Computational Optimization. Constrained Optimization Algorithms
|
|
|
- Anna Leona Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computational Optimization Constrained Optimization Algorithms
2 Same basic algorithms Repeat Determine descent direction Determine step size Take a step Until Optimal But now must consider feasibility, e.g. Pick a feasible descent directions Choose step size to maintain feasibility Need dual multipliers to check optimality
3 Builds on Prior Approaches Unconstrained: min f ( x) Lots of approaches Linear Equality Constrained: min f ( x) st.. Ax= b Convert to unconstrained and solve
4 Prior Approaches (cont) Linear Inequality Constrained: min f ( x) st.. Ax b Identify active constraints Solve subproblems Nonlinear Inequality Constrained: min f( x) st.. g( x) 0 Linearize constraints Solve subproblems
5 Feasible Direction Methods Use feasible descent directs. Consider 1 min xqx ' + cx ' 2 st.. Ax= b If we have feasible point ˆx then all x = xˆ + Zp are feasible.
6 Reduced Problem 1 min p ( x ˆ + Zp) ' Q( x ˆ + Zp) + c'( x ˆ + Zp) min ' ' ( ˆ ) ' ˆ ˆ ' ˆ p p Z QZp + Qx + c Zp + xqx + c x min ' ' ( ˆ p pzqzp+ Qx+ c) ' Zp 2 ZQZ ' : = Reduced Hessian Z'( Q( xˆ + Zp) + c) : = Reduced Gradient
7 Reduced Newton s Equation For general problems Z 2 ' f( x) Z : = Reduced Hessian Z' f( x) : = Reduced Gradient Reduced Newton Equations Z f x Z v Z f x 2 ' ( ) = - ' ( ) v = Z f x Z Z f x 2 1 ( ' ( ) ) ' ( ) in reduced space 2 1 p = Zv = Z( Z' f( x) Z ) Z' f( x) in original space Then apply usual Newton s Method
8 Reduced Steepest Descent Use reduced steepest descent direction v = Z' f( x) in reduced space d = Zv = ZZ' f( x) in original space Convergence rate depends on condition number of reduced Hessian Cond Z f x Z Cond Z Z Cond f x 2 2 ( ' ( ) ) ( ' ) ( ( )) KEY POINT Construct Z to have good conditioning!
9 Ways to Compute Z Projection Method (orthogonal and non-orthogonal) Variable Reduction QR Factorization What are they and how do they effect conditioning? How can you use them to compute multipliers?
10 Projection Method Find closest feasible point min c x Ax = 0 x Compute a KKT point: This is optimal projection since problem is convex
11 min c x Ax = 0 x Projection Method Lx (, λ) = c x + ( Ax)' λ ( ) xlx (, λ) = c x + A' λ = 0 KKT are Ax b = 0 Ac Ax AA' λ = 0 ( ') 1 ( ') ( ') 1 AA' λ = Ac λ = AA Ac x = c A' AA Ac 1 x = I A' AA A c ( ) 1 Projection Matrix P = I A' AA' A
12 Project method The matrix ( ) ' 1 Z = I A' AA A is a basis for the null space matrix of A. Check ( ) AZ = A I A' AA' 1 A = A A = 0
13 Get Lagrangian Multipliers for free! The matrix 1 1 A A' AA' = where AA = AA' AA' = I r ( ) ( ) is the right inverse matrix for A. For general problems r min f ( x) st.. Ax λ ' r * = A f( x*) = b
14 Let s try it For min f( x) = 2 x + x + x + x st.. x + x + x + x = 1 Projection matrix Z = I A' AA' A= ( ) [ ] [ ] =
15 Solve FONC for Optimal Point FONC x 1 1 x 1 f( x) A' λ λ x 1 x 1 4 x + x + x + x = 1 2 = =
16 Check Optimality Conditions For x* = [1111]/ 4 f( x*) = [1111]/ 4 Ax* = b Z f(*) x = * = Using Lagrangian ( ) 1 1 Ar = A' AA' = [1111]' 4 λ = A f(*) x = 1/4 r Clearly f(*) x = A' λ
17 For min f( x) = x' Cx 1 2 st.. Ax= b You try it C = A= b = Find projection matrix Confirm optimality conds are Z Cx*=0, Ax* = b Find x* Compute Lagrangian multipliers Check Lagrangian form of the multipliers.
18 Projected Gradient Method Algorithm for min f(x) s.t. Ax=b Let Z=I-A (AA ) -1 A x 0 given g =gradf(x 0 ) While not optimal d=-z g x i+1 = x i+ αd (use linesearch) g =gradf(x i+1 ) i=i+1
19 Projected Gradient Method Equivalent to steepest descent on f(x+zp) where x is some feasible point. So convergence rate depends on condition number of this problem The condition number is less than equal condition of Hessian of f * Compute Z HZ for last example and check it s conditioning:
20 Lagrangian Multipliers Each null space method yields a corresponding calculation of the right inverse. Thus each yields calculation of corresponding dual multipliers.
21 Variable Reduction Method Let A=[B N] A is m by n B is m by m assume m < n Z 1 B N = I is a basis matrix for null space of A 1 1 B B A [ ] r = AAr = BN = I
22 Try on our example Take for example first two columns for B Then A= = [ B N] = Z = A r = Condition number of Z CZ = 158 better but not great
23 QR Factorization Use Gram-Schmidt algorithm to make orthogonal factorize A =QR with Q orthogonal and R upper triangular R1 A' = QR = [ Q1 Q2] 0 where A m n, Q n m, Q n ( n m), R m m Z = Q A = QR T 2 r
24 QR on problem Use matlab command QR [Q R ] = qr(a ) Q2 = Q(:,3:4) Cond(Q2 *C*Q2) = 9.79
25 Next Problem Consider Next Hardest Problem min f ( x) s.. t Ax b How could we adapt gradient projection or other linear equality constrained problem to this problem?
