Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007
|
|
|
- Barnaby Nichols
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simpler Soft Shadow Mapping Lee Salzman September 20, 2007 Lightmaps, as do other precomputed lighting methods, provide an efficient and pleasing solution for lighting and shadowing of relatively static scenes. Most of the work of lighting computations can be offloaded to a precomputation step and only leave simple texture lookups to be performed at the time of rendering. As one makes the technological leap to dynamic lighting and shadowing, one is confronted by methods, such as stencil shadow volumes and shadow mapping, which at first appear simple, yet become increasingly complex and expensive as one tries to recover the quality of appearance provided by simple lightmapping. One can either use these methods uniformly throughout a scene to give the lighting a uniform appearance, but at much greater expense than precomputed lighting, or integrate precomputed lighting with a dynamic shadowing method with disparate appearance such as hard-edged or blocky, aliased dynamic shadows over soft, static lighting. Ideally, one needs dynamic shadowing tools that provide a pleasing level of consistency when integrated with precomputed lighting without the leap in cost of applying dynamic lighting and shadowing to everything in the scene. Background and Motivation: Variance Shadow Mapping Variance shadow mapping [1] is a recent shadow mapping variant for efficiently approximating the soft-edged shadows caused by area lighting, helping reduce the visual quality gap with precomputed lighting. It overcomes some of the efficiency concerns of previous techniques by allowing the shadow map to be directly linearly filtered, as by a separable blur or the 3D hardware's provided bilinear and trilinear filtering, as opposed to requiring specialized filtering methods at the time of shadow map lookup. It accomplishes this by storing in a shadow map, for each depth value d of a pixel as viewed from a light source, both d and d². Let E(d) and E(d²) correspond to each of these values after some arbitrary linear filtering applied to the shadow map, respectively. It then interprets E(d) as the mean u and E(d²)-E(d)² as the variance v. Finally, given the depth z of a point to be shadowed, if z is greater than (farther from the light) than the mean occluder depth u, then it is determined to be in shadow and then approximates a shadowing term v/[v + (z-u)²], where lower values imply more shadow and higher values more light. Otherwise, If z is less than or equal to (closer to the light) the mean u, then the pixel is assumed not occluded and to be fully lit. Suppose one wishes to integrate this method with precomputed lighting, ideally by only rendering dynamic elements of the scene into the variance shadow map. Initially, the shadow map is cleared with depth values representing the far plane of the light source. Assuming the depth values are normalized, this value is simply 1. Then only dynamic elements of the scene are rendered into the
2 shadow map with normalized depth values in the range of [0,1]. Finally, suppose a linear filter is applied to two texels straddling the edge of a dynamic scene elements shadow in this sparse shadow map. One texel lies outside the shadow and has a depth value of 1, and the other lies inside with an intermediate depth value s. If s is small relative to the depth range, then after linear filtering between the two texels, the resulting mean u term readily skews towards the far plane depth value of 1. Thus, any depth z for a point to be shadowed very close to the occluder depth s will tend to be rejected as lit by testing against this skewed mean u. One can work around this problem by rendering the entire scene into the variance shadow map but at added cost. Even ignoring this difficulty, variance shadow maps store a squared term d² which effectively doubles the precision requirements of the shadow map. This, for most practical purposes, compels one to use 16 or 32 bit-per-component textures to represent the shadow map, which do not necessarily have guaranteed or even efficient bilinear and trilinear filtering on available consumer 3D hardware. Another Approach Consider the supposed use case again. One wants to be able to linearly filter the depth values of dynamic scene elements and the far plane together to get a resulting shadowing term that can be applied to static elements of the scene and mask off their precomputed lighting. Taking inspiration from variance shadow maps, assume the desired mask is a blurred (by a separate filter) gray-scale image of the shadows of the dynamic parts of the scene that need to be projected on the static parts of the scene. Suppose this image is augmented, before blurring it, with depth values for each occluding texel as in a standard shadow map. If only the shadow mask is blurred, then the blurred mask will extend outside where the depth values were rendered and cut off much of the faux-penumbra of the shadow. If the depth values are also blurred, the depth values will extend as far as the faux-penumbra, but using these depth values as-is for the shadowing test will result in the previous problem observed with variance shadow mapping. A method of recovering the original, unfiltered depth value from the filtered depth value is needed. Consider the same two texels on a shadow boundary as in the above example, such that a linear filter p has been applied to the occluder's depth value s and the far plane depth 1. Then the resulting depth value d retrieved from the shadow map should satisfy the following: d = p*s + (1-p)*1 = p*(s-1) + 1. Now, suppose the shadow map is augmented with a shadow mask (a grayscale image of the shadow), that contains the value 1 where there is shadow and 0 where there is none. The resulting mask value m retrieved from the shadow map should also satisfy the following: m = p*1 + (1-p)*0 = p. Thus this shadow mask will, within the limits of the shadow map precision, both serve as the shadowing to be applied and give the filter p that was applied to this shadow map texel. Since p is known, one may directly solve for the actual depth of the occluder s: s = (d-1)/m + 1. Finally, once you have the occluder depth s, you test the depth z of the point
