Motion Detection and Projection Based Block Motion Estimation Using the Radon Transform for Video Coding
|
|
|
- Alexandra Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Computer Science 6 (9): , 2010 ISSN Science Publications Motion Detection and Projection Based Block Motion Estimation Using the Radon Transform for Video Coding 1 Shilpa P. Metkar and 2 Sanjay N. Talbar 1 Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, College of Engineering, An Autonomous Institute of Government of Maharashtra, Pune, India 2 Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, S.G.G.S. Institute of Engineering and Technology, Nanded, Maharashtra, India Abstract: Problem statement: Motion estimation and compensation is the most computationally complex module of video coder. In this study, an innovative algorithm was proposed for a further complexity reduction of the Motion Estimation (ME) module of video coder by employing motion detection prior to motion compensation. Approach: A Motion Detection (MD) module can be added to the video coder in order to decide whether the current block contains motion or is with zero motion. This study propounded a MD module that depends on motion activity. Generally, the correlation of the two consecutive frames is a good criterion to measure motion activity. We applied the correlation as a threshold to detect the motion activity. To assure the correct motion vector and thus better video quality, to calculate motion vector of motion blocks this study also proposed a new block matching motion estimation criterion based on the Radon transform using projection-matching method. However, computationally complex, the method had the ability to be implemented in real time by using pipeline architecture. Results: A comparative result showed that the MD module reduced the number of search points for motion estimation and compared with some well-known algorithm that uses minimum absolute difference criterion, the new criterion can provide much higher performance. Conclusion: The result showed that this proposed scheme can simplify the encoder complexity maintaining good video quality. Key words: Motion detection, block motion estimation, radon transform INTRODUCTION The wide range of multimedia applications based on video compression (video telephony, video surveillance, digital television) leads to different kind of requirements for a video coding standard (image quality, compression efficiency). Several multimedia application areas require high power efficiency (especially in the video encoder part) in order to work on embedded systems and mobile terminals (Paul et al., 2005; Richardson, 2002). This requirement implies the need to dramatically reduce the complexity of the video encoder. Algorithmic analysis shows that motion estimation is the most complex module in the video encoder. This is mainly due to the great number of calculation in motion estimation. Having this in mind, the present study postulates motion detection for fast and efficient video coding (Bailo et al., 2006). Many algorithms are suggested in the literature to reduce the number of calculation intended for motion estimation based on spatial and temporal correlation of motion vector (Nakaya and Harashima, 1994; Korada and Krishna, 2001; Nam et al., 2000a). We suggest motion detection method to separate out an active region and an inactive region within a frame. A novel reduced complexity motion detection technique is presented in this study. It is based on segmenting the current frame in to blocks containing moving objects (an active region) and stationary background (an inactive region). The inactive region is assumed with zero motion vectors. It has been experimentally proved that about 75% of the total blocks within frame corresponds to stationary background and that can be considered with zero motion vector. The early detection of blocks with zero motion vector leads to significant redundant computation being skipped and thus speed up the coding of video sequence. In this study more precise threshold value is proposed to decide motion activity of Corresponding Author: Shilpa P. Metkar, Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, College of Engineering, Pune An Autonomous Institute of Government of Maharashtra, India 979
2 a block. The threshold value is derived from the concept of correlation and no assumption is adopted, ensuring that video quality is not degraded. And for the motion vector estimation of an active region a new feature based bock matching criterion using the concept of projections that is built by the radon transform is presented in this study. Various matching criterion were presented in the literature for motion vector estimation. In order to reduce the computational effort, a sub sampling scheme was performed in (Bierling, 1988). Only every second pixel is taken into account for estimation of distortion in both horizontal and vertical directions and the computational burden is reduced by a factor of four. Aliasing effects can be avoided by lowpass filtering. In (Zaccarin and Liu, 1992; Liu and Zaccarin, 1993), periodic alternation of four subsampling patterns was adopted on different search positions to solve the aliasing without filtering. Adaptive pixel-decimation scheme was further proposed in (Wang et al., 2000). It does not require an initial division of a block and selects pixels only when they have the features important in determining a match. Pixel Difference Classification (PDC) (Gharavi and Mills, 1990) is to threshold every pixel absolute difference and classifies it into match or mismatch. The best candidate block has the highest number of match pixels. However, the threshold value affects the quality a lot and is not easy to be decided automatically. Minimax criterion (Chen et al., 1995) finds the maximum error among all pixels in a candidate block and then chooses the final MV by minimizing the maximum errors of all candidate blocks. Boundary match (Chen, 1997) is also a simplified matching criterion. Moreover, it is often adopted for error concealment from loss of motion vectors. The concept of integral projection was introduced in (Kim and Park, 1992; Sauer and Schwartz, 1996). For simple translational motion, the information on the axes in the Fourier transform domain is sufficient to estimate motion between two images. Computing the horizontal and vertical frequency information is equivalent to discrete approximation as integral projections at these two orientations. The simple equivalence between shifts in integral projection measurements and shifts in the corresponding segments of images suggests the comparison of integral projections as a computationally efficient technique for block matching estimation since the pair of horizontal and vertical projections contain fewer data than the pixels in a candidate block. The sum of absolute difference and mean square error matching criterion involves all pixels in the current block and the candidate block and it does not consider orientation of pixel in different directions hence it fails J. Computer Sci., 6 (9): , to find the best match using only pixel differences. Structural information plays important role for image quality. In this study, structural information is modeled as the energy of directional projections using the radon transform. Block distortion could be modeled as the difference between the directional projections of reference and current bock. MATERIALS AND METHODS Motion detection: Motion detection is carried out prior to motion estimation to avoid the heavy computational overhead. This study recommends a simple method for motion detection based on correlation. Calculate the correlation of the frame as: cor = M N i= 1 j= 1 [A(i, j) A][B(i, j) B] M N M N 2 [A(i, j) A] [B(i, j) B)] i= 1 j= 1 i= 1 j= 1 2 (1) Where: A = Denotes the reference frame B = Denotes the current frame M N = The frame size A, B = The mean of the reference and current frame respectively cor = The threshold value An input frame is partitioned into blocks of p q pixels and then the local correlation of p q block is premeditated by: corb = p q i= 1 j= 1 [A(i, j) A ][B(i, j) B ] p q p q 2 b i= 1 j= 1 i= 1 j= 1 b [A(i, j) A ] [B(i, j) B )] b b 2 (2) where, A b and B b denotes the mean of the block difference of current and reference frame respectively. There is comparisons made between corb and threshold cor to classify the block under consideration as a part of moving objects (active region) or as part of stationary back ground (inactive region). If corb<cor, the block is a part of moving objects and if corb>cor the block is a part of stationary background and is considered with zero motion vector. The motion activity is not constant over the entire frame of an image sequence thus the block correlation (threshold), is not taken as a constant value but it is locally calculated. Figure 1a and b shows the two successive frames of News sequence, Fig. 1d and e shows two successive frames of Silent sequence and Fig. 1g and h shows two successive frames of Claire sequence.
3 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) Fig. 1: Performance of motion detection method: For news sequence; (a) 65th frame; (b) 66th frame; (c) active region, For Silent sequence; (d) 60th frame; (e) 61st frame; (f) active region and for Claire sequence; (g) 60th frame; (h) 61st frame; (i) active region Figure 1c, f and i depicts the motion detected region obtained by the motion detection algorithm. It is apparent that, approximately 25% of the frame area is detected as an active region. Remaining 75% frame area is found as an inactive region. The inactive region is consider with zero motion vectors. Thus we can save intense computations involved in finding motion vectors. Only active region will be consider for motion estimation The proposed criterion: In general way, an image may be segmented into two kinds of areas: Structure and 981 texture and especially between them, structural information plays a more important role. Natural images are of much structure that carries important information about the objects structure for the visual scene (Wng et al., 2004). The pixels, edges and shape with directional characteristics contribute a lot to the structural information. The distortion of the structural information could be modeled as the alteration of the directional characteristics. In this study we try to use a directional projections vector to present the directional characteristics built by the Radon transform (Deans, 1983).
