Name: Unit 7 Beaumont Middle School 8th Grade, Introduction to Algebra
|
|
|
- Pamela Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 7 Beaumont Middle School 8th Grade, Introduction to Algebra Name: I can recognize and create reflections on a coordinate grid. I can recognize and create translations on a coordinate grid. I can recognize and create rotations on a coordinate grid. I can identify congruency within reflections, translations, and rotations. I can recognize and create dilations on a coordinate grid. I can identify similarity within dilations. I can write a general rule for transformations on a coordinate grid. I can recognize and create combined transformations.
2 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 2 ~~ Reflectional Symmetry An image has Reflectional Symmetry if there is at least one line which splits the image in half so that one side is the mirror image of the other. Reflectional symmetry is also called line symmetry or mirror symmetry because there is a line in the figure where a mirror could be placed, and the figure would look the same. Think of a figure on a piece of paper, then folding the paper in two so that the two halves match up, or actually placing a mirror on the line of symmetry. It is possible to have more than one line of reflectional symmetry. Draw all of the lines of symmetry for each figure. Indicate the number of lines of symmetry for each figure. If the figure does not have reflectional symmetry, write none #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines:
3 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 3 ~~ Notes for Reflectional Symmetry on a Coordinate Grid The vertices of a polygon are listed. Graph and label each polygon and its image after a reflection over the given line. Name the coordinates of the image. State the rule for the transformation. 1. Reflect over the x-axis. (The x-axis can also be described as the line y = 0.) A (0, 2) B (-2, 5) C (-5, 1) A B C General rule: 2. Reflect over the y-axis. (The y-axis can also be described as the line x = 0.) E (1, 4) F (3, -2) G (5, 4) H (3, 6) E F G H General rule: A reflectional transformation results in a congruent figure. All angles and segments maintain the same measurements. Identify the congruent parts for the following triangle that was reflected over the line y = x. AB A A BC CA ABC B C C B Q R N State the coordinates of A and its corresponding vertex: A: Write the general rule for a reflection over the line x = y
4 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 4 ~~ Homework for Reflectional Symmetry The vertices of a polygon are listed. Graph and label each polygon and its image after a reflection over the given line. Name the coordinates of the image. State the rule for the transformation. 1. Reflect over the y-axis. W (2,-4) X (1, 3) Y (4, 1) Z (5, -2) W X Y Z General rule: 2. Reflect over the x-axis. J (-2, 1) J K (1, 6) L (4, 2) K L General rule: 3. Reflect over the x-axis. D (-2, 1) D E (5, 2) F (3, -4) E F General rule:
5 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 5 ~~ 4. Identify the congruent parts for the following triangle that was reflected over the y- axis. AB BC CA A B C ABC Draw all of the lines of symmetry for each figure. If the figure does not have reflectional symmetry, write none #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: #of lines: Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer Use the letter in the box to answer the following question. Which of the following shows the image above reflected over the dotted line? Which shows the letter after it has been FLIPPED ONCE?
6 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 6 ~~ Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer. 13. Anna noticed the following sign on the wall 14. Which figure is a reflection of figure P in respect to the x-axis? Which shows the sign after it has been flipped across the line? 15. If trapezoid KLMN shown below is reflected across the x-axis to form trapezoid K L M N, what are the apparent coordinates of M? 16. Which of the following is a single reflection of figure N over the y-axis to form N? A. ( 4, 5) B. ( 4, 5) C. (4, 5) D. (4, 5)
7 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 7 ~~ Translational Symmetry An image has Translational Symmetry if it can be divided by straight lines into a sequence of identical figures. Translational symmetry results from moving a figure a certain distance in a certain direction also called translating (moving) by a vector (length and direction). A tessellation is created when a shape is repeated over and over again covering a plane without any gaps or overlaps. Another word for a tessellation is a tiling. NOTES for Translational Symmetry 1. Name the coordinates of the image and its translation. State the rule for the transformation. W W W X X Z Z X Z W General rule: X Z
8 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 8 ~~ NOTES for Translational Symmetry, continued 2. The vertices of a polygon are listed. Name the coordinates of the image s translation given the general rule for the transformation. Graph and label the original polygon and its image. General rule: ( x, y ) (x 5, y + 2) D (4, 2) D E (6, -3) E F (0, -3) F G (2, 2) G 3. A point and its image after a translation are given. Write a rule to describe the translation. a. The translation that takes A(8, -6) to A (9, -3) (x, y) b. The translation that takes B(2, -10) to B (2, -12) (x, y) 4. A translational transformation also results in a congruent figure. Identify the congruent parts for triangle XYZ that was translated 2 units to the left and 4 units up. B N W X Z Y XY YZ ZX XYZ W N B State the coordinates of W and its corresponding vertex: W: Write the general rule for the translation
9 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 9 ~~ HOMEWORK for Translational Symmetry 1. Name the coordinates of the image and its translation. State the rule for the transformation. J J K K L L M M General rule: 2. The vertices of a polygon are listed. Name the coordinates of the image s translation given the general rule for the transformation. Graph and label the original polygon and its image. General rule: ( x, y ) (x + 4, y 2) D (-2, 0) D E (2, -3) E F (-4, -3) F 3. The vertices of a polygon are listed. Name the coordinates of the image s translation given the general rule for the transformation. Graph and label the original polygon and its image. General rule: ( x, y ) (x 6, y) R (6, 5) R S (4, -1) S T (0, -1) T U (2, 5) U
10 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 10 ~~ 4. A point and its image after a translation are given. Write a rule to describe the translation. a. The translation that takes A(10, 5) to A ( 5, 3) (x, y) b. The translation that takes B(2, 3) to B (7, 8) (x, y) 5. Identify the congruent parts for triangle XYZ that was translated 3 units to the right and 5 units down. XY X YZ ZX Y Z XYZ State the coordinates of X and its corresponding vertex: X: Write the general rule for the translation Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer. 6. Which pair of shapes shows a 7. Which shows a slide of translation (slide)?
11 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 11 ~~ Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer
12 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 12 ~~ Review Reflectional and Translational Symmetry Draw all of the lines of symmetry for each figure. If the figure does not have reflectional symmetry, write none The vertices of a polygon are listed. Graph and label each polygon and its image after a reflection over the given line. Name the coordinates of the image. State the rule for the transformation. (It is okay for the images to overlap each other.) 9. Reflect over the x-axis. A (-1, 2) A B (4, -2) C (6, 5) B C General rule: 10. Reflect over the y-axis. E (-1, 4) E F (3, 2) F G (6, -6) G H (-3, -4) H General rule:
13 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 13 ~~ 11. Name the coordinates of the image and its translation. State the rule for the transformation. V V X W V W W X X Y Z W Y Y X V Z Z Y Z General rule: 12. The vertices of a polygon are listed. Name the coordinates of the image s translation given the general rule for the transformation. Graph and label the original polygon and its image. General rule: ( x, y ) (x + 3, y 5) D (-4, 2) D E (-6, 1) E F (0, -1) F G (2, 2) G A point and its image after a translation are given. Write a rule to describe the translation. 13. The translation that takes A(-8, -6) to A (2, 3) (x, y) 14. The translation that takes B(5, -1) to B (-9, -5) (x, y)
14 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 14 ~~ 15. Amy transformed triangle ABC to create triangle RST. State the type of transformation and give the general rule. Type: Rule: Original Seth transformed triangle ABC to create triangle NPQ. State the type of transformation and give the general rule. Type: Rule: Name the corresponding parts for the triangles. For Amy's transformation AB A BC B Amy's CA ABC C Seth's For Seth's transformation AB BC CA ABC A B C Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer Which figure is a reflection of figure P in respect to the x-axis?
