Welcome to the Using Objects lab!
|
|
|
- Roy Bryant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Welcome to the Using Objects lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 3 terms. 2. Describe reference variables and compare with primitive data type variables. 3. Draw memory model diagrams contrasting primitive with reference types. Include int, Integer, String, Scanner, etc. 4. Describe char and Character. 5. Describe how calling an instance (non-static) method is different from calling a class (static) method. 6. Use API to lookup Scanner, String, Random, Integer, and Double methods. 7. Trace multiple instance methods calls for Scanner and String. 8. Trace multiple method calls. 9. Describe String concatenation and immutability. Exercise A: Terms Discuss these terms with your lab partner and write out (on paper or notepad) your understanding. If this takes more than about 10 minutes, move on to other lab exercises and come back to this later. As you are doing the lab, consider whether your understanding is confirmed or clarified. Review your understanding with a TA. object vs instance vs class, binary, decimal, char, char literal, ASCII, escape sequence (\n, \t, \\, \"), primitive type vs. reference type, reference, int vs Integer, double vs Double, wrapper class, Random, Scanner, static (class) method call, non-static (instance) method call, API, immutable, package, import, debugging Exercise B: Trace and Explain Week 2 we saw primitive data type variables simply hold a value in memory. Declaring a variable m is giving that name to a location in memory. int m = 9; Can be drawn as: m 9 Or m 9 Week 3 we saw that reference variables contain the reference (location or address) of where to find the value in memory. Technically, references contain the information needed for the JVM to find the value. For simplicity, we can think of a reference as an address.
2 Integer p = new Integer(7); The value (e.g., 132) in the memory location we have named p is the reference (address) to go to find the actual value 7, in this case. Since p is a reference variable (declared as Integer class) we know the value 132 is another location in memory. Going to that location (location 132) we then find the value 7. When we follow the reference we "dereference" the variable. Since the location, 132 in this case, could be a different place in memory every time the program is run we typically draw the reference as an arrow pointing to referred to location. Draw the contents of reference variables with an arrow. Sometimes references are referred to as pointers. With your partner, trace and explain each of the following (also found in traceexplain.txt ). Check your understanding using Java Visualizer. 1. double num1 = 9.0; Double num2 = 9.0; When tracing these, draw a picture of each. Check your picture by viewing in Java Visualizer. In Java Visualizer, remember to check: options > Show String/Integer/etc objects, not just values. When explaining, describe where the compiler will do an implicit type conversion. 2. int numa; numa = 3; Integer numb; numb = new Integer(3); //Can you draw a diagram and then describe in detail what is happening here? //Sample Answer: numa is a primitive variable declared with data type int. The statement numa = 3; puts the int literal 3 into the variable numa. The statement Integer numb; declares numb to be a reference variable intended to hold a reference to an instance of Integer. The expression new Integer(3) instantiates/creates an instance/object of class Integer with the initial value of 3. The result of the expression is a reference/address/pointer to the location in memory of the newly created instance. The assignment statement puts the reference into the variable numb. 3. String str; str = "Your Name"; //Is String a class or primitive data type? //Are the characters "Your Name" stored in the memory location referred to by str? //What is stored in str? 4. String abc = " a b c ";
3 System.out.println( abc.trim().charat(0)); //Look in the String class API, find the trim() description and 3 more methods. 5. String str = "HELLO"; str.tolowercase(); System.out.println( str); //Is the string printed out in all uppercase letters? Why/Why not? What does immutable mean? 6. String str = "Read " + " Java carefully."; System.out.println( str.substring(10,15)); //What exactly will be print out? //What is the meaning of each of the parameters to the substring method? 7. char ch = Character.toUpperCase('a'); System.out.println( ch); 8. Random numgenerator = new Random(); //remember to import java.util.random int num1 = numgenerator.nextint(10); int num2 = numgenerator.nextint(10); int num3 = numgenerator.nextint(10); //Does the value returned from nextint method call change each time? //What are the possible values returned? //If you re-run this same code are the results the same? 9. Random rand = new Random(); rand.setseed( 365); int num1 = rand.nextint(6); int num2 = rand.nextint(6); int num3 = rand.nextint(6); //How does setting a seed affect the results? //What would you change to get the values 1-6, such as for simulating a dice roll? To learn more about Scanner see //Exactly what is printed out? Remember to import java.util.scanner Scanner input = new Scanner("This is the input."); String str = input.next(); str = input.next(); System.out.println( str); 11. Scanner input = new Scanner("one 1 2.0"); System.out.println( input.nextdouble()); //Change this code to read each token using the appropriate method and print each out. 12. Scanner input = new Scanner("1 2 3\n 4 5 6"); System.out.println( input.nextint());