Computational Optimization. Constrained Optimization
 Computational Optimization Constrained Optimization Easiest Problem Linear equality constraints min f( ) f R s.. t A b A R, b R n m n m Null Space Representation Let * be a feasible point, A*b. Any other
Computational Optimization Constrained Optimization Easiest Problem Linear equality constraints min f( ) f R s.. t A b A R, b R n m n m Null Space Representation Let * be a feasible point, A*b. Any other
Contents. I Basics 1. Copyright by SIAM. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
LECTURE 13: SOLUTION METHODS FOR CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION. 1. Primal approach 2. Penalty and barrier methods 3. Dual approach 4. Primal-dual approach
 LECTURE 13: SOLUTION METHODS FOR CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION 1. Primal approach 2. Penalty and barrier methods 3. Dual approach 4. Primal-dual approach Basic approaches I. Primal Approach - Feasible Direction
LECTURE 13: SOLUTION METHODS FOR CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION 1. Primal approach 2. Penalty and barrier methods 3. Dual approach 4. Primal-dual approach Basic approaches I. Primal Approach - Feasible Direction
Ellipsoid Algorithm :Algorithms in the Real World. Ellipsoid Algorithm. Reduction from general case
 Ellipsoid Algorithm 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming II Ellipsoid algorithm Interior point methods First polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming (Khachian 79)
Ellipsoid Algorithm 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming II Ellipsoid algorithm Interior point methods First polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming (Khachian 79)
Computational Methods. Constrained Optimization
 Computational Methods Constrained Optimization Manfred Huber 2010 1 Constrained Optimization Unconstrained Optimization finds a minimum of a function under the assumption that the parameters can take on
Computational Methods Constrained Optimization Manfred Huber 2010 1 Constrained Optimization Unconstrained Optimization finds a minimum of a function under the assumption that the parameters can take on
Programming, numerics and optimization
 Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-4: Constrained optimization Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428 June
Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-4: Constrained optimization Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428 June
Unconstrained Optimization Principles of Unconstrained Optimization Search Methods
 1 Nonlinear Programming Types of Nonlinear Programs (NLP) Convexity and Convex Programs NLP Solutions Unconstrained Optimization Principles of Unconstrained Optimization Search Methods Constrained Optimization
1 Nonlinear Programming Types of Nonlinear Programs (NLP) Convexity and Convex Programs NLP Solutions Unconstrained Optimization Principles of Unconstrained Optimization Search Methods Constrained Optimization
Local and Global Minimum
 Local and Global Minimum Stationary Point. From elementary calculus, a single variable function has a stationary point at if the derivative vanishes at, i.e., 0. Graphically, the slope of the function
Local and Global Minimum Stationary Point. From elementary calculus, a single variable function has a stationary point at if the derivative vanishes at, i.e., 0. Graphically, the slope of the function
Introduction to Optimization Problems and Methods
 Introduction to Optimization Problems and Methods wjch@umich.edu December 10, 2009 Outline 1 Linear Optimization Problem Simplex Method 2 3 Cutting Plane Method 4 Discrete Dynamic Programming Problem Simplex
Introduction to Optimization Problems and Methods wjch@umich.edu December 10, 2009 Outline 1 Linear Optimization Problem Simplex Method 2 3 Cutting Plane Method 4 Discrete Dynamic Programming Problem Simplex
David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye. Linear and Nonlinear. Programming. Fourth Edition. ö Springer
 David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye Linear and Nonlinear Programming Fourth Edition ö Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Optimization 1 1.2 Types of Problems 2 1.3 Size of Problems 5 1.4 Iterative Algorithms
David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye Linear and Nonlinear Programming Fourth Edition ö Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Optimization 1 1.2 Types of Problems 2 1.3 Size of Problems 5 1.4 Iterative Algorithms
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods
 Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING
 INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING DAVID G. LUENBERGER Stanford University TT ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California London Don Mills, Ontario CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING DAVID G. LUENBERGER Stanford University TT ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California London Don Mills, Ontario CONTENTS
PRIMAL-DUAL INTERIOR POINT METHOD FOR LINEAR PROGRAMMING. 1. Introduction
 PRIMAL-DUAL INTERIOR POINT METHOD FOR LINEAR PROGRAMMING KELLER VANDEBOGERT AND CHARLES LANNING 1. Introduction Interior point methods are, put simply, a technique of optimization where, given a problem
PRIMAL-DUAL INTERIOR POINT METHOD FOR LINEAR PROGRAMMING KELLER VANDEBOGERT AND CHARLES LANNING 1. Introduction Interior point methods are, put simply, a technique of optimization where, given a problem
Lecture Notes: Constraint Optimization
 Lecture Notes: Constraint Optimization Gerhard Neumann January 6, 2015 1 Constraint Optimization Problems In constraint optimization we want to maximize a function f(x) under the constraints that g i (x)
Lecture Notes: Constraint Optimization Gerhard Neumann January 6, 2015 1 Constraint Optimization Problems In constraint optimization we want to maximize a function f(x) under the constraints that g i (x)
Introduction to Optimization
 Introduction to Optimization Second Order Optimization Methods Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Planned Outline Gradient-based optimization (1st order methods) plain grad., steepest descent, conjugate grad.,
Introduction to Optimization Second Order Optimization Methods Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Planned Outline Gradient-based optimization (1st order methods) plain grad., steepest descent, conjugate grad.,
Characterizing Improving Directions Unconstrained Optimization
 Final Review IE417 In the Beginning... In the beginning, Weierstrass's theorem said that a continuous function achieves a minimum on a compact set. Using this, we showed that for a convex set S and y not
