Introduction to Quadratic Functions
|
|
|
- Amos Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Quadratic Functions The St. Louis Gateway Arch was constructed from 1963 to It cost 13 million dollars to build..1 Up and Down or Down and Up Exploring Quadratic Functions Just U and I Comparing Linear and Quadratic Functions Walking the... Curve? Domain, Range, Zeros, and Intercepts Are You Afraid of Ghosts? Factored Form of a Quadratic Function Just Watch that Pumpkin Fly! Investigating the Vertex of a Quadratic Function The Form Is Key Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function More Than Meets the Eye Transformations of Quadratic Functions
2 856
3 Up and Down or Down and Up Exploring Quadratic Functions.1 Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Model real-world problems using quadratic functions. Analyze tables, graphs, and equations for quadratic functions. Use the Distributive Property to write a quadratic equation in standard form. Compare graphs of quadratic functions. Use a graphing calculator to determine the absolute minimum or absolute maximum of a quadratic function. standard form (general form) of a quadratic function parabola Take a necklace and hold it at both ends with your fingers. What function would you say describes the shape of the necklace? Quadratic? Wrong. This shape is formed by a catenary function. From bridges to spider webs to architectural arches, catenaries are all around us and they look so much like parabolas, it s easy to be fooled. In future math classes distant future you ll learn about the differences between catenary functions and quadratic functions. For now, let s just focus on quadratics. 857
4 Problem 1 Who Put the Dogs In? A dog trainer is fencing in an enclosure, represented by the shaded region in the diagram. The trainer will also have two square-shaped storage units on either side of the enclosure to store equipment and other materials. She can make the enclosure and storage units as wide as she wants, but she can t exceed 100 feet in total length. 100 ft 1. Let s represent a side length, in feet, of one of the square storage units. a. Write an expression to represent the width of the enclosure. Label the width in the diagram. Explain your reasoning. b. Write an expression to represent the length of the enclosure. Label the length in the diagram. Explain your reasoning. c. Write an expression to represent the area of the enclosure. Explain your reasoning. 858 Chapter Introduction to Quadratic Functions
5 You know that you can use the Distributive Property to rewrite a mathematical expression. For example, to rewrite 2(5 2 4), you can distribute the 2: 2(5 2 4) 5 2(5) 2 2(4) You can also distribute variables: The expression n? 3n is equivalent to n? 3? n, which is the same as n? n? 3, or n 2? 3, or 3n 2. n(4 2 3n) 5 n(4) 2 n(3n) 5 4n 2 3n 2 2. Use the Distributive Property to rewrite the expression representing the area of the enclosure. Show your work. The expression you wrote is a quadratic expression. Recall that a quadratic function written in the form f(x) 5 ax 2 1 bx 1 c, where a fi 0, is in standard form, or general form. In this form, a and b represent numerical coefficients and c represents a constant. 3. Write the area of the enclosure as a function, A(s), in standard form. Then, identify a, b, and c for the function. 4. Identify the independent and dependent quantities and their units in this problem situation..1 Exploring Quadratic Functions 859
6 The progression of diagrams at the right shows how the area of the enclosure, A(s), changes as the side length s of each square storage unit increases. 5. Describe how the area of the enclosure changes. 6. Predict what the graph of the function will look like. Explain your reasoning. 7. Use a graphing calculator to graph the function you wrote in Question 3. Then sketch the graph and label the axes. How can you tell the graph is a quadratic function? y x 860 Chapter Introduction to Quadratic Functions
7 The shape that a quadratic function forms when graphed is called a parabola. 8. Think about the possible areas of the enclosure. Is there a maximum area that the enclosure can contain? Explain your reasoning in terms of the graph and in terms of the problem situation. You can use a graphing calculator to identify the absolute maximum of a quadratic function. Step 1: Enter the function and press GRAPH. Step 2: Press 2ND and then CALC. Select 4: maximum. Step 3: Move your cursor to any point on the curve where the graph is increasing and press ENTER. Step 4: Move your cursor to a point directly opposite the point in Step 3 on the curve where the graph is decreasing and press ENTER. Then press ENTER one more time. A graph is increasing when it is going up from left to right. It is decreasing when it is going down from left to right. 9. Use a graphing calculator to determine the absolute maximum of A(s). Then describe what the x- and y-coordinates of the absolute maximum represent in this problem situation. 10. Determine the dimensions of the enclosure that will provide the maximum area. Show your work and explain your reasoning..1 Exploring Quadratic Functions 861
8 Problem 2 Handshake Problem Suppose that there is a monthly meeting at CIA headquarters for all employees. How many handshakes will it take for every employee at the meeting to shake the hand of every other employee at the meeting once? 1. Use the figures shown to determine the number of handshakes that will occur between 2 employees, 3 employees, and 4 employees. 2 employees 3 employees 4 employees 2. Draw figures to represent the number of handshakes that occur between 5 employees, 6 employees, and 7 employees and determine the number of handshakes that will occur in each situation. 862 Chapter Introduction to Quadratic Functions
9 3. Complete the table to record your results. Number of Employees n Number of Handshakes 4. Write an expression in the table to represent the number of handshakes given any number of employees. 5. Rewrite the expression representing the handshake pattern as the quadratic function H(n) in standard form. Identify the independent and dependent quantities. Look at the relationship between the number of consecutive employees and the number of handshakes. Hint: (2 3) 2 = Graph this function on a graphing calculator. Sketch the graph on the coordinate plane and label the axes. y x Determine the absolute minimum of H(n). Then, describe what the x- and y-coordinates of this point represent in this problem situation..1 Exploring Quadratic Functions 863
10 Talk the Talk Let s compare the two functions you graphed in this lesson. Graph both functions together on a graphing calculator. Area of dog enclosure: A(s) 5 22s s Handshake Pattern: H(n) n n 1. Describe the domain in terms of the function and each problem situation. Do you remember completing the Quadratic Function Family Graphic Organizer? 2. How can you determine whether the graph of a quadratic function opens up or down based on the equation? Experiment with your graphing calculator to help you explain your reasoning. 3. How can you determine whether the graph of a quadratic function has an absolute minimum or an absolute maximum? Be prepared to share your solutions and methods. 864 Chapter Introduction to Quadratic Functions
Introduction to Quadratic Functions
 Introduction to Quadratic Functions The St. Louis Gateway Arch was constructed from 1963 to 1965. It cost 13 million dollars to build..1 Up and Down or Down and Up Exploring Quadratic Functions.................
