GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison
|
|
|
- Michael Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering
2 Contents. SIGMAW: Stress Bulbs beneath tank. SEEPW: Seepage through embankment. SLOPEW: Strength reduction comparison Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering
3 Stress Changes in the Ground Beneath a Round Tank (SIGMA W Comparison) Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering
4 Introduction The primary purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to get started using MIDAS, to introduce the steps to run analysis, and to illustrate how to get results. This problem show how to obtain stress changes in the ground beneath a round tank filled with a fluid. A direct comparison will be done against Intro SIGMA/w Tutorial under same conditions. When studying a problem that is symmetric about a vertical axis, the three-dimensional effects can be analyzed with a twodimensional finite element mesh. Axisymmetric modeling in for this case considers the stresses in the X-Y plane as well as the circumferential stresses. 4
5 Symmetry Axis Initial model dimensions Model Conditions Axisymmetric 5 meter radius tank Ground is 8 m wide, 5 m deep layers. Upper soil: E = 000 kpa and Poisson s ratio ν = Lower soil: E = 4000 kpa and Poisson s ratio ν = Kpa pressure load Figures show the corresponding problem setup. The radius of the tank is 5 m and the applied pressure is 40 kpa. The soil region is 8 m wide and 5 m high. The upper 5 m of soil has different properties than the underlying 0 m. 5
6 Start Axisymetric File Open New. File > New. Axisymmetric. Units kn, m, sec 6
7 Materials and Properties Define Materials and Properties Define material properties of the layers. Menu > Mesh > Material> Create> Isotropic > Elastic. Define upper and lower layers as shown. Menu > Mesh > Properties > Create > D > Axis symmetric 4. Create Axis symmetric properties for the layers Upper soil: E = 000 kpa Poisson s ratio ν = 0.45 Lower soil: E = 4000 kpa Poisson s ratio ν =
8 Geometry Create Geometry Outline Define the WORK GRID as a drawing plane with lines spaced m apart to create rectangles. Menu > SHOW GRID. Menu > Define Grid > Width m, User Define 40 m. Menu>Geometry > Rectangle 4. Select the corner method, set st Location as 0,0 press Apply 5. Set nd location as 8,
9 Geometry Create Geometry Outline Draw additional lines to divide model into 4 segments. Menu>Geometry > Line. Draw a horizontal line from (0,0) to (8,0). Draw a Vertical Line from (5,5) to (5,0) 4. Draw a Vertical Line from (0,5) to (0,0) 5. Geometry > Intersect > Select All > Apply
10 Mesh Size Control Define Mesh Conditions. Menu> Mesh > Size Control. Define Linear Grading 0.5m -> m from left to right. Define Interval Length of m for the upper left corners 4. Define Interval Length of m for upper right corner 5. Define Integral length 0.5m for left horizontal lines 5 4 0
11 Mesh Mesh Mesh Upper and Lower Domains. Menu> Mesh > Generate > D > Auto Area. Mesh lower areas with m and lower axis property. Click>> and select quadrilateral and higher order elements. Click OK > Apply 4. Mesh upper areas with m and upper axis property 4
12 Boundary Boundary Apply Boundary Conditions. Menu> Static/Slope Analysis>Boundary>Constraint. Select Auto>Apply
13 Load Load Apply Pressure Load. Menu> Static/Slope Analysis>Load>Pressure. Select Axisymmetric and apply 40kN/m^ load to upper left nodes as shown.
14 Analysis Case Analysis Case Create Static Analysis Case. Menu> Analysis>Analysis Case >General. Select Linear Static. Activate All 4. Run Analysis > Press OK 4 4
15 Results Post Processor Check Vertical Stresses SYY. Works Tree > Results > Stresses > S-YY. Right Click Legend > Color Type > Reverse. Activate Iso surface > Lower Part > Set to -5 5
16 Results Post Processor Check Displacements. Menu> Results>Show>Min/Max. Works Tree > Results > Displacements > Total. Change units to mm 6
17 Results Post Processor Check Horizontal Displacements. Menu> Results>Advanced>Cutting Diagram. Set to X direction. Draw vertical diagram by selecting points (top and bottom as shown) 7
18 Results Post Processor Graph Displacements. Menu> Results>Advanced>Extract. Set Type > Displacements / Results > TX Translation. Select nodes as shown > Click Table 4. Select depth and displacement columns, right click export to excel to graph. 4 8
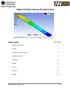
19 Compare Results to SIGMAW Tutorial Displacement and Stresses match exactly with results from SIGMA W tank tutorial MIDAS 9
20 D Case Study: Tanks in Clay (Colombia) Long term consolidation analysis of water treatment tanks in soft clay D isometric view of tanks D side view of tanks in clay Material Espesor (m) Wn (%) LL (%) IP(%) Peso unitario total γt (kn/m) Es (MPa) Valor conservador PERFIL MODELACIÓN e Presión de preconsolidación (kpa) OCR Cc Cr K (m/día) c' (kpa) φ`(º) E E E E E ? E Material table of clay layers 0
21 D Case Study: Tanks in Clay (Colombia) Plane cut of layers Initial CS stage Stage: Excavation Stage: Installation Stage: Reinforcement Stage4: Loads
22 D Case Study: Tanks in Clay (Colombia) Stage: Excavation Stage4: Loads 0 year consolidation 0 year consolidation 50 year consolidation
23 Seepage Thru Earth Embankment (SEEPW Comparison) Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering
24 Introduction The objective of the tutorial is look at the D flow through an embankment dam. This seepage analysis is a common example and consequently most users will have a good idea as to what the solution should look like. It shows how easy it is to find the downstream seepage outflow when the dam has a homogenous material. The tutorial will also look at cases were a toe under-drain is included and when the central core s hydraulic conductivities are lowered. 4
25 Initial model dimensions Model Conditions D Steady State Seepage 0m tall X 47m wide Dam layers. Core. Shell. Toe Drain 8 m water level on right side of dam Figures show the corresponding problem setup. The dam consists of a center core (4m wide at top, 8m wide at base), shells and a toe drain on the right bottom corner. Water level on left side is 8m. 5
