SHOW ALL NEEDED WORK IN YOUR NOTEBOOK.
|
|
|
- Brett Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DO NOW: 1 3: NO CALCULATORS 1. Consider the function f () x the value of f (4.1)? SHOW ALL NEEDED WORK IN YOUR NOTEBOOK. x. We all know that f (4), but without a calculator, what is
2 . The approximate value of y 4 sin() x at x 0.1, obtained from the tangent to the graph at x 0, is A..00 B..03 C..06 D..1 E..4
3 3. For small values of h, the function 4 16 h is best approximated by which of the following? A. 4 3 h B. 3 h C. h 3 h h D. 4 E. 3 3
4 4: CALCULATOR NEEDED 4. Let f be the function given by f () x x x 3. The tangent line to the graph of f at x is used to approximate the values of f () x. Which of the following is the greatest value for which the error resulting from this tangent line approximation is less than 0.5? A..4 B..5 C..6 D..7 E..8
5 DIFFERENTIALS Approximations aren t exact! (Aren t you glad you woke up this morning to hear that enlightening bit of information?!) If we use a line to approximate a curve, it gives us a good estimate, as long as we don t go too far away from the center point. Wouldn t be nice if we knew how far off our approximation is going to be? Well, whether you are excited about this or not, here we go!
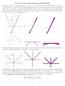
6 Let s consider the function f(x) to the right, and the corresponding tangent line at the point with coordinates (c, f(c)). y If we want to approximate the value of f(x) for values of x close enough to x we may use the tangent line for such approximation. Equation of the Tangent Line at (c, f(c)) y f ()() c m x c ' y f ()()() c f c x c x y f ' ()()() c x c f c The tangent line is the graph is the graph of the Linear Function ' L()()()() x f c x c f c For as long as the line remains close to the graph of f, L(x) gives a good approximation of f(x). DEFINITION: Linearization If f is differentiable at x = c, then the approximating function ' L()()()() x f c x c f c Is the linearization of f(x) at x=c. Example #1: Find the linearization of f () x 1 x at x = 0.
7
8 Example #: Find the linearization of f () x 1 x k at x = 0, for any constant k.
9 Example #3: Find the linearization of f () x cos() x at x
10 Example #4: Consider the function f below. Label the point c,() f c, and draw the tangent line at that point. y x a) What is the equation of the tangent line you drew? Keep in mind this is just a linearization of the curve. Move a small distance to the right of c. Normally, we would call this distance x is very small, we will instead use the notation dx, the differential of x. b) What is the function value at this point (when x c dx )? x, but when c) What is the value of this point on the tangent line (when x c dx )? d) How much did the y-values ACTUALLY change? e) How much did the y-values APPROXIMATELY change? (This is called dy the differential in y) In other words, if we were to use any value of x, the approximate change in y after a small change in x would be written This should look VERY familiar dy f ' () x dx
11 What differentials allow us to do is to say that if the ration of the differentials exists, it will be equal to the derivative. It allows us to write dy as the derivative of y with respect to x, but use the dy and dx dx as separate terms. Example #5: Find the differential dy if 3 y x 5x
12 Example #6: Find d cos(5) x.
13 Example #7: Since dy is the approximate change in the y-values when x is changed a small amount, we can use differentials to estimate the change in other problems if we know the small change in x. a) Find the differential dy when dx 0.01 and x, if y x x EXPLAIN what you ve found. b) Find the differential dy when dx 0. and x 1, if y x sin() x. EXPLAIN what you ve found. c) Without a calculator, use differentials to approximate 4..
