End mills are widely used in industry for high-speed machining. End milling cutters are C H A P T E R 2
|
|
|
- Albert Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C H A P T E R End Mill End mills are widely used in industry for high-speed mahining. End milling utters are multi-point milling utters with utting edges both on the fae end as well as on the periphery, and may be single or double end onstrution [33, 58, ]. The teeth of the utter may be straight (parallel to the axis of rotation or helial (at a helix angle. The utter may be righthand (to turn lokwise or left-hand (to turn ounter lokwise. The end mills have a straight or tapered shank for mounting and driving. End mills ombine the abilities of end utting, peripheral utting and fae milling into one tool. End mills an be used on vertial and horizontal milling mahines for a variety of faing, slotting, and profiling operations. End mills an be lassified based upon: (i Configuration of end profile - Flat, Chamfer, Radius, Ball, Taper, Bull Nose end mills and their ombinations.
2 Chapter. End Mill 5 (ii Shank type Srewed parallel shank, Plain shank, Weldon shank, Taper shank, Whistle noth parallel shank and Combination shank. (iii Mounting type - Cylindrial, Cylindrial threaded, Cylindrial power huk, Weldon and Weldon threaded. Geometry of utting flutes and surfaes of end mills is one of the ruial parameters affeting the quality of the mahining in the ase of end milling. In the present work, the results of the generi definitions of flat end mills proposed by Tandon et al. [8] have been further developed, validated and applied for finite element analysis. Here, a generi flat end mill is modeled as it an be generalized to other types of end mills with omplex shapes. A mathematial model of the geometry of a flat end mill is formulated in terms of its surfae pathes using the onept of surfae modeling. The model is generated keeping in mind that it is to be used for diret analysis, prototyping, manufaturing and grinding of the utters. The orientation of the surfae pathes is defined in a right hand oordinate frame of referene by three-dimensional angles, termed as rotational angles. The flutes of the flat end mill are modeled by sweeping the setional profile of the utter along the perpendiular diretion. Mapping relations are developed between the proposed three-dimensional nomenlature and traditional two-dimensional (D projeted geometry based nomenlatures. The output in the form of graphial model of the flat end mill is shown in OpenGL [50-5] for verifiation of the methodology. Besides, an interfae is also developed to diretly pull the detailed mathematial / parametri definition of the end mill in a ommerial CAD pakage for further validation (in the form of a solid model. This exat solid model is analyzed for stati and transient dynami load onditions. Also, the advantages offered by the detailed CAD model over an approximated CAD model are shown.. Surfae Modeling of Flat End Mill The geometry of a flat end mill projeted on two-dimensional orthographi planes with its tehnial features is shown in Figure.(a and the setional view of its flute is shown in Figure.(b. L and L are the lengths of the fluted shank and the end mill respetively. D and D s are the utter diameter and shank diameter of the end mill respetively. For an end mill,,,, and R are axial relief angle, end utting edge angle, radial relief angle, A e R R radial learane angle and radial rake angle respetively and are shown in Figure.. The geometry of an end mill an be divided into three groups, namely
3 Chapter. End Mill 6 Geometry of fluted shank. End surfae geometry. Shank geometry. The fluted shank geometry onsists of irumferential surfae pathes formed by helial sweeping a profile of a setion of the fluted shank. The sweep operation is a ombined rotational and parallel sweep, perpendiular to the axis of the utter. The end geometry is dependent on the onfiguration of the flat end profile. A single tooth of a flat end mill may be modeled with the help of nine surfae pathes, labeled to 9 as shown in Figure.. They are Rake fae (, Peripheral land, Rake fae extension ( ( 9. Shank geometry of the utter may be a straight shank or tapered shank with surfae pathes modeled as axisymmetri surfae of revolution along with a flat end surfae. (a (b Figure.: (a Two-Dimensional Projeted Geometry of a Flat End Mill (b Setional View of End Mill Flutes
4 Chapter. End Mill 7.. Modeling of Fluted Surfae Geometry of End Mill Surfaes to 6 are the surfae pathes on the fluted shank. These surfaes are formed when a omposite urve in XY plane is swept with a sweeping rule, omposed of ombined rotational and parallel sweep, known as helioidal surfaes. Figure.3 shows the omposite setional urve V..., onsisting of six segments. Out of these six, three segments V V, ( V7 V V 3 and V 6V7 orrespond to the three land widths, namely peripheral land, heel and fae, and are shown as straight lines on a two-dimensional projeted plane. The other three segments V 3V 4, V 4V5 and V 5V6 are irular ars of radii r 3,r and R respetively, orresponding to fillet, bak of tooth and blending surfae. The surfae pathes ould better be visualized from the unfolded view of an end mill tooth (Figure. (a. The tip geometry of the flat end mill is shown in Figure. (b. In modeling the ross-setional profile of fluted shank in a two-dimensional plane, the input parameters are (i widths of lands i.e. fae, peripheral land and heel or seondary land given by l,l and l 3 respetively, (ii 3D angles obtained to form fae (, land ( and heel ( 3 about Z axis, (iii radii of fillet (R, bak of tooth ( r and blending surfae ( r 3, (iv diameter of utting end of the end mill ( D and (v number of flutes (N. The position Figure. (a: Unfolded View of an End Mill Tooth Figure. (b: Tip Geometry of a Flat End Mill
5 Chapter. End Mill 8 vetors of the end verties of different setions of the omposite profile urve V... and ( V7 enter points of the three irular ars,, are evaluated [8] to parametrially model the profile urve. ( 3 The ross-setional profile of a fluted setion of an end mill onsists of three parametri linear edges and three parametri irular ars, namely, p ( to p (. Edges p s, p ( and p ( are straight, while p s, p ( and p ( are irular in two-dimensional ( s 6 s ( 3 4 s 5 s s 6 s spae. The generi definition of the setional profile p (s in XY plane in terms of parameter s may be represented by, p s f ( s f ( 0. i( i i s The fluted surfae is obtained by ombined rotational and parallel sweeping and is parametrially desribed by, p( s, p( s. T s i, where transformation matrix is os sin 0 0 sin os 0 0 L Ts for 0. P P 0 0 In the above equation, L is the length of fluted shank for flat end mills, be the parameter denoting the angular movement and P.is the pith of the end mill. Figure.3: Composite Setional Curve of an End Mill Flute
6 Chapter. End Mill 9 Sweeping rules The fluted setion of an end mill an have right helix or left helix. If the flute's spiral has a lokwise ontour when looked along the utter axis from either end, then it is a right helix else the helix is left [30, 33]. For a right helix utter, the ross-setion urve rotates by an angle + about the axis in right hand sense. Three different sweeping rules an be formulated for the fluted shank and the end profile of the utter. These rules are for (i Cylindrial Helial Path (ii Conial Helial Path (iii Hemispherial Helial Path Cylindrial Helial Path - The path when the omposite profile urve is swept helially along a ylinder is known as ylindrial helial path. For a helial utter let be the parameter denoting the angular movement, P the pith of the helix, D the ylindrial utter diameter and L the length of the fluted part of utter, then the mathematial definition of the helix is, x ( D y ( D / os / sin z ( P /(, where 0 (L / P (. Conial Helial Path - The helial path along a frustum of one of utting end diameter D C and shank side diameter D S x ( D / os y ( D / sin z ( P /(, is defined by, where D D ( D s D z / L and 0 (L / P. (. This is valid for both types of frustum of ones i.e. when D Ds and when Ds D. Hemispherial Helial Path - The helial path along the hemispherial objet of diameter is given as, x ( D / os os y ( D / os sin z ( D / ( sin, where 0 D / P and 0 /. D (.3
7 Chapter. End Mill 30 Here, is the angle about Z axis and is the angle with XY plane and the relation between them is, sin P.. D.. Modeling of End Surfae Geometry The end surfae geometry of a flat end mill onsists of three planes and one blending surfae (Figure.. (a Fae Land ( 7 (b Minor Flank ( 8 and ( Rake Fae Extension ( 9 are the three planes whereas the blending surfae, 9 blends surfae path 8 of the first tooth with surfae path 9 Fae land ( 7 of the seond tooth of the end mill. is formed when an XY plane given by 0 u is transformed 7 v 7 through rotation by a 3D rotational angle 7 about X axis R x, ], followed by rotation by an angle about Z axis R ] and is defined as, [ z, [ 7 p u, v ( u os v os sin ( u sin v os os v sin (.4 7( [ 8 Minor Flank ( 8 is formed when the XY plane is rotated by an angle 8 about X axis R x, ], followed by an angle about Z axis R z, ], and then translated by a distane d8 l os along Y axis and 83 l os sin 7 [ d along Z diretion T ] and is given as, [ yz p u, v ( u os vos sin ( u sin v os os d ( v sin (.5 8( d83 an angle 9 Rake Fae Extension ( 9 is formed when a ZX plane (u 9 0 w9 is rotated by about X axis R x, ] and by an angle about Z axis R z, ]. Here, helix angle [ 9 [ * * tan ( P/ DC, 90 and (5 5 but 90. The surfae 9 satisfies the relation, 9 p u, w ( u os w sin sin ( u sin w sin os ( w os (.6 9(
8 Chapter. End Mill 3..3 Modeling of Shank Surfae Geometry The shank surfae of a flat end mill may be modeled as a ombination of two surfae pathes (a ylindrial surfae of revolution 50 (for straight and tapered shank and (b planar end surfae 5(as shown in Figure.4. The ylindrial surfae of shank in terms of parameter w, may be parametrially defined by, D' D' p 50( w, os sin { L w( L L } (.7 for 0, 0 w. The term L stands for overall length of end mill and diameter D' may be given by, modeled as, Ds ( D /, / w( D s D /, for straight shank for tapered shank The planar end surfae forming the end opposite to utting end is parametrially p u, v u v (.8 5( L for u, v. A unit width, 45 hamfer between shank surfae pathes 50 and 5 is the only blending surfae on the shank body of the utter. The hamfer 50, 5 is modeled by revolving the edge having end point oordinates as (( D s / 0.707, 0, L and ( D /, 0, ( L s about Z axis and is given by, ( Ds Ds 50,5 u, { 0.707( u}os { 0.707( u}sin ( L 0.707u (.9 for 0 u and 0.
