Finding the Static Analysis Sweet Spot
|
|
|
- Noreen Briana Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Finding the Static Analysis Sweet Spot UMSEC Summer Software Symposium 2012 Presented by: Paul Anderson, VP of Engineering, GrammaTech Inc. GrammaTech, Inc. 317 N Aurora St. Ithaca, NY Tel: info@grammatech.com
2 Key Takeaways Advanced Static Analysis Tools can and do find serious bugs Maximizing ROI is non-obvious Truth is subjective Tools and code bases have very different characteristics Tools in default configurations are unlikely to be optimal Beware of instant gratification What feels best does not necessarily make sense Consider the long-term economics Page 2
3 Agenda What is Advanced Static Analysis? Warning Classifications The Business Case Case Studies Conclusions Page 3
4 Introduction to Static Analysis Infers information about software behavior based on a static representation In contrast to dynamic analysis, such as profiling, debugging, testing Analyzes code instead of executing it So no test cases are needed Is usually a two-phase process Extract semantic information from source code Use information to discover defects or other properties of interest This talk is about Advanced static analysis for Bug Finding As exemplified by CodeSonar Page 4
5 Early-generation Static Analysis Tools Tools whose primary purpose is stronger static type and style checking E.g., Lint Key Techniques Syntactic analysis using imprecise parsing Intraprocedural dataflow analysis Primitive ways to specify inter-procedural or inter-module information Some functionality absorbed by modern compilers Tools whose primary purpose is to find violations of coding rules E.g., Misra checkers Page 5
6 Risks of Blind Elimination of Violations Low correlation between Misra violations and actual defects Only 9/72 Misra rules were observed to be better than random at predicting defects C. Boogerd and L. Moonen. Assessing the Value of Coding Standards: An Empirical Study. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Software Maintenance (ICSM), pages IEEE Computer Society Press, All changes risk introducing new defects Probability of introducing an error while making your code Misra-C compliant: 15% L. Hatton. Language Subsetting in an Industrial Context: A Comparison of Misra C 1998 and Misra C Information & Software Technology, 49(5): , Page 6
7 Advanced Static Analysis Tools Tools whose primary purpose is to find serious bugs Key Analysis Techniques High-precision program model Interprocedural Whole program Flow sensitive Context sensitive Path sensitive Highly customizable Page 7
8 Benefits of Advanced Static Analysis Benefits of advanced static analysis are based on Can examine far more execution paths than conventional testing Can be applied automatically, early in the development cycle Advanced static analysis Catches problems that test suites miss Catches bugs early, when they are less expensive to fix Pinpoints defects automatically, improving productivity Shows if code quality is improving over time Improves software quality (and security) Reduces time to market Page 8
9 Zune Bug: 1 Bad Line of Code Page 9
10 Zune Bug: 1 Bad Line of Code Page 10
11 Example Bug found by CodeSonar s malloc newloc B U F F E R \0 B U F F E R \0 Buffer Overrun!!!! Page 11
12 Some Checks Buffer Overrun Null-Pointer Dereference Divide by Zero Uninitialized Variable Free Non-Heap Variable Use After Free Double Free/Close Free Null Pointer Format String Vulnerability Race Conditions Unreachable Code Memory/Resource Leak Return Pointer to Local Mismatched Array New/Delete Invalid Parameter Missing Return Statement Dangerous Cast Inconsistent form User-Defined Checks Many More... Page 12
13 Agenda What is Advanced Static Analysis? Warning Classifications The Business Case Case Studies Conclusions Page 13
14 Definitions Recall The probability of finding a real bug Perfect recall => sound R = TT N = TT TT+FF Precision The probability that a result is a real bug Perfect precision => complete P = TT TT+FF Page 14
15 To: From: Dear Santa: I would like a tool that finds all bugs in my program. Thanks, Bob Page 15
16 Here is a static analysis tool has NO FALSE NEGATIVES!!! It is guaranteed to find every bug in your code. It s called the Code Assurance Tool: cat. Watch it list every line in your program that has a bug on it: % cat foo.c #include <stdio.h> It also can be used in a mode that reports ZERO FALSE POSITIVES! int main(char argc, char *argv[]) { printf( Hello world!\n ); return 0; } % % cat foo.c >/dev/null Page 16
17 All practical Static- Analysis Tools have false negatives and false positives Page 17
18 Warning Classifications Traditional technical interpretations True Positive The tool reports a real bug False Positive The tool reports a bug that doesn t exist False Negative The tool fails to report a real bug True Negative The tool succeeds in not reporting a non-existing bug Better interpretation True Positive Worth doing something about False Positive Not worth doing something about Page 18
19 Why not fix a (technical) True Positive? Every change has a cost Re-programming, re-testing, re-certification, etc. Every change to the code has a risk of introducing a new bug Estimated to be 15%! Cost of fixing might exceed cost of leaving it alone Page 19
20 Why fix a (technical) False Positive? False Positives imply tool confusion Tool confusion may lead to False Negatives Fixing False Positives may lead to fewer False Negatives If the compiler or the static analyzer gets confused, the code causing the confusion should be rewritten so that it becomes more trivially valid. Many have been caught in the assumption that a warning was likely invalid, only to realize much later that the report was in fact valid for less obvious reasons. Gerard J. Holzmann's "rule 10" from The Power of Ten Rules for Writing Safety Critical Code. Cost to not change the code may exceed cost to change it Page 20
21 Role of Tool User Code author Needs to churn out code fast. Hates distractions. Likes maintainability. Code reviewer Acts as a check on the author. Cares about consistency. Low time commitment. Tester Seeks out bugs. Concerned with testability. Safety engineer Checks for compliance Internal security analyst Looks for potential security vulnerabilities. Red Team/Attacker Looks for exploitable vulnerabilities. Page 21
22 Role influences Diagnosis Author Reviewer Tester Safety Engr Security Attacker Buffer overrun Y Y Y Y Y? Leak Y Y Y?? N Redundant condition N? Y N N N Null test after dereference Recursion? Y Y N N N N N N Y N N Function too long N N N Y N N Use of mktemp N N N N Y? Page 22
23 Other Influences on Diagnoses Platform-specific considerations Deployment environment Risk of code change Page 23
24 Buffer Underrun Example int pvm_pkstr(cp) char *cp; { int l = strlen(cp) + 1; int cc; Buffer Underrun reported Look at caller to see the real reason: p = getenv( PVM_EXPORT );... p = p 11;... pvm_pkstr(p); Suspicious code! This code does work p = xyz p 11 = PVM_EXPORT=xyz Page 24
25 getenv() issue char environ[] = USER=paul\0PVM_EXPORT=xyz\0PATH=/usr/bin... p - 11 p Code relies on the implementation of getenv(). This behavior is not specified (or precluded) by the specification of getenv(). Possible diagnoses: False positive because the target platform works this way? True positive because this may not port? True positive because it is confusing? Insignificant? Page 25
