Software Tools and Systems Programming: Assignment 3
|
|
|
- Miranda Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Software Tools and Systems Programming: Assignment 3 Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario CS211 b Winter 2011 Posted: Friday 11, 2011 Due: Friday, March 4, 2011 Problems 1 to 6 deal with shell commands. You need to collect your answers in one txt file and submit both the electronic and printed version of this txt file. Using the script command to capture the screen is *not* required for this assignment. Problems 7 and 8 involve C programming. You need to submit both the electronic and printed version of the.c file for each of them. 1 Problem 1 Study the manual page of the Unix utility tee. Then, try the following Unix command ls -lrt tee > newfile and explain why does this command produce nothing on the screen? 2 Problem 2 Create a text file called f1 with at least 30 lines. This file may contain any text: acprogram, amakefile, etc. Giveaone-lineUnixcommandforsorting and printing on the screen lines 10 to 15 from file f1. 1
2 3 Problem 3 We assume that the bash shell interpreter is used. We assume also that the current working directory contains a file called f1 but does not contain any files (or links, or subdirectories) called f2. Do the following commands produce the same results? ls f1 f2 2>&1 >log ls f1 f2 >log 2>&1 Explain their similarities and differences, if any. 4 Problem 4 We assume that the bash shell interpreter is used. We assume also that the current directory contains a text file called f consisting of the following single line: ls -l What does the file f contain after executing the following command? Explain. bash < f > f 5 Problem 5 For each of the patterns below, give a Unix regular expression (to be used with the grep command, for instance) that will match any line satisfying this pattern a line consisting of a single character, a line containing a word with a length of 17 or 18 characters, a line where all vowels (if any) are upper-case characters, a line containing a word starting and ending with the same character, a line starting with a capital letter S, followed by a lower-case letter, followed by a vowel, followed by three occurrences of the second letter. 2
3 6 Problem 6 Describe in plain words what will be matched by each of the following Unix regular expressions: 1. [] 2. [0] 3. [0-9] 4. [^0-9] 5. [0-9-] 6. [^-0-9] 7. []0-9] 8. [0-9]] 9. [0-9-z] 10. [0-9\-a\]] 7 Problem Preliminaries A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, called the left child and the right child. Binary trees are a very popular data-structure in computer science. We shall see in this exercise how we can encode it using C arrays. The formal recursive definition of a binary tree is as follows. A binary tree is either empty, or a node with two children, each of which is a binary tree. The following terminology is convenient: A node with no children is called a leaf and a node with children is called an internal node. 3
4 If a node A is a child of a node X then we say that X is the parent of A. In a non-empty binary tree, there is one and only one node with no parent; this node is called the root node of the tree. You will find examples and comments at the wiki page: R X Y A B E F M N U R X Y A B E F M N U Figure 1: A binary tree and its array encoding. A non-empty binary tree T with n nodes can be encoded in an array A. Indeed, one can always label the nodes with the integers 1,2,...,n such that: the root has label 1, if an internal node has label i then its left child (if any) has label 2i and its right child (if any) has label 2i+1. Using this observation, we can store the nodes of T in A as follows: the root of the tree is in A[1], and its left and right children are stored in A[2] and A[3] respectively, given the index i of an internal node, different from the root, the indices of its parent PARENT(i), left child LEFT(i), and right child RIGHT(i) can be computed simply by: 4
5 PARENT(i) = i/2 LEFT(i) = 2i RIGHT(i) = 2i+1 Consider the binary tree of the above figure: The root node R is stored in slot 1, its left child X is in slot 2, its right child Y is at slot 3, for X, its left child A is in slot 4 and its right child B is in slot 5, Questions Thepurposeofthisproblem istorealize asimple Cimplementation ofbinary trees encoded as arrays. This program will actually make use of the example in the above figure. To guide you toward this goal, we provide a template program hereafter. We ask you to use this template and fill in the missing code. In this template, we use the array binarytree[] to encode the binary tree in Figure 1. The first slot of binarytree[] is used to record the number of nodes in the tree. The rest of the slots keep the values contained in the nodes. You are asked to implement 4 functions: 1. printparentnode(int *bt, int node). For a given node index, this function will print the corresponding parent node. Your code should handle exceptional cases. If the given node is the root node, that is, if node is 1, then there is no parent. If the given node is not in the given tree, that is, if the given node index is too large or non-positive, then an error message should be printed. 