The make Utility in Unix SEEM
|
|
|
- Gavin Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The make Utility in Unix SEEM
2 Recall the reverse Module reverse.h 1 /* reverse.h */ 2 3 void reverse (char *before, char *after); 4 /* Declare but do not define this function */ SEEM
3 Recall the reverse Module reverse.c 1 /* reverse.c */ 2 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include reverse.h 5 6 /********************************************/ 7 8 void reverse (char *before, char *after) 9 10 { 11 int i; 12 int j; 13 int len; len = strlen (before); for (j = len 1, i=0; j>= 0; j--,i++) /*Reverse loop*/ 18 after[i] = before[j]; after[len] = \0 ; /* NULL terminate reversed string */ 21 } SEEM
4 Recall the main program Here s a listing of a main program that uses reverse(): main1.c 1 /* main1.c */ 2 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include reverse.h /*Contains the prototype of reverse)*/ 5 6 /***********************************************/ 7 8 void main () 9 10 { 11 char str [100]; reverse ( cat, str); /* Invoke external function */ 14 printf ( reverse (\ cat\ ) = %s\n, str); 15 reverse ( noon, str); /* Invoke external function */ 16 printf ( reverse (\ noon\ ) = %s\n, str); 17 } SEEM
5 Compiling And Linking Modules Separately To compile each source code file separately, use the -c option of gcc. This creates a separate object module for each source code file, each with a.o suffix. The following commands are illustrative: cuse93:> gcc -c reverse.c compile reverse.c to reverse.o. cuse93:> gcc -c main1.c compile main1.c to main1.o. cuse93:> ls -l reverse.o main1.o -rw-r--r-- 1 glass 311 Jan 5 18:24 main1.o -rw-r--r-- 1 glass 181 Jan 5 18:08 reverse.o cuse93:> _ SEEM
6 Compiling And Linking Modules Separately (con t) To link them all together into an executable called main1, list the names of all the object modules after the gcc command: cuse93:> gcc reverse.o main1.o o main1 link object modules. cuse93:> ls -l main1 -rwxr xr-x 1 glass Jan 5 18:25 main1* cuse93:>./main1 run the executable. reverse ( cat ) = tac reverse ( noon ) = noon cuse93:> _ SEEM
7 Compiling And Linking Modules Separately Facilitate Code Sharing main1.c gcc -c main1.c (compiling) main1.o gcc reverse.o main1.o o main1 (linking) #include reverse.h : : reverse.c #include reverse.h : gcc -c reverse.c (compiling) reverse.o main1 SEEM
8 Reusing a Function Here s a listing of another program that uses reverse(): main8.c 1 /* main8.c */ 2 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include reverse.h /*Contains the prototype of reverse)*/ 5 6 /***********************************************/ 7 8 int main () 9 { 10 char person[100]; 11 reverse ("tom", person); /* Invoke external function */ 12 strcat(person, " Berth"); 13 printf ("person = (%s)\n", person); 14 } SEEM
9 Re-using a Function The reverse function (module) can also be used by other programs such as main8.c and the compilation is as follows. cuse93:> gcc -c main8.c compile cuse93:> gcc reverse.o main8.o o main8 link object modules SEEM
10 Compiling And Linking Modules Separately Facilitate Code Sharing main1.c gcc -c main1.c (compiling) main1.o gcc reverse.o main1.o o main1 (linking) #include reverse.h : : main1 reverse.c #include reverse.h : gcc -c reverse.c (compiling) reverse.o main8.c #include reverse.h : : gcc -c main8.c (compiling) main8.o gcc reverse.o main8.o o main8 (linking) main8 SEEM
11 Maintaining Multi-module Programs Several different issues must be considered in maintaining multi-module systems: 1. What ensures that object modules and executable files are kept up to date? 2. What stores the object modules? 3. What tracks each version of source and header files? Fortunately, there are UNIX utilities that address each problem such as the make utility The make utility is the UNIX file dependency system SEEM
12 The Unix File Dependency System: make You ve now seen how several independent object modules may be linked into a single executable file. You ve also seen that the same object module may be linked to several different executable files. Although multi-module programs are efficient in terms of reusability and disk space, they must be carefully maintained. For example, let s assume that we change the source code of reverse.c so that it uses pointers instead of array subscripts. This would result in a faster reverse function. In order to update the two main program executable files, such as main1 and main8, manually, we d have to perform the following steps, in order: 1. Recompile reverse.c. 2. Link reverse.o and main1.o to produce a new version of main1. 3. Link reverse.o and main8.o to produce a new version of main8. SEEM
13 The Unix File Dependency System: make (con t) Similarly, imagine a situation where a #define statement in a header file is changed. All of the source code files that directly or indirectly include the file must be recompiled, and then all of the executable modules that refer to the changed object modules must be re-linked. Although this might not seem like a big deal, imagine a system with a thousand object modules and 50 executable programs. Remembering all of the relationships among the headers, source code files, object modules, and executable files would be a nightmare. One way to avoid this problem is to use the UNIX make utility, which allows you to create a makefile that contains a list of all interdependencies for each executable file. Once such a file is created, re-creating the executable file is easy: You just use the make command cuse93:> make -f makefile SEEM
14 The Unix File Dependency System: make (con t) Utility: make [-f makefile ] make is a utility that updates a file on the basis of a series of dependency rules stored in a text file with a special format, make file. The -f option allows you to specify your own make filename; if none is specified, the name makefile is assumed. SEEM
15 Make Files To use the make utility to maintain an executable file, you must first create a text file known as make file. This file contains a list of all the interdependencies that exist between the files that are used to create the executable file. A make file may have any name; I recommend that you name it by taking the name of the executable file and adding the suffix.make. Thus, the name of the make file for main1 would be called main1.make. SEEM
16 Make Files In its simplest form, a make file contains rules of the form shown below targetlist: dependencylist commandlist where targetlist is a list of target files and dependencylist is a list of files that the files in targetlist depend on. commandlist is a list of zero or more commands, separated by newlines, that reconstruct the target files from the dependency files. Each line in commandlist must start with a tab character. Rules must be separated by at least one blank line. SEEM
17 Make Files (con t) For example, let s think about the file interdependencies related to the executable file main1. This file is built out of two object modules: main1.o and reverse.o. If either file is changed, then main1 may be reconstructed by linking the files, using the gcc utility. Therefore, one rule in the text file main1.make would be: main1: main1.o reverse.o gcc main1.o reverse.o o main1 SEEM
18 Make Files (con t) This line of reasoning must now be carried forward to the two object files. The file main1.o is built from two files: main1.c and reverse.h. (Remember that any file which is either directly or indirectly #included in a source file is effectively part of that file.) If either file is changed, then main1.o may be reconstructed by compiling main1.c. Here, therefore, are the remaining rules in main1.make : main1.o: main1.c reverse.h gcc -c main1.c reverse.o: reverse.c reverse.h gcc -c reverse.c SEEM
