Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks,
|
|
|
- Vincent Bruce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks, Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 1 Modeling complex objects/motion Decompose object hierarchically into parts Model each part in local frame, and use affine transformations to position it at its proper place in the part above it in the hierarchy Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 2 1
2 The pipeline conceptually Construct shapes from geometric primitives Arrange the objects in three dimensional space and select the desired vantage point for viewing the composed scene. Calculate the color of all the objects. The color might be explicitly assigned by the application, determined from specified lighting conditions, or obtained by pasting a texture onto the objects. Convert the mathematical description of objects and their associated color information to pixels on the screen. During these stages, an API might perform other operations, such as eliminating parts of objects that are hidden by other objects. Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 3 The Rendering Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 4 2
3 World Coordinates and Model Coordinates Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 5 World Coordinates and Model Coordinates Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 6 3
4 Viewing the World Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 7 Viewing Transformation Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 8 4
5 MVT, Lights, Material, Shading, Rendering Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 9 Coordinate Systems Object/Model World Camera/eye Image/Normalized View Volume Screen, Pixel Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 10 5
6 CTM=PT*MVT. Current Transformation MVT and PT are usually part of the current state Matrix Stacks in OpenGL Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 11 Possible approaches Symbols and instancing, instancing transforms: can be represented by a table. Hierarchical modeling. Scene graphs (SG). (Scene) Trees DAGs Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 12 6
7 Instancing in OpenGL In OpenGL, instancing is created by modifying the model-view matrix: glmatrixmode( GL_MODELVIEW ); glloadidentity(); glpushmatrix( ); gltranslatef(... ); glrotatef(... ); glscalef(... ); symbol(); glpopmatrix( ); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 13 Symbols & Instances Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 14 7
8 Village code glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadidentity(); setview(); //instance 1 Basic simple house house(); //simple house instance 2 Big house Translated gltranslatef(6, 0, 0); glscalef(2,2,2); house(); //simple house instance 3 Intermed. house Rotated 15deg and Translated gltranslatef(0, 6, 0); glrotated(15, 0,0,1); glscalef(2,1,1); house(); //david house Instance 1 gltranslatef(-6,0,0); glscalef(2,2,2); david_house(); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 15 Hierarchical Modeling DAG allow high-level sharing of objects but often make the memory costs and code complexity too high. DAGs are natural in many applications, e.g., modeling polygonal meshes where many edges and vertices are shared by higher level objects. Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 16 8
9 DAG example: polygonal mesh surface Polygon 1 Polygon 2 Polygon 3 Polygon n Edge 1 Edge 2 Edge 3 Vertex 1 Vertex 2 Vertex 3 Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 17 Hierarchical Modeling using Trees Primitives that can be drawn directly, at leaves Internal nodes become instances Transformations that position instances of objects label the edges Traverse in pre-order (visit parent, visit children left to right). Stack based implementation Model independent traversal algorithm Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 18 9
10 Example: simple 2D drawing Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 19 Hierarchical modeling: tree of transformations T1.T2.T5.T7.T9(LINE) Final picture, obtained by traversing in pre-order the tree Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 20 10
11 Compress the tree If an edge (A,B) is labeled with identity transformation, remove it, and move any drawings from node B into A If edges (A,B) and (A,C) have the same labels, merge the nodes B and C Example: in the previous tree T8 will be removed, and the unit square moved to the parent node Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 21 From the tree model to OpenGL code Start from the root, traverse tree in pre-order When visiting a node, if there is a primitive at the node that can be drawn, draw it If going down from a node which has more then one unvisited child, store(push) CTM and attributes before continuing down If coming back up an edge to a node which has unvisited children, pop CTM and attributes Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 22 11
