Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide
|
|
|
- Trevor Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Circles Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide Definitions Radius (r) = distance from the center of a circle to the circle s edge Diameter (d) = distance across a circle, from edge to edge, through the circle s center Pi (π) = A constant used to determine the circumference of a circle. It rounds to Circumference (C) = distance around a circle *Note: The radius is always half the distance of the diameter, so d = 2r or r = d/2 Useful Formulas and Relationships C = 2πr or πd A = πr^2 π = 3.14 d = 2r r = d/2 Example Problems Circumference 1) A bouncy ball has a diameter if 6 inches. What is the circumference of the ball? Round to the nearest inch. 2) There is a globe in your history class. On the globe, there is an equator drawn on that divides the globe into equal halves. The length of this equator is 26 inches. What is the radius of the globe? Round to the nearest inch. Area 3) The shape of both of the following pizzas is a semicircle. The first pizza has a diameter of 12 inches. The second pizza has a diameter of 18 inches. a. Find the area of each pizza. b. Approximately how much larger is the area of the second pizza compared to the first pizza? Use π = 3.14.
2 Use the following information for questions 4-6: Ted thinks that if a pizza with a radius of 4 in. costs $12, then a pizza with a radius of 8 in. should cost $24. He explains that since the radius is twice as big, the cost should be twice as much. 4 in 8 in 4) Do you agree or disagree with Ted? 5) Explain your reasoning. 6) Calculate the area of each pizza to illustrate your explanation. Show your work.
3 Polygons Definitions Polygon = a closed shape with at least 3 straight sides and angles. Regular polygon = a special polygon where all sides and angles are equal Area of a polygon = the two-dimensional space inside of a polygon measured in squares Apothem = a line segment from the center of a polygon to the midpoint of one of its sides Useful Formulas and Relationships Area of triangle: 1/2 base height = bh 2 Area of rectangle: length width = lw Area of regular polygon: 1/2 apothem perimeter = ap 2 Example Problems Use the following for problems 7 and 8: regular hexagon regular pentagon regular octogon 7) What are the three different areas of the three shapes above? 8) Approximately how much bigger is the pentagon than the octagon? Remember to convert to matching units!
4 Ratio & Scale Definitions Ratio = a comparison of two numbers. A ratio of 1 to 3 can be written in the following ways: 1 to 3 1:3 1 3 Scale = a proportional relationship, in the form of a ratio, usually comparing the size of a model to an actual object. Uses units. Example scales: 3 inches 1 foot : 10 miles 7 feet Useful Formulas and Relationships To solve a scale problem, convert the units and the numerical ratio given in the scale. Example problems 9) What is the ratio of the two figures below? 10) If a third rectangle C had dimensions of 1.5 kilometers by 4.5 kilometers, what would be the scale from rectangles B to C?
5 3D Shapes Definitions Volume (V) = the quantity of 3-dimensional space enclosed by a closed or solid surface. It is measured in cubes. Surface Area (SA) = the measure of the total area that the surface of an object occupies. It is measured in squares. Face = A side of a 3-dimensional object. Cross Section = the intersection of a 3-dimensional body with a 2-dimensional plane Useful Formulas and Relationships Calculate the volume of a 3-dimensional shape by multiplying the area of its base by its height. For complex shapes, you will need to decompose them into smaller shapes, calculate the volume of each separately, and then combine their separate volumes together. Calculate the surface area of 3-dimensional object by adding the areas of each of its faces together. Example Problems Volume Use the following figure for problems ) Find the volume of the figure above. Label the units. 12) What would the volume be if all three dimensions (base, width, height) doubled? Label the units.
6 Use the complex figure to the right for problems ) Find the volume of the triangular prism. Notice that a smaller triangular prism has been removed from the middle, and is not included in the total volume! Label the units. 14) Find the area of the front side of the figure (the large triangle with the smaller triangle cut out). Label the units. Surface Area Use the following information to solve problems 15-16: An architect uses this model to represent a building design she would like to create. The scale of the unit cube model is 1:121. This model is made up of 6 cubes. The side length of each cube is 1 in. 15) What is the surface area of this model, not including the sides that are facing the ground? Label the units. SA = 16) What would be the surface area of the real building in square feet, not including the sides that are facing the ground? Label the units. SA =
7 Use the following figure for problem ) Calculate the surface area of the above figure, including the face that is facing the ground. Label the units. SA = Cross Sections Use the following figure for problems The following diagram shows a cross section of a place passing through a cube, resulting in a trapezoid. 18) Which of the following figures can be the result of a plane slicing through a cube? Circle all that apply: A B C D E F
8 19) Besides the shapes you ve selected above, can you come up with any other shapes that will result from a cross-section of a cube?