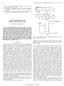
4 So the general equation of the Radon transformation is acquired (Deans, 1983): ( ) g (s, θ ) = R θ [f x, y ] g(s, θ ) = f (x, y). δ(x cosθ + ysin θ s)dxdy (5) Fig. 2: The radon transform computation The radon transform: Firstly the Radon Transform is introduced before we begin the discussion of the use of projections in motion estimation. The 2D Radon transformation is the projection of the image intensity along a radial line oriented at a specific angle (Deans, 1983). Suppose a 2-D function f(x, y) as shown in Fig. 2. Integrating along the line, whose normal vector is in θ direction, results in the g(s, θ) function, which is the projection of the 2D function f(x, y) on the axis s of θ direction. When s is zero, the g function has the value g(0, θ) which is obtained by the integration along the line passing the origin of (x, y)-coordinate. The points on the line whose normal vector is in θ direction and passes the origin of (x, y)-coordinate satisfy the equation: y π cosθ = tan( θ + ) = x cos θ + ysin θ = 0 x 2 sin θ The integration along the line whose normal vector is in θ direction and that passes the origin of (x, y)- coordinate means the integration of f(x, y) only at the points satisfying the previous equation. With the help of the Dirac functionδ, which is zero for every argument except to 0 and its integral is one, g(0, θ) is expressed as: g(0, θ ) = f (x, y). δ(x cosθ + ysin θ)dxdy (3) Similarly, the line with normal vector in θ direction and distance s from the origin is satisfying the following equation: (x s cos θ) cos θ + (y s sin θ) sin θ = 0 x cosθ + ysin θ s = 0 We note here that while the above definition represents the model for the Radon transform of a continuous image, we will in practice use a discrete version of the Radon transform. Very early works such as (Alliney and Morandi, 1986) use image projections at 0 and 90 to register translated images using a relative phase approach. In these works, the projections used to estimate translational motion were confined to 0 and 90. Similarly, in (Cain et al., 2001) the authors use correlation between pairs of image projections at 0 and 90 to again register translated images. The above methods have not addressed the performance issues concerning the application of projections in estimating motion vectors. The present study justifies the use of projections based on the Radon transform to estimate the motion vectors. Radon Projection Matching (RPM) criterion for block motion estimation: To understand how to estimate motion parameters indirectly using projections, we must first explore the relationship between motion in the original image sequence and the induced motion or transformation in the projections. We begin our analysis for the simple case of translational motion which is completely characterized by the shift vector v r 0. The simple relationship known as the shift property of the Radon transform (Gharavi and Mills, 1990), relates motion in images to the motion in projections by: r R θ[f (x v, y v )] = g(s w, θ ) = g(s u ( θ), θ) (4) the proposed criterion. 982 r v T 0x 0y 0 0 (6) r T where, w = [cos( θ),sin( θ)] is a unit direction vector. Intuitively, each projection at angle θ sees the component of the vector v r 0 in the direction of the vector w r. Thus, a pure translation or shift given by v r 0 in the image domain results in a corresponding shift in T the projection given by v r u ( θ ) = w. This property of v 0 0 the Radon transform is being utilized in defining the new criterion for block motion estimation. The current and reference image is divided into small blocks with the block size M N. The following steps describe the steps to compute
5 Step 1: Compute the projections of the n th current (B C ) and reference frame (B R ) block using the Radon transform: P = R [B ] (7) nc nr θ C P = R [B ] (8) θ R where, P nc and P nr are the directional projection vectors corresponding to θ. Step 2: The distortion is calculated as: Dn = PnC PnR (9) Step 3: Reference block with minimum distortion is consider as the best matched block this specifies the motion vector for the current block. In this study we build the directional projection vectors of the blocks based on the Radon transform. The difference of the projection vector represents the distortion. The lower the value of the distortion better the match is. In Eq. 5 there are two parameters s and θ. θ is varied to achieve scalable efficiency and computational cost. Owing to find out the projections at different angles the RPM criterion is computationally complex. But Sanz (1988) have shown that the Radon transform is suitable for being implemented in a powerful and flexible pipeline architecture that they call a Parallel Pipeline Projection Engine. Moreover, as the projection considers the pixel orientation within block in different directions the RPM assures the accurate motion vector. The projected criterion can be used along with any conventional block-matching algorithm to find the motion vector. are the most popular motion estimation methods, which are adopted by various video coding standards such as MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 due to their less computational complexity (Zhu and Ma, 2000; ISO/IEC , 1995). One of the first algorithms to be used for block based motion estimation is Full Search Algorithm (FSA) or Exhaustive Search Algorithm (ESA), which evaluates the Block Distortion Measure (BDM) function at every possible pixel locations in the search area (Jain and Jain, 1981). Although this algorithm is the best in terms of quality of the predicted frame and simplicity, it is computationally intensive. In the past two decades, several fast search methods for motion estimation have been introduced to reduce the computational complexity of block matching, for examples, two dimensional Logarithmic Search (LOGS) (Nam et al., 2000b), three-step Search (3SS) (Koga et al., 1981), four Step Search (4SS) (Lai-Man and Wing-Chung, 1996), Modified Orthogonal Search Algorithm (MOSA) (Metkar and Talbar, 2009). Among these algorithms, 3SS becomes most popular one for low bit rate application owing to its simplicity and effectiveness The three-step Search algorithm (3SS) is proposed by Koga et al. (1981). This algorithm is based on a coarse-to-fine approach with logarithmic decreasing in step size as shown in Fig. 3. The initial step size is half of the maximum motion displacement d. For each step, nine checking points are matched and the minimum BDM point of that step is chosen as the starting center of the next step. The three Step Search algorithm (3SS) tests eight points around the center. For a center [cx,cy] and step size d, all the eight positions [cx-d, cy-d ], [cx-d, cy], [cx-d, cy+d], [cx, cy-d], [cx, cy], [cx, cy+d], [cx+d, cy-d], [cx+d, cy], [cx+d, cy+d] are examined. Motion estimation: The proposed motion detection module is utilized to find the active region of motion. Motion detection decides whether to subject the block for the motion vector estimation or block is consider with zero motion vector. The complexity of the video coder is strongly influenced by the number of calculations required to find motion vector. Consequently by reducing the number of blocks for motion estimation can save a measurable time in the encoder process with minor effects on the quality of the produced video sequence. Block matching algorithms Fig. 3: Search pattern used in the first step of 3SS 983
6 After each stage the step size is halved and minimum distortion of that stage is chosen as the starting center of the next stage. The procedure continues till the step size becomes one. The number of checking points required equals to [1+ log (d+1) ]. The proposed study suggests three-step search algorithm with Radon Projection Matching (RPM) criterion for motion vector estimation of active region blocks. RESULTS The test sequences used in the experimental results are the seven standard QCIF ( ) videos (100 frames) of Foreman, Carphone, Silent, News, Grandma, Miss America and Salesman defining different motion content. We had selected block size as 8 8 as a tradeoff between computational complexity and the quality of the image. Out of total 396 blocks, Table 1 list the average number of inactive blocks detected by the motion detection module. It is not essential to execute motion estimation and compensation for all these blocks. These blocks are considered with zero motion vectors. As a result, numerous unnecessary calculations required for motion estimation of these blocks are saved. To find the motion vectors of the blocks in the active region the study tested the result of the projected method by adopting standard three Step Search (3SS) algorithm. The computational complexity of the different techniques in terms of average number of search points is shown in Table 2. We can observe the measurable difference in number of search points required by the MD technique as compared to the full search