Introduction to Quadratic Functions The St. Louis Gateway Arch was constructed from 1963 to 1965. It cost 13 million dollars to build..1 Up and Down or Down and Up Exploring Quadratic Functions.................
Unit 6 Quadratic Functions
 Unit 6 Quadratic Functions 12.1 & 12.2 Introduction to Quadratic Functions What is A Quadratic Function? How do I tell if a Function is Quadratic? From a Graph The shape of a quadratic function is called
Unit 6 Quadratic Functions 12.1 & 12.2 Introduction to Quadratic Functions What is A Quadratic Function? How do I tell if a Function is Quadratic? From a Graph The shape of a quadratic function is called
Unit 2 Day 9. FRED Functions
 Unit 2 Day 9 FRED Functions 1 1. Graph 2. Test a point (0,0) 3. Shade Warm Up You may want to try the problems on this slide by hand! Practice for the non-calculator part of the test! 2 2 1. 2. y x 2x
Unit 2 Day 9 FRED Functions 1 1. Graph 2. Test a point (0,0) 3. Shade Warm Up You may want to try the problems on this slide by hand! Practice for the non-calculator part of the test! 2 2 1. 2. y x 2x
Warm-Up Exercises. Find the x-intercept and y-intercept 1. 3x 5y = 15 ANSWER 5; y = 2x + 7 ANSWER ; 7
 Warm-Up Exercises Find the x-intercept and y-intercept 1. 3x 5y = 15 ANSWER 5; 3 2. y = 2x + 7 7 2 ANSWER ; 7 Chapter 1.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form A quadratic function is a function that
Warm-Up Exercises Find the x-intercept and y-intercept 1. 3x 5y = 15 ANSWER 5; 3 2. y = 2x + 7 7 2 ANSWER ; 7 Chapter 1.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form A quadratic function is a function that
Properties of Quadratic functions
 Name Today s Learning Goals: #1 How do we determine the axis of symmetry and vertex of a quadratic function? Properties of Quadratic functions Date 5-1 Properties of a Quadratic Function A quadratic equation
Name Today s Learning Goals: #1 How do we determine the axis of symmetry and vertex of a quadratic function? Properties of Quadratic functions Date 5-1 Properties of a Quadratic Function A quadratic equation
Quadratics Functions: Review
 Quadratics Functions: Review Name Per Review outline Quadratic function general form: Quadratic function tables and graphs (parabolas) Important places on the parabola graph [see chart below] vertex (minimum
Quadratics Functions: Review Name Per Review outline Quadratic function general form: Quadratic function tables and graphs (parabolas) Important places on the parabola graph [see chart below] vertex (minimum
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
Chapter 2. Polynomial and Rational Functions. 2.2 Quadratic Functions
 Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.2 Quadratic Functions 1 /27 Chapter 2 Homework 2.2 p298 1, 5, 17, 31, 37, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 53, 55 2 /27 Chapter 2 Objectives Recognize characteristics of
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.2 Quadratic Functions 1 /27 Chapter 2 Homework 2.2 p298 1, 5, 17, 31, 37, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 53, 55 2 /27 Chapter 2 Objectives Recognize characteristics of
Section 4.4: Parabolas
 Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
9.1 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Date: 2. Decide whether to use a solid line or dotted line:
 9.1 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Date: Key Ideas: Example Solve the inequality by graphing 3y 2x 6. steps 1. Rearrange the inequality so it s in mx ± b form. Don t forget to flip the inequality
9.1 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Date: Key Ideas: Example Solve the inequality by graphing 3y 2x 6. steps 1. Rearrange the inequality so it s in mx ± b form. Don t forget to flip the inequality
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models
 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models Objectives: 1. Identify the vertex & axis of symmetry of a quadratic function. 2. Graph a quadratic function using its vertex, axis and intercepts. 3. Use the maximum
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models Objectives: 1. Identify the vertex & axis of symmetry of a quadratic function. 2. Graph a quadratic function using its vertex, axis and intercepts. 3. Use the maximum
But a vertex has two coordinates, an x and a y coordinate. So how would you find the corresponding y-value?
