Removing Shadows from Images
|
|
|
- Laurence Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Removing Shadows from Images Zeinab Sadeghipour Kermani School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC, V5A 1S6 Mark S. Drew School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC, V5A 1S6 Abstract We attempt to recover a 2D chromaticity intrinsic variation of a single RGB image which is independent of lighting, without requiring any prior knowledge about the camera. The proposed algorithm aims to learn an invariant direction for projecting from 2D color space to the greyscale intrinsic image. We notice that along this direction, the entropy in the derived invariant image is minimized. The experiments conducted on various inputs indicate that this method achieves intrinsic 2D chromaticity images which are free of shadows. In addition, we examined the idea to utilize projection pursuit instead of entropy minimization to find the desired direction. 1. Introduction It has been investigated that many vision algorithms including image segmentation, object tracking or recognition may fail due to some specific illumination conditions [1][2][3]. To illustrate, shadows are the result of changes in lighting conditions in images which can cause some difficulties in the aforementioned set of algorithms. Hence, the problem of removing shadows from color images has stimulated increasing interest in the field of computer vision. One of the suggested solutions is based on the observation that greyscale intrinsic images extracted from the original color ones do not contain any shadows because they are not dependent on illumination conditions. In [2], after generating a 2D chromaticity color map from the original image, they acquire a 1D illumination invariant image in which shadows are removed using the prior information about the camera. Afterwards, with the help of inverse conversions and shadow edges extracted from the source, they reconstruct a full color, shadow free image. This report is based on the method proposed in [3] that eliminates the need to calibrate camera. Instead, we seek the best direction for the projection line through minimizing entropy in the resulting greyscale image. Furthermore, the idea of using Independent Component Analysis (ICA) and projection pursuit to obtain the invariant direction is also discussed. The rest of this report is organized as follows: in section 2, we study the details of the algorithm. Section 3 provides the results for a number of experiments and finally, the complete method is summerized in section 4 along with some suggestions for future work. 2. System Model As stated in the previous section, our main goal in this project is to remove shadows from images through producing a greyscale intrinsic image. Note that our method assumed that camera sensors are fairly narrow-band or we applied spectral sharpening on them to simulate narrow-band behavior [4]. The light present in the images also should act similar to a Planckian light, such as daylight. In the following parts, we describe the steps of the algorithm in detail. 2.1 Geometric Mean 2D Chromaticity Space Following the arguements and proofs in [3], at first we need to map the 3D original image to a 2D space. In order to accomplish this goal, we divided three color channels by the geometric mean 3 R G B. Thus the chromaticity would be: c k = R k / 3 3 R i R k /R M, (1) i=1 If we take the log of the above equation, we get: with ρ k = log c k = log ( s k ) + e k e M, k = 1..3, (2) s M T s k = k 1 λ 5 k S(λ k)q k, s M = 3 3 s j, j=1 e k = k 2 k 2, e M = λ k 3 p j=1 λ, j 1
2 and we calculate the entropy for each angle by η = i p i log p i, (5) with the height of the i-th bin denoted as p i, to determine the minimum value. Figure 1: Inuition for using entropy minimization However, we still have three components for the color space which should be projected into a proper plane to get a 2D representation of chromaticity. To accomplish this conversion, we form a plane {χ 1, χ 2 } such that straight lines in the color space ρ, each related to a single surface in the original image, remain straight in this plane[3]. As a result, if we plot 2D log-chromaticities, a pattern of parallel lines is identifieble that enables projection onto a line to derive an illuminant invariant image. 2.2 Entropy Minimization To recover the greyscale intrinsic image, we require to learn the invariant direction in which the straight lines in the 2D chromaticity space mentioned above, point in. According to the observation in [3], the right invariant direction is the one that minimizes the entropy of the greyscale image. As illustrated in Fig. 1(b), if we project onto a line which causes the entropy to be larger than the minimum, then the distribution of pixels along this line is not aggregated in a set of points. In other words, the desired line is perpendicular to the 2D log-chromaticity straight lines, leading to sharp peaks for corresponding surfaces after projection to 1D, as in Fig. 1(a). Regarding the concept of entropy, these sharp peaks can be associated with small values for entropy. To formulate this observation into algorithm steps, we require to iterate through every possible projection direction and select the one that minimizes the entropy. Accordingly, for angles θ = , we produce the greyscale image I from 2D chromaticity color map by: I = χ 1 cos θ + χ 2 sin θ, (3) Next, for each angle, we compose histogram of the middle 90% of data with the intention to remove outliers. The bin width differes for every θ and is established using Scott s Rule [5]: bin width = 3.5std(I)N(I) 1/3, (4) Vector Representation The final step of the method involves converting the greyscale intrinsic image back to a 3D representation for visualizing the results. To accomplish this, we form a 2x2 matrix P θ as the projector for the candidate angle θ and utilize that to obtain 2-vector χ θ as: χ θ = P θ χ (6) Employing this 2D representation, we estimate the 3D color space and afterwards add a constant extra light to all pixels to retreive the original chromaticity [3]. 2.4 Algorithm Steps To sum up, we present the algorithm to reconstruct the greyscale intrinsic image in a number of explicit steps: 1. Project the original color image into a 2D logchromaticity space. 2. For θ = (a) Project the 2D representation of the image onto the line defined by the direction θ to retain a 1D greyscale image. (b) Calculate the entropy for pixels in the resulting greyscale image. (c) Select the angle that ensures the minimum entropy. 2.5 Independent Component Analysis and Projection Pursuit The major purpose of the algorithm in [3] is to identify a line achieving a set of sharp peaks which are well-seperated from each other after pojection rather than attaining an outspread distribution for pixels. This concept can also be modeled by applying Independent Component Analysis (ICA) to the 2D log-chromaticity representation of the image. The general definition for ICA concerns estimating a linear representation for the given mixed signal such that the components are statistically as independent as possible [6]. An alternative comprehension for ICA is maximizing the nongaussianity present in the data. Indeed this is one of the 2