3 to be shadow against s, and if it is farther, then use the mask m as the intensity of shadowing to apply. Implementation The steps to apply this representation become: 1) clear the shadow map so all depth values are at the far plane 1, and all mask values are 0 2) for each occluder render depth d as in a normal shadow map, but also a mask value of 1 3) apply a desired linear filter as with variance shadow mapping 4) when shading, recover the unfiltered depth s = (d-1)/m + 1 and test against it. If shadowed, use the filtered mask m directly as the shadow intensity. Advantages The advantages of this representation are that there are no squared terms as in variance shadow mapping, so the precision demands are much less. An 8- bit-per-component shadow map texture, which can be bilinearly and trilinearly filtered on most consumer 3D hardware, is feasible provided the depth range of the light is not extreme. Larger depth values biases may also suffice to accommodate reduced precision usages, as for the intended use one is merely trying to cast shadows from objects onto a scene, rather than compute finegrained self-shadowing within any individual object. Disadvantages The representation is only suitable for casting a soft-edged shadow of the fused silhouette of some shadow casters onto a scene. While it can be used for self-shadowing as in a normal shadow map, it would fail to provide soft shadowing for that purpose. In the case occluders at different depths are filtered together, the reconstructed occluder depth will end up some weighted average of them, which can cause shadowing artifacts in some cases. In the case that there is a shadow receiver between two shadow casters along a single light ray, the reconstructed occluder depth value may be pushed behind the shadow receiver such that that receiver fails to shadow. The representation is most suitable for scenes where there is not a complex intermingling of objects and scene or where such artifacts would be transient and not often noticed. Integrating with Single-pass Lightmaps If one uses a single-pass lightmapping system that combines the contribution of all lights in a scene into a single lightmap and uses a single shadow map to mask off this lightmap and create faux-shadows, the resulting faux-shadows may bleed through surfaces. This is, however, not a weakness of
4 the above representation, but of applying a shadow map to a single-pass combined lightmap. Suppose a character model is standing above a bridge, with a single sunlight casting down upon him. The shadow map is likewise oriented to cast faux-shadows downward and will determine that all points below the character are in shadow. Assuming the sunlight is the only light source, the lightmaps would already encode the fact that the area under the bridge is in shadow, so that masking off any light underneath would only shadow an area that is already in shadow. Thus, in the case of a single light per lightmap, masking off the light it provides should not cause artifacts. Suppose, however, that there is a torch underneath the bridge. The character's faux-shadow will also mask off this torch's light, even though the character is not visible in the are underneath the bridge. Similar artifacts might occur if indirect lighting were to brighten the area in which the character's shadow fell. Ideally, the character should only cast a faux-shadow on the surface immediately behind him from the light's point of view. This clamping of the shadow can be accomplished by adding an additional value to the shadow map that sets a far bound on the shadowing region, in addition to the near bound already set by the occluder depth stored in the shadow map. A method to generate this far bound, inspired by depth peeling, proceeds as follows: 1) clear a third component of the shadow map storing the far bound to the far plane 1 when clearing the other two components 2) render occluder depths and mask values into the shadow map, leaving the far bound untouched 3) invert the z-buffer test so that only surfaces behind the occluders will render into the shadow map, and disable z-buffer writes so that all such surfaces behind the occluders will be rendered 4) using min-max blending functionality, such as the GL_EXT_blend_minmax extension in OpenGL, set the blend function to accumulate the minimum value in this third far bound component, either by utilizing a color mask if available so that only the third component is written to, or by setting the other values of components to be blended to some suitable value such as 1 so that they remain unaltered 5) render the shadow receivers - preferably the back faces so as to minimize depth biasing problems 6) when shading, reconstruct the far bound in parallel with the occluder depth (taking advantage of the vector nature of instructions on GPUs), using the same method described above, and verify that the pixel to be shadowed also lies within this far bound to determine if it is actually shadowed This method, while requiring the shadow receivers to be rendered into the shadow map, is still never-the-less likely more efficient than rendering the entire scene into an entire shadow map, as due to the inverted z-buffer test and the fact that unshadowed texels of the shadow map have their z-buffer values initialized to a suitable far plane, most of the shadow map will be effectively stenciled off by
5 the 3D hardware, rejecting all writes to the shadow map except to specifically those areas where there are shadow casters. Also, since renderable two-component formats are, at the time of this writing, relatively rare, the space overhead of this extra component is amortized the extra component would otherwise go unused. Efficient Blurring Even using a separate blur filter, the number of texture lookups per shadow map texel to achieve a desirable blur can become expensive on older 3D hardware. Taking advantage of the fact that the shadow casters occupy the shadow map only sparsely, one can limit the blur to take place only within specific portions of the shadow map containing the shadow casters where it is actually needed. One simple way to achieve this is to subdivide the shadow map into a grid, rendering the bounding square of the shadow casters into the grid. The grid can then be grouped into maximally sized quadrilateral regions using a simple runlength step upon non-empty grid squares. Blurring is then performed only within these quadrilaterals. If size of the grid is adequately chosen, each row of the grid can be efficiently represented by a bit vector, reducing the cost of managing the grid. This same grid can also be used to test if a shadow receiver is within the area of influence of any shadow caster, by checking its bounding square in the shadow map against this grid, also making efficient usage of the bit vector representation of grid rows. Possible Extensions If one considers that mask values for shadows may be rendered as anywhere in the range of [0,1], rather than just 0 to indicate a background and 1 to represent an occluder, one may directly render the transparency of an object into a third shadow contribution component, which gets used as the final shadowing contribution instead of the mask value, allowing a transparent occluder to only contribute partial shadowing. References [1] William Donnelly and Andrew Lauritzen, "Variance Shadow Maps," In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games 2006.
