November 22, Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM. Olmo S. Zavala Romero
|
|
|
- Stephanie Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM November 22, 2017
2 Jean-Baptiste Joseph Jean-Baptiste Joseph ( ) was a French mathematician and physicist born in Auxerre and best known for initiating the investigation of series and their applications to problems of heat transfer and vibrations. Son of tailor and orphaned at age 9. Promoted the French revolution. Imprisoned in He claimed: any function of a variable, whether continuous or discontinuous, can be expanded in a series of sines of multiples of the variable.
3 Applications of (start at 3:54)
4 series with respect to t Consider a function f (x) that is periodic with period. f (x + ) = f (x) the period of the function to 2π, define t = 2π x, so that: f (t + 2π) = f (t) (1) The series are defined as: f (t) = 1 2 a 0 + a k cos(kt) + b k sin(kt) (2) k=1
5 series with respect to t Consider a function f (x) that is periodic with period. f (x + ) = f (x) the period of the function to 2π, define t = 2π x, so that: f (t + 2π) = f (t) (1) The series are defined as: f (t) = 1 2 a 0 + a k cos(kt) + b k sin(kt) (2) a 0 = 1 π a k = 1 π b k = 1 π k=1 π π π π π π f (x)dx f (x) cos(kt)dt f (x) sin(kt)dt (3) Does this work for every function f? (out of scope) Functions for which first and second order derivatives exist almost everywhere, are finite and have at most a finite number of discontinuities and zero crossings in the interval ( π, π)
6 series with respect to x Consider a function f (x) that is periodic with period 2. f (x + 2) = f (x) the period of the function to 2π, define t = 2π x = π x, so 2 that: f (t + 2π) = f (t) (4) The series (in this case) are defined as: f (x) = 1 2 a 0 + a 0 = 1 a k = 1 b k = 1 a k cos k=1 f (x)dx ( kπx f (x)cos ( kx f (x)sin ( ) kπx + b k sin ) dx ) dx ( ) kπx (5)
7 Summary of numerical integration OPEN NEW SIDES!
8 program series Convince me, using Python, that series are real! Approximate f (x) = x 2 with series. f (x) = 1 2 a 0 + ( ) ( ) N k=1 a k cos kπx + b k sin kπx Step 1 Define your function f = x 2 (as a function), your period = 2 and N the total number of terms that we want to use for the approximation.
9 program series Convince me, using Python, that series are real! Approximate f (x) = x 2 with series. f (x) = 1 2 a 0 + ( ) ( ) N k=1 a k cos kπx + b k sin kπx Step 1 Define your function f = x 2 (as a function), your period = 2 and N the total number of terms that we want to use for the approximation. Step 2 How can we compute this first integral (do you remember numerical integration)? a 0 = 1 f (x)dx (6)
10 program series Convince me, using Python, that series are real! Approximate f (x) = x 2 with series. f (x) = 1 2 a 0 + ( ) ( ) N k=1 a k cos kπx + b k sin kπx Step 1 Define your function f = x 2 (as a function), your period = 2 and N the total number of terms that we want to use for the approximation. Step 2 How can we compute this first integral (do you remember numerical integration)? a 0 = 1 f (x)dx (6) Step 3 Compute the first coefficient a 0.
11 program series Convince me, using Python, that series are real! Approximate f (x) = x 2 with series. f (x) = 1 2 a 0 + ( ) ( ) N k=1 a k cos kπx + b k sin kπx Step 1 Define your function f = x 2 (as a function), your period = 2 and N the total number of terms that we want to use for the approximation. Step 2 How can we compute this first integral (do you remember numerical integration)? a 0 = 1 f (x)dx (6) Step 3 Compute the first coefficient a 0. Step 4. Compute simirarly (using a loop or a comprehension): a k = 1 ( ) kπx f (x)cos dx (7)
12 program series Convince me, using Python, that series are real! Approximate f (x) = x 2 with series. f (x) = 1 2 a 0 + ( ) ( ) N k=1 a k cos kπx + b k sin kπx Step 1 Define your function f = x 2 (as a function), your period = 2 and N the total number of terms that we want to use for the approximation. Step 2 How can we compute this first integral (do you remember numerical integration)? a 0 = 1 f (x)dx (6) Step 3 Compute the first coefficient a 0. Step 4. Compute simirarly (using a loop or a comprehension): a k = 1 ( ) kπx f (x)cos dx (7) Step 5. Compute the series: f (x) = 1 N ( ) ( ) kπx kπx 2 a 0 + a k cos + b k sin k=1 (8)
13 program series Show the example!
