Specular Reflection. Lecture 19. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Oct 4, 2017
|
|
|
- Jonathan Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Specular Reflection Lecture 19 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 4, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
2 Outline 1 Specular Reflection 2 The Specular Calculations The Phong Lighting Model The Blinn Lighting Model 3 Assignment Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
3 Outline 1 Specular Reflection 2 The Specular Calculations The Phong Lighting Model The Blinn Lighting Model 3 Assignment Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
4 Specular Reflection Specular reflection is different. The specular reflection represents the shininess of the surface. Thus, the color of the specular reflection is typically the color of the light source (which is usually white). Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
5 Specular Reflection Specular Reflection vec3 specular(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); GLuint spec_loc = glgetuniformlocation(program, "specular"); gluniform3fv(spec_loc, 1, specular); GLfloat shiny = 20.0f; GLuint shiny_loc = glgetuniformlocation(program, "shiny"); gluniform1f(shiny_loc, 1, shiny); We pass the specular light and the shininess as uniform variables the shaders. Note that shiny is a float, not a vec3. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
6 Outline 1 Specular Reflection 2 The Specular Calculations The Phong Lighting Model The Blinn Lighting Model 3 Assignment Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
7 Specular Reflection Specular reflections takes into account The specular light (intensity of reflection) The shininess of the material (narrowness of reflection) Orientation of the surface (normal vector N) Direction of the light source (light vector L) Direction of the viewer (view vector V) Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
8 Outline 1 Specular Reflection 2 The Specular Calculations The Phong Lighting Model The Blinn Lighting Model 3 Assignment Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
9 Blinn and Phong Lighting There are two standard lighting models for specular reflection. Phong lighting model Blinn lighting model The Phong model is more intuitive, but the Blinn model is more efficient. The results are very similar, but not identical. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
10 Phong Lighting Model In the Phong model, the intensity of the reflection is a function of the angle between direction V to the viewer and the ideal direction R of reflection from the light source off the surface. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
11 Phong Lighting Model Light Source L N Ideal Reflection R Viewer θ θ ϕ V P Surface Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
12 Phong Lighting Model To compute R, note that R + L equals twice the projection of L onto N. R L N L θ θ R Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
13 Phong Lighting Model The projection of L onto N is ( ) L N N = (L N)N. N N Therefore, so R + L = 2(L N)N R = L + 2(L N)N. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
14 Computing Specular Reflection According to the Phong lighting model, the specular reflection is proportional to the cosine of the angle between V and R, raised to the α power, where α is a positive number. This is calculated as (cos ϕ) α = (R V) α. The larger α, the narrower the cone of reflection. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
15 Computing Specular Reflection According to the Phong lighting model, the specular reflection is proportional to the cosine of the angle between V and R, raised to the α power, where α is a positive number. This is calculated as (cos ϕ) α = (R V) α. The larger α, the narrower the cone of reflection. α is called the shininess. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
16 Computing Specular Reflection Two other factors are Intensity of the incident light spec. Material specular property of the surface mat_spec. Therefore, the formula for specular reflection is spec_refl = specular max((r V), 0) α. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
17 Outline 1 Specular Reflection 2 The Specular Calculations The Phong Lighting Model The Blinn Lighting Model 3 Assignment Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
18 Blinn Lighting Model The Blinn model is more efficient. Let H be the halfway vector, which is the unit vector halfway between L and V. Then use H N instead of R V. spec_refl = specular max((h N), 0) α. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
19 Blinn Lighting Model Light Source L N ζ H R Eye ω ω ϕ V P Surface Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
20 Blinn Lighting Model H is computed as H = L + V L + V. How does H N compare to L V? If L, N, and V are coplanar, then the angle between H and N is half of the angle between R and V. Pretty much the same results can be obtained by adjusting α. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
21 Blinn Lighting Model Why is Blinn lighting more efficient? The calculation of H uses L and V, but not N. Therefore, if the light source is directional and the viewer is at infinity, then the halfway vector may be computed only once for the entire scene, not once for every vertex. The halfway vector would be passed as a uniform variable. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