14 NEWTON S METHOD Let s find a root for f x x 3 (between and 3) STEP 1 9 f (3) (3,1.5) ' f () x x ' f ( 3) 3 m 3 y 1.5 3( x 3) y 3x y 3x x 7. 5 Finding the y-int. for the tangent line, to be used as the new approximation for the root 7.5 x 3 x. 5 STEP 6.5 f (.5) (.5, 0.15) ' f () x x ' f (.5).5 m.5 y ( x.5) y.5x y.5x x 6.15 Finding the y-int. for the tangent line, to be used as the new approximation for the root 6.15 x.5 x.45
15 STEP f (.45) (.45, ) ' f () x x ' f (.45).45 m.45 y ( x.45) y.45x y.45x x Finding the y-int. for the tangent line, to be used as the new approximation for the root x.45 x
16 Newton s Method: x x f n 1 n f x x n n Example 8:
17 Example 9: Use the Newton s Method to solve x 3 3x 1 0.
18 CLASSWORK: V, where V 0 is the initial velocity in feet per 3 second and is the angle of elevation. If V 0 = 00 feet per second and changed from 10 to 11, use differentials to approximate the change in the range The range R of a projectile is R sin()
19 . The measurement of a side of a square is found to be 15 centimeters. The possible error in measuring the side is 0.05 centimeter. a) Approximate the percent error in computing the area of the square. b) Estimate the maximum allowable percent error in measuring the side if the error in computing the area cannot exceed.5%. c) Find the error.
20 3. A surveyor standing 50 feet from the base of a large tree measures the angle of elevation to the top of the tree as How accurately must the angle be measured if the percent error in estimating the height of the tree is to be less than 6%?
21
First of all, we need to know what it means for a parameterize curve to be differentiable. FACT:
 CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
Direction Fields; Euler s Method
 Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials
 2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
Differentiation. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem 10/9/2014. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Differentiation Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Find the slope of the tangent
Differentiation Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Find the slope of the tangent
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
Euler s Method for Approximating Solution Curves
 Euler s Method for Approximating Solution Curves As you may have begun to suspect at this point, time constraints will allow us to learn only a few of the many known methods for solving differential equations.
Euler s Method for Approximating Solution Curves As you may have begun to suspect at this point, time constraints will allow us to learn only a few of the many known methods for solving differential equations.
3.1 Maxima/Minima Values
 3.1 Maxima/Minima Values Ex 1: Find all critical points for the curve given by f (x)=x 5 25 3 x3 +20x 1 on the interval [-3, 2]. Identify the min and max values. We're guaranteed max and min points if
3.1 Maxima/Minima Values Ex 1: Find all critical points for the curve given by f (x)=x 5 25 3 x3 +20x 1 on the interval [-3, 2]. Identify the min and max values. We're guaranteed max and min points if
THS Step By Step Calculus Chapter 3
 Name: Class Period: Throughout this packet there will be blanks you are expected to fill in prior to coming to class. This packet follows your Larson Textbook. Do NOT throw away! Keep in 3 ring-binder
Name: Class Period: Throughout this packet there will be blanks you are expected to fill in prior to coming to class. This packet follows your Larson Textbook. Do NOT throw away! Keep in 3 ring-binder
WJEC LEVEL 2 CERTIFICATE 9550/01 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number WJEC LEVEL 2 CERTIFICATE 9550/01 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS A.M. MONDAY, 24 June 2013 2 1 hours 2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A calculator will be required for
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number WJEC LEVEL 2 CERTIFICATE 9550/01 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS A.M. MONDAY, 24 June 2013 2 1 hours 2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A calculator will be required for
Tangent Lines and Linear Approximations Solutions
 Solutions We have intentionally included more material than can be covered in most Student Study Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions at a faster rate. Use your own judgment,
Solutions We have intentionally included more material than can be covered in most Student Study Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions at a faster rate. Use your own judgment,
Quiz 6 Practice Problems
 Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Math 126 Winter CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems.
 Math 126 Winter 2016 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems. This exam is closed book. You may use one 8 1 11 sheet of hand-written
Math 126 Winter 2016 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name CHECK that your exam contains 8 problems. This exam is closed book. You may use one 8 1 11 sheet of hand-written
Final Exam Review Algebra Semester 1
 Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes
 1 of 11 1) Give f(g(1)), given that Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes 2) Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f at x = 4, given that 3) Determine
1 of 11 1) Give f(g(1)), given that Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes 2) Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f at x = 4, given that 3) Determine
Problem #3 Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page Mark Sparks 2012
 Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
During the timed portion for Part A, you may work only on the problems in Part A.