26 Start Axisymetric File Open New. File > New. D. Units kn, m, sec 6
27 Materials Define Materials. Menu > Mesh > Material> Create> Isotropic. Define General Fill material as shown for the General tab.. In the Porous tab, active Unsaturated Property>ADD>Individual>User Defined and copy paste corresponding excel sheets. Press Ok 4. Repeat for core 0X less and core 00X less materials 4 7
28 Properties Define Materials and Properties. Menu > Mesh > Properties > Create > D > Plain Strain. Create 4 D Plain Strain properties for the layers. Match the name with the material property. 4 8
29 Geometry Create Geometry Outline Define the WORK GRID as a drawing plane with lines spaced m apart to create rectangles. Menu > SHOW GRID. Menu > Define Grid > Width m, User Define 55 m. Menu>Geometry > PolyLine 4. Select the ABS x,y method, set st Location as 0,0 press Apply 5. Set End location as,
30 Geometry Create Geometry Outline. Input next location (4,0). Input next location (0, -0). Input next location (-47,0) 4. Press OK 0
31 Geometry Create Geometry Outline 4 5. Draw a Vertical Line Start (,0) End (-,0). Draw a Vertical Line Start (7,0) End (-,0). Draw a Rectangle Start Corner (40,0) End Corner(0,-) 4. Geometry > Intersect > Select All > Apply 4 5
32 Mesh Mesh. Menu> Mesh > Generate > D > Auto Area. Mesh the Core with 0.5m size and General Fill Property. Repeat for Core for 0X less and 00X less property 4. Mesh the Shells with m size and General Fill 5. Mesh Toe Drain with m size and Toe Property 4 4
33 Seepage Boundary Boundary Apply Seepage Boundary Conditions. Menu> Seepage/Consolidation Analysis>Nodal Head. Select the left Edge, apply Total head 8m as shown. Select Toe Drain Nodes, apply Total head of 0m 4. Select right Edge, apply Review boundary 4
34 Analysis Case Create 4 Seepage Steady State Analysis Cases. Menu> Analysis>Analysis Case >General. Select Seepage Steady State Solution Type. Create Case and activate sets as shown. Press Apply 4. Create Case and activate sets as shown. Press Ok 4 4
35 Analysis Case Create 4 Seepage Steady State Analysis Cases. Menu> Analysis>Analysis Case >General. Select Seepage Steady State Solution Type. Create Case and activate sets as shown. Press Apply 4. Create Case 4 and activate sets as shown. Press Ok 4 5
36 Run Analysis Run all 4. Menu > Analysis > Perform. Select All. Press OK 6
37 Results Post Processor Check the Total Head and water level for Case. Results > Nodal Seepage > Total Head. Results > Nodal Seepage > Pore Pressure. Results>Advanced>Multi Step Iso>Pore Pressure>0 7
38 Results Post Processor Check the Total Head and water level for Case. Results > Nodal Seepage > Total Head. Results > Nodal Seepage > Pore Pressure. Results>Advanced>Multi Step Iso>Pore Pressure>0 8
39 Results Post Processor Check the Total Head and water level for Case. Results > Nodal Seepage > Total Head. Results > Nodal Seepage > Pore Pressure. Results>Advanced>Multi Step Iso>Pore Pressure>0 9
40 Results Post Processor Check the Total Head and water level for Case 4. Results > Nodal Seepage > Total Head. Results > Nodal Seepage > Pore Pressure. Results>Advanced>Multi Step Iso>Pore Pressure>0 40
41 Compare Results to SEEPW Tutorial Total Head and Pore Pressure distribution match SEEPW tutorial. Shown here are Case and Case 4 results. MIDAS 4
42 D Case Study: CS of Dam(S. Korea) Construction stage analysis of dam reflecting full water level hydrostatic pressure Buhang Dam, South Korea Stage: Banking Height 60m Stage5: Banking Height 0m + Hydrostatic pressure 4
43 D Case Study: CS of Dam(S. Korea) Stage : Total Displacements Stage 5: Horizontal Displacements Stage 4: Vertical deflection Stage 5: Hydrostatic pressure 4
44 D Case Study: CS of Dam(S. Korea) Stage 5: Total Head Stage 5: Hydraulic Gradient Stage 5: Flow Paths Stage 5: Flow Rate 44
45 Strength Reduction Stability Comparison (SLOPEW Comparison) Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering
46 Introduction Introduction Stability by strength reduction is a procedure where the factor of safety is obtained by weakening the soil in steps in an elastic-plastic finite element analysis until the slope fails. The factor of safety is deemed to be the factor by which the soil strength needs to be reduced to reach failure (Dawson et al., 999; Griffiths and Lane, 999). Numerically, the failure occurs when it is no longer possible to obtain a converged solution. The finite element equations for a stressstrain formulation are in essence equations of equilibrium. Not being able to obtain a converged solution therefore infers the system is beyond the point of limiting equilibrium. An alternative way to define failure is the point at which the deformations become excessive. In the Strength Reduction method, the soil strength is artificially reduced, and so there is a need to redistribute the stresses. This can be done by the Stress Redistribution algorithm, and so this option can be indirectly used to do a Strength Reduction stability analysis. 46
47 Initial model dimensions Model Conditions D Strength Reduction Method Analysis 0m tall X 5m wide X 0 m Slope layer 4 materials Figures show the corresponding problem setup. It illustrates how a Strength Reduction Method analysis can be done with MIDAS. In addition, the results are compared as the soil strength is reduced in stages. For each stage, the factor of safety is obtained for the new material. Each strength reduction analysis uses the previous analysis as its initial conditions. Lastly, the results are compared to a SLOPEW tutorial. 47
48 Start Axisymetric File Open New. File > New. D. Units kn, m, sec 48
49 Materials Define Materials. Menu > Mesh > Material> Create> Isotropic>Mohr Coulomb. Define 6 materials as shown in the General tab. Define Non linear properties as shown in table Name Cohesion Friction Angle In situ 5 8 SRF SRF SRF SRF SRF
50 Properties Define Materials and Properties. Menu > Mesh > Properties > Create > D > Plain Strain. Create 6 D Plain Strain properties for the layers. Match the name with the material property. 50