15 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 15 ~~ Rotational Symmetry An image has Rotational Symmetry if there is a center point where an object is turned a certain number of degrees and still look the same. A rotation is sometimes called a TURN. These examples have rotational symmetry, but no reflectional symmetry. How many matches there are as you go once around is called the Order. Examples of Different Rotational Symmetry Order Example Angle of Rotation Order Shape 360 o 2 = 180 o 360 o 3 = 120 o 360 o 4 = 90 o... and there is also Order 5, 6, 7, and o 8 = 45 o... and then there is Order 9, 10, and so on... Is there Rotational Symmetry of Order 1? Not really! If a shape only matches itself once as you go around (ie it matches itself after one full rotation) there is really no symmetry at all, because the word "Symmetry" comes from syn- together and metron measure, and there can't be "together" if there is just one thing.
16 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 16 ~~ Practice: For each figure state the order and the angle of rotation Order: Order: Order: Order: Angle : Angle : Angle : Angle : Notes for Rotational Symmetry on a Coordinate Grid The vertices of a polygon are listed. Graph and label each polygon and its image after a given rotation. Name the coordinates of the image. 1. Rotate figure STU about the origin 90 o clockwise. S (0, 2) T (-2, 5) U (-5, 1) S T U Write the general rule: 2. Rotate figure EFG about the origin 180 o. E (1, 4) F (3, -2) G (5, 4) E F G Write the general rule:
17 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 17 ~~ Homework for Rotational Symmetry The vertices of a polygon are listed. Graph and label each polygon and its image after a given rotation. Name the coordinates of the image. 1. Rotate figure WXY about the origin 90 o counterclockwise. W (2,-4) X (1, 3) Y (4, 1) W X Y Write the general rule: 2. Rotate figure JKL about the origin 90 o clockwise J (-2, 1) J K (1, 6) L (4, 2) K L Write the general rule: For each figure state the order and the angle of rotation Order: Order: Angle : Angle : Order: Angle : Order: Angle : Order: Angle : Order: Angle :
18 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 18 ~~ Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer
19 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 19 ~~ More Rotational Symmetry Plot and label the figure on each coordinate grid. Make the transformation that is indicated. State the transformed coordinates and the general rule. 1. Rotation 90 o clockwise 2. Rotation 180 o A (-2, -1) A D (-4, 5) D B (-2, 3) B E (-6, -4) E C (-5, 3) C F (-2, -1) F General Rule: General Rule: 3. Rotation 90 o counterclockwise 4. Rotation 270 o clockwise G (2, -4) G J (-1, 4) J H (4, 3) H K (-6, 1) K I (6, -4) I L (-1, 1) L General Rule: General Rule:
20 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 20 ~~ Multiple c hoice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer
21 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 21 ~~ A B C D E F G H
22 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 22 ~~ Dilations Dilations A transformation in which a polygon is enlarged or reduced by a given factor around a given center point. Dilation is where the polygon grows or shrinks but keeps the same overall shape. It's a little like zooming in or out on a camera. The transformed figure is called the dilated image of the original Scale factor The amount by which the image grows or shrinks is called the "Scale Factor". If the scale factor is say 2, the image is enlarged to twice the size of the original. If it is 0.5, the image is reduced to half the size. When the scale factor is 1, the image is the exact same size as the original. Remember: In dilation, multiply the dimensions of the original by the scale factor to get the dimensions of the image. Original and image are similar In dilation, the image and the original are similar, in that they are the same shape but not necessarily the same size. They are not congruent because that requires them to be the same shape and the same size, which they are not (unless the scale factor happens to be 1.0). NOTES for Dilations 1. Dilate figure WXY by a scale factor of 2. Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. W (-1, 2) W X (-2, -3) X Y (2, -3) Y Find the area of the original figure: Find the area of the dilated figure: Write a general rule for the dilation:
23 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 23 ~~ NOTES for Dilations 2. Dilate figure ABCD by a scale factor of 1 3. Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. A (-3, 6) A B (-9, -9) B C (6, -9) C D (3, 6) D' Find the area of the original figure: Write a general rule for the dilation: Find the area of the dilated figure: State the scale factor of the following dilations: 3. (2, 4) (10, 20) 4. (-15, 27) (-5, 9) 5. (3, 7) (12, 28) Write the general rule for the transformation. 6. (14, 6) (7, 3) 7. (-1, 3) (-5, 15) Name the scale factor for the folowing dilations. #8. Scale Factor: #9 Scale Factor:
24 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 24 ~~ Homework for Dilations 1. Dilate figure WXYZ by a scale factor of 3. Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. W (0, 3) W X (2, 3) X Y (3, -3) Y Z (-3, -3) Z Find the area of the original figure: Write a general rule for the dilation: Find the area of the dilated figure: 2. Dilate figure ABC by a scale factor of 1. 2 Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. A (-10, 8) A B (6, 8) B C (6, -10) C Find the area of the original figure: Find the area of the dilated figure: State the scale factor of the following dilations: Write a general rule for the dilation: 3. (3, 4) (12, 16) 4. (-15, 50) (-3, 10) 5. (1, 9) (6, 54) Write the general rule for the dilation. 6. (21, 6) (7, 2) 7. (2, 15) (4, 30)
25 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 25 ~~ 8. Draw the dilation image of triangle ABC with the center of dilation at the origin and a scale factor of 2. (Hint: write down the coordinates first.) Is the dilation an enlargement or reduction? 9. Draw the dilation image of pentagon ABCDE with the center of dilation at the origin and a scale factor of 1/3. (Hint: write down the coordinates first.) A B C E D Is the dilation an enlargement or reduction? Multiple choice: The following are mu ltiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer
26 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 26 ~~ Dilations and Similar Figures Under a transformation of a dilation, a figure will be similar to the pre-image. This means Note: the angle measures will remain the same (be congruent) parallel lines remain parallel BUT lengths of segments are NOT congruent, but be in equal ratio Triangle ABC was dilated by a factor of 2 to create triangle XYZ means congruent to ~ means similar to ABC~ XYZ CA = 4units BC = 3units AB = 5 units XZ = units YZ = units XY = units Name the congruent angles. A B C Notice the ratio of all the segment measures remains the same. Parallelogram QRST was dilated by a scale factor of 1. Fill in the missing values. 3 Parallelogram QRST ~ Parallelogram QR = units TS = units QT 16 units SR 16 units AX = units HF = units SR units FX units Name the congruent angles in the smaller parallelogram. Q R S T If QR TS, then AX HF. Therefore if QT RS, then name two other parallel segments.
27 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 27 ~~ Dilate figure ABC by a scale factor of 3 2. Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. A (-2, 0) A B (4, 2) B C (-4, -4) C State the general rule: Homework 1) Dilate figure ABC by a scale factor of 2. Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. A (-2, 1) A B (-2, 3) B C (3, 2) C State the general rule: 2) Dilate figure ABC by a scale factor of 1 2. Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. A (-10, 8) A B (-8, 6) B C (-6, -10) C State the general rule:
28 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 28 ~~ 3) Dilate figure ABC by a scale factor of 2. 3 Plot and label the original and the dilated figure. A (-12, 9) A B (9, 6) B C (6, -12) C State the general rule: Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer.
29 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 29 ~~
30 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 30 ~~ 8.