22 Blinn Lighting Model Why is Blinn lighting more efficient? The calculation of H uses L and V, but not N. Therefore, if the light source is directional and the viewer is at infinity, then the halfway vector may be computed only once for the entire scene, not once for every vertex. The halfway vector would be passed as a uniform variable. In other situations, the two methods are about equally efficient. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
23 Outline 1 Specular Reflection 2 The Specular Calculations The Phong Lighting Model The Blinn Lighting Model 3 Assignment Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
24 Assignment Assignment Assignment 16. Read pp : Fragment Shaders for Different Light Styles. Read pp : Moving Calculations to the Vertex Shader. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, / 22
The Critical-Path Algorithm
 The Critical-Path Algorithm Lecture 32 Sections 8.3-8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 19, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Critical-Path Algorithm Wed, Nov 19, 2014 1
The Critical-Path Algorithm Lecture 32 Sections 8.3-8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 19, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Critical-Path Algorithm Wed, Nov 19, 2014 1
Ambient and Diffuse Light
 Ambient and Diffuse Light Lecture 20 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 12, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Ambient and Diffuse Light Mon, Oct 12, 2015 1 / 29 Outline 1 Lighting
Ambient and Diffuse Light Lecture 20 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 12, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Ambient and Diffuse Light Mon, Oct 12, 2015 1 / 29 Outline 1 Lighting
The Projection Matrix
 The Projection Matrix Lecture 5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Aug 30, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Projection Matrix Wed, Aug 30, 2017 1 / 21 Outline 1 The World Coordinate
The Projection Matrix Lecture 5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Aug 30, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Projection Matrix Wed, Aug 30, 2017 1 / 21 Outline 1 The World Coordinate
The Graphics Pipeline
 The Graphics Pipeline Lecture 2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Aug 23, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Graphics Pipeline Wed, Aug 23, 2017 1 / 19 Outline 1 Vertices 2 The
The Graphics Pipeline Lecture 2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Aug 23, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Graphics Pipeline Wed, Aug 23, 2017 1 / 19 Outline 1 Vertices 2 The
The Mesh Class. Lecture 23. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Oct 18, 2017
 The Mesh Class Lecture 23 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 18, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Mesh Class Wed, Oct 18, 2017 1 / 21 Outline 1 The Mesh Class 2 Assignment
The Mesh Class Lecture 23 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 18, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Mesh Class Wed, Oct 18, 2017 1 / 21 Outline 1 The Mesh Class 2 Assignment
Minimal Spanning Trees
 Minimal Spanning Trees Lecture 33 Sections 7.1-7.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 20 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Minimal Spanning Trees Wed, Apr 11, 20 1 / 17 1 Networks
Minimal Spanning Trees Lecture 33 Sections 7.1-7.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 20 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Minimal Spanning Trees Wed, Apr 11, 20 1 / 17 1 Networks
The Graphics Pipeline
 The Graphics Pipeline Lecture 2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Aug 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Graphics Pipeline Fri, Aug 28, 2015 1 / 19 Outline 1 Vertices 2 The
The Graphics Pipeline Lecture 2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Aug 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Graphics Pipeline Fri, Aug 28, 2015 1 / 19 Outline 1 Vertices 2 The
The Projection Matrix
 The Projection Matrix Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 11, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Projection Matrix Fri, Sep 11, 2015 1 / 43 Outline 1 Coordinate Systems
The Projection Matrix Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 11, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Projection Matrix Fri, Sep 11, 2015 1 / 43 Outline 1 Coordinate Systems
Illumination & Shading
 Illumination & Shading Goals Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can be used with real time graphics hardware Why we need Illumination
Illumination & Shading Goals Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can be used with real time graphics hardware Why we need Illumination
Stack Applications. Lecture 27 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Mar 29, 2017
 Stack Applications Lecture 27 Sections 18.7-18.8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 29, 2017 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College) Stack Applications Wed, Mar 29, 2017 1 / 27 1 Function
Stack Applications Lecture 27 Sections 18.7-18.8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 29, 2017 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College) Stack Applications Wed, Mar 29, 2017 1 / 27 1 Function