19 Make Files (con t) As a result, the whole content of main1.make is: main1: main1.o reverse.o gcc main1.o reverse.o -o main1 main1.o: main1.c reverse.h gcc -c main1.c reverse.o: reverse.c reverse.h gcc -c reverse.c SEEM
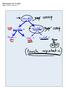
20 The Order Of Make Rules The order of make rules is important. The make utility creates a tree of interdependencies by initially examining the first rule. Each target file in the first rule is a root node of a dependency tree, and each file in its dependency list is added as a leaf of each root node. In our example, the initial tree would look like Figure SEEM
21 The Order Of Make Rules (con t) The make utility then visits each rule associated with each file in the dependency list and performs the same actions. In our example, the final tree would, therefore, look like Figure SEEM
22 The Order Of Make Rules (con t) Finally, the make utility works up the tree from the bottom leaf nodes to the root node, looking to see if the last modification time of each child node is more recent than the last modification time of its immediate parent node. For every case where this is so, the associated parent s rule is executed. If a file is not present, its rule is executed regardless of the last modification times of its children. To illustrate the order in which the nodes would be examined, we show a number for each element as below: SEEM
23 Executing A Make Once a make file has been created, you re ready to run make to re-create the executable file whose dependency information is specified by the make file. To show you how this works, suppose we deleted all of the object modules and the executable file to force every command list to execute. When I then performed the make, here s what I saw: cuse93:> make -f main1.make make executable up-to-date gcc -c main1.c gcc -c reverse.c gcc main1.o reverse.o -o main1 cuse93:> _ SEEM
24 Reusing The Reverse Function for Building Another Re-usable Function Similar to previous example, the reverse module can be used to build the palindrome program. Here are the header and source code listing of the palindrome function: palindrome.h 1 /* palindrome.h */ 2 3 int palindrome (char *str); 4 /* Declare but do not define */ SEEM
25 Reusing The Reverse Function for Building Another Re-usable Function palindrome.c 1 /* palindrome.c */ 2 3 #include palindrome.h 4 #include reverse.h 5 #include <string.h> 6 7 /*********************************************/ 8 9 int palindrome (char *str) { 12 char reversedstr [100]; 13 reverse (str, reversedstr); /* Reverse original */ 14 return (strcmp (str, reversedstr) ==0); 15 /* Compare the two */ 16 } SEEM
26 Reusing The Reverse Function for Building Another Re-usable Function The program main2.c that tests the palindrome function 1 /* main2.c */ 2 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include palindrome.h 5 6 /*******************************************/ 7 8 void main () 9 10 { 11 printf ( palindrome (\ cat\ ) = %d\n, palindrome ( cat )); 12 printf ( palindrome (\ noon\ ) = %d\n, palindrome( noon )); 13 } SEEM
27 Reusing The Reverse Function for Building Another Re-usable Function cuse93:> gcc c palindrome.c compile palindrome.c to palindrome.o cuse93:> gcc -c main2.c compile main2.c to main2.o cuse93:> gcc reverse.o palindrome.o main2.o -o main2 link them all. cuse93:> ls -l reverse.o palincdrome.o main2.o main2 -rwxr-xr-x 1 glass Jan 5 19:09 main2* -rw-r--r-- 1 glass 306 Jan 5 19:00 main2.o -rw-r--r-- 1 glass 189 Jan 5 18:59 palindrome.o -rw-r--r-- 1 glass 181 Jan 5 18:08 reverse.o cuse93:>./main2 run the program. palindrome ( cat ) = 0 palindrome ( noon ) = 1 cuse93:> _ SEEM
28 Executing A Make Notice that every make rule was executed. Since we created a second executable file when we made the palindrome program, we also fashioned a second make file, called main2.make. Here it is: main2: main2.o reverse.o palindrome.o gcc main2.o reverse.o palindrome.o -o main2 main2.o: main2.c palindrome.h gcc -c main2.c reverse.o: reverse.c reverse.h gcc -c reverse.c palindrome.o: palindrome.c palindrome.h reverse.h gcc -c palindrome.c SEEM
29 Executing A Make (con t) When we performed a make using this file, we saw the following output: cuse93:> make -f main2.make make executable up-to-date gcc -c main2.c gcc -c palindrome.c gcc main2.o reverse.o palindrome.o -o main2 cuse93:> _ Notice that reverse.c was not recompiled. This is because the previous make had already created an up-to-date object module, and make recompiles files only when necessary. SEEM
30 The touch Utility To confirm that the new version of the make file worked, we requested a make and obtained the following output: cuse93:> make -f main2.make main2 is up to date. cuse93:> _ Obviously, since we d already performed a successful make, another one wasn t going to trigger any rules! To force a make for testing purposes, we can use a handy utility called touch, which makes the last modification time of all the named files equal to the current system time. SEEM
31 The touch Utility (con t) Utility: touch -c { filename }+ touch updates the last modification and access times of the named files to equal the current time. By default, if a specified file doesn t exist, it is created with zero size. To prevent this, use the -c option. I touched the file reverse.h, which subsequently caused the recompilation of several source files: cuse93:> touch reverse.h fool make cuse93:> make -f main2.make gcc -c -o reverse.c gcc -c -o palindrome.c gcc main2.o reverse.o palindrome.o -o main2 cuse93:> _ SEEM
The make Utility in Unix SEEM
 The make Utility in Unix SEEM 3460 1 Recall the reverse Module reverse.h 1 /* reverse.h */ 2 3 void reverse (char before[], char after[]); 4 /* Declare but do not define this function */ SEEM 3460 2 Recall
The make Utility in Unix SEEM 3460 1 Recall the reverse Module reverse.h 1 /* reverse.h */ 2 3 void reverse (char before[], char after[]); 4 /* Declare but do not define this function */ SEEM 3460 2 Recall
Unix and C Program Development SEEM
 Unix and C Program Development SEEM 3460 1 Operating Systems A computer system cannot function without an operating system (OS). There are many different operating systems available for PCs, minicomputers,
Unix and C Program Development SEEM 3460 1 Operating Systems A computer system cannot function without an operating system (OS). There are many different operating systems available for PCs, minicomputers,
C Program Development and Debugging under Unix SEEM 3460
 C Program Development and Debugging under Unix SEEM 3460 1 C Basic Elements SEEM 3460 2 C - Basic Types Type (32 bit) Smallest Value Largest Value short int -32,768(-2 15 ) 32,767(2 15-1) unsigned short
C Program Development and Debugging under Unix SEEM 3460 1 C Basic Elements SEEM 3460 2 C - Basic Types Type (32 bit) Smallest Value Largest Value short int -32,768(-2 15 ) 32,767(2 15-1) unsigned short
#include <stdio.h> int main() { char s[] = Hsjodi, *p; for (p = s + 5; p >= s; p--) --*p; puts(s); return 0;
![#include <stdio.h> int main() { char s[] = Hsjodi, *p; for (p = s + 5; p >= s; p--) --*p; puts(s); return 0; #include <stdio.h> int main() { char s[] = Hsjodi, *p; for (p = s + 5; p >= s; p--) --*p; puts(s); return 0;](/thumbs/80/81398999.jpg) 1. Short answer questions: (a) Compare the typical contents of a module s header file to the contents of a module s implementation file. Which of these files defines the interface between a module and
