Course: Grade 9 Applied Mathematics (MFM1P) Unit 1: Measurement (2D & 3D)
|
|
|
- Hillary Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course: Grade 9 Applied Mathematics (MFM1P) Unit 1: Measurement (2D & 3D)
2 Unit 1 Measurement (2D & 3D) Section Activity Page Investigation - Comparing Volumes Pair Share Volume Melting Ice Cream J Journal Activity Applications of Volume P Practice Scale Drawing Details P Practice Composite Figures Notes Exploring Composite Shapes P Practice Use What You Know Frayer Model The Rope Stretchers Right or Not? The Pythagorean Theorem Notes P Practice Pythagorean Theorem Puzzle Coach or Be Coached The Container! P Practice J Journal Activity 38 1.W Definition Page 39 1.S Unit Summary Page 41 1.R Reflecting on My Learning (3, 2, 1) 42 1.RLS Reflecting on Learning Skills 43 MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-2
3 1.1.1: Investigation Comparing Volumes Purpose Compare volumes of shapes that have the same base and height. Hypothesis I think that = 2. = 3. = Investigate How many times will the volume of the shape on the left fill the shape on the right? 1. V cone = V cylinder 2. V square pyramid = V square prism 3. V triangular pyramid = V triangular prism Conclusion MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-3
4 1.1.2: Pair Share Volume A Prisms Circle the shapes that are prisms. Volume of a prism = area of. B Pyramids Circle the shapes that are pyramids. Volume of a pyramid = volume of a prism. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-4
5 1.1.2: Pair Share Volume (continued) Calculate the volume of the following figures. Show your work. A Calculate the volume of the following figures. Show your work. A B 8 mm 15 mm 12 cm 5 cm MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-5
6 1.2.1: Melting Ice Cream Heather purchased an ice cream cone. The scoop of ice cream was a sphere. The height of the cone equals the diameter of both the cone and the sphere. If the ice cream melts, how much will overflow the cone? In Pairs A. What do we already know? 1. = Volume cone = Volume 2. Volume cylinder = (Area of Base) ( ) 3. Volume cone = (Area of Base) ( ) B. Using the two 3-D relational solids of the cone and sphere, compare. 1. Height cone and Height sphere Comparison: 2. Radius cone and Radius sphere Comparison: 3. Volume cone and Volume sphere Comparison: C. Conclusion = D. How much ice cream will overflow? Write a relationship statement. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-6
7 1.2.J: Journal Activity 1. Using words, pictures, numbers, and symbols, describe the relationships you discovered today. 2. Use the 3-D relational sets and record as many paired relationships as you can. For example, the small triangular prism is half the volume of the small squarebased prism. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-7
8 1.2.3: Applications of Volume 1. Calculate the volume of the perfume bottle. 5 cm 5 cm 3 cm 15 cm 8 cm 2. How much soup can this container hold? 7 cm 10 cm 3. Calculate the volume of the rectangular prism. 5 cm. 6 cm. 4 cm. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-8
9 1.2.3: Applications of Volume (continued) 4. Which popcorn container will hold more? 16 cm 16 cm 15 cm 8 cm 15 cm 5. How many times bigger is the second sphere? 5 m 15 m MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-9
10 1.2.3: Applications of Volume (continued) 6. How much more expensive should the large aquarium be than the small aquarium if the cost is based on the volume? 16 cm. 8 cm. 12 cm. 24 cm. 32 cm. 16 cm. 7. Determine the volume of the cabin. Show your work. 2 m 3 m 6 m 6 m MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-10
11 1.2.P: Practice 1. Using the relationships you have discovered, calculate the volume of each of the following 3-D figures. (a) 4 mm 6 mm 14 mm 5mm (b) 3 m 8 m (c) 4 m 2 m MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-11
12 1.2.P: Practice (continued) 2. A movie theatre wants to compare the volumes of popcorn in two containers, a cube with edge length 8.1 cm and a cylinder with radius 4.5 cm and height 8.0 cm. Which container holds more popcorn? Draw diagrams to support your solution An entertainment room is 10.5 m long by 7.5 m wide by 3.5 m high. If 5 m of air is needed for each person, how many people can use the room at one time? MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-12
13 1.3.2: Scale Drawing Details 1. Consider the two composite figures. (a) Identify the geometric shapes in each. Write the names on the diagrams. Figure 1 Figure 2 (b) Area For determining the area of the shaded regions, describe the features and calculations that are: i) the same ii) different (c) Which of the two figures is larger? By how much? Justify your answer using pictures, symbols, and words. (d) Perimeter Use a coloured pencil to outline the perimeters of the two figures. How do these two perimeters compare? MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-13
14 1.3.2: Scale Drawing Details (continued) 2. Use the diagram above a) What dimensions are needed to determine the perimeter? b) What dimensions are needed to determine the area? c) Calculate: Area Perimeter 3. Provide an example in daily life of a figure that involves more than one geometric shape. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-14
15 1.3.2: Scale Drawing Details (continued) 5 cm 40 cm 2. Use the diagram above a) What dimensions are needed to determine the area of the square? b) What dimensions are needed to determine the area of the circle? c) Calculate: Area of square Area of circle Area of shaded area 3. Provide an example in daily life of a figure that involves more than one geometric shape. Example: a church window MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-15
16 1.3.P: Practice 1. (a) Design a logo of your first and last initial, made of two or more simple geometric shapes. Make the appropriate measurements and calculate the total area and perimeter of your logo. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-16
17 1.4.2: Composite Figures Notes MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-17
18 1.4.2: Composite Figures Notes (continued) MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-18
19 1.4.3: Exploring Composite Shapes 3 cm 3 cm Perimeter Calculation 7 cm 4 cm 8 cm 4 cm 7 cm 14 cm Shape Divisions Area Calculations Option A Option B? Option C MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-19
20 1.4.P: Practice 2 1. Carpeting costs $12.50/m. How much would it cost to carpet the room below including GST and PST? 5 m 6 m 10 m 7 m MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-20
21 1.4.P: Practice (continued) 2. Calculate the area and perimeter of each figure. (a) 12 cm 8 cm 4 cm (b) 4.6 cm 5 cm 6.7 m (c) 7 m 4m 6 m MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-21
22 1.4.P: Practice (continued) 3. Find the area of the shaded regions only. a) 150 cm 30 cm 200 cm b) MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-22