2. printleftchildnode(int *bt, int node). For a given node index, this function will print its left child node. As above, your code should handle exceptional cases. Namely, when the given node has no left child, or the given node is not in the given tree, then an error message should be printed. 3. printrightchildnode(int *bt, int node). Similar to the above function, except that it deals with the right child node instead of the left child node 5
6 4. printnearestcommonancestor(int *bt, int node1, int node2). For two given nodes, this function returns their nearest common ancestor in the tree. See the sample output below. Remark. In the template code below, we also provide the prototype of an extra function getindex, which you could use for implementing the above four functions. The template code. #include <stdio.h> // INPUT: bt, a binary tree. // node, a node in the tree. // OUTPUT: the index of given value in the tree. int getindex(int *bt, int node){ //... // INPUT: bt, a binary tree. // node, a node in the tree. // OUPUT: print the parent node of node. void printparentnode (int *bt, int node){ //... // INPUT: bt, a binary tree // node, a node in the tree. // OUPUT: print the left child of node void printleftchildnode (int *bt, int node){ //... // INPUT: bt, a binary tree // node, a node in the tree. // OUPUT: print the right child of node void printrightchildnode (int *bt, int node){ 6
7 //... // INPUT: bt, a binary tree // node1, a node in the tree. // node2, a node in the tree. // OUPUT: print the nearest ancestor of node1 and node2. void printnearestcommonancestor(int *bt, int node1, int node2){ //... int main(){ /* binarytree is an array to encode a binary tree. The first element of this array is used to encode the number of nodes. */ int binarytree[11] = {10, 16, 14, 10, 8, 7, 9, 3, 2, 4, 1; printparentnode(binarytree, 16); printparentnode(binarytree, 3); printleftchildnode(binarytree, 7); printleftchildnode(binarytree, 9); printrightchildnode(binarytree, 7); printrightchildnode(binarytree, 10); printnearestcommonancestor(binarytree, 8, 1); printnearestcommonancestor(binarytree, 8, 9); return 0; 7
8 The sample output from above template. Node 16 is the root and has no parent. The parent node of 3 is 10. The left child node of 7 is 1. Node 9 has no children! Node 7 has no right child! The right child node of Node 10 is 3. The nearest common ancesor of Node 8 and Node 1 is Node 14. The nearest common ancesor of Node 8 and Node 9 is Node Problem Preliminaries In computer science, a graph consists of finitely many elements, called vertices and a sequence of pairs of these points, called edges. If these pairs have an orientation (or direction) then the graph is said directed. otherwise it is undirected. You will find examples and comments at the wiki page: Graphs can be represented in the form of matrices. In the following example, the undirected graph G has 5 vertices: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 4 undirected edges. For this example, we use a 5 by 5 matrix M to encode the graph. If there is an edge E between a pair of vertices i and j, the entry M[i][j] is set to be 1, otherwise, M[i][j] = 0. For instance, in Figure 2 there is an edge vertex 0 and 1, so both M[0][1] and M[1][0] are set to be 1. 8
9 Questions Figure 2: A graph and its encoding. We ask to use the following template and fill in the required code. printvetices(int N, int G[][N]). This function prints the vertices of a given graph G with N vertices. See sample output. printedges(int N, int G[][N]). This function prints the edges of a given graph G with N vertices. see sample output. isthereapath(int N, int G[][N], int v1, int v2). This function identifies if there is a path between two given vertices v1, v2, and print out the answer. The template code. #include <stdio.h> void printvetices(int N, int G[][N]){ void printedges(int N, int G[][N]){ 9
10 void isthereapath(int N, int G[][N], int v1, int v2){ #define N 5 int main(){ int Graph[N][N] = { {0,1,0,0,1, {1,0,0,0,1, {0,0,0,1,0, {0,0,1,0,0, {1,1,0,0,0 ; printvetices(n, Graph); printedges(n, Graph); isthereapath(n, Graph, 0, 1); isthereapath(n, Graph, 0, 3); return 0; The sample output from above template. The graph has vertices: Vertex 0 Vertex 1 Vertex 2 Vertex 3 Vertex 4 10
11 The graph has edges: [0, 1] [0, 4] [1, 0] [1, 4] [2, 3] [3, 2] [4, 0] [4, 1] Yes, there is a path between Vertex 0 and Vertex 1. No, there is no path between Vertex 0 and Vertex 3. 11
An undirected graph is a tree if and only of there is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices.
 Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Chapter 10: Trees. A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits.
 Chapter 10: Trees A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits. Properties: o There is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices. o No loops. o No multiple edges. Example
Chapter 10: Trees A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits. Properties: o There is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices. o No loops. o No multiple edges. Example
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Lecture 32. No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions?
 Lecture 32 No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions? Friday, April 1 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 32 1 Outline Introduction
Lecture 32 No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions? Friday, April 1 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 32 1 Outline Introduction
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26. Graphs. CS 441 Discrete mathematics for CS. Final exam
 CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26 Graphs Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Final exam Saturday, April 26, 2014 at 10:00-11:50am The same classroom as lectures The exam
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26 Graphs Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Final exam Saturday, April 26, 2014 at 10:00-11:50am The same classroom as lectures The exam
1 Tree Sort LECTURE 4. OHSU/OGI (Winter 2009) ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS
 OHSU/OGI (Winter 2009) CS532 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS LECTURE 4 1 Tree Sort Suppose a sequence of n items is given. We can sort it using TreeInsert and DeleteMin: TreeSort Initialize an empty
OHSU/OGI (Winter 2009) CS532 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ALGORITHMS LECTURE 4 1 Tree Sort Suppose a sequence of n items is given. We can sort it using TreeInsert and DeleteMin: TreeSort Initialize an empty
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
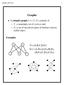 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Recursive definition of sets and structural induction
 CS2209A 2017 Applied Logic for Computer Science Lecture 21, 22 Recursive definition of sets and structural induction Instructor: Marc Moreno Maza 1 Tower of Hanoi game Rules of the game: Start with all
CS2209A 2017 Applied Logic for Computer Science Lecture 21, 22 Recursive definition of sets and structural induction Instructor: Marc Moreno Maza 1 Tower of Hanoi game Rules of the game: Start with all
Figure 1. A breadth-first traversal.
 4.3 Tree Traversals Stepping, or iterating, through the entries of a linearly ordered list has only two obvious orders: from front to back or from back to front. There is no obvious traversal of a general
4.3 Tree Traversals Stepping, or iterating, through the entries of a linearly ordered list has only two obvious orders: from front to back or from back to front. There is no obvious traversal of a general
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Module 8: Binary trees
 Module 8: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Module 8: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
CSC148 Week 6. Larry Zhang
 CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
Figure 4.1: The evolution of a rooted tree.
 106 CHAPTER 4. INDUCTION, RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 4.6 Rooted Trees 4.6.1 The idea of a rooted tree We talked about how a tree diagram helps us visualize merge sort or other divide and conquer algorithms.
106 CHAPTER 4. INDUCTION, RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 4.6 Rooted Trees 4.6.1 The idea of a rooted tree We talked about how a tree diagram helps us visualize merge sort or other divide and conquer algorithms.
Outline. Preliminaries. Binary Trees Binary Search Trees. What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications
 Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
Fibonacci Heaps Priority Queues. John Ross Wallrabenstein
 Fibonacci Heaps Priority Queues John Ross Wallrabenstein Updates Project 4 Grades Released Project 5 Questions? Review *This usually refers to the size of the structure Review What is a static data structure?
Fibonacci Heaps Priority Queues John Ross Wallrabenstein Updates Project 4 Grades Released Project 5 Questions? Review *This usually refers to the size of the structure Review What is a static data structure?