Volume of Cylinders. Volume of Cones. Example Find the volume of the cylinder. Round to the nearest tenth.
 Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Geometry. Geometry is the study of shapes and sizes. The next few pages will review some basic geometry facts. Enjoy the short lesson on geometry.
 Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
11.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Learning Objectives Find the volume of a prism. Find the volume of a cylinder. Review Queue 1. Define volume in your own words. 2. What is the surface area of a cube
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections
 Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
February 07, Dimensional Geometry Notebook.notebook. Glossary & Standards. Prisms and Cylinders. Return to Table of Contents
 Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon
 Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
C in. 2. D in Find the volume of a 7-inch tall drinking glass with a 4-inch diameter. C lateral faces. A in. 3 B in.
 Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Free Response. Test A. 1. What is the estimated area of the figure?
 Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
Test A 1. What is the estimated area of the 6. An 8.5 in. by 11 in. sheet of paper is enlarged to make a poster by doubling its length and width. What is the new perimeter? 7. How does the area of a square
Part I Multiple Choice
 Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Pre-Algebra, Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Chapter 11. Area of Polygons and Circles
 Chapter 11 Area of Polygons and Circles 11.1 & 11.2 Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, Trapezoids, Rhombi, and Kites Use your formula chart to find the formula for the Areas of the following Polygons
Chapter 11 Area of Polygons and Circles 11.1 & 11.2 Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, Trapezoids, Rhombi, and Kites Use your formula chart to find the formula for the Areas of the following Polygons
Name: Target 12.2: Find and apply surface of Spheres and Composites 12.2a: Surface Area of Spheres 12.2b: Surface Area of Composites Solids
 Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula
 Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Surface Area and Volume
 Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Practice Test Unit 8. Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it!
 Geometry Practice Test Unit 8 Name Period: Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it! Trigonometric Functions (p. 53 of the Geometry Handbook, version 2.1) SOH CAH TOA sin
Geometry Practice Test Unit 8 Name Period: Note: this page will not be available to you for the test. Memorize it! Trigonometric Functions (p. 53 of the Geometry Handbook, version 2.1) SOH CAH TOA sin
Geometry B. The University of Texas at Austin Continuing & Innovative Education K 16 Education Center 1
 Geometry B Credit By Exam This Credit By Exam can help you prepare for the exam by giving you an idea of what you need to study, review, and learn. To succeed, you should be thoroughly familiar with the
Geometry B Credit By Exam This Credit By Exam can help you prepare for the exam by giving you an idea of what you need to study, review, and learn. To succeed, you should be thoroughly familiar with the
Unit E Geometry Unit Review Packet
 Unit E Geometry Unit Review Packet Name Directions: Do ALL (A) Questions. Check Your Answers to (A) Questions. If ALL (A) Questions are correct, skip (B) Questions and move onto next I can statement. If
Unit E Geometry Unit Review Packet Name Directions: Do ALL (A) Questions. Check Your Answers to (A) Questions. If ALL (A) Questions are correct, skip (B) Questions and move onto next I can statement. If
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. apothem. center of a circle. center of a regular polygon. central angle of a regular polygon
 CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
CIRCLES ON TAKS NAME CLASS PD DUE
 CIRCLES ON TAKS NAME CLASS PD DUE 1. On the calculator: Let s say the radius is 2. Find the area. Now let s double the radius to 4 and find the area. How do these two numbers relate? 2. The formula for
CIRCLES ON TAKS NAME CLASS PD DUE 1. On the calculator: Let s say the radius is 2. Find the area. Now let s double the radius to 4 and find the area. How do these two numbers relate? 2. The formula for
PYRAMIDS AND CONES WHAT YOU LL LEARN. Ø Finding the surface areas and volume of pyramids Ø Finding the surface areas and volume of cones
 PYRAMIDS AND CONES A pyramid is a solid with a polygonal base and triangular lateral faces that meet at a vertex. In this lesson, you will work with regular pyramids. The base of a regular pyramid is a
PYRAMIDS AND CONES A pyramid is a solid with a polygonal base and triangular lateral faces that meet at a vertex. In this lesson, you will work with regular pyramids. The base of a regular pyramid is a
422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES. The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power.
 UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry
 Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Day Classwork Day Homework Monday 2/12 Tuesday 2/13 Wednesday 2/14 Areas of Regular Polygons 1 HW 11.1 Volume of Prisms & Cylinders 2 HW 11.4 Volume of Pyramids and Cones
Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Day Classwork Day Homework Monday 2/12 Tuesday 2/13 Wednesday 2/14 Areas of Regular Polygons 1 HW 11.1 Volume of Prisms & Cylinders 2 HW 11.4 Volume of Pyramids and Cones
9 Find the area of the figure. Round to the. 11 Find the area of the figure. Round to the
 Name: Period: Date: Show all work for full credit. Provide exact answers and decimal (rounded to nearest tenth, unless instructed differently). Ch 11 Retake Test Review 1 Find the area of a regular octagon
Name: Period: Date: Show all work for full credit. Provide exact answers and decimal (rounded to nearest tenth, unless instructed differently). Ch 11 Retake Test Review 1 Find the area of a regular octagon
3 Dimensional Geometry Chapter Questions. 1. What are the differences between prisms and pyramids? Cylinders and cones?
 3 Dimensional Geometry Chapter Questions 1. What are the differences between prisms and pyramids? Cylinders and cones? 2. What is volume and how is it found? 3. How are the volumes of cylinders, cones
3 Dimensional Geometry Chapter Questions 1. What are the differences between prisms and pyramids? Cylinders and cones? 2. What is volume and how is it found? 3. How are the volumes of cylinders, cones
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
CHAPTER 12. Extending Surface Area and Volume
 CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 1 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 1 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
Someone else might choose to describe the closet by determining how many square tiles it would take to cover the floor. 6 ft.
 Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes
 26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
Area of Regular Polygons
 Area of Regular Polygons Name:_ Find the area of each regular polygon. Leave your answer in simplest (radical) form. If your answer does not have a radical form, then round to the nearest tenth. 8 14.4
Area of Regular Polygons Name:_ Find the area of each regular polygon. Leave your answer in simplest (radical) form. If your answer does not have a radical form, then round to the nearest tenth. 8 14.4
Geometry Vocabulary. Name Class
 Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume
 HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
Name (s) Class Date ERROR ANALYSIS GEOMETRY WORD PROBLEMS
 7 th Grade Common Core Name (s) Class Date ERROR ANALYSIS GEOMETRY WORD PROBLEMS Includes: * Angles * Triangles * Scale Drawings * Area and Circumference of a Circle * Volume of Prisms and Pyramids * Surface
7 th Grade Common Core Name (s) Class Date ERROR ANALYSIS GEOMETRY WORD PROBLEMS Includes: * Angles * Triangles * Scale Drawings * Area and Circumference of a Circle * Volume of Prisms and Pyramids * Surface
Area rectangles & parallelograms
 Area rectangles & parallelograms Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot
Area rectangles & parallelograms Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot
Study Guide and Review
 State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. The center of a trapezoid is the perpendicular distance between the bases. false; height false; height
State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. The center of a trapezoid is the perpendicular distance between the bases. false; height false; height
Geometry Unit 10 Note Sheets Date Name of Lesson. 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures Areas of Circles and Sectors
 Date Name of Lesson 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures 11.3 Areas of Circles and Sectors Quiz 11.1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombi and Kites 11.4 Areas of Regular Polygons
Date Name of Lesson 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures 11.3 Areas of Circles and Sectors Quiz 11.1 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombi and Kites 11.4 Areas of Regular Polygons
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Chapter 7. Description or Example. Found on Page. Vocabulary Term. Definition. base. center. circumference. chord. complex figure. cone.