23 1.4.4: Use What You Know Knowledge and Skills Calculate the area of the given circle. Reasoning and Proving Westview School has a track. Show your work. r = 2.5 cm You want to run 2 km every day. Determine how many times you have to go around the track. Show your work. Hint: A =πr 2 Communicating Gemma wants to tile her bathroom counter with mini tiles. She needs to determine the area of her counter space. Explain with words, diagrams, and symbols how she should determine the area. Connecting This figure has a radius of r units. r Which of the following formulas could be used to determine the perimeter? 1 2 a) 2 πr + r + r b) 0.75πr c) (2 π r) + r + r d) 2πr 4 4 Give reasons for your answer. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-23
24 1.4.5: Frayer Model Definition Facts/Characteristics Examples Composite Figures Non- Examples MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-24
25 1.5.1: The Rope Stretchers In ancient Egypt, mathematicians developed many useful ideas for everyday living. One example was used by Egyptian farmers. Each year the Nile River flooded, leaving behind a stretch of fertile land where the Egyptians grew their crops of barley and emmer wheat. But, when the river flooded, the boundaries of the fields were lost and had to be accurately redrawn. Egyptian surveyors or rope stretchers used lengths of ropes with equally spaced knots tied in them to measure land boundaries. When two fields bordered one another, the rope stretchers had to measure a right angle to form the corners of the fields. The establishment of boundaries was also important because the area of the land determined the amount of taxes, and the scribes kept the accounts for taxation. Excerpted from July 26, 2005 Literacy Connections 1. Why do the rope stretchers need to redraw the boundaries every year. 2. Why is it important to have boundaries? 3. Why is it important that the boundaries are 90? 4. Provide examples where you could use this technique today. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-25
26 1.5.3: Right or Not? Part A: Group Work 1) Record the three side lengths: Card A Card B 2) Follow the instructions on the overhead to construct your two triangles. Draw a labelled diagram of the triangle created by the three squares. Show side lengths. Card A Card B 3) Complete the table: Card Square with Square with Largest Square Type of Triangle side a side b with side c Right or Not 4) Share your data with another group. What observations can you make about the data? MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-26
27 1.5.3: Right or Not? (continued) Part B: Class Work 5) Complete the data table: Group Area of Square with side a Area of Square with side b Area of Largest Square with side c Type of Triangle Right or Not 6) What other observations can you make about the class data set? Verbal Model: Visual Model: Algebraic Model: MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-27
28 1.5.5: The Pythagorean Theorem Notes MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-28
29 1.5.5: The Pythagorean Theorem Notes (Continued) MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-29
30 1.5.P: Practice 1. Imagine you are a rope stretcher. Find two different combinations, not in the class list, which would create right-angled triangles. Explain how you know that the triangles are right-angled. Hint: Class Triangle 1: 3, 4, 5 Class Triangle 2: 6, 8, 10 What do you notice about these two triangles? MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-30
31 1.5.6: Pythagorean Theorem Puzzle Instructions: 1. Colour the 5 pieces of the puzzle above and the 5 pieces you received from your teacher. 2. Cut out pieces 1-5 only from copy your teacher provided. 3. Fit the 5 pieces of the puzzle into the large square above. Be sure that the pieces fit exactly into the square (There should be no paper overlapping, and no blank spaces) MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-31
32 1.6.1: Coach and Be Coached A coaches B B coaches A 5 mm x 12 mm 10 cm y 14 cm 12 m z 9 m 2 cm x 2 cm 3 m 12 m 8 m p 8 m m MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-32
33 1.6.1: Coach and Be Coached (continued) A coaches B B coaches A 55 cm 130 cm 60 cm w 44 cm h A hydro pole casts a shadow that is 10 m long. A technician measures the wire that runs from the top of the pole to the end of the shadow and finds it to be 26 m. How tall is the pole? Don is building a loft in his garage. The ladder he is using extends to 10 metres. The loft is 8 m from the floor. How far away from the wall should he anchor the ladder? MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-33
34 1.6.2: The Container! The Geobellies company wishes to make a new type of container for their product. The designer has created two containers: one the shape of a square-based pyramid, and the other a cone. Your job is to determine which container holds more. 1) Label the dimensions from your group card. Pyramid Cone slant height base length slant height diameter 2) Discuss with your partner how you could find the height of each container. 3) Record your ideas using words, pictures, and symbols. 4) Determine the height of each container. Show all of your work. Pyramid Cone MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-34
35 1.6.2: The Container! (Continued) 5) How much can each container hold? Show your work. Pyramid Cone 6) If the geobellies cost $0.005/cm 3, how much will it cost to fill each container? 7) Identify the shape with the greater volume. 8) Make a recommendation for the preferred design shape. Provide at least two reasons for your choice. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-35
36 1.6.P : Practice 1. Calculate the length of the missing side in each triangle. (a) 10 cm c 13 cm (b) 9 cm b 15 cm (c) y 12 m 5 m MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-36
37 1.6.P : Practice (continued) 2. A 5-m ladder is leaning against a house. Draw a diagram and add in any given measurements. The foot of the ladder is 3 m from the base of the wall. How high up the wall does the ladder reach? 3. Adam has made a picture frame. Draw a diagram and add in any given measurements. The frame is 60 cm long and 25 cm wide. To check that the frame has square corners, Adam measures the diagonal. How long should the diagonal be? Sketch a diagram to support your answer. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-37
38 1.6.J: Journal Activity Your friend was away for today s lesson. Write an describing how to find the height of a pyramid or cone when given the base length and slant height or diameter and slant height. Provide your own example. MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-38
39 1.W: Definition Page Term Picture / Sketch Definition Perimeter Length Width Radius Diameter Circumference Circle Area Rectangle Square Rhombus Parallelogram MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-39
40 1.W: Definition Page (Continued) Term Picture / Sketch Definition Triangle Right-Angled Triangle Hypotenuse Composite Figure Volume Prism Rectangular Prism Cylinder Sphere Hemisphere Cone Pyramid MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-40
41 1.S: Unit Summary Page Complete the following table to summarize the formulas you used in this unit. 2D Shape Sketch / Description Area Formula Example Rectangle / Square Triangle Circle Parallelogram Trapezoid 3D Solid Sketch / Description Volume Formula Example Rectangular Prism Cylinder Sphere Cone Pyramid MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-41