26 Truth is Subjective Page 26
27 Warning Triage Warnings from Tool Diagnosis False Positives True Positives Page 27
28 Which is better? Time wasted by Tool A Bugs missed by Tool B Tool A Tool B Page 28
29 Everyone Hates False Positives Page 29
30 Page 30
31 Page 31
32 Where s Waldo (Wally, Walter, Charlie, Hugo, ウォーリー, 威利 )? Page 32
33 You don t know what a real Waldo looks like Lots of other figures may resemble Waldo You don t know how many Waldos there are You WILL make misdiagnoses Page 33
34 Consequences of Misdiagnoses TP diagnosed as FP Warning report is suppressed in future reports Bug remains in the program FP diagnosed as TP Engineer may modify the code Change may be benign, or may introduce a new bug Risk of new bug strongly coupled to warning class Analysis is unlikely to notice the new bug Page 34
35 Probability of Misdiagnosis Waldo is easier to find among fewer non-waldoes More false positives => more misdiagnoses Page 35
36 100% 90% Probability of Correct Judgment 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% Good! All warnings are true positives, and all are judged correctly 10% 0% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Precision Bad! All warnings are false positives, so nobody uses the tool. Page 36
37 100% 90% Probability of Correct Judgment 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% Linear Quadratic Cubic 0% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Precision Page 37
38 Bugs in Deployed Product Bugs not found by tool Bugs found by tool, but misjudged as False Positives Bugs introduced as a consequence of changes, and subsequently undetected Page 38
39 Which is better? Time wasted by Tool A Bugs missed by Tool B Tool A Tool B Page 39
40 Look at the Business Case Page 40
41 Agenda What is Advanced Static Analysis? Warning Classifications The Business Case Case Studies Conclusions Page 41
42 How to model the business case? Costs Engineering time Time to fix a bug early vs. late Time to inspect a warning Cost of bug incident Downtime Customer dissatisfaction Safety or security violation Risks Number of bugs in product Probability of bug triggering an incident Probability of new bug introduced by fix Consequences of warning misjudgment Tool variables Recall (probability of finding a real bug) Precision (probability of a warning being real) = 1-False positive rate Page 42
43 Inputs Number of bugs 100 Cost of bug incident $40,000 Probability of bug triggering an incident 5% Engineer hourly rate* (adjusted for inflation) $75 Hours to fix a bug early* 4 Hours to fix a bug late* 20 Time to inspect a warning 10 minutes Probability of FP misjudgment 0% Probability of necessary change introducing new undetected bug 0% Probability of un-necessary change introducing new undetected bug 0% * Source: The Economic Impacts of Inadequate Infrastructure for Software Testing. NIST Page 43
44 Tool Variables Tool Recall Precision Cost Tool A 60% 50% $20,000 Tool B 30% 80% $20,000 Tool C 95% 10% $20,000 No tool 0% n/a $0 Perfect tool 100% 100% $0 Page 44
45 Warning Results Bugs not detected by tool False positives True positives Tool A Tool B Tool C No tool Perfect tool Page 45
46 Remaining Bugs Linear Cubic Page 46
47 Return on Investment (cubic model) Linear Cubic Page 47
48 How to Compare Two tools, or two different configurations of the same tool Recall is impossible to quantify accurately And difficult to estimate But it is easy to count results Page 48
49 How to Compare Tools Let f(p) be the probability of true-positive misjudgment given precision p Tool 1 and 2 have the same value if: Or, N R 1 f(p 1 ) = N R 2 f(p 2 ) FF 2 = TT 2 f 1 ( TT 1 TT f( 1 )) TT 2 TT 1 + FF 1 TT 2 Page 49
50 Example Tool 1 TP 1 = 40, FP 1 = 10 Tool 2 TP 2 = 50 How many False Positives is it worth tolerating for those extra 10 real bugs? Linear model: 28 Cubic model (more realistic): 72 Page 50
51 Economics vs. Emotions Two factors dominate the economics: Cost of incident Consequence of misjudgments One factor dominates the emotions False positive rate Recall is impossible to quantify Consequently: Tools demonstrated with low FP rate feel better In production, tools are seldom configured optimally Page 51
52 Beware of Instant Gratification Page 52
53 Agenda What is Advanced Static Analysis? Warning Classifications The Business Case Case Studies Conclusions Page 53
54 Case Study: Software not Delivered Patient Monitoring Device: 900K LOC Buffer overflow found late in testing Bug found by developer fixing a different issue Bug fixed in such a way that a new bug was introduced Entire product shipment held up Loss of confidence led to code re-review, weeks of effort Static analysis found the issue immediately Also showed how the fix was not really a fix Analysis also identified additional issues that reviews and testing had missed Page 55 Page 55
55 NASA Satellite Network NASA s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) Nine geosynchronous satellites and three ground stations Launch support and on-orbit communications and tracking services for most NASA missions Striving for 99.9% availability (excluding scheduled down times) Detailed study of ROI of using CodeSonar on ground station software Conducted by NASA White Sands under the sponsorship of NASA Ames Research Center and the NASA IV&V Facility Found that tool price plus cost of labor to use was about equal to debugging labor cost However, tool use prevents outages, whereas reactive debugging does not Result of study: CodeSonar was adopted to reduce software errors Page 56
56 Agenda What is Advanced Static Analysis? Warning Classifications The Business Case Case Studies Conclusions Page 57
57 Conclusions and Recommendations Static-analysis tools have different characteristics All code bases have different characteristics Value of tool depends strongly on individual circumstances Best approach: Try them out on your own code But be careful to judge benefit rationally False-positive rate may not be the most important factor Consider customizations to find domain-specific issues Page 58
58 The End Me: Paper: Measuring the Value of Static Analysis Tool Deployments, Paul Anderson, IEEE Security and Privacy, May/June 2012 Product: CodeSonar Sign up for a fully-functional free evaluation on your code Web site: Page 59
Static Analysis of C++ Projects with CodeSonar
 Static Analysis of C++ Projects with CodeSonar John Plaice, Senior Scientist, GrammaTech jplaice@grammatech.com 25 July 2017, Meetup C++ de Montréal Abstract Static program analysis consists of the analysis
Static Analysis of C++ Projects with CodeSonar John Plaice, Senior Scientist, GrammaTech jplaice@grammatech.com 25 July 2017, Meetup C++ de Montréal Abstract Static program analysis consists of the analysis
WHITE PAPER. 10 Reasons to Use Static Analysis for Embedded Software Development
 WHITE PAPER 10 Reasons to Use Static Analysis for Embedded Software Development Overview Software is in everything. And in many embedded systems like flight control, medical devices, and powertrains, quality