 SECTION II Time: hour and 30 minutes Percent of total grade: 50 Part A: 45 minutes, 3 problems (A graphing calculator is required for some problems or parts of problems.) During the timed portion for Part
SECTION II Time: hour and 30 minutes Percent of total grade: 50 Part A: 45 minutes, 3 problems (A graphing calculator is required for some problems or parts of problems.) During the timed portion for Part
The Straight Line. m is undefined. Use. Show that mab
 The Straight Line What is the gradient of a horizontal line? What is the equation of a horizontal line? So the equation of the x-axis is? What is the gradient of a vertical line? What is the equation of
The Straight Line What is the gradient of a horizontal line? What is the equation of a horizontal line? So the equation of the x-axis is? What is the gradient of a vertical line? What is the equation of
MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2015 Exam 2 Tuesday, 20 October Multiple Choice Answers. Question
 MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2015 Exam 2 Tuesday, 20 October 2015 Name: Section: Last digits of student ID #: This exam has ten multiple choice questions (five points each) and five free response questions (ten
MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2015 Exam 2 Tuesday, 20 October 2015 Name: Section: Last digits of student ID #: This exam has ten multiple choice questions (five points each) and five free response questions (ten
HSC Mathematics - Extension 1. Workshop E2
 HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
PRACTICE FINAL - MATH 1210, Spring 2012 CHAPTER 1
 PRACTICE FINAL - MATH 2, Spring 22 The Final will have more material from Chapter 4 than other chapters. To study for chapters -3 you should review the old practice eams IN ADDITION TO what appears here.
PRACTICE FINAL - MATH 2, Spring 22 The Final will have more material from Chapter 4 than other chapters. To study for chapters -3 you should review the old practice eams IN ADDITION TO what appears here.
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), Goals. Warm-up: Differentiability. Notes. Notes.
 The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
MEI GeoGebra Tasks for A2 Core
 Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function 1. Plot the graph of y = x : use y = x or y = abs(x) 2. Plot the graph of y = ax+b : use y = ax + b or y = abs(ax+b) If prompted click Create Sliders. What combination
Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function 1. Plot the graph of y = x : use y = x or y = abs(x) 2. Plot the graph of y = ax+b : use y = ax + b or y = abs(ax+b) If prompted click Create Sliders. What combination
Derivatives. Day 8 - Tangents and Linearizations
 Derivatives Day 8 - Tangents and Linearizations Learning Objectives Write an equation for the tangent line to a graph Write an equation for the normal line to a graph Find the locations of horizontal and
Derivatives Day 8 - Tangents and Linearizations Learning Objectives Write an equation for the tangent line to a graph Write an equation for the normal line to a graph Find the locations of horizontal and
f xx (x, y) = 6 + 6x f xy (x, y) = 0 f yy (x, y) = y In general, the quantity that we re interested in is
 1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule
 Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
Math 21a Tangent Lines and Planes Fall, What do we know about the gradient f? Tangent Lines to Curves in the Plane.
 Math 21a Tangent Lines and Planes Fall, 2016 What do we know about the gradient f? Tangent Lines to Curves in the Plane. 1. For each of the following curves, find the tangent line to the curve at the point
Math 21a Tangent Lines and Planes Fall, 2016 What do we know about the gradient f? Tangent Lines to Curves in the Plane. 1. For each of the following curves, find the tangent line to the curve at the point
minutes/question 26 minutes
 st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Precalculus CP Final Exam Review - 01 Name Date: / / MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Convert the angle in degrees to radians. Express
Precalculus CP Final Exam Review - 01 Name Date: / / MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Convert the angle in degrees to radians. Express
MEI Casio Tasks for A2 Core
 Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function The modulus function, abs(x), is found using OPTN > NUMERIC > Abs 2. Add the graph y = x, Y1=Abs(x): iyqfl 3. Add the graph y = ax+b, Y2=Abs(Ax+B): iyqaff+agl 4.