9 Chapter. End Mill 3. Mapping Relations In this work, relations to map the proposed 3D rotational angles, used to define the geometry of the flat end mills, into onventional D projeted angles and vie versa are developed. The former is alled forward mapping while the latter is known as inverse mapping [8]. The onventional angles are formed by projeting the surfae pathes of the end mill on planes of projetion and the traditional geometry of end mill an be referred in the literature [30, 33, 49, 65, 69]. Table. shows the forward mapping relations for a flat end mill. The solution of these forward mapping relations establishes inverse mapping that helps to evaluate the 3D rotational angles if tool angles speified by onventional nomenlatures are known. Table. presents the inverse mapping for an end mill. Figure.4: Modeling of Shank Table.: Forward Mapping Relations for Flat End Mill Conventional D Angles Radial Rake Angle, R Radial Relief Angle, R Radial Clearane Angle, R 3 Axial Relief Angle, A End Cutting Edge Angle, e Rotational 3D Angles os os os 7 os sin 7 os 7 os 7 sin sin 7 os 7
10 Chapter. End Mill 33 Table.: Inverse Mapping Relations for Flat End Mill Rotational Angles 3 7 Conventional Angles R R R os os A.os e os A os e os A.os e.3 Modeling Algorithm Based on the above proposed generi definition, the parameters needed to ompletely desribe a four-flute helial flat end mill and the relevant data for these parameters to exemplify the methodology are shown in Table.3(a and.3(b. The algorithm that geometrially models a fluted helial end mill based on the proposed three-dimensional nomenlature (3D rotational angles and other dimensional parameters is as follows: Step : The omposite setional urve of the flute in two-dimensional Cartesian oordinate plane, with enter of the flat end mill's ross setion oiniding with global origin is generated as desribed in Setion... Step : The solid flute is generated by ombined rotational and parallel sweeping of omposite setional urve as illustrated in Setion... Step 3: The end geometry of flat end mill is formed through Boolean operations on the surfae pathes and the blending surfaes as mentioned in Setion... Step 4: The Shank is generated by applying Boolean operation on surfae pathes 50 and, and blending surfae as mentioned in Setion ( 50, 5 Step 5: The detailed and omplete CAD model of the end mill is generated. The details of the implementation depend on the speifi CAD environment, where they are implemented, and are disussed in Setion.4.
11 Chapter. End Mill 34 Table.3(a: Geometri Parameters (Dimensional and Input Data for an End Mill Dimensional Parameters Number of flutes (N 4 Values Cutter diameter ( D C 5.0 mm Length of utter ( L 3.0 mm Length of flutes ( L 7.0 mm Root diameter ( D R.0 mm Shank side diameter ( D S 5.0 mm Pith (P mm Width of primary land ( l.0 mm Width of heel ( l mm Width of rake fae ( l 7.0 mm Fillet Radius (R.0 mm Radius of bak of tooth ( r 5.0 mm Radius of blending surfae ( r 3.0 mm Table.3(b: Geometri Parameters (Angular and Input Data for an End Mill Rotational Angles Value (degrees Helix angle ( Implementation of Algorithm The algorithm has been implemented in OpenGL environment [5], a general purpose graphial modeling kernel, as well as in a ommerial CAD environment (here, CATIA V5 [3, 6]. The rendering of the end mill utter (input data as in Table.3(a and.3(b by using the 3D parameters proposed in the work, diretly in OpenGL and CATIA V5, validates the modeling methodology.
12 Chapter. End Mill Implementation in OpenGL Environment OpenGL is an Appliation Programming Interfae (API. It is graphial software that uses boundary representations to desribe models. To diretly render the helial flat end mill using 3D geometri parameters as proposed in this work, a tool design program is developed in C programming language. All geometri primitives are defined in terms of verties. The 3D geometri parameters were supplied as input in a text file. The program developed in C easily all funtions in the API for rendering. The libraries like GLU, GLX, GLUT, Open Inventor, et, simplify our programming tasks for rendering the utter in OpenGL [63]. The output is the rendered image of the flat end mill in OpenGL graphial environment as shown in Figure.5(a. OpenGL file formats are used for rendering purpose only. It is diffiult to aurately export the rendered image of OpenGL file format to a ommerial CAD/CAE/CAM environment for any meaningful tehnologial appliation..4. Implementation in Commerial CAD Environment To fully utilize the aurate and omprehensive parametri definition of the utter, there is a need to pull this model in a ommerial modeling pakage so as to take advantages of the tools of the modeler for further proessing. An interfae is developed here to diretly generate the model in a solid modeling environment (CATIA V5 using the omprehensive definition of the utter. This leads to a wide range of downstream appliations. Figure.5: Rendering of an End Mill in (a OpenGL environment and (b CATIA V5
13 Chapter. End Mill 36 CATIA V5 is a ommerial solid modeler that allows users to reate 3D models in a Graphial User Interfae (GUI. Solid models an also be reated using Visual Basi funtion alls through an appliation programming interfae (API [8, 6]. A Visual Basi, C++ program is developed here that uses this API to generate the model of the helial flat end mill based on the user defined 3D geometri parameters diretly in CATIA. The model is not reated using the GUI of the software but uses the parametri definitions of the surfaes developed, as desribed in Setion.. The users an hange the geometri parameters of the end mill in a ustom developed user interfae and based on the hosen parameters, the end mill model is diretly generated in CATIA modeling environment (as shown in Figure.5(b. Using the GUI, if one has to reate another model for a different set of parameters, one has to rebuild the model, may be, from srath. With the parametri definitions and the interfae developed here, the user an reate a set of models by simply hanging the input values. It is possible to save the geometri model of the end mill in a variety of file formats, inluding CAT PART, IGES, and STL. The CATIA implementation gives more ontrol to the user beause the end mill is modeled diretly in a modeling environment where further modifiations and embellishments an be easily done..5 Appliation of Helial Flat End Mill Models Numerous tehnologial down stream appliations may be performed on the geometri models of the helial flat end mill utters developed by the above defined tehnique. One suh tehnologial appliation is finite element based engineering analysis (FEA of the end mill. This setion presents an exerise on FEA on the 3D model of the helial end mill. This exerise highlights the advantages and utilities available, one a omprehensive 3D definition of the utter is available. The purpose here is not to present any detailed analysis of the end mill during mahining. The end mills are generated in CATIA as desribed in Setion.4. and exported to Generative Strutural Analysis module in CATIA Analysis and Simulation pakage for Strutural Stati and Transient Dynami Analysis. For the auray of simulation, the utting fore data taken in the work are based on results of the utting tests onduted by Li et al. [7]. For our simulation, we have hosen the utter material and the utting onditions as follows:
14 Chapter. End Mill 37 Cutter: A four-fluted M4 High Speed Steel with a helix angle = 30 and other geometri parameters as mentioned in Table.3. Material properties of the High Speed Steel utter [68]: It is Molybdenum based high speed steel with Weight % of C =.05-.5, Mn = , Si = , Cr = , Ni = 0.3, Mo = , W =.5-.85, V = , Co = , Cu = 0.5, P = 0.03, S = It is an isotropi material with Young s modulus =. e+n/m, Poisson s ratio = 0.3, density = 7980 kg/m 3, thermal expansion =.33 e- 005 K and tensile strength = 970N/mm. Work piee: Plain arbon steel whih has a hemial omposition of approximately 0.5% C, 0.5% Mn, 0.5% Si. Cutting Parameters: Axial depth of ut mm, spindle speed 600 rpm, feedrate 40 mm/min i.e. the feed per tooth per revolution = 0. mm. The end mill is meshed using paraboli tetrahedral elements. The tetrahedral element is a ten node iso-parametri solid element having 3 (translational degrees of freedom. It has a quadrati displaement behavior and is well suited to model irregular meshes. Quadrati tetrahedral (QT element is preferred for the development of smooth automati mesh FE model for the geometry of omplex solid models like femur, fluted utters, et. [04, 47]. For automati mesh generation, meshes omprising entirely of tetrahedral elements (or alltetrahedral mesh are frequently generated as opposed to a mesh omprising of purely hexahedral elements (or all-hexahedral mesh. This is beause a physial domain, as in the ase of geometrially omplex strutures, annot always be deomposed into an assembly of hexahedral elements. It an however be easily represented as a olletion of tetrahedral elements, as these elements are geometrially more versatile [4]. Infat, performing FEA using QT mesh models is effiient in terms of both auray and CPU time [8, 47]. Also, QT finite element models are more stable and less influened to the degree of refinement of the mesh, when modeling omplex solids [04]. The element also has plastiity, reep, swelling, stress stiffening, large defletion, and large strain apabilities. The meshing information of the end mill is presented in Table.4. Figure.6 shows the finite element mesh of the end mill utter. The next step is to restrain the end mill model by lamping the shank of the tool followed by load appliation.