WHITE PAPER 10 Reasons to Use Static Analysis for Embedded Software Development Overview Software is in everything. And in many embedded systems like flight control, medical devices, and powertrains, quality
Verification Using Static Analysis
 Verification Using Static Analysis Outline Today we will discuss static analysis and how it differs from dynamic analysis We will also look at the different types of static analysis including: Control
Verification Using Static Analysis Outline Today we will discuss static analysis and how it differs from dynamic analysis We will also look at the different types of static analysis including: Control
CERT C++ COMPLIANCE ENFORCEMENT
 CERT C++ COMPLIANCE ENFORCEMENT AUTOMATED SOURCE CODE ANALYSIS TO MAINTAIN COMPLIANCE SIMPLIFY AND STREAMLINE CERT C++ COMPLIANCE The CERT C++ compliance module reports on dataflow problems, software defects,
CERT C++ COMPLIANCE ENFORCEMENT AUTOMATED SOURCE CODE ANALYSIS TO MAINTAIN COMPLIANCE SIMPLIFY AND STREAMLINE CERT C++ COMPLIANCE The CERT C++ compliance module reports on dataflow problems, software defects,
Finding Concurrency Bugs in Java
 July 25, 2004 Background Our Work Recommendations Background Our Work Programmers are Not Scared Enough Java makes threaded programming too easy Language often hides consequences of incorrect synchronization
July 25, 2004 Background Our Work Recommendations Background Our Work Programmers are Not Scared Enough Java makes threaded programming too easy Language often hides consequences of incorrect synchronization
Tracing Data Flows to Find Concurrency Errors
 Tracing Data Flows to Find Concurrency Errors Presented by: Benjamin Ylvisaker Senior Scientist GrammaTech, Inc. 531 Esty Street, Ithaca, NY 14850 Tel: 607 273-7340 E-mail: benjaminy@grammatech.com GrammaTech
Tracing Data Flows to Find Concurrency Errors Presented by: Benjamin Ylvisaker Senior Scientist GrammaTech, Inc. 531 Esty Street, Ithaca, NY 14850 Tel: 607 273-7340 E-mail: benjaminy@grammatech.com GrammaTech
Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures
 Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures Presented by Brian Walker Senior Software Engineer, Video Product Line, Tektronix, Inc. Pacific Northwest Software Quality Conference,
Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures Presented by Brian Walker Senior Software Engineer, Video Product Line, Tektronix, Inc. Pacific Northwest Software Quality Conference,
Static Analysis in C/C++ code with Polyspace
 1 Static Analysis in C/C++ code with Polyspace Yongchool Ryu Application Engineer gary.ryu@mathworks.com 2016 The MathWorks, Inc. 2 Agenda Efficient way to find problems in Software Category of Static
1 Static Analysis in C/C++ code with Polyspace Yongchool Ryu Application Engineer gary.ryu@mathworks.com 2016 The MathWorks, Inc. 2 Agenda Efficient way to find problems in Software Category of Static
Objectives. Chapter 19. Verification vs. validation. Topics covered. Static and dynamic verification. The V&V process
 Objectives Chapter 19 Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user s need are to introduce software verification and validation (V&V) and to discuss the distinction between
Objectives Chapter 19 Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user s need are to introduce software verification and validation (V&V) and to discuss the distinction between
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 15: Software Security II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Vulnerabilities Buffer overflow vulnerabilities account
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 15: Software Security II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Vulnerabilities Buffer overflow vulnerabilities account
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE. The University of Tokyo
 Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues
 Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Verification and Validation
 Verification and Validation Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Topics Covered 1. Verification and Validation 2. Software Inspections 3. Automated Static Analysis 4. Verification and Formal Methods 2 2 1. Verification
Verification and Validation Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Topics Covered 1. Verification and Validation 2. Software Inspections 3. Automated Static Analysis 4. Verification and Formal Methods 2 2 1. Verification
18-642: Code Style for Compilers
 18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/25/2017 1 Anti-Patterns: Coding Style: Language Use Code compiles with warnings Warnings are turned off or over-ridden Insufficient warning level set Language safety
18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/25/2017 1 Anti-Patterns: Coding Style: Language Use Code compiles with warnings Warnings are turned off or over-ridden Insufficient warning level set Language safety
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
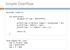 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Leveraging Formal Methods Based Software Verification to Prove Code Quality & Achieve MISRA compliance
 Leveraging Formal Methods Based Software Verification to Prove Code Quality & Achieve MISRA compliance Prashant Mathapati Senior Application Engineer MATLAB EXPO 2013 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The problem
Leveraging Formal Methods Based Software Verification to Prove Code Quality & Achieve MISRA compliance Prashant Mathapati Senior Application Engineer MATLAB EXPO 2013 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The problem
Verification and Validation
 Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user's needs Ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapter 19 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification
Verification and Validation Assuring that a software system meets a user's needs Ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapter 19 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study. Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU
 Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
18-642: Code Style for Compilers
 18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/6/2018 2017-2018 Philip Koopman Programming can be fun, so can cryptography; however they should not be combined. Kreitzberg and Shneiderman 2017-2018 Philip Koopman
18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/6/2018 2017-2018 Philip Koopman Programming can be fun, so can cryptography; however they should not be combined. Kreitzberg and Shneiderman 2017-2018 Philip Koopman
Analyzing Systems. Steven M. Bellovin November 26,
 Analyzing Systems When presented with a system, how do you know it s secure? Often, you re called upon to analyze a system you didn t design application architects and programmers build it; security people
Analyzing Systems When presented with a system, how do you know it s secure? Often, you re called upon to analyze a system you didn t design application architects and programmers build it; security people
CS 161 Computer Security. Security Throughout the Software Development Process
 Popa & Wagner Spring 2016 CS 161 Computer Security 1/25 Security Throughout the Software Development Process Generally speaking, we should think of security is an ongoing process. For best results, it