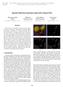
3 ICA estimation principles which states that each local maxima of nongaussianity in the given data with the constant variance, corresponds with one of the independent components. The preceding principle connects ICA with another method named projection pursuit which also has the objective to detect maximally nongaussian linear combinations of the data. In other words, the directions for projection pursuit are another interpretation for the independent components resulting from ICA. Reconsidering the problem of verifying the correct invariant direction, we notice that recognizing the aforementioned set of peaks can be explained as maximizing the nongaussianity which is the intention of projection pursuit. Thus, a substitute for entropy minimization used in this project could be a robust implementation of ICA in [7] to learn the projection pursuit directions. 3. Experiments and Results To evaluate our algorithm, we did three rounds of experiments. At first, we tried the algorithm for the data from [3] and extracted both the greyscale and L 1 chromaticity invariant images, shown in the last two columns of Fig. 2. As we can see, the method is quite successful in this round as the results are nearly shadow free. The second time, we looked at the outputs of performing the approach on some JPEG images from unknown cameras which are provided in Fig. 3 (the dataset from [8]). We note that shadows are not removed as well as the previous case. It seems that a number of processing operations, e.g. compression in these images causes the procedure to fail since the assumptions made in the beginning of section 2 do not hold. Finally, we investigate the idea of using projection pursuit instead of entropy minimization on the same set of images from Fig. 2. We used the first independet component of the 2D log-chromaticity to create the greyscale intrinsic images which are presented in the middle column of Fig. 4. The right column is repeated from Fig. 2 to compare two approaches. We notice that projection pursuit can work as effective as entropy minimizaion but is better in terms of performance; for instance, learning the invariant direction with entropy minimization takes almost 60 seconds for an original image of size pixels while projection pursuit accomplishes the task in 10 seconds. 4. Conclusions In this project, we implemented the algorithm demonstrated in [3] to reconstruct a greyscale and then an L 1 chromaticity illumination invariant image through entropy minimization with the aim to remove shadows from the original image. One of the crucial properties of suggested method is its independence on any specific information about camera or Figure 3: The result of applying entropy minimization method on JPEG images: columns show original image, L 1 chromaticity image and intrinsic greyscale image. Figure 4: The result of applying projection pursuit method: columns show original image, intrinsic greyscale image obtained from projection pursuit and entropy minimization. 3
4 Figure 2: The result of applying entropy minimization method on data from [3]: columns show original image, L 1 chromaticity image, intrinsic greyscale image and invariant L 1 chromaticity. 4
5 image. We also looked into projection pursuit and ICA to distinguish the invariant direction and came to this conclusion that it can be a replacement to entropy minimization. Future work could concentrate on improving the approach to also work on JPEG images. Also it may be possible to enhance the reconstructed RGB shadow free image following the notion of projection pursuit. Acknowledgments I would like to show my gratitude to Ali Madooei for his helpful suggestions. I also thank Zhaopeng Cui for assistance to find an appropriate implementation for ICA. References [1] Graham D Finlayson and Mark S Drew, 4-sensor camera calibration for image representation invariant to shading, shadows, lighting, and specularities, in Computer Vision, ICCV Proceedings. Eighth IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2001, vol. 2, pp [2] Graham D Finlayson, Steven D Hordley, and Mark S Drew, Removing shadows from images, in Computer VisionECCV 2002, pp Springer, [3] Graham D Finlayson, Mark S Drew, and Cheng Lu, Intrinsic images by entropy minimization, in Computer Vision-ECCV 2004, pp Springer, [4] Graham D Finlayson, Mark S Drew, and Brian V Funt, Spectral sharpening: sensor transformations for improved color constancy, JOSA A, vol. 11, no. 5, pp , [5] David W Scott, Multivariate density estimation: theory, practice, and visualization, vol. 383, John Wiley & Sons, [6] Aapo Hyvärinen, Juha Karhunen, and Erkki Oja, Independent component analysis, vol. 46, John Wiley & Sons, [7] Vicente Zarzoso and Pierre Comon, Robust independent component analysis by iterative maximization of the kurtosis contrast with algebraic optimal step size, Neural Networks, IEEE Transactions on, vol. 21, no. 2, pp , [8] Ruiqi Guo, Qieyun Dai, and Derek Hoiem, Singleimage shadow detection and removal using paired regions, in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2011, pp
Abstract. 1. Introduction
 Recovery of Chromaticity Image Free from Shadows via Illumination Invariance Mark S. Drew School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada V5A 1S6 mark@cs.sfu.ca Graham
Recovery of Chromaticity Image Free from Shadows via Illumination Invariance Mark S. Drew School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada V5A 1S6 mark@cs.sfu.ca Graham
Multispectral Image Invariant to Illumination Colour, Strength, and Shading
 Digital Photography VII, San Francisco, 23-27 January 2011. http://www.cs.sfu.ca/~mark/ftp/ei2011/ei2011.pdf Multispectral Image Invariant to Illumination Colour, Strength, and Shading Mark S. Drew and
Digital Photography VII, San Francisco, 23-27 January 2011. http://www.cs.sfu.ca/~mark/ftp/ei2011/ei2011.pdf Multispectral Image Invariant to Illumination Colour, Strength, and Shading Mark S. Drew and
An Algorithm to Determine the Chromaticity Under Non-uniform Illuminant
 An Algorithm to Determine the Chromaticity Under Non-uniform Illuminant Sivalogeswaran Ratnasingam and Steve Collins Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, OX1 3PJ, Oxford, United Kingdom
An Algorithm to Determine the Chromaticity Under Non-uniform Illuminant Sivalogeswaran Ratnasingam and Steve Collins Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, OX1 3PJ, Oxford, United Kingdom
Computational Photography and Video: Intrinsic Images. Prof. Marc Pollefeys Dr. Gabriel Brostow
 Computational Photography and Video: Intrinsic Images Prof. Marc Pollefeys Dr. Gabriel Brostow Last Week Schedule Computational Photography and Video Exercises 18 Feb Introduction to Computational Photography
Computational Photography and Video: Intrinsic Images Prof. Marc Pollefeys Dr. Gabriel Brostow Last Week Schedule Computational Photography and Video Exercises 18 Feb Introduction to Computational Photography
HOW USEFUL ARE COLOUR INVARIANTS FOR IMAGE RETRIEVAL?