15 Chapter. End Mill 38 For our simulation, load has been applied on a single flute in radial, tangential and axial diretions for an axial depth of mm. Figure.7 shows the oordinate system and the utting fore diretion on the flute of the end mill utter. The simulated and measured utting fores in the time domain of two revolutions of utter rotation as worked out by Li et al. [7] is shown in Figure.8. Using the utting fores mentioned in Figure.8, the fores ating in radial, tangential and axial diretions on the end mill flute an be alulated from the angle domain onvolution integral theory mentioned by Zheng et al. [6]. Table.4: Meshing Information of an End Mill Cutter Parameters Values Global mesh size 7 mm Loal mesh size mm Jaobian 0.3 Nodes 489 Elements 764 Warp 60 Absolute sag 0.3 mm Proportional sag 0. mm Figure.6: Meshing of an End Mill Cutter Figure.7: Coordinate Systems of the End Mill Cutter
16 Chapter. End Mill Strutural Stati Analysis For stati analysis at any partiular instantaneous time or utter angle rotation (, fores are onsidered on a single flute in radial, tangential and axial diretions for an axial depth of mm. For 3, the applied fores in radial, tangential and axial diretions are F 57.5N, F 38.77N and F 49.77N. Figures.9 -. shows the result for stati r t a analysis with Von mises stress, deformed mesh and translational displaement respetively for the applied load. Here, maximum equivalent stress reahed is 47. MPa and maximum total displaement is 0.0mm..5. Strutural Transient Dynami Analysis For transient dynami analysis, only time fator has been onsidered. Vibrations and other dynami fators are not inluded in this work. The transient dynami analysis is arried out for a total time domain of 0.05 se (for utter angle rotation of 90, with a time interval of se. Table.5 shows the fores ating on the flute for a time profile of se. Figures.,.3 and.4 shows the result for transient dynami analysis with Von mises stress, deformed mesh and translational displaement respetively for the applied load. For the dynami ase, the result shown is maximum equivalent stress of 978 MPa and maximum total displaement of mm at time 0.05 se. Table.5: Fores Ating on a Partiular Flute of a Helial End Mill θ Time (se F t (N F r (N F a (N
17 Chapter. End Mill 40 Figure.9: Von Mises Stress for Stati Load Condition Figure.0: Deformed Mesh for Stati Load Condition Figure.8: Simulated and Measured Cutting Fores for Up Milling, with axial depth of Cut = mm. (a Fore in X Diretion, (b Fore in Y Diretion, ( Fore in Z Diretion [7] Figure.: Translational Displaement for Stati Load Condition
18 Chapter. End Mill 4 Figure.: Von Mises Stress for Transient Dynami Load Condition at 54 Figure.3: Deformed Mesh for Transient Dynami Load Condition at 54 Figure.4: Translational Displaement for Transient Dynami Load Condition at 54 Figure.5: Deformed Mesh of approximated CAD Model at 36.6 Results and Disussions This Setion highlights the advantages offered by the detailed CAD model over an approximated CAD model. Figure.5 shows an approximated CAD model with one of its flute, analyzed for finite element simulation under the load onditions at utter angle rotation ( of 36 (same as for exat CAD model. Using the analytial utting fore model and stress relationships for end milling operations, desribed by Chiou et al. [5] and Armarego et
19 Chapter. End Mill 4 al. [5], the shear stresses are alulated at one of the utting flutes under the load onditions. Table.6 presents the values of shear stresses alulated analytially as well as that obtained by performing finite element simulation on the same flute using approximated CAD model and detailed CAD model. The analytial values of the shear stress are ompared with the finite element simulation results of the two types of CAD models at 3 and 36. The differene in the values of the shear stresses between the analytial and two finite element omputations is tabulated in the form of error analysis in Table.6. The error analysis proves that the results of the FEA simulation on the detailed CAD model are loser to the analytial data than the results of approximated CAD model. It has also been observed while performing the finite element analysis using the approximate CAD model that the stress values sharply overshoots at some points on the utter flute as shown at the tip of utting edge (Table.6. This may be due to the fat that approximate CAD model approximates the geometry at ertain loations. It is evident that the detailed CAD model is onsistently in better agreement with the analytially alulated data rather than the approximated model and an lead to aurate design and fabriation of the utters. Table.6(a: Comparative Results of Finite Element Simulation at 3 3 At tip of the utting edge, Global Maxima At flank of the side utting edge, Loal Maxima & Analytial Shear Stress (MPa Approximated CAD Model Error (% Von Mises Stress (MPa Translational Displaement (mm Von Mises Stress (MPa Detailed CAD Model Error (% Translational Displaemen t (mm
20 Chapter. End Mill 43 Table.6(b: Comparative Results of Finite Element Simulation at At tip of the utting edge, Global Maxima At flank of the side utting edge, Loal Maxima & Analytial Shear Stress (MPa Approximated CAD Model Von Error Translational Mises (% Displaement Stress (mm (MPa Von Mises Stress (MPa Detailed CAD Model Error (% Translational Displaement (mm Chapter Summary Traditionally, the geometry of utting tools has been defined using the priniples of projeted geometry (D nomenlature approah. This hapter desribes in detail the methodology to model the geometry of a flat end mill in terms of three-dimensional parameters. The proposed model defines the end mill in terms of three-dimensional rotational angles rather than the onventional two dimensional angles. The model is validated while rendering the utter diretly in OpenGL environment in terms of three dimensional parameters. Further, an interfae is developed that diretly pulls the proposed three-dimensional model defined with the help of parametri equations into a ommerial CAD modeling environment (here CATIA V5. Besides, the modeled tool is used for finite element simulations to study the utting flutes under stati and transient dynami load onditions. The results show that the methodology offers a simple and intuitive way of generating aurate surfae models for use in mahining proess simulations.