Final Review IE417 In the Beginning... In the beginning, Weierstrass's theorem said that a continuous function achieves a minimum on a compact set. Using this, we showed that for a convex set S and y not
Constrained Optimization COS 323
 Constrained Optimization COS 323 Last time Introduction to optimization objective function, variables, [constraints] 1-dimensional methods Golden section, discussion of error Newton s method Multi-dimensional
Constrained Optimization COS 323 Last time Introduction to optimization objective function, variables, [constraints] 1-dimensional methods Golden section, discussion of error Newton s method Multi-dimensional
Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods
 Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods Kin Cheong Sou December 2, 2013 TMA947 Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods 1 / 1 Feasible-direction methods, I Intro Consider the problem
Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods Kin Cheong Sou December 2, 2013 TMA947 Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods 1 / 1 Feasible-direction methods, I Intro Consider the problem
Demo 1: KKT conditions with inequality constraints
 MS-C5 Introduction to Optimization Solutions 9 Ehtamo Demo : KKT conditions with inequality constraints Using the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker conditions, see if the points x (x, x ) (, 4) or x (x, x ) (6, ) are
MS-C5 Introduction to Optimization Solutions 9 Ehtamo Demo : KKT conditions with inequality constraints Using the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker conditions, see if the points x (x, x ) (, 4) or x (x, x ) (6, ) are
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Lecture 4: Optimization
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Lecture 4: Optimization 13 Sep 2015 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj (slides largely by Najim Dehak, JHU) 11-755/18-797 1 Index 1. The problem of optimization 2. Direct optimization
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Lecture 4: Optimization 13 Sep 2015 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj (slides largely by Najim Dehak, JHU) 11-755/18-797 1 Index 1. The problem of optimization 2. Direct optimization
Convex Optimization and Machine Learning
 Convex Optimization and Machine Learning Mengliu Zhao Machine Learning Reading Group School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University March 12, 2014 Mengliu Zhao SFU-MLRG March 12, 2014 1 / 25 Introduction
Convex Optimization and Machine Learning Mengliu Zhao Machine Learning Reading Group School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University March 12, 2014 Mengliu Zhao SFU-MLRG March 12, 2014 1 / 25 Introduction
A FACTOR GRAPH APPROACH TO CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION. A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty. Ivan Dario Jimenez
 A FACTOR GRAPH APPROACH TO CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty By Ivan Dario Jimenez In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree B.S. in Computer Science with
A FACTOR GRAPH APPROACH TO CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty By Ivan Dario Jimenez In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree B.S. in Computer Science with
Optimization III: Constrained Optimization
 Optimization III: Constrained Optimization CS 205A: Mathematical Methods for Robotics, Vision, and Graphics Doug James (and Justin Solomon) CS 205A: Mathematical Methods Optimization III: Constrained Optimization
Optimization III: Constrained Optimization CS 205A: Mathematical Methods for Robotics, Vision, and Graphics Doug James (and Justin Solomon) CS 205A: Mathematical Methods Optimization III: Constrained Optimization
15.082J and 6.855J. Lagrangian Relaxation 2 Algorithms Application to LPs
 15.082J and 6.855J Lagrangian Relaxation 2 Algorithms Application to LPs 1 The Constrained Shortest Path Problem (1,10) 2 (1,1) 4 (2,3) (1,7) 1 (10,3) (1,2) (10,1) (5,7) 3 (12,3) 5 (2,2) 6 Find the shortest
15.082J and 6.855J Lagrangian Relaxation 2 Algorithms Application to LPs 1 The Constrained Shortest Path Problem (1,10) 2 (1,1) 4 (2,3) (1,7) 1 (10,3) (1,2) (10,1) (5,7) 3 (12,3) 5 (2,2) 6 Find the shortest
Sparse Optimization Lecture: Proximal Operator/Algorithm and Lagrange Dual
 Sparse Optimization Lecture: Proximal Operator/Algorithm and Lagrange Dual Instructor: Wotao Yin July 2013 online discussions on piazza.com Those who complete this lecture will know learn the proximal
Sparse Optimization Lecture: Proximal Operator/Algorithm and Lagrange Dual Instructor: Wotao Yin July 2013 online discussions on piazza.com Those who complete this lecture will know learn the proximal
CS231A. Review for Problem Set 1. Saumitro Dasgupta
 CS231A Review for Problem Set 1 Saumitro Dasgupta On today's menu Camera Model Rotation Matrices Homogeneous Coordinates Vanishing Points Matrix Calculus Constrained Optimization Camera Calibration Demo
CS231A Review for Problem Set 1 Saumitro Dasgupta On today's menu Camera Model Rotation Matrices Homogeneous Coordinates Vanishing Points Matrix Calculus Constrained Optimization Camera Calibration Demo
Inverse KKT Motion Optimization: A Newton Method to Efficiently Extract Task Spaces and Cost Parameters from Demonstrations
 Inverse KKT Motion Optimization: A Newton Method to Efficiently Extract Task Spaces and Cost Parameters from Demonstrations Peter Englert Machine Learning and Robotics Lab Universität Stuttgart Germany
Inverse KKT Motion Optimization: A Newton Method to Efficiently Extract Task Spaces and Cost Parameters from Demonstrations Peter Englert Machine Learning and Robotics Lab Universität Stuttgart Germany
A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial
 A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial j.p.lewis CGIT Lab / IMSC U. Southern California version 0.zz dec 004 This tutorial assumes you are familiar with linear algebra and equality-constrained optimization/lagrange
A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial j.p.lewis CGIT Lab / IMSC U. Southern California version 0.zz dec 004 This tutorial assumes you are familiar with linear algebra and equality-constrained optimization/lagrange
Introduction to optimization methods and line search
 Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
CONLIN & MMA solvers. Pierre DUYSINX LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic year
 CONLIN & MMA solvers Pierre DUYSINX LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic year 2018-2019 1 CONLIN METHOD 2 LAY-OUT CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS DUAL METHOD APPROACH FOR CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS SEQUENTIAL QUADRATIC PROGRAMMING