1. Short answer questions: (a) Compare the typical contents of a module s header file to the contents of a module s implementation file. Which of these files defines the interface between a module and
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 7/25/16 Sample Solution. Question 1. (10 points) Preprocessor. Suppose we have the following two files:
 Question 1. (10 points) Preprocessor. Suppose we have the following two files: defs.h: #define DIV(a,b) a / b #define INCDIV(c,d) DIV(c + 1, d + 1) main.c: #include #include "defs.h" int main()
Question 1. (10 points) Preprocessor. Suppose we have the following two files: defs.h: #define DIV(a,b) a / b #define INCDIV(c,d) DIV(c + 1, d + 1) main.c: #include #include "defs.h" int main()
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 7/25/16. Name UW ID#
 Name UW ID# There are 7 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Name UW ID# There are 7 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017*
 600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
Student Number: Computer Science 211b Final Examination. 28 April hours
 Computer Science 211b Final Examination 28 April 2006 3 hours Student Number: Surname: Given name: Instructions/Notes: The examination has 40 questions on 15 pages, and a total of 150 marks. Put all answers
Computer Science 211b Final Examination 28 April 2006 3 hours Student Number: Surname: Given name: Instructions/Notes: The examination has 40 questions on 15 pages, and a total of 150 marks. Put all answers
Lab 2.2. Out: 9 February 2005
 CS034 Intro to Systems Programming Doeppner & Van Hentenryck Lab 2.2 Out: 9 February 2005 What you ll learn. In this lab, you will practice much of what you did in Lab 2.1, but for a slightly more challenging
CS034 Intro to Systems Programming Doeppner & Van Hentenryck Lab 2.2 Out: 9 February 2005 What you ll learn. In this lab, you will practice much of what you did in Lab 2.1, but for a slightly more challenging
Final Exam 1 /12 2 /12 3 /10 4 /7 5 /4 6 /10 7 /8 8 /9 9 /8 10 /11 11 /8 12 /10 13 /9 14 /13 15 /10 16 /10 17 /12. Faculty of Computer Science
 Faculty of Computer Science Page 1 of 21 Final Exam Term: Fall 2018 (Sep4-Dec4) Student ID Information Last name: First name: Student ID #: CS.Dal.Ca userid: Course ID: CSCI 2132 Course Title: Instructor:
Faculty of Computer Science Page 1 of 21 Final Exam Term: Fall 2018 (Sep4-Dec4) Student ID Information Last name: First name: Student ID #: CS.Dal.Ca userid: Course ID: CSCI 2132 Course Title: Instructor:
A Fast Review of C Essentials Part II
 A Fast Review of C Essentials Part II Structural Programming by Z. Cihan TAYSI Outline Macro processing Macro substitution Removing a macro definition Macros vs. functions Built-in macros Conditional compilation
A Fast Review of C Essentials Part II Structural Programming by Z. Cihan TAYSI Outline Macro processing Macro substitution Removing a macro definition Macros vs. functions Built-in macros Conditional compilation
2 Compiling a C program
 2 Compiling a C program This chapter describes how to compile C programs using gcc. Programs can be compiled from a single source file or from multiple source files, and may use system libraries and header
2 Compiling a C program This chapter describes how to compile C programs using gcc. Programs can be compiled from a single source file or from multiple source files, and may use system libraries and header
ARRAYS(II Unit Part II)
 ARRAYS(II Unit Part II) Array: An array is a collection of two or more adjacent cells of similar type. Each cell in an array is called as array element. Each array should be identified with a meaningful
ARRAYS(II Unit Part II) Array: An array is a collection of two or more adjacent cells of similar type. Each cell in an array is called as array element. Each array should be identified with a meaningful
Week 5 Lecture 3. Compiler Errors
 Lecture 3 Compiler Errors Agile Development Backlog of stories defines projects Backlog contains all of the requirements currently known Stories define features of the project Three elements: feature user,
Lecture 3 Compiler Errors Agile Development Backlog of stories defines projects Backlog contains all of the requirements currently known Stories define features of the project Three elements: feature user,
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 5/9/14 Sample Solution
 Question 1. (20 points) C programming. Implement the C library function strncpy. The specification of srncpy is as follows: Copy characters (bytes) from src to dst until either a '\0' character is found
Question 1. (20 points) C programming. Implement the C library function strncpy. The specification of srncpy is as follows: Copy characters (bytes) from src to dst until either a '\0' character is found
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Fall Programming Assignment 1 (updated 9/16/2017)
 UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Fall 2017 Programming Assignment 1 (updated 9/16/2017) Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Fall 2017 Programming Assignment 1 (updated 9/16/2017) Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you
CSCI 2132 Final Exam Solutions
 Faculty of Computer Science 1 CSCI 2132 Final Exam Solutions Term: Fall 2018 (Sep4-Dec4) 1. (12 points) True-false questions. 2 points each. No justification necessary, but it may be helpful if the question
Faculty of Computer Science 1 CSCI 2132 Final Exam Solutions Term: Fall 2018 (Sep4-Dec4) 1. (12 points) True-false questions. 2 points each. No justification necessary, but it may be helpful if the question
CSE 333 Midterm Exam July 24, Name UW ID#
 Name UW ID# There are 6 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Name UW ID# There are 6 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
today cs3157-fall2002-sklar-lect05 1
 today homework #1 due on monday sep 23, 6am some miscellaneous topics: logical operators random numbers character handling functions FILE I/O strings arrays pointers cs3157-fall2002-sklar-lect05 1 logical
today homework #1 due on monday sep 23, 6am some miscellaneous topics: logical operators random numbers character handling functions FILE I/O strings arrays pointers cs3157-fall2002-sklar-lect05 1 logical
To declare an array in C, a programmer specifies the type of the elements and the number of elements required by an array as follows
 Unti 4: C Arrays Arrays a kind of data structure that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful
Unti 4: C Arrays Arrays a kind of data structure that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful
The Make Utility. Independent compilation. Large programs are difficult to maintain. Problem solved by breaking the program into separate files
 The Make Utility Independent compilation Large programs are difficult to maintain Problem solved by breaking the program into separate files Different functions placed in different files The main function
The Make Utility Independent compilation Large programs are difficult to maintain Problem solved by breaking the program into separate files Different functions placed in different files The main function
CSSE 332 Standard Library, Storage classes, and Make
 CSSE 332 Standard Library, Storage classes, and Make 1 Provides a simple and efficient buffered I/O interface from man stdio Prototypes standard I/O functions (Mostly) system-independent (e.g.