Popa & Wagner Spring 2016 CS 161 Computer Security 1/25 Security Throughout the Software Development Process Generally speaking, we should think of security is an ongoing process. For best results, it
Memory Analysis tools
 Memory Analysis tools PURIFY The Necessity TOOL Application behaviour: Crashes intermittently Uses too much memory Runs too slowly Isn t well tested Is about to ship You need something See what your code
Memory Analysis tools PURIFY The Necessity TOOL Application behaviour: Crashes intermittently Uses too much memory Runs too slowly Isn t well tested Is about to ship You need something See what your code
정형기법을활용한 AUTOSAR SWC 의구현확인및정적분석
 정형기법을활용한 AUTOSAR SWC 의구현확인및정적분석 Develop high quality embedded software 이영준 Principal Application Engineer 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Agendas Unit-proving of AUTOSAR Component and Runtime error Secure Coding
정형기법을활용한 AUTOSAR SWC 의구현확인및정적분석 Develop high quality embedded software 이영준 Principal Application Engineer 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Agendas Unit-proving of AUTOSAR Component and Runtime error Secure Coding
Limitations of the stack
 The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
Static Program Analysis Part 1 the TIP language
 Static Program Analysis Part 1 the TIP language http://cs.au.dk/~amoeller/spa/ Anders Møller & Michael I. Schwartzbach Computer Science, Aarhus University Questions about programs Does the program terminate
Static Program Analysis Part 1 the TIP language http://cs.au.dk/~amoeller/spa/ Anders Møller & Michael I. Schwartzbach Computer Science, Aarhus University Questions about programs Does the program terminate
Secure Programming Lecture 13: Static Analysis
 Secure Programming Lecture 13: Static Analysis David Aspinall 10th March 2014 Outline Overview Vulnerabilities and analysis Using static analysis Simple static analysis tasks Type checking Style checking
Secure Programming Lecture 13: Static Analysis David Aspinall 10th March 2014 Outline Overview Vulnerabilities and analysis Using static analysis Simple static analysis tasks Type checking Style checking
Part 5. Verification and Validation
 Software Engineering Part 5. Verification and Validation - Verification and Validation - Software Testing Ver. 1.7 This lecture note is based on materials from Ian Sommerville 2006. Anyone can use this
Software Engineering Part 5. Verification and Validation - Verification and Validation - Software Testing Ver. 1.7 This lecture note is based on materials from Ian Sommerville 2006. Anyone can use this
Race Catcher. Automatically Pinpoints Concurrency Defects in Multi-threaded JVM Applications with 0% False Positives.
 Race Catcher US and International Patents Issued and Pending. Automatically Pinpoints Concurrency Defects in Multi-threaded JVM Applications with 0% False Positives. Whitepaper Introducing Race Catcher
Race Catcher US and International Patents Issued and Pending. Automatically Pinpoints Concurrency Defects in Multi-threaded JVM Applications with 0% False Positives. Whitepaper Introducing Race Catcher
Verification & Validation of Open Source
 Verification & Validation of Open Source 2011 WORKSHOP ON SPACECRAFT FLIGHT SOFTWARE Gordon Uchenick Coverity, Inc Open Source is Ubiquitous Most commercial and proprietary software systems have some open
Verification & Validation of Open Source 2011 WORKSHOP ON SPACECRAFT FLIGHT SOFTWARE Gordon Uchenick Coverity, Inc Open Source is Ubiquitous Most commercial and proprietary software systems have some open
Fiji VM Safety Critical Java
 Fiji VM Safety Critical Java Filip Pizlo, President Fiji Systems Inc. Introduction Java is a modern, portable programming language with wide-spread adoption. Goal: streamlining debugging and certification.
Fiji VM Safety Critical Java Filip Pizlo, President Fiji Systems Inc. Introduction Java is a modern, portable programming language with wide-spread adoption. Goal: streamlining debugging and certification.
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture C Pointers. Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic & Nicholas Weaver
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture C Pointers Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic & Nicholas Weaver http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp16 1 Agenda Pointers Arrays in C 2 Address vs. Value Consider
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture C Pointers Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic & Nicholas Weaver http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp16 1 Agenda Pointers Arrays in C 2 Address vs. Value Consider
Lecture 9 Assertions and Error Handling CS240
 Lecture 9 Assertions and Error Handling CS240 The C preprocessor The C compiler performs Macro expansion and directive handling Preprocessing directive lines, including file inclusion and conditional compilation,
Lecture 9 Assertions and Error Handling CS240 The C preprocessor The C compiler performs Macro expansion and directive handling Preprocessing directive lines, including file inclusion and conditional compilation,
Question 1: What is a code walk-through, and how is it performed?
 Question 1: What is a code walk-through, and how is it performed? Response: Code walk-throughs have traditionally been viewed as informal evaluations of code, but more attention is being given to this
Question 1: What is a code walk-through, and how is it performed? Response: Code walk-throughs have traditionally been viewed as informal evaluations of code, but more attention is being given to this
HW1 due Monday by 9:30am Assignment online, submission details to come
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #2 - C Pointers and Arrays Administrivia Buggy Start Lab schedule, lab machines, HW0 due tomorrow in lab 2009-06-24 HW1 due Monday by 9:30am
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #2 - C Pointers and Arrays Administrivia Buggy Start Lab schedule, lab machines, HW0 due tomorrow in lab 2009-06-24 HW1 due Monday by 9:30am
Gaps in Static Analysis Tool Capabilities. Providing World-Class Services for World-Class Competitiveness
 Gaps in Static Analysis Tool Capabilities 1 Overview Gaps in Static Analysis tools as identified during the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Collaborative effort between
Gaps in Static Analysis Tool Capabilities 1 Overview Gaps in Static Analysis tools as identified during the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Collaborative effort between
Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1
 Verification and Validation Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification and validation and to discuss the distinction between them To describe the program inspection process and its role in V
Verification and Validation Slide 1 Objectives To introduce software verification and validation and to discuss the distinction between them To describe the program inspection process and its role in V
Type Checking and Type Equality
 Type Checking and Type Equality Type systems are the biggest point of variation across programming languages. Even languages that look similar are often greatly different when it comes to their type systems.