12 Stack implementation of the compressed tree glscalef(1.0,-1.0,1.0); //T1 gltranslatef(1.5, 3.0, 0.0); //T2 glscalef(1.0, 2.0, 1.0); //T5 glbegin(gl_line_loop); //BOX glvertex3f(0.0,0.0,0.0); glvertex3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glvertex3f(1.0,1.0,0.0); glvertex3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); glend(); gltranslatef(0.5,0.0, 0.0); //T7 glrotatef(90.0,0.0,0.0,1.0); //T9 glbegin(gl_lines); //LINE glvertex3f(0.0,0.0,0.0); glvertex3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glend(); gltranslatef(2.0,1.0,0.0); //T3 glscalef(0.5, 0.5, 1.0); //T6 drawunitcircle(num_slices); glscalef(4.0,5.0,1.0); // T4 glbegin(gl_line_loop); // BOX glvertex3f(0.0,0.0,0.0); glvertex3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glvertex3f(1.0,1.0,0.0); glvertex3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); glend(); glflush(); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 23 Display Lists Need to draw the display at a rate sufficient to avoid noticeable flicker Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 24 12
13 Display Processor Display processor special purpose, limited instruction set, oriented toward drawing graphics primitives Display memory holds lists of instructions called display lists Display list executed repeatedly at a rate sufficient to avoid flicker Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 25 Display Modes Immediate Mode as soon as the program executes a statement that defines a primitive, it is sent to the server Retained Mode define the object once, then put its description in a display list. Redisplayed with a simple function call Reduced network traffic Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 26 13
14 OpenGL Display Lists #define BOX 1 glnewlist(box, GL_COMPILE); glbegin(gl_polygon); glcolor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glvertex2f(-1.0, -1.0); glvertex2f( 1.0, -1.0); glvertex2f( 1.0, 1.0); glvertex2f(-1.0, 1.0); glend( ); glendlist( ); Send list to server but don t display contents GL_COMPILE_AND_EXECUTE This can change the original state and leave it altered glcalllist(box); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 27 Definition and Execution #define BOX 1 glnewlist(box, GL_COMPILE); glpushattrib(gl_all_attrib_bits); glpushmatrix( ); glbegin(gl_polygon); glcolor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glvertex2f(-1.0, -1.0); glvertex2f( 1.0, -1.0); glvertex2f( 1.0, 1.0); glvertex2f(-1.0, 1.0); glend( ); glpopattrib( ); glpopmatrix( ); glendlist( ); Push and pop attributes and coordinates to the stacks Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 28 14
15 Stack implementation of the tree of transformations glscalef(1.0,-1.0,1.0); gltranslatef(1.5, 3.0, 0.0); glscalef(1.0, 2.0, 1.0); glcalllist(box); gltranslatef(0.5,0.0, 0.0); glrotatef(90.0,0.0,0.0,1.0); glbegin(gl_lines); glvertex3f(0.0,0.0,0.0); glvertex3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glend(); gltranslatef(2.0,1.0,0.0); glscalef(0.5, 0.5, 1.0); drawunitcircle(num_slices); glscalef(4.0,5.0,1.0); glcalllist(box); glflush(); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 29 Example: cart with two wheels Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 30 15
16 Example: wheel Model a red wheel of radius WHEEL_RAD, consisting of a circle and two crossed spikes. Primitive components are unit circle and crossed orthogonal spikes of length 2. glnewlist(wheel,gl_compile); glpushattrib(gl_color); // red wheel with WHEEL_RAD glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); // red glscalef(wheel_rad, WHEEL_RAD, 1.0); // scale to wheel radius glbegin(gl_lines); // cross, each bar length 2 glvertex2f( -1.0, 0.0); glvertex2f(1.0, 0.0); glvertex2f( 0.0, -1.0); glvertex2f( 0.0, 1.0); glend(); drawunitcircle(num_slices); // unit circle glpopattrib(); glendlist(); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 31 Example: rod with 2 fixed wheels Model the cart consisting of two red wheels of radius WHEEL_RAD, positioned at the ends of a green rod of length 2*HALF_AXIS_LENGTH. The two wheels are rotated at different angles. glnewlist(cart,gl_compile); glpushattrib(gl_color); glcolor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); // green glbegin(gl_lines); // rod glvertex2f(-half_axis_length, 0.0); glvertex2f( HALF_AXIS_LENGTH, 0.0); glend(); gltranslatef(-half_axis_length, 0.0, 0.0); //position front WHEEL at axis glrotatef(th, 0.0,0.0,1.0); // rotate a WHEEL by TH glcalllist(wheel); gltranslatef(half_axis_length, 0.0, 0.0); //position back WHEEL at axis glrotatef(th+incr, 0.0,0.0,1.0); // rotate a WHEEL by TH+INCR glcalllist(wheel); glpopattrib(); glendlist(); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 32 16
17 Example: cart with 2 wheels void display() { glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); glcalllist(cart); glflush(); } void myinit() { glclearcolor(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.0); glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); gluortho2d(-225.0, 225.0, -225, 225.0); glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); defineparts(); // WHEEL and CART are display lists defined here, } main(). As usual, negotiate with Windows Sys, register callbacks, run loop to process events Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 33 Example: spin the wheels Limitations of display lists Use of functions in drawing instances of objects at tree nodes Continuously keep changing the value of rotation angle for turning a wheel Need of double buffering Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 34 17