CONLIN & MMA solvers Pierre DUYSINX LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic year 2018-2019 1 CONLIN METHOD 2 LAY-OUT CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS DUAL METHOD APPROACH FOR CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS SEQUENTIAL QUADRATIC PROGRAMMING
Augmented Lagrangian Methods
 Augmented Lagrangian Methods Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Augmented Lagrangian IMA, August 2016 1 /
Augmented Lagrangian Methods Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Augmented Lagrangian IMA, August 2016 1 /
Lecture 18: March 23
 0-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Spring 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 8: March 23 Scribes: James Duyck Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have not
0-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Spring 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 8: March 23 Scribes: James Duyck Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have not
Shiqian Ma, MAT-258A: Numerical Optimization 1. Chapter 2. Convex Optimization
 Shiqian Ma, MAT-258A: Numerical Optimization 1 Chapter 2 Convex Optimization Shiqian Ma, MAT-258A: Numerical Optimization 2 2.1. Convex Optimization General optimization problem: min f 0 (x) s.t., f i
Shiqian Ma, MAT-258A: Numerical Optimization 1 Chapter 2 Convex Optimization Shiqian Ma, MAT-258A: Numerical Optimization 2 2.1. Convex Optimization General optimization problem: min f 0 (x) s.t., f i
Lecture 12: convergence. Derivative (one variable)
 Lecture 12: convergence More about multivariable calculus Descent methods Backtracking line search More about convexity (first and second order) Newton step Example 1: linear programming (one var., one
Lecture 12: convergence More about multivariable calculus Descent methods Backtracking line search More about convexity (first and second order) Newton step Example 1: linear programming (one var., one
Optimal Control Techniques for Dynamic Walking
 Optimal Control Techniques for Dynamic Walking Optimization in Robotics & Biomechanics IWR, University of Heidelberg Presentation partly based on slides by Sebastian Sager, Moritz Diehl and Peter Riede
Optimal Control Techniques for Dynamic Walking Optimization in Robotics & Biomechanics IWR, University of Heidelberg Presentation partly based on slides by Sebastian Sager, Moritz Diehl and Peter Riede
Augmented Lagrangian Methods
 Augmented Lagrangian Methods Mário A. T. Figueiredo 1 and Stephen J. Wright 2 1 Instituto de Telecomunicações, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of
Augmented Lagrangian Methods Mário A. T. Figueiredo 1 and Stephen J. Wright 2 1 Instituto de Telecomunicações, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of
Convex Optimization CMU-10725
 Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Conjugate Direction Methods Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Conjugate Direction Methods 2 Books to Read David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye: Linear and Nonlinear Programming Nesterov:
Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Conjugate Direction Methods Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Conjugate Direction Methods 2 Books to Read David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye: Linear and Nonlinear Programming Nesterov:
Optimization Methods. Final Examination. 1. There are 5 problems each w i t h 20 p o i n ts for a maximum of 100 points.
 5.93 Optimization Methods Final Examination Instructions:. There are 5 problems each w i t h 2 p o i n ts for a maximum of points. 2. You are allowed to use class notes, your homeworks, solutions to homework
5.93 Optimization Methods Final Examination Instructions:. There are 5 problems each w i t h 2 p o i n ts for a maximum of points. 2. You are allowed to use class notes, your homeworks, solutions to homework
5 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization
 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization 25 5 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization ML ABSTRACTIONS [some meta comments on machine learning] [When you write a large computer
Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization 25 5 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization ML ABSTRACTIONS [some meta comments on machine learning] [When you write a large computer
Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints
 Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints Constrained optimization The idea of constrained optimisation is that the choice of one variable often affects the amount of another variable that can be
Lecture 2 Optimization with equality constraints Constrained optimization The idea of constrained optimisation is that the choice of one variable often affects the amount of another variable that can be
(1) Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14)z = a + 2
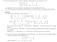 (1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
(1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
Programs. Introduction
 16 Interior Point I: Linear Programs Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen
16 Interior Point I: Linear Programs Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen
A Brief Overview of Optimization Problems. Steven G. Johnson MIT course , Fall 2008
 A Brief Overview of Optimization Problems Steven G. Johnson MIT course 18.335, Fall 2008 Why optimization? In some sense, all engineering design is optimization: choosing design parameters to improve some
A Brief Overview of Optimization Problems Steven G. Johnson MIT course 18.335, Fall 2008 Why optimization? In some sense, all engineering design is optimization: choosing design parameters to improve some
Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part II)
 Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part II) 4. Convexity and Optimization Massimiliano Pontil (based on previous lecture by Andreas Argyriou) 1 Today s Plan Convex sets and functions Types
Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part II) 4. Convexity and Optimization Massimiliano Pontil (based on previous lecture by Andreas Argyriou) 1 Today s Plan Convex sets and functions Types
ISM206 Lecture, April 26, 2005 Optimization of Nonlinear Objectives, with Non-Linear Constraints
 ISM206 Lecture, April 26, 2005 Optimization of Nonlinear Objectives, with Non-Linear Constraints Instructor: Kevin Ross Scribe: Pritam Roy May 0, 2005 Outline of topics for the lecture We will discuss