Task 1: Functions The Modulus Function The modulus function, abs(x), is found using OPTN > NUMERIC > Abs 2. Add the graph y = x, Y1=Abs(x): iyqfl 3. Add the graph y = ax+b, Y2=Abs(Ax+B): iyqaff+agl 4.
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations
 27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
Part I. Problems in this section are mostly short answer and multiple choice. Little partial credit will be given. 5 points each.
 Math 106/108 Final Exam Page 1 Part I. Problems in this section are mostly short answer and multiple choice. Little partial credit will be given. 5 points each. 1. Factor completely. Do not solve. a) 2x
Math 106/108 Final Exam Page 1 Part I. Problems in this section are mostly short answer and multiple choice. Little partial credit will be given. 5 points each. 1. Factor completely. Do not solve. a) 2x
`Three sides of a 500 square foot rectangle are fenced. Express the fence s length f as a function of height x.
 Math 140 Lecture 9 See inside text s front cover for area and volume formulas Classwork, remember units Don t just memorize steps, try to understand instead If you understand, every test problem will be
Math 140 Lecture 9 See inside text s front cover for area and volume formulas Classwork, remember units Don t just memorize steps, try to understand instead If you understand, every test problem will be
PRECALCULUS MATH Trigonometry 9-12
 1. Find angle measurements in degrees and radians based on the unit circle. 1. Students understand the notion of angle and how to measure it, both in degrees and radians. They can convert between degrees
1. Find angle measurements in degrees and radians based on the unit circle. 1. Students understand the notion of angle and how to measure it, both in degrees and radians. They can convert between degrees
Surfaces and Partial Derivatives
 Surfaces and Partial Derivatives James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 9, 2016 Outline Partial Derivatives Tangent Planes
Surfaces and Partial Derivatives James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 9, 2016 Outline Partial Derivatives Tangent Planes
MEI Desmos Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
2. Suppose we drew many tangent lines for this second curve. How do the slopes of these tangent lines change as we look from left to right?
 Do now as a warm up: 1. Suppose we drew many tangent lines for this first curve. How do the slopes of these tangent lines change as we look from left to right? 2. Suppose we drew many tangent lines for
Do now as a warm up: 1. Suppose we drew many tangent lines for this first curve. How do the slopes of these tangent lines change as we look from left to right? 2. Suppose we drew many tangent lines for
Pure Math 30: Explained!
 www.puremath30.com 30 part i: stretches about other lines Stretches about other lines: Stretches about lines other than the x & y axis are frequently required. Example 1: Stretch the graph horizontally
www.puremath30.com 30 part i: stretches about other lines Stretches about other lines: Stretches about lines other than the x & y axis are frequently required. Example 1: Stretch the graph horizontally
Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4:
 Announcements Topics: In the Functions of Several Variables module: - Section 1: Introduction to Functions of Several Variables (Basic Definitions and Notation) - Section 2: Graphs, Level Curves + Contour
Announcements Topics: In the Functions of Several Variables module: - Section 1: Introduction to Functions of Several Variables (Basic Definitions and Notation) - Section 2: Graphs, Level Curves + Contour
Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test
 Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test I. Solving quadratic equations (LT 4.2, 4.3, 4.4) Key Facts To factor a polynomial, first factor out any common factors, then use the box method to factor the quadratic.
Review for Quarter 3 Cumulative Test I. Solving quadratic equations (LT 4.2, 4.3, 4.4) Key Facts To factor a polynomial, first factor out any common factors, then use the box method to factor the quadratic.