31 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 31 ~~
32 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 32 ~~ Combined Transformations A combined transformation is just a series of two or more transformations performed on the same figure. EXAMPLES of Double Transformations 1. Using triangle JKL, find each point of reflection over the y-axis and then a translation up 5 units. J J' J'' K K' K'' L L' L'' J Draw triangle J'K'L' and J''K''L'' L K 2. Using figure PQR, find each point for a rotation 180 o about the origin and a translation right 5 units and up 1 units. Q P P' P'' Q Q' Q'' R R' R'' Draw triangle P'Q'R' and P''Q''R'' P R
33 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 33 ~~ Homework on Combined Transformations 1. Using figure JKLM, find each point for a reflection over the x-axis and a translation down 3 units. J K J J' J'' K K' K'' L L' L'' M M' M'' M L Draw figure J'K'L'M' and J''K''L''M'' Find the area of figure JKLM. Show all work. Area: 2. Using figure ABC, find each point for a translation left 2 and down 3 and then a rotation of 90 o counterclock wise. A A' A'' B B' B'' C C' C'' A C B Draw triangle A'B'C' and A''B''C'' Find the area of figure ABC. Show all work. Area:
34 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 34 ~~ Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer Which figure shows the flag on the left after it has been flipped across the line and then rotated 90 o clockwise? 6.
35 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 35 ~~
36 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 36 ~~ Review for Unit Test 1. Identify the coordinates of the pre-image and the image. State the line of reflection and the general rule for the reflection. A B C D A B C D Line of reflection: General rule: What is the area of the pre-image? Formula: Work: 2. Identify the coordinates of the pre-image and the image. State the line of reflection and the general rule for the reflection. P P L L T T Line of reflection: General rule: What is the area of the pre-image? Formula: Work:
37 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 37 ~~ Graph and label each polygon. Reflect the pre-image over the given line. Name the coordinates of the image. State the rule for the transformation. 3. Reflect over y = 0. This is also named the x-axis. A (0, 3) A B (4, 3) C (5, 2) D (1, 0) B C D General rule: 4. Reflect over x = 0. This is also named the y-axis. P (-7, 2) P O (-6, -6) O L (-1, -2) L General rule: Draw all of the lines of symmetry for each figure. If the figure does not have reflectional (or line) symmetry, write none (Hint: This is a regular hexagon.)
38 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 38 ~~ 8. Name the coordinates of the pre-image and its image. State the general rule for the transformation. T T A A R R General rule: 9. The vertices of a polygon are listed. Name the coordinates of the image given the general rule for the translation. Graph and label the original polygon and its image. General rule: ( x, y ) (x + 3, y) D (-4, 1) D R (0, 6) R A (0, 1) A 10. A point and its image after a translation are given. Write a rule to describe the translation. a. The translation that takes A (1, -5) to A (-5, -2) (x, y) b. The translation that takes B (7, -3) to B (7, -8) (x, y) 11. A figure is moved on a coordinate plane the number of units indicated below. Write a general rule for the transformation. a. 3 units down and 5 units to the right General rule: b. 2 units left and 1 unit up General rule:
39 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 39 ~~ 12. a. Plot and label these points: A(1, 1); B(-1, -1); C(1, 2) b. Using the following transformation (x, y) (3x, 3y) Write the new coordinates: A B C c. Plot the new points. d. Name the scale factor: 13. A point and its image after a dilation are given. Write a rule to describe the dilation. a. The dilation that takes A (1, -5) to A (5, -25) (x, y) b. The dilation that takes B (4, 20) to B (1, 5) (x, y) c. The dilation that takes C (-27, -9) to C (-9, -3) (x, y) d. The dilation that takes D (2, 8) to D (4, 16) (x, y) 14. For each figure state the order and the angle of rotation. a. b. c. Order: Angle : Order: Angle : Order: Angle : 15. The vertices of a polygon are listed. Graph and label the polygon and its image after a given rotation. Name the coordinates of the image. Rotate figure CDE about the origin 90 o counterclockwise. C (0, 1) D (-2, 6) E (-4, 1) C D E Write the general rule:
40 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 40 ~~ 16. Using figure ABC, find each point for a reflection over the y-axis and then a rotation of 90 o counterclock wise. A A' A'' B B' B'' B C C' C'' A C Draw triangle A'B'C' and A''B''C'' Use the transformation below for questions 17 and 18. Triangle ABC is rotated 90 o counterclockwise to create triangle AED E D B 17. Which angle is congruent to B? 18. Which side is congruent to AC? C A S' T' T S Use the coordinate plane to the right for questions Parallelogram QRST is reflected over the y-axis to create parallelogram Q'R'S'T' R' Q' Q R 19. Which angle is congruent to S? 20. Which side is congruent to QT? 21. QR is parallel to TS. Which side is parallel to Q R?
41 ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 41 ~~ 22. Multiple choice: The following are multiple choice questions. Circle the letter next to the answer
42 28. ~ ~ U n i t 7, P a g e 42 ~~
4-7 Study Guide and Intervention Congruence Transformations
 4-7 Study Guide and Intervention Congruence Transformations Identify Congruence Transformations A congruence transformation is a transformation where the original figure, or preimage, and the transformed
4-7 Study Guide and Intervention Congruence Transformations Identify Congruence Transformations A congruence transformation is a transformation where the original figure, or preimage, and the transformed
Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page
 Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page image pre-image transformation translation image pre-image reflection clockwise counterclockwise origin rotate 180 degrees rotate 270 degrees rotate
Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page image pre-image transformation translation image pre-image reflection clockwise counterclockwise origin rotate 180 degrees rotate 270 degrees rotate
Unit 7. Transformations
 Unit 7 Transformations 1 A transformation moves or changes a figure in some way to produce a new figure called an. Another name for the original figure is the. Recall that a translation moves every point
Unit 7 Transformations 1 A transformation moves or changes a figure in some way to produce a new figure called an. Another name for the original figure is the. Recall that a translation moves every point
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 6: TRANSFORMATIONS AND SIMILARITY. Date: Lesson: Chapter 6: Transformations and Similarity
 Chapter 6: Transformations and Similarity CHAPTER 6: TRANSFORMATIONS AND SIMILARITY Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 6: Transformations and Similarity Date: Lesson:
Chapter 6: Transformations and Similarity CHAPTER 6: TRANSFORMATIONS AND SIMILARITY Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 6: Transformations and Similarity Date: Lesson:
Transformations Worksheet. How many units and in which direction were the x-coordinates of parallelogram ABCD moved? C. D.
 Name: Date: 1. Parallelogram ABCD was translated to parallelogram A B C D. 2. A shape is shown below. Which shows this shape transformed by a flip? A. B. How many units and in which direction were the
Name: Date: 1. Parallelogram ABCD was translated to parallelogram A B C D. 2. A shape is shown below. Which shows this shape transformed by a flip? A. B. How many units and in which direction were the
Reflections and Translations
 Name: ate: 1. Parallelogram ABC was translated to parallelogram A B C. 2. Alyssa made the design shown below. How many units and in which direction were the x-coordinates of parallelogram ABC moved? A.
Name: ate: 1. Parallelogram ABC was translated to parallelogram A B C. 2. Alyssa made the design shown below. How many units and in which direction were the x-coordinates of parallelogram ABC moved? A.