techniques. The Signal-to Noise Ratio (SNR) of the reconstructed image with the original image is used as a quality measure to compare the performance of the mentioned Radon projection-matching criterion with that of the corresponding mean absolute difference criterion. Table 3 indicates the prediction performance for the conventional block-matching algorithms and proposed Motion Detection+3SS (MD+3SS) algorithm using MAD and RPM criterion. A set of experiments have been done to compare the performance of proposed Radon projection matching criterion and well known mean absolute difference criterion for motion vector calculations. In our experiment for RPM we calculate the distortion for θ = 0, θ = 45 and θ = 90. The proposed RPM criterion has better SNR performance than MAD criterion as indicated in Table 3. However, RPM has a more computational complexity as compared with MAD. To compare the computational complexity of the proposed approach of RPM for different algorithms the average time in seconds to process entire sequence is reported in Fig. 4. DISCUSSION For MAD criterion, Table 3 indicates that the performance of the proposed MD+3SS method degrades for the sequence of high motion content like Foreman, News and Salesman. Where as the proposed technique shows good performance for the sequence of moderate to slow motion sequences. It is seen that quality of the presented technique is close to the standard methods as FSA and 3SS with much more reduced complexity. Table 1: Average number of inactive blocks for different video sequences detected by MD technique Foreman Carphone Silent News Grandma Miss America Salesman Table 2: Average search points for different algorithms and different sequences BMA Foreman Carphone Silent News Grandma Miss America Salesman FSA SS MD+3SS Table 3: Average snr for different video sequences for MAD and RPM criterion FSA 3SS MD+3SS Algorithms Criterion Criterion Criterion Sequences MAD RPM MAD RPM MAD RPM Foreman Carphone Silent News Grandma Miss America Salesman
7 Fig. 4: Computational complexity of RPM for different algorithms As seen in Fig. 4 the processing time of the FSA is extremely high for all benchmark sequences. For MD+3SS less time is required for Silent and Grandma Sequences as compared to 3SS. As these are sow motion sequences and most of the blocks are being categorized as Type 1 blocks and we can save intense computations required for motion vector estimation for these blocks. Where as time required for the proposed algorithm is more as compared to 3SS for Carphone, News and Foreman sequence as these are high motion sequence and most of the blocks are categorized as active blocks by MD module and hence require more time to process active blocks using the RPM block matching criterion. CONCLUSION Thus to conclude, this study propounds the motion detection technique which is presented and tested on a set of sequences. MD is an innovative method for motion estimation complexity reduction based on active motion detection. A classifier based on the frame correlation has been employed to detect active and inactive blocks. Additionally the threshold value in the algorithm is calculated automatically, which avoids user interaction. It has been experimentally proved that the majorities of the blocks within a frame are inactive and can be taken with zero motion vectors. As a result we saved measurable computational time required for motion vector estimation for these blocks. This study also introduced an efficient approach to block motion estimation using the Radon transform. Our criterion appears to compare favorably with existing MAD criterion with increase in computational complexity. We can avail the advantage of RPM by combining it with motion detection approach and compensate for the J. Computer Sci., 6 (9): , computational complexity. It should be noted that the projected criterion performs well for most of the video sequences and can be used with any conventional block-matching algorithm. REFERENCES Alliney, S. and C. Morandi, Digital image registration using projections. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intel., 8: Bailo, G., M. Bariani, A. Chiappori and F. Sguanci, H.264 search window size algorithm for fast and efficient video coding with single pixel precision and no background estimation for motion detection. Proceeding of the 3rd IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, Jan. 8-10, IEEE Xplore Press, USA., pp: Bierling, M., Displacement estimation by hierarchical block matching. Proceeding of SPIE Visual Commun. Image Process., 1001: Cain, S.C., M.M. Hayat and E.E. Armstrong, Projection-based image registration in the presence of fixed-pattern noise. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 10: Chen, M.J., Predictive motion estimation algorithms for video compression. J. St. John s St. Mary Inst. Technol., 15: Chen, M.J., L.G. Chen, T.D. Chiueh and Y.P. Lee, A new block-matching criterion for motion estimation and its implementation. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 5: Deans, S.R., The Radon Transform and Some of its Applications. Dover Publications, USA., ISBN: , pp: 304. Gharavi, H. and M. Mills, Block matching motion estimation algorithm-new results. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst., 37: ISO/IEC , Information technologygeneric coding of moving pictures and associated audio information: Video. ISO/IEC. Jain, J. and A. Jain, Displacement measurement and its application in interframe image coding. IEEE Trans. Commun., COM-29: Kim, J.S. and R.H. Park, A Fast feature-based block matching algorithm using integral projections. IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun., 10: Koga, T., K. Iinuma, A. Hirano, Y. Iijima and T. Ishiguro, Motion compensated interframe coding for video conferencing. Proceeding of the National Telecommunication Conference, Dec. 1981, New Orleans, LA., pp: G5.3.1-G5.3.5.
8 Korada, R. and S. Krishna, Spatio-temporal correlation based fast motion estimation algorithm for MPEG-2. Proceeding of the 35th IEEE Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, (SSC 01), IEEE Computer Society, California, pp: Lai-Man, P. and M. Wing-Chung, A novel fourstep search algorithm for fast block motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 6: Metkar, S.P. and S.N. Talbar, Fast motion estimation using modified orthogonal search algorithm for video compression. Signal Image Video Process., 4: DOI: /s Liu, B. and A. Zaccarin, New fast algorithms for the estimation of block motion vectors. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 3: Nakaya, Y. and H. Harashima, Motion compensation based on spatial transformations. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 4: Nam, J.Y., J.S. Seo, J.S. Kwak, M.H. Lee and H.H. Yeong, 2000a. New fast-search algorithm for block matching motion estimation using temporal and spatial correlation of motion vector. IEEE Trans. Consumer Elect., 46: Nam, J.Y., J.S. Seo, J.S. Kwak, M.H. Lee and H.H. Yeong, 2000b. New fast-search algorithm for block matching motion estimation using temporal and spatial correlation of motion vector. IEEE Trans. Consum. Elect., 46: Paul, M., M. Murshed and L. Dooley, A real time pattern selection algorithm for very low bit-rate video coding using relevance and similarity metrics. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 15: Richardson, I.E.G., Video Codec Design. Wiley, New York, ISBN: , pp: 299. Sanz, J.L.C., Radon and Projection Transform- Based Computer Vision: Algorithm, A Pipeline Architecture and Industrial Applications. Springer- Verlog, New York, ISBN: 10: , pp: 123. Sauer, K. and B. Schwartz, Efficient block motion estimation using integral projections. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 6: Wang, Y., Y. Wang and H. Kuroda, A globally adaptive pixel decimation algorithm for blockmotion estimation. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol., 10: Wng, Z., A.C. Bovik, H.R. Sheikh and E.P. Simoncelli, Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 13: Zaccarin, A. and B. Liu, Fast algorithms for block motion estimation. Proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Mar , IEEE Computers Society, San Francisco, CA., USA., pp: DOI: /ICASSP Zhu, S. and K.K. Ma, A new diamond search algorithm for fast block matching motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 9:
A New Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm. - Literature Survey. Instructor: Brian L. Evans. Authors: Yue Chen, Yu Wang, Ying Lu.
 A New Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm - Literature Survey Instructor: Brian L. Evans Authors: Yue Chen, Yu Wang, Ying Lu Date: 10/19/1998 A New Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm 1. Abstract Video compression
A New Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm - Literature Survey Instructor: Brian L. Evans Authors: Yue Chen, Yu Wang, Ying Lu Date: 10/19/1998 A New Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm 1. Abstract Video compression