 HOW USEFUL ARE COLOUR INVARIANTS FOR IMAGE RETRIEVAL? Gerald Schaefer School of Computing and Technology Nottingham Trent University Nottingham, U.K. Gerald.Schaefer@ntu.ac.uk Abstract Keywords: The images
HOW USEFUL ARE COLOUR INVARIANTS FOR IMAGE RETRIEVAL? Gerald Schaefer School of Computing and Technology Nottingham Trent University Nottingham, U.K. Gerald.Schaefer@ntu.ac.uk Abstract Keywords: The images
Supplementary Material: Specular Highlight Removal in Facial Images
 Supplementary Material: Specular Highlight Removal in Facial Images Chen Li 1 Stephen Lin 2 Kun Zhou 1 Katsushi Ikeuchi 2 1 State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2 Microsoft Research 1. Computation
Supplementary Material: Specular Highlight Removal in Facial Images Chen Li 1 Stephen Lin 2 Kun Zhou 1 Katsushi Ikeuchi 2 1 State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2 Microsoft Research 1. Computation
An ICA based Approach for Complex Color Scene Text Binarization
 An ICA based Approach for Complex Color Scene Text Binarization Siddharth Kherada IIIT-Hyderabad, India siddharth.kherada@research.iiit.ac.in Anoop M. Namboodiri IIIT-Hyderabad, India anoop@iiit.ac.in
An ICA based Approach for Complex Color Scene Text Binarization Siddharth Kherada IIIT-Hyderabad, India siddharth.kherada@research.iiit.ac.in Anoop M. Namboodiri IIIT-Hyderabad, India anoop@iiit.ac.in
Estimating the wavelength composition of scene illumination from image data is an
 Chapter 3 The Principle and Improvement for AWB in DSC 3.1 Introduction Estimating the wavelength composition of scene illumination from image data is an important topics in color engineering. Solutions
Chapter 3 The Principle and Improvement for AWB in DSC 3.1 Introduction Estimating the wavelength composition of scene illumination from image data is an important topics in color engineering. Solutions
Color Constancy from Illumination Changes
 (MIRU2004) 2004 7 153-8505 4-6-1 E E-mail: {rei,robby,ki}@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Finlayson [10] Color Constancy from Illumination Changes Rei KAWAKAMI,RobbyT.TAN, and Katsushi IKEUCHI Institute of Industrial
(MIRU2004) 2004 7 153-8505 4-6-1 E E-mail: {rei,robby,ki}@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Finlayson [10] Color Constancy from Illumination Changes Rei KAWAKAMI,RobbyT.TAN, and Katsushi IKEUCHI Institute of Industrial
Illumination Estimation Using a Multilinear Constraint on Dichromatic Planes
 Illumination Estimation Using a Multilinear Constraint on Dichromatic Planes Javier Toro 1 and Brian Funt 2 LBMU 1, Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Montréal, QC, Canada H2L 2W5 School of
Illumination Estimation Using a Multilinear Constraint on Dichromatic Planes Javier Toro 1 and Brian Funt 2 LBMU 1, Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Montréal, QC, Canada H2L 2W5 School of
Shadow detection and removal from a single image
 Shadow detection and removal from a single image Corina BLAJOVICI, Babes-Bolyai University, Romania Peter Jozsef KISS, University of Pannonia, Hungary Zoltan BONUS, Obuda University, Hungary Laszlo VARGA,
Shadow detection and removal from a single image Corina BLAJOVICI, Babes-Bolyai University, Romania Peter Jozsef KISS, University of Pannonia, Hungary Zoltan BONUS, Obuda University, Hungary Laszlo VARGA,
Mobile Human Detection Systems based on Sliding Windows Approach-A Review
 Mobile Human Detection Systems based on Sliding Windows Approach-A Review Seminar: Mobile Human detection systems Njieutcheu Tassi cedrique Rovile Department of Computer Engineering University of Heidelberg
Mobile Human Detection Systems based on Sliding Windows Approach-A Review Seminar: Mobile Human detection systems Njieutcheu Tassi cedrique Rovile Department of Computer Engineering University of Heidelberg
Improvements to Gamut Mapping Colour Constancy Algorithms
 Improvements to Gamut Mapping Colour Constancy Algorithms Kobus Barnard Department of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University, 888 University Drive, Burnaby, BC, Canada, V5A 1S6 email: kobus@cs.sfu.ca
Improvements to Gamut Mapping Colour Constancy Algorithms Kobus Barnard Department of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University, 888 University Drive, Burnaby, BC, Canada, V5A 1S6 email: kobus@cs.sfu.ca
Video-Based Illumination Estimation
 Video-Based Illumination Estimation Ning Wang 1,2, Brian Funt 2, Congyan Lang 1, and De Xu 1 1 School of Computer Science and Infromation Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China 2 School
Video-Based Illumination Estimation Ning Wang 1,2, Brian Funt 2, Congyan Lang 1, and De Xu 1 1 School of Computer Science and Infromation Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China 2 School
Illuminant-Invariant Model-Based Road Segmentation
 Illuminant-Invariant Model-Based Road Segmentation J.M. Álvarez, A. López and R. Baldrich Abstract Road segmentation is an essential functionality for supporting advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
Illuminant-Invariant Model-Based Road Segmentation J.M. Álvarez, A. López and R. Baldrich Abstract Road segmentation is an essential functionality for supporting advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
Physics-based Vision: an Introduction
 Physics-based Vision: an Introduction Robby Tan ANU/NICTA (Vision Science, Technology and Applications) PhD from The University of Tokyo, 2004 1 What is Physics-based? An approach that is principally concerned
Physics-based Vision: an Introduction Robby Tan ANU/NICTA (Vision Science, Technology and Applications) PhD from The University of Tokyo, 2004 1 What is Physics-based? An approach that is principally concerned
CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3
 CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3 Due: Nov. 13 th, 2012 (2:15pm) 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking (20 points) In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest
CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3 Due: Nov. 13 th, 2012 (2:15pm) 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking (20 points) In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest
NOVEL METHODS FOR EXTRACTING ILLUMINATION-INVARIANT IMAGES AND FAST CLASSIFICATION OF TEXTURES
 NOVEL METHODS FOR EXTRACTING ILLUMINATION-INVARIANT IMAGES AND FAST CLASSIFICATION OF TEXTURES by Muntaseer Salahuddin B. Sc., Independent University, Bangladesh, 2005 a Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment
NOVEL METHODS FOR EXTRACTING ILLUMINATION-INVARIANT IMAGES AND FAST CLASSIFICATION OF TEXTURES by Muntaseer Salahuddin B. Sc., Independent University, Bangladesh, 2005 a Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment
CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3
 CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 22 nd, 2011 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest through a sequence of images.
CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 22 nd, 2011 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest through a sequence of images.