Shadows in the graphics pipeline
 Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
High Quality Adaptive Soft Shadow Mapping
 High Quality Adaptive Soft Shadow Mapping A paper by Gaël Guennebaud, Loïc Barthe and Mathias Paulin Roy Triesscheijn Overview - Algorithms from 2 papers, initial 2006 version and improved version from
High Quality Adaptive Soft Shadow Mapping A paper by Gaël Guennebaud, Loïc Barthe and Mathias Paulin Roy Triesscheijn Overview - Algorithms from 2 papers, initial 2006 version and improved version from
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques
 Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
Soft shadows. Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February
 Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Shadow Techniques. Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation
 Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Non-Linearly Quantized Moment Shadow Maps
 Non-Linearly Quantized Moment Shadow Maps Christoph Peters 2017-07-30 High-Performance Graphics 2017 These slides include presenter s notes for your convenience. 1 In this presentation we discuss non-linearly
Non-Linearly Quantized Moment Shadow Maps Christoph Peters 2017-07-30 High-Performance Graphics 2017 These slides include presenter s notes for your convenience. 1 In this presentation we discuss non-linearly
CS354R: Computer Game Technology
 CS354R: Computer Game Technology Real-Time Global Illumination Fall 2018 Global Illumination Mirror s Edge (2008) 2 What is Global Illumination? Scene recreates feel of physically-based lighting models
CS354R: Computer Game Technology Real-Time Global Illumination Fall 2018 Global Illumination Mirror s Edge (2008) 2 What is Global Illumination? Scene recreates feel of physically-based lighting models
Computer Graphics. Shadows
 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.
 Shadows Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.com Practical & Robust Stenciled Shadow Volumes for Hardware-Accelerated
Shadows Acknowledgement: Images and many slides from presentations by Mark J. Kilgard and other Nvidia folks, from slides on developer.nvidia.com Practical & Robust Stenciled Shadow Volumes for Hardware-Accelerated
Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering
 Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 1 Why, oh why? (1) Shadows provide cues about spatial relationships among objects 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 2 Why, oh why?
Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 1 Why, oh why? (1) Shadows provide cues about spatial relationships among objects 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 2 Why, oh why?
Chapter 10 Computation Culling with Explicit Early-Z and Dynamic Flow Control
 Chapter 10 Computation Culling with Explicit Early-Z and Dynamic Flow Control Pedro V. Sander ATI Research John R. Isidoro ATI Research Jason L. Mitchell ATI Research Introduction In last year s course,
Chapter 10 Computation Culling with Explicit Early-Z and Dynamic Flow Control Pedro V. Sander ATI Research John R. Isidoro ATI Research Jason L. Mitchell ATI Research Introduction In last year s course,
Advanced Computer Graphics CS 563: Screen Space GI Techniques: Real Time
 Advanced Computer Graphics CS 563: Screen Space GI Techniques: Real Time William DiSanto Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Overview Deferred Shading Ambient Occlusion Screen
Advanced Computer Graphics CS 563: Screen Space GI Techniques: Real Time William DiSanto Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Overview Deferred Shading Ambient Occlusion Screen
Physically-Based Laser Simulation
 Physically-Based Laser Simulation Greg Reshko Carnegie Mellon University reshko@cs.cmu.edu Dave Mowatt Carnegie Mellon University dmowatt@andrew.cmu.edu Abstract In this paper, we describe our work on
Physically-Based Laser Simulation Greg Reshko Carnegie Mellon University reshko@cs.cmu.edu Dave Mowatt Carnegie Mellon University dmowatt@andrew.cmu.edu Abstract In this paper, we describe our work on
SDK White Paper. Soft Shadows
 SDK White Paper Soft Shadows TB-01409-001_v01 July 2004 Abstract This paper describes how Shader Model 3.0 s conditional branching accelerates the computation of soft shadows. Note that you are not generating
SDK White Paper Soft Shadows TB-01409-001_v01 July 2004 Abstract This paper describes how Shader Model 3.0 s conditional branching accelerates the computation of soft shadows. Note that you are not generating
Soft Shadow Maps. Soft Shadow Maps for Linear Lights
 Soft Shadow Maps for Linear Lights (with Stefan Brabec, Hans-Peter Seidel, MPI Informatik) Overview Motivation Soft Shadow Maps Hardware Implementation Sampling the Light Source Results Conclusion 1 Motivation
Soft Shadow Maps for Linear Lights (with Stefan Brabec, Hans-Peter Seidel, MPI Informatik) Overview Motivation Soft Shadow Maps Hardware Implementation Sampling the Light Source Results Conclusion 1 Motivation
What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations. Vienna University of Technology 2
 Shadows What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects Vienna University of Technology 2 What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects And
Shadows What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects Vienna University of Technology 2 What for? Shadows tell us about the relative locations and motions of objects And
Building a Fast Ray Tracer
 Abstract Ray tracing is often used in renderers, as it can create very high quality images at the expense of run time. It is useful because of its ability to solve many different problems in image rendering.
Abstract Ray tracing is often used in renderers, as it can create very high quality images at the expense of run time. It is useful because of its ability to solve many different problems in image rendering.
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes. CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan
 Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
Page 1. Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms
 Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms
 Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Real-Time Shadows. Computer Graphics. MIT EECS Durand 1
 Real-Time Shadows Computer Graphics MIT EECS 6.837 Durand 1 Why are Shadows Important? Depth cue Scene Lighting Realism Contact points 2 Shadows as a Depth Cue source unknown. All rights reserved. This
Real-Time Shadows Computer Graphics MIT EECS 6.837 Durand 1 Why are Shadows Important? Depth cue Scene Lighting Realism Contact points 2 Shadows as a Depth Cue source unknown. All rights reserved. This
Overview. A real-time shadow approach for an Augmented Reality application using shadow volumes. Augmented Reality.