18 Example: spin the wheels,2 void draw_cart() { glpushattrib(gl_color); glcolor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); // draw axis in green glbegin(gl_lines); glvertex2f(-half_axis_length,0.0); glvertex2f(half_axis_length,0.0); glend(); gltranslatef(-half_axis_length,0.0, 0.0); // position front wheel at axis, T1 glrotatef(theta,0.0,0.0,1.0); // spin front WHEEL by theta glcalllist(wheel); // draw wheel gltranslatef(half_axis_length,0.0, 0.0); // position back wheel at axis, T2 glrotatef(theta, 0.0,0.0,1.0); // spin back WHEEL by theta glcalllist(wheel); // draw wheel glpopattrib(); } Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 35 Open GL interactive program structure int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc,argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutcreatewindow( generic example"); myinit (); glutreshapefunc (myreshape); glutmousefunc (mouse); glutmotionfunc(do_on_motion); glutidlefunction(idle); glutdisplayfunc(display); glutmainloop(); } Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 36 18
19 Example: spin the wheels,3, the Idle Function void idle(void) // IDLE callback function updates { // rotation angle that spins a wheel theta += INCR_ANGLE; glutpostredisplay(); } void mousemotion(int x, int y) // MOTION callback function updates { // translation vector that moves whole transx = x; transy = y; glutpostredisplay(); } void display() // DISPLAY callback draws whole object { // in back buffer then swaps buffers glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); // translate whole object axis with spinning wheels gltranslatef( (float)transx, (float)(windowh-transy), 0.0); draw_cart(); } glutswapbuffers(); // SWAP BUFFERS Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 37 Example: spin the wheels, 4, the Idle Function int main( ) { glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGB); // double buffering... glutdisplayfunc(display); glutmotionfunc(mousemotion); glutidlefunc(idle); glutmainloop(); } Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 38 19
20 HW: Model hierarchically a 3D scene consisting of a circular road, a car, at least 2 trees along the road. Each component has a different color than the rest. Allow for interactively changing the camera position, allowing the camera to rotate around the horizontal and vertical axis of the coordinate system attached to the scene, and also for interactively choosing an option to move the car forward or backward A car has a rectangular body and 4 wheels A tree has a trunk (cylinder) and a crown (sphere) The road is a circular loop Model each object (object part) in its own local coordinate system; use transformations to position all objects in the scene. Trees of transformations should help in modeling the individual objects (tree, car), and also in putting the whole scene together. Use functions or display lists to model the components HW is due in 2 weeks. Pace yourself well: complete the modeling in a week, so the week after you could deal with the interaction and the animation. Model and test each object individually, first. Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 39 Example: model circular road // ROAD_RAD1, ROAD_RAD2, ROAD_SL, ROAD_RINGS defined globally void draw_road() { GLUquadric* q; q = glunewquadric(); // dynamic array to hold vertices of road // creates and returns a ptr to new quadric object glpushattrib(gl_all_attrib_bits); glcolor3f(0.5,0.5,0.5); // road is gray gludisk(q, ROAD_RAD1, ROAD_RAD2, ROAD_SL, ROAD_RINGS); glpopattrib(); } gludeletequadric(q); Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 40 20
21 Example: model circular road void display() { glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); // glrotatef(45,1.0,0.0,0.0); //glulookat(0.0,0.0,0.0, -1.0,-1.0,-1.0, 0.0,0.0,1.0); draw_road(); glflush(); } Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 41 21
Computer graphics MN1
 Computer graphics MN1 Hierarchical modeling Transformations in OpenGL glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadidentity(); // identity matrix gltranslatef(4.0, 5.0, 6.0); glrotatef(45.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0); gltranslatef(-4.0,
Computer graphics MN1 Hierarchical modeling Transformations in OpenGL glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadidentity(); // identity matrix gltranslatef(4.0, 5.0, 6.0); glrotatef(45.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0); gltranslatef(-4.0,
CSC 470 Computer Graphics
 CSC 470 Computer Graphics Transformations of Objects CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 1 Transformations of objects - 2D CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 2 Using