Fobe Algorithm for Video Processing Applications
 Fobe Algorithm for Video Processing Applications Christo Ananth 1, A.Sujitha Nandhini 2, A.Subha Shree 3, S.V.Ramyaa 4, J.Princess 5 Assistant Professor, Dept. Of ECE, Francis Xavier Engineering College,
Fobe Algorithm for Video Processing Applications Christo Ananth 1, A.Sujitha Nandhini 2, A.Subha Shree 3, S.V.Ramyaa 4, J.Princess 5 Assistant Professor, Dept. Of ECE, Francis Xavier Engineering College,
Enhanced Hexagon with Early Termination Algorithm for Motion estimation
 Volume No - 5, Issue No - 1, January, 2017 Enhanced Hexagon with Early Termination Algorithm for Motion estimation Neethu Susan Idiculay Assistant Professor, Department of Applied Electronics & Instrumentation,
Volume No - 5, Issue No - 1, January, 2017 Enhanced Hexagon with Early Termination Algorithm for Motion estimation Neethu Susan Idiculay Assistant Professor, Department of Applied Electronics & Instrumentation,
Motion Vector Estimation Search using Hexagon-Diamond Pattern for Video Sequences, Grid Point and Block-Based
 Motion Vector Estimation Search using Hexagon-Diamond Pattern for Video Sequences, Grid Point and Block-Based S. S. S. Ranjit, S. K. Subramaniam, S. I. Md Salim Faculty of Electronics and Computer Engineering,
Motion Vector Estimation Search using Hexagon-Diamond Pattern for Video Sequences, Grid Point and Block-Based S. S. S. Ranjit, S. K. Subramaniam, S. I. Md Salim Faculty of Electronics and Computer Engineering,
An Adaptive Cross Search Algorithm for Block Matching Motion Estimation
 An Adaptive Cross Search Algorithm for Block Matching Motion Estimation Jiancong Luo', Ishfaq Ahmad' and Xzhang Luo' 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington,
An Adaptive Cross Search Algorithm for Block Matching Motion Estimation Jiancong Luo', Ishfaq Ahmad' and Xzhang Luo' 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington,
Efficient Block Matching Algorithm for Motion Estimation
 Efficient Block Matching Algorithm for Motion Estimation Zong Chen International Science Inde Computer and Information Engineering waset.org/publication/1581 Abstract Motion estimation is a key problem
Efficient Block Matching Algorithm for Motion Estimation Zong Chen International Science Inde Computer and Information Engineering waset.org/publication/1581 Abstract Motion estimation is a key problem
Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards
 Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Introduction of Motion Estimation The goal of video compression
Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Introduction of Motion Estimation The goal of video compression
A High Quality/Low Computational Cost Technique for Block Matching Motion Estimation
 A High Quality/Low Computational Cost Technique for Block Matching Motion Estimation S. López, G.M. Callicó, J.F. López and R. Sarmiento Research Institute for Applied Microelectronics (IUMA) Department
A High Quality/Low Computational Cost Technique for Block Matching Motion Estimation S. López, G.M. Callicó, J.F. López and R. Sarmiento Research Institute for Applied Microelectronics (IUMA) Department
AN ADJUSTABLE BLOCK MOTION ESTIMATION ALGORITHM BY MULTIPATH SEARCH
 AN ADJUSTABLE BLOCK MOTION ESTIMATION ALGORITHM BY MULTIPATH SEARCH Thou-Ho (Chou-Ho) Chen Department of Electronic Engineering, National Kaohsiung University of Applied Sciences thouho@cc.kuas.edu.tw
AN ADJUSTABLE BLOCK MOTION ESTIMATION ALGORITHM BY MULTIPATH SEARCH Thou-Ho (Chou-Ho) Chen Department of Electronic Engineering, National Kaohsiung University of Applied Sciences thouho@cc.kuas.edu.tw
Express Letters. A Simple and Efficient Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation. Jianhua Lu and Ming L. Liou
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 2, APRIL 1997 429 Express Letters A Simple and Efficient Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation Jianhua Lu and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 2, APRIL 1997 429 Express Letters A Simple and Efficient Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation Jianhua Lu and
Prediction-based Directional Search for Fast Block-Matching Motion Estimation
 Prediction-based Directional Search for Fast Block-Matching Motion Estimation Binh P. Nguyen School of Information and Communication Technology, Hanoi University of Technology, Vietnam binhnp@it-hut.edu.vn
Prediction-based Directional Search for Fast Block-Matching Motion Estimation Binh P. Nguyen School of Information and Communication Technology, Hanoi University of Technology, Vietnam binhnp@it-hut.edu.vn
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 7, July-2014 25 A Study on Block Matching Algorithms for Motion Estimation in Video Coding L.C.Manikandan, Dr.R.K.Selvakumar,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 7, July-2014 25 A Study on Block Matching Algorithms for Motion Estimation in Video Coding L.C.Manikandan, Dr.R.K.Selvakumar,
Fast Decision of Block size, Prediction Mode and Intra Block for H.264 Intra Prediction EE Gaurav Hansda
 Fast Decision of Block size, Prediction Mode and Intra Block for H.264 Intra Prediction EE 5359 Gaurav Hansda 1000721849 gaurav.hansda@mavs.uta.edu Outline Introduction to H.264 Current algorithms for
Fast Decision of Block size, Prediction Mode and Intra Block for H.264 Intra Prediction EE 5359 Gaurav Hansda 1000721849 gaurav.hansda@mavs.uta.edu Outline Introduction to H.264 Current algorithms for
Fast Motion Estimation for Shape Coding in MPEG-4
 358 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 13, NO. 4, APRIL 2003 Fast Motion Estimation for Shape Coding in MPEG-4 Donghoon Yu, Sung Kyu Jang, and Jong Beom Ra Abstract Effective
358 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 13, NO. 4, APRIL 2003 Fast Motion Estimation for Shape Coding in MPEG-4 Donghoon Yu, Sung Kyu Jang, and Jong Beom Ra Abstract Effective
Module 7 VIDEO CODING AND MOTION ESTIMATION
 Module 7 VIDEO CODING AND MOTION ESTIMATION Lesson 22 Other fast search motion estimation algorithms At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. Provide an overview of the following fast
Module 7 VIDEO CODING AND MOTION ESTIMATION Lesson 22 Other fast search motion estimation algorithms At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. Provide an overview of the following fast
Toward Optimal Pixel Decimation Patterns for Block Matching in Motion Estimation
 th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communications Toward Optimal Pixel Decimation Patterns for Block Matching in Motion Estimation Avishek Saha Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communications Toward Optimal Pixel Decimation Patterns for Block Matching in Motion Estimation Avishek Saha Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Redundancy and Correlation: Temporal
 Redundancy and Correlation: Temporal Mother and Daughter CIF 352 x 288 Frame 60 Frame 61 Time Copyright 2007 by Lina J. Karam 1 Motion Estimation and Compensation Video is a sequence of frames (images)
Redundancy and Correlation: Temporal Mother and Daughter CIF 352 x 288 Frame 60 Frame 61 Time Copyright 2007 by Lina J. Karam 1 Motion Estimation and Compensation Video is a sequence of frames (images)
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering Website: (ISSN , Volume 2, Issue 4, April 2012)
 A Technical Analysis Towards Digital Video Compression Rutika Joshi 1, Rajesh Rai 2, Rajesh Nema 3 1 Student, Electronics and Communication Department, NIIST College, Bhopal, 2,3 Prof., Electronics and
A Technical Analysis Towards Digital Video Compression Rutika Joshi 1, Rajesh Rai 2, Rajesh Nema 3 1 Student, Electronics and Communication Department, NIIST College, Bhopal, 2,3 Prof., Electronics and
A Low Bit-Rate Video Codec Based on Two-Dimensional Mesh Motion Compensation with Adaptive Interpolation
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 11, NO. 1, JANUARY 2001 111 A Low Bit-Rate Video Codec Based on Two-Dimensional Mesh Motion Compensation with Adaptive Interpolation
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 11, NO. 1, JANUARY 2001 111 A Low Bit-Rate Video Codec Based on Two-Dimensional Mesh Motion Compensation with Adaptive Interpolation
Video Compression System for Online Usage Using DCT 1 S.B. Midhun Kumar, 2 Mr.A.Jayakumar M.E 1 UG Student, 2 Associate Professor
 Video Compression System for Online Usage Using DCT 1 S.B. Midhun Kumar, 2 Mr.A.Jayakumar M.E 1 UG Student, 2 Associate Professor Department Electronics and Communication Engineering IFET College of Engineering
Video Compression System for Online Usage Using DCT 1 S.B. Midhun Kumar, 2 Mr.A.Jayakumar M.E 1 UG Student, 2 Associate Professor Department Electronics and Communication Engineering IFET College of Engineering
Semi-Hierarchical Based Motion Estimation Algorithm for the Dirac Video Encoder
 Semi-Hierarchical Based Motion Estimation Algorithm for the Dirac Video Encoder M. TUN, K. K. LOO, J. COSMAS School of Engineering and Design Brunel University Kingston Lane, Uxbridge, UB8 3PH UNITED KINGDOM