 We will work with the vertex, orientation, and x- and y-intercepts of these functions. Intermediate algebra Class notes More Graphs of Quadratic Functions (section 11.6) In the previous section, we investigated
We will work with the vertex, orientation, and x- and y-intercepts of these functions. Intermediate algebra Class notes More Graphs of Quadratic Functions (section 11.6) In the previous section, we investigated
Lesson 3: Investigating the Parts of a Parabola
 Opening Exercise 1. Use the graph at the right to fill in the Answer column of the chart below. (You ll fill in the last column in Exercise 9.) Question Answer Bring in the Math! A. What is the shape of
Opening Exercise 1. Use the graph at the right to fill in the Answer column of the chart below. (You ll fill in the last column in Exercise 9.) Question Answer Bring in the Math! A. What is the shape of
A. Lesson Context. B. Lesson Objectives. C. Fast Five (Skills Review Focus)
 A. Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: How & why do we build NEW knowledge in Mathematics? What NEW IDEAS & NEW CONCEPTS can we now explore with specific references to QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS? How can
A. Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: How & why do we build NEW knowledge in Mathematics? What NEW IDEAS & NEW CONCEPTS can we now explore with specific references to QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS? How can
MAFS Algebra 1. Quadratic Functions. Day 17 - Student Packet
 MAFS Algebra 1 Quadratic Functions Day 17 - Student Packet Day 17: Quadratic Functions MAFS.912.F-IF.3.7a, MAFS.912.F-IF.3.8a I CAN graph a quadratic function using key features identify and interpret
MAFS Algebra 1 Quadratic Functions Day 17 - Student Packet Day 17: Quadratic Functions MAFS.912.F-IF.3.7a, MAFS.912.F-IF.3.8a I CAN graph a quadratic function using key features identify and interpret
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 Quadratic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic
2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 Quadratic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic
Quadratic Functions. *These are all examples of polynomial functions.
 Look at: f(x) = 4x-7 f(x) = 3 f(x) = x 2 + 4 Quadratic Functions *These are all examples of polynomial functions. Definition: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n 1,..., a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
Look at: f(x) = 4x-7 f(x) = 3 f(x) = x 2 + 4 Quadratic Functions *These are all examples of polynomial functions. Definition: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n 1,..., a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
Lesson 8 Introduction to Quadratic Functions
 Lesson 8 Introduction to Quadratic Functions We are leaving exponential and logarithmic functions behind and entering an entirely different world. As you work through this lesson, you will learn to identify
Lesson 8 Introduction to Quadratic Functions We are leaving exponential and logarithmic functions behind and entering an entirely different world. As you work through this lesson, you will learn to identify
6.4 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function
 6.4 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function Recall from 6.1 and 6.2: Standard Form The standard form of a quadratic is: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c or y = ax 2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0.
6.4 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function Recall from 6.1 and 6.2: Standard Form The standard form of a quadratic is: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c or y = ax 2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0.
Quadratic Functions CHAPTER. 1.1 Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions p. 31
 CHAPTER Quadratic Functions Arches are used to support the weight of walls and ceilings in buildings. Arches were first used in architecture by the Mesopotamians over 4000 years ago. Later, the Romans
CHAPTER Quadratic Functions Arches are used to support the weight of walls and ceilings in buildings. Arches were first used in architecture by the Mesopotamians over 4000 years ago. Later, the Romans
Quadratic Functions In Standard Form In Factored Form In Vertex Form Transforming Graphs. Math Background
 Graphing In Standard Form In Factored Form In Vertex Form Transforming Graphs Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Graphing In Standard Form In Factored Form In Vertex Form Transforming Graphs Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
More Ways to Solve & Graph Quadratics The Square Root Property If x 2 = a and a R, then x = ± a
 More Ways to Solve & Graph Quadratics The Square Root Property If x 2 = a and a R, then x = ± a Example: Solve using the square root property. a) x 2 144 = 0 b) x 2 + 144 = 0 c) (x + 1) 2 = 12 Completing
More Ways to Solve & Graph Quadratics The Square Root Property If x 2 = a and a R, then x = ± a Example: Solve using the square root property. a) x 2 144 = 0 b) x 2 + 144 = 0 c) (x + 1) 2 = 12 Completing
5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials
 Math 3201 5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials In Math 1201/2201, we examined three types of polynomial functions: Constant Function - horizontal line such as y = 2 Linear Function - sloped line,
Math 3201 5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials In Math 1201/2201, we examined three types of polynomial functions: Constant Function - horizontal line such as y = 2 Linear Function - sloped line,
Unit: Quadratic Functions
 Unit: Quadratic Functions Learning increases when you have a goal to work towards. Use this checklist as guide to track how well you are grasping the material. In the center column, rate your understand
Unit: Quadratic Functions Learning increases when you have a goal to work towards. Use this checklist as guide to track how well you are grasping the material. In the center column, rate your understand
Sketching graphs of polynomials
 Sketching graphs of polynomials We want to draw the graphs of polynomial functions y = f(x). The degree of a polynomial in one variable x is the highest power of x that remains after terms have been collected.
Sketching graphs of polynomials We want to draw the graphs of polynomial functions y = f(x). The degree of a polynomial in one variable x is the highest power of x that remains after terms have been collected.