CSSE 332 Standard Library, Storage classes, and Make 1 Provides a simple and efficient buffered I/O interface from man stdio Prototypes standard I/O functions (Mostly) system-independent (e.g.
The Make Utility. Independent compilation. Large programs are difficult to maintain. Problem solved by breaking the program into separate files
 The Make Utility Independent compilation Large programs are difficult to maintain Problem solved by breaking the program into separate files Different functions placed in different files The main function
The Make Utility Independent compilation Large programs are difficult to maintain Problem solved by breaking the program into separate files Different functions placed in different files The main function
MIDTERM EXAM. CS 217 October 28, Name: Precept: Honor Code: Score: Problem Score Max
 MIDTERM EXAM CS 217 October 28, 1999 Name: Precept: Honor Code: Score: Problem Score Max 1 15 2 5 3 10 4 15 5 5 6 10 7 10 Total 70 1 1. Number Systems (a) Translate the following decimal numbers to binary,
MIDTERM EXAM CS 217 October 28, 1999 Name: Precept: Honor Code: Score: Problem Score Max 1 15 2 5 3 10 4 15 5 5 6 10 7 10 Total 70 1 1. Number Systems (a) Translate the following decimal numbers to binary,
Personal SE. Functions, Arrays, Strings & Command Line Arguments
 Personal SE Functions, Arrays, Strings & Command Line Arguments Functions in C Syntax like Java methods but w/o public, abstract, etc. As in Java, all arguments (well, most arguments) are passed by value.
Personal SE Functions, Arrays, Strings & Command Line Arguments Functions in C Syntax like Java methods but w/o public, abstract, etc. As in Java, all arguments (well, most arguments) are passed by value.
C introduction: part 1
 What is C? C is a compiled language that gives the programmer maximum control and efficiency 1. 1 https://computer.howstuffworks.com/c1.htm 2 / 26 3 / 26 Outline Basic file structure Main function Compilation
What is C? C is a compiled language that gives the programmer maximum control and efficiency 1. 1 https://computer.howstuffworks.com/c1.htm 2 / 26 3 / 26 Outline Basic file structure Main function Compilation
Lab 5 Pointers and Arrays
 Lab 5 Pointers and Arrays The purpose of this lab is to practice using pointers to manipulate the data in arrays in this case, in arrays of characters. We will be building functions that add entries to,
Lab 5 Pointers and Arrays The purpose of this lab is to practice using pointers to manipulate the data in arrays in this case, in arrays of characters. We will be building functions that add entries to,
CSI 402 Spring 2014 Programming Assignment I 1 / 15
 CSI 402 Spring 2014 Programming Assignment I 1 / 15 Administrative Information Deadline: 11 PM, Friday, Feb. 14, 2014. Cutoff: 11 PM, Sunday, Feb. 16, 2014. The program must have three or more C source
CSI 402 Spring 2014 Programming Assignment I 1 / 15 Administrative Information Deadline: 11 PM, Friday, Feb. 14, 2014. Cutoff: 11 PM, Sunday, Feb. 16, 2014. The program must have three or more C source
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 7/27/15 Sample Solution
 Question 1. (24 points) C programming. In this problem we want to implement a set of strings in C. A set is represented as a linked list of strings with no duplicate values. The nodes in the list are defined
Question 1. (24 points) C programming. In this problem we want to implement a set of strings in C. A set is represented as a linked list of strings with no duplicate values. The nodes in the list are defined
CSC209H1S Day Midterm Solutions Winter 2010
 Duration: Aids Allowed: 50 minutes 1-8.5x11 sheet Student Number: Last Name: SOLUTION First Name: Instructor: Karen Reid Do not turn this page until you have received the signal to start. (In the meantime,
Duration: Aids Allowed: 50 minutes 1-8.5x11 sheet Student Number: Last Name: SOLUTION First Name: Instructor: Karen Reid Do not turn this page until you have received the signal to start. (In the meantime,
CS240: Programming in C. Lecture 2: Overview
 CS240: Programming in C Lecture 2: Overview 1 Programming Model How does C view the world? Stack Memory code Globals 2 Programming Model Execution mediated via a stack function calls and returns local
CS240: Programming in C Lecture 2: Overview 1 Programming Model How does C view the world? Stack Memory code Globals 2 Programming Model Execution mediated via a stack function calls and returns local
The C standard library
 C introduction The C standard library The C standard library 1 / 12 Contents Do not reinvent the wheel Useful headers Man page The C standard library 2 / 12 The Hitchhiker s Guide to the standard library
C introduction The C standard library The C standard library 1 / 12 Contents Do not reinvent the wheel Useful headers Man page The C standard library 2 / 12 The Hitchhiker s Guide to the standard library
Programming in C. Pointers and Arrays
 Programming in C Pointers and Arrays NEXT SET OF SLIDES FROM DENNIS FREY S FALL 2011 CMSC313 http://www.csee.umbc.edu/courses/undergraduate/313/fall11/" Pointers and Arrays In C, there is a strong relationship
Programming in C Pointers and Arrays NEXT SET OF SLIDES FROM DENNIS FREY S FALL 2011 CMSC313 http://www.csee.umbc.edu/courses/undergraduate/313/fall11/" Pointers and Arrays In C, there is a strong relationship
BIL 104E Introduction to Scientific and Engineering Computing. Lecture 14
 BIL 104E Introduction to Scientific and Engineering Computing Lecture 14 Because each C program starts at its main() function, information is usually passed to the main() function via command-line arguments.
BIL 104E Introduction to Scientific and Engineering Computing Lecture 14 Because each C program starts at its main() function, information is usually passed to the main() function via command-line arguments.