CUTTING FORCES AND CONSECUTIVE DEFORMATIONS AT MILLING PARTS WITH THIN WALLS
 Proeedings of the International Conferene on Manufaturing Systems ICMaS Vol. 4, 2009, ISSN 1842-3183 University POLITEHNICA of Buharest, Mahine and Manufaturing Systems Department Buharest, Romania CUTTING
Proeedings of the International Conferene on Manufaturing Systems ICMaS Vol. 4, 2009, ISSN 1842-3183 University POLITEHNICA of Buharest, Mahine and Manufaturing Systems Department Buharest, Romania CUTTING
Cracked Hole Finite Element Modeling
 Craked Hole Finite Element Modeling (E-20-F72) Researh Report Submitted to: Lokheed Martin, Program Manager: Dr. Stephen P. Engelstad Prinipal Investigator: Dr. Rami M. Haj-Ali Shool of Civil and Environmental
Craked Hole Finite Element Modeling (E-20-F72) Researh Report Submitted to: Lokheed Martin, Program Manager: Dr. Stephen P. Engelstad Prinipal Investigator: Dr. Rami M. Haj-Ali Shool of Civil and Environmental
CHAPTER 4 INCREASING SPUR GEAR TOOTH STRENGTH BY PROFILE MODIFICATION
 68 CHAPTER 4 INCREASING SPUR GEAR TOOTH STRENGTH BY PROFILE MODIFICATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION There is a demand for the gears with higher load carrying capacity and increased fatigue life. Researchers in the
68 CHAPTER 4 INCREASING SPUR GEAR TOOTH STRENGTH BY PROFILE MODIFICATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION There is a demand for the gears with higher load carrying capacity and increased fatigue life. Researchers in the
BENDING STIFFNESS AND DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A ROTOR WITH SPLINE JOINTS
 Proeedings of ASME 0 International Mehanial Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE0 November 5-, 0, San Diego, CA IMECE0-6657 BENDING STIFFNESS AND DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A ROTOR WITH SPLINE JOINTS
Proeedings of ASME 0 International Mehanial Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE0 November 5-, 0, San Diego, CA IMECE0-6657 BENDING STIFFNESS AND DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A ROTOR WITH SPLINE JOINTS
Smooth Trajectory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Velocity Constraints
 Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
1. Introduction. 2. The Probable Stope Algorithm
 1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physics
 The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physis Zhiliang Cao, Henry Cao williamao15000@yahoo.om, henry.gu.ao@gmail.om July 18, 010 Abstrat In the enter of the unierse, there isn t a super massie blak hole or any speifi
The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physis Zhiliang Cao, Henry Cao williamao15000@yahoo.om, henry.gu.ao@gmail.om July 18, 010 Abstrat In the enter of the unierse, there isn t a super massie blak hole or any speifi
Orientation of the coordinate system
 Orientation of the oordinate system Right-handed oordinate system: -axis by a positive, around the -axis. The -axis is mapped to the i.e., antilokwise, rotation of The -axis is mapped to the -axis by a
Orientation of the oordinate system Right-handed oordinate system: -axis by a positive, around the -axis. The -axis is mapped to the i.e., antilokwise, rotation of The -axis is mapped to the -axis by a
Algorithms, Mechanisms and Procedures for the Computer-aided Project Generation System
 Algorithms, Mehanisms and Proedures for the Computer-aided Projet Generation System Anton O. Butko 1*, Aleksandr P. Briukhovetskii 2, Dmitry E. Grigoriev 2# and Konstantin S. Kalashnikov 3 1 Department
Algorithms, Mehanisms and Proedures for the Computer-aided Projet Generation System Anton O. Butko 1*, Aleksandr P. Briukhovetskii 2, Dmitry E. Grigoriev 2# and Konstantin S. Kalashnikov 3 1 Department
arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017](/thumbs/96/126543346.jpg) An effiient lustering algorithm from the measure of loal Gaussian distribution Yuan-Yen Tai (Dated: May 27, 2018) In this paper, I will introdue a fast and novel lustering algorithm based on Gaussian distribution
An effiient lustering algorithm from the measure of loal Gaussian distribution Yuan-Yen Tai (Dated: May 27, 2018) In this paper, I will introdue a fast and novel lustering algorithm based on Gaussian distribution
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
We P9 16 Eigenray Tracing in 3D Heterogeneous Media
 We P9 Eigenray Traing in 3D Heterogeneous Media Z. Koren* (Emerson), I. Ravve (Emerson) Summary Conventional two-point ray traing in a general 3D heterogeneous medium is normally performed by a shooting
We P9 Eigenray Traing in 3D Heterogeneous Media Z. Koren* (Emerson), I. Ravve (Emerson) Summary Conventional two-point ray traing in a general 3D heterogeneous medium is normally performed by a shooting
HIGHER ORDER full-wave three-dimensional (3-D) large-domain techniques in
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 21, no. 2, August 2008, 209-220 Comparison of Higher Order FEM and MoM/SIE Approahes in Analyses of Closed- and Open-Region Eletromagneti Problems Milan
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 21, no. 2, August 2008, 209-220 Comparison of Higher Order FEM and MoM/SIE Approahes in Analyses of Closed- and Open-Region Eletromagneti Problems Milan
Comparative Analysis of two Types of Leg-observation-based Visual Servoing Approaches for the Control of a Five-bar Mechanism
 Proeedings of Australasian Conferene on Robotis and Automation, 2-4 De 2014, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia Comparative Analysis of two Types of Leg-observation-based Visual Servoing
Proeedings of Australasian Conferene on Robotis and Automation, 2-4 De 2014, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia Comparative Analysis of two Types of Leg-observation-based Visual Servoing
Automated Drill Design Software
 Automated Drill Design Software Athulan Vijayaraghavan March 19, 2006 Abstract This section of the report discusses a tool which can create automated 3D CAD drill models based on geometric as well as manufacturing
Automated Drill Design Software Athulan Vijayaraghavan March 19, 2006 Abstract This section of the report discusses a tool which can create automated 3D CAD drill models based on geometric as well as manufacturing
Optimization of Two-Stage Cylindrical Gear Reducer with Adaptive Boundary Constraints
 5 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE VOL. 8 NO. 8 AUGUST Optimization of Two-Stage Cylindrial Gear Reduer with Adaptive Boundary Constraints Xueyi Li College of Mehanial and Eletroni Engineering Shandong University of
5 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE VOL. 8 NO. 8 AUGUST Optimization of Two-Stage Cylindrial Gear Reduer with Adaptive Boundary Constraints Xueyi Li College of Mehanial and Eletroni Engineering Shandong University of
Simulation of Crystallographic Texture and Anisotropie of Polycrystals during Metal Forming with Respect to Scaling Aspects
 Raabe, Roters, Wang Simulation of Crystallographi Texture and Anisotropie of Polyrystals during Metal Forming with Respet to Saling Aspets D. Raabe, F. Roters, Y. Wang Max-Plank-Institut für Eisenforshung,
Raabe, Roters, Wang Simulation of Crystallographi Texture and Anisotropie of Polyrystals during Metal Forming with Respet to Saling Aspets D. Raabe, F. Roters, Y. Wang Max-Plank-Institut für Eisenforshung,
Outline: Software Design
 Outline: Software Design. Goals History of software design ideas Design priniples Design methods Life belt or leg iron? (Budgen) Copyright Nany Leveson, Sept. 1999 A Little History... At first, struggling
Outline: Software Design. Goals History of software design ideas Design priniples Design methods Life belt or leg iron? (Budgen) Copyright Nany Leveson, Sept. 1999 A Little History... At first, struggling
Torpedo Trajectory Visual Simulation Based on Nonlinear Backstepping Control
 orpedo rajetory Visual Simulation Based on Nonlinear Bakstepping Control Peng Hai-jun 1, Li Hui-zhou Chen Ye 1, 1. Depart. of Weaponry Eng, Naval Univ. of Engineering, Wuhan 400, China. Depart. of Aeronautial
orpedo rajetory Visual Simulation Based on Nonlinear Bakstepping Control Peng Hai-jun 1, Li Hui-zhou Chen Ye 1, 1. Depart. of Weaponry Eng, Naval Univ. of Engineering, Wuhan 400, China. Depart. of Aeronautial