CSC 470 Computer Graphics Transformations of Objects CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 1 Transformations of objects - 2D CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 2 Using
Order of Transformations
 Order of Transformations Because the same transformation is applied to many vertices, the cost of forming a matrix M=ABCD is not significant compared to the cost of computing Mp for many vertices p Note
Order of Transformations Because the same transformation is applied to many vertices, the cost of forming a matrix M=ABCD is not significant compared to the cost of computing Mp for many vertices p Note
Input and Interaction. 1. Interaction. Chapter 3. Introduction: - We now turn to the development of interactive graphics programs.
 Input and Interaction Chapter 3 Introduction: - We now turn to the development of interactive graphics programs. - Our discussion has three main parts First, we consider the variety of devices available
Input and Interaction Chapter 3 Introduction: - We now turn to the development of interactive graphics programs. - Our discussion has three main parts First, we consider the variety of devices available
Modeling Transform. Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations. Overview. Instancing. Specify transformation for objects 李同益
 Modeling Transform Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations 李同益 Specify transformation for objects Allow definitions of objects in own coordinate systems Allow use of object definition multiple times in a scene
Modeling Transform Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations 李同益 Specify transformation for objects Allow definitions of objects in own coordinate systems Allow use of object definition multiple times in a scene
// double buffering and RGB glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGBA); // your own initializations
 #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
#include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
Modeling Objects by Polygonal Approximations. Linear and Affine Transformations (Maps)
 Modeling Objects by Polygonal Approximations Define volumetric objects in terms of surfaces patches that surround the volume Each surface patch is approximated set of polygons Each polygon is specified
Modeling Objects by Polygonal Approximations Define volumetric objects in terms of surfaces patches that surround the volume Each surface patch is approximated set of polygons Each polygon is specified
Scene Graphs. CS4620/5620: Lecture 7. Announcements. HW 1 out. PA 1 will be out on Wed
 CS4620/5620: Lecture 7 Scene Graphs 1 Announcements HW 1 out PA 1 will be out on Wed Next week practicum will have an office hour type session on Open GL 2 Example Can represent drawing with flat list
CS4620/5620: Lecture 7 Scene Graphs 1 Announcements HW 1 out PA 1 will be out on Wed Next week practicum will have an office hour type session on Open GL 2 Example Can represent drawing with flat list
Lecture 3. Understanding of OPenGL programming
 Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
OpenGL/GLUT Intro. Week 1, Fri Jan 12
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
Introduction to 3D Graphics with OpenGL. Z-Buffer Hidden Surface Removal. Binghamton University. EngiNet. Thomas J. Watson
 Binghamton University EngiNet State University of New York EngiNet Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science WARNING All rights reserved. No Part of this video lecture series may be reproduced
Binghamton University EngiNet State University of New York EngiNet Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science WARNING All rights reserved. No Part of this video lecture series may be reproduced
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Computer graphics MN1
 Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? How do I use it? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines,, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code
Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? How do I use it? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines,, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Autumn 2009 CS4815
 Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring Department of Computer and Information Science
 Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions
 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011
 Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Graphics Programming
 Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
To Do. Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) Course Outline. Course Outline. Methodology for Lecture. Demo: Surreal (HW 3)
 Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
C OMPUTER G RAPHICS Thursday
 C OMPUTER G RAPHICS 2017.04.27 Thursday Professor s original PPT http://calab.hanyang.ac.kr/ Courses Computer Graphics practice3.pdf TA s current PPT not uploaded yet GRAPHICS PIPELINE What is Graphics
C OMPUTER G RAPHICS 2017.04.27 Thursday Professor s original PPT http://calab.hanyang.ac.kr/ Courses Computer Graphics practice3.pdf TA s current PPT not uploaded yet GRAPHICS PIPELINE What is Graphics
 OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Spring CS4815
 Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Basic Graphics Programming
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 424 Computer Graphics 2D Transformations Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: Introduction to Computer Graphics course notes by Doug Bowman Interactive Computer Graphics, Fourth Edition, Ed Angle Transformations
CS 424 Computer Graphics 2D Transformations Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: Introduction to Computer Graphics course notes by Doug Bowman Interactive Computer Graphics, Fourth Edition, Ed Angle Transformations
Display Lists in OpenGL
 Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
Lecture 5: Viewing. CSE Computer Graphics (Fall 2010)
 Lecture 5: Viewing CSE 40166 Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) Review: from 3D world to 2D pixels 1. Transformations are represented by matrix multiplication. o Modeling o Viewing o Projection 2. Clipping
Lecture 5: Viewing CSE 40166 Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) Review: from 3D world to 2D pixels 1. Transformations are represented by matrix multiplication. o Modeling o Viewing o Projection 2. Clipping
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger Reception hours: by - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using
 Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson
 C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
API for creating a display window and using keyboard/mouse interations. See RayWindow.cpp to see how these are used for Assignment3
 OpenGL Introduction Introduction OpenGL OpenGL is an API for computer graphics. Hardware-independent Windowing or getting input is not included in the API Low-level Only knows about triangles (kind of,
OpenGL Introduction Introduction OpenGL OpenGL is an API for computer graphics. Hardware-independent Windowing or getting input is not included in the API Low-level Only knows about triangles (kind of,
CS 591B Lecture 9: The OpenGL Rendering Pipeline
 CS 591B Lecture 9: The OpenGL Rendering Pipeline 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications use rendering of 3D polygons with direct illumination Spring 2007 Rui Wang 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications
CS 591B Lecture 9: The OpenGL Rendering Pipeline 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications use rendering of 3D polygons with direct illumination Spring 2007 Rui Wang 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications
3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering them
 SE313: Computer Graphics and Visual Programming Computer Graphics Notes Gazihan Alankus, Spring 2012 Computer Graphics 3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering
SE313: Computer Graphics and Visual Programming Computer Graphics Notes Gazihan Alankus, Spring 2012 Computer Graphics 3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering
Lecture 4 of 41. Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics
 Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://snipurl.com/1y5gc Course web site: http://www.kddresearch.org/courses/cis636 Instructor
Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://snipurl.com/1y5gc Course web site: http://www.kddresearch.org/courses/cis636 Instructor
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole. Real Pinhole. Real + lens. Depth of field
 Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Interaction Computer Graphics I Lecture 3
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
Lectures OpenGL Introduction
 Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT
 Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
Better Interactive Programs
 Better Interactive Programs Objectives Learn to build more sophisticated interactive programs using Picking Select objects from the display Rubberbanding Interactive drawing of lines and rectangles Display
Better Interactive Programs Objectives Learn to build more sophisticated interactive programs using Picking Select objects from the display Rubberbanding Interactive drawing of lines and rectangles Display
SOURCES AND URLS BIBLIOGRAPHY AND REFERENCES
 In this article, we have focussed on introducing the basic features of the OpenGL API. At this point, armed with a handful of OpenGL functions, you should be able to write some serious applications. In
In this article, we have focussed on introducing the basic features of the OpenGL API. At this point, armed with a handful of OpenGL functions, you should be able to write some serious applications. In
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING. 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M
 UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs Computer Graphics I, Fall
 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Graphics Programming. August 31, Programming of the Sierpinski gasket. Programming with OpenGL and C/C++
 Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# March 25 th 2007 p1/15
 COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# 3257 495 9 March 25 th 2007 p1/15 Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student#: 3257 495 9 COS340A Date submitted: March 25, 2007 Question 1... p2 3 Question 2... p4 Question
COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# 3257 495 9 March 25 th 2007 p1/15 Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student#: 3257 495 9 COS340A Date submitted: March 25, 2007 Question 1... p2 3 Question 2... p4 Question
Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL
 Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL What we are going to do OpenGL Glut Small Example using OpenGl and Glut Alexandra Junghans 2 What is OpenGL? OpenGL Two Parts most widely used and supported graphics API
Exercise 1 Introduction to OpenGL What we are going to do OpenGL Glut Small Example using OpenGl and Glut Alexandra Junghans 2 What is OpenGL? OpenGL Two Parts most widely used and supported graphics API
Interaction. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2
 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Lectures Display List
 Lectures Display List By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is it? What
Lectures Display List By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is it? What
Computer Graphics. Making Pictures. Computer Graphics CSC470 1
 Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Computer Graphics. OpenGL
 Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
CS380: Computer Graphics 2D Imaging and Transformation. Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL:
 CS380: Computer Graphics 2D Imaging and Transformation Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Write down simple 2D transformation matrixes Understand the
CS380: Computer Graphics 2D Imaging and Transformation Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Write down simple 2D transformation matrixes Understand the
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
Modeling with Transformations
 Modeling with Transformations Prerequisites This module requires some understanding of 3D geometry, particularly a sense of how objects can be moved around in 3-space. The student should also have some
Modeling with Transformations Prerequisites This module requires some understanding of 3D geometry, particularly a sense of how objects can be moved around in 3-space. The student should also have some
Using GLU/GLUT Objects
 Using GLU/GLUT Objects GLU/GLUT provides very simple object primitives glutwirecone glutwirecube glucylinder glutwireteapot GLU/GLUT Objects Each glu/glut object has its default size, position, and orientation
Using GLU/GLUT Objects GLU/GLUT provides very simple object primitives glutwirecone glutwirecube glucylinder glutwireteapot GLU/GLUT Objects Each glu/glut object has its default size, position, and orientation
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction
 Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Input and Interaction
 Input and Interaction Interactive program is something make CG look interesting Suriyong L., Computer Multimedia 1 Physical Input Devices 2 Types Pointing devices Locate or indicate position on screen
Input and Interaction Interactive program is something make CG look interesting Suriyong L., Computer Multimedia 1 Physical Input Devices 2 Types Pointing devices Locate or indicate position on screen
3.2 Hierarchical Modeling
 Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 3.2 Hierarchical Modeling Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Importance of shadows Source: UNC 2 Importance of shadows Source: UNC 3 Importance of shadows Source: UNC
Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 3.2 Hierarchical Modeling Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Importance of shadows Source: UNC 2 Importance of shadows Source: UNC 3 Importance of shadows Source: UNC
QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009
![QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009 QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009](/thumbs/91/107455423.jpg) 2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
Drawing Primitives. OpenGL basics
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
CS D Transformation. Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤
 CS10101001 3D Transformation Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Review Translation Linear transformation
CS10101001 3D Transformation Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Review Translation Linear transformation
Chapter 7 Display Lists
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 7 Display Lists Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Understand how display lists can
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 7 Display Lists Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Understand how display lists can
GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_PROJECTION, GL_MODELVIEW
 OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
Hierarchical Modeling. University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell
 Hierarchical Modeling University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Angel, sections 9.1-9.6 [reader pp. 169-185] OpenGL Programming Guide, chapter 3 Focus especially