CSE 333 Lecture 6 - data structures
 CSE 333 Lecture 6 - data structures Hal Perkins Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia Exercises: - ex5 is out: clean up the code from section yesterday, split
CSE 333 Lecture 6 - data structures Hal Perkins Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia Exercises: - ex5 is out: clean up the code from section yesterday, split
Computer Science 2500 Computer Organization Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring Topic Notes: C and Unix Overview
 Computer Science 2500 Computer Organization Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring 2009 Topic Notes: C and Unix Overview This course is about computer organization, but since most of our programming is
Computer Science 2500 Computer Organization Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring 2009 Topic Notes: C and Unix Overview This course is about computer organization, but since most of our programming is
CSCI 2132 Final Exam Solutions
 Faculty of Computer Science 1 CSCI 2132 Final Exam Solutions Term: Fall 2018 (Sep4-Dec4) 1. (12 points) True-false questions. 2 points each. No justification necessary, but it may be helpful if the question
Faculty of Computer Science 1 CSCI 2132 Final Exam Solutions Term: Fall 2018 (Sep4-Dec4) 1. (12 points) True-false questions. 2 points each. No justification necessary, but it may be helpful if the question
CSI 402 Lecture 1 (Programs in Multiple Files and make) 1 1 / 20
 CSI 402 Lecture 1 (Programs in Multiple Files and make) 1 1 / 20 Program in a Single File prog.c #include int main(void) { int max(int, int); float average(int, int); int i = 17, j = -20; printf("%d\n",
CSI 402 Lecture 1 (Programs in Multiple Files and make) 1 1 / 20 Program in a Single File prog.c #include int main(void) { int max(int, int); float average(int, int); int i = 17, j = -20; printf("%d\n",
Lecture 12 CSE July Today we ll cover the things that you still don t know that you need to know in order to do the assignment.
 Lecture 12 CSE 110 20 July 1992 Today we ll cover the things that you still don t know that you need to know in order to do the assignment. 1 The NULL Pointer For each pointer type, there is one special
Lecture 12 CSE 110 20 July 1992 Today we ll cover the things that you still don t know that you need to know in order to do the assignment. 1 The NULL Pointer For each pointer type, there is one special
THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO. COMPUTER SCIENCE 211a FINAL EXAMINATION 17 DECEMBER HOURS
 Computer Science 211a Final Examination 17 December 2002 Page 1 of 17 THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO LONDON CANADA COMPUTER SCIENCE 211a FINAL EXAMINATION 17 DECEMBER 2002 3 HOURS NAME: STUDENT NUMBER:
Computer Science 211a Final Examination 17 December 2002 Page 1 of 17 THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO LONDON CANADA COMPUTER SCIENCE 211a FINAL EXAMINATION 17 DECEMBER 2002 3 HOURS NAME: STUDENT NUMBER:
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 7/29/13
 Name There are 5 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
Name There are 5 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
CIS 190: C/C++ Programming. Lecture 2 Pointers and More
 CIS 190: C/C++ Programming Lecture 2 Pointers and More Separate Compilation to prevent the file containing main() from getting too crowded and long function prototypes in their own file (functions.h) function
CIS 190: C/C++ Programming Lecture 2 Pointers and More Separate Compilation to prevent the file containing main() from getting too crowded and long function prototypes in their own file (functions.h) function
COL100 Lab 2. I semester Week 2, Open the web-browser and visit the page and visit the COL100 course page.
 COL100 Lab 2 I semester 2017-18 Week 2, 2017 Objective More familiarisation with Linux and its standard commands Part 1 1. Login to your system and open a terminal window. 2. Open the web-browser and visit
COL100 Lab 2 I semester 2017-18 Week 2, 2017 Objective More familiarisation with Linux and its standard commands Part 1 1. Login to your system and open a terminal window. 2. Open the web-browser and visit
Programs. Function main. C Refresher. CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems
 Programs CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems C Program Structure Libraries and header files Compiling and building programs Executing and debugging Instructor: Abhishek Chandra Assume familiarity
Programs CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems C Program Structure Libraries and header files Compiling and building programs Executing and debugging Instructor: Abhishek Chandra Assume familiarity
JTSK Programming in C II C-Lab II. Lecture 3 & 4
 JTSK-320112 Programming in C II C-Lab II Lecture 3 & 4 Xu (Owen) He Spring 2018 Slides modified from Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Planned Syllabus The C Preprocessor Bit Operations Pointers and Arrays (Dynamically
JTSK-320112 Programming in C II C-Lab II Lecture 3 & 4 Xu (Owen) He Spring 2018 Slides modified from Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Planned Syllabus The C Preprocessor Bit Operations Pointers and Arrays (Dynamically
CS2351 Data Structures. Lecture 7: A Brief Review of Pointers in C
 CS2351 Data Structures Lecture 7: A Brief Review of Pointers in C 1 About this lecture Pointer is a useful object that allows us to access different places in our memory We will review the basic use of
CS2351 Data Structures Lecture 7: A Brief Review of Pointers in C 1 About this lecture Pointer is a useful object that allows us to access different places in our memory We will review the basic use of
Executables and Linking. CS449 Spring 2016
 Executables and Linking CS449 Spring 2016 Remember External Linkage Scope? #include int global = 0; void foo(); int main() { foo(); printf( global=%d\n, global); return 0; } extern int
Executables and Linking CS449 Spring 2016 Remember External Linkage Scope? #include int global = 0; void foo(); int main() { foo(); printf( global=%d\n, global); return 0; } extern int
Characters in C consist of any printable or nonprintable character in the computer s character set including lowercase letters, uppercase letters,
 Strings Characters in C consist of any printable or nonprintable character in the computer s character set including lowercase letters, uppercase letters, decimal digits, special characters and escape
Strings Characters in C consist of any printable or nonprintable character in the computer s character set including lowercase letters, uppercase letters, decimal digits, special characters and escape
Lecture 10: Potpourri: Enum / struct / union Advanced Unix #include function pointers
 ....... \ \ \ / / / / \ \ \ \ / \ / \ \ \ V /,----' / ^ \ \.--..--. / ^ \ `--- ----` / ^ \. ` > < / /_\ \. ` / /_\ \ / /_\ \ `--' \ /. \ `----. / \ \ '--' '--' / \ / \ \ / \ / / \ \ (_ ) \ (_ ) / / \ \
....... \ \ \ / / / / \ \ \ \ / \ / \ \ \ V /,----' / ^ \ \.--..--. / ^ \ `--- ----` / ^ \. ` > < / /_\ \. ` / /_\ \ / /_\ \ `--' \ /. \ `----. / \ \ '--' '--' / \ / \ \ / \ / / \ \ (_ ) \ (_ ) / / \ \
gcc hello.c a.out Hello, world gcc -o hello hello.c hello Hello, world
 alun@debian:~$ gcc hello.c alun@debian:~$ a.out Hello, world alun@debian:~$ gcc -o hello hello.c alun@debian:~$ hello Hello, world alun@debian:~$ 1 A Quick guide to C for Networks and Operating Systems
alun@debian:~$ gcc hello.c alun@debian:~$ a.out Hello, world alun@debian:~$ gcc -o hello hello.c alun@debian:~$ hello Hello, world alun@debian:~$ 1 A Quick guide to C for Networks and Operating Systems
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 2/14/14
 Name There are 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
Name There are 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
Floating-point lab deadline moved until Wednesday Today: characters, strings, scanf Characters, strings, scanf questions clicker questions
 Announcements Thursday Extras: CS Commons on Thursdays @ 4:00 pm but none next week No office hours next week Monday or Tuesday Reflections: when to use if/switch statements for/while statements Floating-point
Announcements Thursday Extras: CS Commons on Thursdays @ 4:00 pm but none next week No office hours next week Monday or Tuesday Reflections: when to use if/switch statements for/while statements Floating-point
CGS 3460 Summer 07 Midterm Exam
 Short Answer 3 Points Each 1. What would the unix command gcc somefile.c -o someotherfile.exe do? 2. Name two basic data types in C. 3. A pointer data type holds what piece of information? 4. This key