February 8 th February 12 th. Unit 6: Polynomials & Introduction to Quadratics
 Algebra I February 8 th February 12 th Unit 6: Polynomials & Introduction to Quadratics Jump Start 1) Use the elimination method to solve the system of equations below. x + y = 2 3x + y = 8 2) Solve: 13
Algebra I February 8 th February 12 th Unit 6: Polynomials & Introduction to Quadratics Jump Start 1) Use the elimination method to solve the system of equations below. x + y = 2 3x + y = 8 2) Solve: 13
UNIT 3 EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Lesson 3: Creating Quadratic Equations in Two or More Variables
 Guided Practice Example 1 Find the y-intercept and vertex of the function f(x) = 2x 2 + x + 3. Determine whether the vertex is a minimum or maximum point on the graph. 1. Determine the y-intercept. The
Guided Practice Example 1 Find the y-intercept and vertex of the function f(x) = 2x 2 + x + 3. Determine whether the vertex is a minimum or maximum point on the graph. 1. Determine the y-intercept. The
Algebra II Chapter 4: Quadratic Functions and Factoring Part 1
 Algebra II Chapter 4: Quadratic Functions and Factoring Part 1 Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Vocabulary 1 Example 1: Graph a Function of the Form y = ax 2 Steps: 1. Make
Algebra II Chapter 4: Quadratic Functions and Factoring Part 1 Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Vocabulary 1 Example 1: Graph a Function of the Form y = ax 2 Steps: 1. Make
CHAPTER 6 Quadratic Functions
 CHAPTER 6 Quadratic Functions Math 1201: Linear Functions is the linear term 3 is the leading coefficient 4 is the constant term Math 2201: Quadratic Functions Math 3201: Cubic, Quartic, Quintic Functions
CHAPTER 6 Quadratic Functions Math 1201: Linear Functions is the linear term 3 is the leading coefficient 4 is the constant term Math 2201: Quadratic Functions Math 3201: Cubic, Quartic, Quintic Functions
UNIT 8: SOLVING AND GRAPHING QUADRATICS. 8-1 Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations. Solve each equation:
 UNIT 8: SOLVING AND GRAPHING QUADRATICS 8-1 Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations Zero Product Property For all numbers a & b Solve each equation: If: ab 0, 1. (x + 3)(x 5) = 0 Then one of these is true:
UNIT 8: SOLVING AND GRAPHING QUADRATICS 8-1 Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations Zero Product Property For all numbers a & b Solve each equation: If: ab 0, 1. (x + 3)(x 5) = 0 Then one of these is true:
10.3 vertex and max values with comparing functions 2016 ink.notebook. March 14, Vertex and Max Value & Page 101.
 10.3 vertex and max values with comparing functions 2016 ink.notebook Page 101 Page 102 10.3 Vertex and Value and Comparing Functions Algebra: Transformations of Functions Page 103 Page 104 Lesson Objectives
10.3 vertex and max values with comparing functions 2016 ink.notebook Page 101 Page 102 10.3 Vertex and Value and Comparing Functions Algebra: Transformations of Functions Page 103 Page 104 Lesson Objectives
Quadratic Functions Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory A quadratic function in the variable x is a polynomial where the highest power of x is 2. We will explore the domains, ranges, and graphs of quadratic
1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory A quadratic function in the variable x is a polynomial where the highest power of x is 2. We will explore the domains, ranges, and graphs of quadratic
8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions
 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up For each quadratic function, find the axis of symmetry and vertex, and state whether the function opens upward
8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up For each quadratic function, find the axis of symmetry and vertex, and state whether the function opens upward
Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola. Day #1
 Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
Objective. 9-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions. Graph and transform quadratic functions.
 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up For each quadratic function, find the axis of symmetry and vertex, and state whether the function opens upward or downward. 1. y = x 2 + 3 2. y = 2x 2 x
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up For each quadratic function, find the axis of symmetry and vertex, and state whether the function opens upward or downward. 1. y = x 2 + 3 2. y = 2x 2 x
Introduction to Quadratics
 Name: Date: Block: Introduction to Quadratics An quadratic function (parabola) can be expressed in two different forms. Vertex form: Standard form: a( x h) k ax bx c In this activit, ou will see how these
Name: Date: Block: Introduction to Quadratics An quadratic function (parabola) can be expressed in two different forms. Vertex form: Standard form: a( x h) k ax bx c In this activit, ou will see how these
Family of Functions Lesson
 Family of Functions Lesson Introduction: Show pictures of family members to illustrate that even though family members are different (in most cases) they have very similar characteristics (DNA). Today
Family of Functions Lesson Introduction: Show pictures of family members to illustrate that even though family members are different (in most cases) they have very similar characteristics (DNA). Today
2.2 Transformers: More Than Meets the y s
 10 SECONDARY MATH II // MODULE 2 STRUCTURES OF EXPRESSIONS 2.2 Transformers: More Than Meets the y s A Solidify Understanding Task Writetheequationforeachproblembelow.Useasecond representationtocheckyourequation.
10 SECONDARY MATH II // MODULE 2 STRUCTURES OF EXPRESSIONS 2.2 Transformers: More Than Meets the y s A Solidify Understanding Task Writetheequationforeachproblembelow.Useasecond representationtocheckyourequation.
5.3 Vertex Form of Quadratics 2017.notebook. October 20, Homework Answers:
 Homework Answers: 21. 23. 25. 27. 52. 69. 70. 71. 50. a. Vertex (315, 630) b. Domain: (0, 630) Range: (0, 630) c. 360 ft d. 630ft 1 Graph WARM UP 1) Find the vertex of the quadratic function: 2) Complete
Homework Answers: 21. 23. 25. 27. 52. 69. 70. 71. 50. a. Vertex (315, 630) b. Domain: (0, 630) Range: (0, 630) c. 360 ft d. 630ft 1 Graph WARM UP 1) Find the vertex of the quadratic function: 2) Complete
Up and Down or Down and Up
 Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Up and Down or Down and Up Eploring Quadratic Functions Vocabular Write the given quadratic function in standard form. Then describe the shape of the graph and whether
Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Up and Down or Down and Up Eploring Quadratic Functions Vocabular Write the given quadratic function in standard form. Then describe the shape of the graph and whether
Name: Chapter 7 Review: Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Name: Chapter Review: Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: = ax + bx+ c A is a function that can be written in the form = ax + bx+ c where a, b, and c are real numbers
Name: Chapter Review: Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: = ax + bx+ c A is a function that can be written in the form = ax + bx+ c where a, b, and c are real numbers
SM2H 4.3 HW- Writing Quadratic Equations
 SM2H Name: Period: SM2H 4.3 HW- Writing Quadratic Equations For each of the parabolas described below, write a quadratic equation in Vertex Form. SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. 1. Vertex: ( 0, 6 ), passes through
SM2H Name: Period: SM2H 4.3 HW- Writing Quadratic Equations For each of the parabolas described below, write a quadratic equation in Vertex Form. SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. 1. Vertex: ( 0, 6 ), passes through
4-1 (Part 2) Graphing Quadratics, Interpreting Parabolas
 4-1 (Part 2) Graphing Quadratics, Interpreting Parabolas Objectives Students will be able to: Find the vertex and y-intercept of a parabola Graph a parabola Use quadratic models to analyze problem situations.