42 1.R Reflecting on My Learning (3, 2, 1) 3 Things I know well from this unit 2 Things I need explained more 1 Question I still have MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-42
43 1.RLS: Reflecting on Learning Skills Students should be aware of the importance that these skills have on your performance. After receiving your marked assessment, answer the following questions. Be honest with yourself. Good Learning Skills will help you now, in other courses and in the future. E Always G Sometimes S Need Improvement N Never Organization E G S N E G S N E G S N Work Habits E G S N E G S N E G S N E G S N E G S N E G S N Team Work E G S N E G S N E G S N Initiative E G S N E G S N E G S N E G S N I came prepared for class with all materials My work is submitted on time I keep my notebook organized. I attempt all of my homework I use my class time efficiently I limit my talking to the math topic on hand I am on time If I am away, I ask someone what I missed, I complete the work from the day that I missed. I am an active participant in pairs/group work I co-operate with others within my group I respect the opinions of others I participate in class discussion/lessons When I have difficulty I seek extra help After I resolve my difficulties, I reattempt the problem I review the daily lesson/ideas/concepts Works Independently E G S N I attempt the work on my own E G S N I try before seeking help E G S N If I have difficulties I ask others but I stay on task E G S N I am committed to tasks at hand Yes No I know all the different ways available in my school, where I can seek extra help. Yes No I tried my best. What will I do differently in the next unit to improve? MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-43
44 MFM 1P - Grade 9 Applied Mathematics Unit 1: Measurement 2D & 3D (DPCDSB Dec 2008) 1-44
MEASUREMENT Grade 9 Academic Mathematics Student Workbook MPM1D1 Making decisions in light of gospel values with an informed moral conscience
 Name: Teacher: 1-1 P a g e MEASUREMENT Grade 9 Academic Mathematics Student Workbook MPM1D1 Making decisions in light of gospel values with an informed moral conscience Cardinal Ambrozic C.S.S. http://www.dpcdsb.org/ambro
Name: Teacher: 1-1 P a g e MEASUREMENT Grade 9 Academic Mathematics Student Workbook MPM1D1 Making decisions in light of gospel values with an informed moral conscience Cardinal Ambrozic C.S.S. http://www.dpcdsb.org/ambro
Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem
 MPM 1D Unit 6: Measurement Lesson 1 Date: Learning goal: how to use Pythagorean Theorem to find unknown side length in a right angle triangle. Investigate: 1. What type of triangle is in the centre of
MPM 1D Unit 6: Measurement Lesson 1 Date: Learning goal: how to use Pythagorean Theorem to find unknown side length in a right angle triangle. Investigate: 1. What type of triangle is in the centre of
UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
 UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use the idea of measuring volume that we studied to find the volume of various 3 dimensional figures. We will also learn about
UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use the idea of measuring volume that we studied to find the volume of various 3 dimensional figures. We will also learn about
Unit 6: Day 5: Project Renovation
 Unit 6: Day 5: Project Renovation Minds On: 10 Action: 55 Consolidate:10 Math Learning Goals: Solve problems involving the areas of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, triangles, and circles and related
Unit 6: Day 5: Project Renovation Minds On: 10 Action: 55 Consolidate:10 Math Learning Goals: Solve problems involving the areas of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, triangles, and circles and related
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, D Geometry
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing 2D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, 2018 3D Geometry Two-dimensional shapes
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing 2D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, 2018 3D Geometry Two-dimensional shapes
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 20/21/22 February, D Geometry Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario NL 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0/1/ February, 018 3D Geometry Solutions Two-dimensional shapes
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario NL 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing D Geometry Review Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 0/1/ February, 018 3D Geometry Solutions Two-dimensional shapes
EMERGENCY SHELTER DESIGN STEM LEARNING AT ITS BEST
 KSB * 1 ( * KNOWLEDGE AND SKILL BUILDER) Geometric shapes student Name: Period: school: date: Hofstra University Center for Technological Literacy Simulations and Modeling for Technology Education This
KSB * 1 ( * KNOWLEDGE AND SKILL BUILDER) Geometric shapes student Name: Period: school: date: Hofstra University Center for Technological Literacy Simulations and Modeling for Technology Education This
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Someone else might choose to describe the closet by determining how many square tiles it would take to cover the floor. 6 ft.
 Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Areas Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot room. In fact, that is how
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon
 Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Unit 7: 3D Figures 10.1 & 10.2 2D formulas & Area of Regular Polygon NAME Name the polygon with the given number of sides: 3-sided: 4-sided: 5-sided: 6-sided: 7-sided: 8-sided: 9-sided: 10-sided: Find
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM. The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of
 Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Measurement 1 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Remember the Pythagorean Theorem: The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Name: Period: 2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review
 2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the number of lunch combinations that can be created if you order a soup, sandwich, drink and dessert. There are 4 soup choices, 5 sandwich choices, 3 drink
2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the number of lunch combinations that can be created if you order a soup, sandwich, drink and dessert. There are 4 soup choices, 5 sandwich choices, 3 drink
Name: DUE: HOUR: 2015/2016 Geometry Final Exam Review
 Name: DUE: HOUR: 2015/2016 Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Find x. 2. Find y. x = 3. A right triangle is shown below. Find the lengths x, y, and z. y = 4. Find x. x = y = z = x = 5. Find x. x = 6. ABC ~
Name: DUE: HOUR: 2015/2016 Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Find x. 2. Find y. x = 3. A right triangle is shown below. Find the lengths x, y, and z. y = 4. Find x. x = y = z = x = 5. Find x. x = 6. ABC ~
Pre-Algebra, Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Converse of the. Pythagorean Theorem 8.7.C. Decide whether the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem is true.