Short Answer 3 Points Each 1. What would the unix command gcc somefile.c -o someotherfile.exe do? 2. Name two basic data types in C. 3. A pointer data type holds what piece of information? 4. This key
ONE DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS
 LECTURE 14 ONE DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS Array : An array is a fixed sized sequenced collection of related data items of same data type. In its simplest form an array can be used to represent a list of numbers
LECTURE 14 ONE DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS Array : An array is a fixed sized sequenced collection of related data items of same data type. In its simplest form an array can be used to represent a list of numbers
Programming Language B
 Programming Language B Takako Nemoto (JAIST) 16 January Takako Nemoto (JAIST) 16 January 1 / 15 Strings and pointers #include //11-1.c char str[] = "ABC"; char *ptr = "123"; printf("str = \"%s\"\n",
Programming Language B Takako Nemoto (JAIST) 16 January Takako Nemoto (JAIST) 16 January 1 / 15 Strings and pointers #include //11-1.c char str[] = "ABC"; char *ptr = "123"; printf("str = \"%s\"\n",
Computers Programming Course 10. Iulian Năstac
 Computers Programming Course 10 Iulian Năstac Recap from previous course 5. Values returned by a function A return statement causes execution to leave the current subroutine and resume at the point in
Computers Programming Course 10 Iulian Năstac Recap from previous course 5. Values returned by a function A return statement causes execution to leave the current subroutine and resume at the point in
Operating Systems, Unix Files and Commands SEEM
 Operating Systems, Unix Files and Commands SEEM 3460 1 Major Components of Operating Systems (OS) Process management Resource management CPU Memory Device File system Bootstrapping SEEM 3460 2 Programs
Operating Systems, Unix Files and Commands SEEM 3460 1 Major Components of Operating Systems (OS) Process management Resource management CPU Memory Device File system Bootstrapping SEEM 3460 2 Programs
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Summer 2016 Programming Assignment 1 Introduction The purpose of this
 UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Summer 2016 Programming Assignment 1 Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you some experience
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Summer 2016 Programming Assignment 1 Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you some experience
make and makefile CS 211
 make and makefile CS 211 Steps of a C Program Compilation Step 1 Run the Preprocessor Deals with #include, #define, #ifndef, Step 2 Compile C code into Machine Code Step 2a Lexical Analysis Step 2b Parsing
make and makefile CS 211 Steps of a C Program Compilation Step 1 Run the Preprocessor Deals with #include, #define, #ifndef, Step 2 Compile C code into Machine Code Step 2a Lexical Analysis Step 2b Parsing
Scheme G. Sample Test Paper-I. Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Course Code : CO/CD/CM/CW/IF Semester : Second Subject Tile : Programming in C
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 Hrs. Q1. Attempt any THREE 09 Marks a) State four relational operators with meaning. b) State the use of break statement. c) What is constant? Give any two examples.
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 Hrs. Q1. Attempt any THREE 09 Marks a) State four relational operators with meaning. b) State the use of break statement. c) What is constant? Give any two examples.
Midterm Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 18, Duration of examination: 75 minutes STUDENT NAME: STUDENT ID NUMBER:
 Page 1 of 8 School of Computer Science 60-141-01 Introduction to Algorithms and Programming Winter 2015 Midterm Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 18, 2015 ANSWERS Duration of examination: 75 minutes STUDENT
Page 1 of 8 School of Computer Science 60-141-01 Introduction to Algorithms and Programming Winter 2015 Midterm Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 18, 2015 ANSWERS Duration of examination: 75 minutes STUDENT
CSE 303 Final Exam. March 16, 2009
 CSE 303 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name The exam is closed book, except that you may have a single page of hand written notes for reference, plus the single page of notes from the midterm. If you have questions
CSE 303 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name The exam is closed book, except that you may have a single page of hand written notes for reference, plus the single page of notes from the midterm. If you have questions
PROGRAMMAZIONE I A.A. 2017/2018
 PROGRAMMAZIONE I A.A. 2017/2018 FUNCTIONS INTRODUCTION AND MAIN All the instructions of a C program are contained in functions. üc is a procedural language üeach function performs a certain task A special
PROGRAMMAZIONE I A.A. 2017/2018 FUNCTIONS INTRODUCTION AND MAIN All the instructions of a C program are contained in functions. üc is a procedural language üeach function performs a certain task A special
CSE 374 Final Exam 3/15/17. Name UW ID#
 Name UW ID# There are 10 questions worth a total of 110 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Name UW ID# There are 10 questions worth a total of 110 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Oregon State University School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. CS 261 Recitation 1. Spring 2011
 Oregon State University School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science CS 261 Recitation 1 Spring 2011 Outline Using Secure Shell Clients GCC Some Examples Intro to C * * Windows File transfer client:
Oregon State University School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science CS 261 Recitation 1 Spring 2011 Outline Using Secure Shell Clients GCC Some Examples Intro to C * * Windows File transfer client:
Creating a Shell or Command Interperter Program CSCI411 Lab
 Creating a Shell or Command Interperter Program CSCI411 Lab Adapted from Linux Kernel Projects by Gary Nutt and Operating Systems by Tannenbaum Exercise Goal: You will learn how to write a LINUX shell
Creating a Shell or Command Interperter Program CSCI411 Lab Adapted from Linux Kernel Projects by Gary Nutt and Operating Systems by Tannenbaum Exercise Goal: You will learn how to write a LINUX shell
CSE 333 Midterm Exam Sample Solution 7/29/13
 Question 1. (44 points) C hacking a question of several parts. The next several pages are questions about a linked list of 2-D points. Each point is represented by a Point struct containing the point s
Question 1. (44 points) C hacking a question of several parts. The next several pages are questions about a linked list of 2-D points. Each point is represented by a Point struct containing the point s
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATING SYSTEMS Tutorial-1&2: C Review CPSC 457, Spring 2015 May 20-21, 2015 Department of Computer Science, University of Calgary Connecting to your VM Open a terminal (in your linux machine)
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATING SYSTEMS Tutorial-1&2: C Review CPSC 457, Spring 2015 May 20-21, 2015 Department of Computer Science, University of Calgary Connecting to your VM Open a terminal (in your linux machine)
20 Dynamic allocation of memory: malloc and calloc
 20 Dynamic allocation of memory: malloc and calloc As noted in the last lecture, several new functions will be used in this section. strlen (string.h), the length of a string. fgets(buffer, max length,
20 Dynamic allocation of memory: malloc and calloc As noted in the last lecture, several new functions will be used in this section. strlen (string.h), the length of a string. fgets(buffer, max length,
SYSC 2006 C Winter String Processing in C. D.L. Bailey, Systems and Computer Engineering, Carleton University
 SYSC 2006 C Winter 2012 String Processing in C D.L. Bailey, Systems and Computer Engineering, Carleton University References Hanly & Koffman, Chapter 9 Some examples adapted from code in The C Programming
SYSC 2006 C Winter 2012 String Processing in C D.L. Bailey, Systems and Computer Engineering, Carleton University References Hanly & Koffman, Chapter 9 Some examples adapted from code in The C Programming
Maemo Diablo GNU Make and makefiles Training Material
 Maemo Diablo GNU Make and makefiles Training Material February 9, 2009 Contents 1 GNU Make and makefiles 2 1.1 What is GNU Make?......................... 2 1.2 How does make work?........................