Quadrilaterals & Transformations Study Guide
 s & Transformations Study Guide What do I need to know for the upcoming Summative Assessment? s Classifications and Properties of: o o Trapezoid o Kite o Parallelogram o Rhombus o Rectangle o Square The
s & Transformations Study Guide What do I need to know for the upcoming Summative Assessment? s Classifications and Properties of: o o Trapezoid o Kite o Parallelogram o Rhombus o Rectangle o Square The
Guided Problem Solving
 -1 Guided Problem Solving GPS Student Page 57, Exercises 1 1: Match each rule with the correct translation. A. (x, y) (x, y 1 ) I. P(, 1) P (3, ) B. (x, y) (x 1 3, y) II. Q(3, 0) Q (3, ) C. (x, y) (x 1,
-1 Guided Problem Solving GPS Student Page 57, Exercises 1 1: Match each rule with the correct translation. A. (x, y) (x, y 1 ) I. P(, 1) P (3, ) B. (x, y) (x 1 3, y) II. Q(3, 0) Q (3, ) C. (x, y) (x 1,
Unit 1 Test Review: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Unit 1 Test Review: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane 1. As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A B C D E F. Under this transformation,
Unit 1 Test Review: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane 1. As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A B C D E F. Under this transformation,
Chapter 12 Transformations: Shapes in Motion
 Name Geometry Honors Date Per. Teacher Chapter 12 Transformations: Shapes in Motion 1 Table of Contents Reflections Day 1.... Page 3 Translations Day 2....... Page 10 Rotations/Dilations Day 3.... Page
Name Geometry Honors Date Per. Teacher Chapter 12 Transformations: Shapes in Motion 1 Table of Contents Reflections Day 1.... Page 3 Translations Day 2....... Page 10 Rotations/Dilations Day 3.... Page
Unit 2: Transformations. 2. Which of the following best shows a reflection (flip) of the shaded shape across the dashed line?
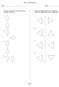 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best represents only a translation (slide) up? 2. Which of the following best shows a reflection (flip) of the shaded shape across the dashed line? D. D. page 1 3.
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best represents only a translation (slide) up? 2. Which of the following best shows a reflection (flip) of the shaded shape across the dashed line? D. D. page 1 3.
Math 9: Chapter Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Math 9: Chapter 7.5-7.7 Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which shapes have at least 2 lines of symmetry?
Class: Date: Math 9: Chapter 7.5-7.7 Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which shapes have at least 2 lines of symmetry?
Unit 1 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Unit 1 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Table of Contents Title Page # Formula Sheet...2 Lesson 1 1: Introduction to Transformations and Rotations 3 Lesson 1 2: Reflections and Translations..9 Lesson
Unit 1 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Table of Contents Title Page # Formula Sheet...2 Lesson 1 1: Introduction to Transformations and Rotations 3 Lesson 1 2: Reflections and Translations..9 Lesson
Integrated Algebra A Packet 1
 Name Date Integrated Algebra A Packet 1 Lesson/Notes Homework Coordinate Plane HW #1 Connecting Points To Make Figures HW #2 Intro to Transformations/Translations HW #3 Reflections HW #4 Symmetry HW #5
Name Date Integrated Algebra A Packet 1 Lesson/Notes Homework Coordinate Plane HW #1 Connecting Points To Make Figures HW #2 Intro to Transformations/Translations HW #3 Reflections HW #4 Symmetry HW #5
Chapter 2: Transformations. Chapter 2 Transformations Page 1
 Chapter 2: Transformations Chapter 2 Transformations Page 1 Unit 2: Vocabulary 1) transformation 2) pre-image 3) image 4) map(ping) 5) rigid motion (isometry) 6) orientation 7) line reflection 8) line
Chapter 2: Transformations Chapter 2 Transformations Page 1 Unit 2: Vocabulary 1) transformation 2) pre-image 3) image 4) map(ping) 5) rigid motion (isometry) 6) orientation 7) line reflection 8) line
Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper
 Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper Investigation #3: Transforming Coordinates Investigation #4: Dilations and Similar Figures Name Butterflies, Pinwheels and Wallpaper Investigation #3 Transforming
Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper Investigation #3: Transforming Coordinates Investigation #4: Dilations and Similar Figures Name Butterflies, Pinwheels and Wallpaper Investigation #3 Transforming
Unit 1 NOTES Honors Math 2 1
 Unit 1 NOTES Honors Math 2 1 Day 1: Introduction to Transformations and Translations Warm-Up: Prerequisite Skill: Graphing Lines Graph the following lines. 1) x = 2 2) y = 4 3) y = x (Hint: this is y =
Unit 1 NOTES Honors Math 2 1 Day 1: Introduction to Transformations and Translations Warm-Up: Prerequisite Skill: Graphing Lines Graph the following lines. 1) x = 2 2) y = 4 3) y = x (Hint: this is y =
Section 12.1 Translations and Rotations
 Section 12.1 Translations and Rotations Any rigid motion that preserves length or distance is an isometry. We look at two types of isometries in this section: translations and rotations. Translations A
Section 12.1 Translations and Rotations Any rigid motion that preserves length or distance is an isometry. We look at two types of isometries in this section: translations and rotations. Translations A
CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13. Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date:
 CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13 Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Idea Pages Unit 9 Vocabulary 2 Translations 3 10 Rotations 11 17 Reflections 18 22 Transformations
CCM6+/7+ - Unit 13 - Page 1 UNIT 13 Transformations CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Idea Pages Unit 9 Vocabulary 2 Translations 3 10 Rotations 11 17 Reflections 18 22 Transformations
L2 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Pre-Assessment Per Date
 L Translations, Reflections, and Rotations.1 - Pre-Assessment Per Date Have you ever wanted to rearrange the furniture in your room? First you might want to make sure that the furniture would fit in the
L Translations, Reflections, and Rotations.1 - Pre-Assessment Per Date Have you ever wanted to rearrange the furniture in your room? First you might want to make sure that the furniture would fit in the
Translations SLIDE. Example: If you want to move a figure 5 units to the left and 3 units up we would say (x, y) (x-5, y+3).
 Translations SLIDE Every point in the shape must move In the same direction The same distance Example: If you want to move a figure 5 units to the left and 3 units up we would say (x, y) (x-5, y+3). Note:
Translations SLIDE Every point in the shape must move In the same direction The same distance Example: If you want to move a figure 5 units to the left and 3 units up we would say (x, y) (x-5, y+3). Note:
Chapters 7 & 8. Parallel and Perpendicular Lines/Triangles and Transformations
 Chapters 7 & 8 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines/Triangles and Transformations 7-2B Lines I can identify relationships of angles formed by two parallel lines cut by a transversal. 8.G.5 Symbolic Representations
Chapters 7 & 8 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines/Triangles and Transformations 7-2B Lines I can identify relationships of angles formed by two parallel lines cut by a transversal. 8.G.5 Symbolic Representations
Name: Target 4 Perform compositions of figures to determine the coordinates and location of the image
 Unit 8 Similarity Figures and Dilations Target 1 Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures Target 2 Perform and identify dilations Target 3 Use ratios of lengths, perimeter,
Unit 8 Similarity Figures and Dilations Target 1 Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures Target 2 Perform and identify dilations Target 3 Use ratios of lengths, perimeter,
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 * Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Vocabulary Transformation- changes the position or orientation of a figure. Image- the resulting figure after a transformation. Preimage- the original figure.
* Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Vocabulary Transformation- changes the position or orientation of a figure. Image- the resulting figure after a transformation. Preimage- the original figure.
Geometry Practice. 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles.
 Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane
 Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
UNIT 1 SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS Lesson 6: Defining and Applying Similarity Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: creating ratios solving proportions identifying congruent triangles calculating the lengths of triangle sides using the distance
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: creating ratios solving proportions identifying congruent triangles calculating the lengths of triangle sides using the distance
Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper
 Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper Day Topic Homework Grade 1 Intro Day start work on notes, vocab, and ACE questions 2 Inv 1/ACE # 1-6, 8-12, 14-17, 19-20, 30-34, 36a, 37a due by Friday 1/9 at 3:15
Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper Day Topic Homework Grade 1 Intro Day start work on notes, vocab, and ACE questions 2 Inv 1/ACE # 1-6, 8-12, 14-17, 19-20, 30-34, 36a, 37a due by Friday 1/9 at 3:15
GRADE 8 ADAPTED NJDOE ASSESSMENT. Assessed Standards: 8.G.1 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.G.4 8.G.5. (To be administered after NPS Grade 8 Scope and Sequence Unit 2)
 ADAPTED NJDOE ASSESSMENT GRADE 8 (To be administered after NPS Grade 8 Scope and Sequence Unit 2) Assessed Standards: 8.G.1 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.G.4 8.G.5 The Newark Public Schools - Office of Mathematics 2013
ADAPTED NJDOE ASSESSMENT GRADE 8 (To be administered after NPS Grade 8 Scope and Sequence Unit 2) Assessed Standards: 8.G.1 8.G.2 8.G.3 8.G.4 8.G.5 The Newark Public Schools - Office of Mathematics 2013
Name: 1) Which of the following properties of an object are not preserved under a rotation? A) orientation B) none of these C) shape D) size
 Name: 1) Which of the following properties of an object are not preserved under a rotation? A) orientation B) none of these C) shape D) size 2) Under a certain transformation, A B C is the image of ABC.
Name: 1) Which of the following properties of an object are not preserved under a rotation? A) orientation B) none of these C) shape D) size 2) Under a certain transformation, A B C is the image of ABC.
Geometry Transformations
 Geometry Transformations NAME Period 1 Transformations Notes Transformation: Maps an, called a, onto a final, called an. Reflection: a transformation representing a of a figure Reflecting over the x-axis,
Geometry Transformations NAME Period 1 Transformations Notes Transformation: Maps an, called a, onto a final, called an. Reflection: a transformation representing a of a figure Reflecting over the x-axis,
For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet.
 Accelerated Review 9: Geometric Relationships Name: For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet. Caleb drew a quadrilateral on his paper. Which of the following
Accelerated Review 9: Geometric Relationships Name: For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet. Caleb drew a quadrilateral on his paper. Which of the following
Shape & Space Part C: Transformations
 Name: Homeroom: Shape & Space Part C: Transformations Student Learning Expectations Outcomes: I can describe and analyze position and motion of objects and shapes by Checking for Understanding identifying
Name: Homeroom: Shape & Space Part C: Transformations Student Learning Expectations Outcomes: I can describe and analyze position and motion of objects and shapes by Checking for Understanding identifying
5-Minute Check Solve.
 5-Minute Check (over Chapter 9) Use with Lesson 10-1 Solve. 1. There are 12 balls in a hat and 3 are red. What is the probability of drawing a red ball? 2. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find
5-Minute Check (over Chapter 9) Use with Lesson 10-1 Solve. 1. There are 12 balls in a hat and 3 are red. What is the probability of drawing a red ball? 2. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find
Study Guide and Review
 Choose the term that best completes each sentence. 1. When a transformation is applied to a figure, and then another transformation is applied to its image, this is a(n) (composition of transformations,
Choose the term that best completes each sentence. 1. When a transformation is applied to a figure, and then another transformation is applied to its image, this is a(n) (composition of transformations,
Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper
 Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper Day Topic Homework IXL Grade 1 Inv 1.1 Inv 1/ACE # 1-6 2 Inv 1.2 Inv 1/ACE # 19-20 3 Inv 1.3 Inv 1/ACE # 8-12 (all part a only!) 4 Inv 1.4 Inv 1/ACE # 14-17, 30-34,
Butterflies, Pinwheels, and Wallpaper Day Topic Homework IXL Grade 1 Inv 1.1 Inv 1/ACE # 1-6 2 Inv 1.2 Inv 1/ACE # 19-20 3 Inv 1.3 Inv 1/ACE # 8-12 (all part a only!) 4 Inv 1.4 Inv 1/ACE # 14-17, 30-34,
9 Transformations CHAPTER. Chapter Outline.
 Chapter 9 www.ck12.org CHAPTER 9 Transformations Chapter Outline 9.1 EXPLORING SYMMETRY 9.2 TRANSLATIONS AND VECTORS 9.3 REFLECTIONS 9.4 ROTATIONS 9.5 COMPOSITION OF TRANSFORMATIONS 9.6 DILATIONS 9.7 TESSELLATIONS
Chapter 9 www.ck12.org CHAPTER 9 Transformations Chapter Outline 9.1 EXPLORING SYMMETRY 9.2 TRANSLATIONS AND VECTORS 9.3 REFLECTIONS 9.4 ROTATIONS 9.5 COMPOSITION OF TRANSFORMATIONS 9.6 DILATIONS 9.7 TESSELLATIONS
Transformations. Transformations. Reflections. Rotations. Composition of Transformations
 Reflections Rotations omposition of Transformations ongruence Transformations ilations Similarity Transformations Transformations Transformations transformation of a geometric figure is a mapping that
Reflections Rotations omposition of Transformations ongruence Transformations ilations Similarity Transformations Transformations Transformations transformation of a geometric figure is a mapping that
COORDINATE ALGEBRA UNIT 5: TRANSFORMATIONS IN THE COORDINATE PLANE. 1. On this coordinate plane, UVW has been transformed to form its image U''V''W''.
 1. On this coordinate plane, UVW has been transformed to form its image U''V''W''. 3.Graph the figure and its image under the given translation: EFG with vertices E (-2, -3), F (-3, -2), G (-1, -1) under
1. On this coordinate plane, UVW has been transformed to form its image U''V''W''. 3.Graph the figure and its image under the given translation: EFG with vertices E (-2, -3), F (-3, -2), G (-1, -1) under
Unit 3 Similarity Figures and Dilations
 Unit 3 Similarity Figures and Dilations Date Target Assignment Done! M 9-25 3.1 3.1 Worksheet T 9-26 3.2 3.2 Worksheet W 9-27 3.1-3.2 3.1-3.2 Review Worksheet R 9-28 Quiz Quiz 3.1-3.2 F 9-29 3.3a 3.3a
Unit 3 Similarity Figures and Dilations Date Target Assignment Done! M 9-25 3.1 3.1 Worksheet T 9-26 3.2 3.2 Worksheet W 9-27 3.1-3.2 3.1-3.2 Review Worksheet R 9-28 Quiz Quiz 3.1-3.2 F 9-29 3.3a 3.3a
Dilations. Dilations. Enlarges or Reduces a figure using a scale factor. Name: Period: Date: Dilations. Scale Factor =
 Name: Period: Date: Dilations Dilations Enlarges or Reduces a figure using a scale factor. Dilations B B B 6 2 2 C 6 C Scale Factor = B C BC has been enlarged by a scale factor of 3. What are the coordinates
Name: Period: Date: Dilations Dilations Enlarges or Reduces a figure using a scale factor. Dilations B B B 6 2 2 C 6 C Scale Factor = B C BC has been enlarged by a scale factor of 3. What are the coordinates
Chapter 5. Transforming Shapes
 Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
In this translation, CDE is being translated to the right by the same length as segment AB. What do you think is true about CDE and C'D'E'?