51 Geometry Create Geometry Outline Define the WORK GRID as a drawing plane with lines spaced m apart to create rectangles. Menu > SHOW GRID. Menu > Define Grid > Width m, User Define 55 m. Menu>Geometry > PolyLine 4. Select the ABS x,y method, set st Location as 0,0 press Apply 5. Set End location as 0,
52 Geometry Polyline points. Input next location (5,0). Input next location (0, -0). Input next location (6, 0) 4. Input next location (0, -0) 5. Input next location (-5, 0) 6. Press OK 5
53 Mesh Mesh. Menu> Mesh > Generate > D > Auto Area. Mesh with m size and in situ Property. Select >> Advance Option and activate Higher Order Element 4. Repeat meshing same area with the remaining materials
54 Boundary Boundary Apply Seepage Boundary Conditions. Menu> Static > Slope > Boundary > Constrain > Auto. Menu> Static > Slope > Load > Self Weight> Gy 4 54
55 Construction Stages Create Construction Stage Analysis. Menu> Static/Slope > Construction Stage> Stage Set. Select Stress Solution Type > Define CS. Create Stage and activate sets as shown. Press Save > New 4. Create Stage and activate sets as shown. Press Save > New 4 55
56 Construction Stages Continue Stages. Create Stage and activate sets as shown. Press Save > New. Create Stage 4 and activate sets as shown. Press Save > New 56
57 Construction Stages Continue Stages. Create Stage 5 and activate sets as shown. Press Save > New. Create Stage 6 and activate sets as shown. Press Save > New. Create Stage 7 and activate sets as shown. Press Save > Close 57
58 Analysis Case Create and Run CS Case. Menu > Analysis > General. Create Construction Case Analysis Control > Initialize Stress > In situ (Stage ). Menu > Analysis > Perform 4. Press OK 4 58
59 Results Check the FOS for the SRM stages. Results > initial srm > Plane Strain Strains > E-equivalent. Repeat for all other cases 4 Case FOS Result Initial.565. SRM.906. SRM SRM.06.5 SRM SRM
60 Compare Results to SLOPEW Tutorial Results match SLOPEW tutorial. Shown here are FOS for all 6 cases
61 Compare Results to SLOPEW Tutorial Results match SLOPEW tutorial. Compare Shear Stresses for In Situ case 6
62 D Case Study: Slope Stability (Colombia) Construction stage excavation of slope for housing hydroelectric dam machinery Initial Condition Final Excavation 6
63 D Case Study: Slope Stability (Colombia) Initial Condition Final Excavation Displacement Contours 6
64 D Case Study: Slope Stability (Colombia) Movement Vectors Initial Condition Failure Iso Surfaces Final Excavation 64
65 Conclusions Comparison between and Geostudio D Suite gives comparable results for the different kinds of analysis. can additionally jump to D case from D starting file, but only practical for symmetrical cases. has geometry modeling features and CAD compatibility that make it easy to create analysis cases for complex D problems. allows coupled (stress seepage slope seismic) analysis that would require multiple models in different platforms of Geostudio. 65
66 Next Sesion 66
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series
 MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
2D & 3D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope
 D & D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASoft NY office Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform Finite Element
D & D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASoft NY office Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform Finite Element
Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure
 1 Introduction Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure One of the most powerful features of GeoStudio is the smooth integration that exists between all the individual programs. For simple pore-water pressure
1 Introduction Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure One of the most powerful features of GeoStudio is the smooth integration that exists between all the individual programs. For simple pore-water pressure
An Introductory SIGMA/W Example
 1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
Slope Stability of Open Pit Mine in 2D & 3D
 Slope Stability of Open Pit Mine in D & D MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer Email : a.martinez@midasit.com Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation64-bit platform Finite
Slope Stability of Open Pit Mine in D & D MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer Email : a.martinez@midasit.com Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation64-bit platform Finite
Stability with FE Stresses
 1 Introduction Stability with FE Stresses In the finite element stresses stability analysis method, the stresses in the ground can be computed using SIGMA/W, and then SLOPE/W uses the SIGMA/W stresses
1 Introduction Stability with FE Stresses In the finite element stresses stability analysis method, the stresses in the ground can be computed using SIGMA/W, and then SLOPE/W uses the SIGMA/W stresses
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D
 Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Sheet Pile Wall
 1 Introduction Sheet Pile Wall Deep excavation on a level group usually results in a very low factor of safety, unless it is properly reinforced. The purpose of this example is to illustrate how the stability
1 Introduction Sheet Pile Wall Deep excavation on a level group usually results in a very low factor of safety, unless it is properly reinforced. The purpose of this example is to illustrate how the stability
RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS
 RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS 6 RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS This example concerns the stability of a reservoir dam under conditions of drawdown. Fast reduction of the reservoir level may lead to instability of the
RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS 6 RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS This example concerns the stability of a reservoir dam under conditions of drawdown. Fast reduction of the reservoir level may lead to instability of the
This is the script for the SEEP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, SEEP/W Getting Started.