Hierarchical Modeling University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Angel, sections 9.1-9.6 [reader pp. 169-185] OpenGL Programming Guide, chapter 3 Focus especially
1.2 Basic Graphics Programming
 Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
Using OpenGL with CUDA
 Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations
 Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations
Basic Graphics Programming
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming January 11, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s12/ Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming January 11, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s12/ Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API
Assignment 1. Simple Graphics program using OpenGL
 Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Reading. Hierarchical Modeling. Symbols and instances. Required: Angel, sections , 9.8. Optional:
 Reading Required: Angel, sections 9.1 9.6, 9.8 Optional: Hierarchical Modeling OpenGL rogramming Guide, the Red Book, chapter 3 cse457-07-hierarchical 1 cse457-07-hierarchical 2 Symbols and instances Most
Reading Required: Angel, sections 9.1 9.6, 9.8 Optional: Hierarchical Modeling OpenGL rogramming Guide, the Red Book, chapter 3 cse457-07-hierarchical 1 cse457-07-hierarchical 2 Symbols and instances Most
11/1/13. Basic Graphics Programming. Teaching Assistant. What is OpenGL. Course Producer. Where is OpenGL used. Graphics library (API)
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Teaching Assistant Yijing Li Office hours TBA Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines,
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Teaching Assistant Yijing Li Office hours TBA Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines,
Better Interactive Programs. Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico
 Better Interactive Programs Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Learn to build more sophisticated interactive
Better Interactive Programs Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Learn to build more sophisticated interactive
Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL
 Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it OpenGL parts: GL = Graphics Library (core lib) GLU = GL Utilities (always present) GLX, AGL,
Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it OpenGL parts: GL = Graphics Library (core lib) GLU = GL Utilities (always present) GLX, AGL,
Modeling Objects. Modeling. Symbol-Instance Table. Instance Transformation. Each appearance of the object in the model is an instance
 Modeling Objects Modeling Hierarchical Transformations Hierarchical Models Scene Graphs A prototype has a default size, position, and orientation You need to perform modeling transformations to position
Modeling Objects Modeling Hierarchical Transformations Hierarchical Models Scene Graphs A prototype has a default size, position, and orientation You need to perform modeling transformations to position
Hidden Surface Removal. 3D Graphics with OpenGL. Back-Face Culling
 Hidden Surface Removal Back Face Culling 3D Surfaces Bicubic Parametric Bezier Surface Patches 3D Graphics with OpenGL Back-Face Culling Define one side of each polygon to be the visible side That side
Hidden Surface Removal Back Face Culling 3D Surfaces Bicubic Parametric Bezier Surface Patches 3D Graphics with OpenGL Back-Face Culling Define one side of each polygon to be the visible side That side
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013
 CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 11: Implementing Transformations. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
Hierarchical Modelling
 Gregor Miller gregor{at}ece.ubc.ca Hierarchical Modelling Limitations of linear modelling Articulated models Tree and DAG models Traversal Strategies Instance Transformation Start with a prototype object
Gregor Miller gregor{at}ece.ubc.ca Hierarchical Modelling Limitations of linear modelling Articulated models Tree and DAG models Traversal Strategies Instance Transformation Start with a prototype object
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Hierarchical Modeling and scene graphs
 Hierarchical Modeling and scene graphs Overview Examine the limitations of linear modeling Introduce hierarchical models Introduce Tree and DAG models Build a tree-structured model of a humanoid figure
Hierarchical Modeling and scene graphs Overview Examine the limitations of linear modeling Introduce hierarchical models Introduce Tree and DAG models Build a tree-structured model of a humanoid figure
Chapter 3: Modeling Transformation
 Chapter 3: Modeling Transformation Graphics Programming, 8th Sep. Graphics and Media Lab. Seoul National University 2011 Fall OpenGL Steps Every step in the graphics pipeline is related to the transformation.
Chapter 3: Modeling Transformation Graphics Programming, 8th Sep. Graphics and Media Lab. Seoul National University 2011 Fall OpenGL Steps Every step in the graphics pipeline is related to the transformation.