1. Inversions. A geometric construction relating points O, A and B looks as follows.
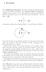 1. Inversions. 1.1. Definitions of inversion. Inversion is a kind of symmetry about a irle. It is defined as follows. he inversion of degree R 2 entered at a point maps a point to the point on the ray
1. Inversions. 1.1. Definitions of inversion. Inversion is a kind of symmetry about a irle. It is defined as follows. he inversion of degree R 2 entered at a point maps a point to the point on the ray
Extracting Partition Statistics from Semistructured Data
 Extrating Partition Statistis from Semistrutured Data John N. Wilson Rihard Gourlay Robert Japp Mathias Neumüller Department of Computer and Information Sienes University of Strathlyde, Glasgow, UK {jnw,rsg,rpj,mathias}@is.strath.a.uk
Extrating Partition Statistis from Semistrutured Data John N. Wilson Rihard Gourlay Robert Japp Mathias Neumüller Department of Computer and Information Sienes University of Strathlyde, Glasgow, UK {jnw,rsg,rpj,mathias}@is.strath.a.uk
NONLINEAR BACK PROJECTION FOR TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION. Ken Sauer and Charles A. Bouman
 NONLINEAR BACK PROJECTION FOR TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION Ken Sauer and Charles A. Bouman Department of Eletrial Engineering, University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556, (219) 631-6999 Shool of
NONLINEAR BACK PROJECTION FOR TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION Ken Sauer and Charles A. Bouman Department of Eletrial Engineering, University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556, (219) 631-6999 Shool of
the data. Structured Principal Component Analysis (SPCA)
 Strutured Prinipal Component Analysis Kristin M. Branson and Sameer Agarwal Department of Computer Siene and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9193-114 Abstrat Many tasks involving
Strutured Prinipal Component Analysis Kristin M. Branson and Sameer Agarwal Department of Computer Siene and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9193-114 Abstrat Many tasks involving
with respect to the normal in each medium, respectively. The question is: How are θ
 Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
OFF-LINE ROBOT VISION SYSTEM PROGRAMMING USING A COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN SYSTEM S. SRIDARAN. Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the
 OFF-LINE ROBOT VISION SYSTEM PROGRAMMING USING A COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN SYSTEM by S. SRIDARAN Thesis submitted to the Faulty of the Virginia Polytehni Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
OFF-LINE ROBOT VISION SYSTEM PROGRAMMING USING A COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN SYSTEM by S. SRIDARAN Thesis submitted to the Faulty of the Virginia Polytehni Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Chemical, Biological and Radiological Hazard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a Complex Urban Environment
 hemial, Biologial and Radiologial Haard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a omplex Urban Environment Skvortsov, A.T., P.D. Dawson, M.D. Roberts and R.M. Gailis HPP Division, Defene Siene and Tehnology
hemial, Biologial and Radiologial Haard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a omplex Urban Environment Skvortsov, A.T., P.D. Dawson, M.D. Roberts and R.M. Gailis HPP Division, Defene Siene and Tehnology
特集 Road Border Recognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Processing
 デンソーテクニカルレビュー Vol. 15 2010 特集 Road Border Reognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Proessing 高木聖和 バーゼル ファルディ Kiyokazu TAKAGI Basel Fardi ヘンドリック ヴァイゲル Hendrik Weigel ゲルド ヴァニーリック Gerd Wanielik This paper
デンソーテクニカルレビュー Vol. 15 2010 特集 Road Border Reognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Proessing 高木聖和 バーゼル ファルディ Kiyokazu TAKAGI Basel Fardi ヘンドリック ヴァイゲル Hendrik Weigel ゲルド ヴァニーリック Gerd Wanielik This paper
Gray Codes for Reflectable Languages
 Gray Codes for Refletable Languages Yue Li Joe Sawada Marh 8, 2008 Abstrat We lassify a type of language alled a refletable language. We then develop a generi algorithm that an be used to list all strings
Gray Codes for Refletable Languages Yue Li Joe Sawada Marh 8, 2008 Abstrat We lassify a type of language alled a refletable language. We then develop a generi algorithm that an be used to list all strings
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes
 CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
Contributions to the cinematic and dynamic study of parallel mechanism robots with four degrees of freedom
 Equation Chapter Setion Forgó Zoltán, eng. hd. andidate Contributions to the inemati and dynami study of parallel mehanism robots with four degrees of freedom Abstrat of hd hesis Sientifi oordinator: Niolae
Equation Chapter Setion Forgó Zoltán, eng. hd. andidate Contributions to the inemati and dynami study of parallel mehanism robots with four degrees of freedom Abstrat of hd hesis Sientifi oordinator: Niolae
Plot-to-track correlation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surface Movement Radar
 Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Projections. Let us start with projections in 2D, because there are easier to visualize.
 Projetions Let us start ith projetions in D, beause there are easier to visualie. Projetion parallel to the -ais: Ever point in the -plane ith oordinates (, ) ill be transformed into the point ith oordinates
Projetions Let us start ith projetions in D, beause there are easier to visualie. Projetion parallel to the -ais: Ever point in the -plane ith oordinates (, ) ill be transformed into the point ith oordinates
Chapter 2: Introduction to Maple V
 Chapter 2: Introdution to Maple V 2-1 Working with Maple Worksheets Try It! (p. 15) Start a Maple session with an empty worksheet. The name of the worksheet should be Untitled (1). Use one of the standard
Chapter 2: Introdution to Maple V 2-1 Working with Maple Worksheets Try It! (p. 15) Start a Maple session with an empty worksheet. The name of the worksheet should be Untitled (1). Use one of the standard
Review (Law of sines and cosine) cosines)
 Date:03/7,8/01 Review 6.1-6. Objetive: Apply the onept to use the law of the sines and osines to solve oblique triangles Apply the onept to find areas using the law of sines and osines Agenda: Bell ringer
Date:03/7,8/01 Review 6.1-6. Objetive: Apply the onept to use the law of the sines and osines to solve oblique triangles Apply the onept to find areas using the law of sines and osines Agenda: Bell ringer
arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015](/thumbs/92/109500704.jpg) REAL-TIME TOOL FOR AFFINE TRANSFORMATIONS OF TWO DIMENSIONAL IFS FRACTALS ELENA HADZIEVA AND MARIJA SHUMINOSKA arxiv:1504.02744v1 s.gr 10 Apr 2015 Abstrat. This work introdues a novel tool for interative,
REAL-TIME TOOL FOR AFFINE TRANSFORMATIONS OF TWO DIMENSIONAL IFS FRACTALS ELENA HADZIEVA AND MARIJA SHUMINOSKA arxiv:1504.02744v1 s.gr 10 Apr 2015 Abstrat. This work introdues a novel tool for interative,
What are Cycle-Stealing Systems Good For? A Detailed Performance Model Case Study
 What are Cyle-Stealing Systems Good For? A Detailed Performane Model Case Study Wayne Kelly and Jiro Sumitomo Queensland University of Tehnology, Australia {w.kelly, j.sumitomo}@qut.edu.au Abstrat The
What are Cyle-Stealing Systems Good For? A Detailed Performane Model Case Study Wayne Kelly and Jiro Sumitomo Queensland University of Tehnology, Australia {w.kelly, j.sumitomo}@qut.edu.au Abstrat The
End-effector pose estimation of the Monash Epicyclic-Parallel Manipulator through the visual observation of its legs
 End-effetor pose estimation of the Monash Epiyli-Parallel Manipulator through the visual observation of its legs Alessia Vignolo,Sébastien Briot, Philippe Martinet,, Chao Chen 3 Abstrat Past researh works
End-effetor pose estimation of the Monash Epiyli-Parallel Manipulator through the visual observation of its legs Alessia Vignolo,Sébastien Briot, Philippe Martinet,, Chao Chen 3 Abstrat Past researh works
Detection and Recognition of Non-Occluded Objects using Signature Map
 6th WSEAS International Conferene on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS,CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Cairo, Egypt, De 9-31, 007 65 Detetion and Reognition of Non-Oluded Objets using Signature Map Sangbum Park,
6th WSEAS International Conferene on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS,CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Cairo, Egypt, De 9-31, 007 65 Detetion and Reognition of Non-Oluded Objets using Signature Map Sangbum Park,
Algorithms for External Memory Lecture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking
 Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
Multi-Piece Mold Design Based on Linear Mixed-Integer Program Toward Guaranteed Optimality
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MANUFACTURING AUTOMATION (ICMA200) Multi-Piee Mold Design Based on Linear Mixed-Integer Program Toward Guaranteed Optimality Stephen Stoyan, Yong Chen* Epstein Department of
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MANUFACTURING AUTOMATION (ICMA200) Multi-Piee Mold Design Based on Linear Mixed-Integer Program Toward Guaranteed Optimality Stephen Stoyan, Yong Chen* Epstein Department of
Drawing lines. Naïve line drawing algorithm. drawpixel(x, round(y)); double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx; double y = y0;
 Naïve line drawing algorithm // Connet to grid points(x0,y0) and // (x1,y1) by a line. void drawline(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1) { int x; double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx;
Naïve line drawing algorithm // Connet to grid points(x0,y0) and // (x1,y1) by a line. void drawline(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1) { int x; double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx;
Adaptive Implicit Surface Polygonization using Marching Triangles
 Volume 20 (2001), Number 2 pp. 67 80 Adaptive Impliit Surfae Polygonization using Marhing Triangles Samir Akkouhe Eri Galin L.I.G.I.M L.I.G.I.M Eole Centrale de Lyon Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 B.P.
Volume 20 (2001), Number 2 pp. 67 80 Adaptive Impliit Surfae Polygonization using Marhing Triangles Samir Akkouhe Eri Galin L.I.G.I.M L.I.G.I.M Eole Centrale de Lyon Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 B.P.
MPhys Final Year Project Dissertation by Andrew Jackson
 Development of software for the omputation of the properties of eletrostati eletro-optial devies via both the diret ray traing and paraxial approximation tehniques. MPhys Final Year Projet Dissertation
Development of software for the omputation of the properties of eletrostati eletro-optial devies via both the diret ray traing and paraxial approximation tehniques. MPhys Final Year Projet Dissertation
Triangles. Learning Objectives. Pre-Activity
 Setion 3.2 Pre-tivity Preparation Triangles Geena needs to make sure that the dek she is building is perfetly square to the brae holding the dek in plae. How an she use geometry to ensure that the boards
Setion 3.2 Pre-tivity Preparation Triangles Geena needs to make sure that the dek she is building is perfetly square to the brae holding the dek in plae. How an she use geometry to ensure that the boards
Abstract. We describe a parametric hybrid Bezier patch that, in addition. schemes are local in that changes to part of the data only aect portions of
 A Parametri Hyrid Triangular Bezier Path Stephen Mann and Matthew Davidhuk Astrat. We desrie a parametri hyrid Bezier path that, in addition to lending interior ontrol points, lends oundary ontrol points.