Type Checking and Type Equality Type systems are the biggest point of variation across programming languages. Even languages that look similar are often greatly different when it comes to their type systems.
Lecture 4 September Required reading materials for this class
 EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
Vulnerabilities and analysis. Simple static analysis tasks Type checking Style checking
 Outline Recap Secure Programming Lecture 13: Static Analysis David Aspinall 10th March 2014 Overview Vulnerabilities and analysis Using static analysis Simple static analysis tasks Type checking Style
Outline Recap Secure Programming Lecture 13: Static Analysis David Aspinall 10th March 2014 Overview Vulnerabilities and analysis Using static analysis Simple static analysis tasks Type checking Style
CSE 403: Software Engineering, Fall courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse403/16au/ Static Analysis. Emina Torlak
 CSE 403: Software Engineering, Fall 2016 courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse403/16au/ Static Analysis Emina Torlak emina@cs.washington.edu Outline What is static analysis? How does it work? Free and
CSE 403: Software Engineering, Fall 2016 courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse403/16au/ Static Analysis Emina Torlak emina@cs.washington.edu Outline What is static analysis? How does it work? Free and
Bugs in software. Using Static Analysis to Find Bugs. David Hovemeyer
 Bugs in software Programmers are smart people We have good techniques for finding bugs early: Unit testing, pair programming, code inspections So, most bugs should be subtle, and require sophisticated
Bugs in software Programmers are smart people We have good techniques for finding bugs early: Unit testing, pair programming, code inspections So, most bugs should be subtle, and require sophisticated
Evaluating Bug Finders
 Evaluating Bug Finders Test and Measurement of Static Code Analyzers Aurelien DELAITRE Bertrand STIVALET http://samate.nist.gov ICSE - COUFLESS 2015 May 23, 2015 Authors Aurelien DELAITRE West Virginia
Evaluating Bug Finders Test and Measurement of Static Code Analyzers Aurelien DELAITRE Bertrand STIVALET http://samate.nist.gov ICSE - COUFLESS 2015 May 23, 2015 Authors Aurelien DELAITRE West Virginia
Memory Corruption 101 From Primitives to Exploit
 Memory Corruption 101 From Primitives to Exploit Created by Nick Walker @ MWR Infosecurity / @tel0seh What is it? A result of Undefined Behaviour Undefined Behaviour A result of executing computer code
Memory Corruption 101 From Primitives to Exploit Created by Nick Walker @ MWR Infosecurity / @tel0seh What is it? A result of Undefined Behaviour Undefined Behaviour A result of executing computer code
Hacking in C. Pointers. Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Spring 2019
 Hacking in C Pointers Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Spring 2019 Allocation of multiple variables Consider the program main(){ char x; int i; short s; char y;... } What will the layout of
Hacking in C Pointers Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Spring 2019 Allocation of multiple variables Consider the program main(){ char x; int i; short s; char y;... } What will the layout of
Lessons Learned in Static Analysis Tool Evaluation. Providing World-Class Services for World-Class Competitiveness
 Lessons Learned in Static Analysis Tool Evaluation 1 Overview Lessons learned in the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Topics Licensing Performance Measurement Limitations
Lessons Learned in Static Analysis Tool Evaluation 1 Overview Lessons learned in the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Topics Licensing Performance Measurement Limitations
Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures
 Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures David Brumley, James Newsome, Dawn Song, Hao Wang, and Somesh Jha (presented by Boniface Hicks) Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security
Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures David Brumley, James Newsome, Dawn Song, Hao Wang, and Somesh Jha (presented by Boniface Hicks) Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security
OWASP 5/07/09. The OWASP Foundation OWASP Static Analysis (SA) Track Session 1: Intro to Static Analysis
 Static Analysis (SA) Track Session 1: Intro to Static Analysis Eric Dalci Cigital edalci at cigital dot com 5/07/09 Copyright The Foundation Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this
Static Analysis (SA) Track Session 1: Intro to Static Analysis Eric Dalci Cigital edalci at cigital dot com 5/07/09 Copyright The Foundation Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this
Outline. Security as an economic good. Risk budgeting with ALE. Failure: Risk compensation. Failure: Displacement activity
 CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 2: Intro to Software and OS Security Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Security as an economic good Security is a
CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 2: Intro to Software and OS Security Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Security as an economic good Security is a
EURECOM 6/2/2012 SYSTEM SECURITY Σ
 EURECOM 6/2/2012 Name SYSTEM SECURITY 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Σ Course material is not allowed during the exam. Try to keep your answers precise and short. You will not get extra points
EURECOM 6/2/2012 Name SYSTEM SECURITY 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Σ Course material is not allowed during the exam. Try to keep your answers precise and short. You will not get extra points
Software Engineering
 Software Engineering chap 4. Software Reuse 1 SuJin Choi, PhD. Sogang University Email: sujinchoi@sogang.ac.kr Slides modified, based on original slides by Ian Sommerville (Software Engineering 10 th Edition)
Software Engineering chap 4. Software Reuse 1 SuJin Choi, PhD. Sogang University Email: sujinchoi@sogang.ac.kr Slides modified, based on original slides by Ian Sommerville (Software Engineering 10 th Edition)
Static Analysis Techniques
 oftware Design (F28SD2): Static Analysis Techniques 1 Software Design (F28SD2) Static Analysis Techniques Andrew Ireland School of Mathematical and Computer Science Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh oftware
oftware Design (F28SD2): Static Analysis Techniques 1 Software Design (F28SD2) Static Analysis Techniques Andrew Ireland School of Mathematical and Computer Science Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh oftware
Verification and Test with Model-Based Design
 Verification and Test with Model-Based Design Flight Software Workshop 2015 Jay Abraham 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The software development process Develop, iterate and specify requirements Create high
Verification and Test with Model-Based Design Flight Software Workshop 2015 Jay Abraham 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The software development process Develop, iterate and specify requirements Create high
Announcements. Working on requirements this week Work on design, implementation. Types. Lecture 17 CS 169. Outline. Java Types
 Announcements Types Working on requirements this week Work on design, implementation Lecture 17 CS 169 Prof. Brewer CS 169 Lecture 16 1 Prof. Brewer CS 169 Lecture 16 2 Outline Type concepts Where do types
Announcements Types Working on requirements this week Work on design, implementation Lecture 17 CS 169 Prof. Brewer CS 169 Lecture 16 1 Prof. Brewer CS 169 Lecture 16 2 Outline Type concepts Where do types
Agenda. Peer Instruction Question 1. Peer Instruction Answer 1. Peer Instruction Question 2 6/22/2011
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Introduction to C (Part II) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. Patterson http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp11 Spring 2011 -- Lecture
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Introduction to C (Part II) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. Patterson http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp11 Spring 2011 -- Lecture
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency (Part 2: Designing (Sub )Systems)
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency (Part 2: Designing (Sub )Systems) More Analysis for Functional Correctness Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency (Part 2: Designing (Sub )Systems) More Analysis for Functional Correctness Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science
C++ Undefined Behavior What is it, and why should I care?
