. One edge of the ruler is placed along the line representing the direction of the course to be taken. Then the other ruler is moved until its
GH Midterm Exam Review #2 (Ch 4-7 and Constructions)
 Name Period ID: A GH Midterm Exam Review #2 (Ch 4-7 and Constructions) 1. Name the smallest angle of ABC. The diagram is not to scale. 7. Find the missing values of the variables. The diagram is not to
Name Period ID: A GH Midterm Exam Review #2 (Ch 4-7 and Constructions) 1. Name the smallest angle of ABC. The diagram is not to scale. 7. Find the missing values of the variables. The diagram is not to
Parallelograms. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 05
 Parallelograms MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 05 Definitions A quadrilateral is a polygon with 4 distinct sides and four vertices. Is there a more precise definition? P 1 P 2 P 3 09-Sept-2011 MA 341
Parallelograms MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 05 Definitions A quadrilateral is a polygon with 4 distinct sides and four vertices. Is there a more precise definition? P 1 P 2 P 3 09-Sept-2011 MA 341