14 Relations between cosine, sine and exponential functions and more i 2 = 1 x = a + bi defines a complex number e ±iθ = cos(θ) ± i sin(θ) cos(θ) = 1 (e +iθ + e iθ) 2 sin(θ) = 1 (e +iθ e iθ) 2i (9)
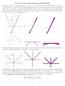
7.2 Trigonometric Integrals
 7. Trigonometric Integrals The three identities sin x + cos x, cos x (cos x + ) and sin x ( cos x) can be used to integrate expressions involving powers of Sine and Cosine. The basic idea is to use an
7. Trigonometric Integrals The three identities sin x + cos x, cos x (cos x + ) and sin x ( cos x) can be used to integrate expressions involving powers of Sine and Cosine. The basic idea is to use an
2 Unit Bridging Course Day 10
 1 / 31 Unit Bridging Course Day 10 Circular Functions III The cosine function, identities and derivatives Clinton Boys / 31 The cosine function The cosine function, abbreviated to cos, is very similar
1 / 31 Unit Bridging Course Day 10 Circular Functions III The cosine function, identities and derivatives Clinton Boys / 31 The cosine function The cosine function, abbreviated to cos, is very similar
Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1
 Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
SUM AND DIFFERENCES. Section 5.3 Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 2017
 SUM AND DIFFERENCES Section 5. Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 2017 Viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8/1/2018 12:41 AM 5.4: Sum and Differences of Trig Functions 1 IDENTITY Question 1: What is Cosine 45? Question
SUM AND DIFFERENCES Section 5. Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 2017 Viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8/1/2018 12:41 AM 5.4: Sum and Differences of Trig Functions 1 IDENTITY Question 1: What is Cosine 45? Question
Angle Measure 1. Use the relationship π rad = 180 to express the following angle measures in radian measure. a) 180 b) 135 c) 270 d) 258
 Chapter 4 Prerequisite Skills BLM 4-1.. Angle Measure 1. Use the relationship π rad = 180 to express the following angle measures in radian measure. a) 180 b) 135 c) 70 d) 58. Use the relationship 1 =!
Chapter 4 Prerequisite Skills BLM 4-1.. Angle Measure 1. Use the relationship π rad = 180 to express the following angle measures in radian measure. a) 180 b) 135 c) 70 d) 58. Use the relationship 1 =!
PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9)
 PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9) Name Date Directions: You may NOT use Right Triangle Trigonometry for any of these problems! Use your unit circle knowledge to solve these problems.
PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9) Name Date Directions: You may NOT use Right Triangle Trigonometry for any of these problems! Use your unit circle knowledge to solve these problems.
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Volume of Revolution Paper 2
 Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Limits and Continuity: section 12.2
 Limits and Continuity: section 1. Definition. Let f(x,y) be a function with domain D, and let (a,b) be a point in the plane. We write f (x,y) = L if for each ε > 0 there exists some δ > 0 such that if
Limits and Continuity: section 1. Definition. Let f(x,y) be a function with domain D, and let (a,b) be a point in the plane. We write f (x,y) = L if for each ε > 0 there exists some δ > 0 such that if
Problem Set 8: Complex Numbers
 Goal: Become familiar with math operations using complex numbers; see how complex numbers can be used to show the frequency response of an RC circuit. Note: This PSet will be much easier if you have already
Goal: Become familiar with math operations using complex numbers; see how complex numbers can be used to show the frequency response of an RC circuit. Note: This PSet will be much easier if you have already
SECTION 4.5: GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONS
 SECTION 4.5: GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONS 4.33 PART A : GRAPH f ( θ ) = sinθ Note: We will use θ and f ( θ) for now, because we would like to reserve x and y for discussions regarding the Unit Circle.
SECTION 4.5: GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONS 4.33 PART A : GRAPH f ( θ ) = sinθ Note: We will use θ and f ( θ) for now, because we would like to reserve x and y for discussions regarding the Unit Circle.
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
Pre-Calc Trig ~1~ NJCTL.org. Unit Circle Class Work Find the exact value of the given expression. 7. Given the terminal point ( 3, 2 10.
 Unit Circle Class Work Find the exact value of the given expression.. cos π. tan 5π 6. sin 7π 5. cot 5π. sec π 6. csc 9π 7. Given the terminal point (, 0 ) find tanθ 7 tan θ = 0 7 8. Given the terminal
Unit Circle Class Work Find the exact value of the given expression.. cos π. tan 5π 6. sin 7π 5. cot 5π. sec π 6. csc 9π 7. Given the terminal point (, 0 ) find tanθ 7 tan θ = 0 7 8. Given the terminal
SOME PROPERTIES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. 5! x7 7! + = 6! + = 4! x6
 SOME PROPERTIES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS PO-LAM YUNG We defined earlier the sine cosine by the following series: sin x = x x3 3! + x5 5! x7 7! + = k=0 cos x = 1 x! + x4 4! x6 6! + = k=0 ( 1) k x k+1
SOME PROPERTIES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS PO-LAM YUNG We defined earlier the sine cosine by the following series: sin x = x x3 3! + x5 5! x7 7! + = k=0 cos x = 1 x! + x4 4! x6 6! + = k=0 ( 1) k x k+1
SM 2. Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or
 SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
Worksheet 5. 3 Less trigonometry and more dishonesty/linear algebra knowledge Less trigonometry, less dishonesty... 4
 Worksheet 5 Contents 1 Just look at the book, on page 74 1 2 Trigonometry and honesty 1 3 Less trigonometry and more dishonesty/linear algebra knowledge 3 3.1 Less trigonometry, less dishonesty...............................
Worksheet 5 Contents 1 Just look at the book, on page 74 1 2 Trigonometry and honesty 1 3 Less trigonometry and more dishonesty/linear algebra knowledge 3 3.1 Less trigonometry, less dishonesty...............................