Objectives. Materials
 Activity 6 Local Linearity, Differentiability, and Limits of Difference Quotients Objectives Connect the concept of local linearity to differentiability through numerical explorations of limits of difference
Activity 6 Local Linearity, Differentiability, and Limits of Difference Quotients Objectives Connect the concept of local linearity to differentiability through numerical explorations of limits of difference
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
Math 113 Exam 1 Practice
 Math Exam Practice January 6, 00 Exam will cover sections 6.-6.5 and 7.-7.5 This sheet has three sections. The first section will remind you about techniques and formulas that you should know. The second
Math Exam Practice January 6, 00 Exam will cover sections 6.-6.5 and 7.-7.5 This sheet has three sections. The first section will remind you about techniques and formulas that you should know. The second
C3 Numerical methods
 Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
Verulam School C3 Numerical methods 138 min 108 marks 1. (a) The diagram shows the curve y =. The region R, shaded in the diagram, is bounded by the curve and by the lines x = 1, x = 5 and y = 0. The region
Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables
 Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April 4, 2014 Outline 1 Continuity
Continuity and Tangent Lines for functions of two variables James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April 4, 2014 Outline 1 Continuity
Parametric Surfaces. Substitution
 Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Sec.4.1 Increasing and Decreasing Functions
 U4L1: Sec.4.1 Increasing and Decreasing Functions A function is increasing on a particular interval if for any, then. Ie: As x increases,. A function is decreasing on a particular interval if for any,
U4L1: Sec.4.1 Increasing and Decreasing Functions A function is increasing on a particular interval if for any, then. Ie: As x increases,. A function is decreasing on a particular interval if for any,
Unit 7: Trigonometry Part 1
 100 Unit 7: Trigonometry Part 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Hypotenuse a) Sine sin( α ) = d) Cosecant csc( α ) = α Adjacent Opposite b) Cosine cos( α ) = e) Secant sec( α ) = c) Tangent f) Cotangent tan(
100 Unit 7: Trigonometry Part 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Hypotenuse a) Sine sin( α ) = d) Cosecant csc( α ) = α Adjacent Opposite b) Cosine cos( α ) = e) Secant sec( α ) = c) Tangent f) Cotangent tan(
while its direction is given by the right hand rule: point fingers of the right hand in a 1 a 2 a 3 b 1 b 2 b 3 A B = det i j k
 I.f Tangent Planes and Normal Lines Again we begin by: Recall: (1) Given two vectors A = a 1 i + a 2 j + a 3 k, B = b 1 i + b 2 j + b 3 k then A B is a vector perpendicular to both A and B. Then length
I.f Tangent Planes and Normal Lines Again we begin by: Recall: (1) Given two vectors A = a 1 i + a 2 j + a 3 k, B = b 1 i + b 2 j + b 3 k then A B is a vector perpendicular to both A and B. Then length
Surfaces and Partial Derivatives
 Surfaces and James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 15, 2017 Outline 1 2 Tangent Planes Let s go back to our simple surface
Surfaces and James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 15, 2017 Outline 1 2 Tangent Planes Let s go back to our simple surface
4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS
 4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS 4. Equation of the Tangent at a Point Recall that the slope of a curve at a point is the slope of the tangent at that point. The slope of the tangent is the value of the derivative
4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS 4. Equation of the Tangent at a Point Recall that the slope of a curve at a point is the slope of the tangent at that point. The slope of the tangent is the value of the derivative
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV. Exam I (Friday, April 29) will cover sections
 REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
AP Calculus AB Unit 2 Assessment
 Class: Date: 203-204 AP Calculus AB Unit 2 Assessment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. A calculator may NOT be used on this part of the exam.
Class: Date: 203-204 AP Calculus AB Unit 2 Assessment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. A calculator may NOT be used on this part of the exam.
7-5 Parametric Equations
 3. Sketch the curve given by each pair of parametric equations over the given interval. Make a table of values for 6 t 6. t x y 6 19 28 5 16.5 17 4 14 8 3 11.5 1 2 9 4 1 6.5 7 0 4 8 1 1.5 7 2 1 4 3 3.5
3. Sketch the curve given by each pair of parametric equations over the given interval. Make a table of values for 6 t 6. t x y 6 19 28 5 16.5 17 4 14 8 3 11.5 1 2 9 4 1 6.5 7 0 4 8 1 1.5 7 2 1 4 3 3.5
Solution 2. ((3)(1) (2)(1), (4 3), (4)(2) (3)(3)) = (1, 1, 1) D u (f) = (6x + 2yz, 2y + 2xz, 2xy) (0,1,1) = = 4 14
 Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Detailed instructions for video analysis using Logger Pro.