 SEEP/W Tutorial This is the script for the SEEP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, SEEP/W Getting Started. Introduction Here are some results obtained by using SEEP/W to analyze unconfined
SEEP/W Tutorial This is the script for the SEEP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, SEEP/W Getting Started. Introduction Here are some results obtained by using SEEP/W to analyze unconfined
SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd , 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: Fax:
 Grid and Radius GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction In early limit equilibrium slope
Grid and Radius GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction In early limit equilibrium slope
Sequential Excavation for Mining in 2D and 3D
 Sequential Excavation for Mining in 2D and 3D MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer Email : a.martinez@midasuser.com Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform
Sequential Excavation for Mining in 2D and 3D MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer Email : a.martinez@midasuser.com Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform
SSR Polygonal Search Area
 SSR Polygonal Search Area 22-1 SSR Polygonal Search Area In this tutorial, Phase2 is used to determine the factor of safety of a slope using the shear strength reduction (SSR) method. The SSR Polygon Search
SSR Polygonal Search Area 22-1 SSR Polygonal Search Area In this tutorial, Phase2 is used to determine the factor of safety of a slope using the shear strength reduction (SSR) method. The SSR Polygon Search
Developer s Tips. Groundwater analysis using Slide
 Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
3D Excavation by Tunnel Boring Machine
 3D Excavation by Tunnel Boring Machine Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS NY Content 01 Introduction 02 Advantages of GTS NX for Tunneling 03 TBM Demo Introduction About MIDAS No. 1 in
3D Excavation by Tunnel Boring Machine Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS NY Content 01 Introduction 02 Advantages of GTS NX for Tunneling 03 TBM Demo Introduction About MIDAS No. 1 in
Introduction: RS 3 Tutorial 1 Quick Start
 Introduction: RS 3 Tutorial 1 Quick Start Welcome to RS 3. This tutorial introduces some basic features of RS 3. The model analyzes the effect of tank loading on an existing sloped underground tunnel.
Introduction: RS 3 Tutorial 1 Quick Start Welcome to RS 3. This tutorial introduces some basic features of RS 3. The model analyzes the effect of tank loading on an existing sloped underground tunnel.
PHASED EXCAVATION OF A SHIELD TUNNEL
 5 PHASED EXCAVATION OF A SHIELD TUNNEL The lining of a shield tunnel is often constructed using prefabricated concrete ring segments, which are bolted together within the tunnel boring machine to form
5 PHASED EXCAVATION OF A SHIELD TUNNEL The lining of a shield tunnel is often constructed using prefabricated concrete ring segments, which are bolted together within the tunnel boring machine to form
v GMS 10.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
FLAC/Slope User s Guide Contents - 1
 FLAC/Slope User s Guide Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 FLAC/SLOPE 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 Guide to the FLAC/Slope Manual... 1-2 1.1.3 Summary of Features... 1-2 1.1.4 Analysis
FLAC/Slope User s Guide Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 FLAC/SLOPE 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 Guide to the FLAC/Slope Manual... 1-2 1.1.3 Summary of Features... 1-2 1.1.4 Analysis
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK
 THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK 15 THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK A navigable lock is temporarily 'empty' due to maintenance. After some time there is significant increase of the air temperature,
THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK 15 THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK A navigable lock is temporarily 'empty' due to maintenance. After some time there is significant increase of the air temperature,
PLAXIS 2D. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 2D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 8601 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Settlement of a circular footing on sand 7 1.1 Geometry 7 1.2 Case A: Rigid footing 8 1.3 Case B: Flexible footing 23 2 Submerged
PLAXIS 2D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 8601 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Settlement of a circular footing on sand 7 1.1 Geometry 7 1.2 Case A: Rigid footing 8 1.3 Case B: Flexible footing 23 2 Submerged
Seepage_CSM8. A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems.