A Survey of Light Source Detection Methods
 A Survey of Light Source Detection Methods Nathan Funk University of Alberta Mini-Project for CMPUT 603 November 30, 2003 Abstract This paper provides an overview of the most prominent techniques for light
A Survey of Light Source Detection Methods Nathan Funk University of Alberta Mini-Project for CMPUT 603 November 30, 2003 Abstract This paper provides an overview of the most prominent techniques for light
Module 6: Pinhole camera model Lecture 32: Coordinate system conversion, Changing the image/world coordinate system
 The Lecture Contains: Back-projection of a 2D point to 3D 6.3 Coordinate system conversion file:///d /...(Ganesh%20Rana)/MY%20COURSE_Ganesh%20Rana/Prof.%20Sumana%20Gupta/FINAL%20DVSP/lecture%2032/32_1.htm[12/31/2015
The Lecture Contains: Back-projection of a 2D point to 3D 6.3 Coordinate system conversion file:///d /...(Ganesh%20Rana)/MY%20COURSE_Ganesh%20Rana/Prof.%20Sumana%20Gupta/FINAL%20DVSP/lecture%2032/32_1.htm[12/31/2015
HISTOGRAMS OF ORIENTATIO N GRADIENTS
 HISTOGRAMS OF ORIENTATIO N GRADIENTS Histograms of Orientation Gradients Objective: object recognition Basic idea Local shape information often well described by the distribution of intensity gradients
HISTOGRAMS OF ORIENTATIO N GRADIENTS Histograms of Orientation Gradients Objective: object recognition Basic idea Local shape information often well described by the distribution of intensity gradients
COLOR FIDELITY OF CHROMATIC DISTRIBUTIONS BY TRIAD ILLUMINANT COMPARISON. Marcel P. Lucassen, Theo Gevers, Arjan Gijsenij
 COLOR FIDELITY OF CHROMATIC DISTRIBUTIONS BY TRIAD ILLUMINANT COMPARISON Marcel P. Lucassen, Theo Gevers, Arjan Gijsenij Intelligent Systems Lab Amsterdam, University of Amsterdam ABSTRACT Performance
COLOR FIDELITY OF CHROMATIC DISTRIBUTIONS BY TRIAD ILLUMINANT COMPARISON Marcel P. Lucassen, Theo Gevers, Arjan Gijsenij Intelligent Systems Lab Amsterdam, University of Amsterdam ABSTRACT Performance
Light-Invariant Fitting of Active Appearance Models
 Light-Invariant Fitting of Active Appearance Models Daniel Pizarro Alcalà University- Madrid Julien Peyras LASMEA- Clermont-Ferrand Adrien Bartoli LASMEA- Clermont-Ferrand Abstract This paper deals with
Light-Invariant Fitting of Active Appearance Models Daniel Pizarro Alcalà University- Madrid Julien Peyras LASMEA- Clermont-Ferrand Adrien Bartoli LASMEA- Clermont-Ferrand Abstract This paper deals with
Shadow Removal from a Single Image
 Shadow Removal from a Single Image Li Xu Feihu Qi Renjie Jiang Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai JiaoTong University, P.R. China E-mail {nathan.xu, fhqi, blizard1982}@sjtu.edu.cn
Shadow Removal from a Single Image Li Xu Feihu Qi Renjie Jiang Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai JiaoTong University, P.R. China E-mail {nathan.xu, fhqi, blizard1982}@sjtu.edu.cn
then assume that we are given the image of one of these textures captured by a camera at a different (longer) distance and with unknown direction of i
 Image Texture Prediction using Colour Photometric Stereo Xavier Lladó 1, Joan Mart 1, and Maria Petrou 2 1 Institute of Informatics and Applications, University of Girona, 1771, Girona, Spain fllado,joanmg@eia.udg.es
Image Texture Prediction using Colour Photometric Stereo Xavier Lladó 1, Joan Mart 1, and Maria Petrou 2 1 Institute of Informatics and Applications, University of Girona, 1771, Girona, Spain fllado,joanmg@eia.udg.es
Local Linear Models for Improved von Kries Adaptation
 Appeared in Proc. of 10th Colour Imaging Conf., Scottsdale AZ, 2002 1 Local Linear Models for Improved von Kries Adaptation G. D. Finlayson, A. Alsam, and S. D. Hordley School of Information Systems University
Appeared in Proc. of 10th Colour Imaging Conf., Scottsdale AZ, 2002 1 Local Linear Models for Improved von Kries Adaptation G. D. Finlayson, A. Alsam, and S. D. Hordley School of Information Systems University
Material-Based Object Segmentation Using Near-Infrared Information
 Material-Based Object Segmentation Using Near-Infrared Information N. Salamati and S. Süsstrunk School of Computer and Communication Sciences, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne,
Material-Based Object Segmentation Using Near-Infrared Information N. Salamati and S. Süsstrunk School of Computer and Communication Sciences, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne,
A Novel Approach for Shadow Removal Based on Intensity Surface Approximation
 A Novel Approach for Shadow Removal Based on Intensity Surface Approximation Eli Arbel THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER DEGREE University of Haifa Faculty of Social
A Novel Approach for Shadow Removal Based on Intensity Surface Approximation Eli Arbel THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MASTER DEGREE University of Haifa Faculty of Social
Accurate and Dense Wide-Baseline Stereo Matching Using SW-POC
 Accurate and Dense Wide-Baseline Stereo Matching Using SW-POC Shuji Sakai, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University, Sendai, 980 8579, Japan Email: sakai@aoki.ecei.tohoku.ac.jp
Accurate and Dense Wide-Baseline Stereo Matching Using SW-POC Shuji Sakai, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University, Sendai, 980 8579, Japan Email: sakai@aoki.ecei.tohoku.ac.jp
CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2014) Problem Set 3
 CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2014) Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 18 th, 2015 (11:59pm) 1 Single Object Recognition Via SIFT (45 points) In his 2004 SIFT paper, David Lowe demonstrates impressive object recognition
CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2014) Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 18 th, 2015 (11:59pm) 1 Single Object Recognition Via SIFT (45 points) In his 2004 SIFT paper, David Lowe demonstrates impressive object recognition
Part-Based Skew Estimation for Mathematical Expressions
 Soma Shiraishi, Yaokai Feng, and Seiichi Uchida shiraishi@human.ait.kyushu-u.ac.jp {fengyk,uchida}@ait.kyushu-u.ac.jp Abstract We propose a novel method for the skew estimation on text images containing
Soma Shiraishi, Yaokai Feng, and Seiichi Uchida shiraishi@human.ait.kyushu-u.ac.jp {fengyk,uchida}@ait.kyushu-u.ac.jp Abstract We propose a novel method for the skew estimation on text images containing
MULTISPECTRAL AND HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGES INVARIANT TO ILLUMINATION
 MULTISPECTRAL AND HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGES INVARIANT TO ILLUMINATION by Amin Yazdani Salekdeh B.Sc., Sharif University of Technology, 2009 a Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
MULTISPECTRAL AND HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGES INVARIANT TO ILLUMINATION by Amin Yazdani Salekdeh B.Sc., Sharif University of Technology, 2009 a Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
An ICA-Based Multivariate Discretization Algorithm
 An ICA-Based Multivariate Discretization Algorithm Ye Kang 1,2, Shanshan Wang 1,2, Xiaoyan Liu 1, Hokyin Lai 1, Huaiqing Wang 1, and Baiqi Miao 2 1 Department of Information Systems, City University of
An ICA-Based Multivariate Discretization Algorithm Ye Kang 1,2, Shanshan Wang 1,2, Xiaoyan Liu 1, Hokyin Lai 1, Huaiqing Wang 1, and Baiqi Miao 2 1 Department of Information Systems, City University of
Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model
 Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model TAE IN SEOL*, SUN-TAE CHUNG*, SUNHO KI**, SEONGWON CHO**, YUN-KWANG HONG*** *School of Electronic Engineering
Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model TAE IN SEOL*, SUN-TAE CHUNG*, SUNHO KI**, SEONGWON CHO**, YUN-KWANG HONG*** *School of Electronic Engineering
Color and Shading. Color. Shapiro and Stockman, Chapter 6. Color and Machine Vision. Color and Perception
 Color and Shading Color Shapiro and Stockman, Chapter 6 Color is an important factor for for human perception for object and material identification, even time of day. Color perception depends upon both
Color and Shading Color Shapiro and Stockman, Chapter 6 Color is an important factor for for human perception for object and material identification, even time of day. Color perception depends upon both