Recursive Sequences. Lecture 24 Section 5.6. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Feb 27, 2013
 Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 / 21 1 Recursive Sequences
Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 / 21 1 Recursive Sequences
Rotations and Translations
 Rotations and Translations Lecture 33 Sections 11.3-11.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 20, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Rotations and Translations Wed, Nov 20, 2013 1
Rotations and Translations Lecture 33 Sections 11.3-11.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 20, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Rotations and Translations Wed, Nov 20, 2013 1
Recursive Sequences. Lecture 24 Section 5.6. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Feb 26, 2014
 Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 26, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 26, 2014 1 / 26 1 Recursive Sequences
Recursive Sequences Lecture 24 Section 5.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 26, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Sequences Wed, Feb 26, 2014 1 / 26 1 Recursive Sequences
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics. Spring Shading
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
Density Curves Sections
 Density Curves Sections 3.1-3.2 Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 27, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Density CurvesSections 3.1-3.2 Wed, Jan 27, 2016 1 / 18 Outline
Density Curves Sections 3.1-3.2 Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 27, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Density CurvesSections 3.1-3.2 Wed, Jan 27, 2016 1 / 18 Outline
Street-Routing Problems
 Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
The Decreasing-Time Algorithm
 The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Lecture 36 Sections 8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 18, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Wed, Apr 18, 2018 1
The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Lecture 36 Sections 8.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 18, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Decreasing-Time Algorithm Wed, Apr 18, 2018 1
while Loops Lecture 13 Sections Robb T. Koether Wed, Sep 26, 2018 Hampden-Sydney College
 while Loops Lecture 13 Sections 5.8-5.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) while Loops Wed, Sep 26, 2018 1 / 25 1 while Loops 2 Input Loops
while Loops Lecture 13 Sections 5.8-5.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) while Loops Wed, Sep 26, 2018 1 / 25 1 while Loops 2 Input Loops
The Pairwise-Comparison Method
 The Pairwise-Comparison Method Lecture 10 Section 1.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Sep 11, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Pairwise-Comparison Method Mon, Sep 11, 2017
The Pairwise-Comparison Method Lecture 10 Section 1.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Sep 11, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Pairwise-Comparison Method Mon, Sep 11, 2017
Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5
 Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5 Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Sampling Distribution ExamplesSections 15.4,
Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5 Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Sampling Distribution ExamplesSections 15.4,
Shading I Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008
 Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
Shader Programs. Lecture 30 Subsections 2.8.2, Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Nov 16, 2011
 Shader Programs Lecture 30 Subsections 2.8.2, 2.8.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 16, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shader Programs Wed, Nov 16, 2011 1 / 43 Outline 1
Shader Programs Lecture 30 Subsections 2.8.2, 2.8.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 16, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shader Programs Wed, Nov 16, 2011 1 / 43 Outline 1
The View Frustum. Lecture 9 Sections 2.6, 5.1, 5.2. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Sep 14, 2011
 The View Frustum Lecture 9 Sections 2.6, 5.1, 5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 14, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The View Frustum Wed, Sep 14, 2011 1 / 36 Outline 1 The
The View Frustum Lecture 9 Sections 2.6, 5.1, 5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 14, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The View Frustum Wed, Sep 14, 2011 1 / 36 Outline 1 The
Objectives. Shading II. Distance Terms. The Phong Reflection Model
 Shading II Objectives Introduce distance terms to the shading model. More details about the Phong model (lightmaterial interaction). Introduce the Blinn lighting model (also known as the modified Phong
Shading II Objectives Introduce distance terms to the shading model. More details about the Phong model (lightmaterial interaction). Introduce the Blinn lighting model (also known as the modified Phong
Lecture 15: Shading-I. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
WHY WE NEED SHADING. Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something like.