A Parametri Hyrid Triangular Bezier Path Stephen Mann and Matthew Davidhuk Astrat. We desrie a parametri hyrid Bezier path that, in addition to lending interior ontrol points, lends oundary ontrol points.
Defect Detection and Classification in Ceramic Plates Using Machine Vision and Naïve Bayes Classifier for Computer Aided Manufacturing
 Defet Detetion and Classifiation in Cerami Plates Using Mahine Vision and Naïve Bayes Classifier for Computer Aided Manufaturing 1 Harpreet Singh, 2 Kulwinderpal Singh, 1 Researh Student, 2 Assistant Professor,
Defet Detetion and Classifiation in Cerami Plates Using Mahine Vision and Naïve Bayes Classifier for Computer Aided Manufaturing 1 Harpreet Singh, 2 Kulwinderpal Singh, 1 Researh Student, 2 Assistant Professor,
IJMH - International Journal of Management and Humanities ISSN:
 EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
EXPERIMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS SPUR GEAR USING ANSYS SOFTWARE T.VADIVELU 1 (Department of Mechanical Engineering, JNTU KAKINADA, Kodad, India, vadimay28@gmail.com) Abstract Spur Gear is one of the most important
Design, Optimization and Finite Element Analysis of Crankshaft
 ISSN Design, Optimization and Finite Element Analysis of Crankshaft # Bhalerao Ganesh Nandkumar, # Prof. Zope Sanjay Bhaskar bhaleraoganesh35@gmail.om P. G. Student, Mehanial (Design Engineering), Prinipal
ISSN Design, Optimization and Finite Element Analysis of Crankshaft # Bhalerao Ganesh Nandkumar, # Prof. Zope Sanjay Bhaskar bhaleraoganesh35@gmail.om P. G. Student, Mehanial (Design Engineering), Prinipal
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 6
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
Measurement of the stereoscopic rangefinder beam angular velocity using the digital image processing method
 Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
Empirical Modeling of Cutting Forces in Ball End Milling using Experimental Design
 5 th International & 26 th All India Manufacturing Technology, Design and Research Conference (AIMTDR 2014) December 12 th 14 th, 2014, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India Empirical Modeling of Cutting Forces in
5 th International & 26 th All India Manufacturing Technology, Design and Research Conference (AIMTDR 2014) December 12 th 14 th, 2014, IIT Guwahati, Assam, India Empirical Modeling of Cutting Forces in
A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR
 Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
Computer Life (CPL) ISSN: Finite Element Analysis of Bearing Box on SolidWorks
 Computer Life (CPL) ISSN: 1819-4818 Delivering Quality Science to the World Finite Element Analysis of Bearing Box on SolidWorks Chenling Zheng 1, a, Hang Li 1, b and Jianyong Li 1, c 1 Shandong University
Computer Life (CPL) ISSN: 1819-4818 Delivering Quality Science to the World Finite Element Analysis of Bearing Box on SolidWorks Chenling Zheng 1, a, Hang Li 1, b and Jianyong Li 1, c 1 Shandong University
A radiometric analysis of projected sinusoidal illumination for opaque surfaces
 University of Virginia tehnial report CS-21-7 aompanying A Coaxial Optial Sanner for Synhronous Aquisition of 3D Geometry and Surfae Refletane A radiometri analysis of projeted sinusoidal illumination
University of Virginia tehnial report CS-21-7 aompanying A Coaxial Optial Sanner for Synhronous Aquisition of 3D Geometry and Surfae Refletane A radiometri analysis of projeted sinusoidal illumination
3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE
 3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
Unsupervised Stereoscopic Video Object Segmentation Based on Active Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks
 Unsupervised Stereosopi Video Objet Segmentation Based on Ative Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks KLIMIS NTALIANIS, ANASTASIOS DOULAMIS, and NIKOLAOS DOULAMIS National Tehnial University of Athens
Unsupervised Stereosopi Video Objet Segmentation Based on Ative Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks KLIMIS NTALIANIS, ANASTASIOS DOULAMIS, and NIKOLAOS DOULAMIS National Tehnial University of Athens
System-Level Parallelism and Throughput Optimization in Designing Reconfigurable Computing Applications
 System-Level Parallelism and hroughput Optimization in Designing Reonfigurable Computing Appliations Esam El-Araby 1, Mohamed aher 1, Kris Gaj 2, arek El-Ghazawi 1, David Caliga 3, and Nikitas Alexandridis
System-Level Parallelism and hroughput Optimization in Designing Reonfigurable Computing Appliations Esam El-Araby 1, Mohamed aher 1, Kris Gaj 2, arek El-Ghazawi 1, David Caliga 3, and Nikitas Alexandridis
RANGE DOPPLER ALGORITHM FOR BISTATIC SAR PROCESSING BASED ON THE IMPROVED LOFFELD S BISTATIC FORMULA
 Progress In Eletromagnetis Researh Letters, Vol. 27, 161 169, 2011 RANGE DOPPLER ALGORITHM FOR ISTATIC SAR PROCESSING ASED ON THE IMPROVED LOFFELD S ISTATIC FORMULA X. Wang 1, * and D. Y. Zhu 2 1 Nanjing
Progress In Eletromagnetis Researh Letters, Vol. 27, 161 169, 2011 RANGE DOPPLER ALGORITHM FOR ISTATIC SAR PROCESSING ASED ON THE IMPROVED LOFFELD S ISTATIC FORMULA X. Wang 1, * and D. Y. Zhu 2 1 Nanjing
Particle Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffraction Efficient Holographic Grating
 Original Artile Partile Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffration Effiient Holographi Grating A.K. Tripathy 1, S.K. Das, M. Sundaray 3 and S.K. Tripathy* 4 1, Department of Computer Siene, Berhampur
Original Artile Partile Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffration Effiient Holographi Grating A.K. Tripathy 1, S.K. Das, M. Sundaray 3 and S.K. Tripathy* 4 1, Department of Computer Siene, Berhampur
Learning Convention Propagation in BeerAdvocate Reviews from a etwork Perspective. Abstract
 CS 9 Projet Final Report: Learning Convention Propagation in BeerAdvoate Reviews from a etwork Perspetive Abstrat We look at the way onventions propagate between reviews on the BeerAdvoate dataset, and
CS 9 Projet Final Report: Learning Convention Propagation in BeerAdvoate Reviews from a etwork Perspetive Abstrat We look at the way onventions propagate between reviews on the BeerAdvoate dataset, and
Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis
 Journal of Computer Siene 4 (): 9-97, 008 ISSN 549-3636 008 Siene Publiations Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis Deepti Gaur, Aditya Shastri and Ranjit Biswas Department of Computer
Journal of Computer Siene 4 (): 9-97, 008 ISSN 549-3636 008 Siene Publiations Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis Deepti Gaur, Aditya Shastri and Ranjit Biswas Department of Computer
Parametric Modeling Program of Fillet End Mill
 Parametric Modeling Program of Fillet End Mill Jiapu Zhu A Thesis In the Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Master
Parametric Modeling Program of Fillet End Mill Jiapu Zhu A Thesis In the Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Master
2: Static analysis of a plate
 2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
TLP 350CV Setup Guide
 TLP 350V Setup Guide The Extron TouhLink 3.5 inh able ubby TLP 350V provide users with aess to AV onnetivity using onvenient pullout ables. It also provides simple and versatile onfiguration and ontrol
TLP 350V Setup Guide The Extron TouhLink 3.5 inh able ubby TLP 350V provide users with aess to AV onnetivity using onvenient pullout ables. It also provides simple and versatile onfiguration and ontrol
An Approach to Physics Based Surrogate Model Development for Application with IDPSA
 An Approah to Physis Based Surrogate Model Development for Appliation with IDPSA Ignas Mikus a*, Kaspar Kööp a, Marti Jeltsov a, Yuri Vorobyev b, Walter Villanueva a, and Pavel Kudinov a a Royal Institute
An Approah to Physis Based Surrogate Model Development for Appliation with IDPSA Ignas Mikus a*, Kaspar Kööp a, Marti Jeltsov a, Yuri Vorobyev b, Walter Villanueva a, and Pavel Kudinov a a Royal Institute
Numerical simulation of hemolysis: a comparison of Lagrangian and Eulerian modelling
 Modelling in Mediine and Biology VI 361 Numerial simulation of hemolysis: a omparison of Lagrangian and Eulerian modelling S. Pirker 1, H. Shima 2 & M. Stoiber 2 1 Johannes Kepler University, 4040 Linz,
Modelling in Mediine and Biology VI 361 Numerial simulation of hemolysis: a omparison of Lagrangian and Eulerian modelling S. Pirker 1, H. Shima 2 & M. Stoiber 2 1 Johannes Kepler University, 4040 Linz,
Abstract A method for the extrusion of arbitrary polygon meshes is introduced. This method can be applied to model a large class of complex 3-D
 Abstrat A method for the extrusion of arbitrary polygon meshes is introdued. This method an be applied to model a large lass of omplex 3-D losed surfaes. It onsists of defining a (typially small) set of
Abstrat A method for the extrusion of arbitrary polygon meshes is introdued. This method an be applied to model a large lass of omplex 3-D losed surfaes. It onsists of defining a (typially small) set of
Analysis and verification of multi-rotors attitude control algorithms in. Pixhawk. Fangzhen Lin 1, a
