ICS 161 Algorithms Winter 1998 Final Exam. 1: out of 15. 2: out of 15. 3: out of 20. 4: out of 15. 5: out of 20. 6: out of 15.
|
|
|
- Piers James Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ICS 161 Algorithms Winter 1998 Final Exam Name: ID: 1: out of 15 2: out of 15 3: out of 20 4: out of 15 5: out of 20 6: out of 15 total: out of 100
2 1. Solve the following recurrences. (Just give the solutions; you do not need to prove that your answers are correct.) (a) T (n) = 4T (n/2) + O(n) (b) T (n) = 3T (n/3) + O(n log n) (c) T (n) = T (n/2) + O( n)
3 2. The following routine takes as input a list of n numbers, and returns the first value of i for which L[i] < L[i 1], or n if no such number exists. int firstdecrease(int * L, int n) { for (int i = 1; i < n && L[i] >= L[i-1]; i++) { } return i; } (a) How much time does the routine take, measured as a function of its return value i? (b) If the numbers are chosen independently at random, then the probability that firstdecrease(l) returns i is (i 1)/i!, except for the special case of i = n for which the probability is 1/n!. Use this fact to write an expression for the average value returned by the algorithm. (Your answer can be expressed as a sum, it does not have to be solved in closed form. Do not use O-notation.) (c) What is the average case running time of the routine? (Use O-notation.)
4 3. Suppose you are implementing a spreadsheet program, in which you must maintain a grid of cells. Some cells of the spreadsheet contain numbers, but other cells contain expressions that depend on other cells for their value. However, the expressions are not allowed to form a cycle of dependencies: for example, if the expression in cell E1 depends on the value of cell A5, and the expression in cell A5 depends on the value of cell C2, then C2 must not depend on E1. (a) Describe an algorithm for making sure that no cycle of dependencies exists (or finding one and complaining to the spreadsheet user if it does exist). (b) If the spreadsheet changes, all its expressions may need to be recalculated. Describe an efficient method for sorting the expression evaluations, so that each cell is recalculated only after the cells it depends on have been recalculated. (20 points)
5 4. Suppose you are given the convex hull of a set of n points, and one additional point (x, y). Describe how to test in time O(log n) whether or not (x, y) is contained inside the convex hull. (You may assume that you can test whether the point is above or below a line segment in constant time.)
6 5.Consider the following approximation to the longest common subsequence of two sequences A[0...n 1] and B[0...m 1], each of which contain character values in the range 0...k 1: simply find the longest sequence in which all characters are the same. Equivalently, define f (S, c) to be the number of copies of character c occurring in sequence S, and return max c (min( f (A, c), f (B, c))). For instance, if the character values are 0 and 1, and the sequences are A =0,1,1,0,1,1,0 and B =1,0,1,0,1, then f (A, 0) = 3, f (A, 1) = 4, f (B, 0) = 2, and f (B, 1) = 3, and the length of the approximate longest subsequence would be 3 (there is a common subsequence of 3 ones). (a) Describe how to implement this algorithm in time O(m + n + k). (b) What is the approximation ratio for this algorithm, measured as a function of m, n, and k? (c) Why might it be useful to find approximation algorithms for problems that we already know how to solve exactly in polynomial time? (20 points)
7 6. Consider the following two problems. In P1 we are given as input a set of n squares (specified by their corner points), and a number k. The problem is to determine whether there is any point in the plane that is covered by k or more squares. In P2 we are given as input an n-vertex graph, and a number k; the problem is to determine whether there is a set of k mutually adjacent vertices. (E.g. for k = 3 we are just looking for a triangle in the graph.) Obviously, the problems are both in NP. There exists a simple translation from P1 to P2: just make a graph vertex for each square, and add an edge between a pair of vertices if the corresponding two squares overlap. (a) If P1 is NP-complete, would this translation imply that P2 is NP-complete? (b) If P2 is NP-complete, would this translation imply that P1 is NP-complete? (c) Show that if we change P1 by making the input be a set of circles instead of squares, then the same translation doesn t work: there exists a set of circles such that no point is covered by 3 or more circles, even though there is a set of 3 mutually adjacent vertices in the corresponding graph.
Exam Sample Questions CS3212: Algorithms and Data Structures
 Exam Sample Questions CS31: Algorithms and Data Structures NOTE: the actual exam will contain around 0-5 questions. 1. Consider a LinkedList that has a get(int i) method to return the i-th element in the
Exam Sample Questions CS31: Algorithms and Data Structures NOTE: the actual exam will contain around 0-5 questions. 1. Consider a LinkedList that has a get(int i) method to return the i-th element in the
AtCoder World Tour Finals 2019
 AtCoder World Tour Finals 201 writer: rng 58 February 21st, 2018 A: Magic Suppose that the magician moved the treasure in the order y 1 y 2 y K+1. Here y i y i+1 for each i because it doesn t make sense
AtCoder World Tour Finals 201 writer: rng 58 February 21st, 2018 A: Magic Suppose that the magician moved the treasure in the order y 1 y 2 y K+1. Here y i y i+1 for each i because it doesn t make sense
1 Definition of Reduction
 1 Definition of Reduction Problem A is reducible, or more technically Turing reducible, to problem B, denoted A B if there a main program M to solve problem A that lacks only a procedure to solve problem
1 Definition of Reduction Problem A is reducible, or more technically Turing reducible, to problem B, denoted A B if there a main program M to solve problem A that lacks only a procedure to solve problem
Using Euler s Theorem
 Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Using Euler s Theorem Suppose that a connected, planar graph has 249 vertices and 57 faces. How many edges does it have? A: 106 B: 194 C: 304 D: 306 E: We don t have enough information Using Euler s Theorem
Practice Problems for the Final
 ECE-250 Algorithms and Data Structures (Winter 2012) Practice Problems for the Final Disclaimer: Please do keep in mind that this problem set does not reflect the exact topics or the fractions of each
ECE-250 Algorithms and Data Structures (Winter 2012) Practice Problems for the Final Disclaimer: Please do keep in mind that this problem set does not reflect the exact topics or the fractions of each
Decomposing Coverings and the Planar Sensor Cover Problem
 Intro. previous work. Restricted Strip Cover Decomposing Multiple Coverings Decomposing Coverings and the Planar Sensor Cover Problem Matt Gibson Kasturi Varadarajan presented by Niv Gafni 2012-12-12 Intro.
