More Specific Announcements in BGP. Geoff Huston APNIC
|
|
|
- Edmund Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 More Specific Announcements in BGP Geoff Huston APNIC
2 What s a more specific? A prefix advertisement that refines a covering advertisement / /16
3 Why advertise a more specific? I: To redirect packets to a different network: hole punching prefixes /8 AS Different Origin AS /16 AS
4 Example: Type I Network Path >* / >* /
5 Why advertise a more specific? II: To redirect incoming traffic to different network paths: traffic engineering prefixes /8 AS /9 AS /9 AS Same Origin AS, different AS Path AS AS 65537
6 Example: Type II Network Path *> / i *> / i *> / i
7 Why advertise a more specific? III: To prevent more specific prefix hijacking: more specific overlays /22 AS /24 AS Same Origin AS, same AS Path /24 AS /24 AS /24 AS 65530
8 Example: Type III Network Path *> / i *> / i *> / i *> / i *> / i
9 How many ebgp route advertisements are more specifics? AS June 2017 Routes Advertised Address Span ebgp Routes: 671, B /32s More Specifics: 357,372 (53%) 0.82B /32s (28%)
10 Has this changed over time? IPv
11 Has this changed over time? IPv4 IPv6
12 Has this changed over time? 38% 50% IPv4 IPv6 Ratio of More Specifics : Total Advertisements (%)
13 Has this changed over time? Surprisingly not for IPv4! In the IPv4 network more specifics have been ~50% of the Internet s announced route set for the past 10 years. In IPv6 the relative number of more specifics is climbing, and now stands at 40% of the total set of announced IPv6 prefixes
14 More Specific Types Prefix Counts
15 More Specific Types Prefix Counts IPv4 IPv6
16 More Specific Types Relative Counts IPv4 IPv6
17 More Specific Types In both IPv4 and IPv6: Type I prefixes ( hole punching ) are declining over time (relatively) Type II prefixes ( traffic engineering ) have been relatively constant at some 30% of more specifics Type III prefixes ( overlays ) have risen (relatively) and are now the more prevalent form of advertised more specifics in both IPv4 and IPv6
18 What about Address Spans covered by more specifics?
19 What about Address Spans covered by more specifics? Despite IPv4 address exhaustion from 2011, the span of addresses that are announced by more specifics continues to grow by some 32M /32 s per year
20 What about Address Spans covered by more specifics? IPv6
21 What about Address Spans covered by more specifics? 26% 2.5% IPv4 IPv6 Ratio of More Specific Address Span : Total Advertised Span (%)
22 Address Span: Breakdown into Types IPv4 IPv6
23 % of Total Span: Breakdown into Types IPv4 IPv6
24 Overlays are the majority of More Specifics In both protocols the largest block of more specific announcements in terms of address span are overlays where the AS Path of the enclosing aggregate and the more specific are identical The initial IPv6 network had little in the way of overlays and had a high proportion of Type I (Hole Punching) more specifics. This has changed over time and the recent profile is similar to IPv4
25 BGP Updates Overlays do not change routing, but do they add to the routing load? Are more specifics noisier than aggregates? Are overlays more active in terms of BGP Updates than other more specific types?
26 Update count by Prefix Type
27 Update count by Prefix Type IPv4 IPv6
28 Update Count In IPv4 the update count for more specific prefixes is greater than the comparable count for root prefixes, while the opposite is the case in IPv6. But the relative count of more specifics is ten times lower in IPv6 Let s normalise this by dividing the update count by the number of prefixes to get the average update count per prefix of each type
29 Relative Update count by Prefix Type
30 Relative Update count by Prefix Type IPv4 IPv6
31 Relative Updates On average, in IPv4 More Specifics are slightly noisier than Roots, while in IPv6 roots and more specifics are equally likely to be the subject of BGP updates Are different types of more specifics more or less stable in BGP terms?
32 Average Number of Updates Per More Specific Prefix Type
33 Average Number of Updates Per More Specific Prefix Type IPv4 IPv6
34 Average Number of Updates Per More Specific Prefix Type In IPv4 Type II Traffic Engineering Prefixes show a slightly higher level of BGP instability on average over Type I Hole Punching Prefixes, while Type III Overlay Prefixes show the lowest average update rate of more specifics In IPv6 this has only been apparent in the past three years, where Type II Traffic Engineering Prefixes are showing the greatest levels of BGP instability and Type I Hole Punching more specifics showing the lowest update rates
35 BGP Instability is heavily skewed IPv4 IPv6
36 BGP Instability is heavily skewed Instead of looking at update profiles averaged across all prefixes, lets now look only at those prefixes that showed instability (were updated) each day ( active prefixes)
37 What Type of Active Prefixes are more Unstable?
38 What Type of Active Prefixes are more Unstable? IPv4 IPv6
39 What Type of Prefixes are more Unstable? Type II More Specific Prefixes (Traffic Engineering) are approximately twice as likely to be unstable than either root prefixes or other types of More Specifics in both IPv4 and IPv6 This matches a rough intuition about the nature of more specifics, where overlays and hole punching would be expected to be as stable as root announcements
40 Average Number of Updates per Active Prefix Type IPv4 IPv6
41 Average Number of Updates per Active Prefix Type In IPv4 Type II Traffic Engineering Prefixes have a greater average number of updates than other prefix types In IPv6 Root Prefixes tend to have a lower average number of updates than other prefix types Perhaps the significant message here is that IPv6 has a higher inherent level of routing instability unstable prefixes in IPv6 have 100x more instability events per unstable prefix on average than unstable prefixes in IPv4
42 What if All Overlay more specific prefixes were removed from the routing table?
43 Table Size Implications IPv4 IPv6
44 Update Count Implications IPv4 IPv6
45 What if All Overlay more specific prefixes were removed from the routing table? Both IPv4 and IPv6 routing tables would drop in size by approximately 30%, as Overlay more specifics are now the predominate type of more specifics in the routing tables The rate of dynamic instability in BGP would not change by any significant amount, as overlay more specifics are relatively stable prefixes
46 Summary of Findings More specifics add to both the size and the update load of BGP
47 Summary of Findings More specifics add to both the size and the update load of BGP However BGP itself is both a reachability and a traffic engineering tool, and more specifics are often used to qualify reachability by traffic engineering. We have no other viable internet-wide traffic engineering tools, so this particular use of BGP really has no alternative
48 Summary of Findings More specifics add to both the size and the update load of BGP However BGP itself is both a reachability and a traffic engineering tool, and more specifics are often used to qualify reachability by traffic engineering. We have no other viable internet-wide traffic engineering tools, so this particular use of BGP really has no alternative Recent years have seen the decline of hole punching as more providers tend to treat their address blocks as integral units.