 6th International Conferene on Advaned Design and Manufaturing Engineering (ICADME 2016) Analysis and verifiation of multi-rotors attitude ontrol algorithms in Pixhawk Fangzhen Lin 1, a 1 Beihang University,
6th International Conferene on Advaned Design and Manufaturing Engineering (ICADME 2016) Analysis and verifiation of multi-rotors attitude ontrol algorithms in Pixhawk Fangzhen Lin 1, a 1 Beihang University,
Pipelined Multipliers for Reconfigurable Hardware
 Pipelined Multipliers for Reonfigurable Hardware Mithell J. Myjak and José G. Delgado-Frias Shool of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene, Washington State University Pullman, WA 99164-2752 USA {mmyjak,
Pipelined Multipliers for Reonfigurable Hardware Mithell J. Myjak and José G. Delgado-Frias Shool of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene, Washington State University Pullman, WA 99164-2752 USA {mmyjak,
PERSISTENT NAMING FOR PARAMETRIC MODELS
 PERSISTENT NAMING FOR PARAMETRIC MODELS Dago AGBODAN, David MARCHEIX and Guy PIERRA Laboratory of Applied Computer Siene (LISI) National Shool of Engineers in Mehanis and Aeronautis (ENSMA) Téléport 2
PERSISTENT NAMING FOR PARAMETRIC MODELS Dago AGBODAN, David MARCHEIX and Guy PIERRA Laboratory of Applied Computer Siene (LISI) National Shool of Engineers in Mehanis and Aeronautis (ENSMA) Téléport 2
Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work
 Week beginning 6 th 13 th 20 th HALF TERM 27th Topis for revision Fators, multiples and primes Indies Frations, Perentages, Deimals Rounding 6 th Marh Ratio Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work Understand
Week beginning 6 th 13 th 20 th HALF TERM 27th Topis for revision Fators, multiples and primes Indies Frations, Perentages, Deimals Rounding 6 th Marh Ratio Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work Understand
3D Ideal Flow For Non-Lifting Bodies
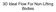 3D Ideal Flow For Non-Lifting Bodies 3D Doublet Panel Method 1. Cover body with 3D onstant strength doublet panels of unknown strength (N panels) 2. Plae a ontrol point at the enter of eah panel (N ontrol
3D Ideal Flow For Non-Lifting Bodies 3D Doublet Panel Method 1. Cover body with 3D onstant strength doublet panels of unknown strength (N panels) 2. Plae a ontrol point at the enter of eah panel (N ontrol
Calculation of typical running time of a branch-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-cover problem
 Calulation of typial running time of a branh-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-over problem Joni Pajarinen, Joni.Pajarinen@iki.fi Otober 21, 2007 1 Introdution The vertex-over problem is one of a olletion
Calulation of typial running time of a branh-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-over problem Joni Pajarinen, Joni.Pajarinen@iki.fi Otober 21, 2007 1 Introdution The vertex-over problem is one of a olletion
Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example
 14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
Trajectory Tracking Control for A Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Fuzzy Logic Controller
 Trajetory Traking Control for A Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Fuzzy Logi Controller K N FARESS 1 M T EL HAGRY 1 A A EL KOSY 2 1 Eletronis researh institute, Cairo, Egypt 2 Faulty of Engineering, Cairo University,
Trajetory Traking Control for A Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Fuzzy Logi Controller K N FARESS 1 M T EL HAGRY 1 A A EL KOSY 2 1 Eletronis researh institute, Cairo, Egypt 2 Faulty of Engineering, Cairo University,
Graph-Based vs Depth-Based Data Representation for Multiview Images
 Graph-Based vs Depth-Based Data Representation for Multiview Images Thomas Maugey, Antonio Ortega, Pasal Frossard Signal Proessing Laboratory (LTS), Eole Polytehnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Email:
Graph-Based vs Depth-Based Data Representation for Multiview Images Thomas Maugey, Antonio Ortega, Pasal Frossard Signal Proessing Laboratory (LTS), Eole Polytehnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Email:
An Event Display for ATLAS H8 Pixel Test Beam Data
 An Event Display for ATLAS H8 Pixel Test Beam Data George Gollin Centre de Physique des Partiules de Marseille and University of Illinois April 17, 1999 g-gollin@uiu.edu An event display program is now
An Event Display for ATLAS H8 Pixel Test Beam Data George Gollin Centre de Physique des Partiules de Marseille and University of Illinois April 17, 1999 g-gollin@uiu.edu An event display program is now
Time-dependent adjoint-based aerodynamic shape optimization applied to helicopter rotors
 ime-dependent adjoint-based aerodynami shape optimization applied to heliopter rotors Asitav Mishra Karthik Mani Dimitri Mavriplis Jay Sitaraman Department of Mehanial Engineering,University of Wyoming,
ime-dependent adjoint-based aerodynami shape optimization applied to heliopter rotors Asitav Mishra Karthik Mani Dimitri Mavriplis Jay Sitaraman Department of Mehanial Engineering,University of Wyoming,
EXODUS II: A Finite Element Data Model
 SAND92-2137 Unlimited Release Printed November 1995 Distribution Category UC-705 EXODUS II: A Finite Element Data Model Larry A. Shoof, Vitor R. Yarberry Computational Mehanis and Visualization Department
SAND92-2137 Unlimited Release Printed November 1995 Distribution Category UC-705 EXODUS II: A Finite Element Data Model Larry A. Shoof, Vitor R. Yarberry Computational Mehanis and Visualization Department
THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Haval Kamal Asker Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Duhok University, Duhok,
THREE DIMENSIONAL DYNAMIC STRESS ANALYSES FOR A GEAR TEETH USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Haval Kamal Asker Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Duhok University, Duhok,
Effect of Change of Spur Gear Tooth Parameter On Contact stress
 Effect of Change of Spur Gear Tooth Parameter On Contact stress Nikhil B. Abattini 1, M. M. Mirza 2, P. V. Pawar 3 1 Dept. of Mech. Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Sakharale, Islampur,
Effect of Change of Spur Gear Tooth Parameter On Contact stress Nikhil B. Abattini 1, M. M. Mirza 2, P. V. Pawar 3 1 Dept. of Mech. Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Sakharale, Islampur,
The Minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance Approach to Building Sparse Support Vector Machines
 The Minimum Redundany Maximum Relevane Approah to Building Sparse Support Vetor Mahines Xiaoxing Yang, Ke Tang, and Xin Yao, Nature Inspired Computation and Appliations Laboratory (NICAL), Shool of Computer
The Minimum Redundany Maximum Relevane Approah to Building Sparse Support Vetor Mahines Xiaoxing Yang, Ke Tang, and Xin Yao, Nature Inspired Computation and Appliations Laboratory (NICAL), Shool of Computer
Enhancing Productivity of a Roller Stand through Design Optimization using Manufacturing Simulation
 Enhancing Productivity of a Roller Stand through Design Optimization using Manufacturing Simulation B.R. Krishna Tej 1, N.Sasank Sai 1 and S.Deepak kumar* 1 Engineering Design and Research Center (EDRC)
Enhancing Productivity of a Roller Stand through Design Optimization using Manufacturing Simulation B.R. Krishna Tej 1, N.Sasank Sai 1 and S.Deepak kumar* 1 Engineering Design and Research Center (EDRC)
Face and Facial Feature Tracking for Natural Human-Computer Interface
 Fae and Faial Feature Traking for Natural Human-Computer Interfae Vladimir Vezhnevets Graphis & Media Laboratory, Dept. of Applied Mathematis and Computer Siene of Mosow State University Mosow, Russia
Fae and Faial Feature Traking for Natural Human-Computer Interfae Vladimir Vezhnevets Graphis & Media Laboratory, Dept. of Applied Mathematis and Computer Siene of Mosow State University Mosow, Russia
Lecture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperbolic Plane
 Applied Mathematis, 04, 5, 6-5 Published Online August 04 in SiRes http://wwwsirporg/journal/am http://dxdoiorg/0436/am04555 Leture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperboli Plane Rania B M Amer Department
Applied Mathematis, 04, 5, 6-5 Published Online August 04 in SiRes http://wwwsirporg/journal/am http://dxdoiorg/0436/am04555 Leture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperboli Plane Rania B M Amer Department
Modeling of Wire Electrochemical Machining
 A publiation of 91 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 41, 214 Guest Editors: Simonetta Palmas, Mihele Masia, Annalisa Vaa Copyright 214, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-32-7; ISSN 2283-9216
A publiation of 91 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 41, 214 Guest Editors: Simonetta Palmas, Mihele Masia, Annalisa Vaa Copyright 214, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-32-7; ISSN 2283-9216
A Unified Subdivision Scheme for Polygonal Modeling
 EUROGRAPHICS 2 / A. Chalmers and T.-M. Rhyne (Guest Editors) Volume 2 (2), Number 3 A Unified Subdivision Sheme for Polygonal Modeling Jérôme Maillot Jos Stam Alias Wavefront Alias Wavefront 2 King St.