 C++ Undefined Behavior What is it, and why should I care? Marshall Clow Qualcomm marshall@idio.com http://cplusplusmusings.wordpress.com (intermittent) Twitter: @mclow ACCU 2014 April 2014 What is Undefined
C++ Undefined Behavior What is it, and why should I care? Marshall Clow Qualcomm marshall@idio.com http://cplusplusmusings.wordpress.com (intermittent) Twitter: @mclow ACCU 2014 April 2014 What is Undefined
CMPSC 497: Static Analysis
 CMPSC 497: Static Analysis Trent Jaeger Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security (SIIS) Lab Computer Science and Engineering Department Pennsylvania State University Page 1 Our Goal In this course,
CMPSC 497: Static Analysis Trent Jaeger Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security (SIIS) Lab Computer Science and Engineering Department Pennsylvania State University Page 1 Our Goal In this course,
Secure Development Lifecycle
 Secure Development Lifecycle Strengthening Cisco Products The Cisco Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) is a repeatable and measurable process designed to increase Cisco product resiliency and trustworthiness.
Secure Development Lifecycle Strengthening Cisco Products The Cisco Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) is a repeatable and measurable process designed to increase Cisco product resiliency and trustworthiness.
High Performance Computing MPI and C-Language Seminars 2009
 High Performance Computing - Seminar Plan Welcome to the High Performance Computing seminars for 2009. Aims: Introduce the C Programming Language. Basic coverage of C and programming techniques needed
High Performance Computing - Seminar Plan Welcome to the High Performance Computing seminars for 2009. Aims: Introduce the C Programming Language. Basic coverage of C and programming techniques needed
CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development
 CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development Hal Perkins Winter 2009 Lecture 7 Introduction to C: The C-Level of Abstraction CSE 303 Winter 2009, Lecture 7 1 Welcome to C Compared to Java, in rough
CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development Hal Perkins Winter 2009 Lecture 7 Introduction to C: The C-Level of Abstraction CSE 303 Winter 2009, Lecture 7 1 Welcome to C Compared to Java, in rough
Threat Modeling. Bart De Win Secure Application Development Course, Credits to
 Threat Modeling Bart De Win bart.dewin@ascure.com Secure Application Development Course, 2009 Credits to Frank Piessens (KUL) for the slides 2 1 Overview Introduction Key Concepts Threats, Vulnerabilities,
Threat Modeling Bart De Win bart.dewin@ascure.com Secure Application Development Course, 2009 Credits to Frank Piessens (KUL) for the slides 2 1 Overview Introduction Key Concepts Threats, Vulnerabilities,
Software and Web Security 1. Root Cause Analysis. Abstractions Assumptions Trust. sws1 1
 Software and Web Security 1 Reflections on using C(++) Root Cause Analysis Abstractions Assumptions Trust sws1 1 There are only two kinds of programming languages: the ones people complain about and the
Software and Web Security 1 Reflections on using C(++) Root Cause Analysis Abstractions Assumptions Trust sws1 1 There are only two kinds of programming languages: the ones people complain about and the
Lecture 20: SW Testing Presented by: Mohammad El-Ramly, PhD
 Cairo University Faculty of Computers and Information CS251 Software Engineering Lecture 20: SW Testing Presented by: Mohammad El-Ramly, PhD http://www.acadox.com/join/75udwt Outline Definition of Software
Cairo University Faculty of Computers and Information CS251 Software Engineering Lecture 20: SW Testing Presented by: Mohammad El-Ramly, PhD http://www.acadox.com/join/75udwt Outline Definition of Software
Kurt Schmidt. October 30, 2018
 to Structs Dept. of Computer Science, Drexel University October 30, 2018 Array Objectives to Structs Intended audience: Student who has working knowledge of Python To gain some experience with a statically-typed
to Structs Dept. of Computer Science, Drexel University October 30, 2018 Array Objectives to Structs Intended audience: Student who has working knowledge of Python To gain some experience with a statically-typed
Automated Assessment Tools
 Automated Assessment Tools Barton P. Miller Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin bart@cs.wisc.edu Elisa Heymann Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin & Universitat Autònoma
Automated Assessment Tools Barton P. Miller Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin bart@cs.wisc.edu Elisa Heymann Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin & Universitat Autònoma
ΗΜΥ 317 Τεχνολογία Υπολογισμού
 ΗΜΥ 317 Τεχνολογία Υπολογισμού Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2008 ΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 18-19: Έλεγχος και Πιστοποίηση Λειτουργίας ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙ ΗΣ Λέκτορας ΗΜΜΥ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) [Προσαρμογή από Ian Sommerville, Software
ΗΜΥ 317 Τεχνολογία Υπολογισμού Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2008 ΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 18-19: Έλεγχος και Πιστοποίηση Λειτουργίας ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙ ΗΣ Λέκτορας ΗΜΜΥ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) [Προσαρμογή από Ian Sommerville, Software
Topics in Software Testing
 Dependable Software Systems Topics in Software Testing Material drawn from [Beizer, Sommerville] Software Testing Software testing is a critical element of software quality assurance and represents the
Dependable Software Systems Topics in Software Testing Material drawn from [Beizer, Sommerville] Software Testing Software testing is a critical element of software quality assurance and represents the
Determining the Fundamental Basis of Software Vulnerabilities. Larry Wagoner NSA
 Determining the Fundamental Basis of Software Vulnerabilities Larry Wagoner NSA Agenda Background Analogous background Matt Bishop work CWEs Tool reporting of CWEs KDM Analytics Determining the fundamental
Determining the Fundamental Basis of Software Vulnerabilities Larry Wagoner NSA Agenda Background Analogous background Matt Bishop work CWEs Tool reporting of CWEs KDM Analytics Determining the fundamental
TI2725-C, C programming lab, course
 Valgrind tutorial Valgrind is a tool which can find memory leaks in your programs, such as buffer overflows and bad memory management. This document will show per example how Valgrind responds to buggy
Valgrind tutorial Valgrind is a tool which can find memory leaks in your programs, such as buffer overflows and bad memory management. This document will show per example how Valgrind responds to buggy
Brave New 64-Bit World. An MWR InfoSecurity Whitepaper. 2 nd June Page 1 of 12 MWR InfoSecurity Brave New 64-Bit World
 Brave New 64-Bit World An MWR InfoSecurity Whitepaper 2 nd June 2010 2010-06-02 Page 1 of 12 Abstract Abstract Memory requirements on server and desktop systems have risen considerably over the past few