Maemo Diablo GNU Make and makefiles Training Material February 9, 2009 Contents 1 GNU Make and makefiles 2 1.1 What is GNU Make?......................... 2 1.2 How does make work?........................
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 7/22/12
 Name There are 6 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
Name There are 6 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
Singly linked lists in C.
 Singly linked lists in C http://www.cprogramming.com/tutorial/c/lesson15.html By Alex Allain Linked lists are a way to store data with structures so that the programmer can automatically create a new place
Singly linked lists in C http://www.cprogramming.com/tutorial/c/lesson15.html By Alex Allain Linked lists are a way to store data with structures so that the programmer can automatically create a new place
CSE 374 Midterm Exam 2/6/17 Sample Solution. Question 1. (12 points, 4 each) Suppose we have the following files and directories:
 Question 1. (12 points, 4 each) Suppose we have the following files and directories: $ pwd /home/user $ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 user uw 10 Feb 4 15:49 combine.sh drwxr-xr-x 2 user uw 2 Feb 4 15:51 hws -rw-r--r--
Question 1. (12 points, 4 each) Suppose we have the following files and directories: $ pwd /home/user $ ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 user uw 10 Feb 4 15:49 combine.sh drwxr-xr-x 2 user uw 2 Feb 4 15:51 hws -rw-r--r--
CS113: Lecture 4. Topics: Functions. Function Activation Records
 CS113: Lecture 4 Topics: Functions Function Activation Records 1 Why functions? Functions add no expressive power to the C language in a formal sense. Why have them? Breaking tasks into smaller ones make
CS113: Lecture 4 Topics: Functions Function Activation Records 1 Why functions? Functions add no expressive power to the C language in a formal sense. Why have them? Breaking tasks into smaller ones make
Programming in C week 1 meeting Tiina Niklander
 Programming in C week 1 meeting 2.9.2015 Tiina Niklander Faculty of Science Department of Computer Science 3.9.2015 1 Course structure Based on C programming course in Aalto, but with some exercises created
Programming in C week 1 meeting 2.9.2015 Tiina Niklander Faculty of Science Department of Computer Science 3.9.2015 1 Course structure Based on C programming course in Aalto, but with some exercises created
Approximately a Final Exam CPSC 206
 Approximately a Final Exam CPSC 206 Sometime in History based on Kelley & Pohl Last name, First Name Last 4 digits of ID Write your section number: All parts of this exam are required unless plainly and
Approximately a Final Exam CPSC 206 Sometime in History based on Kelley & Pohl Last name, First Name Last 4 digits of ID Write your section number: All parts of this exam are required unless plainly and
CSE 374 Final Exam Sample Solution 6/10/10
 Question 1. (8 points) (testing) Suppose we are testing a list data structure implementation similar to a Java ArrayList. The list uses a fixed-size array as the underlying data structure to store the
Question 1. (8 points) (testing) Suppose we are testing a list data structure implementation similar to a Java ArrayList. The list uses a fixed-size array as the underlying data structure to store the
CSE374 Winter 2016, Midterm Examination February 8, 2016 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings.
 CSE374 Winter 2016, Midterm Examination February 8, 2016 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed-calculator, and closed-electronics. Please
CSE374 Winter 2016, Midterm Examination February 8, 2016 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed-calculator, and closed-electronics. Please
Approximately a Test II CPSC 206
 Approximately a Test II CPSC 206 Sometime in history based on Kelly and Pohl Last name, First Name Last 5 digits of ID Write your section number(s): All parts of this exam are required unless plainly and
Approximately a Test II CPSC 206 Sometime in history based on Kelly and Pohl Last name, First Name Last 5 digits of ID Write your section number(s): All parts of this exam are required unless plainly and
CS240: Programming in C
 CS240: Programming in C Lecture 2: Hello World! Cristina Nita-Rotaru Lecture 2/ Fall 2013 1 Introducing C High-level programming language Developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Labs
CS240: Programming in C Lecture 2: Hello World! Cristina Nita-Rotaru Lecture 2/ Fall 2013 1 Introducing C High-level programming language Developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Labs
The output will be: marks all or nothing. 1 #include <stdio.h> 2 main() { 3 int i; int j; 4 int *p; int *q; 6 p = &i; 7 q = &j; 8 i = 1;
 p. 2 of 9 Q1. [5 marks] The following program compiles and runs with no problems. Indicate what the output of the program is going to be (no explanation necessary). 1 #include 2 main() { 3 int
p. 2 of 9 Q1. [5 marks] The following program compiles and runs with no problems. Indicate what the output of the program is going to be (no explanation necessary). 1 #include 2 main() { 3 int
Arrays and Pointers in C. Alan L. Cox
 Arrays and Pointers in C Alan L. Cox alc@rice.edu Objectives Be able to use arrays, pointers, and strings in C programs Be able to explain the representation of these data types at the machine level, including
Arrays and Pointers in C Alan L. Cox alc@rice.edu Objectives Be able to use arrays, pointers, and strings in C programs Be able to explain the representation of these data types at the machine level, including
Embedded Software TI2726 B. 3. C tools. Koen Langendoen. Embedded Software Group
 Embedded Software 3. C tools TI2726 B Koen Langendoen Embedded Software Group C development cycle 1. [Think] 2. Edit 3. Compile 4. Test 5. Debug 6. Tune UNIX toolbox 2. vi, emacs, gedit 3. gcc, make 4.