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
Module 9: Binary trees
 Module 9: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Module 9: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
Trees. Trees. CSE 2011 Winter 2007
 Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
5/8/2012. Creating and Changing Directories Chapter 7
 Creating and Changing Directories Chapter 7 Types of files File systems concepts Using directories to create order. Managing files in directories. Using pathnames to manage files in directories. Managing
Creating and Changing Directories Chapter 7 Types of files File systems concepts Using directories to create order. Managing files in directories. Using pathnames to manage files in directories. Managing
11 TREES DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IMPLEMENTATION & APPLICATIONS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS 11 TREES IMPLEMENTATION & APPLICATIONS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM LECTURES ADAPTED FROM: DANIEL KANE, NEIL RHODES DEPARTMENT
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS 11 TREES IMPLEMENTATION & APPLICATIONS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM LECTURES ADAPTED FROM: DANIEL KANE, NEIL RHODES DEPARTMENT
Shell scripting and system variables. HORT Lecture 5 Instructor: Kranthi Varala
 Shell scripting and system variables HORT 59000 Lecture 5 Instructor: Kranthi Varala Text editors Programs built to assist creation and manipulation of text files, typically scripts. nano : easy-to-learn,
Shell scripting and system variables HORT 59000 Lecture 5 Instructor: Kranthi Varala Text editors Programs built to assist creation and manipulation of text files, typically scripts. nano : easy-to-learn,
Unit #2: Priority Queues
 Unit #2: Priority Queues CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures Will Evans 201W1 Unit Outline Rooted Trees, Briefly Priority Queue ADT Heaps Implementing Priority Queue ADT Focus on Create: Heapify Brief
Unit #2: Priority Queues CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures Will Evans 201W1 Unit Outline Rooted Trees, Briefly Priority Queue ADT Heaps Implementing Priority Queue ADT Focus on Create: Heapify Brief
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Trees. See Chapter 18 of Weiss
 Trees See Chapter 18 of Weiss By the way, I am Bob Geitz www.cs.oberlin.edu/~bob/cs151 Ben is at a conference in Kansas City (where, according to Rogers and Hammerstein, everything is up to date and they've
Trees See Chapter 18 of Weiss By the way, I am Bob Geitz www.cs.oberlin.edu/~bob/cs151 Ben is at a conference in Kansas City (where, according to Rogers and Hammerstein, everything is up to date and they've
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 02 / 24 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Trees binary trees two ideas for representing them in code traversals start binary
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 02 / 24 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Trees binary trees two ideas for representing them in code traversals start binary
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) Course 9 Lists / Graphs / Trees. Iulian Năstac
 Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) Course 9 Lists / Graphs / Trees Iulian Năstac Recapitulation It is considered the following type: typedef struct nod { ; struct nod *next; } NOD; 2 Circular
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) Course 9 Lists / Graphs / Trees Iulian Năstac Recapitulation It is considered the following type: typedef struct nod { ; struct nod *next; } NOD; 2 Circular
Introduction to Algorithms 3 rd edition
 Introduction to Algorithms 3 rd edition Heapsort Mohammad Heidari Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Khansar March 6, 2017 M.Heidari (Computer Science Khansar) Introduction to Algorithms March 6, 2017
Introduction to Algorithms 3 rd edition Heapsort Mohammad Heidari Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Khansar March 6, 2017 M.Heidari (Computer Science Khansar) Introduction to Algorithms March 6, 2017
Section Summary. Introduction to Trees Rooted Trees Trees as Models Properties of Trees
 Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Lecture 34. Wednesday, April 6 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 34 1
 Lecture 34 Log into Linux. Copy files on csserver from /home/hwang/cs215/lecture33/*.* In order to compile these files, also need bintree.h from last class. Project 7 posted. Due next week Friday, but
Lecture 34 Log into Linux. Copy files on csserver from /home/hwang/cs215/lecture33/*.* In order to compile these files, also need bintree.h from last class. Project 7 posted. Due next week Friday, but
Trees. Introduction & Terminology. February 05, 2018 Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1
 Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))
![8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F)) 8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))](/thumbs/89/97773603.jpg) DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
First of all, these notes will cover only a small subset of the available commands and utilities, and will cover most of those in a shallow fashion.
 Warnings Linux Commands 1 First of all, these notes will cover only a small subset of the available commands and utilities, and will cover most of those in a shallow fashion. Read the relevant material
Warnings Linux Commands 1 First of all, these notes will cover only a small subset of the available commands and utilities, and will cover most of those in a shallow fashion. Read the relevant material
2.2 Syntax Definition
 42 CHAPTER 2. A SIMPLE SYNTAX-DIRECTED TRANSLATOR sequence of "three-address" instructions; a more complete example appears in Fig. 2.2. This form of intermediate code takes its name from instructions
42 CHAPTER 2. A SIMPLE SYNTAX-DIRECTED TRANSLATOR sequence of "three-address" instructions; a more complete example appears in Fig. 2.2. This form of intermediate code takes its name from instructions
Trees. A tree is a directed graph with the property
 2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations. (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207.
 MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207 paul.gibson@it-sudparis.eu http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/ Graphs and Trees http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/l2-graphsandtrees.pdf
MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207 paul.gibson@it-sudparis.eu http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/ Graphs and Trees http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/l2-graphsandtrees.pdf
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
COSC Advanced Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Lab 3: Heapsort
 COSC 320 - Advanced Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Lab 3: Heapsort Dr. Joe Anderson Due: 21 February 2019 1 Objectives In this lab you will focus on the following objectives: 1. Develop familiarity
COSC 320 - Advanced Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis Lab 3: Heapsort Dr. Joe Anderson Due: 21 February 2019 1 Objectives In this lab you will focus on the following objectives: 1. Develop familiarity
Chapter Summary. Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees
 Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
The tree data structure. Trees COL 106. Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal. Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo
 The tree data structure 1 Trees COL 106 Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo 1 Trees The tree data structure 3 A rooted tree data structure stores
The tree data structure 1 Trees COL 106 Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo 1 Trees The tree data structure 3 A rooted tree data structure stores
Data Structure and Algorithm Homework #3 Due: 2:20pm, Tuesday, April 9, 2013 TA === Homework submission instructions ===
 Data Structure and Algorithm Homework #3 Due: 2:20pm, Tuesday, April 9, 2013 TA email: dsa1@csientuedutw === Homework submission instructions === For Problem 1, submit your source code, a Makefile to compile
Data Structure and Algorithm Homework #3 Due: 2:20pm, Tuesday, April 9, 2013 TA email: dsa1@csientuedutw === Homework submission instructions === For Problem 1, submit your source code, a Makefile to compile
First of all, these notes will cover only a small subset of the available commands and utilities, and will cover most of those in a shallow fashion.
 Warnings 1 First of all, these notes will cover only a small subset of the available commands and utilities, and will cover most of those in a shallow fashion. Read the relevant material in Sobell! If
Warnings 1 First of all, these notes will cover only a small subset of the available commands and utilities, and will cover most of those in a shallow fashion. Read the relevant material in Sobell! If
DATA STRUCTURES USING C
 DATA STRUCTURES USING C The British Constitution Crown Church of England Cabinet House of Commons House of Lords Supreme Court Ministers County Metropolitan Council police Rural District County Borough
DATA STRUCTURES USING C The British Constitution Crown Church of England Cabinet House of Commons House of Lords Supreme Court Ministers County Metropolitan Council police Rural District County Borough
Out: April 19, 2017 Due: April 26, 2017 (Wednesday, Reading/Study Day, no late work accepted after Friday)
 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II Spring 2017 Programming Project 7 30 points Out: April 19, 2017 Due: April 26, 2017 (Wednesday, Reading/Study Day, no late work accepted after Friday) This project
CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II Spring 2017 Programming Project 7 30 points Out: April 19, 2017 Due: April 26, 2017 (Wednesday, Reading/Study Day, no late work accepted after Friday) This project
CS 3114 Data Structures and Algorithms DRAFT Project 2: BST Generic
 Binary Search Tree This assignment involves implementing a standard binary search tree as a Java generic. The primary purpose of the assignment is to ensure that you have experience with some of the issues
Binary Search Tree This assignment involves implementing a standard binary search tree as a Java generic. The primary purpose of the assignment is to ensure that you have experience with some of the issues
Binary Trees. Examples:
 Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Introduction to Programming, Aug-Dec 2006
 Introduction to Programming, Aug-Dec 2006 Lecture 3, Friday 11 Aug 2006 Lists... We can implicitly decompose a list into its head and tail by providing a pattern with two variables to denote the two components
Introduction to Programming, Aug-Dec 2006 Lecture 3, Friday 11 Aug 2006 Lists... We can implicitly decompose a list into its head and tail by providing a pattern with two variables to denote the two components
Comparisons. Θ(n 2 ) Θ(n) Sorting Revisited. So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers. What is the advantage of merge sort?