49 Summary of Findings More specifics add to both the size and the update load of BGP However BGP itself is both a reachability and a traffic engineering tool, and more specifics are often used to qualify reachability by traffic engineering. We have no other viable internet-wide traffic engineering tools, so this particular use of BGP really has no alternative Recent years have seen the decline of hole punching as more providers tend to treat their address blocks as integral units. Overlays are becoming more prevalent as a means of protecting a routing block from more specific hijack threats. While this has implications in terms of total table size it has no significant impact on BGP update rates.
50 Summary of Findings More specifics add to both the size and the update load of BGP However BGP itself is both a reachability and a traffic engineering tool, and more specifics are often used to qualify reachability by traffic engineering. We have no other viable internet-wide traffic engineering tools, so this particular use of BGP really has no alternative Recent years have seen the decline of hole punching as more providers tend to treat their address blocks as integral units. Overlays are becoming more prevalent as a mean of protecting a routing block from more specific hijack threats. While this has implications in terms of total table size it has no significant impact on BGP update rates. There is the question of total instability in IPv6 being far greater than IPv4, but this is not intrinsically an issue with more specifics, but a more general issue of BGP routing instability in IPv6
51 Thanks
More Specific Announcements in BGP. Geoff Huston APNIC
 More Specific Announcements in BGP Geoff Huston APNIC What s a more specific? A prefix advertisement that refines a covering advertisement 10.0.0.0/8 10.1.0.0/16 Why advertise a more specific? I: To redirect
More Specific Announcements in BGP Geoff Huston APNIC What s a more specific? A prefix advertisement that refines a covering advertisement 10.0.0.0/8 10.1.0.0/16 Why advertise a more specific? I: To redirect
BGP The Movie. Geoff Huston September 2004 APNIC
 BGP The Movie Geoff Huston September 2004 APNIC 1 IPv4 Routing Table Size Data assembled from a variety of sources, Including Surfnet, Telstra, KPN and Route Views. Each colour represents a time series
BGP The Movie Geoff Huston September 2004 APNIC 1 IPv4 Routing Table Size Data assembled from a variety of sources, Including Surfnet, Telstra, KPN and Route Views. Each colour represents a time series
Routing Table Status Report
 Routing Table Status Report Routing SIG Feb 24 2005 APNIC19, Kyoto, Japan Geoff Huston IPv4 Routing Table Size Data assembled from a variety of sources, Including Surfnet, Telstra, KPN and Route Views.
Routing Table Status Report Routing SIG Feb 24 2005 APNIC19, Kyoto, Japan Geoff Huston IPv4 Routing Table Size Data assembled from a variety of sources, Including Surfnet, Telstra, KPN and Route Views.
Measuring IPv6 Deployment
 Measuring IPv6 Deployment Geoff Huston George Michaelson research@apnic.net The story so far In case you hadn t heard by now, we appear to be running quite low on IPv4 addresses! IANA Pool Exhaustion Prediction
Measuring IPv6 Deployment Geoff Huston George Michaelson research@apnic.net The story so far In case you hadn t heard by now, we appear to be running quite low on IPv4 addresses! IANA Pool Exhaustion Prediction
Routing in Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC
 Routing in 2016 Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC Through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to assemble a single view of the entire Internet The lens of routing is one of the ways in which information
Routing in 2016 Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC Through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to assemble a single view of the entire Internet The lens of routing is one of the ways in which information
Measuring IPv6 Deployment
 Measuring IPv6 Deployment Geoff Huston George Michaelson research@apnic.net Available data sets We have access to dual stack data for: Available data sets We have access to dual stack data for: BGP Route
Measuring IPv6 Deployment Geoff Huston George Michaelson research@apnic.net Available data sets We have access to dual stack data for: Available data sets We have access to dual stack data for: BGP Route
Routing Table Status Report
 Routing Table Status Report The Route-Views View March 2005 Geoff Huston IPv4 Routing Table Size Data assembled from Route Views data. Each colour represents a time series for a single AS. The major point
Routing Table Status Report The Route-Views View March 2005 Geoff Huston IPv4 Routing Table Size Data assembled from Route Views data. Each colour represents a time series for a single AS. The major point
Routing Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC. #apricot2017
 Routing 2016 Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC #apricot2017 2017 Through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to assemble a single view of the entire Internet The lens of routing is one of the ways
Routing 2016 Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC #apricot2017 2017 Through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to assemble a single view of the entire Internet The lens of routing is one of the ways
Measuring BGP. Geoff Huston. CAIA SEMINAR 31 May
 Measuring BGP Geoff Huston BGP is An instance of the Bellman-Ford Distance Vector family of routing protocols And a relatively vanilla one at that The routing protocol used to support inter-domain routing
Measuring BGP Geoff Huston BGP is An instance of the Bellman-Ford Distance Vector family of routing protocols And a relatively vanilla one at that The routing protocol used to support inter-domain routing
Tracking the Internet s BGP Table
 Tracking the Internet s BGP Table Geoff Huston Telstra December 2000 Methodology! The BGP table monitor uses a router at the boundary of AS1221 which has a default-free ebgp routing table 1. Capture the