 LIGHTING 1 OUTLINE Learn to light/shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can
LIGHTING 1 OUTLINE Learn to light/shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can
Applying Textures. Lecture 27. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Fri, Nov 3, 2017
 Applying Textures Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Applying Textures Fri, Nov 3, 2017 1 / 24 Outline 1 Applying Textures 2 Photographs
Applying Textures Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Applying Textures Fri, Nov 3, 2017 1 / 24 Outline 1 Applying Textures 2 Photographs
Shading. Why we need shading. Scattering. Shading. Objectives
 Shading Why we need shading Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something
Shading Why we need shading Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something
Scope and Parameter Passing
 Scope and Parameter Passing Lecture 16 Sections 6.5, 6.10, 6.13 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 7, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scope and Parameter Passing Mon, Oct 7,
Scope and Parameter Passing Lecture 16 Sections 6.5, 6.10, 6.13 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Oct 7, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scope and Parameter Passing Mon, Oct 7,
Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration
 Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration Lecture 25 Section 5.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Thu, Feb 28, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration
Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration Lecture 25 Section 5.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Thu, Feb 28, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Solving Recursive Sequences by Iteration
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Ken Joy.! Winter 2014
 ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
CS452/552; EE465/505. Lighting & Shading
 CS452/552; EE465/505 Lighting & Shading 2-17 15 Outline! More on Lighting and Shading Read: Angel Chapter 6 Lab2: due tonight use ASDW to move a 2D shape around; 1 to center Local Illumination! Approximate
CS452/552; EE465/505 Lighting & Shading 2-17 15 Outline! More on Lighting and Shading Read: Angel Chapter 6 Lab2: due tonight use ASDW to move a 2D shape around; 1 to center Local Illumination! Approximate
Lessons Learned from HW4. Shading. Objectives. Why we need shading. Shading. Scattering
 Lessons Learned from HW Shading CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Only have an idle() function if something is animated Set idle function to NULL, when
Lessons Learned from HW Shading CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Only have an idle() function if something is animated Set idle function to NULL, when
Shading II. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Shading II CITS3003 Graphics & Animation Objectives Introduce distance terms to the shading model. More details about the Phong model (lightmaterial interaction). Introduce the Blinn lighting model (also
Shading II CITS3003 Graphics & Animation Objectives Introduce distance terms to the shading model. More details about the Phong model (lightmaterial interaction). Introduce the Blinn lighting model (also
Recursive Descent Parsers
 Recursive Descent Parsers Lecture 7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Descent Parsers Wed, Jan 28, 2015 1 / 18 1 Parsing 2 LL Parsers
Recursive Descent Parsers Lecture 7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Recursive Descent Parsers Wed, Jan 28, 2015 1 / 18 1 Parsing 2 LL Parsers
CS452/552; EE465/505. Intro to Lighting
 CS452/552; EE465/505 Intro to Lighting 2-10 15 Outline! Projection Normalization! Introduction to Lighting (and Shading) Read: Angel Chapter 5., sections 5.4-5.7 Parallel Projections Chapter 6, sections
CS452/552; EE465/505 Intro to Lighting 2-10 15 Outline! Projection Normalization! Introduction to Lighting (and Shading) Read: Angel Chapter 5., sections 5.4-5.7 Parallel Projections Chapter 6, sections
The Class Construct Part 1
 The Class Construct Part 1 Lecture 23 Sections 7.5-7.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Class Construct Part 1 Fri, Oct 26, 2018 1 /
The Class Construct Part 1 Lecture 23 Sections 7.5-7.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 26, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Class Construct Part 1 Fri, Oct 26, 2018 1 /
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
The string Class. Lecture 21 Sections 2.9, 3.9, Robb T. Koether. Wed, Oct 17, Hampden-Sydney College
 The string Class Lecture 21 Sections 2.9, 3.9, 3.10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 17, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The string Class Wed, Oct 17, 2018 1 / 18 1 The String
The string Class Lecture 21 Sections 2.9, 3.9, 3.10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 17, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The string Class Wed, Oct 17, 2018 1 / 18 1 The String
C O M P U T E R G R A P H I C S. Computer Graphics. Three-Dimensional Graphics V. Guoying Zhao 1 / 65
 Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 65 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 65 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 65 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 65 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
Overview. Shading. Shading. Why we need shading. Shading Light-material interactions Phong model Shading polygons Shading in OpenGL
 Overview Shading Shading Light-material interactions Phong model Shading polygons Shading in OpenGL Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor.
Overview Shading Shading Light-material interactions Phong model Shading polygons Shading in OpenGL Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor.