ISM206 Lecture, April 26, 2005 Optimization of Nonlinear Objectives, with Non-Linear Constraints Instructor: Kevin Ross Scribe: Pritam Roy May 0, 2005 Outline of topics for the lecture We will discuss
A Truncated Newton Method in an Augmented Lagrangian Framework for Nonlinear Programming
 A Truncated Newton Method in an Augmented Lagrangian Framework for Nonlinear Programming Gianni Di Pillo (dipillo@dis.uniroma1.it) Giampaolo Liuzzi (liuzzi@iasi.cnr.it) Stefano Lucidi (lucidi@dis.uniroma1.it)
A Truncated Newton Method in an Augmented Lagrangian Framework for Nonlinear Programming Gianni Di Pillo (dipillo@dis.uniroma1.it) Giampaolo Liuzzi (liuzzi@iasi.cnr.it) Stefano Lucidi (lucidi@dis.uniroma1.it)
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 LAGRANGIAN RELAXATION FOR GATE IMPLEMENTATION SELECTION Yi-Le Huang, Jiang Hu and Weiping Shi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University OUTLINE Introduction and motivation
LAGRANGIAN RELAXATION FOR GATE IMPLEMENTATION SELECTION Yi-Le Huang, Jiang Hu and Weiping Shi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University OUTLINE Introduction and motivation
Optimization under uncertainty: modeling and solution methods
 Optimization under uncertainty: modeling and solution methods Paolo Brandimarte Dipartimento di Scienze Matematiche Politecnico di Torino e-mail: paolo.brandimarte@polito.it URL: http://staff.polito.it/paolo.brandimarte
Optimization under uncertainty: modeling and solution methods Paolo Brandimarte Dipartimento di Scienze Matematiche Politecnico di Torino e-mail: paolo.brandimarte@polito.it URL: http://staff.polito.it/paolo.brandimarte
Least-Squares Minimization Under Constraints EPFL Technical Report #
 Least-Squares Minimization Under Constraints EPFL Technical Report # 150790 P. Fua A. Varol R. Urtasun M. Salzmann IC-CVLab, EPFL IC-CVLab, EPFL TTI Chicago TTI Chicago Unconstrained Least-Squares minimization
Least-Squares Minimization Under Constraints EPFL Technical Report # 150790 P. Fua A. Varol R. Urtasun M. Salzmann IC-CVLab, EPFL IC-CVLab, EPFL TTI Chicago TTI Chicago Unconstrained Least-Squares minimization
A new mini-max, constrained optimization method for solving worst case problems
 Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Institute of Technology 1979 A new mini-max, constrained optimization method for solving worst
Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Institute of Technology 1979 A new mini-max, constrained optimization method for solving worst
Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms
 Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms Evelien van der Hurk DTU Managment Engineering Class Exercises From Last Time 2 DTU Management Engineering 42111: Static and Dynamic Optimization (6) 09/10/2017 Class
Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms Evelien van der Hurk DTU Managment Engineering Class Exercises From Last Time 2 DTU Management Engineering 42111: Static and Dynamic Optimization (6) 09/10/2017 Class
Parallel and Distributed Graph Cuts by Dual Decomposition
 Parallel and Distributed Graph Cuts by Dual Decomposition Presented by Varun Gulshan 06 July, 2010 What is Dual Decomposition? What is Dual Decomposition? It is a technique for optimization: usually used
Parallel and Distributed Graph Cuts by Dual Decomposition Presented by Varun Gulshan 06 July, 2010 What is Dual Decomposition? What is Dual Decomposition? It is a technique for optimization: usually used
Department of Mathematics Oleg Burdakov of 30 October Consider the following linear programming problem (LP):
 Linköping University Optimization TAOP3(0) Department of Mathematics Examination Oleg Burdakov of 30 October 03 Assignment Consider the following linear programming problem (LP): max z = x + x s.t. x x
Linköping University Optimization TAOP3(0) Department of Mathematics Examination Oleg Burdakov of 30 October 03 Assignment Consider the following linear programming problem (LP): max z = x + x s.t. x x
A Brief Overview of Optimization Problems. Steven G. Johnson MIT course , Fall 2008
 A Brief Overview of Optimization Problems Steven G. Johnson MIT course 18.335, Fall 2008 Why optimization? In some sense, all engineering design is optimization: choosing design parameters to improve some
A Brief Overview of Optimization Problems Steven G. Johnson MIT course 18.335, Fall 2008 Why optimization? In some sense, all engineering design is optimization: choosing design parameters to improve some
1) Give a set-theoretic description of the given points as a subset W of R 3. a) The points on the plane x + y 2z = 0.
 ) Give a set-theoretic description of the given points as a subset W of R. a) The points on the plane x + y z =. x Solution: W = {x: x = [ x ], x + x x = }. x b) The points in the yz-plane. Solution: W
) Give a set-theoretic description of the given points as a subset W of R. a) The points on the plane x + y z =. x Solution: W = {x: x = [ x ], x + x x = }. x b) The points in the yz-plane. Solution: W
TMA946/MAN280 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION. Exam instructions
 Chalmers/GU Mathematics EXAM TMA946/MAN280 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION Date: 03 05 28 Time: House V, morning Aids: Text memory-less calculator Number of questions: 7; passed on one question requires 2 points
Chalmers/GU Mathematics EXAM TMA946/MAN280 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION Date: 03 05 28 Time: House V, morning Aids: Text memory-less calculator Number of questions: 7; passed on one question requires 2 points
Fast-Lipschitz Optimization
 Fast-Lipschitz Optimization DREAM Seminar Series University of California at Berkeley September 11, 2012 Carlo Fischione ACCESS Linnaeus Center, Electrical Engineering KTH Royal Institute of Technology
Fast-Lipschitz Optimization DREAM Seminar Series University of California at Berkeley September 11, 2012 Carlo Fischione ACCESS Linnaeus Center, Electrical Engineering KTH Royal Institute of Technology
Short Reminder of Nonlinear Programming
 Short Reminder of Nonlinear Programming Kaisa Miettinen Dept. of Math. Inf. Tech. Email: kaisa.miettinen@jyu.fi Homepage: http://www.mit.jyu.fi/miettine Contents Background General overview briefly theory
Short Reminder of Nonlinear Programming Kaisa Miettinen Dept. of Math. Inf. Tech. Email: kaisa.miettinen@jyu.fi Homepage: http://www.mit.jyu.fi/miettine Contents Background General overview briefly theory
Optimization. Industrial AI Lab.
 Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
Linear and Integer Programming :Algorithms in the Real World. Related Optimization Problems. How important is optimization?