 LESSON 8. Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem ESSENTIAL QUESTION Expressions, equations, and relationships Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems. How can you test the converse
LESSON 8. Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem ESSENTIAL QUESTION Expressions, equations, and relationships Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems. How can you test the converse
Student Outcomes. Classwork. Opening Exercises 1 2 (5 minutes)
 Student Outcomes Students use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine an unknown dimension of a cone or a sphere. Students know that a pyramid is a special type of cone with triangular faces and a rectangular
Student Outcomes Students use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine an unknown dimension of a cone or a sphere. Students know that a pyramid is a special type of cone with triangular faces and a rectangular
My Notes CONNECT TO SCIENCE. Horticulture is the science and art of growing fruit, flowers, ornamental plants, and vegetables.
 SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Summarize/Paraphrase/ Retell, Use Manipulatives, Activating Prior Knowledge, Self/ Peer Revision The Horticulture Club has been given some land to build a greenhouse. The
SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Summarize/Paraphrase/ Retell, Use Manipulatives, Activating Prior Knowledge, Self/ Peer Revision The Horticulture Club has been given some land to build a greenhouse. The
Determine the surface area of the following square-based pyramid. Determine the volume of the following triangular prism. ) + 9.
 MPM 1D Name: Unit: Measurement Date: Calculating and of Three Dimensional Figures Use the Formula Sheet attached to help you to answer each of the following questions. Three problems are worked out for
MPM 1D Name: Unit: Measurement Date: Calculating and of Three Dimensional Figures Use the Formula Sheet attached to help you to answer each of the following questions. Three problems are worked out for
17.2 Surface Area of Prisms
 h a b c h a b c Locker LESSON 17. Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.11.C Apply the formulas for the total and lateral surface area of three-dimensional
h a b c h a b c Locker LESSON 17. Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Texas Math Standards The student is expected to: G.11.C Apply the formulas for the total and lateral surface area of three-dimensional
S3 (3.1) N5 Volume.notebook April 30, 2018
 Daily Practice 16.3.2018 Q1. Multiply out and simplify (3x - 2)(x 2-7x + 3) Daily Practice 19.3.2018 Q1. Multiply out and simplify (2x + 3)(x 2 + 7x + 4) Q2. Factorise fully 3x 2-75 Q2. Simplify x 3 (x
Daily Practice 16.3.2018 Q1. Multiply out and simplify (3x - 2)(x 2-7x + 3) Daily Practice 19.3.2018 Q1. Multiply out and simplify (2x + 3)(x 2 + 7x + 4) Q2. Factorise fully 3x 2-75 Q2. Simplify x 3 (x
GEOMETRY REVIEW PACKET
 Obstacles are those frightful things you see when you take your eyes off your goal -Henry Ford As of Spring 2016, geometry is no longer a prerequisite for MTH101 and MTH165 Spend time with the material
Obstacles are those frightful things you see when you take your eyes off your goal -Henry Ford As of Spring 2016, geometry is no longer a prerequisite for MTH101 and MTH165 Spend time with the material
Name: Target 12.2: Find and apply surface of Spheres and Composites 12.2a: Surface Area of Spheres 12.2b: Surface Area of Composites Solids
 Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume
 HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
S3 (3.1) Volume.notebook March 02, 2016
 Daily Practice 22.2.2016 Q1. Multiply out and simplify (3x - 2)(x 2-7x + 3) Q2. Factorise fully 3x 2-75 L.I: Today we will be revising how to find the volume of a prism. Q3. Calculate the value of a house
Daily Practice 22.2.2016 Q1. Multiply out and simplify (3x - 2)(x 2-7x + 3) Q2. Factorise fully 3x 2-75 L.I: Today we will be revising how to find the volume of a prism. Q3. Calculate the value of a house
Measurement Unit. This booklet belongs to:
 Measurement Unit This booklet belongs to: LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Questions to review This booklet is homework and will be collected on the test day. Your teacher has important
Measurement Unit This booklet belongs to: LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Questions to review This booklet is homework and will be collected on the test day. Your teacher has important
Perfect square numbers are formed when we multiply a number (factor) by itself, or square a number. 9 is a perfect square, and 3 is it s factor.
 Math Unit 1: Square Roots and Surface Area. Review from Grade 8: Perfect Squares What is a perfect square? Perfect square numbers are formed when we multiply a number (factor) by itself, or square a number.
Math Unit 1: Square Roots and Surface Area. Review from Grade 8: Perfect Squares What is a perfect square? Perfect square numbers are formed when we multiply a number (factor) by itself, or square a number.