Semi-Hierarchical Based Motion Estimation Algorithm for the Dirac Video Encoder M. TUN, K. K. LOO, J. COSMAS School of Engineering and Design Brunel University Kingston Lane, Uxbridge, UB8 3PH UNITED KINGDOM
Complexity Reduced Mode Selection of H.264/AVC Intra Coding
 Complexity Reduced Mode Selection of H.264/AVC Intra Coding Mohammed Golam Sarwer 1,2, Lai-Man Po 1, Jonathan Wu 2 1 Department of Electronic Engineering City University of Hong Kong Kowloon, Hong Kong
Complexity Reduced Mode Selection of H.264/AVC Intra Coding Mohammed Golam Sarwer 1,2, Lai-Man Po 1, Jonathan Wu 2 1 Department of Electronic Engineering City University of Hong Kong Kowloon, Hong Kong
FAST MOTION ESTIMATION WITH DUAL SEARCH WINDOW FOR STEREO 3D VIDEO ENCODING
 FAST MOTION ESTIMATION WITH DUAL SEARCH WINDOW FOR STEREO 3D VIDEO ENCODING 1 Michal Joachimiak, 2 Kemal Ugur 1 Dept. of Signal Processing, Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland 2 Jani Lainema,
FAST MOTION ESTIMATION WITH DUAL SEARCH WINDOW FOR STEREO 3D VIDEO ENCODING 1 Michal Joachimiak, 2 Kemal Ugur 1 Dept. of Signal Processing, Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland 2 Jani Lainema,
Context based optimal shape coding
 IEEE Signal Processing Society 1999 Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing September 13-15, 1999, Copenhagen, Denmark Electronic Proceedings 1999 IEEE Context based optimal shape coding Gerry Melnikov,
IEEE Signal Processing Society 1999 Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing September 13-15, 1999, Copenhagen, Denmark Electronic Proceedings 1999 IEEE Context based optimal shape coding Gerry Melnikov,
Multimedia Systems Video II (Video Coding) Mahdi Amiri April 2012 Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Video II (Video Coding) Mahdi Amiri April 2012 Sharif University of Technology Video Coding Correlation in Video Sequence Spatial correlation Similar pixels seem
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Video II (Video Coding) Mahdi Amiri April 2012 Sharif University of Technology Video Coding Correlation in Video Sequence Spatial correlation Similar pixels seem
Area Efficient SAD Architecture for Block Based Video Compression Standards
 IJCAES ISSN: 2231-4946 Volume III, Special Issue, August 2013 International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences Special Issue on National Conference on Information and Communication
IJCAES ISSN: 2231-4946 Volume III, Special Issue, August 2013 International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences Special Issue on National Conference on Information and Communication
A Study on Block Matching Algorithms for Motion Estimation
 A Study on Block Matching Algorithms for Motion Estimation S. Immanuel Alex Pandian Asst. Prof., Dept. of ECE, Dr.G. Josemin Bala Prof & Head, Dept.of EMT, Karunya University, Coimbatore,India. Becky Alma
A Study on Block Matching Algorithms for Motion Estimation S. Immanuel Alex Pandian Asst. Prof., Dept. of ECE, Dr.G. Josemin Bala Prof & Head, Dept.of EMT, Karunya University, Coimbatore,India. Becky Alma
Comparative Study of Partial Closed-loop Versus Open-loop Motion Estimation for Coding of HDTV
 Comparative Study of Partial Closed-loop Versus Open-loop Motion Estimation for Coding of HDTV Jeffrey S. McVeigh 1 and Siu-Wai Wu 2 1 Carnegie Mellon University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Comparative Study of Partial Closed-loop Versus Open-loop Motion Estimation for Coding of HDTV Jeffrey S. McVeigh 1 and Siu-Wai Wu 2 1 Carnegie Mellon University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Star Diamond-Diamond Search Block Matching Motion Estimation Algorithm for H.264/AVC Video Codec
 Star Diamond-Diamond Search Block Matching Motion Estimation Algorithm for H.264/AVC Video Codec Satish Kumar Sahu 1* and Dolley Shukla 2 Electronics Telecommunication Department, SSTC, SSGI, FET, Junwani,
Star Diamond-Diamond Search Block Matching Motion Estimation Algorithm for H.264/AVC Video Codec Satish Kumar Sahu 1* and Dolley Shukla 2 Electronics Telecommunication Department, SSTC, SSGI, FET, Junwani,
Pattern based Residual Coding for H.264 Encoder *
 Pattern based Residual Coding for H.264 Encoder * Manoranjan Paul and Manzur Murshed Gippsland School of Information Technology, Monash University, Churchill, Vic-3842, Australia E-mail: {Manoranjan.paul,
Pattern based Residual Coding for H.264 Encoder * Manoranjan Paul and Manzur Murshed Gippsland School of Information Technology, Monash University, Churchill, Vic-3842, Australia E-mail: {Manoranjan.paul,
Image Quality Assessment Techniques: An Overview
 Image Quality Assessment Techniques: An Overview Shruti Sonawane A. M. Deshpande Department of E&TC Department of E&TC TSSM s BSCOER, Pune, TSSM s BSCOER, Pune, Pune University, Maharashtra, India Pune
Image Quality Assessment Techniques: An Overview Shruti Sonawane A. M. Deshpande Department of E&TC Department of E&TC TSSM s BSCOER, Pune, TSSM s BSCOER, Pune, Pune University, Maharashtra, India Pune
Motion estimation for video compression
 Motion estimation for video compression Blockmatching Search strategies for block matching Block comparison speedups Hierarchical blockmatching Sub-pixel accuracy Motion estimation no. 1 Block-matching
Motion estimation for video compression Blockmatching Search strategies for block matching Block comparison speedups Hierarchical blockmatching Sub-pixel accuracy Motion estimation no. 1 Block-matching
Video Compression An Introduction
 Video Compression An Introduction The increasing demand to incorporate video data into telecommunications services, the corporate environment, the entertainment industry, and even at home has made digital
Video Compression An Introduction The increasing demand to incorporate video data into telecommunications services, the corporate environment, the entertainment industry, and even at home has made digital
Improving Energy Efficiency of Block-Matching Motion Estimation Using Dynamic Partial Reconfiguration
 , pp.517-521 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.1 Improving Energy Efficiency of Block-Matching Motion Estimation Using Dynamic Partial Reconfiguration Jooheung Lee 1 and Jungwon Cho 2, * 1 Dept. of
, pp.517-521 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.1 Improving Energy Efficiency of Block-Matching Motion Estimation Using Dynamic Partial Reconfiguration Jooheung Lee 1 and Jungwon Cho 2, * 1 Dept. of
DIGITAL TELEVISION 1. DIGITAL VIDEO FUNDAMENTALS
 DIGITAL TELEVISION 1. DIGITAL VIDEO FUNDAMENTALS Television services in Europe currently broadcast video at a frame rate of 25 Hz. Each frame consists of two interlaced fields, giving a field rate of 50
DIGITAL TELEVISION 1. DIGITAL VIDEO FUNDAMENTALS Television services in Europe currently broadcast video at a frame rate of 25 Hz. Each frame consists of two interlaced fields, giving a field rate of 50
Reduced 4x4 Block Intra Prediction Modes using Directional Similarity in H.264/AVC
 Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Multimedia, Internet & Video Technologies, Beijing, China, September 15-17, 2007 198 Reduced 4x4 Block Intra Prediction Modes using Directional
Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Multimedia, Internet & Video Technologies, Beijing, China, September 15-17, 2007 198 Reduced 4x4 Block Intra Prediction Modes using Directional
OPTIMIZATION OF LOW DELAY WAVELET VIDEO CODECS
 OPTIMIZATION OF LOW DELAY WAVELET VIDEO CODECS Andrzej Popławski, Marek Domański 2 Uniwersity of Zielona Góra, Institute of Computer Engineering and Electronics, Poland 2 Poznań University of Technology,
OPTIMIZATION OF LOW DELAY WAVELET VIDEO CODECS Andrzej Popławski, Marek Domański 2 Uniwersity of Zielona Góra, Institute of Computer Engineering and Electronics, Poland 2 Poznań University of Technology,
Fast Mode Decision for H.264/AVC Using Mode Prediction
 Fast Mode Decision for H.264/AVC Using Mode Prediction Song-Hak Ri and Joern Ostermann Institut fuer Informationsverarbeitung, Appelstr 9A, D-30167 Hannover, Germany ri@tnt.uni-hannover.de ostermann@tnt.uni-hannover.de
Fast Mode Decision for H.264/AVC Using Mode Prediction Song-Hak Ri and Joern Ostermann Institut fuer Informationsverarbeitung, Appelstr 9A, D-30167 Hannover, Germany ri@tnt.uni-hannover.de ostermann@tnt.uni-hannover.de
Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm using Hybrid Search Patterns for Video Streaming Application
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS COMMUNICATIONS & CONTROL ISSN 1841-9836, 12(5), 715-727, October 2017. Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm using Hybrid Search Patterns for Video Streaming Application R.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS COMMUNICATIONS & CONTROL ISSN 1841-9836, 12(5), 715-727, October 2017. Fast Motion Estimation Algorithm using Hybrid Search Patterns for Video Streaming Application R.