 Overview A real-time shadow approach for an Augmented Reality application using shadow volumes Introduction of Concepts Standard Stenciled Shadow Volumes Method Proposed Approach in AR Application Experimental
Overview A real-time shadow approach for an Augmented Reality application using shadow volumes Introduction of Concepts Standard Stenciled Shadow Volumes Method Proposed Approach in AR Application Experimental
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods. Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
Computergrafik. Matthias Zwicker. Herbst 2010
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2010 Today Bump mapping Shadows Shadow mapping Shadow mapping in OpenGL Bump mapping Surface detail is often the result of small perturbations in
GUERRILLA DEVELOP CONFERENCE JULY 07 BRIGHTON
 Deferred Rendering in Killzone 2 Michal Valient Senior Programmer, Guerrilla Talk Outline Forward & Deferred Rendering Overview G-Buffer Layout Shader Creation Deferred Rendering in Detail Rendering Passes
Deferred Rendering in Killzone 2 Michal Valient Senior Programmer, Guerrilla Talk Outline Forward & Deferred Rendering Overview G-Buffer Layout Shader Creation Deferred Rendering in Detail Rendering Passes
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Today. Why are Shadows Important? Shadows as a Depth Cue. For Intuition about Scene Lighting
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Today Why are Shadows Important? Shadows & Soft Shadows in Ray Tracing Planar Shadows Projective Texture Shadows Shadow Maps Shadow Volumes Why are Shadows Important? Depth
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Today Why are Shadows Important? Shadows & Soft Shadows in Ray Tracing Planar Shadows Projective Texture Shadows Shadow Maps Shadow Volumes Why are Shadows Important? Depth
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion TSBK03: Advanced Game Programming
 Screen Space Ambient Occlusion TSBK03: Advanced Game Programming August Nam-Ki Ek, Oscar Johnson and Ramin Assadi March 5, 2015 This project report discusses our approach of implementing Screen Space Ambient
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion TSBK03: Advanced Game Programming August Nam-Ki Ek, Oscar Johnson and Ramin Assadi March 5, 2015 This project report discusses our approach of implementing Screen Space Ambient
Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows
 Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows Tom Thorne Slides courtesy of Taku Komura www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/cg Overview Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow textures Shadow volume Shadow map Soft
Computer Graphics 10 - Shadows Tom Thorne Slides courtesy of Taku Komura www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/cg Overview Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow textures Shadow volume Shadow map Soft
Applications of Explicit Early-Z Culling
 Applications of Explicit Early-Z Culling Jason L. Mitchell ATI Research Pedro V. Sander ATI Research Introduction In past years, in the SIGGRAPH Real-Time Shading course, we have covered the details of
Applications of Explicit Early-Z Culling Jason L. Mitchell ATI Research Pedro V. Sander ATI Research Introduction In past years, in the SIGGRAPH Real-Time Shading course, we have covered the details of
Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment. Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment
 Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment Screen-space techniques Deferred rendering Screen-space ambient occlusion Depth of Field
Dominic Filion, Senior Engineer Blizzard Entertainment Rob McNaughton, Lead Technical Artist Blizzard Entertainment Screen-space techniques Deferred rendering Screen-space ambient occlusion Depth of Field
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
Shadows. COMP 575/770 Spring 2013
 Shadows COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 Shadows in Ray Tracing Shadows are important for realism Basic idea: figure out whether a point on an object is illuminated by a light source Easy for ray tracers Just
Shadows COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 Shadows in Ray Tracing Shadows are important for realism Basic idea: figure out whether a point on an object is illuminated by a light source Easy for ray tracers Just
Shadows. Real-Time Hard Shadows. Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec
 Shadows Real-Time Hard Shadows Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec Hard Shadows Planar (Projected) Shadows Shadow Maps Volume (Stencil) Shadows 1 Soft Shadows
Shadows Real-Time Hard Shadows Collected by Ronen Gvili. Most slides were taken from : Fredu Durand Stefan Brabec Hard Shadows Planar (Projected) Shadows Shadow Maps Volume (Stencil) Shadows 1 Soft Shadows
Hello, Thanks for the introduction
 Hello, Thanks for the introduction 1 In this paper we suggest an efficient data-structure for precomputed shadows from point light or directional light-sources. Because, in fact, after more than four decades
Hello, Thanks for the introduction 1 In this paper we suggest an efficient data-structure for precomputed shadows from point light or directional light-sources. Because, in fact, after more than four decades
Rendering. Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image. Camera. Light. Rendering. View Plane
 Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
Chapter IV Fragment Processing and Output Merging. 3D Graphics for Game Programming
 Chapter IV Fragment Processing and Output Merging Fragment Processing The per-fragment attributes may include a normal vector, a set of texture coordinates, a set of color values, a depth, etc. Using these
Chapter IV Fragment Processing and Output Merging Fragment Processing The per-fragment attributes may include a normal vector, a set of texture coordinates, a set of color values, a depth, etc. Using these
Real-Time Shadows. André Offringa Timo Laman
 Real-Time Shadows André Offringa Timo Laman Real-Time rendering Radiosity/Raytracing not feasible in real-time applications Scene rendered using projection & scan conversion of polygons Advantage: significant
Real-Time Shadows André Offringa Timo Laman Real-Time rendering Radiosity/Raytracing not feasible in real-time applications Scene rendered using projection & scan conversion of polygons Advantage: significant
Multiview Reconstruction
 Multiview Reconstruction Why More Than 2 Views? Baseline Too short low accuracy Too long matching becomes hard Why More Than 2 Views? Ambiguity with 2 views Camera 1 Camera 2 Camera 3 Trinocular Stereo
Multiview Reconstruction Why More Than 2 Views? Baseline Too short low accuracy Too long matching becomes hard Why More Than 2 Views? Ambiguity with 2 views Camera 1 Camera 2 Camera 3 Trinocular Stereo