 C H A P T E R 7 This is an alphabetical list of new vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 7. As you complete the study notes for the chapter, you will see Build Your Vocabulary reminders to complete
C H A P T E R 7 This is an alphabetical list of new vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 7. As you complete the study notes for the chapter, you will see Build Your Vocabulary reminders to complete
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Lesson 21: Surface Area
 Lesson 21: Surface Area Classwork Opening Exercise: Surface Area of a Right Rectangular Prism On the provided grid, draw a net representing the surfaces of the right rectangular prism (assume each grid
Lesson 21: Surface Area Classwork Opening Exercise: Surface Area of a Right Rectangular Prism On the provided grid, draw a net representing the surfaces of the right rectangular prism (assume each grid
UNIT 3 - MEASUREMENT & PROPORTIONAL REASONING TEST
 Class: Date: UNIT 3 - MEASUREMENT & PROPORTIONAL REASONING TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When designing a building, you must be
Class: Date: UNIT 3 - MEASUREMENT & PROPORTIONAL REASONING TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When designing a building, you must be
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all its outer surfaces or faces.
 Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
Practice A Introduction to Three-Dimensional Figures
 Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM. The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of
 Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons
 10.6. Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons www.ck12.org 10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons Learning Objectives Calculate the area and perimeter of a regular polygon. Review Queue 1. What is
10.6. Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons www.ck12.org 10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons Learning Objectives Calculate the area and perimeter of a regular polygon. Review Queue 1. What is
Math 6 Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry, Area/Volume
 Math 6 Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry, rea/volume erimeter Objectives: (5.5) The student will model formulas to find the perimeter, circumference and area of plane figures. (5.6) The student will
Math 6 Unit 9 Notes: Measurement and Geometry, rea/volume erimeter Objectives: (5.5) The student will model formulas to find the perimeter, circumference and area of plane figures. (5.6) The student will
A plane that is to the base of the figure will create a cross section that is the same shape as the base.
 Objective: 9.1 3 Notes: Surface Area of Solids Name Cross Sections: A cuts through a solid figure to create a cross section. Depending on the way in which the plane cuts through the figure will determine
Objective: 9.1 3 Notes: Surface Area of Solids Name Cross Sections: A cuts through a solid figure to create a cross section. Depending on the way in which the plane cuts through the figure will determine
Lesson Polygons
 Lesson 4.1 - Polygons Obj.: classify polygons by their sides. classify quadrilaterals by their attributes. find the sum of the angle measures in a polygon. Decagon - A polygon with ten sides. Dodecagon
Lesson 4.1 - Polygons Obj.: classify polygons by their sides. classify quadrilaterals by their attributes. find the sum of the angle measures in a polygon. Decagon - A polygon with ten sides. Dodecagon
SPRINGBOARD UNIT 5 GEOMETRY
 SPRINGBOARD UNIT 5 GEOMETRY 5.1 Area and Perimeter Perimeter the distance around an object. To find perimeter, add all sides. Area the amount of space inside a 2 dimensional object. Measurements for area
SPRINGBOARD UNIT 5 GEOMETRY 5.1 Area and Perimeter Perimeter the distance around an object. To find perimeter, add all sides. Area the amount of space inside a 2 dimensional object. Measurements for area
MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS
 MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS Objectives Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Vocabulary: Volume, right vs oblique Assignments:
MODULE 18 VOLUME FORMULAS Objectives Use formulas routinely for finding the perimeter and area of basic prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. Vocabulary: Volume, right vs oblique Assignments:
My Notes CONNECT TO SCIENCE. Horticulture is the science and art of growing fruit, flowers, ornamental plants, and vegetables.
 SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Summarize/Paraphrase/ Retell, Use Manipulatives, Activating Prior Knowledge, Self/ Peer Revision The Horticulture Club has been given some land to build a greenhouse. The
SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Summarize/Paraphrase/ Retell, Use Manipulatives, Activating Prior Knowledge, Self/ Peer Revision The Horticulture Club has been given some land to build a greenhouse. The
To find the surface area of a pyramid and a cone
 11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
Grade 6 Mathematics Item Specifications Florida Standards Assessments
 Content Standard MAFS.6.G Geometry MAFS.6.G.1 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume. Assessment Limits Calculator s Context A shape is shown. MAFS.6.G.1.1
Content Standard MAFS.6.G Geometry MAFS.6.G.1 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume. Assessment Limits Calculator s Context A shape is shown. MAFS.6.G.1.1
6. If QRSTU is a regular pentagon, what is the measure of T? 1. If STUV is a parallelogram, what are the coordinates of point U?