Lighting and Shading II. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Lighting and Shading II 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors 2 Ambient Light Ambient light is the result of multiple interactions
Lighting and Shading II 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors 2 Ambient Light Ambient light is the result of multiple interactions
Displaying Distributions - Quantitative Variables
 Displaying Distributions - Quantitative Variables Lecture 13 Sections 4.4.1-4.4.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 8, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Displaying Distributions
Displaying Distributions - Quantitative Variables Lecture 13 Sections 4.4.1-4.4.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 8, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Displaying Distributions
Scheduling and Digraphs
 Scheduling and Digraphs Lecture 35 Sections 8.1, 8.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 21, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scheduling and Digraphs Mon, Nov 21, 2016 1 / 25 1
Scheduling and Digraphs Lecture 35 Sections 8.1, 8.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 21, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scheduling and Digraphs Mon, Nov 21, 2016 1 / 25 1
Scope and Parameter Passing
 Scope and Parameter Passing Lecture 17 Sections 6.5, 6.10, 6.13 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 5, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scope and Parameter Passing Fri, Oct 5,
Scope and Parameter Passing Lecture 17 Sections 6.5, 6.10, 6.13 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 5, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Scope and Parameter Passing Fri, Oct 5,
TSBK 07! Computer Graphics! Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY
 1(84) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH TSBK 07 Computer Graphics Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY 1(84) Lecture 5 3D graphics part 3 Illumination Illumination applied: Shading Surface detail: Mappings
1(84) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH TSBK 07 Computer Graphics Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY 1(84) Lecture 5 3D graphics part 3 Illumination Illumination applied: Shading Surface detail: Mappings
Objectives. Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading.
 Shading II 1 Objectives Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading Flat Smooth Gouraud 2 Phong Lighting Model A simple model
Shading II 1 Objectives Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading Flat Smooth Gouraud 2 Phong Lighting Model A simple model
Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading
Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading
Computer Graphics MTAT Raimond Tunnel
 Computer Graphics MTAT.03.015 Raimond Tunnel The Road So Far... Last week This week Color What is color? Color We represent color values with 3 channels: Red Green Blue Color We represent color values
Computer Graphics MTAT.03.015 Raimond Tunnel The Road So Far... Last week This week Color What is color? Color We represent color values with 3 channels: Red Green Blue Color We represent color values
Shading Triangles. Lecture 37. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Mon, Nov 30, 2015
 Shading Triangles Lecture 37 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 30, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shading Triangles Mon, Nov 30, 2015 1 / 35 Outline 1 Shading Triangles Barycentric
Shading Triangles Lecture 37 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Nov 30, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Shading Triangles Mon, Nov 30, 2015 1 / 35 Outline 1 Shading Triangles Barycentric
CS5620 Intro to Computer Graphics
 So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
Illumination Models & Shading
 Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Boxplots. Lecture 17 Section Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Feb 10, 2010
 Boxplots Lecture 17 Section 5.3.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 10, 2010 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boxplots Wed, Feb 10, 2010 1 / 34 Outline 1 Boxplots TI-83 Boxplots 2
Boxplots Lecture 17 Section 5.3.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 10, 2010 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boxplots Wed, Feb 10, 2010 1 / 34 Outline 1 Boxplots TI-83 Boxplots 2
CS130 : Computer Graphics Lecture 8: Lighting and Shading. Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside
 CS130 : Computer Graphics Lecture 8: Lighting and Shading Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color
CS130 : Computer Graphics Lecture 8: Lighting and Shading Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color
Boolean Expressions. Lecture 31 Sections 6.6, 6.7. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Apr 8, 2015
 Boolean Expressions Lecture 31 Sections 6.6, 6.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 8, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boolean Expressions Wed, Apr 8, 2015 1 / 22 1 Relational