A Novel Hexagonal Search Algorithm for Fast Block Matching Motion Estimation
 EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing :6, 9 6 c Hindawi Publishing Corporation A Novel Hexagonal Search Algorithm for Fast Block Matching Motion Estimation Anastasios Hamosfakidis Department of
EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing :6, 9 6 c Hindawi Publishing Corporation A Novel Hexagonal Search Algorithm for Fast Block Matching Motion Estimation Anastasios Hamosfakidis Department of
MOTION COMPENSATION IN BLOCK DCT CODING BASED ON PERSPECTIVE WARPING
 MOTION COMPENSATION IN BLOCK DCT CODING BASED ON PERSPECTIVE WARPING L. Capodiferro*, S. Puledda*, G. Jacovitti** * Fondazione Ugo Bordoni c/o ISPT, Viale Europa 190, 00149 Rome, Italy Tel: +39-6-54802132;
MOTION COMPENSATION IN BLOCK DCT CODING BASED ON PERSPECTIVE WARPING L. Capodiferro*, S. Puledda*, G. Jacovitti** * Fondazione Ugo Bordoni c/o ISPT, Viale Europa 190, 00149 Rome, Italy Tel: +39-6-54802132;
Joint Adaptive Block Matching Search (JABMS) Algorithm
 Joint Adaptive Block Matching Search (JABMS) Algorithm V.K.Ananthashayana and Pushpa.M.K Abstract In this paper a new Joint Adaptive Block Matching Search (JABMS) algorithm is proposed to generate motion
Joint Adaptive Block Matching Search (JABMS) Algorithm V.K.Ananthashayana and Pushpa.M.K Abstract In this paper a new Joint Adaptive Block Matching Search (JABMS) algorithm is proposed to generate motion
Research Article Block-Matching Translational and Rotational Motion Compensated Prediction Using Interpolated Reference Frame
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 2010, Article ID 385631, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2010/385631 Research Article Block-Matching Translational and Rotational
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 2010, Article ID 385631, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2010/385631 Research Article Block-Matching Translational and Rotational
SINGLE PASS DEPENDENT BIT ALLOCATION FOR SPATIAL SCALABILITY CODING OF H.264/SVC
 SINGLE PASS DEPENDENT BIT ALLOCATION FOR SPATIAL SCALABILITY CODING OF H.264/SVC Randa Atta, Rehab F. Abdel-Kader, and Amera Abd-AlRahem Electrical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Port
SINGLE PASS DEPENDENT BIT ALLOCATION FOR SPATIAL SCALABILITY CODING OF H.264/SVC Randa Atta, Rehab F. Abdel-Kader, and Amera Abd-AlRahem Electrical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Port
Deblocking Filter Algorithm with Low Complexity for H.264 Video Coding
 Deblocking Filter Algorithm with Low Complexity for H.264 Video Coding Jung-Ah Choi and Yo-Sung Ho Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 261 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju, 500-712, Korea
Deblocking Filter Algorithm with Low Complexity for H.264 Video Coding Jung-Ah Choi and Yo-Sung Ho Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 261 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju, 500-712, Korea
Digital Image Stabilization and Its Integration with Video Encoder
 Digital Image Stabilization and Its Integration with Video Encoder Yu-Chun Peng, Hung-An Chang, Homer H. Chen Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering National Taiwan University Taipei, Taiwan {b889189,
Digital Image Stabilization and Its Integration with Video Encoder Yu-Chun Peng, Hung-An Chang, Homer H. Chen Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering National Taiwan University Taipei, Taiwan {b889189,
Zonal MPEG-2. Cheng-Hsiung Hsieh *, Chen-Wei Fu and Wei-Lung Hung
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2007. 5, 2: 151-158 Zonal MPEG-2 Cheng-Hsiung Hsieh *, Chen-Wei Fu and Wei-Lung Hung Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2007. 5, 2: 151-158 Zonal MPEG-2 Cheng-Hsiung Hsieh *, Chen-Wei Fu and Wei-Lung Hung Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering
A VLSI Architecture for H.264/AVC Variable Block Size Motion Estimation
 Journal of Automation and Control Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, February 20 A VLSI Architecture for H.264/AVC Variable Block Size Motion Estimation Dam. Minh Tung and Tran. Le Thang Dong Center of Electrical
Journal of Automation and Control Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, February 20 A VLSI Architecture for H.264/AVC Variable Block Size Motion Estimation Dam. Minh Tung and Tran. Le Thang Dong Center of Electrical
Transactions Briefs. An Adaptive Search Length Algorithm for Block Matching Motion Estimation
 906 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 6, DECEMBER 1997 Transactions Briefs An Adaptive Search Length Algorithm for Block Matching Motion Estimation Mark R. Pickering,
906 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 6, DECEMBER 1997 Transactions Briefs An Adaptive Search Length Algorithm for Block Matching Motion Estimation Mark R. Pickering,
An Efficient Mode Selection Algorithm for H.264
 An Efficient Mode Selection Algorithm for H.64 Lu Lu 1, Wenhan Wu, and Zhou Wei 3 1 South China University of Technology, Institute of Computer Science, Guangzhou 510640, China lul@scut.edu.cn South China
An Efficient Mode Selection Algorithm for H.64 Lu Lu 1, Wenhan Wu, and Zhou Wei 3 1 South China University of Technology, Institute of Computer Science, Guangzhou 510640, China lul@scut.edu.cn South China
Mesh Based Interpolative Coding (MBIC)
 Mesh Based Interpolative Coding (MBIC) Eckhart Baum, Joachim Speidel Institut für Nachrichtenübertragung, University of Stuttgart An alternative method to H.6 encoding of moving images at bit rates below
Mesh Based Interpolative Coding (MBIC) Eckhart Baum, Joachim Speidel Institut für Nachrichtenübertragung, University of Stuttgart An alternative method to H.6 encoding of moving images at bit rates below
Frequency Band Coding Mode Selection for Key Frames of Wyner-Ziv Video Coding
 2009 11th IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia Frequency Band Coding Mode Selection for Key Frames of Wyner-Ziv Video Coding Ghazaleh R. Esmaili and Pamela C. Cosman Department of Electrical and
2009 11th IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia Frequency Band Coding Mode Selection for Key Frames of Wyner-Ziv Video Coding Ghazaleh R. Esmaili and Pamela C. Cosman Department of Electrical and
No-reference visually significant blocking artifact metric for natural scene images
 No-reference visually significant blocking artifact metric for natural scene images By: Shan Suthaharan S. Suthaharan (2009), No-reference visually significant blocking artifact metric for natural scene
No-reference visually significant blocking artifact metric for natural scene images By: Shan Suthaharan S. Suthaharan (2009), No-reference visually significant blocking artifact metric for natural scene
DIGITAL video compression is essential for the reduction. Two-Bit Transform for Binary Block Motion Estimation
 938 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2005 Two-Bit Transform for Binary Block Motion Estimation Alp Ertürk and Sarp Ertürk, Member, IEEE Abstract One-bit
938 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2005 Two-Bit Transform for Binary Block Motion Estimation Alp Ertürk and Sarp Ertürk, Member, IEEE Abstract One-bit
Implementation of H.264 Video Codec for Block Matching Algorithms
 Implementation of H.264 Video Codec for Block Matching Algorithms Vivek Sinha 1, Dr. K. S. Geetha 2 1 Student of Master of Technology, Communication Systems, Department of ECE, R.V. College of Engineering,
Implementation of H.264 Video Codec for Block Matching Algorithms Vivek Sinha 1, Dr. K. S. Geetha 2 1 Student of Master of Technology, Communication Systems, Department of ECE, R.V. College of Engineering,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 2, February ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 2, February-2014 1048 Video Compression Motion Estimation A Survey 1. C.Arunkumar Madhuvappan, Research Scholar, Anna University,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 2, February-2014 1048 Video Compression Motion Estimation A Survey 1. C.Arunkumar Madhuvappan, Research Scholar, Anna University,
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF BLOCK MATCHING ALGORITHMS FOR VIDEO COMPRESSION
 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF BLOCK MATCHING ALGORITHMS FOR VIDEO COMPRESSION S.Sowmyayani #1, P.Arockia Jansi Rani *2 #1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Manonmaniam Sundaranar
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF BLOCK MATCHING ALGORITHMS FOR VIDEO COMPRESSION S.Sowmyayani #1, P.Arockia Jansi Rani *2 #1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Manonmaniam Sundaranar
Enhanced Hexagonal Search for Fast Block Motion Estimation
 1 Enhanced Hexagonal Search for Fast Block Motion Estimation Ce Zhu, Xiao Lin, Lap-Pui Chau, Lai-Man Po Abstract Fast block motion estimation normally consists of low-resolution coarse search and the following
1 Enhanced Hexagonal Search for Fast Block Motion Estimation Ce Zhu, Xiao Lin, Lap-Pui Chau, Lai-Man Po Abstract Fast block motion estimation normally consists of low-resolution coarse search and the following
Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial Region Segmentation
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.13 No.11, November 2013 1 Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.13 No.11, November 2013 1 Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume-02, Issue-04, April 2015 A Performance
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume-02, Issue-04, April 2015 A Performance
Reduction of Blocking artifacts in Compressed Medical Images
 ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 8, No. 2, 2013, pp. 096-102 Reduction of Blocking artifacts in Compressed Medical Images Jagroop Singh 1, Sukhwinder Singh
ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 8, No. 2, 2013, pp. 096-102 Reduction of Blocking artifacts in Compressed Medical Images Jagroop Singh 1, Sukhwinder Singh
IBM Research Report. Inter Mode Selection for H.264/AVC Using Time-Efficient Learning-Theoretic Algorithms
 RC24748 (W0902-063) February 12, 2009 Electrical Engineering IBM Research Report Inter Mode Selection for H.264/AVC Using Time-Efficient Learning-Theoretic Algorithms Yuri Vatis Institut für Informationsverarbeitung
RC24748 (W0902-063) February 12, 2009 Electrical Engineering IBM Research Report Inter Mode Selection for H.264/AVC Using Time-Efficient Learning-Theoretic Algorithms Yuri Vatis Institut für Informationsverarbeitung
Variable Temporal-Length 3-D Discrete Cosine Transform Coding
 758 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 6, NO. 5, MAY 1997 [13] T. R. Fischer, A pyramid vector quantizer, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, pp. 568 583, July 1986. [14] R. Rinaldo and G. Calvagno, Coding
758 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 6, NO. 5, MAY 1997 [13] T. R. Fischer, A pyramid vector quantizer, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, pp. 568 583, July 1986. [14] R. Rinaldo and G. Calvagno, Coding
Overview: motion-compensated coding
 Overview: motion-compensated coding Motion-compensated prediction Motion-compensated hybrid coding Motion estimation by block-matching Motion estimation with sub-pixel accuracy Power spectral density of
Overview: motion-compensated coding Motion-compensated prediction Motion-compensated hybrid coding Motion estimation by block-matching Motion estimation with sub-pixel accuracy Power spectral density of
A deblocking filter with two separate modes in block-based video coding
 A deblocing filter with two separate modes in bloc-based video coding Sung Deu Kim Jaeyoun Yi and Jong Beom Ra Dept. of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology 7- Kusongdong
A deblocing filter with two separate modes in bloc-based video coding Sung Deu Kim Jaeyoun Yi and Jong Beom Ra Dept. of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology 7- Kusongdong
Multiresolution motion compensation coding for video compression
 Title Multiresolution motion compensation coding for video compression Author(s) Choi, KT; Chan, SC; Ng, TS Citation International Conference On Signal Processing Proceedings, Icsp, 1996, v. 2, p. 1059-1061
Title Multiresolution motion compensation coding for video compression Author(s) Choi, KT; Chan, SC; Ng, TS Citation International Conference On Signal Processing Proceedings, Icsp, 1996, v. 2, p. 1059-1061
Direction-Length Code (DLC) To Represent Binary Objects
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 18, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar-Apr. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Direction-Length Code (DLC) To Represent Binary
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 18, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar-Apr. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Direction-Length Code (DLC) To Represent Binary
Optimal Estimation for Error Concealment in Scalable Video Coding
 Optimal Estimation for Error Concealment in Scalable Video Coding Rui Zhang, Shankar L. Regunathan and Kenneth Rose Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California Santa Barbara,
Optimal Estimation for Error Concealment in Scalable Video Coding Rui Zhang, Shankar L. Regunathan and Kenneth Rose Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California Santa Barbara,
IN RECENT years, multimedia application has become more
 578 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 17, NO. 5, MAY 2007 A Fast Algorithm and Its VLSI Architecture for Fractional Motion Estimation for H.264/MPEG-4 AVC Video Coding
578 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 17, NO. 5, MAY 2007 A Fast Algorithm and Its VLSI Architecture for Fractional Motion Estimation for H.264/MPEG-4 AVC Video Coding
Efficient Method for Half-Pixel Block Motion Estimation Using Block Differentials
 Efficient Method for Half-Pixel Block Motion Estimation Using Block Differentials Tuukka Toivonen and Janne Heikkilä Machine Vision Group Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering
Efficient Method for Half-Pixel Block Motion Estimation Using Block Differentials Tuukka Toivonen and Janne Heikkilä Machine Vision Group Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering
Fast Wavelet-based Macro-block Selection Algorithm for H.264 Video Codec
 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 8 Vol I IMECS 8, 19-1 March, 8, Hong Kong Fast Wavelet-based Macro-block Selection Algorithm for H.64 Video Codec Shi-Huang
Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 8 Vol I IMECS 8, 19-1 March, 8, Hong Kong Fast Wavelet-based Macro-block Selection Algorithm for H.64 Video Codec Shi-Huang
FAST MOTION ESTIMATION DISCARDING LOW-IMPACT FRACTIONAL BLOCKS. Saverio G. Blasi, Ivan Zupancic and Ebroul Izquierdo
 FAST MOTION ESTIMATION DISCARDING LOW-IMPACT FRACTIONAL BLOCKS Saverio G. Blasi, Ivan Zupancic and Ebroul Izquierdo School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University of London
FAST MOTION ESTIMATION DISCARDING LOW-IMPACT FRACTIONAL BLOCKS Saverio G. Blasi, Ivan Zupancic and Ebroul Izquierdo School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University of London
Content Based Image Retrieval Using Color Quantizes, EDBTC and LBP Features
 Content Based Image Retrieval Using Color Quantizes, EDBTC and LBP Features 1 Kum Sharanamma, 2 Krishnapriya Sharma 1,2 SIR MVIT Abstract- To describe the image features the Local binary pattern (LBP)
Content Based Image Retrieval Using Color Quantizes, EDBTC and LBP Features 1 Kum Sharanamma, 2 Krishnapriya Sharma 1,2 SIR MVIT Abstract- To describe the image features the Local binary pattern (LBP)
VIDEO streaming applications over the Internet are gaining. Brief Papers
 412 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BROADCASTING, VOL. 54, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2008 Brief Papers Redundancy Reduction Technique for Dual-Bitstream MPEG Video Streaming With VCR Functionalities Tak-Piu Ip, Yui-Lam Chan,
412 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BROADCASTING, VOL. 54, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2008 Brief Papers Redundancy Reduction Technique for Dual-Bitstream MPEG Video Streaming With VCR Functionalities Tak-Piu Ip, Yui-Lam Chan,
By Charvi Dhoot*, Vincent J. Mooney &,
 By Charvi Dhoot*, Vincent J. Mooney &, -Shubhajit Roy Chowdhury*, Lap Pui Chau # *International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad, India & School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Georgia
By Charvi Dhoot*, Vincent J. Mooney &, -Shubhajit Roy Chowdhury*, Lap Pui Chau # *International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad, India & School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Georgia
Rate Distortion Optimization in Video Compression
 Rate Distortion Optimization in Video Compression Xue Tu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of New York at Stony Brook 1. Introduction From Shannon s classic rate distortion
Rate Distortion Optimization in Video Compression Xue Tu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of New York at Stony Brook 1. Introduction From Shannon s classic rate distortion
Noise Reduction in Image Sequences using an Effective Fuzzy Algorithm
 Noise Reduction in Image Sequences using an Effective Fuzzy Algorithm Mahmoud Saeid Khadijeh Saeid Mahmoud Khaleghi Abstract In this paper, we propose a novel spatiotemporal fuzzy based algorithm for noise
Noise Reduction in Image Sequences using an Effective Fuzzy Algorithm Mahmoud Saeid Khadijeh Saeid Mahmoud Khaleghi Abstract In this paper, we propose a novel spatiotemporal fuzzy based algorithm for noise
Fast Block-Matching Motion Estimation Using Modified Diamond Search Algorithm
 Fast Block-Matching Motion Estimation Using Modified Diamond Search Algorithm Bichu Vijay 1, Ganapathi Hegde 2, Sanju S 3 Amrita School of Engineering, Bangalore, India Email: vijaybichu.in@gmail.com 1,
Fast Block-Matching Motion Estimation Using Modified Diamond Search Algorithm Bichu Vijay 1, Ganapathi Hegde 2, Sanju S 3 Amrita School of Engineering, Bangalore, India Email: vijaybichu.in@gmail.com 1,
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF BIT PLANE ENTROPY ENCODER FOR 3 D DWT BASED VIDEO COMPRESSION
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF BIT PLANE ENTROPY ENCODER FOR 3 D DWT BASED VIDEO COMPRESSION 1 GOPIKA G NAIR, 2 SABI S. 1 M. Tech. Scholar (Embedded Systems), ECE department, SBCE, Pattoor, Kerala, India, Email:
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF BIT PLANE ENTROPY ENCODER FOR 3 D DWT BASED VIDEO COMPRESSION 1 GOPIKA G NAIR, 2 SABI S. 1 M. Tech. Scholar (Embedded Systems), ECE department, SBCE, Pattoor, Kerala, India, Email:
Multiframe Blocking-Artifact Reduction for Transform-Coded Video
 276 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 12, NO. 4, APRIL 2002 Multiframe Blocking-Artifact Reduction for Transform-Coded Video Bahadir K. Gunturk, Yucel Altunbasak, and
276 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 12, NO. 4, APRIL 2002 Multiframe Blocking-Artifact Reduction for Transform-Coded Video Bahadir K. Gunturk, Yucel Altunbasak, and
Fast Implementation of VC-1 with Modified Motion Estimation and Adaptive Block Transform
 Circuits and Systems, 2010, 1, 12-17 doi:10.4236/cs.2010.11003 Published Online July 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Fast Implementation of VC-1 with Modified Motion Estimation and Adaptive Block