 Linear and Integer Programming 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming I Introduction Geometric Interpretation Simplex Method Linear or Integer programming maximize z = c T x
Linear and Integer Programming 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming I Introduction Geometric Interpretation Simplex Method Linear or Integer programming maximize z = c T x
Interior Point I. Lab 21. Introduction
 Lab 21 Interior Point I Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen the discovery
Lab 21 Interior Point I Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen the discovery
4.1 Graphical solution of a linear program and standard form
 4.1 Graphical solution of a linear program and standard form Consider the problem min c T x Ax b x where x = ( x1 x ) ( 16, c = 5 ), b = 4 5 9, A = 1 7 1 5 1. Solve the problem graphically and determine
4.1 Graphical solution of a linear program and standard form Consider the problem min c T x Ax b x where x = ( x1 x ) ( 16, c = 5 ), b = 4 5 9, A = 1 7 1 5 1. Solve the problem graphically and determine
Lecture 9. Introduction to Numerical Techniques
 Lecture 9. Introduction to Numerical Techniques Ivan Papusha CDS270 2: Mathematical Methods in Control and System Engineering May 27, 2015 1 / 25 Logistics hw8 (last one) due today. do an easy problem
Lecture 9. Introduction to Numerical Techniques Ivan Papusha CDS270 2: Mathematical Methods in Control and System Engineering May 27, 2015 1 / 25 Logistics hw8 (last one) due today. do an easy problem
Constrained optimization
 Constrained optimization Problem in standard form minimize f(x) subject to a i (x) = 0, for i =1, 2, p c j (x) 0 for j =1, 2,,q f : R n R a i : R n R c j : R n R f(x )=, if problem is infeasible f(x )=,
Constrained optimization Problem in standard form minimize f(x) subject to a i (x) = 0, for i =1, 2, p c j (x) 0 for j =1, 2,,q f : R n R a i : R n R c j : R n R f(x )=, if problem is infeasible f(x )=,
CS 6210 Fall 2016 Bei Wang. Review Lecture What have we learnt in Scientific Computing?
 CS 6210 Fall 2016 Bei Wang Review Lecture What have we learnt in Scientific Computing? Let s recall the scientific computing pipeline observed phenomenon mathematical model discretization solution algorithm
CS 6210 Fall 2016 Bei Wang Review Lecture What have we learnt in Scientific Computing? Let s recall the scientific computing pipeline observed phenomenon mathematical model discretization solution algorithm
Lecture 19: Convex Non-Smooth Optimization. April 2, 2007
 : Convex Non-Smooth Optimization April 2, 2007 Outline Lecture 19 Convex non-smooth problems Examples Subgradients and subdifferentials Subgradient properties Operations with subgradients and subdifferentials
: Convex Non-Smooth Optimization April 2, 2007 Outline Lecture 19 Convex non-smooth problems Examples Subgradients and subdifferentials Subgradient properties Operations with subgradients and subdifferentials
Distributed Estimation for Spatial Rigid Motion Based on Dual Quaternions
 OPTIMAL CONTROL APPLICATIONS AND METHODS Optim. Control Appl. Meth. ; : 24 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/oca Distributed Estimation for Spatial Rigid Motion
OPTIMAL CONTROL APPLICATIONS AND METHODS Optim. Control Appl. Meth. ; : 24 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/oca Distributed Estimation for Spatial Rigid Motion
5 Day 5: Maxima and minima for n variables.
 UNIVERSITAT POMPEU FABRA INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS ECONOMICS MATHEMATICS III. Pelegrí Viader. 2012-201 Updated May 14, 201 5 Day 5: Maxima and minima for n variables. The same kind of first-order and second-order
UNIVERSITAT POMPEU FABRA INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS ECONOMICS MATHEMATICS III. Pelegrí Viader. 2012-201 Updated May 14, 201 5 Day 5: Maxima and minima for n variables. The same kind of first-order and second-order
Introduction to Optimization
 Introduction to Optimization Constrained Optimization Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Constrained Optimization General constrained optimization problem: Let R n, f : R n R, g : R n R m, h : R n R l find min
Introduction to Optimization Constrained Optimization Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Constrained Optimization General constrained optimization problem: Let R n, f : R n R, g : R n R m, h : R n R l find min
Modern Methods of Data Analysis - WS 07/08
 Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture XV (04.02.08) Contents: Function Minimization (see E. Lohrmann & V. Blobel) Optimization Problem Set of n independent variables Sometimes in addition some constraints
Modern Methods of Data Analysis Lecture XV (04.02.08) Contents: Function Minimization (see E. Lohrmann & V. Blobel) Optimization Problem Set of n independent variables Sometimes in addition some constraints
Lagrangian methods for the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems. G. Landi
 Lagrangian methods for the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems G. Landi Abstract In many science and engineering applications, the discretization of linear illposed problems gives rise to large
Lagrangian methods for the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems G. Landi Abstract In many science and engineering applications, the discretization of linear illposed problems gives rise to large
21-256: Lagrange multipliers
 21-256: Lagrange multipliers Clive Newstead, Thursday 12th June 2014 Lagrange multipliers give us a means of optimizing multivariate functions subject to a number of constraints on their variables. Problems
21-256: Lagrange multipliers Clive Newstead, Thursday 12th June 2014 Lagrange multipliers give us a means of optimizing multivariate functions subject to a number of constraints on their variables. Problems
16.410/413 Principles of Autonomy and Decision Making
 16.410/413 Principles of Autonomy and Decision Making Lecture 17: The Simplex Method Emilio Frazzoli Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 10, 2010 Frazzoli (MIT)
16.410/413 Principles of Autonomy and Decision Making Lecture 17: The Simplex Method Emilio Frazzoli Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 10, 2010 Frazzoli (MIT)
OPTIMIZATION FOR AUTOMATIC HISTORY MATCHING
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 131 137 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information OPTIMIZATION FOR AUTOMATIC HISTORY MATCHING Abstract. SHUGUANG
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 2, Supp, Pages 131 137 c 2005 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information OPTIMIZATION FOR AUTOMATIC HISTORY MATCHING Abstract. SHUGUANG
Computational Methods CMSC/AMSC/MAPL 460. Vectors, Matrices, Linear Systems, LU Decomposition, Ramani Duraiswami, Dept. of Computer Science
 Computational Methods CMSC/AMSC/MAPL 460 Vectors, Matrices, Linear Systems, LU Decomposition, Ramani Duraiswami, Dept. of Computer Science Some special matrices Matlab code How many operations and memory
Computational Methods CMSC/AMSC/MAPL 460 Vectors, Matrices, Linear Systems, LU Decomposition, Ramani Duraiswami, Dept. of Computer Science Some special matrices Matlab code How many operations and memory
Today. Golden section, discussion of error Newton s method. Newton s method, steepest descent, conjugate gradient
 Optimization Last time Root finding: definition, motivation Algorithms: Bisection, false position, secant, Newton-Raphson Convergence & tradeoffs Example applications of Newton s method Root finding in
Optimization Last time Root finding: definition, motivation Algorithms: Bisection, false position, secant, Newton-Raphson Convergence & tradeoffs Example applications of Newton s method Root finding in
1. Introduction. performance of numerical methods. complexity bounds. structural convex optimization. course goals and topics
 1. Introduction EE 546, Univ of Washington, Spring 2016 performance of numerical methods complexity bounds structural convex optimization course goals and topics 1 1 Some course info Welcome to EE 546!