Trigonometry I. Exam 0
 Trigonometry I Trigonometry Copyright I Standards 006, Test Barry Practice Mabillard. Exam 0 www.math0s.com 1. The minimum and the maximum of a trigonometric function are shown in the diagram. a) Write
Trigonometry I Trigonometry Copyright I Standards 006, Test Barry Practice Mabillard. Exam 0 www.math0s.com 1. The minimum and the maximum of a trigonometric function are shown in the diagram. a) Write
Section Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 5. - Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will graph the basic sine function and the basic cosine function and then graph other sine and cosine functions using transformations.
Section 5. - Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will graph the basic sine function and the basic cosine function and then graph other sine and cosine functions using transformations.
is a plane curve and the equations are parametric equations for the curve, with parameter t.
 MATH 2412 Sections 6.3, 6.4, and 6.5 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates. Plane Curves and Parametric Equations Suppose t is contained in some interval I of the real numbers, and = f( t), = gt (
MATH 2412 Sections 6.3, 6.4, and 6.5 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates. Plane Curves and Parametric Equations Suppose t is contained in some interval I of the real numbers, and = f( t), = gt (
MATH 122 FINAL EXAM WINTER March 15, 2011
 MATH 1 FINAL EXAM WINTER 010-011 March 15, 011 NAME: SECTION: ONLY THE CORRECT ANSWER AND ALL WORK USED TO REACH IT WILL EARN FULL CREDIT. Simplify all answers as much as possible unless explicitly stated
MATH 1 FINAL EXAM WINTER 010-011 March 15, 011 NAME: SECTION: ONLY THE CORRECT ANSWER AND ALL WORK USED TO REACH IT WILL EARN FULL CREDIT. Simplify all answers as much as possible unless explicitly stated
HONORS PRECALCULUS Prove the following identities- x x= x x 1.) ( ) 2 2.) 4.) tan x 1 cos x 6.)
 HONORS PRECALCULUS Prove the following identities- 1.) ( ) cosx sinx = 1 sinxcosx.) cos x tan x+ sec x= 1 sinx 3.) 1 + 1 = csc x 1 cos x 1+ cos x 4.) sec x + 1 sin x = tan x 1 cos x 5.) cot cos cos cot
HONORS PRECALCULUS Prove the following identities- 1.) ( ) cosx sinx = 1 sinxcosx.) cos x tan x+ sec x= 1 sinx 3.) 1 + 1 = csc x 1 cos x 1+ cos x 4.) sec x + 1 sin x = tan x 1 cos x 5.) cot cos cos cot
Objectives. Materials. Teaching Time
 Teacher Notes Activity 6 Local Linearity, Differentiability, and Limits of Difference Quotients Objectives Connect the concept of local linearity to differentiability through numerical explorations of
Teacher Notes Activity 6 Local Linearity, Differentiability, and Limits of Difference Quotients Objectives Connect the concept of local linearity to differentiability through numerical explorations of
1. Let be a point on the terminal side of θ. Find the 6 trig functions of θ. (Answers need not be rationalized). b. P 1,3. ( ) c. P 10, 6.
 Q. Right Angle Trigonometry Trigonometry is an integral part of AP calculus. Students must know the basic trig function definitions in terms of opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse as well as the definitions
Q. Right Angle Trigonometry Trigonometry is an integral part of AP calculus. Students must know the basic trig function definitions in terms of opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse as well as the definitions
2. Periodic functions have a repeating pattern called a cycle. Some examples from real-life that have repeating patterns might include:
 GRADE 2 APPLIED SINUSOIDAL FUNCTIONS CLASS NOTES Introduction. To date we have studied several functions : Function linear General Equation y = mx + b Graph; Diagram Usage; Occurence quadratic y =ax 2
GRADE 2 APPLIED SINUSOIDAL FUNCTIONS CLASS NOTES Introduction. To date we have studied several functions : Function linear General Equation y = mx + b Graph; Diagram Usage; Occurence quadratic y =ax 2
Math Boot Camp: Coordinate Systems
 Math Boot Camp: Coordinate Systems You can skip this boot camp if you can answer the following question: Staying on a sphere of radius R, what is the shortest distance between the point (0, 0, R) on the
Math Boot Camp: Coordinate Systems You can skip this boot camp if you can answer the following question: Staying on a sphere of radius R, what is the shortest distance between the point (0, 0, R) on the
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
Function f. Function f -1
 Page 1 REVIEW (1.7) What is an inverse function? Do all functions have inverses? An inverse function, f -1, is a kind of undoing function. If the initial function, f, takes the element a to the element
Page 1 REVIEW (1.7) What is an inverse function? Do all functions have inverses? An inverse function, f -1, is a kind of undoing function. If the initial function, f, takes the element a to the element
Math 144 Activity #4 Connecting the unit circle to the graphs of the trig functions
 144 p 1 Math 144 Activity #4 Connecting the unit circle to the graphs of the trig functions Graphing the sine function We are going to begin this activity with graphing the sine function ( y = sin x).