Tracking the Internet s BGP Table Geoff Huston Telstra December 2000 Methodology! The BGP table monitor uses a router at the boundary of AS1221 which has a default-free ebgp routing table 1. Capture the
Measuring IPv6 Deployment
 Measuring IPv6 Deployment The story so far IANA Pool Exhaustion In this model, IANA allocates its last IPv4 /8 to an RIR on the 18 th January 2011 Ten years ago we had a plan Oops! We were meant to have
Measuring IPv6 Deployment The story so far IANA Pool Exhaustion In this model, IANA allocates its last IPv4 /8 to an RIR on the 18 th January 2011 Ten years ago we had a plan Oops! We were meant to have
Inter-Domain Routing Trends
 Inter-Domain Routing Trends Geoff Huston gih@apnic.net APNIC March 2007 Agenda 1. Some data about the network and BGP over 2006 2. Some observations about the distribution patterns of BGP updates 3. Pointers
Inter-Domain Routing Trends Geoff Huston gih@apnic.net APNIC March 2007 Agenda 1. Some data about the network and BGP over 2006 2. Some observations about the distribution patterns of BGP updates 3. Pointers
Routing the Internet in Geoff Huston APNIC March 2007
 Routing the Internet in 2006 Geoff Huston APNIC March 2007 IPv4 in 2006 Total Advertised BGP Prefixes BGP Table Growth 210000 200000 190000 BGP FIB Entries 180000 2006 170000 2005 160000 150000 Jan Feb
Routing the Internet in 2006 Geoff Huston APNIC March 2007 IPv4 in 2006 Total Advertised BGP Prefixes BGP Table Growth 210000 200000 190000 BGP FIB Entries 180000 2006 170000 2005 160000 150000 Jan Feb
The ISP Column A column on various things Internet. BGP in January 2018 Geoff Huston
 The ISP Column A column on various things Internet January 2018 Geoff Huston BGP in 2017 It has become either a tradition, or a habit, each January for me to report on the experience with the interdomain
The ISP Column A column on various things Internet January 2018 Geoff Huston BGP in 2017 It has become either a tradition, or a habit, each January for me to report on the experience with the interdomain
Comparing IPv4 and IPv6 from the perspec7ve of BGP dynamic ac7vity. Geoff Huston APNIC February 2012
 Comparing IPv4 and IPv6 from the perspec7ve of BGP dynamic ac7vity Geoff Huston APNIC February 2012 The IPv4 Table: 2004 - now The IPv6 Table: 2004 - now AS131072 BGP Updates / day V4 - ~100K updates/day
Comparing IPv4 and IPv6 from the perspec7ve of BGP dynamic ac7vity Geoff Huston APNIC February 2012 The IPv4 Table: 2004 - now The IPv6 Table: 2004 - now AS131072 BGP Updates / day V4 - ~100K updates/day
BGP in Geoff Huston APNIC IETF89
 BGP in 2013 Geoff Huston APNIC IEPG @ IETF89 Conven0onal wisdom about rou0ng: The rapid and sustained growth of the Internet over the past several decades has resulted in large state requirements for IP
BGP in 2013 Geoff Huston APNIC IEPG @ IETF89 Conven0onal wisdom about rou0ng: The rapid and sustained growth of the Internet over the past several decades has resulted in large state requirements for IP
TBGP: A more scalable and functional BGP. Paul Francis Jan. 2004
 TBGP: A more scalable and functional BGP Paul Francis Jan. 2004 BGP: Border Gateway Protocol BGP is the top-level routing protocol in the Internet It holds the Internet together BGP allows routers to tell
TBGP: A more scalable and functional BGP Paul Francis Jan. 2004 BGP: Border Gateway Protocol BGP is the top-level routing protocol in the Internet It holds the Internet together BGP allows routers to tell
"Dark" Traffic in Network /8
 "Dark" Traffic in Network 49.0.0.0/8 September 2010 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address blocks before they are
"Dark" Traffic in Network 49.0.0.0/8 September 2010 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address blocks before they are
A Technique for Reducing BGP Update Announcements through Path Exploration Damping
 A Technique for Reducing BGP Update Announcements through Path Exploration Damping Geoff Huston, Mattia Rossi, Grenville Armitage mrossi@swin.edu.au Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures (CAIA) Swinburne
A Technique for Reducing BGP Update Announcements through Path Exploration Damping Geoff Huston, Mattia Rossi, Grenville Armitage mrossi@swin.edu.au Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures (CAIA) Swinburne
IPv4 Address Report. This report generated at 12-Mar :24 UTC. IANA Unallocated Address Pool Exhaustion: 03-Feb-2011
 IPv4 Address Report This report generated at 12-Mar-2018 08:24 UTC. IANA Unallocated Address Pool Exhaustion: 03-Feb-2011 Projected RIR Address Pool Exhaustion Dates: RIR Projected Exhaustion Remaining
IPv4 Address Report This report generated at 12-Mar-2018 08:24 UTC. IANA Unallocated Address Pool Exhaustion: 03-Feb-2011 Projected RIR Address Pool Exhaustion Dates: RIR Projected Exhaustion Remaining
Taming BGP. An incremental approach to improving the dynamic properties of BGP. Geoff Huston. CAIA Seminar 18 August
 Taming BGP An incremental approach to improving the dynamic properties of BGP Geoff Huston BGP is The inter-domain routing protocol for the Internet An instance of a Distance Vector Protocol with explicit
Taming BGP An incremental approach to improving the dynamic properties of BGP Geoff Huston BGP is The inter-domain routing protocol for the Internet An instance of a Distance Vector Protocol with explicit
Background Traffic to Network /8
 Background Traffic to Network 39.0.0.0/8 March 2010 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address blocks before they are
Background Traffic to Network 39.0.0.0/8 March 2010 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address blocks before they are
Beyond the IPv4 Internet. Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC
 Beyond the IPv4 Internet Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC The IETF s ROAD Trip By 1990 it was evident that IPv4 was not going to have a large enough address span for long term deployment And the routing
Beyond the IPv4 Internet Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC The IETF s ROAD Trip By 1990 it was evident that IPv4 was not going to have a large enough address span for long term deployment And the routing
Auto-Detecting Hijacked Prefixes?