 Seepage_CSM8 A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems. USER S MANUAL J. A. Knappett (2012) This user s manual
Seepage_CSM8 A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems. USER S MANUAL J. A. Knappett (2012) This user s manual
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
GTS NX INTERFACES AUTOCAD MIDAS GEN FOR TUNNEL SOIL PILE INTERACTION ANALYSIS
 INTERFACES AUTOCAD MIDAS GEN FOR TUNNEL SOIL PILE INTERACTION ANALYSIS Angel F. Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASOFT Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions
INTERFACES AUTOCAD MIDAS GEN FOR TUNNEL SOIL PILE INTERACTION ANALYSIS Angel F. Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASOFT Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions
DRY EXCAVATION USING A TIE BACK WALL
 3 This example involves the dry construction of an excavation. The excavation is supported by concrete diaphragm walls. The walls are tied back by prestressed ground anchors. Silt Sand 10 m 2 m 20 m 10
3 This example involves the dry construction of an excavation. The excavation is supported by concrete diaphragm walls. The walls are tied back by prestressed ground anchors. Silt Sand 10 m 2 m 20 m 10
CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT
 CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT 4 CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT The construction of an embankment on soft soil with a high groundwater level leads to an increase in pore pressure. As a result of
CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT 4 CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT The construction of an embankment on soft soil with a high groundwater level leads to an increase in pore pressure. As a result of
PLAXIS 3D. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 9039 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 1.1 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 1.2 Case B: Raft foundation 20 1.3 Case C: Pile-Raft
PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 9039 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 1.1 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 1.2 Case B: Raft foundation 20 1.3 Case C: Pile-Raft
Dam Construction by Stages
 1 Introduction Dam Construction by Stages This simple example demonstrates the simulation of staged construction of an embankment on soft ground. The primary purposes of this example are to demonstrate
1 Introduction Dam Construction by Stages This simple example demonstrates the simulation of staged construction of an embankment on soft ground. The primary purposes of this example are to demonstrate
Stress due to surface load
 Stress due to surface load To analyze problems such as compressibility of soils, bearing capacity of foundations, stability of embankments, and lateral pressure on earth retaining structures, we need to
Stress due to surface load To analyze problems such as compressibility of soils, bearing capacity of foundations, stability of embankments, and lateral pressure on earth retaining structures, we need to
Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage. Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis
 Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis Introduction Within the Slide program, Slide has the capability to carry out
Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis Introduction Within the Slide program, Slide has the capability to carry out
PLAXIS 3D. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2010 Build 2681 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction 5 2 Lesson 1: Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 2.1 Geometry 7 2.2 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 2.3 Case B:
PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2010 Build 2681 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction 5 2 Lesson 1: Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 2.1 Geometry 7 2.2 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 2.3 Case B:
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Lysimeters
 1 Introduction Lysimeters This steady state SEEP/W example illustrates how to model a lysimeter from construction of the model to interpretation of the results. Lysimeters are used to measure flow through
1 Introduction Lysimeters This steady state SEEP/W example illustrates how to model a lysimeter from construction of the model to interpretation of the results. Lysimeters are used to measure flow through
Terrain settlement analysis
 Engineering manual No. 21 Updated: 02/2018 Terrain settlement analysis Program: File: FEM Demo_manual_21.gmk This example contains the solution to terrain settlement under surcharge loading using the Finite
Engineering manual No. 21 Updated: 02/2018 Terrain settlement analysis Program: File: FEM Demo_manual_21.gmk This example contains the solution to terrain settlement under surcharge loading using the Finite
Effects on an earth- and rockfill dam undergoing dam safety measures
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Effects on an earth- and rockfill dam undergoing dam safety measures J. Toromanović,
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Effects on an earth- and rockfill dam undergoing dam safety measures J. Toromanović,
Slope Stability Problem Session
 Slope Stability Problem Session Stability Analysis of a Proposed Soil Slope Using Slide 5.0 Tuesday, February 28, 2006 10:00 am - 12:00 pm GeoCongress 2006 Atlanta, GA software tools for rock and soil
Slope Stability Problem Session Stability Analysis of a Proposed Soil Slope Using Slide 5.0 Tuesday, February 28, 2006 10:00 am - 12:00 pm GeoCongress 2006 Atlanta, GA software tools for rock and soil
Chapter 20. Finite Element Method (FEM) Introduction
 Chapter 20. Finite Element Method (FEM) Introduction The objective of this chapter is to explain basic terms of the particular field of problems and practical application of GEO 5 FEM program to solve
Chapter 20. Finite Element Method (FEM) Introduction The objective of this chapter is to explain basic terms of the particular field of problems and practical application of GEO 5 FEM program to solve
Stability Analysis of Cellular Retaining Structure by PLAXIS Finite Element Code
 The Iraqi Journal For Mechanical And Material Engineering, Special Issue (D) Stability Analysis of Cellular Retaining Structure by PLAXIS Finite Element Code By Kadhim Naief Al-Taee, Sarmad Hameed Al-Rammahi
The Iraqi Journal For Mechanical And Material Engineering, Special Issue (D) Stability Analysis of Cellular Retaining Structure by PLAXIS Finite Element Code By Kadhim Naief Al-Taee, Sarmad Hameed Al-Rammahi
Diamond Engineer: Tunnel Series Training 2
 Diamond Engineer: Tunnel Series Training 2 Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS NY Content 01 Introduction 02 Construction Stages 03 Demo 04 Post - Processing Introduction About MIDAS No.
Diamond Engineer: Tunnel Series Training 2 Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS NY Content 01 Introduction 02 Construction Stages 03 Demo 04 Post - Processing Introduction About MIDAS No.