JPEG compression of monochrome 2D-barcode images using DCT coefficient distributions
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. JPEG compression of monochrome D-barcode images using DCT coefficient distributions Keng Teong Tan Hong Kong Baptist University Douglas Chai
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. JPEG compression of monochrome D-barcode images using DCT coefficient distributions Keng Teong Tan Hong Kong Baptist University Douglas Chai
Diagonal versus affine transformations for color correction
 2108 J. Opt. oc. Am. A/ Vol. 17, No. 11/ November 2000 JOA Communications Diagonal versus affine transformations for color correction Brian V. Funt and Benjamin C. ewis chool of Computing cience, imon
2108 J. Opt. oc. Am. A/ Vol. 17, No. 11/ November 2000 JOA Communications Diagonal versus affine transformations for color correction Brian V. Funt and Benjamin C. ewis chool of Computing cience, imon
Metric Structure from Motion
 CS443 Final Project Metric Structure from Motion Peng Cheng 1 Objective of the Project Given: 1. A static object with n feature points and unknown shape. 2. A camera with unknown intrinsic parameters takes
CS443 Final Project Metric Structure from Motion Peng Cheng 1 Objective of the Project Given: 1. A static object with n feature points and unknown shape. 2. A camera with unknown intrinsic parameters takes
EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm
 EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm Group 1: Mina A. Makar Stanford University mamakar@stanford.edu Abstract In this report, we investigate the application of the Scale-Invariant
EE368 Project Report CD Cover Recognition Using Modified SIFT Algorithm Group 1: Mina A. Makar Stanford University mamakar@stanford.edu Abstract In this report, we investigate the application of the Scale-Invariant
Motion Estimation. There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation:
 Members: D91922016 朱威達 R93922010 林聖凱 R93922044 謝俊瑋 Motion Estimation There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation: Parametric motion (image alignment) The main idea of parametric motion
Members: D91922016 朱威達 R93922010 林聖凱 R93922044 謝俊瑋 Motion Estimation There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation: Parametric motion (image alignment) The main idea of parametric motion
Human Action Recognition Using Independent Component Analysis
 Human Action Recognition Using Independent Component Analysis Masaki Yamazaki, Yen-Wei Chen and Gang Xu Department of Media echnology Ritsumeikan University 1-1-1 Nojihigashi, Kusatsu, Shiga, 525-8577,
Human Action Recognition Using Independent Component Analysis Masaki Yamazaki, Yen-Wei Chen and Gang Xu Department of Media echnology Ritsumeikan University 1-1-1 Nojihigashi, Kusatsu, Shiga, 525-8577,
3D Reconstruction of a Hopkins Landmark
 3D Reconstruction of a Hopkins Landmark Ayushi Sinha (461), Hau Sze (461), Diane Duros (361) Abstract - This paper outlines a method for 3D reconstruction from two images. Our procedure is based on known
3D Reconstruction of a Hopkins Landmark Ayushi Sinha (461), Hau Sze (461), Diane Duros (361) Abstract - This paper outlines a method for 3D reconstruction from two images. Our procedure is based on known
Human Motion Detection and Tracking for Video Surveillance
 Human Motion Detection and Tracking for Video Surveillance Prithviraj Banerjee and Somnath Sengupta Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur,
Human Motion Detection and Tracking for Video Surveillance Prithviraj Banerjee and Somnath Sengupta Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur,
arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018](/thumbs/93/113542646.jpg) Camera Pose Estimation from Sequence of Calibrated Images arxiv:1809.11066v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 Jacek Komorowski 1 and Przemyslaw Rokita 2 1 Maria Curie-Sklodowska University, Institute of Computer Science,
Camera Pose Estimation from Sequence of Calibrated Images arxiv:1809.11066v1 [cs.cv] 28 Sep 2018 Jacek Komorowski 1 and Przemyslaw Rokita 2 1 Maria Curie-Sklodowska University, Institute of Computer Science,
CHAPTER 9. Classification Scheme Using Modified Photometric. Stereo and 2D Spectra Comparison
 CHAPTER 9 Classification Scheme Using Modified Photometric Stereo and 2D Spectra Comparison 9.1. Introduction In Chapter 8, even we combine more feature spaces and more feature generators, we note that
CHAPTER 9 Classification Scheme Using Modified Photometric Stereo and 2D Spectra Comparison 9.1. Introduction In Chapter 8, even we combine more feature spaces and more feature generators, we note that
A Colour Constancy Algorithm Based on the Histogram of Feasible Colour Mappings
 A Colour Constancy Algorithm Based on the Histogram of Feasible Colour Mappings Jaume Vergés-Llahí and Alberto Sanfeliu Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial Technological Park of Barcelona, U
A Colour Constancy Algorithm Based on the Histogram of Feasible Colour Mappings Jaume Vergés-Llahí and Alberto Sanfeliu Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial Technological Park of Barcelona, U
Specular Reflection Separation using Dark Channel Prior
 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Specular Reflection Separation using Dark Channel Prior Hyeongwoo Kim KAIST hyeongwoo.kim@kaist.ac.kr Hailin Jin Adobe Research hljin@adobe.com
2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Specular Reflection Separation using Dark Channel Prior Hyeongwoo Kim KAIST hyeongwoo.kim@kaist.ac.kr Hailin Jin Adobe Research hljin@adobe.com
Spectral Images and the Retinex Model
 Spectral Images and the Retine Model Anahit Pogosova 1, Tuija Jetsu 1, Ville Heikkinen 2, Markku Hauta-Kasari 1, Timo Jääskeläinen 2 and Jussi Parkkinen 1 1 Department of Computer Science and Statistics,
Spectral Images and the Retine Model Anahit Pogosova 1, Tuija Jetsu 1, Ville Heikkinen 2, Markku Hauta-Kasari 1, Timo Jääskeläinen 2 and Jussi Parkkinen 1 1 Department of Computer Science and Statistics,
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Machine learning based automatic extrinsic calibration of an onboard monocular camera for driving assistance applications on smart mobile devices
 Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Research Center www.cv.utcluj.ro Machine learning based automatic extrinsic calibration of an onboard monocular camera for driving
Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Research Center www.cv.utcluj.ro Machine learning based automatic extrinsic calibration of an onboard monocular camera for driving
An Overview of Matchmoving using Structure from Motion Methods
 An Overview of Matchmoving using Structure from Motion Methods Kamyar Haji Allahverdi Pour Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Tehran, Iran Email: allahverdi@ce.sharif.edu
An Overview of Matchmoving using Structure from Motion Methods Kamyar Haji Allahverdi Pour Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Tehran, Iran Email: allahverdi@ce.sharif.edu
Reconstruction of Images Distorted by Water Waves
 Reconstruction of Images Distorted by Water Waves Arturo Donate and Eraldo Ribeiro Computer Vision Group Outline of the talk Introduction Analysis Background Method Experiments Conclusions Future Work
Reconstruction of Images Distorted by Water Waves Arturo Donate and Eraldo Ribeiro Computer Vision Group Outline of the talk Introduction Analysis Background Method Experiments Conclusions Future Work
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V
 HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
Simultaneous surface texture classification and illumination tilt angle prediction
 Simultaneous surface texture classification and illumination tilt angle prediction X. Lladó, A. Oliver, M. Petrou, J. Freixenet, and J. Martí Computer Vision and Robotics Group - IIiA. University of Girona
Simultaneous surface texture classification and illumination tilt angle prediction X. Lladó, A. Oliver, M. Petrou, J. Freixenet, and J. Martí Computer Vision and Robotics Group - IIiA. University of Girona