 So far we have studied: Comparisons Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n 2 ) Θ(nlgn) Best case Θ(n) Θ(nlgn) Sorting Revisited So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers What
So far we have studied: Comparisons Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n 2 ) Θ(nlgn) Best case Θ(n) Θ(nlgn) Sorting Revisited So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers What
Lecture 26. Introduction to Trees. Trees
 Lecture 26 Introduction to Trees Trees Trees are the name given to a versatile group of data structures. They can be used to implement a number of abstract interfaces including the List, but those applications
Lecture 26 Introduction to Trees Trees Trees are the name given to a versatile group of data structures. They can be used to implement a number of abstract interfaces including the List, but those applications
Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington
 Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington 1 Trees Trees are a natural data structure for representing specific data. Family trees. Organizational
Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington 1 Trees Trees are a natural data structure for representing specific data. Family trees. Organizational
Data Structure and Algorithm, Spring 2017 Final Examination
 Data Structure and Algorithm, Spring 2017 Final Examination Date: Tuesday, June 20, 2017 Time: 13:20-16:20pm (180 minutes) 138 points Non-Programming problems Problem 1. In each of the following question,
Data Structure and Algorithm, Spring 2017 Final Examination Date: Tuesday, June 20, 2017 Time: 13:20-16:20pm (180 minutes) 138 points Non-Programming problems Problem 1. In each of the following question,
Definition of a tree. A tree is like a binary tree, except that a node may have any number of children
 Trees Definition of a tree A tree is like a binary tree, except that a node may have any number of children Depending on the needs of the program, the children may or may not be ordered Like a binary tree,
Trees Definition of a tree A tree is like a binary tree, except that a node may have any number of children Depending on the needs of the program, the children may or may not be ordered Like a binary tree,
Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees.
 Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees. Chapter 6 Definition of graphs (I) A directed graph or digraph is a pair G = (V,E) s.t.: V is a finite set called the set of vertices of G. E V
Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees. Chapter 6 Definition of graphs (I) A directed graph or digraph is a pair G = (V,E) s.t.: V is a finite set called the set of vertices of G. E V
Trees Algorhyme by Radia Perlman
 Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
Chapter 8: Data Abstractions
 Chapter 8: Data Abstractions Computer Science: An Overview Eleventh Edition by J. Glenn Brookshear Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8: Data Abstractions 8.1 Data Structure Fundamentals 8.2
Chapter 8: Data Abstractions Computer Science: An Overview Eleventh Edition by J. Glenn Brookshear Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 8: Data Abstractions 8.1 Data Structure Fundamentals 8.2
Comparisons. Heaps. Heaps. Heaps. Sorting Revisited. Heaps. So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers
 So far we have studied: Comparisons Tree is completely filled on all levels except possibly the lowest, which is filled from the left up to a point Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n ) Θ(nlgn) Best
So far we have studied: Comparisons Tree is completely filled on all levels except possibly the lowest, which is filled from the left up to a point Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n ) Θ(nlgn) Best
Assignment: 7. Due: Language level: Allowed recursion:
 Assignment: 7 Due: Language level: Allowed recursion: CS 135 Winter 2018 Graham, Nijjar Tuesday, March 13th, 2018 9:00pm Beginning Student with List Abbreviations Pure Structural and Structural Recursion
Assignment: 7 Due: Language level: Allowed recursion: CS 135 Winter 2018 Graham, Nijjar Tuesday, March 13th, 2018 9:00pm Beginning Student with List Abbreviations Pure Structural and Structural Recursion
403: Algorithms and Data Structures. Heaps. Fall 2016 UAlbany Computer Science. Some slides borrowed by David Luebke
 403: Algorithms and Data Structures Heaps Fall 20 UAlbany Computer Science Some slides borrowed by David Luebke Birdseye view plan For the next several lectures we will be looking at sorting and related
403: Algorithms and Data Structures Heaps Fall 20 UAlbany Computer Science Some slides borrowed by David Luebke Birdseye view plan For the next several lectures we will be looking at sorting and related
Priority Queues and Huffman Trees
 Priority Queues and Huffman Trees 1 the Heap storing the heap with a vector deleting from the heap 2 Binary Search Trees sorting integer numbers deleting from a binary search tree 3 Huffman Trees encoding