 Auto-Detecting Hijacked Prefixes? Geoff Huston APNIC @RIPE 50 May 2005 1 Address Hijacking Is the unauthorized use of an address prefix as an advertised route object on the Internet It s not a bogon the
Auto-Detecting Hijacked Prefixes? Geoff Huston APNIC @RIPE 50 May 2005 1 Address Hijacking Is the unauthorized use of an address prefix as an advertised route object on the Internet It s not a bogon the
Chapter 20 IPv6 BGP Unicast Address Family Commands
 Chapter 20 IPv6 BGP Unicast Address Family Commands NOTE: The IPv6 BGP unicast address family configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6 and the ProCurve 9408sl Routing Switch
Chapter 20 IPv6 BGP Unicast Address Family Commands NOTE: The IPv6 BGP unicast address family configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6 and the ProCurve 9408sl Routing Switch
A Day in the Life of an Address. Bill Fenner AT&T Labs - Research IETF Routing Area Director
 A Day in the Life of an Address Bill Fenner AT&T Labs - Research fenner@research.att.com IETF Routing Area Director 1 Overview Addressing Routing Policy Data 2 Overview Addressing Routing Policy Data 3
A Day in the Life of an Address Bill Fenner AT&T Labs - Research fenner@research.att.com IETF Routing Area Director 1 Overview Addressing Routing Policy Data 2 Overview Addressing Routing Policy Data 3
Current Challenges in Internet Technology
 Current Challenges in Internet Technology with Special Focus on Routing Scalability CNGI, Beijing, June 2007 Jari Arkko Internet Area Director, IETF Researcher, Ericsson Research Outline Overview of the
Current Challenges in Internet Technology with Special Focus on Routing Scalability CNGI, Beijing, June 2007 Jari Arkko Internet Area Director, IETF Researcher, Ericsson Research Outline Overview of the
BGP in 2013 (and a bit of 2014)
 BGP in 2013 (and a bit of 2014) Geoff Huston APNIC RIPE 68 Conven'onal wisdom about rou'ng: The rapid and sustained growth of the Internet over the past several decades has resulted in large state requirements
BGP in 2013 (and a bit of 2014) Geoff Huston APNIC RIPE 68 Conven'onal wisdom about rou'ng: The rapid and sustained growth of the Internet over the past several decades has resulted in large state requirements
Background Traffic to Quarantined Network Blocks administered by APNIC
 Background Traffic to Quarantined Network Blocks administered by APNIC March 2011 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address
Background Traffic to Quarantined Network Blocks administered by APNIC March 2011 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address
The ISP Column A monthly column on things Internet. BGP in The BGP Measurement Environment. January 2015 Geoff Huston
 The ISP Column A monthly column on things Internet January 2015 Geoff Huston BGP in 2014 The Border Gateway Protocol, or BGP, has been holding the Internet together, for more than two decades and nothing
The ISP Column A monthly column on things Internet January 2015 Geoff Huston BGP in 2014 The Border Gateway Protocol, or BGP, has been holding the Internet together, for more than two decades and nothing
Towards a Logic for Wide-Area Internet Routing
 Towards a Logic for Wide-Area Internet Routing Nick Feamster and Hari Balakrishnan M.I.T. Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory {feamster,hari}@lcs.mit.edu ; #, $. ', - -, * - ' * 4 *
Towards a Logic for Wide-Area Internet Routing Nick Feamster and Hari Balakrishnan M.I.T. Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory {feamster,hari}@lcs.mit.edu ; #, $. ', - -, * - ' * 4 *
BGP Issues. Geoff Huston
 BGP Issues Geoff Huston Why measure BGP?! BGP describes the structure of the Internet, and an analysis of the BGP routing table can provide information to help answer the following questions:! What is
BGP Issues Geoff Huston Why measure BGP?! BGP describes the structure of the Internet, and an analysis of the BGP routing table can provide information to help answer the following questions:! What is
Introduction to IP Routing. Geoff Huston
 Introduction to IP Routing Geoff Huston Routing How do packets get from A to B in the Internet? A Internet B Connectionless Forwarding Each router (switch) makes a LOCAL decision to forward the packet
Introduction to IP Routing Geoff Huston Routing How do packets get from A to B in the Internet? A Internet B Connectionless Forwarding Each router (switch) makes a LOCAL decision to forward the packet
IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://
 IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://www.certqueen.com Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version : DEMO 1 / 6 1.How
IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://www.certqueen.com Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Version : DEMO 1 / 6 1.How
A Measurement Study of BGP Misconfiguration
 A Measurement Study of BGP Misconfiguration Ratul Mahajan, David Wetherall, and Tom Anderson University of Washington Motivation Routing protocols are robust against failures Meaning fail-stop link and
A Measurement Study of BGP Misconfiguration Ratul Mahajan, David Wetherall, and Tom Anderson University of Washington Motivation Routing protocols are robust against failures Meaning fail-stop link and
The ISP Column An occasional column on things Internet. Damping BGP. BGP Route Flap Damping. June Geoff Huston
 The ISP Column An occasional column on things Internet June 2007 Geoff Huston Damping BGP The topic of the scalability of the Internet s routing system has been one that has achieved elevated attention
The ISP Column An occasional column on things Internet June 2007 Geoff Huston Damping BGP The topic of the scalability of the Internet s routing system has been one that has achieved elevated attention
Traffic in Network /8. Background. Initial Experience. Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D. April 2010
 Traffic in Network 1.0.0.0/8 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D April 2010 Background The address plan for IPv4 has a reservation for Private Use address space. This reservation, comprising of 3
Traffic in Network 1.0.0.0/8 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D April 2010 Background The address plan for IPv4 has a reservation for Private Use address space. This reservation, comprising of 3