 A translation is nothing more than a geometric transformation that slides each point in a figure the same distance in the same direction In this translation, CDE is being translated to the right by the
A translation is nothing more than a geometric transformation that slides each point in a figure the same distance in the same direction In this translation, CDE is being translated to the right by the
Assignment Guide: Chapter 9 Geometry
 Assignment Guide: Chapter 9 Geometry (105) 9.1 Translations Page 550-552 #7-17 odd, 18, 28, 31, 33 (106) 9.2 Reflections Page 557-560 #7-12, 13-17 odd, 33, 37 (107) 9.3 Rotations Page 564-566 #9-15 odd,
Assignment Guide: Chapter 9 Geometry (105) 9.1 Translations Page 550-552 #7-17 odd, 18, 28, 31, 33 (106) 9.2 Reflections Page 557-560 #7-12, 13-17 odd, 33, 37 (107) 9.3 Rotations Page 564-566 #9-15 odd,
On a coordinate plane, such a change can be described by counting the number of spaces, vertically and horizontally, that the figure has moved.
 Transformations We have studied four different kinds of transformations: translation, rotation, reflection, and dilation. Each one involves moving a figure to a new location on a plane. Translation Translation
Transformations We have studied four different kinds of transformations: translation, rotation, reflection, and dilation. Each one involves moving a figure to a new location on a plane. Translation Translation
Transformations. Transformations: CLASSWORK. Tell whether the transformation appears to be a rigid motion. Explain
 Transformations Transformations: CLASSWORK Tell whether the transformation appears to be a rigid motion. Explain. 1. 2. Preimage Image Preimage Image 3. Identify the type of transformation. What is the
Transformations Transformations: CLASSWORK Tell whether the transformation appears to be a rigid motion. Explain. 1. 2. Preimage Image Preimage Image 3. Identify the type of transformation. What is the
Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles pp
 LESSON 5-1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles pp. 222 224 Vocabulary point (p. 222) line (p. 222) plane (p. 222) segment (p. 222) ray (p. 222) angle (p. 222) right angle (p. 223) acute angle (p. 223) obtuse
LESSON 5-1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles pp. 222 224 Vocabulary point (p. 222) line (p. 222) plane (p. 222) segment (p. 222) ray (p. 222) angle (p. 222) right angle (p. 223) acute angle (p. 223) obtuse
Date Target Assignment Done! W Review Worksheet. F 9-30 Project Cartoon Enlargement Project. T a 3.
 Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations 2016-2017 Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations Target 1: Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures. Target 2: Perform and identify
Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations 2016-2017 Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations Target 1: Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures. Target 2: Perform and identify
4-1 Congruence and Transformations
 4-1 Congruence and Transformations Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt Geometry McDougal Geometry Objectives Draw, identify, and describe transformations in the coordinate plane. Use properties
4-1 Congruence and Transformations Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt Geometry McDougal Geometry Objectives Draw, identify, and describe transformations in the coordinate plane. Use properties
1ACE Exercise 17. Name Date Class. 17. Which figure does NOT have rotation symmetry?
 1ACE Exercise 17 Investigation 1 17. Which figure does NOT have rotation symmetry? HINT Rotation symmetry means you can turn the object around its center to a position in which it looks the same as the
1ACE Exercise 17 Investigation 1 17. Which figure does NOT have rotation symmetry? HINT Rotation symmetry means you can turn the object around its center to a position in which it looks the same as the
Date Target Assignment Done! W Review Worksheet. F 9-30 Project Cartoon Enlargement Project. T a 3.
 Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations Target 1: Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures. Target 2: Perform and identify dilations. Target 3: Use sclae factor and similarity
Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations Target 1: Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures. Target 2: Perform and identify dilations. Target 3: Use sclae factor and similarity
R(-14, 4) R'(-10, -2) S(-10, 7) S'(-6, 1) T(-5, 4) T'(-1, -2)
 1 Transformations Formative Assessment #1 - Translation Assessment Cluster & Content Standards What content standards can be addressed by this formative assessment? 8.G.3 Describe the effect of dilations
1 Transformations Formative Assessment #1 - Translation Assessment Cluster & Content Standards What content standards can be addressed by this formative assessment? 8.G.3 Describe the effect of dilations
Geometry. Topic 1 Transformations and Congruence
 Geometry Topic 1 Transformations and Congruence MAFS.912.G-CO.1.2 Consider the point A at ( 3, 5). A. Find the coordinates of A, the image of A after the transformation: (, ) (, ). B. What type of transformation
Geometry Topic 1 Transformations and Congruence MAFS.912.G-CO.1.2 Consider the point A at ( 3, 5). A. Find the coordinates of A, the image of A after the transformation: (, ) (, ). B. What type of transformation
Pre-Image Rotation Rotational Symmetry Symmetry. EOC Review
 Name: Period GL UNIT 13: TRANSFORMATIONS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Dilation Center of dilation Scale Factor Enlargement Reduction Composition of Transformations Image Isometry
Name: Period GL UNIT 13: TRANSFORMATIONS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Dilation Center of dilation Scale Factor Enlargement Reduction Composition of Transformations Image Isometry
Day 116 Bellringer. 1. Use the triangle below to answer the questions that follow.
 Day 116 Bellringer 1. Use the triangle below to answer the questions that follow. 3 in 5 in 4 in a) Find the area of the triangle. b) Find the perimeter of the triangle. 2. Use the distance formula to
Day 116 Bellringer 1. Use the triangle below to answer the questions that follow. 3 in 5 in 4 in a) Find the area of the triangle. b) Find the perimeter of the triangle. 2. Use the distance formula to
7.1:Transformations And Symmetry 7.2: Properties of Isometries. Pre-Image:original figure. Image:after transformation. Use prime notation
 7.1:Transformations And Symmetry 7.2: Properties of Isometries Transformation: Moving all the points of a geometric figure according to certain rules to create an image of the original figure. Pre-Image:original
7.1:Transformations And Symmetry 7.2: Properties of Isometries Transformation: Moving all the points of a geometric figure according to certain rules to create an image of the original figure. Pre-Image:original
Polygons, Congruence, Similarity Long-Term Memory Review Grade 8 Review 1
 Review 1 1. In the diagram below, XYZ is congruent to CDE XYZ CDE. Y D E X Z C Complete the following statements: a) C b) XZ c) CDE d) YZ e) Z f) DC 2. In the diagram below, ABC is similar to DEF ABC DEF.
Review 1 1. In the diagram below, XYZ is congruent to CDE XYZ CDE. Y D E X Z C Complete the following statements: a) C b) XZ c) CDE d) YZ e) Z f) DC 2. In the diagram below, ABC is similar to DEF ABC DEF.
Section Quiz Lessons 12-1 Through 12-4
 Section Quiz Lessons - Through - hoose the best answer.. What is the image of (, ) when it is reflected across the line y x? (, ) (, ),, Use the figure for Exercises 7. The coordinates of the vertices
Section Quiz Lessons - Through - hoose the best answer.. What is the image of (, ) when it is reflected across the line y x? (, ) (, ),, Use the figure for Exercises 7. The coordinates of the vertices
Reteach. Congruence and Transformations
 Congruence and Transformations TYPES OF TRANSFORMATIONS (centered at (0, 0)) Translation (slide): (x, y) (x a, y b) Reflection y-axis: (x, y) ( x, y) x-axis: (x, y) (x, y) Rotation 90 clockwise: (x, y)
Congruence and Transformations TYPES OF TRANSFORMATIONS (centered at (0, 0)) Translation (slide): (x, y) (x a, y b) Reflection y-axis: (x, y) ( x, y) x-axis: (x, y) (x, y) Rotation 90 clockwise: (x, y)
G.CO.B.6: Properties of Transformations 2
 1 Which expression best describes the transformation shown in the diagram below? 2 As shown in the diagram below, when right triangle DAB is reflected over the x-axis, its image is triangle DCB. 1) same
1 Which expression best describes the transformation shown in the diagram below? 2 As shown in the diagram below, when right triangle DAB is reflected over the x-axis, its image is triangle DCB. 1) same
Chapter 8 Transformations and Congruence
 Lesson 8-1 Translations Page 559 Graph ABC with vertices A(1, 2), B(3, 1), and C(3, 4). Then graph the image of the triangle after it is translated 2 units left and 1 unit up, and write the coordinates
Lesson 8-1 Translations Page 559 Graph ABC with vertices A(1, 2), B(3, 1), and C(3, 4). Then graph the image of the triangle after it is translated 2 units left and 1 unit up, and write the coordinates
Students are not expected to work formally with properties of dilations until high school.