Computer graphics MN1
 Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? HowdoI useit? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code examples
Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? HowdoI useit? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code examples
Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 1. INTRODUCTION TO OpenGL
 Visual Computing and Multimedia Abel J. P. Gomes 1. Getting Started 2. Installing Graphics Libraries: OpenGL and GLUT 3. Setting up an IDE to run graphics programs in OpenGL/GLUT 4. A First OpenGL/GLUT
Visual Computing and Multimedia Abel J. P. Gomes 1. Getting Started 2. Installing Graphics Libraries: OpenGL and GLUT 3. Setting up an IDE to run graphics programs in OpenGL/GLUT 4. A First OpenGL/GLUT
Hierarchical Modeling and Scene Graphs
 Hierarchical Modeling and Scene Graphs Adapted from material prepared by Ed Angel Spring 2009 Objectives Examine the limitations of linear modeling Symbols and instances Introduce hierarchical models Articulated
Hierarchical Modeling and Scene Graphs Adapted from material prepared by Ed Angel Spring 2009 Objectives Examine the limitations of linear modeling Symbols and instances Introduce hierarchical models Articulated
Computer Graphics. Chapter 7 2D Geometric Transformations
 Computer Graphics Chapter 7 2D Geometric Transformations Chapter 7 Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations Part III. OpenGL Functions for Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations OpenGL Geometric Transformation
Computer Graphics Chapter 7 2D Geometric Transformations Chapter 7 Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations Part III. OpenGL Functions for Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations OpenGL Geometric Transformation
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL)
 Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
OpenGL refresher. Advanced Computer Graphics 2012
 Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
Rendering Pipeline/ OpenGL
 Chapter 2 Basics of Computer Graphics: Your tasks for the weekend Piazza Discussion Group: Register Post review questions by Mon noon Use private option, rev1 tag Start Assignment 1 Test programming environment
Chapter 2 Basics of Computer Graphics: Your tasks for the weekend Piazza Discussion Group: Register Post review questions by Mon noon Use private option, rev1 tag Start Assignment 1 Test programming environment
Introduction to OpenGL
 Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
Computer Graphics. Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing
 Computer Graphics Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Part I. Overview of 3D Viewing Concept 3D Viewing Pipeline vs. OpenGL Pipeline 3D Viewing-Coordinate Parameters
Computer Graphics Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Part I. Overview of 3D Viewing Concept 3D Viewing Pipeline vs. OpenGL Pipeline 3D Viewing-Coordinate Parameters
CSC Graphics Programming. Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science
 CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming OpenGL 3D Drawing 2 3D Graphics Projections Getting 3D to 2D 3D scene 2D image 3 Projections Orthographic
CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming OpenGL 3D Drawing 2 3D Graphics Projections Getting 3D to 2D 3D scene 2D image 3 Projections Orthographic
by modifying the glutinitwindowsize() function you can change the screen size to whatever you please.
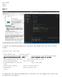 Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Computer Graphics Programming
 Computer Graphics Programming Graphics APIs Using MFC (Microsoft Foundation Class) in Visual C++ Programming in Visual C++ GLUT in Windows and Unix platform Overview and Application Graphics APIs Provide
Computer Graphics Programming Graphics APIs Using MFC (Microsoft Foundation Class) in Visual C++ Programming in Visual C++ GLUT in Windows and Unix platform Overview and Application Graphics APIs Provide
OpenGL Tutorial. Ceng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics
 OpenGL Tutorial Ceng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Adapted from: http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr06/cos426/assn3/opengl_tutorial.ppt OpenGL IS an API OpenGL IS nothing more than
OpenGL Tutorial Ceng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Adapted from: http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr06/cos426/assn3/opengl_tutorial.ppt OpenGL IS an API OpenGL IS nothing more than
Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background
 Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Development of the OpenGL API
Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Development of the OpenGL API
RECITATION - 1. Ceng477 Fall
 RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
Visualizing Molecular Dynamics
 Visualizing Molecular Dynamics Aiichiro Nakano Collaboratory for Advanced Computing & Simulations Department of Computer Science Department of Physics & Astronomy Department of Chemical Engineering & Materials
Visualizing Molecular Dynamics Aiichiro Nakano Collaboratory for Advanced Computing & Simulations Department of Computer Science Department of Physics & Astronomy Department of Chemical Engineering & Materials
OpenGL. Toolkits.
 http://www.opengl.org OpenGL Open Graphics Library Graphics API Delivered with UNIX, Win9x/2000/Me/Nt/Xp, Mac OS Direct3D (DirectX) is only Windows Utilizes the window system and event handling of the
http://www.opengl.org OpenGL Open Graphics Library Graphics API Delivered with UNIX, Win9x/2000/Me/Nt/Xp, Mac OS Direct3D (DirectX) is only Windows Utilizes the window system and event handling of the