Oasys Pdisp. Copyright Oasys 2013
 Oasys Pdisp Copyright Oasys 2013 All rights reserved. No parts of this work may be reproduced in any form or by any means - graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping,
Oasys Pdisp Copyright Oasys 2013 All rights reserved. No parts of this work may be reproduced in any form or by any means - graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping,
GMS 8.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam Profile Analysis Use UTEXAS to find the critical failure surface for a complex earth dam
 v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Use UTEXAS to find the critical failure surface for a complex earth dam Objectives Import a CAD file and convert it to Feature Objects. Use the Feature Objects to create a UTEXAS
v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Use UTEXAS to find the critical failure surface for a complex earth dam Objectives Import a CAD file and convert it to Feature Objects. Use the Feature Objects to create a UTEXAS
Modeling Foundations in RS
 Modeling Foundations in RS 3 Piled Raft Modeling in RS 3 Deep foundation piles are commonly used to increase foundation stability and to increase the bearing capacity of structural systems. The design
Modeling Foundations in RS 3 Piled Raft Modeling in RS 3 Deep foundation piles are commonly used to increase foundation stability and to increase the bearing capacity of structural systems. The design
Lab Practical - Boundary Element Stress Analysis
 Lab Practical - Boundary Element Stress Analysis Part A The Basics In this example we will model a simple set of excavations using the Rocscience program EXAMINE 2D. The first step is to define the geometry
Lab Practical - Boundary Element Stress Analysis Part A The Basics In this example we will model a simple set of excavations using the Rocscience program EXAMINE 2D. The first step is to define the geometry
Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown
 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown 17-1 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown When the water level at a dam drops, the stabilizing force due to the weight of the water is removed. If the dam material has a low permeability
Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown 17-1 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown When the water level at a dam drops, the stabilizing force due to the weight of the water is removed. If the dam material has a low permeability
v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment On Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis
 v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment On Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite
v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment On Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite
FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING
 14 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building consists
14 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building consists
2016(v1.1) Release Notes
 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Ver 4.0.0. 개정내용 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Copyright c 1989~2014. MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 1 / 21 Release Note 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Pre-Processing
2016(v1.1) Release Notes Ver 4.0.0. 개정내용 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Copyright c 1989~2014. MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 1 / 21 Release Note 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Pre-Processing
Lab Practical - Finite Element Stress & Deformation Analysis
 Lab Practical - Finite Element Stress & Deformation Analysis Part A The Basics In this example, some of the basic features of a finite element analysis will be demonstrated through the modelling of a simple
Lab Practical - Finite Element Stress & Deformation Analysis Part A The Basics In this example, some of the basic features of a finite element analysis will be demonstrated through the modelling of a simple
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
Modelling of Tunnels in 2D & 3D
 MIDAS Geotechnical Know-how Sharing Series November 28 th, 2017 (Tue) 10:00 ~ 11:00 AM (CET) Session 3. Modelling of Tunnels in 2D & 3D JaeSeok Yang Principal Geotechnical Engineer, MIDAS IT Integrated
MIDAS Geotechnical Know-how Sharing Series November 28 th, 2017 (Tue) 10:00 ~ 11:00 AM (CET) Session 3. Modelling of Tunnels in 2D & 3D JaeSeok Yang Principal Geotechnical Engineer, MIDAS IT Integrated
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
UTEXAS Embankment on Soft Clay
 GMS TUTORIALS Figure 1. Sample slope stability problem from the Utexam1.dat file provided with the UTEXAS4 software. 1 Introduction UTEXAS4 is a slope stability software package created by Dr. Stephen
GMS TUTORIALS Figure 1. Sample slope stability problem from the Utexam1.dat file provided with the UTEXAS4 software. 1 Introduction UTEXAS4 is a slope stability software package created by Dr. Stephen
Stability Analysis of Slope Based on FLAC3D Using Strength Reduction Method. Speaker: Tran, Thi Kim Tu Advisor: Chuen Fa Ni Date: 2017/03/02
 Stability Analysis of Slope Based on FLAC3D Using Strength Reduction Method Speaker: Tran, Thi Kim Tu Advisor: Chuen Fa Ni Date: 2017/03/02 1. INTRODUCTION 2. METHODOLOGY 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4. CONCLUSION
Stability Analysis of Slope Based on FLAC3D Using Strength Reduction Method Speaker: Tran, Thi Kim Tu Advisor: Chuen Fa Ni Date: 2017/03/02 1. INTRODUCTION 2. METHODOLOGY 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4. CONCLUSION
3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) Figure 3.1 Geometry of a circular footing on a sand layer
 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
GTS. midas GTS Advanced Webinar. Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar
 midas GTS Advanced Webinar Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar Bridging Your Innovations to Realities GTS MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. [1/30] Contents:
midas GTS Advanced Webinar Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar Bridging Your Innovations to Realities GTS MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. [1/30] Contents:
Transient Groundwater Analysis
 Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes
 Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes Part 1: Planar Analysis A Deterministic Analysis This exercise will demonstrate the basics of a deterministic limit equilibrium planar analysis
Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes Part 1: Planar Analysis A Deterministic Analysis This exercise will demonstrate the basics of a deterministic limit equilibrium planar analysis
FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING
 8 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building
8 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building
v GMS 10.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment on Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis
 v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
OPTUM COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS
 OPTUM COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS Version 2016 OptumG2: Analysis K Krabbenhoft, AV Lymain, J Krabbenhoft (Editors) c Optum Computational Engineering 2016 www.optumce.com CONTENTS Contents 1 GENERAL
OPTUM COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS Version 2016 OptumG2: Analysis K Krabbenhoft, AV Lymain, J Krabbenhoft (Editors) c Optum Computational Engineering 2016 www.optumce.com CONTENTS Contents 1 GENERAL
GeoStudio Product Details
 Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Ordinary Yes Yes Yes
Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Ordinary Yes Yes Yes
Copyright by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd
 Copyright 2004-2017 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
Copyright 2004-2017 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING
 TUTORIAL MANUAL 9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading.