 Domain: Geometry (G) Cluster: Understand congruence and similarity using physical models, transparencies, or geometry software. Standard: 8.G.1. Verify experimentally the properties of rotations, reflections,
Domain: Geometry (G) Cluster: Understand congruence and similarity using physical models, transparencies, or geometry software. Standard: 8.G.1. Verify experimentally the properties of rotations, reflections,
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. center of dilation. composition of transformations. enlargement. glide reflection.
 CHAPTER 12 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 12. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. center of dilation Term
CHAPTER 12 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 12. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. center of dilation Term
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Study Guide - Chapter 6
 8 th Grade Name Date Period Study Guide - Chapter 6 1) Label each quadrant with I, II, III, or IV. 2) Use your knowledge of rotations to name the quadrant that each point below will land in after the rotation
8 th Grade Name Date Period Study Guide - Chapter 6 1) Label each quadrant with I, II, III, or IV. 2) Use your knowledge of rotations to name the quadrant that each point below will land in after the rotation
I can identify reflections, rotations, and translations. I can graph transformations in the coordinate plane.
 Page! 1 of! 14 Attendance Problems. 1. Sketch a right angle and its angle bisector. 2. Draw three different squares with (3, 2) as one vertex. 3. Find the values of x and y if (3, 2) = (x + 1, y 3) Vocabulary
Page! 1 of! 14 Attendance Problems. 1. Sketch a right angle and its angle bisector. 2. Draw three different squares with (3, 2) as one vertex. 3. Find the values of x and y if (3, 2) = (x + 1, y 3) Vocabulary
Transformations Geometry
 Transformations Geometry Preimage the original figure in the transformation of a figure in a plane. Image the new figure that results from the transformation of a figure in a plane. Example: If function
Transformations Geometry Preimage the original figure in the transformation of a figure in a plane. Image the new figure that results from the transformation of a figure in a plane. Example: If function
Believethatyoucandoitandyouar. ngascannotdoonlynotyetbelieve. Mathematics. thatyoucandoitandyouarehalfw. Stage 3
 Believethatyoucandoitandyouar ehalfwaytherethereisnosuchthi ngascannotdoonlynotyetbelieve Mathematics thatyoucandoitandyouarehalfw Stage 3 aytherethereisnosuchthingasca Shape & Space nnotdoonlynotyetbelievethatyo
Believethatyoucandoitandyouar ehalfwaytherethereisnosuchthi ngascannotdoonlynotyetbelieve Mathematics thatyoucandoitandyouarehalfw Stage 3 aytherethereisnosuchthingasca Shape & Space nnotdoonlynotyetbelievethatyo
(3) Proportionality. The student applies mathematical process standards to use proportional relationships
 Title: Dilation Investigation Subject: Coordinate Transformations in Geometry Objective: Given grid paper, a centimeter ruler, a protractor, and a sheet of patty paper the students will generate and apply
Title: Dilation Investigation Subject: Coordinate Transformations in Geometry Objective: Given grid paper, a centimeter ruler, a protractor, and a sheet of patty paper the students will generate and apply
Algebra Area of Parallelograms
 Lesson 10.1 Reteach Algebra Area of Parallelograms The formula for the area of a parallelogram is the product of the base and height. The formula for the area of a square is the square of one of its sides.
Lesson 10.1 Reteach Algebra Area of Parallelograms The formula for the area of a parallelogram is the product of the base and height. The formula for the area of a square is the square of one of its sides.
Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane In this unit, students review the definitions of three types of transformations that preserve distance and angle: rotations, reflections, and translations.
Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane In this unit, students review the definitions of three types of transformations that preserve distance and angle: rotations, reflections, and translations.
Constructing Symmetrical Shapes
 1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
Module 2 Test Study Guide. Type of Transformation (translation, reflection, rotation, or none-of-theabove). Be as specific as possible.
 Module 2 Test Study Guide CONCEPTS TO KNOW: Transformation (types) Rigid v. Non-Rigid Motion Coordinate Notation Vector Terminology Pre-Image v. Image Vertex Prime Notation Equation of a Line Lines of
Module 2 Test Study Guide CONCEPTS TO KNOW: Transformation (types) Rigid v. Non-Rigid Motion Coordinate Notation Vector Terminology Pre-Image v. Image Vertex Prime Notation Equation of a Line Lines of
Geometric Transformations: Translation:
 Geometric Transformations: Translation: slide Reflection: Rotation: Dialation: mirror turn enlarge or reduce Notation: Pre-Image: original figure Image: after transformation. Use prime notation C A B C
Geometric Transformations: Translation: slide Reflection: Rotation: Dialation: mirror turn enlarge or reduce Notation: Pre-Image: original figure Image: after transformation. Use prime notation C A B C
CCGPS UNIT 5 Semester 2 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of 38. Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 CCGPS UNIT 5 Semester 2 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of 38 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Name: Date: MCC9-12.G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line,
CCGPS UNIT 5 Semester 2 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of 38 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Name: Date: MCC9-12.G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line,
Name: Date: Period: Score: Linear Algebra Chapters 7, 8, & 9 Study Guide
 1. Triangle ABC is shown on the coordinate grid. 3. Use the parallelogram shown in the coordinate plane to answer each question. Translate 3 units horizontally. Label the image. How are the values in the
1. Triangle ABC is shown on the coordinate grid. 3. Use the parallelogram shown in the coordinate plane to answer each question. Translate 3 units horizontally. Label the image. How are the values in the
12.4 Rotations. Learning Objectives. Review Queue. Defining Rotations Rotations
 12.4. Rotations www.ck12.org 12.4 Rotations Learning Objectives Find the image of a figure in a rotation in a coordinate plane. Recognize that a rotation is an isometry. Review Queue 1. Reflect XY Z with
12.4. Rotations www.ck12.org 12.4 Rotations Learning Objectives Find the image of a figure in a rotation in a coordinate plane. Recognize that a rotation is an isometry. Review Queue 1. Reflect XY Z with
Transformations. Working backwards is performing the inverse operation. + - and x 3. Given coordinate rule
 Transformations In geometry we use input/output process when we determine how shapes are altered or moved. Geometric objects can be moved in the coordinate plane using a coordinate rule. These rules can
Transformations In geometry we use input/output process when we determine how shapes are altered or moved. Geometric objects can be moved in the coordinate plane using a coordinate rule. These rules can
Get Ready. Solving Equations 1. Solve each equation. a) 4x + 3 = 11 b) 8y 5 = 6y + 7
 Get Ready BLM... Solving Equations. Solve each equation. a) 4x + = 8y 5 = 6y + 7 c) z+ = z+ 5 d) d = 5 5 4. Write each equation in the form y = mx + b. a) x y + = 0 5x + y 7 = 0 c) x + 6y 8 = 0 d) 5 0
Get Ready BLM... Solving Equations. Solve each equation. a) 4x + = 8y 5 = 6y + 7 c) z+ = z+ 5 d) d = 5 5 4. Write each equation in the form y = mx + b. a) x y + = 0 5x + y 7 = 0 c) x + 6y 8 = 0 d) 5 0
G.CO.A.2: Identifying Transformations 2
 G.CO.A.2: Identifying Transformations 2 1 In the accompanying diagram, ABC is similar to but not congruent to A B C. 3 In the diagram below, A' B' is the image of AB under which single transformation?