4-1 (Part 2) Graphing Quadratics, Interpreting Parabolas Objectives Students will be able to: Find the vertex and y-intercept of a parabola Graph a parabola Use quadratic models to analyze problem situations.
3x 2 + 7x + 2. A 8-6 Factor. Step 1. Step 3 Step 4. Step 2. Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4
 A 8-6 Factor. Step 1 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 3x 2 + 7x + 2 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Factor. 1. 3x 2 + 4x +1 = 2. 3x 2 +10x + 3 = 3. 3x 2 +13x + 4 = A 8-6 Name BDFM? Why? Factor.
A 8-6 Factor. Step 1 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 3x 2 + 7x + 2 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Factor. 1. 3x 2 + 4x +1 = 2. 3x 2 +10x + 3 = 3. 3x 2 +13x + 4 = A 8-6 Name BDFM? Why? Factor.
Unit 2-2: Writing and Graphing Quadratics NOTE PACKET. 12. I can use the discriminant to determine the number and type of solutions/zeros.
 Unit 2-2: Writing and Graphing Quadratics NOTE PACKET Name: Period Learning Targets: Unit 2-1 12. I can use the discriminant to determine the number and type of solutions/zeros. 1. I can identify a function
Unit 2-2: Writing and Graphing Quadratics NOTE PACKET Name: Period Learning Targets: Unit 2-1 12. I can use the discriminant to determine the number and type of solutions/zeros. 1. I can identify a function
Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form
 Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form Imagine the path of a basketball as it leaves a player s hand and swooshes through the net. Or, imagine the path of an Olympic diver
Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form Imagine the path of a basketball as it leaves a player s hand and swooshes through the net. Or, imagine the path of an Olympic diver
3.1 Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form
 Math 2200 Date: 3.1 Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form Degree of a Function - refers to the highest exponent on the variable in an expression or equation. In Math 1201, you learned about
Math 2200 Date: 3.1 Investigating Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form Degree of a Function - refers to the highest exponent on the variable in an expression or equation. In Math 1201, you learned about
Sample: Do Not Reproduce QUAD4 STUDENT PAGES. QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS Student Pages for Packet 4: Quadratic Functions and Applications
 Name Period Date QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS Student Pages for Packet 4: Quadratic Functions and Applications QUAD 4.1 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function 1 Explore how changing the values of h and
Name Period Date QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS Student Pages for Packet 4: Quadratic Functions and Applications QUAD 4.1 Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function 1 Explore how changing the values of h and
Slide 2 / 222. Algebra II. Quadratic Functions
 Slide 1 / 222 Slide 2 / 222 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 222 Table of Contents Key Terms Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations (review)
Slide 1 / 222 Slide 2 / 222 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 222 Table of Contents Key Terms Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations (review)
2.3 Building the Perfect Square A Solidify Understanding Task
 2.3 Building the Perfect Square A Solidify Understanding Task Part 1: Quadratic Quilts 2013 www.flickr.com/photos/tweedledeedesigns Optima has a quilt shop where she sells many colorful quilt blocks for
2.3 Building the Perfect Square A Solidify Understanding Task Part 1: Quadratic Quilts 2013 www.flickr.com/photos/tweedledeedesigns Optima has a quilt shop where she sells many colorful quilt blocks for
CHAPTER 9: Quadratic Equations and Functions
 CHAPTER : Quadratic Equations and Functions Notes # -: Exploring Quadratic Graphs A. Graphing ax A is a function that can be written in the form ax bx c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. Examples:
CHAPTER : Quadratic Equations and Functions Notes # -: Exploring Quadratic Graphs A. Graphing ax A is a function that can be written in the form ax bx c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. Examples:
2.1 Quadraticsnts.notebook. September 10, 2018
 1 A quadratic function is a polynomial function of second degree. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. 2 Standard Form: Intercept Form: Vertex Form: f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k vertex: (h, k)
1 A quadratic function is a polynomial function of second degree. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. 2 Standard Form: Intercept Form: Vertex Form: f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k vertex: (h, k)
August 29, Quad2b FactoredForm Graphing.notebook
 Quadratics 2b Quadratic Function: Graphing Factored Form Standards: F IF.4 & F IF.7 GLOs: #3 Complex Thinker Math Practice: Look for and make use of structure HW: WS #9 (graph on graph paper!) Learning
Quadratics 2b Quadratic Function: Graphing Factored Form Standards: F IF.4 & F IF.7 GLOs: #3 Complex Thinker Math Practice: Look for and make use of structure HW: WS #9 (graph on graph paper!) Learning
Algebra 2 Honors Lesson 10 Translating Functions
 Algebra 2 Honors Lesson 10 Translating Functions Objectives: The students will be able to translate a base function horizontally and vertically. Students will be able to describe the translation of f(x)
Algebra 2 Honors Lesson 10 Translating Functions Objectives: The students will be able to translate a base function horizontally and vertically. Students will be able to describe the translation of f(x)
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 7: Building Functions Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying linear expressions factoring quadratic equations finding the value of a in the vertex form of a quadratic equation
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying linear expressions factoring quadratic equations finding the value of a in the vertex form of a quadratic equation
Structures of Expressions
 SECONDARY MATH TWO An Integrated Approach MODULE 2 Structures of Expressions The Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis Lemon, Janet Sutorius 2017 Original work 2013 in partnership with
SECONDARY MATH TWO An Integrated Approach MODULE 2 Structures of Expressions The Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis Lemon, Janet Sutorius 2017 Original work 2013 in partnership with
A-SSE.1.1, A-SSE.1.2-