TUTORIAL MANUAL 9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading.
GeoStudio Product Details
 Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Vadose Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Methods Ordinary
Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Vadose Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Methods Ordinary
Engineeringmanuals. Part3
 Engineeringmanuals Part3 Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs Part 3 Chapter 1-12, refer to Engineering Manual Part 1 Chapter 13-19, refer to Engineering Manual Part 2 Chapter 20. Finite Element Method
Engineeringmanuals Part3 Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs Part 3 Chapter 1-12, refer to Engineering Manual Part 1 Chapter 13-19, refer to Engineering Manual Part 2 Chapter 20. Finite Element Method
PLAXIS 3D Tunnel. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 3D Tunnel Tutorial Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 2 Getting started...2-1 2.1 Installation...2-1 2.2 General modelling aspects...2-1 2.3 Input procedures...2-3
PLAXIS 3D Tunnel Tutorial Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 2 Getting started...2-1 2.1 Installation...2-1 2.2 General modelling aspects...2-1 2.3 Input procedures...2-3
Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING
 BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING This document describes an example that has been used to verify the bearing capacity of strip footing in PLAXIS. F 1 m ½ B c ref ν =
BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING BEARING CAPACITY OF STRIP FOOTING This document describes an example that has been used to verify the bearing capacity of strip footing in PLAXIS. F 1 m ½ B c ref ν =
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION
 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION 7 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION In this tutorial the influence of a vibrating source on its surrounding soil is studied.
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION 7 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION In this tutorial the influence of a vibrating source on its surrounding soil is studied.
Pseudo 3-D deposition and large-strain consolidation modeling of tailings deep deposits
 Pseudo 3-D deposition and large-strain consolidation modeling of tailings deep deposits Murray Fredlund, Matt Donaldson, Krishna Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd ABSTRACT The design of deep deposits requires
Pseudo 3-D deposition and large-strain consolidation modeling of tailings deep deposits Murray Fredlund, Matt Donaldson, Krishna Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd ABSTRACT The design of deep deposits requires
Deep Beam With Web Opening
 Deep Beam With Web Opening Name: Path: Keywords: DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam /Examples//DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam analys: linear static. constr: suppor. elemen: cq16m ct12m pstres. load: force
Deep Beam With Web Opening Name: Path: Keywords: DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam /Examples//DeepBeamWithWebOpening/deepbeam analys: linear static. constr: suppor. elemen: cq16m ct12m pstres. load: force
Application Note - Gravity Wall Analysis
 LS-G-AN3 Software: LimitState:GEO 2.0f Date: February 2011 Application Note - Gravity Wall Analysis 1 Introduction This note describes the typical steps followed in setting up and analysing a gravity wall
LS-G-AN3 Software: LimitState:GEO 2.0f Date: February 2011 Application Note - Gravity Wall Analysis 1 Introduction This note describes the typical steps followed in setting up and analysing a gravity wall
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
UTEXAS4 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SLOPE STABILITY CALCULATIONS. Stephen G. Wright. May Revised September Shinoak Software Austin, Texas
 UTEXAS4 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SLOPE STABILITY CALCULATIONS By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 - Revised September 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights
UTEXAS4 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SLOPE STABILITY CALCULATIONS By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 - Revised September 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights
Linear Analysis of an Arch Dam
 Linear Analysis of an Arch Dam Outline 1 Description 2 Finite Element Model 2.1 Coincidence Tolerance 2.2 Units 2.3 Import CAD File 2.4 Properties 2.5 Boundary Conditions 2.6 Loads 2.7 Meshing 3 Linear
Linear Analysis of an Arch Dam Outline 1 Description 2 Finite Element Model 2.1 Coincidence Tolerance 2.2 Units 2.3 Import CAD File 2.4 Properties 2.5 Boundary Conditions 2.6 Loads 2.7 Meshing 3 Linear
Three-Dimensional Slope Stability: Geometry Effects
 Three-Dimensional Slope Staility: Geometry Effects Krishna Bahadur Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, SK, Canada Vanessa Honorato Domingos Universidade Federal de Goias, Goiania, Brazil Gilson
Three-Dimensional Slope Staility: Geometry Effects Krishna Bahadur Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, SK, Canada Vanessa Honorato Domingos Universidade Federal de Goias, Goiania, Brazil Gilson
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
CHAPTER 4. Numerical Models. descriptions of the boundary conditions, element types, validation, and the force
 CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
Elastic Analysis of a Deep Beam with Web Opening
 Elastic Analysis of a Deep Beam with Web Opening Outline 1 Description 2 Finite Element Model 2.1 Units 2.2 Geometry definition 2.3 Properties 2.4 Boundary conditions 2.4.1 Constraints 2.4.2 Vertical load
Elastic Analysis of a Deep Beam with Web Opening Outline 1 Description 2 Finite Element Model 2.1 Units 2.2 Geometry definition 2.3 Properties 2.4 Boundary conditions 2.4.1 Constraints 2.4.2 Vertical load
Oasys Frew. Copyright Oasys 2013
 Oasys Frew Copyright Oasys 2013 All rights reserved. No parts of this work may be reproduced in any form or by any means - graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping,