1. Introduction EE 546, Univ of Washington, Spring 2016 performance of numerical methods complexity bounds structural convex optimization course goals and topics 1 1 Some course info Welcome to EE 546!
Finite Math - J-term Homework. Section Inverse of a Square Matrix
 Section.5-77, 78, 79, 80 Finite Math - J-term 017 Lecture Notes - 1/19/017 Homework Section.6-9, 1, 1, 15, 17, 18, 1, 6, 9, 3, 37, 39, 1,, 5, 6, 55 Section 5.1-9, 11, 1, 13, 1, 17, 9, 30 Section.5 - Inverse
Section.5-77, 78, 79, 80 Finite Math - J-term 017 Lecture Notes - 1/19/017 Homework Section.6-9, 1, 1, 15, 17, 18, 1, 6, 9, 3, 37, 39, 1,, 5, 6, 55 Section 5.1-9, 11, 1, 13, 1, 17, 9, 30 Section.5 - Inverse
Hartley - Zisserman reading club. Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: Presented by Daniel Fontijne
 Hartley - Zisserman reading club Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Iterative estimation methods Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: A Flexible New Technique for Camera Calibration Presented by Daniel Fontijne
Hartley - Zisserman reading club Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Iterative estimation methods Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: A Flexible New Technique for Camera Calibration Presented by Daniel Fontijne
Convex Optimization MLSS 2015
 Convex Optimization MLSS 2015 Constantine Caramanis The University of Texas at Austin The Optimization Problem minimize : f (x) subject to : x X. The Optimization Problem minimize : f (x) subject to :
Convex Optimization MLSS 2015 Constantine Caramanis The University of Texas at Austin The Optimization Problem minimize : f (x) subject to : x X. The Optimization Problem minimize : f (x) subject to :
Search direction improvement for gradient-based optimization problems
 Computer Aided Optimum Design in Engineering IX 3 Search direction improvement for gradient-based optimization problems S Ganguly & W L Neu Aerospace and Ocean Engineering, Virginia Tech, USA Abstract
Computer Aided Optimum Design in Engineering IX 3 Search direction improvement for gradient-based optimization problems S Ganguly & W L Neu Aerospace and Ocean Engineering, Virginia Tech, USA Abstract
A Numerical Study of Active-Set and Interior-Point Methods for Bound Constrained Optimization
 A Numerical Study of Active-Set and Interior-Point Methods for Bound Constrained Optimization Long Hei 1, Jorge Nocedal 2, Richard A. Waltz 2 1 Department of Industrial Engineering and Management Sciences,
A Numerical Study of Active-Set and Interior-Point Methods for Bound Constrained Optimization Long Hei 1, Jorge Nocedal 2, Richard A. Waltz 2 1 Department of Industrial Engineering and Management Sciences,
Linear methods for supervised learning
 Linear methods for supervised learning LDA Logistic regression Naïve Bayes PLA Maximum margin hyperplanes Soft-margin hyperplanes Least squares resgression Ridge regression Nonlinear feature maps Sometimes
Linear methods for supervised learning LDA Logistic regression Naïve Bayes PLA Maximum margin hyperplanes Soft-margin hyperplanes Least squares resgression Ridge regression Nonlinear feature maps Sometimes
Sequential Coordinate-wise Algorithm for Non-negative Least Squares Problem
 CENTER FOR MACHINE PERCEPTION CZECH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Sequential Coordinate-wise Algorithm for Non-negative Least Squares Problem Woring document of the EU project COSPAL IST-004176 Vojtěch Franc, Miro
CENTER FOR MACHINE PERCEPTION CZECH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Sequential Coordinate-wise Algorithm for Non-negative Least Squares Problem Woring document of the EU project COSPAL IST-004176 Vojtěch Franc, Miro
AGloballyConvergentPrimal-DualActive-Set Framework for Large-Scale Convex Quadratic Optimization
 AGloballyConvergentPrimal-DualActive-Set Framewor for Large-Scale Convex Quadratic Optimization Fran E. Curtis, Zheng Han, and Daniel P. Robinson Lehigh Industrial and Systems Engineering COR@L Technical
AGloballyConvergentPrimal-DualActive-Set Framewor for Large-Scale Convex Quadratic Optimization Fran E. Curtis, Zheng Han, and Daniel P. Robinson Lehigh Industrial and Systems Engineering COR@L Technical
Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning
 Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning Part 2 Institute of Bioinformatics Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generalization Error 3 Maximum Likelihood 4 Noise Models 5
Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning Part 2 Institute of Bioinformatics Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generalization Error 3 Maximum Likelihood 4 Noise Models 5
x = 12 x = 12 1x = 16
 2.2 - The Inverse of a Matrix We've seen how to add matrices, multiply them by scalars, subtract them, and multiply one matrix by another. The question naturally arises: Can we divide one matrix by another?