144 p 1 Math 144 Activity #4 Connecting the unit circle to the graphs of the trig functions Graphing the sine function We are going to begin this activity with graphing the sine function ( y = sin x).
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY TUTORIAL SOME MORE RULES OF TRIGONOMETRY This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY TUTORIAL SOME MORE RULES OF TRIGONOMETRY This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves
Digital Image Processing. Lecture 6
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Examples from Section 7.1: Integration by Parts Page 1
 Examples from Section 7.: Integration by Parts Page Questions Example Determine x cos x dx. Example e θ cos θ dθ Example You may wonder why we do not add a constant at the point where we integrate for
Examples from Section 7.: Integration by Parts Page Questions Example Determine x cos x dx. Example e θ cos θ dθ Example You may wonder why we do not add a constant at the point where we integrate for
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17
 Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
1. (a) = tanθ (as required) AG A1 cso 2. Note
 sinθ cosθ. (a) + cos θ sinθ cosθ cosθ cosθ Note tanθ (as required) AG A cso : Uses both a correct identity for sin θ and a correct identityfor cosθ. Also allow a candidate writing +cosθ cos θ on the denominator.
sinθ cosθ. (a) + cos θ sinθ cosθ cosθ cosθ Note tanθ (as required) AG A cso : Uses both a correct identity for sin θ and a correct identityfor cosθ. Also allow a candidate writing +cosθ cos θ on the denominator.
Chapter 10 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Chapter 1 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Homework 1.2 1. Consider the parametric equations x = t and y = 3 t. a. Construct a table of values for t =, 1, 2, 3, and 4 b. Plot the
Chapter 1 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Homework 1.2 1. Consider the parametric equations x = t and y = 3 t. a. Construct a table of values for t =, 1, 2, 3, and 4 b. Plot the
Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231
 1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
HW#50: Finish Evaluating Using Inverse Trig Functions (Packet p. 7) Solving Linear Equations (Packet p. 8) ALL
 MATH 4R TRIGONOMETRY HOMEWORK NAME DATE HW#49: Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Packet pp. 5 6) ALL HW#50: Finish Evaluating Using Inverse Trig Functions (Packet p. 7) Solving Linear Equations (Packet
MATH 4R TRIGONOMETRY HOMEWORK NAME DATE HW#49: Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Packet pp. 5 6) ALL HW#50: Finish Evaluating Using Inverse Trig Functions (Packet p. 7) Solving Linear Equations (Packet
4.7a Trig Inverses.notebook September 18, 2014
 WARM UP 9 18 14 Recall from Algebra 2 (or possibly see for the first time...): In order for a function to have an inverse that is also a function, it must be one to one, which means it must pass the horizontal
WARM UP 9 18 14 Recall from Algebra 2 (or possibly see for the first time...): In order for a function to have an inverse that is also a function, it must be one to one, which means it must pass the horizontal
The following information is for reviewing the material since Exam 3:
 Outcomes List for Math 121 Calculus I Fall 2010-2011 General Information: The purpose of this Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and the skills you should
Outcomes List for Math 121 Calculus I Fall 2010-2011 General Information: The purpose of this Outcomes List is to give you a concrete summary of the material you should know, and the skills you should
Secondary Math 3- Honors. 7-4 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 Secondary Math 3- Honors 7-4 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Warm Up Fill in the Unit What You Will Learn How to restrict the domain of trigonometric functions so that the inverse can be constructed. How
Secondary Math 3- Honors 7-4 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Warm Up Fill in the Unit What You Will Learn How to restrict the domain of trigonometric functions so that the inverse can be constructed. How
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25
 Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
Basic Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Chapter 4: Graphs of the Circular Functions 1 TRIG-Fall 2011-Jordan Trigonometry, 9 th edition, Lial/Hornsby/Schneider, Pearson, 2009 Section 4.1 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Basic Graphs of
Chapter 4: Graphs of the Circular Functions 1 TRIG-Fall 2011-Jordan Trigonometry, 9 th edition, Lial/Hornsby/Schneider, Pearson, 2009 Section 4.1 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Basic Graphs of
What You ll See in This Chapter. Word Cloud. René Descartes. Introduction. Ian Parberry University of North Texas. Fletcher Dunn
 What You ll See in This Chapter Chapter 1: Cartesian Coordinate Systems Fletcher Dunn Valve Software Ian Parberry University of North Texas This chapter describes the basic concepts of 3D math. It is divided
What You ll See in This Chapter Chapter 1: Cartesian Coordinate Systems Fletcher Dunn Valve Software Ian Parberry University of North Texas This chapter describes the basic concepts of 3D math. It is divided
Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position
 Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position PreCalculus - Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 QUIZ Draw the following angles in standard position 50 130 230 320 770-50 2 radians PreCalculus - Santowski 2 Fast
Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position PreCalculus - Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 QUIZ Draw the following angles in standard position 50 130 230 320 770-50 2 radians PreCalculus - Santowski 2 Fast
What is a Function? How to find the domain of a function (algebraically) Domain hiccups happen in 2 major cases (rational functions and radicals)
 What is a Function? Proving a Function Vertical Line Test Mapping Provide definition for function Provide sketch/rule for vertical line test Provide sketch/rule for mapping (notes #-3) How to find the
What is a Function? Proving a Function Vertical Line Test Mapping Provide definition for function Provide sketch/rule for vertical line test Provide sketch/rule for mapping (notes #-3) How to find the
Objectives. Materials
 Activity 6 Local Linearity, Differentiability, and Limits of Difference Quotients Objectives Connect the concept of local linearity to differentiability through numerical explorations of limits of difference
Activity 6 Local Linearity, Differentiability, and Limits of Difference Quotients Objectives Connect the concept of local linearity to differentiability through numerical explorations of limits of difference
Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before.
 Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
Catholic Central High School
 Catholic Central High School Algebra II Practice Examination I Instructions: 1. Show all work on the test copy itself for every problem where work is required. Points may be deducted if insufficient or
Catholic Central High School Algebra II Practice Examination I Instructions: 1. Show all work on the test copy itself for every problem where work is required. Points may be deducted if insufficient or
Math 407 Solutions to Exam 3 April 24, Let f = u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ = (x (t),y(t)) = x (t) +iy (t) for a t b.
 Math 7 Solutions to Exam 3 April, 3 1. (1 Define the following: (a f (z dz, where Γ is a smooth curve with finite length. Γ Let f u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ (x (t,y(t x (t +iy (t for a t b.
Math 7 Solutions to Exam 3 April, 3 1. (1 Define the following: (a f (z dz, where Γ is a smooth curve with finite length. Γ Let f u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ (x (t,y(t x (t +iy (t for a t b.
Catholic Central High School
 Catholic Central High School Algebra II Practice Examination II Instructions: 1. Show all work on the test copy itself for every problem where work is required. Points may be deducted if insufficient or
Catholic Central High School Algebra II Practice Examination II Instructions: 1. Show all work on the test copy itself for every problem where work is required. Points may be deducted if insufficient or
Chapter 3: Trigonometric Identities
 Chapter 3: Trigonometric Identities Chapter 3 Overview Two important algebraic aspects of trigonometric functions must be considered: how functions interact with each other and how they interact with their
Chapter 3: Trigonometric Identities Chapter 3 Overview Two important algebraic aspects of trigonometric functions must be considered: how functions interact with each other and how they interact with their
Trigonometry I -- Answers -- Trigonometry I Diploma Practice Exam - ANSWERS 1
 Trigonometry I -- Answers -- Trigonometry I Diploma Practice Exam - ANSWERS www.puremath.com Formulas These are the formulas for Trig I you will be given on your diploma. a rθ sinθ cosθ tan θ cotθ cosθ
Trigonometry I -- Answers -- Trigonometry I Diploma Practice Exam - ANSWERS www.puremath.com Formulas These are the formulas for Trig I you will be given on your diploma. a rθ sinθ cosθ tan θ cotθ cosθ
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas
 AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
Unit 2: Trigonometry. This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses.
 Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
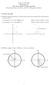 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Exam 3 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 3 Spring Section and/or TA:
 MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions:
 Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Trigonometric functions can be useful models for many real life phenomena. Average monthly temperatures are periodic in nature and can be modeled by sine and/or cosine
Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Trigonometric functions can be useful models for many real life phenomena. Average monthly temperatures are periodic in nature and can be modeled by sine and/or cosine
Exercise: Simulating spatial processing in the visual pathway with convolution
 Exercise: Simulating spatial processing in the visual pathway with convolution This problem uses convolution to simulate the spatial filtering performed by neurons in the early stages of the visual pathway,
Exercise: Simulating spatial processing in the visual pathway with convolution This problem uses convolution to simulate the spatial filtering performed by neurons in the early stages of the visual pathway,
Mathematics for Computer Graphics. Trigonometry
 Mathematics for Computer Graphics Trigonometry Trigonometry...????? The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. trigonon triangle + metron measure
Mathematics for Computer Graphics Trigonometry Trigonometry...????? The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. trigonon triangle + metron measure
4754 Mark Scheme June 2006 Mark Scheme 4754 June 2006
 Mark Scheme 75 June 6 1 sin x cos x R sin(x α) R(sin x cos α cos x sin α) R cos α 1, R sin α R 1 + ( ), R tan α /1 α π/ sin x cos x sin(x π/) x coordinate of P is when x π/ π/ x 5π/6 y So coordinates are
Mark Scheme 75 June 6 1 sin x cos x R sin(x α) R(sin x cos α cos x sin α) R cos α 1, R sin α R 1 + ( ), R tan α /1 α π/ sin x cos x sin(x π/) x coordinate of P is when x π/ π/ x 5π/6 y So coordinates are
A lg e b ra II. Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio
 1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc Length & Area of a Sector
1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc Length & Area of a Sector
Chapter 4 Using Fundamental Identities Section USING FUNDAMENTAL IDENTITIES. Fundamental Trigonometric Identities. Reciprocal Identities
 Chapter 4 Using Fundamental Identities Section 4.1 4.1 USING FUNDAMENTAL IDENTITIES Fundamental Trigonometric Identities Reciprocal Identities csc x sec x cot x Quotient Identities tan x cot x Pythagorean
Chapter 4 Using Fundamental Identities Section 4.1 4.1 USING FUNDAMENTAL IDENTITIES Fundamental Trigonometric Identities Reciprocal Identities csc x sec x cot x Quotient Identities tan x cot x Pythagorean
Sec 4.1 Trigonometric Identities Basic Identities. Name: Reciprocal Identities:
 Sec 4. Trigonometric Identities Basic Identities Name: Reciprocal Identities: Quotient Identities: sin csc cos sec csc sin sec cos sin tan cos cos cot sin tan cot cot tan Using the Reciprocal and Quotient
Sec 4. Trigonometric Identities Basic Identities Name: Reciprocal Identities: Quotient Identities: sin csc cos sec csc sin sec cos sin tan cos cos cot sin tan cot cot tan Using the Reciprocal and Quotient
8-1 Simple Trigonometric Equations. Objective: To solve simple Trigonometric Equations and apply them