Shadow Algorithms. CSE 781 Winter Han-Wei Shen
 Shadow Algorithms CSE 781 Winter 2010 Han-Wei Shen Why Shadows? Makes 3D Graphics more believable Provides additional cues for the shapes and relative positions of objects in 3D What is shadow? Shadow:
Shadow Algorithms CSE 781 Winter 2010 Han-Wei Shen Why Shadows? Makes 3D Graphics more believable Provides additional cues for the shapes and relative positions of objects in 3D What is shadow? Shadow:
3D Rasterization II COS 426
 3D Rasterization II COS 426 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives Modeling Transformation Lighting Viewing Transformation Projection Transformation Clipping Viewport Transformation
3D Rasterization II COS 426 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives Modeling Transformation Lighting Viewing Transformation Projection Transformation Clipping Viewport Transformation
DEFERRED RENDERING STEFAN MÜLLER ARISONA, ETH ZURICH SMA/
 DEFERRED RENDERING STEFAN MÜLLER ARISONA, ETH ZURICH SMA/2013-11-04 DEFERRED RENDERING? CONTENTS 1. The traditional approach: Forward rendering 2. Deferred rendering (DR) overview 3. Example uses of DR:
DEFERRED RENDERING STEFAN MÜLLER ARISONA, ETH ZURICH SMA/2013-11-04 DEFERRED RENDERING? CONTENTS 1. The traditional approach: Forward rendering 2. Deferred rendering (DR) overview 3. Example uses of DR:
Today. Anti-aliasing Surface Parametrization Soft Shadows Global Illumination. Exercise 2. Path Tracing Radiosity
 Today Anti-aliasing Surface Parametrization Soft Shadows Global Illumination Path Tracing Radiosity Exercise 2 Sampling Ray Casting is a form of discrete sampling. Rendered Image: Sampling of the ground
Today Anti-aliasing Surface Parametrization Soft Shadows Global Illumination Path Tracing Radiosity Exercise 2 Sampling Ray Casting is a form of discrete sampling. Rendered Image: Sampling of the ground
Here s the general problem we want to solve efficiently: Given a light and a set of pixels in view space, resolve occlusion between each pixel and
 1 Here s the general problem we want to solve efficiently: Given a light and a set of pixels in view space, resolve occlusion between each pixel and the light. 2 To visualize this problem, consider the
1 Here s the general problem we want to solve efficiently: Given a light and a set of pixels in view space, resolve occlusion between each pixel and the light. 2 To visualize this problem, consider the
Real-Time Shadows. MIT EECS 6.837, Durand and Cutler
 Real-Time Shadows Last Time? The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (two weeks from Thursday)
Real-Time Shadows Last Time? The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Quiz 2: Thursday November 20 th, in class (two weeks from Thursday)
Real-Time Universal Capture Facial Animation with GPU Skin Rendering
 Real-Time Universal Capture Facial Animation with GPU Skin Rendering Meng Yang mengyang@seas.upenn.edu PROJECT ABSTRACT The project implements the real-time skin rendering algorithm presented in [1], and
Real-Time Universal Capture Facial Animation with GPU Skin Rendering Meng Yang mengyang@seas.upenn.edu PROJECT ABSTRACT The project implements the real-time skin rendering algorithm presented in [1], and
Practical Shadow Mapping
 Practical Shadow Mapping Stefan Brabec Thomas Annen Hans-Peter Seidel Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken, Germany Abstract In this paper we propose several methods that can greatly improve
Practical Shadow Mapping Stefan Brabec Thomas Annen Hans-Peter Seidel Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik Saarbrücken, Germany Abstract In this paper we propose several methods that can greatly improve
FRUSTUM-TRACED RASTER SHADOWS: REVISITING IRREGULAR Z-BUFFERS
 FRUSTUM-TRACED RASTER SHADOWS: REVISITING IRREGULAR Z-BUFFERS Chris Wyman, Rama Hoetzlein, Aaron Lefohn 2015 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics & Games CONTRIBUTIONS Full scene, fully dynamic alias-free
FRUSTUM-TRACED RASTER SHADOWS: REVISITING IRREGULAR Z-BUFFERS Chris Wyman, Rama Hoetzlein, Aaron Lefohn 2015 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics & Games CONTRIBUTIONS Full scene, fully dynamic alias-free
Creating soft shadows
 A Hybrid Approach One more shadow algorithm which deserves mention is McCool s clever idea shadow volume reconstruction from depth maps [McCool 2000]. This algorithm is a hybrid of the shadow map and shadow
A Hybrid Approach One more shadow algorithm which deserves mention is McCool s clever idea shadow volume reconstruction from depth maps [McCool 2000]. This algorithm is a hybrid of the shadow map and shadow
Advanced Computer Graphics CS 563: Making Imperfect Shadow Maps View Adaptive. Frederik Clinck lie
 Advanced Computer Graphics CS 563: Making Imperfect Shadow Maps View Adaptive Frederik Clinckemaillie Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Background: Virtual Point Lights Simulates
Advanced Computer Graphics CS 563: Making Imperfect Shadow Maps View Adaptive Frederik Clinckemaillie Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Background: Virtual Point Lights Simulates
Announcements. Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) Computer Graphics
 Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Shear-Warp Volume Rendering. Volume Rendering Overview
 Shear-Warp Volume Rendering R. Daniel Bergeron Department of Computer Science University of New Hampshire Durham, NH 03824 From: Lacroute and Levoy, Fast Volume Rendering Using a Shear-Warp- Factorization
Shear-Warp Volume Rendering R. Daniel Bergeron Department of Computer Science University of New Hampshire Durham, NH 03824 From: Lacroute and Levoy, Fast Volume Rendering Using a Shear-Warp- Factorization
Using Perception-Based Filtering to Hide Shadow Artifacts
 Using Perception-Based Filtering to Hide Shadow Artifacts Felix Kreuzer Supervised by: Michael Hecher Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms TU Wien / Austria Abstract Combining filtering techniques
Using Perception-Based Filtering to Hide Shadow Artifacts Felix Kreuzer Supervised by: Michael Hecher Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms TU Wien / Austria Abstract Combining filtering techniques
Rendering Grass Terrains in Real-Time with Dynamic Lighting. Kévin Boulanger, Sumanta Pattanaik, Kadi Bouatouch August 1st 2006
 Rendering Grass Terrains in Real-Time with Dynamic Lighting Kévin Boulanger, Sumanta Pattanaik, Kadi Bouatouch August 1st 2006 Goal Rendering millions of grass blades, at any distance, in real-time, with:
Rendering Grass Terrains in Real-Time with Dynamic Lighting Kévin Boulanger, Sumanta Pattanaik, Kadi Bouatouch August 1st 2006 Goal Rendering millions of grass blades, at any distance, in real-time, with:
Last Time. Why are Shadows Important? Today. Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization. Why are Shadows Important?