Priority Queues and Huffman Trees 1 the Heap storing the heap with a vector deleting from the heap 2 Binary Search Trees sorting integer numbers deleting from a binary search tree 3 Huffman Trees encoding
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10)
 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
CS F-11 B-Trees 1
 CS673-2016F-11 B-Trees 1 11-0: Binary Search Trees Binary Tree data structure All values in left subtree< value stored in root All values in the right subtree>value stored in root 11-1: Generalizing BSTs
CS673-2016F-11 B-Trees 1 11-0: Binary Search Trees Binary Tree data structure All values in left subtree< value stored in root All values in the right subtree>value stored in root 11-1: Generalizing BSTs
Binary Search Tree 1.0. Generated by Doxygen Mon Jun :12:39
 Binary Search Tree 1.0 Generated by Doxygen 1.7.1 Mon Jun 6 2011 16:12:39 Contents 1 Binary Search Tree Program 1 1.1 Introduction.......................................... 1 2 Data Structure Index 3
Binary Search Tree 1.0 Generated by Doxygen 1.7.1 Mon Jun 6 2011 16:12:39 Contents 1 Binary Search Tree Program 1 1.1 Introduction.......................................... 1 2 Data Structure Index 3
TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due Thursday at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must be complete by
TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due Thursday at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must be complete by
CSE 143 Lecture 19. Binary Trees. read slides created by Marty Stepp
 CSE 143 Lecture 19 Binary Trees read 17.1-17.2 slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Trees tree: A directed, acyclic structure of linked nodes. directed : Has one-way links between
CSE 143 Lecture 19 Binary Trees read 17.1-17.2 slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Trees tree: A directed, acyclic structure of linked nodes. directed : Has one-way links between
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
CS 151. Binary Trees. Friday, October 5, 12
 CS 151 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Examples Without telling you what a binary tree is, here are some examples (that I will draw on the board): The dots/circles are called nodes, or vertices (singular: one
CS 151 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Examples Without telling you what a binary tree is, here are some examples (that I will draw on the board): The dots/circles are called nodes, or vertices (singular: one
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Bash command shell language interpreter
 Principles of Programming Languages Bash command shell language interpreter Advanced seminar topic Louis Sugy & Baptiste Thémine Presentation on December 8th, 2017 Table of contents I. General information
Principles of Programming Languages Bash command shell language interpreter Advanced seminar topic Louis Sugy & Baptiste Thémine Presentation on December 8th, 2017 Table of contents I. General information
Binary search trees. Support many dynamic-set operations, e.g. Search. Minimum. Maximum. Insert. Delete ...
 Binary search trees Support many dynamic-set operations, e.g. Search Minimum Maximum Insert Delete... Can be used as dictionary, priority queue... you name it Running time depends on height of tree: 1
Binary search trees Support many dynamic-set operations, e.g. Search Minimum Maximum Insert Delete... Can be used as dictionary, priority queue... you name it Running time depends on height of tree: 1
Tree traversals and binary trees
 Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
CSE 374 Midterm Exam 11/2/15. Name Id #
 Name Id # There are 8 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Name Id # There are 8 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Tutorial # March 2016 Aniruddha Chattoraj CPSC 319. Data Structures, Algorithms, and Their Applications Tutorial 01/03 Winter 17
 Tutorial # 13-14 6-9 March 2016 Aniruddha Chattoraj CPSC 319 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Their Applications Tutorial 01/03 Winter 17 Trees A tree is a hierarchical data structure A binary tree is
Tutorial # 13-14 6-9 March 2016 Aniruddha Chattoraj CPSC 319 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Their Applications Tutorial 01/03 Winter 17 Trees A tree is a hierarchical data structure A binary tree is
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Heaps I. Lecture 22. Prof. Eric Polizzi
 ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece242/ Heaps I Lecture 22 Prof. Eric Polizzi Motivations Review of priority queue Input F E D B A Output Input Data structure
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece242/ Heaps I Lecture 22 Prof. Eric Polizzi Motivations Review of priority queue Input F E D B A Output Input Data structure
Algorithms and Data Structures CS-CO-412