 Detailed instructions for video analysis using Logger Pro. 1. Begin by locating or creating a video of a projectile (or any moving object). Save it to your computer. Most video file types are accepted,
Detailed instructions for video analysis using Logger Pro. 1. Begin by locating or creating a video of a projectile (or any moving object). Save it to your computer. Most video file types are accepted,
d f(g(t), h(t)) = x dt + f ( y dt = 0. Notice that we can rewrite the relationship on the left hand side of the equality using the dot product: ( f
 Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
Gradients and the Directional Derivative In 14.3, we discussed the partial derivatives f f and, which tell us the rate of change of the x y height of the surface defined by f in the x direction and the
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6. ) is graphed below:
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
13.1. Functions of Several Variables. Introduction to Functions of Several Variables. Functions of Several Variables. Objectives. Example 1 Solution
 13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
13 Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Understand
Polar (BC Only) They are necessary to find the derivative of a polar curve in x- and y-coordinates. The derivative
 Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
Practice Set 44 Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions
 Practice Set Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions No Calculator Objectives Simplify trigonometric expression using the fundamental trigonometric identities Use the trigonometric co-function identities
Practice Set Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions No Calculator Objectives Simplify trigonometric expression using the fundamental trigonometric identities Use the trigonometric co-function identities
Assignment. Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons Determine whether each pair of polygons is similar. If necessary, write the similarity statement. Determine
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons Determine whether each pair of polygons is similar. If necessary, write the similarity statement. Determine
Exam 1 Review. MATH Intuitive Calculus Fall Name:. Show your reasoning. Use standard notation correctly.
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2012 Name:. Exam 1 Review Show your reasoning. Use standard notation correctly. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following (or
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2012 Name:. Exam 1 Review Show your reasoning. Use standard notation correctly. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following (or
Education Resources. This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
 Education Resources Trigonometry Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
Education Resources Trigonometry Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
MATH EXAM 1 - SPRING 2018 SOLUTION
 MATH 140 - EXAM 1 - SPRING 018 SOLUTION 8 February 018 Instructor: Tom Cuchta Instructions: Show all work, clearly and in order, if you want to get full credit. If you claim something is true you must
MATH 140 - EXAM 1 - SPRING 018 SOLUTION 8 February 018 Instructor: Tom Cuchta Instructions: Show all work, clearly and in order, if you want to get full credit. If you claim something is true you must
Topic 2.3: Tangent Planes, Differentiability, and Linear Approximations. Textbook: Section 14.4
 Topic 2.3: Tangent Planes, Differentiability, and Linear Approximations Textbook: Section 14.4 Warm-Up: Graph the Cone & the Paraboloid paraboloid f (x, y) = x 2 + y 2 cone g(x, y) = x 2 + y 2 Do you notice
Topic 2.3: Tangent Planes, Differentiability, and Linear Approximations Textbook: Section 14.4 Warm-Up: Graph the Cone & the Paraboloid paraboloid f (x, y) = x 2 + y 2 cone g(x, y) = x 2 + y 2 Do you notice
The equation of the axis of symmetry is. Therefore, the x-coordinate of the vertex is 2.
 1. Find the y-intercept, the equation of the axis of symmetry, and the x-coordinate of the vertex for f (x) = 2x 2 + 8x 3. Then graph the function by making a table of values. Here, a = 2, b = 8, and c
1. Find the y-intercept, the equation of the axis of symmetry, and the x-coordinate of the vertex for f (x) = 2x 2 + 8x 3. Then graph the function by making a table of values. Here, a = 2, b = 8, and c
GUIDED NOTES 3.1 FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION
 GUIDED NOTES 3.1 FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Determine whether a relation represents a function. Find the value of a function. Determine whether a function
GUIDED NOTES 3.1 FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Determine whether a relation represents a function. Find the value of a function. Determine whether a function
Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 6666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C4 Advanced Level Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included
Paper Reference(s) 6666/0 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C4 Advanced Level Tuesday 22 January 2008 Afternoon Time: hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included
Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational Functions Power Standard #7
 Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational s Power Standard #7 2.1 Quadratic s Lets glance at the finals. Learning Objective: In this lesson you learned how to sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.
Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational s Power Standard #7 2.1 Quadratic s Lets glance at the finals. Learning Objective: In this lesson you learned how to sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.
Mid-Chapter Quiz: Lessons 4-1 through 4-4
 1. Find the y-intercept, the equation of the axis of symmetry, and the x-coordinate of the vertex for f (x) = 2x 2 + 8x 3. Then graph the function by making a table of values. 2. Determine whether f (x)
1. Find the y-intercept, the equation of the axis of symmetry, and the x-coordinate of the vertex for f (x) = 2x 2 + 8x 3. Then graph the function by making a table of values. 2. Determine whether f (x)
Calculus I Review Handout 1.3 Introduction to Calculus - Limits. by Kevin M. Chevalier
 Calculus I Review Handout 1.3 Introduction to Calculus - Limits by Kevin M. Chevalier We are now going to dive into Calculus I as we take a look at the it process. While precalculus covered more static
Calculus I Review Handout 1.3 Introduction to Calculus - Limits by Kevin M. Chevalier We are now going to dive into Calculus I as we take a look at the it process. While precalculus covered more static
Math 213 Calculus III Practice Exam 2 Solutions Fall 2002
 Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Integration. Edexcel GCE. Core Mathematics C4
 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers
Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C Integration Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your answers
Computers in Engineering Root Finding Michael A. Hawker
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 Root Finding Michael A. Hawker Root Finding Many applications involve finding the roots of a function f(x). That is, we want to find a value or values for x such that
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 Root Finding Michael A. Hawker Root Finding Many applications involve finding the roots of a function f(x). That is, we want to find a value or values for x such that
2. Solve for x when x < 22. Write your answer in interval notation. 3. Find the distance between the points ( 1, 5) and (4, 3).
 Math 6 Practice Problems for Final. Find all real solutions x such that 7 3 x = 5 x 3.. Solve for x when 0 4 3x
Math 6 Practice Problems for Final. Find all real solutions x such that 7 3 x = 5 x 3.. Solve for x when 0 4 3x
8/6/2010 Assignment Previewer
 8//2010 Assignment Previewer Week 8 Friday Homework (1324223) Question 12345789101112131415117181920 1. Question Detailsscalcet 3.9.ae.05.nva [129124] EXAMPLE 5 A man walks along a straight path at a speed
8//2010 Assignment Previewer Week 8 Friday Homework (1324223) Question 12345789101112131415117181920 1. Question Detailsscalcet 3.9.ae.05.nva [129124] EXAMPLE 5 A man walks along a straight path at a speed
MAT 1475 Final Exam Review Problems
 MAT1475 Final Review Spring 2016 Spring 2016 MAT 1475 Final Exam Review Problems Revised by Prof. Kostadinov, Fall 2015, Fall 2014, Fall 2013, Fall 2012, Fall 2011, Fall 2010 Revised by Prof. Africk and
MAT1475 Final Review Spring 2016 Spring 2016 MAT 1475 Final Exam Review Problems Revised by Prof. Kostadinov, Fall 2015, Fall 2014, Fall 2013, Fall 2012, Fall 2011, Fall 2010 Revised by Prof. Africk and
f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already familiar with ways of solving
 The Bisection Method and Newton s Method. If f( x ) a function, then a number r for which f( r) 0 is called a zero or a root of the function f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already
The Bisection Method and Newton s Method. If f( x ) a function, then a number r for which f( r) 0 is called a zero or a root of the function f( x ), or a solution to the equation f( x) 0. You are already
Quadratic Functions CHAPTER. 1.1 Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions p. 31
 CHAPTER Quadratic Functions Arches are used to support the weight of walls and ceilings in buildings. Arches were first used in architecture by the Mesopotamians over 4000 years ago. Later, the Romans
CHAPTER Quadratic Functions Arches are used to support the weight of walls and ceilings in buildings. Arches were first used in architecture by the Mesopotamians over 4000 years ago. Later, the Romans
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
Chapter 10 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Chapter 1 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Homework 1.2 1. Consider the parametric equations x = t and y = 3 t. a. Construct a table of values for t =, 1, 2, 3, and 4 b. Plot the
Chapter 1 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Homework 1.2 1. Consider the parametric equations x = t and y = 3 t. a. Construct a table of values for t =, 1, 2, 3, and 4 b. Plot the
Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations
 February 21, 2007 Tangent Planes Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Let P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point on S. Tangent
February 21, 2007 Tangent Planes Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Tangent Planes Let S be a surface with equation z = f (x, y). Let P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point on S. Tangent
Lesson Title 2: Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios
 Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
3.9 Differentials. Tangent Line Approximations. Exploration. Using a Tangent Line Approximation
 3.9 Differentials 3 3.9 Differentials Understand the concept of a tangent line approimation. Compare the value of the differential, d, with the actual change in,. Estimate a propagated error using a differential.