Embedded Software 3. C tools TI2726 B Koen Langendoen Embedded Software Group C development cycle 1. [Think] 2. Edit 3. Compile 4. Test 5. Debug 6. Tune UNIX toolbox 2. vi, emacs, gedit 3. gcc, make 4.
CSE2301. Functions. Functions and Compiler Directives
 Warning: These notes are not complete, it is a Skelton that will be modified/add-to in the class. If you want to us them for studying, either attend the class or get the completed notes from someone who
Warning: These notes are not complete, it is a Skelton that will be modified/add-to in the class. If you want to us them for studying, either attend the class or get the completed notes from someone who
Recitation 2/18/2012
 15-213 Recitation 2/18/2012 Announcements Buflab due tomorrow Cachelab out tomorrow Any questions? Outline Cachelab preview Useful C functions for cachelab Cachelab Part 1: you have to create a cache simulator
15-213 Recitation 2/18/2012 Announcements Buflab due tomorrow Cachelab out tomorrow Any questions? Outline Cachelab preview Useful C functions for cachelab Cachelab Part 1: you have to create a cache simulator
CSE 374 Final Exam 3/15/17 Sample Solution. Question 1. (8 points) Suppose we have the following two statements in a C program:
 Question 1. (8 points) Suppose we have the following two statements in a C program: int *x = malloc(sizeof(int)); int *y = malloc(sizeof(int)); For each of the following expressions, write true if the
Question 1. (8 points) Suppose we have the following two statements in a C program: int *x = malloc(sizeof(int)); int *y = malloc(sizeof(int)); For each of the following expressions, write true if the
BİL200 TUTORIAL-EXERCISES Objective:
 Objective: The purpose of this tutorial is learning the usage of -preprocessors -header files -printf(), scanf(), gets() functions -logic operators and conditional cases A preprocessor is a program that
Objective: The purpose of this tutorial is learning the usage of -preprocessors -header files -printf(), scanf(), gets() functions -logic operators and conditional cases A preprocessor is a program that
Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017*
 600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
Problem 2 Add the two 2 s complement signed 8-bit values given below, and express your answer in decimal.
 Problem 1 Recall the definition of root in project 1. (The declaration of struct entrynode appears below.) struct entrynode * root; Give the type of each of the following expressions. The answer may be
Problem 1 Recall the definition of root in project 1. (The declaration of struct entrynode appears below.) struct entrynode * root; Give the type of each of the following expressions. The answer may be
Workspace for '3-ctips' Page 1 (row 1, column 1)
 Workspace for '3-ctips' Page 1 (row 1, column 1) ECEN 449 Microprocessor System Design Some tips to good programming and Makefiles 1 Objectives of this Lecture Unit Some tips to good programming 2 Variable
Workspace for '3-ctips' Page 1 (row 1, column 1) ECEN 449 Microprocessor System Design Some tips to good programming and Makefiles 1 Objectives of this Lecture Unit Some tips to good programming 2 Variable
Chapter 12: Pointers and Arrays. Chapter 12. Pointers and Arrays. Copyright 2008 W. W. Norton & Company. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 12 Pointers and Arrays 1 Introduction C allows us to perform arithmetic addition and subtraction on pointers to array elements. This leads to an alternative way of processing arrays in which pointers
Chapter 12 Pointers and Arrays 1 Introduction C allows us to perform arithmetic addition and subtraction on pointers to array elements. This leads to an alternative way of processing arrays in which pointers
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-206A Introduction to Software Systems
 McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-206A Introduction to Software Systems Final Exam Wednesday, December 8, 2004 at 9:00 in GYM Instructor: Joseph Vybihal Associate Examiner: Prof. Ratzer
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-206A Introduction to Software Systems Final Exam Wednesday, December 8, 2004 at 9:00 in GYM Instructor: Joseph Vybihal Associate Examiner: Prof. Ratzer
Reminder of midterm 1. Next Thursday, Feb. 14, in class Look at Piazza announcement for rules and preparations
 Reminder of midterm 1 Next Thursday, Feb. 14, in class Look at Piazza announcement for rules and preparations A New Example to see effect of E++ (better than the one in previous lecture) Purpose of showing
Reminder of midterm 1 Next Thursday, Feb. 14, in class Look at Piazza announcement for rules and preparations A New Example to see effect of E++ (better than the one in previous lecture) Purpose of showing
Hello, World! in C. Johann Myrkraverk Oskarsson October 23, The Quintessential Example Program 1. I Printing Text 2. II The Main Function 3
 Hello, World! in C Johann Myrkraverk Oskarsson October 23, 2018 Contents 1 The Quintessential Example Program 1 I Printing Text 2 II The Main Function 3 III The Header Files 4 IV Compiling and Running
Hello, World! in C Johann Myrkraverk Oskarsson October 23, 2018 Contents 1 The Quintessential Example Program 1 I Printing Text 2 II The Main Function 3 III The Header Files 4 IV Compiling and Running
Announcements. Strings and Pointers. Strings. Initializing Strings. Character I/O. Lab 4. Quiz. July 18, Special character arrays
 Strings and Pointers Announcements Lab 4 Why are you taking this course? Lab 5 #, 8: Reading in data from file using fscanf Quiz Quiz Strings Special character arrays End in null character, \ char hi[6];
Strings and Pointers Announcements Lab 4 Why are you taking this course? Lab 5 #, 8: Reading in data from file using fscanf Quiz Quiz Strings Special character arrays End in null character, \ char hi[6];
CSE 333 Midterm Exam 5/10/13
 Name There are 5 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
Name There are 5 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed
CSE 333 Midterm Exam July 24, 2017 Sample Solution
 Sample Solution Question 1. (14 points) Making things. Suppose we have the following C header and implementation files, showing the various #include and #if directives in each one: widget.h #ifndef _WIDGET_H_
Sample Solution Question 1. (14 points) Making things. Suppose we have the following C header and implementation files, showing the various #include and #if directives in each one: widget.h #ifndef _WIDGET_H_
High Performance Computing Prof. Matthew Jacob Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 High Performance Computing Prof. Matthew Jacob Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No # 09 Lecture No # 40 This is lecture forty of the course on
High Performance Computing Prof. Matthew Jacob Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No # 09 Lecture No # 40 This is lecture forty of the course on
CSE 333 Lecture 7 - final C details
 CSE 333 Lecture 7 - final C details Steve Gribble Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Today s topics: - a few final C details header guards and other preprocessor tricks
CSE 333 Lecture 7 - final C details Steve Gribble Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Today s topics: - a few final C details header guards and other preprocessor tricks