Border Gateway Protocol - BGP
 BGP Fundamentals Border Gateway Protocol - BGP Runs over TCP (port 179) TCP connection required before BGP session Need to be reachable! Path vector routing protocol Best path selection based on path attributes
BGP Fundamentals Border Gateway Protocol - BGP Runs over TCP (port 179) TCP connection required before BGP session Need to be reachable! Path vector routing protocol Best path selection based on path attributes
Inter-Autonomous-System Routing: Border Gateway Protocol
 Inter-Autonomous-System Routing: Border Gateway Protocol Antonio Carzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano June 14, 2005 Outline Hierarchical routing BGP Routing Routing Goal: each router u
Inter-Autonomous-System Routing: Border Gateway Protocol Antonio Carzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano June 14, 2005 Outline Hierarchical routing BGP Routing Routing Goal: each router u
Routing in Geoff Huston APNIC
 Routing in 2014 Geoff Huston APNIC Looking through the Routing Lens Looking through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to collect a view of the en2re Internet all at once The lens of rou2ng is one
Routing in 2014 Geoff Huston APNIC Looking through the Routing Lens Looking through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to collect a view of the en2re Internet all at once The lens of rou2ng is one
IPv4 Address Lifetime Expectancy Revisited. Geoff Huston, APNIC 12 October 2005 RIPE 51
 IPv4 Address Lifetime Expectancy Revisited Geoff Huston, APNIC 12 October 2005 RIPE 51 Previous Work Presentation at RIPE, September 2003, using the rate of growth of BGP advertised address space as the
IPv4 Address Lifetime Expectancy Revisited Geoff Huston, APNIC 12 October 2005 RIPE 51 Previous Work Presentation at RIPE, September 2003, using the rate of growth of BGP advertised address space as the
Internet Routing Table Analysis Update. Philip Smith RIPE Routing WG Amsterdam, January 2003
 Internet Routing Table Analysis Update Philip Smith pfs@cisco.com RIPE Routing WG Amsterdam, January 2003 Recent Changes Exhaustive search of 192/8 space for unassigned addresses Now combined with IANA
Internet Routing Table Analysis Update Philip Smith pfs@cisco.com RIPE Routing WG Amsterdam, January 2003 Recent Changes Exhaustive search of 192/8 space for unassigned addresses Now combined with IANA
IBGP internals. BGP Advanced Topics. Agenda. BGP Continuity 1. L49 - BGP Advanced Topics. L49 - BGP Advanced Topics
 IBGP internals BGP Advanced Topics main IBGP aspects inside an AS continuity all packets entering the AS that were not blocked by some policies should reach the proper exit BGP router all transit routers
IBGP internals BGP Advanced Topics main IBGP aspects inside an AS continuity all packets entering the AS that were not blocked by some policies should reach the proper exit BGP router all transit routers
BGP Geoff Huston APNIC
 BGP 2011 Geoff Huston APNIC Conven5onal (Historical) BGP Wisdom IAB Workshop on Inter- Domain rou5ng in October 2006 RFC 4984: routing scalability is the most! important problem facing the! Internet today
BGP 2011 Geoff Huston APNIC Conven5onal (Historical) BGP Wisdom IAB Workshop on Inter- Domain rou5ng in October 2006 RFC 4984: routing scalability is the most! important problem facing the! Internet today
Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering draft-sriram-opsec-urpf-improvements-01
 Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering draft-sriram-opsec-urpf-improvements-01 K. Sriram and D. Montgomery OPSEC Working Group Meeting, IETF-99 July 2017 Acknowledgements: The authors are
Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering draft-sriram-opsec-urpf-improvements-01 K. Sriram and D. Montgomery OPSEC Working Group Meeting, IETF-99 July 2017 Acknowledgements: The authors are
BGP in Geoff Huston APNIC NANOG 60
 BGP in 2013 Geoff Huston APNIC NANOG 60 Conven0onal wisdom about rou0ng: The rapid and sustained growth of the Internet over the past several decades has resulted in large state requirements for IP routers.
BGP in 2013 Geoff Huston APNIC NANOG 60 Conven0onal wisdom about rou0ng: The rapid and sustained growth of the Internet over the past several decades has resulted in large state requirements for IP routers.
TCP and BBR. Geoff Huston APNIC. #apricot
 TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC The IP Architecture At its heart IP is a datagram network architecture Individual IP packets may be lost, re-ordered, re-timed and even fragmented The IP Architecture At
TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC The IP Architecture At its heart IP is a datagram network architecture Individual IP packets may be lost, re-ordered, re-timed and even fragmented The IP Architecture At
Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands
 Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands NOTE: This chapter describes commands in the BGP configuration level, which is present on HP devices that support IPv4 only. For information about BGP commands and configuration
Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands NOTE: This chapter describes commands in the BGP configuration level, which is present on HP devices that support IPv4 only. For information about BGP commands and configuration
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Background Traffic to Network /8
 Background Traffic to Network 103.0.0.0/8 April 2010 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address blocks before they are
Background Traffic to Network 103.0.0.0/8 April 2010 Geoff Huston George Michaelson APNIC R&D research@apnic.net APNIC is now regularly examining the unused state of IPv4 address blocks before they are
Security in inter-domain routing
 DD2491 p2 2011 Security in inter-domain routing Olof Hagsand KTH CSC 1 Literature Practical BGP pages Chapter 9 See reading instructions Beware of BGP Attacks (Nordström, Dovrolis) Examples of attacks
DD2491 p2 2011 Security in inter-domain routing Olof Hagsand KTH CSC 1 Literature Practical BGP pages Chapter 9 See reading instructions Beware of BGP Attacks (Nordström, Dovrolis) Examples of attacks
TCP and BBR. Geoff Huston APNIC
 TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC Computer Networking is all about moving data The way in which data movement is controlled is a key characteristic of the network architecture The Internet protocol passed
TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC Computer Networking is all about moving data The way in which data movement is controlled is a key characteristic of the network architecture The Internet protocol passed
TCP and BBR. Geoff Huston APNIC
 TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC The IP Architecture At its heart IP is a datagram network architecture Individual IP packets may be lost, re-ordered, re-timed and even fragmented The IP Architecture At
TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC The IP Architecture At its heart IP is a datagram network architecture Individual IP packets may be lost, re-ordered, re-timed and even fragmented The IP Architecture At
Understanding IPv6 Internet Background Radia6on
 Understanding IPv6 Internet Background Radia6on Jakub Czyz*, Kyle Lady*, Sam Miller*, Michael Kallitsis, Manish Karir, Michael Bailey* *University of Michigan Merit Network Dept. of Homeland Security S&T
Understanding IPv6 Internet Background Radia6on Jakub Czyz*, Kyle Lady*, Sam Miller*, Michael Kallitsis, Manish Karir, Michael Bailey* *University of Michigan Merit Network Dept. of Homeland Security S&T
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title IPv address allocation and the BGP routing table evolution Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8b6dw Journal Computer Communication Review, () ISSN 6-8
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title IPv address allocation and the BGP routing table evolution Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8b6dw Journal Computer Communication Review, () ISSN 6-8
An Operational Perspective on BGP Security. Geoff Huston February 2005
 An Operational Perspective on BGP Security Geoff Huston February 2005 Disclaimer This is not a description of the approach taken by any particular service provider in securing their network. It is intended
An Operational Perspective on BGP Security Geoff Huston February 2005 Disclaimer This is not a description of the approach taken by any particular service provider in securing their network. It is intended
IPv6 Address Allocation Status in AP region and the way forward
 IPv6 Address Allocation Status in AP region and the way forward APAN30 meeting, Hanoi Vietnam 11 August 2010 Champika Wijayatunga Training Manager, APNIC 1 Regional Internet Registries The Internet community
IPv6 Address Allocation Status in AP region and the way forward APAN30 meeting, Hanoi Vietnam 11 August 2010 Champika Wijayatunga Training Manager, APNIC 1 Regional Internet Registries The Internet community
Routing Geoff Huston APNIC
 Routing 2014 Geoff Huston APNIC Looking through the Routing Lens Looking through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to assemble a single view of the en4re Internet The lens of rou4ng is one of the
Routing 2014 Geoff Huston APNIC Looking through the Routing Lens Looking through the Routing Lens There are very few ways to assemble a single view of the en4re Internet The lens of rou4ng is one of the
IPv4 Address Allocation and Evolution of BGP Routing Tables
 IPv4 Address Allocation and Evolution of BGP Routing Tables Xiaoqiao Meng, xqmeng@cs.ucla.edu Zhiguo Xu, zhiguo@cs.ucla.edu CJ Wittbrodt, cjw@packetdesign.com Songwu Lu, slu@cs.ucla.edu> Lixia Zhang, lixia@cs.ucla.edu
IPv4 Address Allocation and Evolution of BGP Routing Tables Xiaoqiao Meng, xqmeng@cs.ucla.edu Zhiguo Xu, zhiguo@cs.ucla.edu CJ Wittbrodt, cjw@packetdesign.com Songwu Lu, slu@cs.ucla.edu> Lixia Zhang, lixia@cs.ucla.edu
FiberstoreOS BGP Configuration
 FiberstoreOS BGP Configuration Contents 1 Configure BGP...1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Basic Topology (EBGP)... 2 1.2.2 Configuration... 2 1.2.3 Validation... 4 1.3 Basic topology(ibgp)... 5 1.3.2 Configuration...
FiberstoreOS BGP Configuration Contents 1 Configure BGP...1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Basic Topology (EBGP)... 2 1.2.2 Configuration... 2 1.2.3 Validation... 4 1.3 Basic topology(ibgp)... 5 1.3.2 Configuration...
Lecture outline. Internet Routing Security Issues. Previous lecture: Effect of MinRouteAdver Timer. Recap of previous lecture
 Lecture outline Internet Routing Security Issues Z. Morley Mao Lecture 3 Jan 14, 2003 Recap of last lecture, any questions? Existing routing security mechanisms - SBGP General threats to routing protocols
Lecture outline Internet Routing Security Issues Z. Morley Mao Lecture 3 Jan 14, 2003 Recap of last lecture, any questions? Existing routing security mechanisms - SBGP General threats to routing protocols
Securing BGP Networks using Consistent Check Algorithm
 Securing BGP Networks using Consistent Check Algorithm C. K. Man, K.Y. Wong, and K. H. Yeung Abstract The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the critical routing protocol in the Internet infrastructure.
Securing BGP Networks using Consistent Check Algorithm C. K. Man, K.Y. Wong, and K. H. Yeung Abstract The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the critical routing protocol in the Internet infrastructure.
TCP and BBR. Geoff Huston APNIC
 TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC Computer Networking is all about moving data The way in which data movement is controlled is a key characteristic of the network architecture The Internet protocol passed
TCP and BBR Geoff Huston APNIC Computer Networking is all about moving data The way in which data movement is controlled is a key characteristic of the network architecture The Internet protocol passed
From the given configuration taken from RTA and graphic, which network will be filtered from being propagated to RTC from RTA?
 A BGP router has two routes with the same weight, same local preferences and reachable next hops. Both routes originated from peer routers. What is the next tie-breaker in BGP route selection process?
A BGP router has two routes with the same weight, same local preferences and reachable next hops. Both routes originated from peer routers. What is the next tie-breaker in BGP route selection process?