Boolean Expressions Lecture 31 Sections 6.6, 6.7 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 8, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Boolean Expressions Wed, Apr 8, 2015 1 / 22 1 Relational
XPath Lecture 34. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Apr 11, 2012
 XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
Illumination in Computer Graphics
 Illumination in Computer Graphics Ann McNamara Illumination in Computer Graphics Definition of light sources. Analysis of interaction between light and objects in a scene. Rendering images that are faithful
Illumination in Computer Graphics Ann McNamara Illumination in Computer Graphics Definition of light sources. Analysis of interaction between light and objects in a scene. Rendering images that are faithful
Three-Dimensional Graphics V. Guoying Zhao 1 / 55
 Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 55 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 55 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 55 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 55 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
The Normal Distribution
 The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
Pointers. Lecture 1 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Jan 14, 2015
 Pointers Lecture 1 Sections 10.1-10.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 14, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Pointers Wed, Jan 14, 2015 1 / 23 1 Pointers 2 Pointer Initialization
Pointers Lecture 1 Sections 10.1-10.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 14, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Pointers Wed, Jan 14, 2015 1 / 23 1 Pointers 2 Pointer Initialization
CS230 : Computer Graphics Lighting and Shading. Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside
 CS230 : Computer Graphics Lighting and Shading Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside General light source Illumination function: [Angel and Shreiner] integrate contributions from all
CS230 : Computer Graphics Lighting and Shading Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside General light source Illumination function: [Angel and Shreiner] integrate contributions from all
The Mesh Class. Lecture 26. Robb T. Koether. Wed, Oct 28, Hampden-Sydney College
 The Mesh Class Lecture 26 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Mesh Class Wed, Oct 28, 2015 1 / 23 Outline 1 The Mesh Class 2 Assignment
The Mesh Class Lecture 26 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 28, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Mesh Class Wed, Oct 28, 2015 1 / 23 Outline 1 The Mesh Class 2 Assignment
LR Parsing - Conflicts
 LR Parsing - Conflicts Lecture 15 Sections 4.5, 4.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 20, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) LR Parsing - Conflicts Fri, Feb 20, 2015 1 / 15 1 Shift/Reduce
LR Parsing - Conflicts Lecture 15 Sections 4.5, 4.6 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 20, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) LR Parsing - Conflicts Fri, Feb 20, 2015 1 / 15 1 Shift/Reduce
Pointer Arithmetic. Lecture 4 Chapter 10. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Jan 25, 2017
 Pointer Arithmetic Lecture 4 Chapter 10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Pointer Arithmetic Wed, Jan 25, 2017 1 / 36 1 Pointer Arithmetic
Pointer Arithmetic Lecture 4 Chapter 10 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Pointer Arithmetic Wed, Jan 25, 2017 1 / 36 1 Pointer Arithmetic
Total Orders. Lecture 41 Section 8.5. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Mon, Apr 8, 2013
 Total Orders Lecture 41 Section 8.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Apr 8, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Total Orders Mon, Apr 8, 2013 1 / 30 1 Total Orders 2 Topological Sorting
Total Orders Lecture 41 Section 8.5 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Apr 8, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Total Orders Mon, Apr 8, 2013 1 / 30 1 Total Orders 2 Topological Sorting
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING
 CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
The Coefficient of Determination
 The Coefficient of Determination Lecture 46 Section 13.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 17, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Coefficient of Determination Wed, Apr 17,
The Coefficient of Determination Lecture 46 Section 13.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 17, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Coefficient of Determination Wed, Apr 17,
Objectives Shading in OpenGL. Front and Back Faces. OpenGL shading. Introduce the OpenGL shading methods. Discuss polygonal shading
 Objectives Shading in OpenGL Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading vs per fragment shading - Where to carry out Discuss polygonal shading - Flat - Smooth - Gouraud CITS3003 Graphics
Objectives Shading in OpenGL Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading vs per fragment shading - Where to carry out Discuss polygonal shading - Flat - Smooth - Gouraud CITS3003 Graphics