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Grade 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume
 ID : ae-7-mensuration-perimeter-area-volume [1] Grade 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) A teacher gave a rectangular colouring
ID : ae-7-mensuration-perimeter-area-volume [1] Grade 7 Mensuration - Perimeter, Area, Volume For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) A teacher gave a rectangular colouring
11.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones
 11.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Learning Objectives Find the surface area of a pyramid. Find the surface area of a cone. Review Queue 1. A rectangular prism has sides of 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm. What
11.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Learning Objectives Find the surface area of a pyramid. Find the surface area of a cone. Review Queue 1. A rectangular prism has sides of 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm. What
Unit 7: Area and Volume
 Unit 7: Area and Volume Name Math 8, Period Rectangular Prism Triangular Prism Cylinder Cone Sphere Concepts and Skills to be mastered: By the end of this section students should be able to: 1. Find the
Unit 7: Area and Volume Name Math 8, Period Rectangular Prism Triangular Prism Cylinder Cone Sphere Concepts and Skills to be mastered: By the end of this section students should be able to: 1. Find the
Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name a solid that fits each description. 1. a can of beans 2. a shoe box 3. a pyramid with five lateral faces 4. a solid with six vertices 5. a prism with bases shaped
Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name a solid that fits each description. 1. a can of beans 2. a shoe box 3. a pyramid with five lateral faces 4. a solid with six vertices 5. a prism with bases shaped
FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet. Modeling and Geometry
 FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet Modeling and Geometry Table of Contents MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.2 EOC Practice... 6 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.3 EOC Practice... 8 Modeling with
FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet Modeling and Geometry Table of Contents MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.2 EOC Practice... 6 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.3 EOC Practice... 8 Modeling with
Geometry. Week 32: April 13-17, 2015
 G.13 Geometry Week 32: April 13-17, 2015 The student will use formulas for surface area and volume of threedimensional objects to solve real-world problems. G.14 The student will use similar geometric
G.13 Geometry Week 32: April 13-17, 2015 The student will use formulas for surface area and volume of threedimensional objects to solve real-world problems. G.14 The student will use similar geometric
Unit 5. Area & Volume. Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume. Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18. Name: Math Teacher:
 Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18 Name: Unit 5 Area & Volume Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume Review Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5
Math 6 Unit 5 Calendar 1/14 1/15 1/16 1/17 1/18 Name: Unit 5 Area & Volume Area Composite Area Surface Area Volume Review Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5 Test Or Computer Lab Unit 5
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D 2D & 3D GEOMETRY PERIMETER/CIRCUMFERENCE & AREA SURFACE AREA & VOLUME
 Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2016-17 2D & 3D GEOMETRY PERIMETER/CIRCUMFERENCE & AREA SURFACE AREA & VOLUME CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S) Vocabulary
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2016-17 2D & 3D GEOMETRY PERIMETER/CIRCUMFERENCE & AREA SURFACE AREA & VOLUME CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S) Vocabulary
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2013 KCATM Math Competition
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2013 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes You may
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2013 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes You may
Mathematics Background
 Measurement All measurements are approximations. In their work in this Unit, students explore ways to find measures for two and three dimensional figures. Even using exact formulas depends on how students
Measurement All measurements are approximations. In their work in this Unit, students explore ways to find measures for two and three dimensional figures. Even using exact formulas depends on how students
Chapter 1: Symmetry and Surface Area
 Chapter 1: Symmetry and Surface Area Name: Section 1.1: Line Symmetry Line of symmetry(or reflection): divides a shape or design into two parts. Can be found using: A mirra Folding Counting on a grid Section
Chapter 1: Symmetry and Surface Area Name: Section 1.1: Line Symmetry Line of symmetry(or reflection): divides a shape or design into two parts. Can be found using: A mirra Folding Counting on a grid Section
Homework. GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area
 GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area Homework Video tutorials: http://bit.ly/eurekapusd Info for parents: http://bit.ly/pusdmath 5 GRADE Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 5 MODULE
GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area Homework Video tutorials: http://bit.ly/eurekapusd Info for parents: http://bit.ly/pusdmath 5 GRADE Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 5 MODULE
Math 2 Plane Geometry part 1 Unit Updated January 13, 2017
 Complementary angles (two angles whose sum is 90 ) and supplementary angles (two angles whose sum is 180. A straight line = 180. In the figure below and to the left, angle EFH and angle HFG form a straight
Complementary angles (two angles whose sum is 90 ) and supplementary angles (two angles whose sum is 180. A straight line = 180. In the figure below and to the left, angle EFH and angle HFG form a straight
2nd Semester Exam Review
 Geometry 2nd Semester Exam Review Name: Date: Per: Trig & Special Right Triangles 1. At a certain time of the day, a 30 meter high building cast a shadow that is 31 meters long. What is the angle of elevation
Geometry 2nd Semester Exam Review Name: Date: Per: Trig & Special Right Triangles 1. At a certain time of the day, a 30 meter high building cast a shadow that is 31 meters long. What is the angle of elevation
Surface Area and Volume
 Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Surface Area and Volume Day 1 - Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area = The total area of the surface of a three-dimensional object (Or think of it as the amount of paper you ll need to wrap the shape.)
Franklin Math Bowl 2008 Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6
 Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6 1. The fraction 32 17 can be rewritten by division in the form 1 p + q 1 + r Find the values of p, q, and r. 2. Robert has 48 inches of heavy gauge wire. He decided to
Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6 1. The fraction 32 17 can be rewritten by division in the form 1 p + q 1 + r Find the values of p, q, and r. 2. Robert has 48 inches of heavy gauge wire. He decided to
#1 A: Surface Area of Triangular Prisms Calculate the surface area of the following triangular prisms. You must show ALL of your work.
 #1 A: Surface Area of Triangular Prisms Calculate the surface area of the following triangular prisms. You must show ALL of your work. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) #1 B: VOLUME of Triangular Prisms Calculate the
#1 A: Surface Area of Triangular Prisms Calculate the surface area of the following triangular prisms. You must show ALL of your work. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) #1 B: VOLUME of Triangular Prisms Calculate the
Mr. Whelan Name: Block:
 Mr. Whelan Name: Block: Geometry/Trig Unit 10 Area and Volume of Solids Notes Packet Day 1 Notes - Prisms Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 6cm Find the area of each face: Front:
Mr. Whelan Name: Block: Geometry/Trig Unit 10 Area and Volume of Solids Notes Packet Day 1 Notes - Prisms Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 6cm Find the area of each face: Front:
Area rectangles & parallelograms
 Area rectangles & parallelograms Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot
Area rectangles & parallelograms Rectangles One way to describe the size of a room is by naming its dimensions. So a room that measures 12 ft. by 10 ft. could be described by saying its a 12 by 10 foot
9 ft. 10 cm. 8 ft. 9 cm. 17 cm. 10 cm. 8 cm. 15 cm. 18 m 16 m. 14 m. Geometry: Homework Problems. Rectangles & Parallelograms
 Geometry: Homework Problems Rectangles & Parallelograms Homework Find the area of each figure. 11. 9 ft 15. 8 ft 10 cm 9 cm 17 cm 12. 14 mm 16. The length of a rectangle is 17 m and the width is 5.25 m.