The Detection of Faces in Color Images: EE368 Project Report
 The Detection of Faces in Color Images: EE368 Project Report Angela Chau, Ezinne Oji, Jeff Walters Dept. of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 9435 angichau,ezinne,jwalt@stanford.edu
The Detection of Faces in Color Images: EE368 Project Report Angela Chau, Ezinne Oji, Jeff Walters Dept. of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 9435 angichau,ezinne,jwalt@stanford.edu
Experimentation on the use of Chromaticity Features, Local Binary Pattern and Discrete Cosine Transform in Colour Texture Analysis
 Experimentation on the use of Chromaticity Features, Local Binary Pattern and Discrete Cosine Transform in Colour Texture Analysis N.Padmapriya, Ovidiu Ghita, and Paul.F.Whelan Vision Systems Laboratory,
Experimentation on the use of Chromaticity Features, Local Binary Pattern and Discrete Cosine Transform in Colour Texture Analysis N.Padmapriya, Ovidiu Ghita, and Paul.F.Whelan Vision Systems Laboratory,
ROBUST LINE-BASED CALIBRATION OF LENS DISTORTION FROM A SINGLE VIEW
 ROBUST LINE-BASED CALIBRATION OF LENS DISTORTION FROM A SINGLE VIEW Thorsten Thormählen, Hellward Broszio, Ingolf Wassermann thormae@tnt.uni-hannover.de University of Hannover, Information Technology Laboratory,
ROBUST LINE-BASED CALIBRATION OF LENS DISTORTION FROM A SINGLE VIEW Thorsten Thormählen, Hellward Broszio, Ingolf Wassermann thormae@tnt.uni-hannover.de University of Hannover, Information Technology Laboratory,
Real-Time Human Detection using Relational Depth Similarity Features
 Real-Time Human Detection using Relational Depth Similarity Features Sho Ikemura, Hironobu Fujiyoshi Dept. of Computer Science, Chubu University. Matsumoto 1200, Kasugai, Aichi, 487-8501 Japan. si@vision.cs.chubu.ac.jp,
Real-Time Human Detection using Relational Depth Similarity Features Sho Ikemura, Hironobu Fujiyoshi Dept. of Computer Science, Chubu University. Matsumoto 1200, Kasugai, Aichi, 487-8501 Japan. si@vision.cs.chubu.ac.jp,
Self Lane Assignment Using Smart Mobile Camera For Intelligent GPS Navigation and Traffic Interpretation
 For Intelligent GPS Navigation and Traffic Interpretation Tianshi Gao Stanford University tianshig@stanford.edu 1. Introduction Imagine that you are driving on the highway at 70 mph and trying to figure
For Intelligent GPS Navigation and Traffic Interpretation Tianshi Gao Stanford University tianshig@stanford.edu 1. Introduction Imagine that you are driving on the highway at 70 mph and trying to figure
How to Compute the Pose of an Object without a Direct View?
 How to Compute the Pose of an Object without a Direct View? Peter Sturm and Thomas Bonfort INRIA Rhône-Alpes, 38330 Montbonnot St Martin, France {Peter.Sturm, Thomas.Bonfort}@inrialpes.fr Abstract. We
How to Compute the Pose of an Object without a Direct View? Peter Sturm and Thomas Bonfort INRIA Rhône-Alpes, 38330 Montbonnot St Martin, France {Peter.Sturm, Thomas.Bonfort}@inrialpes.fr Abstract. We
Character Recognition
 Character Recognition 5.1 INTRODUCTION Recognition is one of the important steps in image processing. There are different methods such as Histogram method, Hough transformation, Neural computing approaches
Character Recognition 5.1 INTRODUCTION Recognition is one of the important steps in image processing. There are different methods such as Histogram method, Hough transformation, Neural computing approaches
AN IMAGE BASED SYSTEM TO AUTOMATICALLY
 AN IMAGE BASED SYSTEM TO AUTOMATICALLY AND OBJECTIVELY SCORE THE DEGREE OF REDNESS AND SCALING IN PSORIASIS LESIONS. David Delgado Bjarne Ersb ll Jens Michael Carstensen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling,
AN IMAGE BASED SYSTEM TO AUTOMATICALLY AND OBJECTIVELY SCORE THE DEGREE OF REDNESS AND SCALING IN PSORIASIS LESIONS. David Delgado Bjarne Ersb ll Jens Michael Carstensen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling,
Low Cost Motion Capture
 Low Cost Motion Capture R. Budiman M. Bennamoun D.Q. Huynh School of Computer Science and Software Engineering The University of Western Australia Crawley WA 6009 AUSTRALIA Email: budimr01@tartarus.uwa.edu.au,
Low Cost Motion Capture R. Budiman M. Bennamoun D.Q. Huynh School of Computer Science and Software Engineering The University of Western Australia Crawley WA 6009 AUSTRALIA Email: budimr01@tartarus.uwa.edu.au,
Rotation and Scaling Image Using PCA
 wwwccsenetorg/cis Computer and Information Science Vol 5, No 1; January 12 Rotation and Scaling Image Using PCA Hawrra Hassan Abass Electrical & Electronics Dept, Engineering College Kerbela University,
wwwccsenetorg/cis Computer and Information Science Vol 5, No 1; January 12 Rotation and Scaling Image Using PCA Hawrra Hassan Abass Electrical & Electronics Dept, Engineering College Kerbela University,
Applying Synthetic Images to Learning Grasping Orientation from Single Monocular Images
 Applying Synthetic Images to Learning Grasping Orientation from Single Monocular Images 1 Introduction - Steve Chuang and Eric Shan - Determining object orientation in images is a well-established topic
Applying Synthetic Images to Learning Grasping Orientation from Single Monocular Images 1 Introduction - Steve Chuang and Eric Shan - Determining object orientation in images is a well-established topic
Computationally Efficient Serial Combination of Rotation-invariant and Rotation Compensating Iris Recognition Algorithms
 Computationally Efficient Serial Combination of Rotation-invariant and Rotation Compensating Iris Recognition Algorithms Andreas Uhl Department of Computer Sciences University of Salzburg, Austria uhl@cosy.sbg.ac.at
Computationally Efficient Serial Combination of Rotation-invariant and Rotation Compensating Iris Recognition Algorithms Andreas Uhl Department of Computer Sciences University of Salzburg, Austria uhl@cosy.sbg.ac.at
Local invariant features
 Local invariant features Tuesday, Oct 28 Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Today Some more Pset 2 results Pset 2 returned, pick up solutions Pset 3 is posted, due 11/11 Local invariant features Detection of interest
Local invariant features Tuesday, Oct 28 Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Today Some more Pset 2 results Pset 2 returned, pick up solutions Pset 3 is posted, due 11/11 Local invariant features Detection of interest
Salient Region Detection and Segmentation in Images using Dynamic Mode Decomposition
 Salient Region Detection and Segmentation in Images using Dynamic Mode Decomposition Sikha O K 1, Sachin Kumar S 2, K P Soman 2 1 Department of Computer Science 2 Centre for Computational Engineering and
Salient Region Detection and Segmentation in Images using Dynamic Mode Decomposition Sikha O K 1, Sachin Kumar S 2, K P Soman 2 1 Department of Computer Science 2 Centre for Computational Engineering and
Color Constancy from Hyper-Spectral Data
 Color Constancy from Hyper-Spectral Data Th. Gevers, H. M. G. Stokman, J. van de Weijer Faculty of Science, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands fgevers, stokman, joostwg@wins.uva.nl Abstract This
Color Constancy from Hyper-Spectral Data Th. Gevers, H. M. G. Stokman, J. van de Weijer Faculty of Science, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands fgevers, stokman, joostwg@wins.uva.nl Abstract This
Robust color segmentation algorithms in illumination variation conditions
 286 CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS / Vol. 8, No. / March 10, 2010 Robust color segmentation algorithms in illumination variation conditions Jinhui Lan ( ) and Kai Shen ( Department of Measurement and Control Technologies,
286 CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS / Vol. 8, No. / March 10, 2010 Robust color segmentation algorithms in illumination variation conditions Jinhui Lan ( ) and Kai Shen ( Department of Measurement and Control Technologies,
Determination of 3-D Image Viewpoint Using Modified Nearest Feature Line Method in Its Eigenspace Domain
 Determination of 3-D Image Viewpoint Using Modified Nearest Feature Line Method in Its Eigenspace Domain LINA +, BENYAMIN KUSUMOPUTRO ++ + Faculty of Information Technology Tarumanagara University Jl.