 1. If UV is a parallelogram, what are the coordinates of point U?. If RU is a regular pentagon, what is the measure of? (0, y) U(?,?) (, 0) V( + z, 0) 7. hree siblings are to share an inheritance of $1,0
1. If UV is a parallelogram, what are the coordinates of point U?. If RU is a regular pentagon, what is the measure of? (0, y) U(?,?) (, 0) V( + z, 0) 7. hree siblings are to share an inheritance of $1,0
2 nd Semester Geometry Review Packet. In the diagram, ABCDE ~ FGHJK. 1) Find the value of x. 2) Find the perimeter of ABCDE.
 In the diagram, ABCDE ~ FGHJK. 1) Find the value of x. 2) Find the perimeter of ABCDE. Determine whether the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement and the postulate or theorem that
In the diagram, ABCDE ~ FGHJK. 1) Find the value of x. 2) Find the perimeter of ABCDE. Determine whether the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement and the postulate or theorem that
Number/Computation. addend Any number being added. digit Any one of the ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
The Geometry of Solids
 CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
A C E. Applications. Applications Connections Extensions
 A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. Suppose that the polygons below were drawn on centimeter grid paper. How many 1-centimeter cubes (some cut in pieces) would it take to cover each
A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. Suppose that the polygons below were drawn on centimeter grid paper. How many 1-centimeter cubes (some cut in pieces) would it take to cover each
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6
 acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
Chapter 8 Review. 1. Find both the perimeter and the area 2. Find both the perimeter and the area
 Name: Block: 8a. Find the perimeter and the area of polygons. 1. Find both the perimeter and the area 2. Find both the perimeter and the area of parallelogram QRST. (Don t forget UNITS!) of rectangle JKLM.
Name: Block: 8a. Find the perimeter and the area of polygons. 1. Find both the perimeter and the area 2. Find both the perimeter and the area of parallelogram QRST. (Don t forget UNITS!) of rectangle JKLM.
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. cone. cube. cylinder. edge of a threedimensional. figure. face of a polyhedron.
 CHAPTER 10 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 10. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. cone Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 10 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 10. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. cone Term Page Definition
Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014
 Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 2. What is the sum of the angle measures of a 37-gon? 3. Complete this statement: A polygon with all
Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 2. What is the sum of the angle measures of a 37-gon? 3. Complete this statement: A polygon with all
Vocabulary. Triangular pyramid Square pyramid Oblique square pyramid Pentagonal pyramid Hexagonal Pyramid
 CP1 Math 2 Unit 8: S.A., Volume, Trigonometry: Day 7 Name Surface Area Objectives: Define important vocabulary for 3-dimensional figures Find the surface area for various prisms Generalize a formula for
CP1 Math 2 Unit 8: S.A., Volume, Trigonometry: Day 7 Name Surface Area Objectives: Define important vocabulary for 3-dimensional figures Find the surface area for various prisms Generalize a formula for
CARDSTOCK MODELING Math Manipulative Kit. Student Activity Book
 CARDSTOCK MODELING Math Manipulative Kit Student Activity Book TABLE OF CONTENTS Activity Sheet for L.E. #1 - Getting Started...3-4 Activity Sheet for L.E. #2 - Squares and Cubes (Hexahedrons)...5-8 Activity
CARDSTOCK MODELING Math Manipulative Kit Student Activity Book TABLE OF CONTENTS Activity Sheet for L.E. #1 - Getting Started...3-4 Activity Sheet for L.E. #2 - Squares and Cubes (Hexahedrons)...5-8 Activity
Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name a solid that fits each description. 1. a can of beans 2. a shoe box 3. a pyramid with five lateral faces 4. a solid with six vertices 5. a prism with bases shaped
Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name a solid that fits each description. 1. a can of beans 2. a shoe box 3. a pyramid with five lateral faces 4. a solid with six vertices 5. a prism with bases shaped
Length and Area. Charles Delman. April 20, 2010
 Length and Area Charles Delman April 20, 2010 What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 (linear) units What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 2 = 2 1 2 (linear) units What is the perimeter of the shaded
Length and Area Charles Delman April 20, 2010 What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 (linear) units What is the length? Unit Solution Unit 5 2 = 2 1 2 (linear) units What is the perimeter of the shaded
Attendance Questions: Find the area of each shape. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 1. An equilateral triangle with edge length 20 cm.