Geometry: Homework Problems Rectangles & Parallelograms Homework Find the area of each figure. 11. 9 ft 15. 8 ft 10 cm 9 cm 17 cm 12. 14 mm 16. The length of a rectangle is 17 m and the width is 5.25 m.
Chapter 1 Measurement
 Chapter 1 Measurement Math 1201 1 Chapter 1 Measurement Sections 1.1-1.3: Goals: Converting between imperial units by unit analysis Converting between SI units Converting between SI and imperial units
Chapter 1 Measurement Math 1201 1 Chapter 1 Measurement Sections 1.1-1.3: Goals: Converting between imperial units by unit analysis Converting between SI units Converting between SI and imperial units
Sect Volume. 3 ft. 2 ft. 5 ft
 199 Sect 8.5 - Volume Objective a & b: Understanding Volume of Various Solids The Volume is the amount of space a three dimensional object occupies. Volume is measured in cubic units such as in or cm.
199 Sect 8.5 - Volume Objective a & b: Understanding Volume of Various Solids The Volume is the amount of space a three dimensional object occupies. Volume is measured in cubic units such as in or cm.
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D. Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference Surface Area and Volume
 Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2015-16 Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference Surface Area and Volume CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S)
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2015-16 Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference Surface Area and Volume CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S)
11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
 11. Three-Dimensional Figures Essential Question What is the relationship between the numbers of vertices V, edges E, and faces F of a polyhedron? A polyhedron is a solid that is bounded by polygons, called
11. Three-Dimensional Figures Essential Question What is the relationship between the numbers of vertices V, edges E, and faces F of a polyhedron? A polyhedron is a solid that is bounded by polygons, called
Explore Solids
 1212.1 Explore Solids Surface Area and Volume of Solids 12.2 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volume of Pyramids and
1212.1 Explore Solids Surface Area and Volume of Solids 12.2 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.3 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 12.4 Volume of Prisms and Cylinders 12.5 Volume of Pyramids and
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes
 Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Math Mealy Mountain Collegiate. Sample Midterm Exam. Name:
 Math 2202 Mealy Mountain Collegiate Sample Midterm Exam Name: Formulas Square Rectangle A = s 2 A = l x w P 2l 2 w Triangle C 2 r A b h 2 Circle A r 2 C d or Cube Rectangle Prism SA = 6s 2 SA =2(l x w)+2(lxh)+2(wxh)
Math 2202 Mealy Mountain Collegiate Sample Midterm Exam Name: Formulas Square Rectangle A = s 2 A = l x w P 2l 2 w Triangle C 2 r A b h 2 Circle A r 2 C d or Cube Rectangle Prism SA = 6s 2 SA =2(l x w)+2(lxh)+2(wxh)
7 th Grade CCGPS Math LFS Unit 5: Geometry
 7 th Grade CCGPS Math LFS Unit 5: Geometry Standards: Cluster: Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MCC7.G.2 (DOK2) Draw (freehand, with ruler
7 th Grade CCGPS Math LFS Unit 5: Geometry Standards: Cluster: Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MCC7.G.2 (DOK2) Draw (freehand, with ruler
Course 2 Unit 4 Practice
 Course 2 Unit 4 Practice Lesson 13-1 1. Model with mathematics. Two angles are supplementary. One measures (3x)8 and the other measures 518. a. Draw a pair of adjacent, supplementary angles and label them
Course 2 Unit 4 Practice Lesson 13-1 1. Model with mathematics. Two angles are supplementary. One measures (3x)8 and the other measures 518. a. Draw a pair of adjacent, supplementary angles and label them
Part I Multiple Choice
 Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Math 10 C Measurement Unit
 Math 10 C Measurement Unit Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which imperial unit is most appropriate
Math 10 C Measurement Unit Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which imperial unit is most appropriate
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan
 Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
5th Grade Mathematics Essential Standards
 Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
19.2 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders
 Name Class Date 19. Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Essential Question: How can you find the surface area of a prism or cylinder? Resource Locker Explore Developing a Surface Area Formula Surface
Name Class Date 19. Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Essential Question: How can you find the surface area of a prism or cylinder? Resource Locker Explore Developing a Surface Area Formula Surface
Copy the squares below onto 1-cm grid paper.
 Project Making Squares into Cubes Part 1 Copy the squares below onto 1-cm grid paper. Materials 1-cm grid paper wooden or plastic cubes ruler 1-cm grid card stock scissors tape Determine the area of each
Project Making Squares into Cubes Part 1 Copy the squares below onto 1-cm grid paper. Materials 1-cm grid paper wooden or plastic cubes ruler 1-cm grid card stock scissors tape Determine the area of each
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3)
 Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3) (136) 11.1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Page 692-693 #7-23 odd, 35 (137) 11.2/11.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Prisms Page 703-705 #1, 2, 7-9, 11-13, 25,
Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3) (136) 11.1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Page 692-693 #7-23 odd, 35 (137) 11.2/11.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Prisms Page 703-705 #1, 2, 7-9, 11-13, 25,
Unit 8 Syllabus: Surface Area & Volume
 Date Period Day Unit 8 Syllabus: Surface Area & Volume Topic 1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Surface Area and Volume of Spheres 3 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones
Date Period Day Unit 8 Syllabus: Surface Area & Volume Topic 1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Surface Area and Volume of Spheres 3 Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones
Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment GEOMETRY G.14. Topic: Three-Dimensional Figures
 Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment GEOMETRY G.14 Topic: Three-Dimensional Figures Standards of Learning Blueprint Summary Reporting Category Geometry SOL Number of Items Reasoning, Lines, and G.1(a-d),
Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment GEOMETRY G.14 Topic: Three-Dimensional Figures Standards of Learning Blueprint Summary Reporting Category Geometry SOL Number of Items Reasoning, Lines, and G.1(a-d),
16.3 Volume of Cones
 Name Class Date 16. Volume of Cones Essential Question: How do you calculate the volumes of composite figures that include cones? Explore G.11.D Apply the formulas for the volume of three-dimensional figures,
Name Class Date 16. Volume of Cones Essential Question: How do you calculate the volumes of composite figures that include cones? Explore G.11.D Apply the formulas for the volume of three-dimensional figures,
Math 8 Shape and Space Resource Kit Parent Guide
 Math 8 Shape and Space Resource Kit Parent Guide Resources Included with this Resource Kit (To be Returned to HCOS): Parent Guide Student worksheets Jenga blocks (game) Set of mini geosolids (Right Start
Math 8 Shape and Space Resource Kit Parent Guide Resources Included with this Resource Kit (To be Returned to HCOS): Parent Guide Student worksheets Jenga blocks (game) Set of mini geosolids (Right Start
To find the surface area of a pyramid and a cone
 11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
The Skyline Design Challenge
 The Skyline Design Challenge An island named Willingdon has just been human-made. The president of the island is searching for young, creative, and brilliant architects who can build a city in Willingdon.