Visualisatie BMT. Rendering. Arjan Kok
 Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Lighting and Shading Computer Graphics I Lecture 7. Light Sources Phong Illumination Model Normal Vectors [Angel, Ch
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 7 Lighting and Shading February 12, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/ Light Sources Phong Illumination Model
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 7 Lighting and Shading February 12, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/ Light Sources Phong Illumination Model
The Model Stack. Lecture 8. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Sep 6, 2017
 The Model Stack Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 6, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Model Stack Wed, Sep 6, 2017 1 / 19 Outline 1 Drawing Rectangle Man 2 The
The Model Stack Lecture 8 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 6, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Model Stack Wed, Sep 6, 2017 1 / 19 Outline 1 Drawing Rectangle Man 2 The
Function Definition Syntax Tree
 Function Definition Syntax Tree Lecture 34 Section 6.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Function Definition Syntax Tree Wed, Apr 15, 2015
Function Definition Syntax Tree Lecture 34 Section 6.9 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Function Definition Syntax Tree Wed, Apr 15, 2015
Lab 9 - Metal and Glass
 Lab 9 - Metal and Glass Let the form of an object be what it may, light, shade, and perspective will always make it beautiful. -John Constable Prologue Support code: /course/cs1230/src/labs/lab09 This
Lab 9 - Metal and Glass Let the form of an object be what it may, light, shade, and perspective will always make it beautiful. -John Constable Prologue Support code: /course/cs1230/src/labs/lab09 This
Introduction to Databases
 Introduction to Databases Lecture 1 Chapters 1-2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 15, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Introduction to Databases Wed, Jan 15, 2014 1 / 23 1 Overview
Introduction to Databases Lecture 1 Chapters 1-2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Jan 15, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Introduction to Databases Wed, Jan 15, 2014 1 / 23 1 Overview
Binary Tree Applications
 Binary Tree Applications Lecture 30 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Applications Wed, Apr 15, 2015 1 / 56 1 Binary
Binary Tree Applications Lecture 30 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Applications Wed, Apr 15, 2015 1 / 56 1 Binary
The Traveling Salesman Problem Cheapest-Link Algorithm
 The Traveling Salesman Problem heapest-link lgorithm Lecture 3 Sections.5 Robb T. Koether ampden-sydney ollege Wed, Nov 1, 201 Robb T. Koether (ampden-sydney ollege)the Traveling Salesman Problemheapest-Link
The Traveling Salesman Problem heapest-link lgorithm Lecture 3 Sections.5 Robb T. Koether ampden-sydney ollege Wed, Nov 1, 201 Robb T. Koether (ampden-sydney ollege)the Traveling Salesman Problemheapest-Link
Mipmaps. Lecture 35. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Nov 18, 2015
 Mipmaps Lecture 35 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 18, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Mipmaps Wed, Nov 18, 2015 1 / 31 Outline 1 Discrete Sampling 2 Mipmaps 3 Generating
Mipmaps Lecture 35 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Nov 18, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Mipmaps Wed, Nov 18, 2015 1 / 31 Outline 1 Discrete Sampling 2 Mipmaps 3 Generating
The CYK Parsing Algorithm
 The CYK Parsing Algorithm Lecture 19 Section 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 7, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The CYK Parsing Algorithm Fri, Oct 7, 2016 1 / 21 1 The
The CYK Parsing Algorithm Lecture 19 Section 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 7, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The CYK Parsing Algorithm Fri, Oct 7, 2016 1 / 21 1 The
Linked Lists. Lecture 16 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Feb 22, 2017
 Linked Lists Lecture 16 Sections 17.1-17.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 22, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Linked Lists Wed, Feb 22, 2017 1 / 24 1 Linked Lists 2 The LinkedListNode
Linked Lists Lecture 16 Sections 17.1-17.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 22, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Linked Lists Wed, Feb 22, 2017 1 / 24 1 Linked Lists 2 The LinkedListNode
Magnification and Minification
 Magnification and Minification Lecture 30 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 6, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Magnification and Minification Fri, Nov 6, 2015 1 / 17 Outline
Magnification and Minification Lecture 30 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 6, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Magnification and Minification Fri, Nov 6, 2015 1 / 17 Outline
Why we need shading?