Determination of 3-D Image Viewpoint Using Modified Nearest Feature Line Method in Its Eigenspace Domain LINA +, BENYAMIN KUSUMOPUTRO ++ + Faculty of Information Technology Tarumanagara University Jl.
Eugene Borovikov. Human Head Pose Estimation by Facial Features Location. UMCP Human Head Pose Estimation by Facial Features Location
 Human Head Pose Estimation by Facial Features Location Abstract: Eugene Borovikov University of Maryland Institute for Computer Studies, College Park, MD 20742 4/21/1998 We describe a method for estimating
Human Head Pose Estimation by Facial Features Location Abstract: Eugene Borovikov University of Maryland Institute for Computer Studies, College Park, MD 20742 4/21/1998 We describe a method for estimating
A Comparison of Computational Color Constancy Algorithms; Part Two: Experiments with Image Data
 This work has been accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions in Image Processing. 1 (See http://www.ieee.org/about/documentation/copyright/policies.htm for copyright issue details). A Comparison of
This work has been accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions in Image Processing. 1 (See http://www.ieee.org/about/documentation/copyright/policies.htm for copyright issue details). A Comparison of
PCA and KPCA algorithms for Face Recognition A Survey
 PCA and KPCA algorithms for Face Recognition A Survey Surabhi M. Dhokai 1, Vaishali B.Vala 2,Vatsal H. Shah 3 1 Department of Information Technology, BVM Engineering College, surabhidhokai@gmail.com 2
PCA and KPCA algorithms for Face Recognition A Survey Surabhi M. Dhokai 1, Vaishali B.Vala 2,Vatsal H. Shah 3 1 Department of Information Technology, BVM Engineering College, surabhidhokai@gmail.com 2
Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting
 Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11-a Announcements Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 10 in class Non-maximum suppression For every
Generalized Hough Transform, line fitting Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11-a Announcements Assignment 2: Due today Midterm: Thursday, May 10 in class Non-maximum suppression For every
Removing Shadows From Images using Retinex
 Removing Shadows From Images using Retinex G. D. Finlayson, S. D. Hordley M.S. Drew School of Information Systems School of Computing Science University of East Anglia Simon Fraser University Norwich NR4
Removing Shadows From Images using Retinex G. D. Finlayson, S. D. Hordley M.S. Drew School of Information Systems School of Computing Science University of East Anglia Simon Fraser University Norwich NR4
METRIC PLANE RECTIFICATION USING SYMMETRIC VANISHING POINTS
 METRIC PLANE RECTIFICATION USING SYMMETRIC VANISHING POINTS M. Lefler, H. Hel-Or Dept. of CS, University of Haifa, Israel Y. Hel-Or School of CS, IDC, Herzliya, Israel ABSTRACT Video analysis often requires
METRIC PLANE RECTIFICATION USING SYMMETRIC VANISHING POINTS M. Lefler, H. Hel-Or Dept. of CS, University of Haifa, Israel Y. Hel-Or School of CS, IDC, Herzliya, Israel ABSTRACT Video analysis often requires
An Efficient Need-Based Vision System in Variable Illumination Environment of Middle Size RoboCup
 An Efficient Need-Based Vision System in Variable Illumination Environment of Middle Size RoboCup Mansour Jamzad and Abolfazal Keighobadi Lamjiri Sharif University of Technology Department of Computer
An Efficient Need-Based Vision System in Variable Illumination Environment of Middle Size RoboCup Mansour Jamzad and Abolfazal Keighobadi Lamjiri Sharif University of Technology Department of Computer
Practical Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Object Appearance and Motion for Traffic Scene Visual Surveillance
 Practical Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Object Appearance and Motion for Traffic Scene Visual Surveillance Zhaoxiang Zhang, Min Li, Kaiqi Huang and Tieniu Tan National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition,
Practical Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Object Appearance and Motion for Traffic Scene Visual Surveillance Zhaoxiang Zhang, Min Li, Kaiqi Huang and Tieniu Tan National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition,
Flexible Calibration of a Portable Structured Light System through Surface Plane
 Vol. 34, No. 11 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA November, 2008 Flexible Calibration of a Portable Structured Light System through Surface Plane GAO Wei 1 WANG Liang 1 HU Zhan-Yi 1 Abstract For a portable structured
Vol. 34, No. 11 ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA November, 2008 Flexible Calibration of a Portable Structured Light System through Surface Plane GAO Wei 1 WANG Liang 1 HU Zhan-Yi 1 Abstract For a portable structured
Features Points. Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, Mestre (VE)
 Features Points Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Finding Corners Edge detectors perform poorly at corners. Corners provide repeatable points for matching, so
Features Points Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Finding Corners Edge detectors perform poorly at corners. Corners provide repeatable points for matching, so
SELECTION OF A MULTIVARIATE CALIBRATION METHOD
 SELECTION OF A MULTIVARIATE CALIBRATION METHOD 0. Aim of this document Different types of multivariate calibration methods are available. The aim of this document is to help the user select the proper
SELECTION OF A MULTIVARIATE CALIBRATION METHOD 0. Aim of this document Different types of multivariate calibration methods are available. The aim of this document is to help the user select the proper
Level lines based disocclusion
 Level lines based disocclusion Simon Masnou Jean-Michel Morel CEREMADE CMLA Université Paris-IX Dauphine Ecole Normale Supérieure de Cachan 75775 Paris Cedex 16, France 94235 Cachan Cedex, France Abstract
Level lines based disocclusion Simon Masnou Jean-Michel Morel CEREMADE CMLA Université Paris-IX Dauphine Ecole Normale Supérieure de Cachan 75775 Paris Cedex 16, France 94235 Cachan Cedex, France Abstract
An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization
 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -2 th, June 205, Sydney Australia An explicit feature control approach in structural topology optimization Weisheng Zhang, Xu Guo
Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates
 Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates Abdelsalam Masoud William Hoff Colorado School of Mines Colorado School of Mines Golden, CO 800 Golden, CO 800 amasoud@mines.edu whoff@mines.edu Abstract