 Page 1 of 17 Attendance Questions: Find the area of each shape. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 1. An equilateral triangle with edge length 20 cm. Page 1 of 17 Page 2 of 17 2. A regular hexagon
Page 1 of 17 Attendance Questions: Find the area of each shape. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 1. An equilateral triangle with edge length 20 cm. Page 1 of 17 Page 2 of 17 2. A regular hexagon
CCBC Math 081 Geometry Section 2.2
 2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
2.2 Geometry Geometry is the study of shapes and their mathematical properties. In this section, we will learn to calculate the perimeter, area, and volume of a few basic geometric shapes. Perimeter We
MATH DICTIONARY. Number Sense. Number Families. Operations. Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count. Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 }
 Number Sense Number Families MATH DICTIONARY Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count Example: {1, 2, 3, 4 } Whole Numbers The counting numbers plus zero Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } Positive
Number Sense Number Families MATH DICTIONARY Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count Example: {1, 2, 3, 4 } Whole Numbers The counting numbers plus zero Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } Positive
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY. 4 th Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 4 th Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 4 th Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3)
 Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3) (136) 11.1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Page 692-693 #7-23 odd, 35 (137) 11.2/11.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Prisms Page 703-705 #1, 2, 7-9, 11-13, 25,
Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3) (136) 11.1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Page 692-693 #7-23 odd, 35 (137) 11.2/11.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Prisms Page 703-705 #1, 2, 7-9, 11-13, 25,
Appendix E. Plane Geometry
 Appendix E Plane Geometry A. Circle A circle is defined as a closed plane curve every point of which is equidistant from a fixed point within the curve. Figure E-1. Circle components. 1. Pi In mathematics,
Appendix E Plane Geometry A. Circle A circle is defined as a closed plane curve every point of which is equidistant from a fixed point within the curve. Figure E-1. Circle components. 1. Pi In mathematics,
Circular Reasoning. Solving Area and Circumference. Problems. WARM UP Determine the area of each circle. Use 3.14 for π.
 Circular Reasoning Solving Area and Circumference 3 Problems WARM UP Determine the area of each circle. Use 3.14 for π. 1. 4 in. 2. 3.8 cm LEARNING GOALS Use the area and circumference formulas for a circle
Circular Reasoning Solving Area and Circumference 3 Problems WARM UP Determine the area of each circle. Use 3.14 for π. 1. 4 in. 2. 3.8 cm LEARNING GOALS Use the area and circumference formulas for a circle
Write Euler s Theorem. Solving Problems Using Surface Area and Volume. Figure Surface Area Volume. Cl V 5 1 } 3
 CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
CHAPTER SUMMARY Big Idea 1 BIG IDEAS Exploring Solids and Their Properties For Your Notebook Euler s Theorem is useful when finding the number of faces, edges, or vertices on a polyhedron, especially when
EOC Review: Practice: 1. In the circle below, AB = 2BC. What is the probability of hitting the shaded region with a random dart?
 EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
3. Draw the orthographic projection (front, right, and top) for the following solid. Also, state how many cubic units the volume is.
 PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area
 Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
Name: Class: Date: Math 8: Identify Shapes and Surface Area 1. Name the solid according to its description: The figure has one base that is a rectangle and four lateral surfaces that are triangles. 2.
11.6 Start Thinking Warm Up Cumulative Review Warm Up
 11.6 Start Thinking The diagrams show a cube and a pyramid. Each has a square base with an area of 25 square inches and a height of 5 inches. How do the volumes of the two figures compare? Eplain your
11.6 Start Thinking The diagrams show a cube and a pyramid. Each has a square base with an area of 25 square inches and a height of 5 inches. How do the volumes of the two figures compare? Eplain your
Geometry Practice. 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles.
 Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Name: Period: 2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review
 2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the number of lunch combinations that can be created if you order a soup, sandwich, drink and dessert. There are 4 soup choices, 5 sandwich choices, 3 drink
2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the number of lunch combinations that can be created if you order a soup, sandwich, drink and dessert. There are 4 soup choices, 5 sandwich choices, 3 drink
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
3 Dimensional Solids. Table of Contents. 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres
 Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
2. a. approximately cm 3 or 9p cm b. 20 layers c. approximately cm 3 or 180p cm Answers will vary.