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Redistribution & Layer 3 Path Control. Route Redistribution Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Redistribution & Layer 3 Path Control http:// Route Redistribution Overview Process of exchanging reachability information between routing domains e.g. OSPF to EIGRP
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Redistribution & Layer 3 Path Control http:// Route Redistribution Overview Process of exchanging reachability information between routing domains e.g. OSPF to EIGRP
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops
 Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between networks exterior gateway protocol RFC1771 work in progress to update draft-ietf-idr-bgp4-18.txt
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between networks exterior gateway protocol RFC1771 work in progress to update draft-ietf-idr-bgp4-18.txt
History. Configuration and Policy. Assigning IP address and AS numbers (Ideally) Addressing Schemes. Problem #1: Lifetime of Address Space
 Outline The Basics of BGP Routing and its Performance in Today s Internet Nina Taft Sprint, Advanced Technology Labs California, USA May 2001 1. Highlights 2. Addressing and CIDR 3. BGP Messages and Prefix
Outline The Basics of BGP Routing and its Performance in Today s Internet Nina Taft Sprint, Advanced Technology Labs California, USA May 2001 1. Highlights 2. Addressing and CIDR 3. BGP Messages and Prefix
BGP101. Howard C. Berkowitz. (703)
 BGP101 Howard C. Berkowitz hcb@clark.net (703)998-5819 What is the Problem to be Solved? Just configuring the protocol? Participating in the Internet and/or running Virtual Private Networks A Life Cycle
BGP101 Howard C. Berkowitz hcb@clark.net (703)998-5819 What is the Problem to be Solved? Just configuring the protocol? Participating in the Internet and/or running Virtual Private Networks A Life Cycle
Network Protocols. Routing. TDC375 Autumn 03/04 John Kristoff - DePaul University 1
 Network Protocols Routing TDC375 Autumn 03/04 John Kristoff - DePaul University 1 IPv4 unicast routing All Internet hosts perform basic routing for local net destinations, forward to local host for non-local
Network Protocols Routing TDC375 Autumn 03/04 John Kristoff - DePaul University 1 IPv4 unicast routing All Internet hosts perform basic routing for local net destinations, forward to local host for non-local
Addressing and Routing in Geoff Huston APNIC
 Addressing and Routing in 2014 Geoff Huston APNIC The Addressing View Addressing V4 Exhaustion We have been predic.ng that the exhaus.on of the free pool of IPv4 addresses would eventually happen for the
Addressing and Routing in 2014 Geoff Huston APNIC The Addressing View Addressing V4 Exhaustion We have been predic.ng that the exhaus.on of the free pool of IPv4 addresses would eventually happen for the
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 03 Inter-domain Routing
 Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 03 Inter-domain Routing Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 2008 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Autonomous Routing Domains A collection of physical networks
Internet Routing Protocols Lecture 03 Inter-domain Routing Advanced Systems Topics Lent Term, 2008 Timothy G. Griffin Computer Lab Cambridge UK Autonomous Routing Domains A collection of physical networks
4-Byte AS Numbers. The view from the old BGP world. Geoff Huston October 2006 APNIC
 4-Byte AS Numbers The view from the old BGP world Geoff Huston October 2006 APNIC 4 Byte AS Numbers We are running into the exhaustion of the 2 Byte AS Number pool Current estimate: 2200 UTC 14 October
4-Byte AS Numbers The view from the old BGP world Geoff Huston October 2006 APNIC 4 Byte AS Numbers We are running into the exhaustion of the 2 Byte AS Number pool Current estimate: 2200 UTC 14 October
internet technologies and standards
 Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) structure of the Internet Tier 1 ISP Tier 1 ISP Google
Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) structure of the Internet Tier 1 ISP Tier 1 ISP Google
Papers and Articles. Scaling Inter-Domain Routing A View Forward
 Papers and Articles An occasional series of articles on the social and technical evolution of the Internet by Geoff Huston Scaling Inter-Domain Routing A View Forward December 2001 Geoff Huston In the
Papers and Articles An occasional series of articles on the social and technical evolution of the Internet by Geoff Huston Scaling Inter-Domain Routing A View Forward December 2001 Geoff Huston In the
Securing BGP. Geoff Huston November 2007
 Securing BGP Geoff Huston November 2007 Agenda An Introduction to BGP BGP Security Questions Current Work Research Questions An Introduction to BGP Background to Internet Routing The routing architecture
Securing BGP Geoff Huston November 2007 Agenda An Introduction to BGP BGP Security Questions Current Work Research Questions An Introduction to BGP Background to Internet Routing The routing architecture
Some Foundational Problems in Interdomain Routing
 Some Foundational Problems in Interdomain Routing Nick Feamster, Hari Balakrishnan M.I.T. Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs -- Research The state of interdomain
Some Foundational Problems in Interdomain Routing Nick Feamster, Hari Balakrishnan M.I.T. Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs -- Research The state of interdomain
Evolution of Internet Address Space Deaggregation: Myths and Reality
 1 Evolution of Internet Address Space Deaggregation: Myths and Reality Luca Cittadini, Wolfgang Mühlbauer, Steve Uhlig Abstract Internet routing table size growth and BGP update churn are two prominent
1 Evolution of Internet Address Space Deaggregation: Myths and Reality Luca Cittadini, Wolfgang Mühlbauer, Steve Uhlig Abstract Internet routing table size growth and BGP update churn are two prominent
Cisco IPv6 Deployment Statics Shishio Tsuchiya
 Cisco IPv6 Deployment Statics http://6lab.cisco.com/stats/ Shishio Tsuchiya shtsuchi@cisco.com Measuring IPv6 adoption life cycle get IPv6 Prefix from RIR Advertise this prefix on the network make my contents
Cisco IPv6 Deployment Statics http://6lab.cisco.com/stats/ Shishio Tsuchiya shtsuchi@cisco.com Measuring IPv6 adoption life cycle get IPv6 Prefix from RIR Advertise this prefix on the network make my contents
The information in this document is based on Cisco IOS Software Release 15.4 version.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Dataset Comparison. IPv4 vs IPv6 traffic seen at DNS root servers. Bradley Huffaker, Marina Fomenkov, and kc claffy
 Dataset Comparison IPv4 vs IPv6 traffic seen at DNS root servers Bradley Huffaker, Marina Fomenkov, and kc claffy OARC Fall 2014 Workshop October 12, 2014 IPv4 exhaustion RIR Address Pool (/8s) http://www.potaroo.net/tools/ipv4/
Dataset Comparison IPv4 vs IPv6 traffic seen at DNS root servers Bradley Huffaker, Marina Fomenkov, and kc claffy OARC Fall 2014 Workshop October 12, 2014 IPv4 exhaustion RIR Address Pool (/8s) http://www.potaroo.net/tools/ipv4/
If that s the case, then why should we be interested in BGP? Isn t this just a classic case of Nothing to see here, move along?
 The ISP Column A monthly column on things Internet January 2014 Geoff Huston BGP in 2013 The Border Gateway Protocol, or BGP, has been toiling away, literally holding the Internet together, for more than
The ISP Column A monthly column on things Internet January 2014 Geoff Huston BGP in 2013 The Border Gateway Protocol, or BGP, has been toiling away, literally holding the Internet together, for more than
Dynamics of Hot-Potato Routing in IP Networks
 Dynamics of Hot-Potato Routing in IP Networks Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs Research http://www.research.att.com/~jrex Joint work with Renata Teixeira (UCSD), Aman Shaikh (AT&T), and Timothy Griffin (Intel)
Dynamics of Hot-Potato Routing in IP Networks Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs Research http://www.research.att.com/~jrex Joint work with Renata Teixeira (UCSD), Aman Shaikh (AT&T), and Timothy Griffin (Intel)
Configuring BGP community 43 Configuring a BGP route reflector 44 Configuring a BGP confederation 44 Configuring BGP GR 45 Enabling Guard route
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Tag Switching. Background. Tag-Switching Architecture. Forwarding Component CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 Tag Switching Background Rapid changes in the type (and quantity) of traffic handled by the Internet and the explosion in the number of Internet users is putting an unprecedented strain on the
CHAPTER 23 Tag Switching Background Rapid changes in the type (and quantity) of traffic handled by the Internet and the explosion in the number of Internet users is putting an unprecedented strain on the
FIGURE 3. Two-Level Internet Address Structure. FIGURE 4. Principle Classful IP Address Formats
 Classful IP Addressing When IP was first standardized in September 1981, the specification required that each system attached to an IP-based Internet be assigned a unique, 32-bit Internet address value.