G.CO.A.2: Identifying Transformations 2 1 In the accompanying diagram, ABC is similar to but not congruent to A B C. 3 In the diagram below, A' B' is the image of AB under which single transformation?
Unit 3SimilarFigures and Dilations
 Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations Unit 3SimilarFigures and Dilations Target 1 Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures Target 2 Perform and identify dilations Target
Unit 3 Similar Figures and Dilations Unit 3SimilarFigures and Dilations Target 1 Use proportions to identify lengths of corresponding parts in similar figures Target 2 Perform and identify dilations Target
Chapter 6. Similarity
 Chapter 6 Similarity 6.1 Use Similar Polygons Objective: Use proportions to identify similar polygons. Essential Question: If two figures are similar, how do you find the length of a missing side? Two
Chapter 6 Similarity 6.1 Use Similar Polygons Objective: Use proportions to identify similar polygons. Essential Question: If two figures are similar, how do you find the length of a missing side? Two
Transformation, tessellation and symmetry line symmetry
 Transformation, tessellation and symmetry line symmetry Reflective or line symmetry describes mirror image, when one half of a shape or picture matches the other exactly. The middle line that divides the
Transformation, tessellation and symmetry line symmetry Reflective or line symmetry describes mirror image, when one half of a shape or picture matches the other exactly. The middle line that divides the
Points, lines, angles
 Points, lines, angles Point Line Line segment Parallel Lines Perpendicular lines Vertex Angle Full Turn An exact location. A point does not have any parts. A straight length that extends infinitely in
Points, lines, angles Point Line Line segment Parallel Lines Perpendicular lines Vertex Angle Full Turn An exact location. A point does not have any parts. A straight length that extends infinitely in
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6
 acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
UNIT 5: Transformations
 Period: Date: May 11 & 12, 2015 UNIT 5: Transformations Checklist MAX Scored 1 Vocabulary 40 2 Transformations 30 3 Constructions 20 4 Random Transformations 30 Totals 120 Semester 2 Test Prep Section
Period: Date: May 11 & 12, 2015 UNIT 5: Transformations Checklist MAX Scored 1 Vocabulary 40 2 Transformations 30 3 Constructions 20 4 Random Transformations 30 Totals 120 Semester 2 Test Prep Section
Honors Midterm Review
 Name: Date: 1. Draw all lines of symmetry for these shapes. 4. A windmill has eight equally-spaced blades that rotate in the clockwise direction. 2. Use the figure below to answer the question that follows.
Name: Date: 1. Draw all lines of symmetry for these shapes. 4. A windmill has eight equally-spaced blades that rotate in the clockwise direction. 2. Use the figure below to answer the question that follows.
Review for Grade 9 Math Exam - Unit 7 - Similarity and Transformations
 Review for Grade 9 Math Exam - Unit 7 - Similarity and Transformations Name: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the scale
Review for Grade 9 Math Exam - Unit 7 - Similarity and Transformations Name: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the scale
Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation.
 10 8: Polygons and Tesselations Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation. Vocabulary: polygon A simple closed figure in a plane formed by three or more line segments
10 8: Polygons and Tesselations Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation. Vocabulary: polygon A simple closed figure in a plane formed by three or more line segments
Content Standards G.CO.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel
 Content Standards G.CO.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. G.CO.5 Given a geometric figure
Content Standards G.CO.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. G.CO.5 Given a geometric figure
Student Name: Teacher: Date: Miami-Dade County Public Schools. Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 2
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 2 Description: GEO Topic 5: Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Geometry Form: 201 1. If the quadrilateral
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 2 Description: GEO Topic 5: Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Geometry Form: 201 1. If the quadrilateral
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
Chapter 9 Transformations
 Section 9-1: Reflections SOL: G.2 The student will use pictorial representations, including computer software, constructions, and coordinate methods, to solve problems involving smmetr and transformation.
Section 9-1: Reflections SOL: G.2 The student will use pictorial representations, including computer software, constructions, and coordinate methods, to solve problems involving smmetr and transformation.
Composition Transformation
 Name: Date: 1. Describe the sequence of transformations that results in the transformation of Figure A to Figure A. 2. Describe the sequence of transformations that results in the transformation of Figure
Name: Date: 1. Describe the sequence of transformations that results in the transformation of Figure A to Figure A. 2. Describe the sequence of transformations that results in the transformation of Figure
Warm-up. Translations Using arrow notation to write a rule. Example: 1) Write a rule that would move a point 3 units to the right and 5 units down.
 Translations Using arrow notation to write a rule. Example: 1) Write a rule that would move a point 3 units to the right and 5 units down. (x, y) 2) Write a rule that would move a point 6 units down. (x,
Translations Using arrow notation to write a rule. Example: 1) Write a rule that would move a point 3 units to the right and 5 units down. (x, y) 2) Write a rule that would move a point 6 units down. (x,
Period: Date Lesson 13: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means
 : Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
: Analytic Proofs of Theorems Previously Proved by Synthetic Means Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of
Introduction to Transformations. In Geometry
 + Introduction to Transformations In Geometry + What is a transformation? A transformation is a copy of a geometric figure, where the copy holds certain properties. Example: copy/paste a picture on your
+ Introduction to Transformations In Geometry + What is a transformation? A transformation is a copy of a geometric figure, where the copy holds certain properties. Example: copy/paste a picture on your
NOTES: TRANSFORMATIONS
 TABLE OF CONTENT Plotting Points On A Coordinate Plane. Transformations. Translation. Reflections. Rotations Dilations. Congruence And Similarity.. Multiple Transformations In A Coordinate Plane. Parallel
TABLE OF CONTENT Plotting Points On A Coordinate Plane. Transformations. Translation. Reflections. Rotations Dilations. Congruence And Similarity.. Multiple Transformations In A Coordinate Plane. Parallel
Similarity and Congruence EOC Assessment (35%)
 1. What term is used to describe two rays or two line segments that share a common endpoint? a. Perpendicular Lines b. Angle c. Parallel lines d. Intersection 2. What is a term used to describe two lines
1. What term is used to describe two rays or two line segments that share a common endpoint? a. Perpendicular Lines b. Angle c. Parallel lines d. Intersection 2. What is a term used to describe two lines
Lesson 1. Unit 2 Practice Problems. Problem 2. Problem 1. Solution 1, 4, 5. Solution. Problem 3
 Unit 2 Practice Problems Lesson 1 Problem 1 Rectangle measures 12 cm by 3 cm. Rectangle is a scaled copy of Rectangle. Select all of the measurement pairs that could be the dimensions of Rectangle. 1.
Unit 2 Practice Problems Lesson 1 Problem 1 Rectangle measures 12 cm by 3 cm. Rectangle is a scaled copy of Rectangle. Select all of the measurement pairs that could be the dimensions of Rectangle. 1.