 Putnam County Schools Curriculum Map Algebra 1 2016-2017 Module: 4 Quadratic and Exponential Functions Instructional Window: January 9-February 17 Assessment Window: February 20 March 3 MAFS Standards
Putnam County Schools Curriculum Map Algebra 1 2016-2017 Module: 4 Quadratic and Exponential Functions Instructional Window: January 9-February 17 Assessment Window: February 20 March 3 MAFS Standards
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
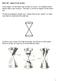 Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
12.6. The Form Is Key. Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function
 The Form Is Key Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function.6 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine key characteristics of parabolas using a graphing calculator. Determine key characteristics
The Form Is Key Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function.6 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine key characteristics of parabolas using a graphing calculator. Determine key characteristics
PR3 & PR4 CBR Activities Using EasyData for CBL/CBR Apps
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Process Page 23. PR3 & PR4 CBR Activities Using EasyData for CBL/CBR Apps The TI Exploration Series for CBR or CBL/CBR books, are all written for the old CBL/CBR Application. Now we can
Summer 2006 I2T2 Process Page 23. PR3 & PR4 CBR Activities Using EasyData for CBL/CBR Apps The TI Exploration Series for CBR or CBL/CBR books, are all written for the old CBL/CBR Application. Now we can
Y. Butterworth Lehmann & 9.2 Page 1 of 11
 Pre Chapter 9 Coverage Quadratic (2 nd Degree) Form a type of graph called a parabola Form of equation we'll be dealing with in this chapter: y = ax 2 + c Sign of a determines opens up or down "+" opens
Pre Chapter 9 Coverage Quadratic (2 nd Degree) Form a type of graph called a parabola Form of equation we'll be dealing with in this chapter: y = ax 2 + c Sign of a determines opens up or down "+" opens
Study Guide and Review
 Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
y 1 ) 2 Mathematically, we write {(x, y)/! y = 1 } is the graph of a parabola with 4c x2 focus F(0, C) and directrix with equation y = c.
 Ch. 10 Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since
Ch. 10 Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since
Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1)
 Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1) Section 2.1, Definition of Polynomial Function f(x) = a is the constant function f(x) = mx + b where m 0 is a linear function f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c with a 0 is a quadratic
Quadratic Functions (Section 2-1) Section 2.1, Definition of Polynomial Function f(x) = a is the constant function f(x) = mx + b where m 0 is a linear function f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c with a 0 is a quadratic
Algebra II Quadratic Functions and Equations - Extrema Unit 05b
 Big Idea: Quadratic Functions can be used to find the maximum or minimum that relates to real world application such as determining the maximum height of a ball thrown into the air or solving problems
Big Idea: Quadratic Functions can be used to find the maximum or minimum that relates to real world application such as determining the maximum height of a ball thrown into the air or solving problems
Solving Quadratics Algebraically Investigation
 Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math 1 Day 1: Factoring Review and Solving For Zeroes Algebraically Warm-Up: 1. Write an equivalent epression for each of the problems below: a. ( + )( + 4) b. ( 5)( + 8)
Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math 1 Day 1: Factoring Review and Solving For Zeroes Algebraically Warm-Up: 1. Write an equivalent epression for each of the problems below: a. ( + )( + 4) b. ( 5)( + 8)
Algebra II Quadratic Functions
 1 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org 2 Ta b le o f C o n te n t Key Terms click on the topic to go to that section Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations
1 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org 2 Ta b le o f C o n te n t Key Terms click on the topic to go to that section Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations
9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1
 9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1 OBJECTIVES I will be able to graph quadratics: Given in Standard Form Given in Vertex Form Given in Intercept Form What does the graph of a quadratic look like? https://www.desmos.com/calculator
9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1 OBJECTIVES I will be able to graph quadratics: Given in Standard Form Given in Vertex Form Given in Intercept Form What does the graph of a quadratic look like? https://www.desmos.com/calculator
Lesson 1: Analyzing Quadratic Functions
 UNIT QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELING Lesson 1: Analyzing Quadratic Functions Common Core State Standards F IF.7 F IF.8 Essential Questions Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features
UNIT QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELING Lesson 1: Analyzing Quadratic Functions Common Core State Standards F IF.7 F IF.8 Essential Questions Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features
Standard Form of Quadratic Functions
 Math Objectives Students will be able to predict how a specific change in the value of a will affect the shape of the graph of the quadratic ax bx c. Students will be able to predict how a specific change
Math Objectives Students will be able to predict how a specific change in the value of a will affect the shape of the graph of the quadratic ax bx c. Students will be able to predict how a specific change
Section 6.1: Quadratic Functions and their Characteristics Vertical Intercept Vertex Axis of Symmetry Domain and Range Horizontal Intercepts
 Lesson 6 Quadratic Functions and Equations Lesson 6 Quadratic Functions and Equations We are leaving exponential functions behind and entering an entirely different world. As you work through this lesson,
Lesson 6 Quadratic Functions and Equations Lesson 6 Quadratic Functions and Equations We are leaving exponential functions behind and entering an entirely different world. As you work through this lesson,
Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational Functions Power Standard #7
 Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational s Power Standard #7 2.1 Quadratic s Lets glance at the finals. Learning Objective: In this lesson you learned how to sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.
Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational s Power Standard #7 2.1 Quadratic s Lets glance at the finals. Learning Objective: In this lesson you learned how to sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.
Assignment Assignment for Lesson 14.1
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date The Origin of Parabolas Parabolas Centered at the Origin 1. Consider the parabola represented by the equation y 2 12x 0. a. Write the equation of the parabola
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date The Origin of Parabolas Parabolas Centered at the Origin 1. Consider the parabola represented by the equation y 2 12x 0. a. Write the equation of the parabola
Lesson 19. Opening Discussion
 Opening Discussion 1. Think about the forms of the quadratic equations you ve written throughout this module. We have gone from vertex form to standard form and from factored form to standard form. Draw
Opening Discussion 1. Think about the forms of the quadratic equations you ve written throughout this module. We have gone from vertex form to standard form and from factored form to standard form. Draw
) 2 + (y 2. x 1. y c x2 = y
 Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since this
Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since this
MAC Learning Objectives. Module 4. Quadratic Functions and Equations. - Quadratic Functions - Solving Quadratic Equations
 MAC 1105 Module 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Understand basic concepts about quadratic functions and their graphs. 2. Complete
MAC 1105 Module 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Understand basic concepts about quadratic functions and their graphs. 2. Complete
Quadratic Equations. Learning Objectives. Quadratic Function 2. where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0
 Quadratic Equations Learning Objectives 1. Graph a quadratic function using transformations. Identify the vertex and axis of symmetry of a quadratic function 3. Graph a quadratic function using its vertex,
Quadratic Equations Learning Objectives 1. Graph a quadratic function using transformations. Identify the vertex and axis of symmetry of a quadratic function 3. Graph a quadratic function using its vertex,
1 Vertical and Horizontal
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Vertical and Horizontal Transformations CHAPTER 1 Vertical and Horizontal Transformations Here you will learn about graphing more complex types of functions easily by applying horizontal
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Vertical and Horizontal Transformations CHAPTER 1 Vertical and Horizontal Transformations Here you will learn about graphing more complex types of functions easily by applying horizontal
Unit 2 Day 5. Characteristics of Quadratic Functions
 Unit 2 Day 5 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions 1 Warm Up 1.) Jason and Jim jumped off a cliff into the ocean in Acapulco while vacationing. Jason s height as a function of time could be modeled by
Unit 2 Day 5 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions 1 Warm Up 1.) Jason and Jim jumped off a cliff into the ocean in Acapulco while vacationing. Jason s height as a function of time could be modeled by
Section 2.1 Graphs. The Coordinate Plane
 Section 2.1 Graphs The Coordinate Plane Just as points on a line can be identified with real numbers to form the coordinate line, points in a plane can be identified with ordered pairs of numbers to form
Section 2.1 Graphs The Coordinate Plane Just as points on a line can be identified with real numbers to form the coordinate line, points in a plane can be identified with ordered pairs of numbers to form
Parabolas have a, a middle point. For. In this example, the equation of the axis of symmetry is
 5.1/5.A Investigating Quadratic Functions in Standard Form: y = a(x ± h) ± k y x Graph y x using a table of values x -3 - -1 0 1 3 Graph Shape: the graph shape is called a and occurs when the equation
5.1/5.A Investigating Quadratic Functions in Standard Form: y = a(x ± h) ± k y x Graph y x using a table of values x -3 - -1 0 1 3 Graph Shape: the graph shape is called a and occurs when the equation
 Specific Objectives Students will understand that that the family of equation corresponds with the shape of the graph. Students will be able to create a graph of an equation by plotting points. In lesson
Specific Objectives Students will understand that that the family of equation corresponds with the shape of the graph. Students will be able to create a graph of an equation by plotting points. In lesson
GSE Algebra 1 Name Date Block. Unit 3b Remediation Ticket
 Unit 3b Remediation Ticket Question: Which function increases faster, f(x) or g(x)? f(x) = 5x + 8; two points from g(x): (-2, 4) and (3, 10) Answer: In order to compare the rate of change (roc), you must
Unit 3b Remediation Ticket Question: Which function increases faster, f(x) or g(x)? f(x) = 5x + 8; two points from g(x): (-2, 4) and (3, 10) Answer: In order to compare the rate of change (roc), you must
Unit 1 Quadratic Functions
 Unit 1 Quadratic Functions This unit extends the study of quadratic functions to include in-depth analysis of general quadratic functions in both the standard form f ( x) = ax + bx + c and in the vertex
Unit 1 Quadratic Functions This unit extends the study of quadratic functions to include in-depth analysis of general quadratic functions in both the standard form f ( x) = ax + bx + c and in the vertex
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS. PROTOTYPE: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c. (1) The leading coefficient a 0 is called the shape parameter.
 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS PROTOTYPE: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c. (1) The leading coefficient a 0 is called the shape parameter. SHAPE-VERTEX FORMULA One can write any quadratic function (1) as f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k,
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS PROTOTYPE: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c. (1) The leading coefficient a 0 is called the shape parameter. SHAPE-VERTEX FORMULA One can write any quadratic function (1) as f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k,
Finding the Maximum or Minimum of a Quadratic Function. f(x) = x 2 + 4x + 2.