Brave New 64-Bit World An MWR InfoSecurity Whitepaper 2 nd June 2010 2010-06-02 Page 1 of 12 Abstract Abstract Memory requirements on server and desktop systems have risen considerably over the past few
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #3 C Strings, Arrays, & Malloc 2007-06-27 Scott Beamer, Instructor Sun announces new supercomputer: Sun Constellation CS61C L3 C Pointers
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #3 C Strings, Arrays, & Malloc 2007-06-27 Scott Beamer, Instructor Sun announces new supercomputer: Sun Constellation CS61C L3 C Pointers
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ Debugging
 CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ Debugging Debugging Tips Examine the most recent change Error likely in, or exposed by, code most recently added Developing code incrementally and testing along
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ Debugging Debugging Tips Examine the most recent change Error likely in, or exposed by, code most recently added Developing code incrementally and testing along
Buffer overflow background
 and heap buffer background Comp Sci 3600 Security Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Address Space and heap buffer
and heap buffer background Comp Sci 3600 Security Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Address Space and heap buffer
Page 1. Stuff. Last Time. Today. Safety-Critical Systems MISRA-C. Terminology. Interrupts Inline assembly Intrinsics
 Stuff Last Time Homework due next week Lab due two weeks from today Questions? Interrupts Inline assembly Intrinsics Today Safety-Critical Systems MISRA-C Subset of C language for critical systems System
Stuff Last Time Homework due next week Lab due two weeks from today Questions? Interrupts Inline assembly Intrinsics Today Safety-Critical Systems MISRA-C Subset of C language for critical systems System
CS61C Machine Structures. Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays. 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek. www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L04 C Pointers (1) Common C Error There is a difference
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L04 C Pointers (1) Common C Error There is a difference
By V-cubed Solutions, Inc. Page1. All rights reserved by V-cubed Solutions, Inc.
 By V-cubed Solutions, Inc. Page1 Purpose of Document This document will demonstrate the efficacy of CODESCROLL CODE INSPECTOR, CONTROLLER TESTER, and QUALITYSCROLL COVER, which has been developed by V-cubed
By V-cubed Solutions, Inc. Page1 Purpose of Document This document will demonstrate the efficacy of CODESCROLL CODE INSPECTOR, CONTROLLER TESTER, and QUALITYSCROLL COVER, which has been developed by V-cubed
Outline. Classic races: files in /tmp. Race conditions. TOCTTOU example. TOCTTOU gaps. Vulnerabilities in OS interaction
 Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Lecture 15 Software Testing
 Lecture 15 Software Testing Includes slides from the companion website for Sommerville, Software Engineering, 10/e. Pearson Higher Education, 2016. All rights reserved. Used with permission. Topics covered
Lecture 15 Software Testing Includes slides from the companion website for Sommerville, Software Engineering, 10/e. Pearson Higher Education, 2016. All rights reserved. Used with permission. Topics covered
Secure Programming. An introduction to Splint. Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E
 Secure Programming An introduction to Splint Christian D. Jensen René Rydhof Hansen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E05-02230 CDJ/RRH (IMM/DTU) Secure Programming
Secure Programming An introduction to Splint Christian D. Jensen René Rydhof Hansen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E05-02230 CDJ/RRH (IMM/DTU) Secure Programming
Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer
 Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer The Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer ensures application reliability and security by detecting application vulnerabilities, including memory leaks and memory
Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer The Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer ensures application reliability and security by detecting application vulnerabilities, including memory leaks and memory
C Review. MaxMSP Developers Workshop Summer 2009 CNMAT
 C Review MaxMSP Developers Workshop Summer 2009 CNMAT C Syntax Program control (loops, branches): Function calls Math: +, -, *, /, ++, -- Variables, types, structures, assignment Pointers and memory (***
C Review MaxMSP Developers Workshop Summer 2009 CNMAT C Syntax Program control (loops, branches): Function calls Math: +, -, *, /, ++, -- Variables, types, structures, assignment Pointers and memory (***
Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs. {livshits,
 Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs {livshits, lam}@cs.stanford.edu 2 Background Software systems are getting bigger Harder to develop Harder to modify Harder
Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs {livshits, lam}@cs.stanford.edu 2 Background Software systems are getting bigger Harder to develop Harder to modify Harder
Is Your Web Application Really Secure? Ken Graf, Watchfire
 Is Your Web Application Really Secure? Ken Graf, Watchfire What we will discuss today Pressures on the application lifecycle Why application security defects matter How to create hacker resistant business
Is Your Web Application Really Secure? Ken Graf, Watchfire What we will discuss today Pressures on the application lifecycle Why application security defects matter How to create hacker resistant business
Announcements. assign0 due tonight. Labs start this week. No late submissions. Very helpful for assign1
 Announcements assign due tonight No late submissions Labs start this week Very helpful for assign1 Goals for Today Pointer operators Allocating memory in the heap malloc and free Arrays and pointer arithmetic
Announcements assign due tonight No late submissions Labs start this week Very helpful for assign1 Goals for Today Pointer operators Allocating memory in the heap malloc and free Arrays and pointer arithmetic
Addressing Future Challenges in the Development of Safe and Secure Software Components The MathWorks, Inc. 1
 Addressing Future Challenges in the Development of Safe and Secure Software Components 2016 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Cybersecurity Emerging Topic in the Auto Industry Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Wifi Hotspot
Addressing Future Challenges in the Development of Safe and Secure Software Components 2016 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Cybersecurity Emerging Topic in the Auto Industry Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Wifi Hotspot
Review! * follows a pointer to its value! & gets the address of a variable! Pearce, Summer 2010 UCB! ! int x = 1000; Pearce, Summer 2010 UCB!