Oasys Frew Copyright Oasys 2013 All rights reserved. No parts of this work may be reproduced in any form or by any means - graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping,
POTATO FIELD MOISTURE CONTENT
 11 POTATO FIELD MOISTURE CONTENT This tutorial demonstrates the applicability of PLAXIS to agricultural problems. The potato field tutorial involves a loam layer on top of a sandy base. The water level
11 POTATO FIELD MOISTURE CONTENT This tutorial demonstrates the applicability of PLAXIS to agricultural problems. The potato field tutorial involves a loam layer on top of a sandy base. The water level
Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe
 Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
CHAPTER 6 EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION STUDIES OF SUPERPLASTIC BOX FORMING
 113 CHAPTER 6 EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION STUDIES OF SUPERPLASTIC BOX FORMING 6.1 INTRODUCTION Superplastic properties are exhibited only under a narrow range of strain rates. Hence, it
113 CHAPTER 6 EXPERIMENTAL AND FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION STUDIES OF SUPERPLASTIC BOX FORMING 6.1 INTRODUCTION Superplastic properties are exhibited only under a narrow range of strain rates. Hence, it
Phase 2. 2D finite element program for calculating stresses and estimating support around underground excavations
 Phase 2 2D finite element program for calculating stresses and estimating support around underground excavations Phase 2 Model Program Reference Manual 1998-2001 Rocscience Inc. Table of Contents Introducing
Phase 2 2D finite element program for calculating stresses and estimating support around underground excavations Phase 2 Model Program Reference Manual 1998-2001 Rocscience Inc. Table of Contents Introducing
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Thermal Stresses in a Bar
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Thermal Stresses in a Bar Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Draw Geometry Create
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Thermal Stresses in a Bar Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Draw Geometry Create
CE Advanced Structural Analysis. Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
v GMS 10.0 Tutorial SEEP2D Sheet Pile Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
Examine 2D 8.0 is here!
 Examine 2D 8.0 is here! Rocscience is pleased to announce the release of Examine 2D version 8.0, an upgrade to our very popular FREE stress analysis program. Examine 2D uses the boundary element method
Examine 2D 8.0 is here! Rocscience is pleased to announce the release of Examine 2D version 8.0, an upgrade to our very popular FREE stress analysis program. Examine 2D uses the boundary element method
Accuracy of the Rubicon Toolbox Finite Element Model
 Accuracy of the Rubicon Toolbox Finite Element Model Introduction This document deals with the accuracy and recommended use of the Rubicon Toolbox Finite Element module. The document is intended to provide
Accuracy of the Rubicon Toolbox Finite Element Model Introduction This document deals with the accuracy and recommended use of the Rubicon Toolbox Finite Element module. The document is intended to provide
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial SEEP2D Sheet Pile Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Prerequisite Tutorials None Time minutes
 v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in GMS.
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in GMS.
v SEEP2D Sheet Pile Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile GMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
 v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
Inverse Analysis of Soil Parameters Based on Deformation of a Bank Protection Structure
 Inverse Analysis of Soil Parameters Based on Deformation of a Bank Protection Structure Yixuan Xing 1, Rui Hu 2 *, Quan Liu 1 1 Geoscience Centre, University of Goettingen, Goettingen, Germany 2 School
Inverse Analysis of Soil Parameters Based on Deformation of a Bank Protection Structure Yixuan Xing 1, Rui Hu 2 *, Quan Liu 1 1 Geoscience Centre, University of Goettingen, Goettingen, Germany 2 School
New Constitutive Material Models in RS 2
 New Constitutive Material Models in RS 2 1.0 The Softening-Hardening Material Model Experimental evidence indicates that plastic deformation in soils starts from the early stages of loading. The typical
New Constitutive Material Models in RS 2 1.0 The Softening-Hardening Material Model Experimental evidence indicates that plastic deformation in soils starts from the early stages of loading. The typical
OP-029. INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST
 INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page 1 of 7 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS KYW Compiled by : Checked by LCH : TYC Approved by : OP-09. INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page of 7 9. INTERPRETATION
INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page 1 of 7 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS KYW Compiled by : Checked by LCH : TYC Approved by : OP-09. INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page of 7 9. INTERPRETATION
In-plane principal stress output in DIANA
 analys: linear static. class: large. constr: suppor. elemen: hx24l solid tp18l. load: edge elemen force node. materi: elasti isotro. option: direct. result: cauchy displa princi stress total. In-plane
analys: linear static. class: large. constr: suppor. elemen: hx24l solid tp18l. load: edge elemen force node. materi: elasti isotro. option: direct. result: cauchy displa princi stress total. In-plane
UTEXAS Underwater Slope
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS Figure 1. Underwater Slope Excavation Problem. 1 Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to build a UTEXAS model in GMS that uses a slope geometry line. This tutorial is similar to
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS Figure 1. Underwater Slope Excavation Problem. 1 Introduction This tutorial illustrates how to build a UTEXAS model in GMS that uses a slope geometry line. This tutorial is similar to