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
SCREEN-SPACE FAR-FIELD AMBIENT OCCLUSION. Ville Timonen
 SCREEN-SPACE FAR-FIELD AMBIENT OCCLUSION Ville Timonen CONTENTS 1. Ambient Occlusion 2. Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion 3. Previous methods 4. Our method 5. Results 2 1 AMBIENT OCCLUSION Components of Light
SCREEN-SPACE FAR-FIELD AMBIENT OCCLUSION Ville Timonen CONTENTS 1. Ambient Occlusion 2. Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion 3. Previous methods 4. Our method 5. Results 2 1 AMBIENT OCCLUSION Components of Light
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Schedule. Questions? Today. Why are Shadows Important?
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Questions? Quiz 2: Thursday November 2 th, in class (two weeks from
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows The graphics pipeline Clipping & rasterization of polygons Visibility the depth buffer (z-buffer) Schedule Questions? Quiz 2: Thursday November 2 th, in class (two weeks from
An Efficient Approach for Emphasizing Regions of Interest in Ray-Casting based Volume Rendering
 An Efficient Approach for Emphasizing Regions of Interest in Ray-Casting based Volume Rendering T. Ropinski, F. Steinicke, K. Hinrichs Institut für Informatik, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster
An Efficient Approach for Emphasizing Regions of Interest in Ray-Casting based Volume Rendering T. Ropinski, F. Steinicke, K. Hinrichs Institut für Informatik, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster
INFOGR Computer Graphics. J. Bikker - April-July Lecture 10: Ground Truth. Welcome!
 INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2015 - Lecture 10: Ground Truth Welcome! Today s Agenda: Limitations of Whitted-style Ray Tracing Monte Carlo Path Tracing INFOGR Lecture 10 Ground Truth
INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2015 - Lecture 10: Ground Truth Welcome! Today s Agenda: Limitations of Whitted-style Ray Tracing Monte Carlo Path Tracing INFOGR Lecture 10 Ground Truth
Today. Texture mapping in OpenGL. Texture mapping. Basic shaders for texturing. Today. Computergrafik
 Computergrafik Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Texture mapping Glue textures (images) onto
Computergrafik Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Texture mapping Glue textures (images) onto
Lecture 17: Shadows. Projects. Why Shadows? Shadows. Using the Shadow Map. Shadow Maps. Proposals due today. I will mail out comments
 Projects Lecture 17: Shadows Proposals due today I will mail out comments Fall 2004 Kavita Bala Computer Science Cornell University Grading HW 1: will email comments asap Why Shadows? Crucial for spatial
Projects Lecture 17: Shadows Proposals due today I will mail out comments Fall 2004 Kavita Bala Computer Science Cornell University Grading HW 1: will email comments asap Why Shadows? Crucial for spatial
Textures. Texture coordinates. Introduce one more component to geometry
 Texturing & Blending Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides by Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Textures Rendering tiny triangles
Texturing & Blending Prof. Aaron Lanterman (Based on slides by Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Textures Rendering tiny triangles
Image Base Rendering: An Introduction
 Image Base Rendering: An Introduction Cliff Lindsay CS563 Spring 03, WPI 1. Introduction Up to this point, we have focused on showing 3D objects in the form of polygons. This is not the only approach to
Image Base Rendering: An Introduction Cliff Lindsay CS563 Spring 03, WPI 1. Introduction Up to this point, we have focused on showing 3D objects in the form of polygons. This is not the only approach to
Advanced Shading and Texturing
 Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Advanced Shading and Texturing 1 Topics Features Bump mapping Environment mapping Shadow
Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Advanced Shading and Texturing 1 Topics Features Bump mapping Environment mapping Shadow
Render-To-Texture Caching. D. Sim Dietrich Jr.
 Render-To-Texture Caching D. Sim Dietrich Jr. What is Render-To-Texture Caching? Pixel shaders are becoming more complex and expensive Per-pixel shadows Dynamic Normal Maps Bullet holes Water simulation
Render-To-Texture Caching D. Sim Dietrich Jr. What is Render-To-Texture Caching? Pixel shaders are becoming more complex and expensive Per-pixel shadows Dynamic Normal Maps Bullet holes Water simulation
FRUSTUM-TRACED RASTER SHADOWS: REVISITING IRREGULAR Z-BUFFERS
 FRUSTUM-TRACED RASTER SHADOWS: REVISITING IRREGULAR Z-BUFFERS Chris Wyman, Rama Hoetzlein, Aaron Lefohn 2015 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics & Games CONTRIBUTIONS Full scene, fully dynamic alias-free
FRUSTUM-TRACED RASTER SHADOWS: REVISITING IRREGULAR Z-BUFFERS Chris Wyman, Rama Hoetzlein, Aaron Lefohn 2015 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics & Games CONTRIBUTIONS Full scene, fully dynamic alias-free
SAMPLING AND NOISE. Increasing the number of samples per pixel gives an anti-aliased image which better represents the actual scene.
 SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
Dynamic Reconstruction for Coded Aperture Imaging Draft Unpublished work please do not cite or distribute.
 Dynamic Reconstruction for Coded Aperture Imaging Draft 1.0.1 Berthold K.P. Horn 2007 September 30. Unpublished work please do not cite or distribute. The dynamic reconstruction technique makes it possible
Dynamic Reconstruction for Coded Aperture Imaging Draft 1.0.1 Berthold K.P. Horn 2007 September 30. Unpublished work please do not cite or distribute. The dynamic reconstruction technique makes it possible
Soft Shadows. Michael Schwarz
 Soft Shadows Michael Schwarz Hard Shadows Umbra Completely lit Soft Shadows Umbra Penumbra Completely lit Shadow Hardening on Contact Shadowing = Point Region Visibility Task: For each receiver sample
Soft Shadows Michael Schwarz Hard Shadows Umbra Completely lit Soft Shadows Umbra Penumbra Completely lit Shadow Hardening on Contact Shadowing = Point Region Visibility Task: For each receiver sample
For Intuition about Scene Lighting. Today. Limitations of Planar Shadows. Cast Shadows on Planar Surfaces. Shadow/View Duality.
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion
 TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion Joakim Gebart, Jimmy Liikala December 15, 2013 Contents 1 Abstract 1 2 History 2 2.1 Crysis method..................................... 2 3 Chosen method 2 3.1 Algorithm
TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion Joakim Gebart, Jimmy Liikala December 15, 2013 Contents 1 Abstract 1 2 History 2 2.1 Crysis method..................................... 2 3 Chosen method 2 3.1 Algorithm
EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics
 Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
Computergrafik. Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016 2 Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures 3 Texture mapping Glue textures (images)
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016 2 Today Basic shader for texture mapping Texture coordinate assignment Antialiasing Fancy textures 3 Texture mapping Glue textures (images)
Accelerated Ambient Occlusion Using Spatial Subdivision Structures
 Abstract Ambient Occlusion is a relatively new method that gives global illumination like results. This paper presents a method to accelerate ambient occlusion using the form factor method in Bunnel [2005]
Abstract Ambient Occlusion is a relatively new method that gives global illumination like results. This paper presents a method to accelerate ambient occlusion using the form factor method in Bunnel [2005]
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing. Schedule. Today. Shadows & Light Sources. Shadows
 Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion
Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion
Layered Variance Shadow Maps
 Layered Variance Shadow Maps Andrew Lauritzen Michael McCool Computer Graphics Lab, David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science, University of Waterloo Figure 1: Comparison of regular variance shadow
Layered Variance Shadow Maps Andrew Lauritzen Michael McCool Computer Graphics Lab, David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science, University of Waterloo Figure 1: Comparison of regular variance shadow
A Shadow Volume Algorithm for Opaque and Transparent Non-Manifold Casters
 jgt 2008/7/20 22:19 page 1 #1 Vol. [VOL], No. [ISS]: 1?? A Shadow Volume Algorithm for Opaque and Transparent Non-Manifold Casters Byungmoon Kim 1, Kihwan Kim 2, Greg Turk 2 1 NVIDIA, 2 Georgia Institute
jgt 2008/7/20 22:19 page 1 #1 Vol. [VOL], No. [ISS]: 1?? A Shadow Volume Algorithm for Opaque and Transparent Non-Manifold Casters Byungmoon Kim 1, Kihwan Kim 2, Greg Turk 2 1 NVIDIA, 2 Georgia Institute
Advanced Ray Tracing
 Advanced Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler The Ray Tree Ni surface normal Ri reflected ray Li shadow ray Ti transmitted (refracted) ray 51 MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Ray Tree
Advanced Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler The Ray Tree Ni surface normal Ri reflected ray Li shadow ray Ti transmitted (refracted) ray 51 MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Ray Tree
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
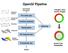 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
Enabling immersive gaming experiences Intro to Ray Tracing
 Enabling immersive gaming experiences Intro to Ray Tracing Overview What is Ray Tracing? Why Ray Tracing? PowerVR Wizard Architecture Example Content Unity Hybrid Rendering Demonstration 3 What is Ray
Enabling immersive gaming experiences Intro to Ray Tracing Overview What is Ray Tracing? Why Ray Tracing? PowerVR Wizard Architecture Example Content Unity Hybrid Rendering Demonstration 3 What is Ray
Enhancing Traditional Rasterization Graphics with Ray Tracing. March 2015
 Enhancing Traditional Rasterization Graphics with Ray Tracing March 2015 Introductions James Rumble Developer Technology Engineer Ray Tracing Support Justin DeCell Software Design Engineer Ray Tracing
Enhancing Traditional Rasterization Graphics with Ray Tracing March 2015 Introductions James Rumble Developer Technology Engineer Ray Tracing Support Justin DeCell Software Design Engineer Ray Tracing
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Ray Tracing. Computer Graphics CMU /15-662, Fall 2016
 Ray Tracing Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Primitive-partitioning vs. space-partitioning acceleration structures Primitive partitioning (bounding volume hierarchy): partitions node s primitives
Ray Tracing Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Primitive-partitioning vs. space-partitioning acceleration structures Primitive partitioning (bounding volume hierarchy): partitions node s primitives
Gaël Guennebaud Loïc Barthe, Mathias Paulin IRIT UPS CNRS TOULOUSE FRANCE Gaël Guennebaud Cyprus June 2006
 Real-time Soft Shadow Mapping by back-projection Gaël Guennebaud Loïc Barthe, Mathias Paulin IRIT UPS CNRS TOULOUSE FRANCE http://www.irit.fr/~gael.guennebaud/ 1 Hard Shadows light source Is the light
Real-time Soft Shadow Mapping by back-projection Gaël Guennebaud Loïc Barthe, Mathias Paulin IRIT UPS CNRS TOULOUSE FRANCE http://www.irit.fr/~gael.guennebaud/ 1 Hard Shadows light source Is the light
An Optimized Soft Shadow Volume Algorithm with Real-Time Performance
 Graphics Hardware (2003) M. Doggett, W. Heidrich, W. Mark, A. Schilling (Editors) An Optimized Soft Shadow Volume Algorithm with Real-Time Performance Ulf Assarsson, 1 Michael Dougherty, 2 Michael Mounier,
Graphics Hardware (2003) M. Doggett, W. Heidrich, W. Mark, A. Schilling (Editors) An Optimized Soft Shadow Volume Algorithm with Real-Time Performance Ulf Assarsson, 1 Michael Dougherty, 2 Michael Mounier,
Real-Time Shadows. Last Time? Textures can Alias. Schedule. Questions? Quiz 1: Tuesday October 26 th, in class (1 week from today!
 Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
Last Time? Real-Time Shadows Perspective-Correct Interpolation Texture Coordinates Procedural Solid Textures Other Mapping Bump Displacement Environment Lighting Textures can Alias Aliasing is the under-sampling
FAST SELF-SHADOWING USING OCCLUDER TEXTURES. A Thesis CHRISTOPHER RYAN COLEMAN
 FAST SELF-SHADOWING USING OCCLUDER TEXTURES A Thesis by CHRISTOPHER RYAN COLEMAN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
FAST SELF-SHADOWING USING OCCLUDER TEXTURES A Thesis by CHRISTOPHER RYAN COLEMAN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students)
 TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
Projective Shadows. D. Sim Dietrich Jr.
 Projective Shadows D. Sim Dietrich Jr. Topics Projective Shadow Types Implementation on DirectX 7 HW Implementation on DirectX8 HW Integrating Shadows into an engine Types of Projective Shadows Static
Projective Shadows D. Sim Dietrich Jr. Topics Projective Shadow Types Implementation on DirectX 7 HW Implementation on DirectX8 HW Integrating Shadows into an engine Types of Projective Shadows Static
Interactive Volumetric Shadows in Participating Media with Single-Scattering
 Interactive Volumetric Shadows in Participating Media with Single-Scattering Chris Wyman University of Iowa Shaun Ramsey Washington College IEEE Symposium on Interactive Ray Tracing 2008 What is Volumetric
Interactive Volumetric Shadows in Participating Media with Single-Scattering Chris Wyman University of Iowa Shaun Ramsey Washington College IEEE Symposium on Interactive Ray Tracing 2008 What is Volumetric
Last Time. Reading for Today: Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
Soft Shadows: Heckbert & Herf. Soft shadows. Heckbert & Herf Soft Shadows. Cornell University CS 569: Interactive Computer Graphics.
 Soft Shadows: Heckbert & Herf Soft shadows [Michael Herf and Paul Heckbert] Cornell University CS 569: Interactive Computer Graphics Figure : Hard shadow images from 2 2 grid of sample points on light
Soft Shadows: Heckbert & Herf Soft shadows [Michael Herf and Paul Heckbert] Cornell University CS 569: Interactive Computer Graphics Figure : Hard shadow images from 2 2 grid of sample points on light
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Shadow Volumes Revisited
 Shadow Volumes Revisited Stefan Roettger, Alexander Irion, and Thomas Ertl University of Stuttgart, Faculty of Computer Science Visualization and Interactive Systems Group! ABSTRACT We present a method
Shadow Volumes Revisited Stefan Roettger, Alexander Irion, and Thomas Ertl University of Stuttgart, Faculty of Computer Science Visualization and Interactive Systems Group! ABSTRACT We present a method
Hardware-driven visibility culling
 Hardware-driven visibility culling I. Introduction 20073114 김정현 The goal of the 3D graphics is to generate a realistic and accurate 3D image. To achieve this, it needs to process not only large amount
Hardware-driven visibility culling I. Introduction 20073114 김정현 The goal of the 3D graphics is to generate a realistic and accurate 3D image. To achieve this, it needs to process not only large amount
Hard Shadows Aliasing and Remedies
 Hard Shadows Aliasing and Remedies Michael Wimmer www.realtimeshadows.com Shadow Map as Signal Reconstruction Initial sampling: shadow-map rendering Resampling: determined by view Reconstruction: nearest
Hard Shadows Aliasing and Remedies Michael Wimmer www.realtimeshadows.com Shadow Map as Signal Reconstruction Initial sampling: shadow-map rendering Resampling: determined by view Reconstruction: nearest
CS 130 Final. Fall 2015
 CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
High-quality Shadows with Improved Paraboloid Mapping
 High-quality Shadows with Improved Paraboloid Mapping Juraj Vanek, Jan Navrátil, Adam Herout, and Pavel Zemčík Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology, Czech Republic http://www.fit.vutbr.cz
High-quality Shadows with Improved Paraboloid Mapping Juraj Vanek, Jan Navrátil, Adam Herout, and Pavel Zemčík Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology, Czech Republic http://www.fit.vutbr.cz
CSM Scrolling: An acceleration technique for the rendering of cascaded shadow maps
 CSM Scrolling: An acceleration technique for the rendering of cascaded shadow maps Abstract This talk will explain how a bitmap-scrolling technique can be combined with a shadow map caching scheme to significantly
CSM Scrolling: An acceleration technique for the rendering of cascaded shadow maps Abstract This talk will explain how a bitmap-scrolling technique can be combined with a shadow map caching scheme to significantly