3.9 Differentials 3 3.9 Differentials Understand the concept of a tangent line approimation. Compare the value of the differential, d, with the actual change in,. Estimate a propagated error using a differential.
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
Practice problems from old exams for math 233
 Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
Practice problems from old exams for math 233 William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012 Disclaimer: Your instructor covers far more materials that we can possibly fit into a four/five questions exams. These
. The differential of y f (x)
 Calculus I - Prof D Yuen Exam Review version 11/14/01 Please report any typos Derivative Rules Of course you have to remember all your derivative rules Implicit Differentiation Differentiate both sides
Calculus I - Prof D Yuen Exam Review version 11/14/01 Please report any typos Derivative Rules Of course you have to remember all your derivative rules Implicit Differentiation Differentiate both sides
Solved Examples. Parabola with vertex as origin and symmetrical about x-axis. We will find the area above the x-axis and double the area.
 Solved Examples Example 1: Find the area common to the curves x 2 + y 2 = 4x and y 2 = x. x 2 + y 2 = 4x (i) (x 2) 2 + y 2 = 4 This is a circle with centre at (2, 0) and radius 2. y = (4x-x 2 ) y 2 = x
Solved Examples Example 1: Find the area common to the curves x 2 + y 2 = 4x and y 2 = x. x 2 + y 2 = 4x (i) (x 2) 2 + y 2 = 4 This is a circle with centre at (2, 0) and radius 2. y = (4x-x 2 ) y 2 = x
You ll use the six trigonometric functions of an angle to do this. In some cases, you will be able to use properties of the = 46
 Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
1. Solve the system by graphing: x y = 2 2. Solve the linear system using any method. 2x + y = -7 2x 6y = 12
 1. Solve the system by graphing: x y =. Solve the linear system using any method. x + y = -7 x 6y = 1 x + y = 8 3. Solve the linear system using any method. 4. A total of $0,000 is invested in two funds
1. Solve the system by graphing: x y =. Solve the linear system using any method. x + y = -7 x 6y = 1 x + y = 8 3. Solve the linear system using any method. 4. A total of $0,000 is invested in two funds
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas
 Section 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas 87 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas Multiple-Angle Formulas In this section, you will study four additional categories of trigonometric
Section 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas 87 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas Multiple-Angle Formulas In this section, you will study four additional categories of trigonometric
Lesson 10: Representing, Naming, and Evaluating Functions
 : Representing, Naming, and Evaluation Functions Classwork Opening Exercise Study the 4 representations of a function below. How are these representations alike? How are they different? TABLE: Input 0
: Representing, Naming, and Evaluation Functions Classwork Opening Exercise Study the 4 representations of a function below. How are these representations alike? How are they different? TABLE: Input 0
Area and Volume. where x right and x left are written in terms of y.
 Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Polar Coordinates. Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar coordinates, Section 10.3: Polar coordinates 27 / 45
 : Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