 Section 5.6 Optimization 529 5.6 Optimization In this section we will explore the science of optimization. Suppose that you are trying to find a pair of numbers with a fixed sum so that the product of
Section 5.6 Optimization 529 5.6 Optimization In this section we will explore the science of optimization. Suppose that you are trying to find a pair of numbers with a fixed sum so that the product of
Writing Equivalent Forms of Quadratic Functions Adapted from Walch Education
 Writing Equivalent Forms of Quadratic Functions Adapted from Walch Education Recall The standard form, or general form, of a quadratic function is written as f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c, where a is the coefficient
Writing Equivalent Forms of Quadratic Functions Adapted from Walch Education Recall The standard form, or general form, of a quadratic function is written as f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c, where a is the coefficient
Lesson 5: Investigating Quadratic Functions in the Standard Form, ff(xx) = aaxx 2 + bbxx + cc
 : Investigating Quadratic Functions in the Standard Form, ff(xx) = aaxx 22 + bbxx + cc Opening Exercise 1. Marshall had the equation y = (x 2) 2 + 4 and knew that he could easily find the vertex. Sarah
: Investigating Quadratic Functions in the Standard Form, ff(xx) = aaxx 22 + bbxx + cc Opening Exercise 1. Marshall had the equation y = (x 2) 2 + 4 and knew that he could easily find the vertex. Sarah
+ bx + c = 0, you can solve for x by using The Quadratic Formula. x
 Math 33B Intermediate Algebra Fall 01 Name Study Guide for Exam 4 The exam will be on Friday, November 9 th. You are allowed to use one 3" by 5" index card on the exam as well as a scientific calculator.
Math 33B Intermediate Algebra Fall 01 Name Study Guide for Exam 4 The exam will be on Friday, November 9 th. You are allowed to use one 3" by 5" index card on the exam as well as a scientific calculator.
WK # Given: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
 Alg2H Chapter 5 Review 1. Given: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c Date or y = ax2 + bx + c Related Formulas: y-intercept: ( 0, ) Equation of Axis of Symmetry: x = Vertex: (x,y) = (, ) Discriminant = x-intercepts: When
Alg2H Chapter 5 Review 1. Given: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c Date or y = ax2 + bx + c Related Formulas: y-intercept: ( 0, ) Equation of Axis of Symmetry: x = Vertex: (x,y) = (, ) Discriminant = x-intercepts: When
1.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions (p. 2) Definitions Standard form of quad. function Steps for graphing Minimums and maximums
 1.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions (p. 2) Definitions Standard form of quad. function Steps for graphing Minimums and maximums Quadratic Function A function of the form y=ax 2 +bx+c where a 0 making a u-shaped
1.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions (p. 2) Definitions Standard form of quad. function Steps for graphing Minimums and maximums Quadratic Function A function of the form y=ax 2 +bx+c where a 0 making a u-shaped
Lesson 3.1 Vertices and Intercepts. Important Features of Parabolas
 Lesson 3.1 Vertices and Intercepts Name: _ Learning Objective: Students will be able to identify the vertex and intercepts of a parabola from its equation. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.IF.C.7.A Graph linear and
Lesson 3.1 Vertices and Intercepts Name: _ Learning Objective: Students will be able to identify the vertex and intercepts of a parabola from its equation. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSF.IF.C.7.A Graph linear and
1.1 Functions. Cartesian Coordinate System
 1.1 Functions This section deals with the topic of functions, one of the most important topics in all of mathematics. Let s discuss the idea of the Cartesian coordinate system first. Cartesian Coordinate
1.1 Functions This section deals with the topic of functions, one of the most important topics in all of mathematics. Let s discuss the idea of the Cartesian coordinate system first. Cartesian Coordinate
Amplifying an Instructional Task Algebra II Example
 Original Task The student is expected to write the equation of a parabola using given attributes, including vertex, focus, directrix, axis of symmetry, and direction of opening. A(4)(B) Write the equations
Original Task The student is expected to write the equation of a parabola using given attributes, including vertex, focus, directrix, axis of symmetry, and direction of opening. A(4)(B) Write the equations
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 1: Interpreting Structure in Expressions Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: translating verbal expressions to algebraic expressions evaluating expressions following the order of operations adding and subtracting
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: translating verbal expressions to algebraic expressions evaluating expressions following the order of operations adding and subtracting
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions
 Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions Section 6.1 Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions Section 6.1 Exploring Quadratic Relations Terminology: Quadratic Relations: A relation that can be written in the standard form
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions Section 6.1 Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions Section 6.1 Exploring Quadratic Relations Terminology: Quadratic Relations: A relation that can be written in the standard form
2-9 Operations with Complex Numbers
 2-9 Operations with Complex Numbers Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Express each number in terms of i. 1. 9i 2. Find each complex conjugate. 3. 4. Find each product. 5. 6. Objective
2-9 Operations with Complex Numbers Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Express each number in terms of i. 1. 9i 2. Find each complex conjugate. 3. 4. Find each product. 5. 6. Objective
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
 Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
It s Not Complex Just Its Solutions Are Complex!
 It s Not Comple Just Its Solutions Are Comple! Solving Quadratics with Comple Solutions 15.5 Learning Goals In this lesson, ou will: Calculate comple roots of quadratic equations and comple zeros of quadratic
It s Not Comple Just Its Solutions Are Comple! Solving Quadratics with Comple Solutions 15.5 Learning Goals In this lesson, ou will: Calculate comple roots of quadratic equations and comple zeros of quadratic
Transformations with Quadratic Functions KEY
 Algebra Unit: 05 Lesson: 0 TRY THIS! Use a calculator to generate a table of values for the function y = ( x 3) + 4 y = ( x 3) x + y 4 Next, simplify the function by squaring, distributing, and collecting
Algebra Unit: 05 Lesson: 0 TRY THIS! Use a calculator to generate a table of values for the function y = ( x 3) + 4 y = ( x 3) x + y 4 Next, simplify the function by squaring, distributing, and collecting