2.2 - The Inverse of a Matrix We've seen how to add matrices, multiply them by scalars, subtract them, and multiply one matrix by another. The question naturally arises: Can we divide one matrix by another?
A primal-dual framework for mixtures of regularizers
 A primal-dual framework for mixtures of regularizers Baran Gözcü baran.goezcue@epfl.ch Laboratory for Information and Inference Systems (LIONS) École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Switzerland
A primal-dual framework for mixtures of regularizers Baran Gözcü baran.goezcue@epfl.ch Laboratory for Information and Inference Systems (LIONS) École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Switzerland
Convexity Theory and Gradient Methods
 Convexity Theory and Gradient Methods Angelia Nedić angelia@illinois.edu ISE Department and Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Outline Convex Functions Optimality
Convexity Theory and Gradient Methods Angelia Nedić angelia@illinois.edu ISE Department and Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Outline Convex Functions Optimality
Composite Self-concordant Minimization
 Composite Self-concordant Minimization Volkan Cevher Laboratory for Information and Inference Systems-LIONS Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) volkan.cevher@epfl.ch Paris 6 Dec 11, 2013 joint
Composite Self-concordant Minimization Volkan Cevher Laboratory for Information and Inference Systems-LIONS Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) volkan.cevher@epfl.ch Paris 6 Dec 11, 2013 joint
Revision Problems for Examination 2 in Algebra 1
 Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
Classical Gradient Methods
 Classical Gradient Methods Note simultaneous course at AMSI (math) summer school: Nonlin. Optimization Methods (see http://wwwmaths.anu.edu.au/events/amsiss05/) Recommended textbook (Springer Verlag, 1999):
Classical Gradient Methods Note simultaneous course at AMSI (math) summer school: Nonlin. Optimization Methods (see http://wwwmaths.anu.edu.au/events/amsiss05/) Recommended textbook (Springer Verlag, 1999):
Optimization Algorithms, Implementations and. Discussions (technical report for self-reference)
 Optimization Algorithms, Implementations and Discussions (technical report for self-reference) By : Lam Ngok Introduction In this preliminary optimization study we tested and implemented six different
Optimization Algorithms, Implementations and Discussions (technical report for self-reference) By : Lam Ngok Introduction In this preliminary optimization study we tested and implemented six different
Applied Lagrange Duality for Constrained Optimization
 Applied Lagrange Duality for Constrained Optimization Robert M. Freund February 10, 2004 c 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1 1 Overview The Practical Importance of Duality Review of Convexity
Applied Lagrange Duality for Constrained Optimization Robert M. Freund February 10, 2004 c 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1 1 Overview The Practical Importance of Duality Review of Convexity
3D Geometry and Camera Calibration
 3D Geometry and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Systems Right-handed vs. left-handed x x y z z y 2D Coordinate Systems 3D Geometry Basics y axis up vs. y axis down Origin at center vs. corner Will often
3D Geometry and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Systems Right-handed vs. left-handed x x y z z y 2D Coordinate Systems 3D Geometry Basics y axis up vs. y axis down Origin at center vs. corner Will often
In other words, we want to find the domain points that yield the maximum or minimum values (extrema) of the function.
 1 The Lagrange multipliers is a mathematical method for performing constrained optimization of differentiable functions. Recall unconstrained optimization of differentiable functions, in which we want
1 The Lagrange multipliers is a mathematical method for performing constrained optimization of differentiable functions. Recall unconstrained optimization of differentiable functions, in which we want
Full waveform inversion by deconvolution gradient method
 Full waveform inversion by deconvolution gradient method Fuchun Gao*, Paul Williamson, Henri Houllevigue, Total), 2012 Lei Fu Rice University November 14, 2012 Outline Introduction Method Implementation
Full waveform inversion by deconvolution gradient method Fuchun Gao*, Paul Williamson, Henri Houllevigue, Total), 2012 Lei Fu Rice University November 14, 2012 Outline Introduction Method Implementation
Distance-to-Solution Estimates for Optimization Problems with Constraints in Standard Form
 Distance-to-Solution Estimates for Optimization Problems with Constraints in Standard Form Philip E. Gill Vyacheslav Kungurtsev Daniel P. Robinson UCSD Center for Computational Mathematics Technical Report
Distance-to-Solution Estimates for Optimization Problems with Constraints in Standard Form Philip E. Gill Vyacheslav Kungurtsev Daniel P. Robinson UCSD Center for Computational Mathematics Technical Report
Conic Optimization via Operator Splitting and Homogeneous Self-Dual Embedding
 Conic Optimization via Operator Splitting and Homogeneous Self-Dual Embedding B. O Donoghue E. Chu N. Parikh S. Boyd Convex Optimization and Beyond, Edinburgh, 11/6/2104 1 Outline Cone programming Homogeneous
Conic Optimization via Operator Splitting and Homogeneous Self-Dual Embedding B. O Donoghue E. Chu N. Parikh S. Boyd Convex Optimization and Beyond, Edinburgh, 11/6/2104 1 Outline Cone programming Homogeneous
Chapter II. Linear Programming
 1 Chapter II Linear Programming 1. Introduction 2. Simplex Method 3. Duality Theory 4. Optimality Conditions 5. Applications (QP & SLP) 6. Sensitivity Analysis 7. Interior Point Methods 1 INTRODUCTION
1 Chapter II Linear Programming 1. Introduction 2. Simplex Method 3. Duality Theory 4. Optimality Conditions 5. Applications (QP & SLP) 6. Sensitivity Analysis 7. Interior Point Methods 1 INTRODUCTION