Intro. previous work. Restricted Strip Cover Decomposing Multiple Coverings Decomposing Coverings and the Planar Sensor Cover Problem Matt Gibson Kasturi Varadarajan presented by Niv Gafni 2012-12-12 Intro.
Lesson 1: Complementary and Supplementary Angles
 lasswork Opening As we begin our study of unknown angles, let us review key definitions. Term Definition Two angles and, with a common side, are angles if is in the interior of. When two lines intersect,
lasswork Opening As we begin our study of unknown angles, let us review key definitions. Term Definition Two angles and, with a common side, are angles if is in the interior of. When two lines intersect,
Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs
 Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs Subhas C. Nandy (nandysc@isical.ac.in) Advanced Computing and Microelectronics Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata 700108, India. Outline
Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs Subhas C. Nandy (nandysc@isical.ac.in) Advanced Computing and Microelectronics Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata 700108, India. Outline
Notes in Computational Geometry Voronoi Diagrams
 Notes in Computational Geometry Voronoi Diagrams Prof. Sandeep Sen and Prof. Amit Kumar Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Voronoi Diagrams In this lecture, we study Voronoi Diagrams, also known as
Notes in Computational Geometry Voronoi Diagrams Prof. Sandeep Sen and Prof. Amit Kumar Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Voronoi Diagrams In this lecture, we study Voronoi Diagrams, also known as
CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam
 CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam Name: ID: Instructions: Answer the questions directly on the exam pages. Show all your work for each question. Providing more detail including
CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam Name: ID: Instructions: Answer the questions directly on the exam pages. Show all your work for each question. Providing more detail including
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Spring 1999
 CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Spring 1999 Final Exam (May 7, 1999) Name: Net ID: Alias: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam! If you brought anything with you besides writing instruments and your
CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Spring 1999 Final Exam (May 7, 1999) Name: Net ID: Alias: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam! If you brought anything with you besides writing instruments and your
Scheduling, Map Coloring, and Graph Coloring
 Scheduling, Map Coloring, and Graph Coloring Scheduling via Graph Coloring: Final Exam Example Suppose want to schedule some ;inal exams for CS courses with following course numbers: 1007, 3137, 3157,
Scheduling, Map Coloring, and Graph Coloring Scheduling via Graph Coloring: Final Exam Example Suppose want to schedule some ;inal exams for CS courses with following course numbers: 1007, 3137, 3157,
EXAM ELEMENTARY MATH FOR GMT: ALGORITHM ANALYSIS NOVEMBER 7, 2013, 13:15-16:15, RUPPERT D
 SOLUTIONS EXAM ELEMENTARY MATH FOR GMT: ALGORITHM ANALYSIS NOVEMBER 7, 2013, 13:15-16:15, RUPPERT D This exam consists of 6 questions, worth 10 points in total, and a bonus question for 1 more point. Using
SOLUTIONS EXAM ELEMENTARY MATH FOR GMT: ALGORITHM ANALYSIS NOVEMBER 7, 2013, 13:15-16:15, RUPPERT D This exam consists of 6 questions, worth 10 points in total, and a bonus question for 1 more point. Using
Geometry. Zachary Friggstad. Programming Club Meeting
 Geometry Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting Points #i n c l u d e typedef complex p o i n t ; p o i n t p ( 1. 0, 5. 7 ) ; p. r e a l ( ) ; // x component p. imag ( ) ; // y component
Geometry Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting Points #i n c l u d e typedef complex p o i n t ; p o i n t p ( 1. 0, 5. 7 ) ; p. r e a l ( ) ; // x component p. imag ( ) ; // y component
Note: For all questions, answer (E) NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees.
 Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
Delaunay Triangulations
 Delaunay Triangulations (slides mostly by Glenn Eguchi) Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally approximate height of points not
Delaunay Triangulations (slides mostly by Glenn Eguchi) Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally approximate height of points not
Olympiad Hamilton Paper
 Olympiad Hamilton Paper 1 All candidates must be in School Year 10 (England and Wales), S (Scotland), or School Year 11 (Northern Ireland). 1. The sum of three positive integers is 11 and the sum of the
Olympiad Hamilton Paper 1 All candidates must be in School Year 10 (England and Wales), S (Scotland), or School Year 11 (Northern Ireland). 1. The sum of three positive integers is 11 and the sum of the
CS161 - Final Exam Computer Science Department, Stanford University August 16, 2008
 CS161 - Final Exam Computer Science Department, Stanford University August 16, 2008 Name: Honor Code 1. The Honor Code is an undertaking of the students, individually and collectively: a) that they will
CS161 - Final Exam Computer Science Department, Stanford University August 16, 2008 Name: Honor Code 1. The Honor Code is an undertaking of the students, individually and collectively: a) that they will
ICS 260 Fall 2001 Second Midterm
 ICS 260 Fall 2001 Second Midterm Name: Answer Key Student ID: 1: 20 2: 30 3: 20 4: 30 5: 20 Total: 1. Longest symmetric subsequence. (20 points) A symmetric sequence or palindrome is a sequence of characters
ICS 260 Fall 2001 Second Midterm Name: Answer Key Student ID: 1: 20 2: 30 3: 20 4: 30 5: 20 Total: 1. Longest symmetric subsequence. (20 points) A symmetric sequence or palindrome is a sequence of characters
CMPSCI611: The SUBSET-SUM Problem Lecture 18
 CMPSCI611: The SUBSET-SUM Problem Lecture 18 We begin today with the problem we didn t get to at the end of last lecture the SUBSET-SUM problem, which we also saw back in Lecture 8. The input to SUBSET-
CMPSCI611: The SUBSET-SUM Problem Lecture 18 We begin today with the problem we didn t get to at the end of last lecture the SUBSET-SUM problem, which we also saw back in Lecture 8. The input to SUBSET-
Improved Bounds for Intersecting Triangles and Halving Planes
 Improved Bounds for Intersecting Triangles and Halving Planes David Eppstein Department of Information and Computer Science University of California, Irvine, CA 92717 Tech. Report 91-60 July 15, 1991 Abstract
Improved Bounds for Intersecting Triangles and Halving Planes David Eppstein Department of Information and Computer Science University of California, Irvine, CA 92717 Tech. Report 91-60 July 15, 1991 Abstract
Angles. An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex.
 Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
2 Geometry Solutions
 2 Geometry Solutions jacques@ucsd.edu Here is give problems and solutions in increasing order of difficulty. 2.1 Easier problems Problem 1. What is the minimum number of hyperplanar slices to make a d-dimensional
2 Geometry Solutions jacques@ucsd.edu Here is give problems and solutions in increasing order of difficulty. 2.1 Easier problems Problem 1. What is the minimum number of hyperplanar slices to make a d-dimensional
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/80/81039886.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 16 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 16 Notes Goals for this week Graph basics Types
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 16 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 16 Notes Goals for this week Graph basics Types
Problem Set 1. Solution. CS4234: Optimization Algorithms. Solution Sketches
 CS4234: Optimization Algorithms Sketches Problem Set 1 S-1. You are given a graph G = (V, E) with n nodes and m edges. (Perhaps the graph represents a telephone network.) Each edge is colored either blue
CS4234: Optimization Algorithms Sketches Problem Set 1 S-1. You are given a graph G = (V, E) with n nodes and m edges. (Perhaps the graph represents a telephone network.) Each edge is colored either blue
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Year 10 Topic Practice Papers: Polygons Polygons 1 Grade 4 Look at the shapes below A B C Shape A, B and C are polygons Write down the mathematical name for each of the polygons
PLC Papers Created For: Year 10 Topic Practice Papers: Polygons Polygons 1 Grade 4 Look at the shapes below A B C Shape A, B and C are polygons Write down the mathematical name for each of the polygons
Computational Geometry
 Lecture 12: Lecture 12: Motivation: Terrains by interpolation To build a model of the terrain surface, we can start with a number of sample points where we know the height. Lecture 12: Motivation: Terrains
Lecture 12: Lecture 12: Motivation: Terrains by interpolation To build a model of the terrain surface, we can start with a number of sample points where we know the height. Lecture 12: Motivation: Terrains
The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9
 Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
CMPSCI611: The Simplex Algorithm Lecture 24
 CMPSCI611: The Simplex Algorithm Lecture 24 Let s first review the general situation for linear programming problems. Our problem in standard form is to choose a vector x R n, such that x 0 and Ax = b,
CMPSCI611: The Simplex Algorithm Lecture 24 Let s first review the general situation for linear programming problems. Our problem in standard form is to choose a vector x R n, such that x 0 and Ax = b,
K-structure, Separating Chain, Gap Tree, and Layered DAG
 K-structure, Separating Chain, Gap Tree, and Layered DAG Presented by Dave Tahmoush Overview Improvement on Gap Tree and K-structure Faster point location Encompasses Separating Chain Better storage Designed
K-structure, Separating Chain, Gap Tree, and Layered DAG Presented by Dave Tahmoush Overview Improvement on Gap Tree and K-structure Faster point location Encompasses Separating Chain Better storage Designed
UNIVERSITY of OSLO. Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences. INF 4130/9135: Algorithms: Design and efficiency Date of exam: 8th December 2016
 UNIVERIY of OLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural ciences Exam in: INF 4130/9135: Algorithms: Design and efficiency Date of exam: 8th December 2016 Exam hours: 09:00 13:00 (4 hours) Exam paper consists
UNIVERIY of OLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural ciences Exam in: INF 4130/9135: Algorithms: Design and efficiency Date of exam: 8th December 2016 Exam hours: 09:00 13:00 (4 hours) Exam paper consists
Introduction to Algorithms May 14, 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professors Erik Demaine and Shafi Goldwasser.