 CS61C L03 Introduction to C (pt 2) (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to C (pt 2) 2010-06-23!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! The typical! development cycle!
CS61C L03 Introduction to C (pt 2) (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to C (pt 2) 2010-06-23!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! The typical! development cycle!
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to C (pt 2) 2010-06-23! C help session: Tonight 7:00-9:00pm @ 306 Soda!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! The typical! development
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to C (pt 2) 2010-06-23! C help session: Tonight 7:00-9:00pm @ 306 Soda!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! The typical! development
Software Design and Analysis for Engineers
 Software Design and Analysis for Engineers by Dr. Lesley Shannon Email: lshannon@ensc.sfu.ca Course Website: http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/~lshannon/courses/ensc251 Simon Fraser University Slide Set: 4 Date:
Software Design and Analysis for Engineers by Dr. Lesley Shannon Email: lshannon@ensc.sfu.ca Course Website: http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/~lshannon/courses/ensc251 Simon Fraser University Slide Set: 4 Date:
CS 370 The Pseudocode Programming Process D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L
 CS 370 The Pseudocode Programming Process D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L 2 0 1 5 Introduction At this point, you are ready to beginning programming at a lower level How do you actually write your
CS 370 The Pseudocode Programming Process D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L 2 0 1 5 Introduction At this point, you are ready to beginning programming at a lower level How do you actually write your
Leveraging Formal Methods for Verifying Models and Embedded Code Prashant Mathapati Application Engineering Group
 Leveraging Formal Methods for Verifying Models and Embedded Code Prashant Mathapati Application Engineering Group 2014 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The Cost of Failure News reports: Recall Due to ECU software
Leveraging Formal Methods for Verifying Models and Embedded Code Prashant Mathapati Application Engineering Group 2014 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 The Cost of Failure News reports: Recall Due to ECU software
Chapter 8 Software Testing. Chapter 8 Software testing
 Chapter 8 Software Testing 1 Topics covered Introduction to testing Stages for testing software system are: Development testing Release testing User testing Test-driven development as interleave approach.
Chapter 8 Software Testing 1 Topics covered Introduction to testing Stages for testing software system are: Development testing Release testing User testing Test-driven development as interleave approach.
Introduction. Background. Document: WG 14/N1619. Text for comment WFW-1 of N1618
 Document: WG 14/N1619 Text for comment WFW-1 of N1618 Introduction Background An essential element of secure coding in the C programming language is a set of well-documented and enforceable coding rules.
Document: WG 14/N1619 Text for comment WFW-1 of N1618 Introduction Background An essential element of secure coding in the C programming language is a set of well-documented and enforceable coding rules.
Testing. ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design. Why is testing so hard? Why do testing?
 Testing ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Scott R. Little Lecture 24: Introduction to Software Testing and Verification What is software testing? Running a program in order to find bugs (faults,
Testing ECE/CS 5780/6780: Embedded System Design Scott R. Little Lecture 24: Introduction to Software Testing and Verification What is software testing? Running a program in order to find bugs (faults,
Introduction A Tiny Example Language Type Analysis Static Analysis 2009
 Introduction A Tiny Example Language Type Analysis 2009 Michael I. Schwartzbach Computer Science, University of Aarhus 1 Questions About Programs Does the program terminate? How large can the heap become
Introduction A Tiny Example Language Type Analysis 2009 Michael I. Schwartzbach Computer Science, University of Aarhus 1 Questions About Programs Does the program terminate? How large can the heap become
Pointers and Memory 1
 Pointers and Memory 1 Pointer values Pointer values are memory addresses Think of them as a kind of integer values The first byte of memory is 0, the next 1, and so on A pointer p can hold the address
Pointers and Memory 1 Pointer values Pointer values are memory addresses Think of them as a kind of integer values The first byte of memory is 0, the next 1, and so on A pointer p can hold the address
Software Vulnerabilities August 31, 2011 / CS261 Computer Security
 Software Vulnerabilities August 31, 2011 / CS261 Computer Security Software Vulnerabilities...1 Review paper discussion...2 Trampolining...2 Heap smashing...2 malloc/free...2 Double freeing...4 Defenses...5
Software Vulnerabilities August 31, 2011 / CS261 Computer Security Software Vulnerabilities...1 Review paper discussion...2 Trampolining...2 Heap smashing...2 malloc/free...2 Double freeing...4 Defenses...5
Software Quality. Chapter What is Quality?
 Chapter 1 Software Quality 1.1 What is Quality? The purpose of software quality analysis, or software quality engineering, is to produce acceptable products at acceptable cost, where cost includes calendar
Chapter 1 Software Quality 1.1 What is Quality? The purpose of software quality analysis, or software quality engineering, is to produce acceptable products at acceptable cost, where cost includes calendar
CS 161 Computer Security
 Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Advanced Software Testing Testing Code with Static Analysis
 Advanced Software Testing Testing Code with Static Analysis Advanced Software Testing A series of webinars, this one excerpted from Advanced Software Testing: V3, a book for technical test analysts, programmers,
Advanced Software Testing Testing Code with Static Analysis Advanced Software Testing A series of webinars, this one excerpted from Advanced Software Testing: V3, a book for technical test analysts, programmers,
T Salausjärjestelmät (Cryptosystems) Security testing. Security testing. Outline. Testing Final stages of life cycle
 T-110.470 Salausjärjestelmät (Cryptosystems) Testing Final stages of life cycle Security testing 15.11.2004 1 3 Outline Security testing Security testing Some testing techniques Final stages of life cycle
T-110.470 Salausjärjestelmät (Cryptosystems) Testing Final stages of life cycle Security testing 15.11.2004 1 3 Outline Security testing Security testing Some testing techniques Final stages of life cycle