 Algorithms and Data Structures CS-CO-412 David Vernon Professor of Informatics University of Skövde Sweden david@vernon.eu www.vernon.eu Algorithms and Data Structures 1 Copyright D. Vernon 2014 Trees
Algorithms and Data Structures CS-CO-412 David Vernon Professor of Informatics University of Skövde Sweden david@vernon.eu www.vernon.eu Algorithms and Data Structures 1 Copyright D. Vernon 2014 Trees
1 Heaps. 1.1 What is a heap? 1.2 Representing a Heap. CS 124 Section #2 Heaps and Graphs 2/5/18
 CS 124 Section #2 Heaps and Graphs 2/5/18 1 Heaps Heaps are data structures that make it easy to find the element with the most extreme value in a collection of elements. They are also known a priority
CS 124 Section #2 Heaps and Graphs 2/5/18 1 Heaps Heaps are data structures that make it easy to find the element with the most extreme value in a collection of elements. They are also known a priority
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
World Inside a Computer is Binary
 C Programming 1 Representation of int data World Inside a Computer is Binary C Programming 2 Decimal Number System Basic symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Radix-10 positional number system. The radix
C Programming 1 Representation of int data World Inside a Computer is Binary C Programming 2 Decimal Number System Basic symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Radix-10 positional number system. The radix
Trees and Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Trees and Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Graphs A graph is formally defined as: A set V of vertices (also called nodes). A set E of
Trees and Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Graphs A graph is formally defined as: A set V of vertices (also called nodes). A set E of
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Trees
 Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Please submit your request directly to Noha Sinno
 Note to Students: This file contains sample solutions to the term test. Please read the solutions carefully. Make sure that you understand why the solutions given here are correct, that you understand
Note to Students: This file contains sample solutions to the term test. Please read the solutions carefully. Make sure that you understand why the solutions given here are correct, that you understand
CSE 374 Midterm Exam 11/2/15 Sample Solution. Question 1. (10 points) Suppose the following files and subdirectories exist in a directory:
 Question 1. (10 points) Suppose the following files and subdirectories exist in a directory:.bashrc.emacs.bash_profile proj proj/data proj/data/dict.txt proj/data/smalldict.txt proj/notes proj/notes/todo.txt
Question 1. (10 points) Suppose the following files and subdirectories exist in a directory:.bashrc.emacs.bash_profile proj proj/data proj/data/dict.txt proj/data/smalldict.txt proj/notes proj/notes/todo.txt
Crossing bridges. Crossing bridges Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science. Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics. Königsberg (Prussia)
 15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Concept Question
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
) $ f ( n) " %( g( n)
 CSE 0 Name Test Spring 008 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is: # A.
CSE 0 Name Test Spring 008 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is: # A.
I2206 Data Structures TS 6: Binary Trees - Binary Search Trees
 Lebanese University BS - Computer Science Faculty of Science 2018-2019 Section I I2206 Data Structures TS 6: Binary Trees - Binary Search Trees Exercise 1 What value does the following C function return?
Lebanese University BS - Computer Science Faculty of Science 2018-2019 Section I I2206 Data Structures TS 6: Binary Trees - Binary Search Trees Exercise 1 What value does the following C function return?
Questions from the material presented in this lecture
 Advanced Data Structures Questions from the material presented in this lecture January 8, 2015 This material illustrates the kind of exercises and questions you may get at the final colloqium. L1. Introduction.
Advanced Data Structures Questions from the material presented in this lecture January 8, 2015 This material illustrates the kind of exercises and questions you may get at the final colloqium. L1. Introduction.
A Formalization of Transition P Systems
 Fundamenta Informaticae 49 (2002) 261 272 261 IOS Press A Formalization of Transition P Systems Mario J. Pérez-Jiménez and Fernando Sancho-Caparrini Dpto. Ciencias de la Computación e Inteligencia Artificial
Fundamenta Informaticae 49 (2002) 261 272 261 IOS Press A Formalization of Transition P Systems Mario J. Pérez-Jiménez and Fernando Sancho-Caparrini Dpto. Ciencias de la Computación e Inteligencia Artificial
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II. Binary Search Trees
 CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