 Introduction to Algorithms May 14, 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Erik Demaine and Shafi Goldwasser Practice Final Practice Final Do not open this exam booklet until
Introduction to Algorithms May 14, 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Erik Demaine and Shafi Goldwasser Practice Final Practice Final Do not open this exam booklet until
2018 AIME I Problems
 2018 AIME I Problems Problem 1 Let be the number of ordered pairs of integers, with and such that the polynomial x + x + can be factored into the product of two (not necessarily distinct) linear factors
2018 AIME I Problems Problem 1 Let be the number of ordered pairs of integers, with and such that the polynomial x + x + can be factored into the product of two (not necessarily distinct) linear factors
COT 6936: Topics in Algorithms! Giri Narasimhan. ECS 254A / EC 2443; Phone: x3748
 COT 6936: Topics in Algorithms! Giri Narasimhan ECS 254A / EC 2443; Phone: x3748 giri@cs.fiu.edu http://www.cs.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/cot6936_s12.html https://moodle.cis.fiu.edu/v2.1/course/view.php?id=174
COT 6936: Topics in Algorithms! Giri Narasimhan ECS 254A / EC 2443; Phone: x3748 giri@cs.fiu.edu http://www.cs.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/cot6936_s12.html https://moodle.cis.fiu.edu/v2.1/course/view.php?id=174
Introduction to Algorithms and Complexity Theory
 Introduction to Algorithms and Complexity Theory Iris Cong UCLA Math Circle - HS II Example 1. Algorithm to find the maximum of a list of N positive integers (call this list L 0, L N-1 ): initialize accumulator
Introduction to Algorithms and Complexity Theory Iris Cong UCLA Math Circle - HS II Example 1. Algorithm to find the maximum of a list of N positive integers (call this list L 0, L N-1 ): initialize accumulator
Optimal Compression of a Polyline with Segments and Arcs
 Optimal Compression of a Polyline with Segments and Arcs Alexander Gribov Esri 380 New York Street Redlands, CA 92373 Email: agribov@esri.com arxiv:1604.07476v5 [cs.cg] 10 Apr 2017 Abstract This paper
Optimal Compression of a Polyline with Segments and Arcs Alexander Gribov Esri 380 New York Street Redlands, CA 92373 Email: agribov@esri.com arxiv:1604.07476v5 [cs.cg] 10 Apr 2017 Abstract This paper
CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes
 1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Lecture Outline Triangulating
1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Lecture Outline Triangulating
Tiling-Harmonic Functions
 Tiling-Harmonic Functions Yilun Du Vyron Vellis (Graduate Student Mentor) Sergiy Merenkov (Faculty Mentor) PRIMES-IGL Fourth Annual PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014 Table of Contents 1 Grid Harmonic Function
Tiling-Harmonic Functions Yilun Du Vyron Vellis (Graduate Student Mentor) Sergiy Merenkov (Faculty Mentor) PRIMES-IGL Fourth Annual PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014 Table of Contents 1 Grid Harmonic Function
MAS341 Graph Theory 2015 exam solutions
 MAS4 Graph Theory 0 exam solutions Question (i)(a) Draw a graph with a vertex for each row and column of the framework; connect a row vertex to a column vertex if there is a brace where the row and column
MAS4 Graph Theory 0 exam solutions Question (i)(a) Draw a graph with a vertex for each row and column of the framework; connect a row vertex to a column vertex if there is a brace where the row and column
11. APPROXIMATION ALGORITHMS
 11. APPROXIMATION ALGORITHMS load balancing center selection pricing method: vertex cover LP rounding: vertex cover generalized load balancing knapsack problem Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005
11. APPROXIMATION ALGORITHMS load balancing center selection pricing method: vertex cover LP rounding: vertex cover generalized load balancing knapsack problem Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005
Department of Computer Applications. MCA 312: Design and Analysis of Algorithms. [Part I : Medium Answer Type Questions] UNIT I
![Department of Computer Applications. MCA 312: Design and Analysis of Algorithms. [Part I : Medium Answer Type Questions] UNIT I Department of Computer Applications. MCA 312: Design and Analysis of Algorithms. [Part I : Medium Answer Type Questions] UNIT I](/thumbs/94/122075835.jpg) MCA 312: Design and Analysis of Algorithms [Part I : Medium Answer Type Questions] UNIT I 1) What is an Algorithm? What is the need to study Algorithms? 2) Define: a) Time Efficiency b) Space Efficiency
MCA 312: Design and Analysis of Algorithms [Part I : Medium Answer Type Questions] UNIT I 1) What is an Algorithm? What is the need to study Algorithms? 2) Define: a) Time Efficiency b) Space Efficiency
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/89/99028465.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 11 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 11 Notes Goals for this week (Tuesday) Linearity
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 11 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 11 Notes Goals for this week (Tuesday) Linearity
Math Summer 2012
 Math 481 - Summer 2012 Final Exam You have one hour and fifty minutes to complete this exam. You are not allowed to use any electronic device. Be sure to give reasonable justification to all your answers.
Math 481 - Summer 2012 Final Exam You have one hour and fifty minutes to complete this exam. You are not allowed to use any electronic device. Be sure to give reasonable justification to all your answers.