 Warm Up Use your knowledge of UC to find at least one value for q. 1) sin θ = 1 2 2) cos θ = 3 2 3) tan θ = 1 State as many angles as you can that are referenced by each: 1) 30 2) π 3 3) 0.65 radians Useful
Warm Up Use your knowledge of UC to find at least one value for q. 1) sin θ = 1 2 2) cos θ = 3 2 3) tan θ = 1 State as many angles as you can that are referenced by each: 1) 30 2) π 3 3) 0.65 radians Useful
Summary. Essential Mathematics. Advanced Methods in Remote Sensing Lectures 9-12: Wavelet Analysis Part 1: Background to Integration and Convolution
 Advanced Methods in Remote Sensing Lectures 9-12: Wavelet Analysis Part 1: Background to Integration and Convolution Recommended Reading: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Erwin Kreyszig (5 th + Edition)
Advanced Methods in Remote Sensing Lectures 9-12: Wavelet Analysis Part 1: Background to Integration and Convolution Recommended Reading: Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Erwin Kreyszig (5 th + Edition)
Verifying Trigonometric Identities
 40 Chapter Analytic Trigonometry. f x sec x Sketch the graph of y cos x Amplitude: Period: One cycle: first. The x-intercepts of y correspond to the vertical asymptotes of f x. cos x sec x 4 x, x 4 4,...
40 Chapter Analytic Trigonometry. f x sec x Sketch the graph of y cos x Amplitude: Period: One cycle: first. The x-intercepts of y correspond to the vertical asymptotes of f x. cos x sec x 4 x, x 4 4,...
Chapter 10 Image Segmentation. Yinghua He
 Chapter 10 Image Segmentation Yinghua He The whole is equal to the sum of its parts. -Euclid The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. -Max Wertheimer The Whole is Not Equal to the Sum of Its Parts:
Chapter 10 Image Segmentation Yinghua He The whole is equal to the sum of its parts. -Euclid The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. -Max Wertheimer The Whole is Not Equal to the Sum of Its Parts:
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 162. Slide 2 / 162. Slide 3 / 162. Trigonometric Functions. Trig Functions
 Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Translation of graphs (2) The exponential function and trigonometric function
 Lesson 35 Translation of graphs (2) The exponential function and trigonometric function Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 2: Functions and Algebra Assessment Standard Generate
Lesson 35 Translation of graphs (2) The exponential function and trigonometric function Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 2: Functions and Algebra Assessment Standard Generate
Precalculus: Graphs of Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant Practice Problems. Questions
 Questions 1. Describe the graph of the function in terms of basic trigonometric functions. Locate the vertical asymptotes and sketch two periods of the function. y = 3 tan(x/2) 2. Solve the equation csc
Questions 1. Describe the graph of the function in terms of basic trigonometric functions. Locate the vertical asymptotes and sketch two periods of the function. y = 3 tan(x/2) 2. Solve the equation csc
Using Fundamental Identities. Fundamental Trigonometric Identities. Reciprocal Identities. sin u 1 csc u. sec u. sin u Quotient Identities
 3330_050.qxd /5/05 9:5 AM Page 374 374 Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry 5. Using Fundamental Identities What you should learn Recognize and write the fundamental trigonometric identities. Use the fundamental
3330_050.qxd /5/05 9:5 AM Page 374 374 Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry 5. Using Fundamental Identities What you should learn Recognize and write the fundamental trigonometric identities. Use the fundamental
Fourier Series. Period 2π over the interval [ π, π]. > > restart:with(plots): Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined
![Fourier Series. Period 2π over the interval [ π, π]. > > restart:with(plots): Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined Fourier Series. Period 2π over the interval [ π, π]. > > restart:with(plots): Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined](/thumbs/88/116963371.jpg) > Fourier Series Period 2 over the interval [, ]. > > restart:with(plots): Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined We begin by considering the function > f:=piecewise(x
> Fourier Series Period 2 over the interval [, ]. > > restart:with(plots): Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined We begin by considering the function > f:=piecewise(x
4.2 Graphing Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 4.2 Graphing Inverse Trigonometric Functions Learning Objectives Understand the meaning of restricted domain as it applies to the inverses of the six trigonometric functions. Apply the domain, range and
4.2 Graphing Inverse Trigonometric Functions Learning Objectives Understand the meaning of restricted domain as it applies to the inverses of the six trigonometric functions. Apply the domain, range and
PLANE TRIGONOMETRY Exam I September 13, 2007
 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time PLANE TRIGONOMETRY Exam I September 13, 2007 Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 TOTAL (10 pts.) (30 pts.) (30 pts.) (30 pts.) (100 pts.) Below you will find 10 problems, each worth
Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time PLANE TRIGONOMETRY Exam I September 13, 2007 Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 TOTAL (10 pts.) (30 pts.) (30 pts.) (30 pts.) (100 pts.) Below you will find 10 problems, each worth
Aliasing. Can t draw smooth lines on discrete raster device get staircased lines ( jaggies ):
 (Anti)Aliasing and Image Manipulation for (y = 0; y < Size; y++) { for (x = 0; x < Size; x++) { Image[x][y] = 7 + 8 * sin((sqr(x Size) + SQR(y Size)) / 3.0); } } // Size = Size / ; Aliasing Can t draw
(Anti)Aliasing and Image Manipulation for (y = 0; y < Size; y++) { for (x = 0; x < Size; x++) { Image[x][y] = 7 + 8 * sin((sqr(x Size) + SQR(y Size)) / 3.0); } } // Size = Size / ; Aliasing Can t draw
Adding vectors. Let s consider some vectors to be added.