Circuits and Systems, 2010, 1, 12-17 doi:10.4236/cs.2010.11003 Published Online July 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Fast Implementation of VC-1 with Modified Motion Estimation and Adaptive Block
Tunnelling-based Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation
 Tunnelling-based Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation María Santamaría*, María Trujillo *Universidad del Valle, Colombia, maria.santamaria@correounivalle.edu.co Universidad del Valle,
Tunnelling-based Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation María Santamaría*, María Trujillo *Universidad del Valle, Colombia, maria.santamaria@correounivalle.edu.co Universidad del Valle,
Adaptive bit-reduced mean absolute difference criterion for block-matching algorithm and its VLSI design
 Adaptive bit-reduced mean absolute difference criterion for block-matching algorithm and its VLSI design Hwang-Seok Oh, MEMBER SPIE Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Department of Computer
Adaptive bit-reduced mean absolute difference criterion for block-matching algorithm and its VLSI design Hwang-Seok Oh, MEMBER SPIE Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Department of Computer
Module 7 VIDEO CODING AND MOTION ESTIMATION
 Module 7 VIDEO CODING AND MOTION ESTIMATION Version ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson Block based motion estimation algorithms Version ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson Objectives At the end of this less, the students
Module 7 VIDEO CODING AND MOTION ESTIMATION Version ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson Block based motion estimation algorithms Version ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson Objectives At the end of this less, the students
Optimizing the Deblocking Algorithm for. H.264 Decoder Implementation
 Optimizing the Deblocking Algorithm for H.264 Decoder Implementation Ken Kin-Hung Lam Abstract In the emerging H.264 video coding standard, a deblocking/loop filter is required for improving the visual
Optimizing the Deblocking Algorithm for H.264 Decoder Implementation Ken Kin-Hung Lam Abstract In the emerging H.264 video coding standard, a deblocking/loop filter is required for improving the visual
Advances of MPEG Scalable Video Coding Standard
 Advances of MPEG Scalable Video Coding Standard Wen-Hsiao Peng, Chia-Yang Tsai, Tihao Chiang, and Hsueh-Ming Hang National Chiao-Tung University 1001 Ta-Hsueh Rd., HsinChu 30010, Taiwan pawn@mail.si2lab.org,
Advances of MPEG Scalable Video Coding Standard Wen-Hsiao Peng, Chia-Yang Tsai, Tihao Chiang, and Hsueh-Ming Hang National Chiao-Tung University 1001 Ta-Hsueh Rd., HsinChu 30010, Taiwan pawn@mail.si2lab.org,
Vidhya.N.S. Murthy Student I.D Project report for Multimedia Processing course (EE5359) under Dr. K.R. Rao
 STUDY AND IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MATCHING PURSUIT ALGORITHM AND QUALITY COMPARISON WITH DISCRETE COSINE TRANSFORM IN AN MPEG2 ENCODER OPERATING AT LOW BITRATES Vidhya.N.S. Murthy Student I.D. 1000602564
STUDY AND IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MATCHING PURSUIT ALGORITHM AND QUALITY COMPARISON WITH DISCRETE COSINE TRANSFORM IN AN MPEG2 ENCODER OPERATING AT LOW BITRATES Vidhya.N.S. Murthy Student I.D. 1000602564
FRAME-RATE UP-CONVERSION USING TRANSMITTED TRUE MOTION VECTORS
 FRAME-RATE UP-CONVERSION USING TRANSMITTED TRUE MOTION VECTORS Yen-Kuang Chen 1, Anthony Vetro 2, Huifang Sun 3, and S. Y. Kung 4 Intel Corp. 1, Mitsubishi Electric ITA 2 3, and Princeton University 1
FRAME-RATE UP-CONVERSION USING TRANSMITTED TRUE MOTION VECTORS Yen-Kuang Chen 1, Anthony Vetro 2, Huifang Sun 3, and S. Y. Kung 4 Intel Corp. 1, Mitsubishi Electric ITA 2 3, and Princeton University 1
Trends and issues in developing fast block motion estimation algorithms
 2016; 2(9): 607-613 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(9): 607-613 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 22-07-2016 Accepted: 23-08-2016 Shaifali M Arora Asstt.
2016; 2(9): 607-613 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(9): 607-613 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 22-07-2016 Accepted: 23-08-2016 Shaifali M Arora Asstt.
IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 9, Issue 4, No 2, July 2012 ISSN (Online):
 www.ijcsi.org 394 An Improvement of Unsymmetrical-Cross Multi-H Hexagon-grid Search algorith m Vu Thanh Nguyen (1), Tran Xuan Chien (2), Phan Cong Canh (3) Software Engineeringg Department, University
www.ijcsi.org 394 An Improvement of Unsymmetrical-Cross Multi-H Hexagon-grid Search algorith m Vu Thanh Nguyen (1), Tran Xuan Chien (2), Phan Cong Canh (3) Software Engineeringg Department, University
Image and Video Quality Assessment Using Neural Network and SVM
 TSINGHUA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSN 1007-0214 18/19 pp112-116 Volume 13, Number 1, February 2008 Image and Video Quality Assessment Using Neural Network and SVM DING Wenrui (), TONG Yubing (), ZHANG Qishan
TSINGHUA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ISSN 1007-0214 18/19 pp112-116 Volume 13, Number 1, February 2008 Image and Video Quality Assessment Using Neural Network and SVM DING Wenrui (), TONG Yubing (), ZHANG Qishan
Low Complexity Block Motion Estimation Using Morphological-based Feature Extraction and XOR Operations
 Low Complexity Block Motion Estimation Using Morphological-based Feature Extraction and XOR Operations *Thinh M. Le, R. Mason, and S. Panchanathan *School of Information Technology and Engineering, University
Low Complexity Block Motion Estimation Using Morphological-based Feature Extraction and XOR Operations *Thinh M. Le, R. Mason, and S. Panchanathan *School of Information Technology and Engineering, University
An Optimized Template Matching Approach to Intra Coding in Video/Image Compression
 An Optimized Template Matching Approach to Intra Coding in Video/Image Compression Hui Su, Jingning Han, and Yaowu Xu Chrome Media, Google Inc., 1950 Charleston Road, Mountain View, CA 94043 ABSTRACT The
An Optimized Template Matching Approach to Intra Coding in Video/Image Compression Hui Su, Jingning Han, and Yaowu Xu Chrome Media, Google Inc., 1950 Charleston Road, Mountain View, CA 94043 ABSTRACT The
Coding for the Network: Scalable and Multiple description coding Marco Cagnazzo
 Coding for the Network: Scalable and Multiple description coding Marco Cagnazzo Overview Examples and motivations Scalable coding for network transmission Techniques for multiple description coding 2 27/05/2013
Coding for the Network: Scalable and Multiple description coding Marco Cagnazzo Overview Examples and motivations Scalable coding for network transmission Techniques for multiple description coding 2 27/05/2013
A Sum Square Error based Successive Elimination Algorithm for Block Motion Estimation
 A Sum Square Error based Successive Elimination Algorithm for Block Motion Estimation J.J. Francis and G. de Jager Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Cape Town Rondebosch, 7700, South
A Sum Square Error based Successive Elimination Algorithm for Block Motion Estimation J.J. Francis and G. de Jager Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Cape Town Rondebosch, 7700, South
A Novel Statistical Distortion Model Based on Mixed Laplacian and Uniform Distribution of Mpeg-4 FGS
 A Novel Statistical Distortion Model Based on Mixed Laplacian and Uniform Distribution of Mpeg-4 FGS Xie Li and Wenjun Zhang Institute of Image Communication and Information Processing, Shanghai Jiaotong
A Novel Statistical Distortion Model Based on Mixed Laplacian and Uniform Distribution of Mpeg-4 FGS Xie Li and Wenjun Zhang Institute of Image Communication and Information Processing, Shanghai Jiaotong
Simplified Block Matching Algorithm for Fast Motion Estimation in Video Compression
 Journal of Computer Science 4 (4): 282-289, 2008 ISSN 1549-3636 2008 Science Publications Simplified Block Matching Algorithm for Fast Motion Estimation in Video Compression M. Ezhilarasan and P. Thambidurai
Journal of Computer Science 4 (4): 282-289, 2008 ISSN 1549-3636 2008 Science Publications Simplified Block Matching Algorithm for Fast Motion Estimation in Video Compression M. Ezhilarasan and P. Thambidurai
Descrambling Privacy Protected Information for Authenticated users in H.264/AVC Compressed Video
 Descrambling Privacy Protected Information for Authenticated users in H.264/AVC Compressed Video R.Hemanth Kumar Final Year Student, Department of Information Technology, Prathyusha Institute of Technology
Descrambling Privacy Protected Information for Authenticated users in H.264/AVC Compressed Video R.Hemanth Kumar Final Year Student, Department of Information Technology, Prathyusha Institute of Technology
Low Bitrate Video Communications
 New Half-Pixel Accuracy Motion Estimation Algorithms for Low Bitrate Video Communications H. Mahdavi-Nasab and Shohreh Kasaei Abstract Fractional-pixel accuracy motion estimation (ME) has shown to result
New Half-Pixel Accuracy Motion Estimation Algorithms for Low Bitrate Video Communications H. Mahdavi-Nasab and Shohreh Kasaei Abstract Fractional-pixel accuracy motion estimation (ME) has shown to result
System Modeling and Implementation of MPEG-4. Encoder under Fine-Granular-Scalability Framework
 System Modeling and Implementation of MPEG-4 Encoder under Fine-Granular-Scalability Framework Literature Survey Embedded Software Systems Prof. B. L. Evans by Wei Li and Zhenxun Xiao March 25, 2002 Abstract
System Modeling and Implementation of MPEG-4 Encoder under Fine-Granular-Scalability Framework Literature Survey Embedded Software Systems Prof. B. L. Evans by Wei Li and Zhenxun Xiao March 25, 2002 Abstract