CS612 Algorithms for Electronic Design Automation
 CS612 Algorithms for Electronic Design Automation Lecture 8 Network Flow Based Modeling 1 Flow Network Definition Given a directed graph G = (V, E): Each edge (u, v) has capacity c(u,v) 0 Each edge (u,
CS612 Algorithms for Electronic Design Automation Lecture 8 Network Flow Based Modeling 1 Flow Network Definition Given a directed graph G = (V, E): Each edge (u, v) has capacity c(u,v) 0 Each edge (u,
18.S34 (FALL 2007) PROBLEMS ON HIDDEN INDEPENDENCE AND UNIFORMITY
 18.S34 (FALL 2007) PROBLEMS ON HIDDEN INDEPENDENCE AND UNIFORMITY All the problems below (with the possible exception of the last one), when looked at the right way, can be solved by elegant arguments
18.S34 (FALL 2007) PROBLEMS ON HIDDEN INDEPENDENCE AND UNIFORMITY All the problems below (with the possible exception of the last one), when looked at the right way, can be solved by elegant arguments
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing. David Eppstein
 Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
UML CS Algorithms Qualifying Exam Fall, 2004 ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM
 ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM This exam is open books & notes and closed neighbors & calculators. The upper bound on exam time is 3 hours. Please put all your work on the exam paper. Please write your name
ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM This exam is open books & notes and closed neighbors & calculators. The upper bound on exam time is 3 hours. Please put all your work on the exam paper. Please write your name
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever.
 Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
6.006 Final Exam Name 2. Problem 1. True or False [30 points] (10 parts) For each of the following questions, circle either True, False or Unknown.
![6.006 Final Exam Name 2. Problem 1. True or False [30 points] (10 parts) For each of the following questions, circle either True, False or Unknown. 6.006 Final Exam Name 2. Problem 1. True or False [30 points] (10 parts) For each of the following questions, circle either True, False or Unknown.](/thumbs/90/102638958.jpg) Introduction to Algorithms December 14, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Fall 2009 Professors Srini Devadas and Constantinos (Costis) Daskalakis Final Exam Final Exam Do not open this quiz
Introduction to Algorithms December 14, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Fall 2009 Professors Srini Devadas and Constantinos (Costis) Daskalakis Final Exam Final Exam Do not open this quiz
1 Format. 2 Topics Covered. 2.1 Minimal Spanning Trees. 2.2 Union Find. 2.3 Greedy. CS 124 Quiz 2 Review 3/25/18
 CS 124 Quiz 2 Review 3/25/18 1 Format You will have 83 minutes to complete the exam. The exam may have true/false questions, multiple choice, example/counterexample problems, run-this-algorithm problems,
CS 124 Quiz 2 Review 3/25/18 1 Format You will have 83 minutes to complete the exam. The exam may have true/false questions, multiple choice, example/counterexample problems, run-this-algorithm problems,
Chapter 8. Voronoi Diagrams. 8.1 Post Oce Problem
 Chapter 8 Voronoi Diagrams 8.1 Post Oce Problem Suppose there are n post oces p 1,... p n in a city. Someone who is located at a position q within the city would like to know which post oce is closest
Chapter 8 Voronoi Diagrams 8.1 Post Oce Problem Suppose there are n post oces p 1,... p n in a city. Someone who is located at a position q within the city would like to know which post oce is closest
Identify parallel lines, skew lines and perpendicular lines.
 Learning Objectives Identify parallel lines, skew lines and perpendicular lines. Parallel Lines and Planes Parallel lines are coplanar (they lie in the same plane) and never intersect. Below is an example
Learning Objectives Identify parallel lines, skew lines and perpendicular lines. Parallel Lines and Planes Parallel lines are coplanar (they lie in the same plane) and never intersect. Below is an example
Bottleneck Steiner Tree with Bounded Number of Steiner Vertices
 Bottleneck Steiner Tree with Bounded Number of Steiner Vertices A. Karim Abu-Affash Paz Carmi Matthew J. Katz June 18, 2011 Abstract Given a complete graph G = (V, E), where each vertex is labeled either
Bottleneck Steiner Tree with Bounded Number of Steiner Vertices A. Karim Abu-Affash Paz Carmi Matthew J. Katz June 18, 2011 Abstract Given a complete graph G = (V, E), where each vertex is labeled either
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
Chapter 16. Greedy Algorithms
 Chapter 16. Greedy Algorithms Algorithms for optimization problems (minimization or maximization problems) typically go through a sequence of steps, with a set of choices at each step. A greedy algorithm
Chapter 16. Greedy Algorithms Algorithms for optimization problems (minimization or maximization problems) typically go through a sequence of steps, with a set of choices at each step. A greedy algorithm
Tropical Orthogonal Representations
 Tropical Orthogonal Representations Los Angeles Math Circle, May, 016 Bryant Mathews, Azusa Pacific University 1 Orthogonal Representations of Graphs A graph G consists of a set V of vertices and a set
Tropical Orthogonal Representations Los Angeles Math Circle, May, 016 Bryant Mathews, Azusa Pacific University 1 Orthogonal Representations of Graphs A graph G consists of a set V of vertices and a set
Reductions. Linear Time Reductions. Desiderata. Reduction. Desiderata. Classify problems according to their computational requirements.
 Desiderata Reductions Desiderata. Classify problems according to their computational requirements. Frustrating news. Huge number of fundamental problems have defied classification for decades. Desiderata'.
Desiderata Reductions Desiderata. Classify problems according to their computational requirements. Frustrating news. Huge number of fundamental problems have defied classification for decades. Desiderata'.