 Why we need shading? Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something like But we want Light-material interactions cause each point to have a different
Why we need shading? Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something like But we want Light-material interactions cause each point to have a different
Abstract Data Types. Lecture 23 Section 7.1. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Oct 24, 2012
 Abstract Data Types Lecture 23 Section 7.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 24, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Abstract Data Types Wed, Oct 24, 2012 1 / 19 1 Abstract Data
Abstract Data Types Lecture 23 Section 7.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 24, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Abstract Data Types Wed, Oct 24, 2012 1 / 19 1 Abstract Data
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Color and Shading
 Preview CS770/870 Spring 2017 Color and Shading Related material Cunningham: Ch 5 Hill and Kelley: Ch. 8 Angel 5e: 6.1-6.8 Angel 6e: 5.1-5.5 Making the scene more realistic Color models representing the
Preview CS770/870 Spring 2017 Color and Shading Related material Cunningham: Ch 5 Hill and Kelley: Ch. 8 Angel 5e: 6.1-6.8 Angel 6e: 5.1-5.5 Making the scene more realistic Color models representing the
Implementing Linked Lists
 Implementing Linked Lists Lecture 16 Sections 17.1-17.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Implementing Linked Lists Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 /
Implementing Linked Lists Lecture 16 Sections 17.1-17.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Feb 27, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Implementing Linked Lists Wed, Feb 27, 2013 1 /
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
Building the Abstract Syntax Trees
 Building the Abstract Syntax Trees Lecture 23 Section 5.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 18, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Building the Abstract Syntax Trees Wed, Mar 18,
Building the Abstract Syntax Trees Lecture 23 Section 5.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 18, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Building the Abstract Syntax Trees Wed, Mar 18,
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Computer Graphics Coursework 1
 Computer Graphics Coursework 1 Deadline Deadline: 4pm, 24/10/2016 4pm 23/10/2015 Outline The aim of the coursework is to modify the vertex and fragment shaders in the provided OpenGL framework to implement
Computer Graphics Coursework 1 Deadline Deadline: 4pm, 24/10/2016 4pm 23/10/2015 Outline The aim of the coursework is to modify the vertex and fragment shaders in the provided OpenGL framework to implement
XML Attributes. Lecture 33. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Apr 25, 2018
 XML Attributes Lecture 33 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 25, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XML Attributes Wed, Apr 25, 2018 1 / 15 1 XML Attributes 2 The getattribute()
XML Attributes Lecture 33 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 25, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XML Attributes Wed, Apr 25, 2018 1 / 15 1 XML Attributes 2 The getattribute()
Orthogonal Projection Matrices. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
Regular Expressions. Lecture 10 Sections Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Sep 14, 2016
 Regular Expressions Lecture 10 Sections 3.1-3.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 14, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Regular Expressions Wed, Sep 14, 2016 1 / 23 Outline 1
Regular Expressions Lecture 10 Sections 3.1-3.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 14, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Regular Expressions Wed, Sep 14, 2016 1 / 23 Outline 1
Shading. Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Shading Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Overview of today s lecture l A simple most basic real-time lighting model
Shading Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Overview of today s lecture l A simple most basic real-time lighting model
CSE 681 Illumination and Phong Shading
 CSE 681 Illumination and Phong Shading Physics tells us What is Light? We don t see objects, we see light reflected off of objects Light is a particle and a wave The frequency of light What is Color? Our
CSE 681 Illumination and Phong Shading Physics tells us What is Light? We don t see objects, we see light reflected off of objects Light is a particle and a wave The frequency of light What is Color? Our
XPath. Lecture 36. Robb T. Koether. Wed, Apr 16, Hampden-Sydney College. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, / 28
 XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
Illumination. Michael Kazhdan ( /657) HB Ch. 14.1, 14.2 FvDFH 16.1, 16.2
 Illumination Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 14.1, 14.2 FvDFH 16.1, 16.2 Ray Casting Image RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { Image image = new Image(width, height); for
Illumination Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 14.1, 14.2 FvDFH 16.1, 16.2 Ray Casting Image RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { Image image = new Image(width, height); for
CS 4600 Fall Utah School of Computing
 Lighting CS 4600 Fall 2015 Utah School of Computing Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection
Lighting CS 4600 Fall 2015 Utah School of Computing Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection
Shading II. Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico
 Shading II Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model
Shading II Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry
 INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Visual appearance Christopher Dyken and Martin Reimers 23.09.2009 Page 1 Visual appearance Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5 Light Sources and materials Shading
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Visual appearance Christopher Dyken and Martin Reimers 23.09.2009 Page 1 Visual appearance Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5 Light Sources and materials Shading
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
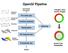 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