 Vectors Some physical quantities have both size and direction. These physical quantities are represented with vectors. A common example of a physical quantity that is represented with a vector is a force.
Vectors Some physical quantities have both size and direction. These physical quantities are represented with vectors. A common example of a physical quantity that is represented with a vector is a force.
Math 1330 Final Exam Review Covers all material covered in class this semester.
 Math 1330 Final Exam Review Covers all material covered in class this semester. 1. Give an equation that could represent each graph. A. Recall: For other types of polynomials: End Behavior An even-degree
Math 1330 Final Exam Review Covers all material covered in class this semester. 1. Give an equation that could represent each graph. A. Recall: For other types of polynomials: End Behavior An even-degree
You can take the arccos of both sides to get θ by itself.
 .7 SOLVING TRIG EQUATIONS Example on p. 8 How do you solve cos ½ for? You can tae the arccos of both sides to get by itself. cos - (cos ) cos - ( ½) / However, arccos only gives us an answer between 0
.7 SOLVING TRIG EQUATIONS Example on p. 8 How do you solve cos ½ for? You can tae the arccos of both sides to get by itself. cos - (cos ) cos - ( ½) / However, arccos only gives us an answer between 0
Math 1330 Section 5.3 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant Functions
 Math 1330 Section 5.3 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant Functions In this section, you will learn to graph the rest of the trigonometric functions. We can use some information from
Math 1330 Section 5.3 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant Functions In this section, you will learn to graph the rest of the trigonometric functions. We can use some information from
Lesson 5 1 Objectives
 Time For Trigonometry!!! Degrees, Radians, Revolutions Arc Length, Area of Sectors SOHCAHTOA Unit Circle Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Tangent Law of Cosines Law of Sines Lesson 5 1 Objectives Convert between
Time For Trigonometry!!! Degrees, Radians, Revolutions Arc Length, Area of Sectors SOHCAHTOA Unit Circle Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Tangent Law of Cosines Law of Sines Lesson 5 1 Objectives Convert between
Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade
 Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight
Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight
Introduction to Computer Vision. Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino
 Introduction to Computer Vision Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Last Week! Image Sensing " Our eyes: rods and cones " CCD, CMOS, Rolling Shutter " Sensing brightness and sensing color! Projective
Introduction to Computer Vision Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Last Week! Image Sensing " Our eyes: rods and cones " CCD, CMOS, Rolling Shutter " Sensing brightness and sensing color! Projective
Integration by parts, sometimes multiple times in the same problem. a. Show your choices. b. Evaluate the integral. a.
 Instructions Complete the homework with a pencil. Show your work. Use extra paper if necessary. Homework can be turned in as follows Turn in homework in person at KPC Scan and e-mail to UAACalculus@yahoo.com
Instructions Complete the homework with a pencil. Show your work. Use extra paper if necessary. Homework can be turned in as follows Turn in homework in person at KPC Scan and e-mail to UAACalculus@yahoo.com
Analytic Spherical Geometry:
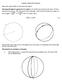 Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using
 Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
Section 5.4: Modeling with Circular Functions
 Section 5.4: Modeling with Circular Functions Circular Motion Example A ferris wheel with radius 25 feet is rotating at a rate of 3 revolutions per minute, When t = 0, a chair starts at its lowest point
Section 5.4: Modeling with Circular Functions Circular Motion Example A ferris wheel with radius 25 feet is rotating at a rate of 3 revolutions per minute, When t = 0, a chair starts at its lowest point
Problem Possible Points Points Earned Problem Possible Points Points Earned Test Total 100
 MATH 1080 Test 2-Version A Fall 2015 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: Section # : You are not allowed to use any textbook, notes, cell phone, laptop, PDA, or any technology on any portion of this test.
MATH 1080 Test 2-Version A Fall 2015 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: Section # : You are not allowed to use any textbook, notes, cell phone, laptop, PDA, or any technology on any portion of this test.