Classful IP Addressing When IP was first standardized in September 1981, the specification required that each system attached to an IP-based Internet be assigned a unique, 32-bit Internet address value.
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
EECS 122, Lecture 17. The Distributed Update Algorithm (DUAL) Optimization Criteria. DUAL Data Structures. Selecting Among Neighbors.
 EECS 122, Lecture 17 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu The Distributed Update Algorithm (DUAL) J.J. Garcia-Luna Luna-Aceves [SIGCOMM 89] Aims at removing transient loops in both DV and LS routing protocols
EECS 122, Lecture 17 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu The Distributed Update Algorithm (DUAL) J.J. Garcia-Luna Luna-Aceves [SIGCOMM 89] Aims at removing transient loops in both DV and LS routing protocols
Routing Basics. SANOG July, 2017 Gurgaon, INDIA
 Routing Basics SANOG 30 14-18 July, 2017 Gurgaon, INDIA Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E
Routing Basics SANOG 30 14-18 July, 2017 Gurgaon, INDIA Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E
Internet Routing Basics
 Internet Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port
Internet Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port
Some Thoughts on Integrity in Routing
 Some Thoughts on Integrity in Routing Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC What we want We want the routing system to advertise the correct reachability information for legitimately connected prefixes at
Some Thoughts on Integrity in Routing Geoff Huston Chief Scientist, APNIC What we want We want the routing system to advertise the correct reachability information for legitimately connected prefixes at
Network Layer (Routing)
 Network Layer (Routing) Border Gateway Protocol Structure of the Internet Networks (ISPs, CDNs, etc.) group with IP prefixes Networks are richly interconnected, often using IXPs Prefix E1 Net E IXP Prefix
Network Layer (Routing) Border Gateway Protocol Structure of the Internet Networks (ISPs, CDNs, etc.) group with IP prefixes Networks are richly interconnected, often using IXPs Prefix E1 Net E IXP Prefix
Module 14 Transit. Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation
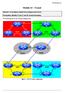 ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 14 Transit Objective: To investigate methods for providing transit services. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Transit Presentation The following will be the common topology
Unicast Forwarding. Unicast. Unicast Forwarding Flows Overview. Intra Subnet Forwarding (Bridging) Unicast, on page 1
 Unicast, on page 1 Unicast Flows Overview Intra and inter subnet forwarding are the possible unicast forwarding flows in the VXLAN BGP EVPN fabric, between leaf/tor switch VTEPs. They are explained in
Unicast, on page 1 Unicast Flows Overview Intra and inter subnet forwarding are the possible unicast forwarding flows in the VXLAN BGP EVPN fabric, between leaf/tor switch VTEPs. They are explained in
A PKI For IDR Public Key Infrastructure and Number Resource Certification
 A PKI For IDR Public Key Infrastructure and Number Resource Certification AUSCERT 2006 Geoff Huston Research Scientist APNIC If You wanted to be Bad on the Internet And you wanted to: Hijack a site Inspect
A PKI For IDR Public Key Infrastructure and Number Resource Certification AUSCERT 2006 Geoff Huston Research Scientist APNIC If You wanted to be Bad on the Internet And you wanted to: Hijack a site Inspect
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab
 2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
On characterizing BGP routing table growth
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Lixin Gao 00 On characterizing BGP routing table growth T Bu LX Gao D Towsley Available at: https://works.bepress.com/lixin_gao/66/ On Characterizing
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Lixin Gao 00 On characterizing BGP routing table growth T Bu LX Gao D Towsley Available at: https://works.bepress.com/lixin_gao/66/ On Characterizing
IPv4 Address Lifetime Expectancy. Geoff Huston, APNIC 31 October 2005 Australian IPv6 Summit
 IPv4 Address Lifetime Expectancy Geoff Huston, APNIC 31 October 2005 Australian IPv6 Summit If 42 is the answer Then what was the question? Part of the reason for differences in outcomes in this area lies
IPv4 Address Lifetime Expectancy Geoff Huston, APNIC 31 October 2005 Australian IPv6 Summit If 42 is the answer Then what was the question? Part of the reason for differences in outcomes in this area lies
The Norwegian Electronic Communications Services Market
 The Norwegian Electronic Communications Services Market 1 st half 2014 30 October 2014 Revised 13 November 2014 Contents 1 Introduction... 6 2 Development trends... 7 2.1 Telephony... 7 2.2 Fied and mobile
The Norwegian Electronic Communications Services Market 1 st half 2014 30 October 2014 Revised 13 November 2014 Contents 1 Introduction... 6 2 Development trends... 7 2.1 Telephony... 7 2.2 Fied and mobile
Routing. Jens A Andersson Communication Systems
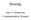 Routing Jens A Andersson Communication Systems R1 Choosing an Optimal Path R4 5 R7 5 10 40 R6 6 5 B R2 15 A 20 4 10 10 R8 R3 5 R5 10 Router A router is a type of internetworking device that passes data
Routing Jens A Andersson Communication Systems R1 Choosing an Optimal Path R4 5 R7 5 10 40 R6 6 5 B R2 15 A 20 4 10 10 R8 R3 5 R5 10 Router A router is a type of internetworking device that passes data
Configuration prerequisites 45 Configuring BGP community 45 Configuring a BGP route reflector 46 Configuring a BGP confederation 46 Configuring BGP
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