The Skyline Design Challenge An island named Willingdon has just been human-made. The president of the island is searching for young, creative, and brilliant architects who can build a city in Willingdon.
UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet 16.1 Circles: Area Establish the area formula for a circle. Apply the area formula for a circle to realistic problems. Demonstrate
Name Period Date UNIT 4: LENGTH, AREA, AND VOLUME WEEK 16: Student Packet 16.1 Circles: Area Establish the area formula for a circle. Apply the area formula for a circle to realistic problems. Demonstrate
6. If QRSTU is a regular pentagon, what is the measure of T? 1. If STUV is a parallelogram, what are the coordinates of point U?
 1. If UV is a parallelogram, what are the coordinates of point U?. If RU is a regular pentagon, what is the measure of? (0, y) U(?,?) (, 0) V( + z, 0) 7. hree siblings are to share an inheritance of $1,0
1. If UV is a parallelogram, what are the coordinates of point U?. If RU is a regular pentagon, what is the measure of? (0, y) U(?,?) (, 0) V( + z, 0) 7. hree siblings are to share an inheritance of $1,0
Practice A Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Parallelograms
 8-1 Practice A Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Parallelograms Find the perimeter of each figure. 1. 5 ft 2. 3. 13 cm 4 ft 6 cm 3x in. 10x in. 18 ft 38 cm 26x in. Graph and find the area of each figure
8-1 Practice A Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Parallelograms Find the perimeter of each figure. 1. 5 ft 2. 3. 13 cm 4 ft 6 cm 3x in. 10x in. 18 ft 38 cm 26x in. Graph and find the area of each figure
Area & Volume. Contents Area and perimeter formulae Finding missing lengths when given area or perimeter...
 Area & Volume Aidan Ryan aidan.ryan@stmichaelscollege.com Contents Area and perimeter formulae... 2 Finding missing lengths when given area or perimeter... 8 Volume and surface area formulae... 9 Finding
Area & Volume Aidan Ryan aidan.ryan@stmichaelscollege.com Contents Area and perimeter formulae... 2 Finding missing lengths when given area or perimeter... 8 Volume and surface area formulae... 9 Finding
Unit 5: Day 4: Maximizing Area for a Given Perimeter
 Unit 5: Day 4: Maximizing Area for a Given Perimeter Minds On: 15 Action: 35 Learning Goal: Students will Explore optimization of two-dimensional figures Solve problems to maximize area for a given perimeter
Unit 5: Day 4: Maximizing Area for a Given Perimeter Minds On: 15 Action: 35 Learning Goal: Students will Explore optimization of two-dimensional figures Solve problems to maximize area for a given perimeter
8th Grade. Slide 1 / 97. Slide 2 / 97. Slide 3 / 97. 3D Geometry. Table of Contents. 3-Dimensional Solids. Volume. Glossary & Standards
 Slide 1 / 97 Slide 2 / 97 8th Grade 3D Geometry 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 97 3-Dimensional Solids Click on the topic to go to that section Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids,
Slide 1 / 97 Slide 2 / 97 8th Grade 3D Geometry 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 97 3-Dimensional Solids Click on the topic to go to that section Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids,
Do You Measure Up? Nancy Crawford, Kathy Jackson, Jennifer Pack Southern Middle School
 Do You Measure Up? Nancy Crawford, Kathy Jackson, Jennifer Pack Southern Middle School Approximate Timeline: Two-three weeks Area(s) of Core Content: Mathematics (Geometry) Organizers: Why do I need to
Do You Measure Up? Nancy Crawford, Kathy Jackson, Jennifer Pack Southern Middle School Approximate Timeline: Two-three weeks Area(s) of Core Content: Mathematics (Geometry) Organizers: Why do I need to
d = (x 2 - x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 - y 1 ) 2 Student Name: Date: Teacher Name: Sunil Dudeja Score:
 Geometry EOC (GSE) Quiz Answer Key Equations and Measurement - (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.4) Use Coordinates For Theorems, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.5 ) Prove Slope Criteria, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.6) Find The Point, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.7
Geometry EOC (GSE) Quiz Answer Key Equations and Measurement - (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.4) Use Coordinates For Theorems, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.5 ) Prove Slope Criteria, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.6) Find The Point, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.7
2x + 3x = 180 5x = (5x) = 1 5 (180) x = 36. Angle 1: 2(36) = 72 Angle 2: 3(36) = 108
 GRADE 7 MODULE 6 TOPIC A LESSONS 1 4 KEY CONCEPT OVERVIEW In this topic, students return to using equations to find unknown angle measures. Students write equations to model various angle relationships
GRADE 7 MODULE 6 TOPIC A LESSONS 1 4 KEY CONCEPT OVERVIEW In this topic, students return to using equations to find unknown angle measures. Students write equations to model various angle relationships
1: #1 4, ACE 2: #4, 22. ACER 3: #4 6, 13, 19. ACE 4: #15, 25, 32. ACE 5: #5 7, 10. ACE
 Homework Answers from ACE: Filling and Wrapping ACE Investigation 1: #1 4, 10 13. ACE Investigation : #4,. ACER Investigation 3: #4 6, 13, 19. ACE Investigation 4: #15, 5, 3. ACE Investigation 5: #5 7,
Homework Answers from ACE: Filling and Wrapping ACE Investigation 1: #1 4, 10 13. ACE Investigation : #4,. ACER Investigation 3: #4 6, 13, 19. ACE Investigation 4: #15, 5, 3. ACE Investigation 5: #5 7,
Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1
 Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1 1 Intersecting lines: When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are supplementary (they make a line and add up to 180 degrees, and vertical angles (angles across from each
Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1 1 Intersecting lines: When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are supplementary (they make a line and add up to 180 degrees, and vertical angles (angles across from each