EUROGRAPHICS 2 / A. Chalmers and T.-M. Rhyne (Guest Editors) Volume 2 (2), Number 3 A Unified Subdivision Sheme for Polygonal Modeling Jérôme Maillot Jos Stam Alias Wavefront Alias Wavefront 2 King St.
Automated System for the Study of Environmental Loads Applied to Production Risers Dustin M. Brandt 1, Celso K. Morooka 2, Ivan R.
 EngOpt 2008 - International Conferene on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 June 2008. Automated System for the Study of Environmental Loads Applied to Prodution Risers Dustin M. Brandt
EngOpt 2008 - International Conferene on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 June 2008. Automated System for the Study of Environmental Loads Applied to Prodution Risers Dustin M. Brandt
FUZZY WATERSHED FOR IMAGE SEGMENTATION
 FUZZY WATERSHED FOR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Ramón Moreno, Manuel Graña Computational Intelligene Group, Universidad del País Vaso, Spain http://www.ehu.es/winto; {ramon.moreno,manuel.grana}@ehu.es Abstrat The
FUZZY WATERSHED FOR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Ramón Moreno, Manuel Graña Computational Intelligene Group, Universidad del País Vaso, Spain http://www.ehu.es/winto; {ramon.moreno,manuel.grana}@ehu.es Abstrat The
Automatic Physical Design Tuning: Workload as a Sequence Sanjay Agrawal Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA, USA +1-(425)
 Automati Physial Design Tuning: Workload as a Sequene Sanjay Agrawal Mirosoft Researh One Mirosoft Way Redmond, WA, USA +1-(425) 75-357 sagrawal@mirosoft.om Eri Chu * Computer Sienes Department University
Automati Physial Design Tuning: Workload as a Sequene Sanjay Agrawal Mirosoft Researh One Mirosoft Way Redmond, WA, USA +1-(425) 75-357 sagrawal@mirosoft.om Eri Chu * Computer Sienes Department University
Capturing Large Intra-class Variations of Biometric Data by Template Co-updating
 Capturing Large Intra-lass Variations of Biometri Data by Template Co-updating Ajita Rattani University of Cagliari Piazza d'armi, Cagliari, Italy ajita.rattani@diee.unia.it Gian Lua Marialis University
Capturing Large Intra-lass Variations of Biometri Data by Template Co-updating Ajita Rattani University of Cagliari Piazza d'armi, Cagliari, Italy ajita.rattani@diee.unia.it Gian Lua Marialis University
C 2 C 3 C 1 M S. f e. e f (3,0) (0,1) (2,0) (-1,1) (1,0) (-1,0) (1,-1) (0,-1) (-2,0) (-3,0) (0,-2)
 SPECIAL ISSUE OF IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION: MULTI-ROBOT SSTEMS, 00 Distributed reonfiguration of hexagonal metamorphi robots Jennifer E. Walter, Jennifer L. Welh, and Nany M. Amato Abstrat
SPECIAL ISSUE OF IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION: MULTI-ROBOT SSTEMS, 00 Distributed reonfiguration of hexagonal metamorphi robots Jennifer E. Walter, Jennifer L. Welh, and Nany M. Amato Abstrat
PARAMETRIC SAR IMAGE FORMATION - A PROMISING APPROACH TO RESOLUTION-UNLIMITED IMAGING. Yesheng Gao, Kaizhi Wang, Xingzhao Liu
 20th European Signal Proessing Conferene EUSIPCO 2012) Buharest, Romania, August 27-31, 2012 PARAMETRIC SAR IMAGE FORMATION - A PROMISING APPROACH TO RESOLUTION-UNLIMITED IMAGING Yesheng Gao, Kaizhi Wang,
20th European Signal Proessing Conferene EUSIPCO 2012) Buharest, Romania, August 27-31, 2012 PARAMETRIC SAR IMAGE FORMATION - A PROMISING APPROACH TO RESOLUTION-UNLIMITED IMAGING Yesheng Gao, Kaizhi Wang,
UCSB Math TI-85 Tutorials: Basics
 3 UCSB Math TI-85 Tutorials: Basis If your alulator sreen doesn t show anything, try adjusting the ontrast aording to the instrutions on page 3, or page I-3, of the alulator manual You should read the
3 UCSB Math TI-85 Tutorials: Basis If your alulator sreen doesn t show anything, try adjusting the ontrast aording to the instrutions on page 3, or page I-3, of the alulator manual You should read the
Directed Rectangle-Visibility Graphs have. Abstract. Visibility representations of graphs map vertices to sets in Euclidean space and
 Direted Retangle-Visibility Graphs have Unbounded Dimension Kathleen Romanik DIMACS Center for Disrete Mathematis and Theoretial Computer Siene Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey P.O. Box 1179,
Direted Retangle-Visibility Graphs have Unbounded Dimension Kathleen Romanik DIMACS Center for Disrete Mathematis and Theoretial Computer Siene Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey P.O. Box 1179,
Reading Object Code. A Visible/Z Lesson
 Reading Objet Code A Visible/Z Lesson The Idea: When programming in a high-level language, we rarely have to think about the speifi ode that is generated for eah instrution by a ompiler. But as an assembly
Reading Objet Code A Visible/Z Lesson The Idea: When programming in a high-level language, we rarely have to think about the speifi ode that is generated for eah instrution by a ompiler. But as an assembly
Boundary Correct Real-Time Soft Shadows
 Boundary Corret Real-Time Soft Shadows Bjarke Jakobsen Niels J. Christensen Bent D. Larsen Kim S. Petersen Informatis and Mathematial Modelling Tehnial University of Denmark {bj, nj, bdl}@imm.dtu.dk, kim@deadline.dk
Boundary Corret Real-Time Soft Shadows Bjarke Jakobsen Niels J. Christensen Bent D. Larsen Kim S. Petersen Informatis and Mathematial Modelling Tehnial University of Denmark {bj, nj, bdl}@imm.dtu.dk, kim@deadline.dk
The Implementation of RRTs for a Remote-Controlled Mobile Robot
 ICCAS5 June -5, KINEX, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea he Implementation of RRs for a Remote-Controlled Mobile Robot Chi-Won Roh*, Woo-Sub Lee **, Sung-Chul Kang *** and Kwang-Won Lee **** * Intelligent Robotis Researh
ICCAS5 June -5, KINEX, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea he Implementation of RRs for a Remote-Controlled Mobile Robot Chi-Won Roh*, Woo-Sub Lee **, Sung-Chul Kang *** and Kwang-Won Lee **** * Intelligent Robotis Researh
SAND Unlimited Release Printed November 1995 Updated November 29, :26 PM EXODUS II: A Finite Element Data Model
 SAND92-2137 Unlimited Release Printed November 1995 Updated November 29, 2006 12:26 PM EXODUS II: A Finite Element Data Model Gregory D. Sjaardema (updated version) Larry A. Shoof, Vitor R. Yarberry Computational
SAND92-2137 Unlimited Release Printed November 1995 Updated November 29, 2006 12:26 PM EXODUS II: A Finite Element Data Model Gregory D. Sjaardema (updated version) Larry A. Shoof, Vitor R. Yarberry Computational
The AMDREL Project in Retrospective
 The AMDREL Projet in Retrospetive K. Siozios 1, G. Koutroumpezis 1, K. Tatas 1, N. Vassiliadis 2, V. Kalenteridis 2, H. Pournara 2, I. Pappas 2, D. Soudris 1, S. Nikolaidis 2, S. Siskos 2, and A. Thanailakis
The AMDREL Projet in Retrospetive K. Siozios 1, G. Koutroumpezis 1, K. Tatas 1, N. Vassiliadis 2, V. Kalenteridis 2, H. Pournara 2, I. Pappas 2, D. Soudris 1, S. Nikolaidis 2, S. Siskos 2, and A. Thanailakis