 Answers Investigation ACE Assignment Choices Problem. Core Other Connections Problem. Core,, Other Applications 7, ; Connections 7 0; unassigned choices from previous problems Problem. Core 7 Other Connections,
Answers Investigation ACE Assignment Choices Problem. Core Other Connections Problem. Core,, Other Applications 7, ; Connections 7 0; unassigned choices from previous problems Problem. Core 7 Other Connections,
Area of Polygons And Circles
 Name: Date: Geometry 2011-2012 Area of Polygons And Circles Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents DAY 1: SWBAT: Calculate the area and perimeter of Parallelograms and Triangles Pgs: 1-5 HW: Pgs: 6-7 DAY
Name: Date: Geometry 2011-2012 Area of Polygons And Circles Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents DAY 1: SWBAT: Calculate the area and perimeter of Parallelograms and Triangles Pgs: 1-5 HW: Pgs: 6-7 DAY
Perimeter, Area, Surface Area, & Volume
 Additional Options: Hide Multiple Choice Answers (Written Response) Open in Microsoft Word (add page breaks and/or edit questions) Generation Date: 11/25/2009 Generated By: Margaret Buell Copyright 2009
Additional Options: Hide Multiple Choice Answers (Written Response) Open in Microsoft Word (add page breaks and/or edit questions) Generation Date: 11/25/2009 Generated By: Margaret Buell Copyright 2009
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review
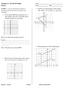 Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Area and Volume 2. Circles. Trapeziums. and Measures. Geometry. Key Point. Key Point. Key Point
 Geometry and Measures Area and Volume 2 You must be able to: Recall and use the formulae for the circumference and area of a circle Recall and use the formula for the area of a trapezium Recall and use
Geometry and Measures Area and Volume 2 You must be able to: Recall and use the formulae for the circumference and area of a circle Recall and use the formula for the area of a trapezium Recall and use
Chapter 11 Review. Period:
 Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
Real-World Problems: Surface Area and Volume. Solve word problems about the volume of rectangular prisms.
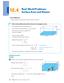 12.4 Real-World Problems: Surface Area and Volume Lesson Objective Solve problems involving surface area and volume of prisms. Learn Solve word problems about the volume of rectangular prisms. A rectangular
12.4 Real-World Problems: Surface Area and Volume Lesson Objective Solve problems involving surface area and volume of prisms. Learn Solve word problems about the volume of rectangular prisms. A rectangular
S P. Geometry Final Exam Review. Name R S P Q P S. Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be:
 Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
( ) ( ) = π r Circumference: 2. Honors Geometry B Exam Review. Areas of Polygons. 1 A = bh Rectangle: A bh 2. Triangle: = Trapezoid: = ( + )
 reas of Polygons Triangle: 1 = bh Rectangle: bh 1 b1 b h = Trapezoid: = ( + ) Parallelogram: = bh Regular Polygon: 1 1 = ap = apothem perimeter Coordinate Geometry y y1 Slope: Circles 1 1 1 Midpoint: +,
reas of Polygons Triangle: 1 = bh Rectangle: bh 1 b1 b h = Trapezoid: = ( + ) Parallelogram: = bh Regular Polygon: 1 1 = ap = apothem perimeter Coordinate Geometry y y1 Slope: Circles 1 1 1 Midpoint: +,
Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
State if each pair of triangles is similar. If so, state how you know they are similar (AA, SAS, SSS) and complete the similarity statement.
 Geometry 1-2 est #7 Review Name Date Period State if each pair of triangles is similar. If so, state how you know they are similar (AA, SAS, SSS) and complete the similarity statement. 1) Q R 2) V F H
Geometry 1-2 est #7 Review Name Date Period State if each pair of triangles is similar. If so, state how you know they are similar (AA, SAS, SSS) and complete the similarity statement. 1) Q R 2) V F H
Year 9 Maths Overview
 Year 9 Maths Overview Unit Duration (lessons) Learning Objectives/Outcomes Data Handling 20 To interpret and discuss the data in a variety of ways To design and criticise a questionnaire To interpret and
Year 9 Maths Overview Unit Duration (lessons) Learning Objectives/Outcomes Data Handling 20 To interpret and discuss the data in a variety of ways To design and criticise a questionnaire To interpret and