4. Describe the correlation shown by the scatter plot. 8. Find the distance between the lines with the equations and.
 Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework. SA of Prisms & Pyramids Pg. 441 # 1, 3, 5a, 7b, 11bc, 16. Surface Area of Cylinders WS 6.6
 UNIT 6 MEASUREMENT Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework May 6.1 8.1 May 4 6. 8. The Pythagorean Theorem Pg. 4 # 1ac, ac, ab, 4ac, 5, 7, 8, 10 Perimeter and Area (NO CIRCLES) Pg. 4 # 1acde, abdf,, 4, 11, 14,
UNIT 6 MEASUREMENT Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework May 6.1 8.1 May 4 6. 8. The Pythagorean Theorem Pg. 4 # 1ac, ac, ab, 4ac, 5, 7, 8, 10 Perimeter and Area (NO CIRCLES) Pg. 4 # 1acde, abdf,, 4, 11, 14,
Geometry: Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Rectangular Prism:
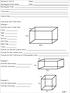 : Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Date: Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 Find the area of each face: 6cm Front: Back: Top: 8cm Bottom: Left Side: Right Side: 10cm Total: How do you
: Unit 11 Rectangular Prism Notes Date: Rectangular Prism: How do we find Total Area? Example 1 Find the area of each face: 6cm Front: Back: Top: 8cm Bottom: Left Side: Right Side: 10cm Total: How do you
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
Geometry Foundations Planning Document
 Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
CHAPTER 12. Extending Surface Area and Volume
 CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 1 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 1 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
, 6.7,, Order the numbers from least to greatest. 1. 1, 0, 2, 5, 4. Simplify the expression. 10.
 Getting Ready for Pre-Algebra or Algebra Summer Math Practice The following are practice questions to evaluate the students understanding of concepts and skills taught in seventh grade as a readiness for
Getting Ready for Pre-Algebra or Algebra Summer Math Practice The following are practice questions to evaluate the students understanding of concepts and skills taught in seventh grade as a readiness for
Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry
 Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Day Classwork Day Homework Monday 2/12 Tuesday 2/13 Wednesday 2/14 Areas of Regular Polygons 1 HW 11.1 Volume of Prisms & Cylinders 2 HW 11.4 Volume of Pyramids and Cones
Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Day Classwork Day Homework Monday 2/12 Tuesday 2/13 Wednesday 2/14 Areas of Regular Polygons 1 HW 11.1 Volume of Prisms & Cylinders 2 HW 11.4 Volume of Pyramids and Cones
Practice Test - Chapter Use isometric dot paper and the orthographic drawings to sketch the solid.
 1. Use isometric dot paper and the orthographic drawings to sketch the solid. top view: There are 3 rows and 6 columns. The dark segments indicate changes in depth at the 2nd and 3rd columns. left view:
1. Use isometric dot paper and the orthographic drawings to sketch the solid. top view: There are 3 rows and 6 columns. The dark segments indicate changes in depth at the 2nd and 3rd columns. left view:
Mathematics Curriculum
 6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
29 GEOMETRY AND MEASURE: AREA AND VOLUME
 29 GEOMETRY AND MEASURE: AREA AND VOLUME Recognise units of measurement used for length, area and volume Know and apply formulae to calculate area of triangles, circles, parallelograms and trapezia Calculate
29 GEOMETRY AND MEASURE: AREA AND VOLUME Recognise units of measurement used for length, area and volume Know and apply formulae to calculate area of triangles, circles, parallelograms and trapezia Calculate
Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes
 26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
S P. Geometry Final Exam Review. Name R S P Q P S. Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be:
 Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
CHAPTER 12 HERON S FORMULA Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 HERON S FORMULA 1.1 Introduction You have studied in earlier classes about figures of different shapes such as squares, rectangles, triangles and quadrilaterals. You have also calculated perimeters
CHAPTER 1 HERON S FORMULA 1.1 Introduction You have studied in earlier classes about figures of different shapes such as squares, rectangles, triangles and quadrilaterals. You have also calculated perimeters
DRAFT CHAPTER. Surface Area GET READY. xxx. Math Link. 5.1 Warm Up xxx. 5.1 Views of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx. 5.
 CHAPTER 5 Surface Area GET READY Math Link xxx xxx 5.1 Warm Up xxx 5.1 Views of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.2 Warm Up xxx 5.2 Nets of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.3 Warm Up xxx 5.3 Surface Area
CHAPTER 5 Surface Area GET READY Math Link xxx xxx 5.1 Warm Up xxx 5.1 Views of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.2 Warm Up xxx 5.2 Nets of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.3 Warm Up xxx 5.3 Surface Area
When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all its outer surfaces or faces.
 Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
Lesson 3 Lesson 3, page 1 of 10 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11. Nets & Surface Area When discussing 3-D solids, it is natural to talk about that solid s Surface Area, which is the sum of the areas of all