Segmentation and Tracking of Partial Planar Templates Abdelsalam Masoud William Hoff Colorado School of Mines Colorado School of Mines Golden, CO 800 Golden, CO 800 amasoud@mines.edu whoff@mines.edu Abstract
2003 Steve Marschner 7 Light detection discrete approx. Cone Responses S,M,L cones have broadband spectral sensitivity This sum is very clearly a dot
 2003 Steve Marschner Color science as linear algebra Last time: historical the actual experiments that lead to understanding color strictly based on visual observations Color Science CONTD. concrete but
2003 Steve Marschner Color science as linear algebra Last time: historical the actual experiments that lead to understanding color strictly based on visual observations Color Science CONTD. concrete but
Simultaneous Vanishing Point Detection and Camera Calibration from Single Images
 Simultaneous Vanishing Point Detection and Camera Calibration from Single Images Bo Li, Kun Peng, Xianghua Ying, and Hongbin Zha The Key Lab of Machine Perception (Ministry of Education), Peking University,
Simultaneous Vanishing Point Detection and Camera Calibration from Single Images Bo Li, Kun Peng, Xianghua Ying, and Hongbin Zha The Key Lab of Machine Perception (Ministry of Education), Peking University,
Projective Geometry and Camera Models
 /2/ Projective Geometry and Camera Models Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Note about HW Out before next Tues Prob: covered today, Tues Prob2: covered next Thurs Prob3:
/2/ Projective Geometry and Camera Models Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Note about HW Out before next Tues Prob: covered today, Tues Prob2: covered next Thurs Prob3:
NOVEL PCA-BASED COLOR-TO-GRAY IMAGE CONVERSION. Ja-Won Seo and Seong Dae Kim
 NOVEL PCA-BASED COLOR-TO-GRAY IMAGE CONVERSION Ja-Won Seo and Seong Dae Kim Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Department of Electrical Engineering 21 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon
NOVEL PCA-BASED COLOR-TO-GRAY IMAGE CONVERSION Ja-Won Seo and Seong Dae Kim Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Department of Electrical Engineering 21 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon
Hypothesis Generation of Instances of Road Signs in Color Imagery Captured by Mobile Mapping Systems
 Hypothesis Generation of Instances of Road Signs in Color Imagery Captured by Mobile Mapping Systems A.F. Habib*, M.N.Jha Department of Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
Hypothesis Generation of Instances of Road Signs in Color Imagery Captured by Mobile Mapping Systems A.F. Habib*, M.N.Jha Department of Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
A New Color Constancy Algorithm Based on the Histogram of Feasible Mappings
 A New Color Constancy Algorithm Based on the Histogram of Feasible Mappings Jaume Vergés Llahí and Alberto Sanfeliu Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial, Technological Park of Barcelona, U Building
A New Color Constancy Algorithm Based on the Histogram of Feasible Mappings Jaume Vergés Llahí and Alberto Sanfeliu Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial, Technological Park of Barcelona, U Building
Exploring Curve Fitting for Fingers in Egocentric Images
 Exploring Curve Fitting for Fingers in Egocentric Images Akanksha Saran Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University 16-811: Math Fundamentals for Robotics Final Project Report Email: asaran@andrew.cmu.edu
Exploring Curve Fitting for Fingers in Egocentric Images Akanksha Saran Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University 16-811: Math Fundamentals for Robotics Final Project Report Email: asaran@andrew.cmu.edu
Shadow Resistant Road Segmentation from a Mobile Monocular System
 Shadow Resistant Road Segmentation from a Mobile Monocular System José ManuelÁlvarez, Antonio M. López, and Ramon Baldrich Computer Vision Center and Computer Science Dpt., Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
Shadow Resistant Road Segmentation from a Mobile Monocular System José ManuelÁlvarez, Antonio M. López, and Ramon Baldrich Computer Vision Center and Computer Science Dpt., Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
SYDE Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition. Clustering
 SYDE 372 - Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Clustering Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 5 All the approaches we have learned
SYDE 372 - Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Clustering Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 5 All the approaches we have learned
Angular Error /Degrees. Angular Error /Degrees Number of Surfaces
 A Theory of Selection for Gamut Mapping Colour Constancy Graham Finlayson University of Derby Colour & Imaging Institute Britannia Mill Mackworth Road Derby DE22 3BL Steven Hordley University of Derby
A Theory of Selection for Gamut Mapping Colour Constancy Graham Finlayson University of Derby Colour & Imaging Institute Britannia Mill Mackworth Road Derby DE22 3BL Steven Hordley University of Derby
Perception and Action using Multilinear Forms
 Perception and Action using Multilinear Forms Anders Heyden, Gunnar Sparr, Kalle Åström Dept of Mathematics, Lund University Box 118, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden email: {heyden,gunnar,kalle}@maths.lth.se Abstract
Perception and Action using Multilinear Forms Anders Heyden, Gunnar Sparr, Kalle Åström Dept of Mathematics, Lund University Box 118, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden email: {heyden,gunnar,kalle}@maths.lth.se Abstract
This blog addresses the question: how do we determine the intersection of two circles in the Cartesian plane?
 Intersecting Circles This blog addresses the question: how do we determine the intersection of two circles in the Cartesian plane? This is a problem that a programmer might have to solve, for example,
Intersecting Circles This blog addresses the question: how do we determine the intersection of two circles in the Cartesian plane? This is a problem that a programmer might have to solve, for example,
Estimating normal vectors and curvatures by centroid weights
 Computer Aided Geometric Design 21 (2004) 447 458 www.elsevier.com/locate/cagd Estimating normal vectors and curvatures by centroid weights Sheng-Gwo Chen, Jyh-Yang Wu Department of Mathematics, National
Computer Aided Geometric Design 21 (2004) 447 458 www.elsevier.com/locate/cagd Estimating normal vectors and curvatures by centroid weights Sheng-Gwo Chen, Jyh-Yang Wu Department of Mathematics, National