Rasterization. COMP 575/770 Spring 2013
 Rasterization COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 The Rasterization Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to
Rasterization COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 The Rasterization Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to
Grids Geometry Computational Geometry
 Grids Geometry Computational Geometry Grids You will encounter many problems whose solutions need grid representation map VLSI layout the most natural way to carve space into regions regular pattern rectangular
Grids Geometry Computational Geometry Grids You will encounter many problems whose solutions need grid representation map VLSI layout the most natural way to carve space into regions regular pattern rectangular
Lecture 3: Totally Unimodularity and Network Flows
 Lecture 3: Totally Unimodularity and Network Flows (3 units) Outline Properties of Easy Problems Totally Unimodular Matrix Minimum Cost Network Flows Dijkstra Algorithm for Shortest Path Problem Ford-Fulkerson
Lecture 3: Totally Unimodularity and Network Flows (3 units) Outline Properties of Easy Problems Totally Unimodular Matrix Minimum Cost Network Flows Dijkstra Algorithm for Shortest Path Problem Ford-Fulkerson
Delaunay Triangulations. Presented by Glenn Eguchi Computational Geometry October 11, 2001
 Delaunay Triangulations Presented by Glenn Eguchi 6.838 Computational Geometry October 11, 2001 Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally
Delaunay Triangulations Presented by Glenn Eguchi 6.838 Computational Geometry October 11, 2001 Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally
MT365 Examination 2007 Part 1. Q1 (a) (b) (c) A
 MT6 Examination Part Solutions Q (a) (b) (c) F F F E E E G G G G is both Eulerian and Hamiltonian EF is both an Eulerian trail and a Hamiltonian cycle. G is Hamiltonian but not Eulerian and EF is a Hamiltonian
MT6 Examination Part Solutions Q (a) (b) (c) F F F E E E G G G G is both Eulerian and Hamiltonian EF is both an Eulerian trail and a Hamiltonian cycle. G is Hamiltonian but not Eulerian and EF is a Hamiltonian
ARC 088/ABC 083. A: Libra. DEGwer 2017/12/23. #include <s t d i o. h> i n t main ( )
 ARC 088/ABC 083 DEGwer 2017/12/23 A: Libra A, B, C, D A + B C + D #include i n t main ( ) i n t a, b, c, d ; s c a n f ( %d%d%d%d, &a, &b, &c, &d ) ; i f ( a + b > c + d ) p r i n t f (
ARC 088/ABC 083 DEGwer 2017/12/23 A: Libra A, B, C, D A + B C + D #include i n t main ( ) i n t a, b, c, d ; s c a n f ( %d%d%d%d, &a, &b, &c, &d ) ; i f ( a + b > c + d ) p r i n t f (
Commando: Solution. Solution 3 O(n): Consider two decisions i<j, we choose i instead of j if and only if : A S j S i
 Commando: Solution Commando: Solution Solution 1 O(n 3 ): Using dynamic programming, let f(n) indicate the maximum battle effectiveness after adjustment. We have transfer equations below: n f(n) = max
Commando: Solution Commando: Solution Solution 1 O(n 3 ): Using dynamic programming, let f(n) indicate the maximum battle effectiveness after adjustment. We have transfer equations below: n f(n) = max
Section 4: Introduction to Polygons Part 1
 The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the
The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the
Dynamic Programming Algorithms
 CSC 364S Notes University of Toronto, Fall 2003 Dynamic Programming Algorithms The setting is as follows. We wish to find a solution to a given problem which optimizes some quantity Q of interest; for
CSC 364S Notes University of Toronto, Fall 2003 Dynamic Programming Algorithms The setting is as follows. We wish to find a solution to a given problem which optimizes some quantity Q of interest; for
Lattice Polygon s and Pick s Theorem From Dana Paquin and Tom Davis 1 Warm-Up to Ponder
 Lattice Polygon s and Pick s Theorem From Dana Paquin and Tom Davis http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles/pick.pdf 1 Warm-Up to Ponder 1. Is it possible to draw an equilateral triangle on graph paper so
Lattice Polygon s and Pick s Theorem From Dana Paquin and Tom Davis http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles/pick.pdf 1 Warm-Up to Ponder 1. Is it possible to draw an equilateral triangle on graph paper so
Math 414 Lecture 30. The greedy algorithm provides the initial transportation matrix.
 Math Lecture The greedy algorithm provides the initial transportation matrix. matrix P P Demand W ª «2 ª2 «W ª «W ª «ª «ª «Supply The circled x ij s are the initial basic variables. Erase all other values
Math Lecture The greedy algorithm provides the initial transportation matrix. matrix P P Demand W ª «2 ª2 «W ª «W ª «ª «ª «Supply The circled x ij s are the initial basic variables. Erase all other values
CSE Winter 2015 Quiz 1 Solutions
 CSE 101 - Winter 2015 Quiz 1 Solutions January 12, 2015 1. What is the maximum possible number of vertices in a binary tree of height h? The height of a binary tree is the length of the longest path from
CSE 101 - Winter 2015 Quiz 1 Solutions January 12, 2015 1. What is the maximum possible number of vertices in a binary tree of height h? The height of a binary tree is the length of the longest path from
Rectangular Partitioning
 Rectangular Partitioning Joe Forsmann and Rock Hymas Introduction/Abstract We will look at a problem that I (Rock) had to solve in the course of my work. Given a set of non-overlapping rectangles each
Rectangular Partitioning Joe Forsmann and Rock Hymas Introduction/Abstract We will look at a problem that I (Rock) had to solve in the course of my work. Given a set of non-overlapping rectangles each
CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 4: Asymptotic Analysis. Aaron Bauer Winter 2014
 CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 4: Asymptotic Analysis Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 Previously, on CSE 373 We want to analyze algorithms for efficiency (in time and space) And do so generally
CSE373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 4: Asymptotic Analysis Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 Previously, on CSE 373 We want to analyze algorithms for efficiency (in time and space) And do so generally
PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 2011 HIGH SCHOOL - PROBLEMS. The ratio of 3 to the positive number n is the same as the ratio of n to 192. Find n.
 PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 2011 HIGH SCHOOL - PROBLEMS Copyright Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem 1 The ratio of 3 to the positive number n is the same as the ratio of n to 192. Find n. Problem
PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 2011 HIGH SCHOOL - PROBLEMS Copyright Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem 1 The ratio of 3 to the positive number n is the same as the ratio of n to 192. Find n. Problem
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms Midterm 3 Review Solution Sketches Fall 2018
 CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms Midterm 3 Review Solution Sketches Fall 2018 Q1: Prove or disprove: You are given a connected undirected graph G = (V, E) with a weight function w defined over its
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms Midterm 3 Review Solution Sketches Fall 2018 Q1: Prove or disprove: You are given a connected undirected graph G = (V, E) with a weight function w defined over its
Lecture 21: Other Reductions Steven Skiena
 Lecture 21: Other Reductions Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/ skiena Problem of the Day Show that the dense
Lecture 21: Other Reductions Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/ skiena Problem of the Day Show that the dense
CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Fall Name: Net ID: Alias: U 3 / 4 1
 CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Fall 2000 Homework 1 (due November 16, 2000 at midnight) Starting with Homework 1, homeworks may be done in teams of up to three people. Each team turns in just one solution,
CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Fall 2000 Homework 1 (due November 16, 2000 at midnight) Starting with Homework 1, homeworks may be done in teams of up to three people. Each team turns in just one solution,
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics
 Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 97 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Optimization vs. Decision
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 97 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Optimization vs. Decision
Algorithms (IX) Guoqiang Li. School of Software, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 Algorithms (IX) Guoqiang Li School of Software, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Q: What we have learned in Algorithm? Algorithm Design Algorithm Design Basic methodologies: Algorithm Design Algorithm Design
Algorithms (IX) Guoqiang Li School of Software, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Q: What we have learned in Algorithm? Algorithm Design Algorithm Design Basic methodologies: Algorithm Design Algorithm Design
Exam 3 Practice Problems
 Exam 3 Practice Problems HONOR CODE: You are allowed to work in groups on these problems, and also to talk to the TAs (the TAs have not seen these problems before and they do not know the solutions but
Exam 3 Practice Problems HONOR CODE: You are allowed to work in groups on these problems, and also to talk to the TAs (the TAs have not seen these problems before and they do not know the solutions but
Definitions. Topology/Geometry of Geodesics. Joseph D. Clinton. SNEC June Magnus J. Wenninger
 Topology/Geometry of Geodesics Joseph D. Clinton SNEC-04 28-29 June 2003 Magnus J. Wenninger Introduction Definitions Topology Goldberg s polyhedra Classes of Geodesic polyhedra Triangular tessellations
Topology/Geometry of Geodesics Joseph D. Clinton SNEC-04 28-29 June 2003 Magnus J. Wenninger Introduction Definitions Topology Goldberg s polyhedra Classes of Geodesic polyhedra Triangular tessellations
On the Minimum Number of Convex Quadrilaterals in Point Sets of Given Numbers of Points
 On the Minimum Number of Convex Quadrilaterals in Point Sets of Given Numbers of Points Hu Yuzhong Chen Luping Zhu Hui Ling Xiaofeng (Supervisor) Abstract Consider the following problem. Given n, k N,
On the Minimum Number of Convex Quadrilaterals in Point Sets of Given Numbers of Points Hu Yuzhong Chen Luping Zhu Hui Ling Xiaofeng (Supervisor) Abstract Consider the following problem. Given n, k N,
INDIAN STATISTICAL INSTITUTE
 INDIAN STATISTICAL INSTITUTE Mid Semestral Examination M. Tech (CS) - I Year, 2016-2017 (Semester - II) Design and Analysis of Algorithms Date : 21.02.2017 Maximum Marks : 60 Duration : 3.0 Hours Note:
INDIAN STATISTICAL INSTITUTE Mid Semestral Examination M. Tech (CS) - I Year, 2016-2017 (Semester - II) Design and Analysis of Algorithms Date : 21.02.2017 Maximum Marks : 60 Duration : 3.0 Hours Note:
Final Exam Math 38 Graph Theory Spring 2017 Due on Friday, June 2, at 12:50 pm. Good Luck!!
 Final Exam Math 38 Graph Theory Spring 2017 Due on Friday, June 2, at 12:50 pm NAME: Instructions: You can use the textbook (Doug West s Introduction to Graph Theory, without solutions), your notes from
Final Exam Math 38 Graph Theory Spring 2017 Due on Friday, June 2, at 12:50 pm NAME: Instructions: You can use the textbook (Doug West s Introduction to Graph Theory, without solutions), your notes from
Which of the following toolbar buttons would you use to find the sum of a group of selected cells?
 Which of the following toolbar buttons would you use to find the sum of a group of selected cells? Selecting a group of cells and clicking on Set Print Area as shown in the figure below has what effect?
Which of the following toolbar buttons would you use to find the sum of a group of selected cells? Selecting a group of cells and clicking on Set Print Area as shown in the figure below has what effect?
1. CONVEX POLYGONS. Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D.
 1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
6.2 Classification of Closed Surfaces
 Table 6.1: A polygon diagram 6.1.2 Second Proof: Compactifying Teichmuller Space 6.2 Classification of Closed Surfaces We saw that each surface has a triangulation. Compact surfaces have finite triangulations.
Table 6.1: A polygon diagram 6.1.2 Second Proof: Compactifying Teichmuller Space 6.2 Classification of Closed Surfaces We saw that each surface has a triangulation. Compact surfaces have finite triangulations.
Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction
 Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction 1. Overview Feng Li 308262 Kuan Tian 308263 This document is written for the 3D reconstruction part in the course Scanning real world objects
Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction 1. Overview Feng Li 308262 Kuan Tian 308263 This document is written for the 3D reconstruction part in the course Scanning real world objects
ON SWELL COLORED COMPLETE GRAPHS
 Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXIII, (1994), pp. 303 308 303 ON SWELL COLORED COMPLETE GRAPHS C. WARD and S. SZABÓ Abstract. An edge-colored graph is said to be swell-colored if each triangle contains
Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXIII, (1994), pp. 303 308 303 ON SWELL COLORED COMPLETE GRAPHS C. WARD and S. SZABÓ Abstract. An edge-colored graph is said to be swell-colored if each triangle contains
Caltech Harvey Mudd Mathematics Competition March 3, 2012
 Team Round Caltech Harvey Mudd Mathematics Competition March 3, 2012 1. Let a, b, c be positive integers. Suppose that (a + b)(a + c) = 77 and (a + b)(b + c) = 56. Find (a + c)(b + c). Solution: The answer
Team Round Caltech Harvey Mudd Mathematics Competition March 3, 2012 1. Let a, b, c be positive integers. Suppose that (a + b)(a + c) = 77 and (a + b)(b + c) = 56. Find (a + c)(b + c). Solution: The answer
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
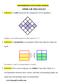 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Graph Algorithms (part 3 of CSC 282),
 Graph Algorithms (part of CSC 8), http://www.cs.rochester.edu/~stefanko/teaching/11cs8 Homework problem sessions are in CSB 601, 6:1-7:1pm on Oct. (Wednesday), Oct. 1 (Wednesday), and on Oct. 19 (Wednesday);
Graph Algorithms (part of CSC 8), http://www.cs.rochester.edu/~stefanko/teaching/11cs8 Homework problem sessions are in CSB 601, 6:1-7:1pm on Oct. (Wednesday), Oct. 1 (Wednesday), and on Oct. 19 (Wednesday);
Graph Algorithms (part 3 of CSC 282),
 Graph Algorithms (part of CSC 8), http://www.cs.rochester.edu/~stefanko/teaching/10cs8 1 Schedule Homework is due Thursday, Oct 1. The QUIZ will be on Tuesday, Oct. 6. List of algorithms covered in the
Graph Algorithms (part of CSC 8), http://www.cs.rochester.edu/~stefanko/teaching/10cs8 1 Schedule Homework is due Thursday, Oct 1. The QUIZ will be on Tuesday, Oct. 6. List of algorithms covered in the
FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 COMP/MATH 3804 Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Fall 2015 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Question 1 (12%). Modify Euclid s algorithm as follows. function Newclid(a,b) if a
COMP/MATH 3804 Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Fall 2015 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Question 1 (12%). Modify Euclid s algorithm as follows. function Newclid(a,b) if a
Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning
 Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 / 29 Y Tao Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning In this lecture, we
Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 / 29 Y Tao Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning In this lecture, we
Advanced Operations Research Techniques IE316. Quiz 1 Review. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Advanced Operations Research Techniques IE316 Quiz 1 Review Dr. Ted Ralphs IE316 Quiz 1 Review 1 Reading for The Quiz Material covered in detail in lecture. 1.1, 1.4, 2.1-2.6, 3.1-3.3, 3.5 Background material
Advanced Operations Research Techniques IE316 Quiz 1 Review Dr. Ted Ralphs IE316 Quiz 1 Review 1 Reading for The Quiz Material covered in detail in lecture. 1.1, 1.4, 2.1-2.6, 3.1-3.3, 3.5 Background material
CS 112 Final May 8, 2008 (Lightly edited for 2012 Practice) Name: BU ID: Instructions
 CS 112 Final May 8, 2008 (Lightly edited for 2012 Practice) Name: BU ID: This exam is CLOSED book and notes. Instructions The exam consists of six questions on 11 pages. Please answer all questions on
CS 112 Final May 8, 2008 (Lightly edited for 2012 Practice) Name: BU ID: This exam is CLOSED book and notes. Instructions The exam consists of six questions on 11 pages. Please answer all questions on
Graph Coloring. Margaret M. Fleck. 3 May This lecture discusses the graph coloring problem (section 9.8 of Rosen).
 Graph Coloring Margaret M. Fleck 3 May 2010 This lecture discusses the graph coloring problem (section 9.8 of Rosen). 1 Announcements Makeup quiz last day of classes (at the start of class). Your room
Graph Coloring Margaret M. Fleck 3 May 2010 This lecture discusses the graph coloring problem (section 9.8 of Rosen). 1 Announcements Makeup quiz last day of classes (at the start of class). Your room
Geometry Midterm Review Vocabulary:
 Name Date Period Geometry Midterm Review 2016-2017 Vocabulary: 1. Points that lie on the same line. 1. 2. Having the same size, same shape 2. 3. These are non-adjacent angles formed by intersecting lines.
Name Date Period Geometry Midterm Review 2016-2017 Vocabulary: 1. Points that lie on the same line. 1. 2. Having the same size, same shape 2. 3. These are non-adjacent angles formed by intersecting lines.
Lecture Tessellations, fractals, projection. Amit Zoran. Advanced Topics in Digital Design
 Lecture Tessellations, fractals, projection Amit Zoran Advanced Topics in Digital Design 67682 The Rachel and Selim Benin School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
Lecture Tessellations, fractals, projection Amit Zoran Advanced Topics in Digital Design 67682 The Rachel and Selim Benin School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
Theorems & Postulates Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