Efficacy of Numerically Approximating Pi with an N-sided Polygon
 Peter Vu Brewer MAT66 Honors Topic Efficacy of umerically Approximating Pi with an -sided Polygon The quest for precisely finding the irrational number pi has been an endeavor since early human history.
Peter Vu Brewer MAT66 Honors Topic Efficacy of umerically Approximating Pi with an -sided Polygon The quest for precisely finding the irrational number pi has been an endeavor since early human history.
Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade)
 Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade) PACING Guide SY 2018-2019 Timeline & Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity
Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade) PACING Guide SY 2018-2019 Timeline & Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity
Problem #3 Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page Mark Sparks 2012
 Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade
 Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to
Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to
ECE569 Fall 2015 Partial Solution to Problem Set 3
 ECE569 Fall 215 Partial Solution to Problem Set 3 These problems are from the textbook by Spong et al. 1, which is the textbook for the ECE569 this Fall 215 semester. As such, many of the problem statements
ECE569 Fall 215 Partial Solution to Problem Set 3 These problems are from the textbook by Spong et al. 1, which is the textbook for the ECE569 this Fall 215 semester. As such, many of the problem statements
Investigating the Sine and Cosine Functions Part 1
 Investigating the Sine and Cosine Functions Part 1 Name: Period: Date: Set-Up Press. Move down to 5: Cabri Jr and press. Press for the F1 menu and select New. Press for F5 and select Hide/Show > Axes.
Investigating the Sine and Cosine Functions Part 1 Name: Period: Date: Set-Up Press. Move down to 5: Cabri Jr and press. Press for the F1 menu and select New. Press for F5 and select Hide/Show > Axes.
Review of Trigonometry
 Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
Trigonometric Graphs Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: About this Laboratory In this laboratory, we will examine trigonometric functions and their graphs. Upon completion of the lab, you should be able to quickly sketch such functions and determine
1 Names: About this Laboratory In this laboratory, we will examine trigonometric functions and their graphs. Upon completion of the lab, you should be able to quickly sketch such functions and determine
Presented, and Compiled, By. Bryan Grant. Jessie Ross
 P a g e 1 Presented, and Compiled, By Bryan Grant Jessie Ross August 3 rd, 2016 P a g e 2 Day 1 Discovering Polar Graphs Days 1 & 2 Adapted from Nancy Stephenson - Clements High School, Sugar Land, Texas
P a g e 1 Presented, and Compiled, By Bryan Grant Jessie Ross August 3 rd, 2016 P a g e 2 Day 1 Discovering Polar Graphs Days 1 & 2 Adapted from Nancy Stephenson - Clements High School, Sugar Land, Texas
HW. Pg. 334 #1-9, 11, 12 WS. A/ Angles in Standard Position: Terminology: Initial Arm. Terminal Arm. Co-Terminal Angles. Quadrants
 MCR 3UI Introduction to Trig Functions Date: Lesson 6.1 A/ Angles in Standard Position: Terminology: Initial Arm HW. Pg. 334 #1-9, 11, 1 WS Terminal Arm Co-Terminal Angles Quadrants Related Acute Angles
MCR 3UI Introduction to Trig Functions Date: Lesson 6.1 A/ Angles in Standard Position: Terminology: Initial Arm HW. Pg. 334 #1-9, 11, 1 WS Terminal Arm Co-Terminal Angles Quadrants Related Acute Angles
Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D
 Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D In today s lecture we are going to have a look at: Transformations in 3-D How do transformations in 3-D work? Contents 3-D homogeneous coordinates and matrix based transformations
Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D In today s lecture we are going to have a look at: Transformations in 3-D How do transformations in 3-D work? Contents 3-D homogeneous coordinates and matrix based transformations
2/3 Unit Math Homework for Year 12
 Yimin Math Centre 2/3 Unit Math Homework for Year 12 Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 12 Trigonometry 2 1 12.1 The Derivative of Trigonometric Functions....................... 1 12.2
Yimin Math Centre 2/3 Unit Math Homework for Year 12 Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 12 Trigonometry 2 1 12.1 The Derivative of Trigonometric Functions....................... 1 12.2
10.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves
 CHAPTER 1. PARAMETRIC AND POLAR 91 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves Example 1. Return to the parametric equations in Example 2 from the previous section: x t + sin() y t + cos() (a) Find the Cartesian
CHAPTER 1. PARAMETRIC AND POLAR 91 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves Example 1. Return to the parametric equations in Example 2 from the previous section: x t + sin() y t + cos() (a) Find the Cartesian
MATH 417 Homework 8 Instructor: D. Cabrera Due August 4. e i(2z) (z 2 +1) 2 C R. z 1 C 1. 2 (z 2 + 1) dz 2. φ(z) = ei(2z) (z i) 2
 MATH 47 Homework 8 Instructor: D. abrera Due August 4. ompute the improper integral cos x (x + ) dx Solution: To evaluate the integral consider the complex integral e i(z) (z + ) dz where is the union
MATH 47 Homework 8 Instructor: D. abrera Due August 4. ompute the improper integral cos x (x + ) dx Solution: To evaluate the integral consider the complex integral e i(z) (z + ) dz where is the union