4 System.out.println( input.nextint()); System.out.println( input.next()); String str = input.nextline(); System.out.println( "#" + str + "#"); System.out.println( input.nextint()); //str refers to what sequence of characters? why? 13. //What is printed out? public class M { public static int methoda(int a) { return a + 2; public static void main(string []args) { double c = 5.2; System.out.println( methodb( c)); public static int methodb(double b) { return methoda((int) (b + 1.0)); 14. //If you have difficulty, review Precedence, Associativity and Order of Evaluation tutorial. int a = 40; System.out.println((a /= 10) + "" + (a /= 2)); //for questions on /=, see "compound operators" in zybooks Exercise C: String Documentation Review the following screenshot of String API and answer the following questions. 1. Which modifier indicates that this is a class method that you call with the class name? 2. What is the data type returned by the method call and that we should use to declare the variable? result = String.valueOf( true);
5 3. How can you tell that you must have a reference to an instance to call the method? 4. Is this touppercase call correct? String result = String.toUpperCase(); 5. Will this print out HELLO? String shout = "hello"; shout = shout.touppercase(); System.out.println( shout); 6. Write a statement using the trim() method to remove the leading and trailing whitespace from the string " happy ". 7. There is also a tolowercase() method in the String class. Will the following print out the lowercase letters? String str = "IS THIS LOWER CASE?"; str.tolowercase(); System.out.println( str); Exercise D: Matching (Scanner) Match each of these explanations with the corresponding code, term or exception. A. a sequence of non-whitespace characters B. space, tab and newline characters C. Reads the next token and returns the first character of the token and saves the character in a variable. D. Read the next token and return as an int value. Skip any leading whitespace and stop at whitespace following token. Will throw an InputMismatchException if the token is not an integer. E. Assign the reference to a new instance of Scanner to the scnr variable. F. Declare reference variable named scnr of class Scanner. G. Declares a variable. Reads and returns the next token as a double saving value in the variable. Will throw an InputMismatchException if the token is not a floating point number. H. Read all characters (including whitespace) up to and including the next newline character. Return a reference to a string containing all the characters except for the newline. Save the string reference in a variable. I. A statement to read in the next token as a String and save the reference into the name variable. J. Closes the instance of the Scanner, typically called when the programmer is done reading from it. K. In Scanner methods, if there is not any more input then this exception is thrown. L. In Scanner methods, if the scanner has already been closed then this exception is thrown. M. In Scanner methods, if the token read doesn't match the expected data type then this exception is thrown. 1. whitespace 2. token 3. Scanner scnr; 4. scnr = new Scanner(System.in); 5. scnr.nextint()
6 6. name = scnr.next(); 7. char choice = scnr.next().charat(0); 8. double price = scnr.nextdouble(); 9. String line = scnr.nextline(); 10. scnr.close(); 11. InputMismatchException 12. NoSuchElementException 13. IllegalStateException Exercise E: Binary, Hexadecimal and Unicode If necessary, review zybooks section 3.1 and What is binary 0111 in hexadecimal and decimal? 2. What is hexadecimal 0045 in binary and decimal and what character is it using the unicode table? 3. What is 75 (decimal) in binary and hexadecimal? Note: If necessary on an exam, a unicode table will be provided, it does not need to be memorized. Exercise TA: Demonstration and Discussion This exercise is utilized to determine 3 points of the lab grade. We suggest reviewing these before you discuss these with your TA. 1. References & Wrapper classes: a. Draw pictures and explain what is happening in memory: float salary = 1.5F; Float salary2 = 1.5F; b. Draw pictures and explain what is happening in memory: Integer numa = new Integer(3); int numb = numa; Integer numc = 3; c. Which wrapper class would you look in for a method to see if a single character is a digit? 2. Method calls a. What is printed out? String str = " This is a puzzle. \n"; str.substring( str.indexof( 'a'), 13); System.out.println( str); b. What is printed out? public class Color { public static void red() {
7 System.out.print("RED "); public static void blue() { red(); System.out.print("BLUE "); public static void main(string []args) { blue(); green(); red(); public static void green() { blue(); System.out.print("GREEN "); blue(); c. In the following code: Random rand = new Random(); rand.setseed( 23); int num1 = rand.nextint(10) + 2; System.out.println( num1); i. Will the number printed out be between 2 and 12 inclusive of both? ii. If this code is run 10 times, will it print out the same number each time or different numbers each time? 3. Scanner a. What will be printed out? Scanner input = new Scanner("This\nhas\n4\nlines\n"); input.next(); System.out.println( "%"+ input.nextline() + "%"); input.nextline(); System.out.println( input.nextint()); System.out.println("#"+ input.nextline() + "#"); System.out.println("*"+ input.nextline() + "*"); Exercise F: Fix Order and Indenting of Lines Using the command-line tools, reorder lines to fix Scanner2.java Output:
8 Job:43125 name: Sara fee: Exercise G: Body Mass Index Body Mass Index (BMI) is used to estimate the amount of muscle, fat and bone in an individual. The BMI is defined as the body mass (kilograms) divided by the square of the body height (meters). Extend BMI.java to calculate a BMI based on height in meters and weight in kilograms. Height (meters): 1.6 Weight (kilograms): 65 BMI: Adapt to take input in inches and pounds. Find the appropriate formulas and constants on the web. There are calculators on the web that you may use to compare results. Express any constant values, such as meters in an inch, as a constant: final double METERS_IN_INCH = ; Height (inches): (meters) Weight (pounds): (kilograms) BMI: Adapt further to take input in feet, inches and pounds. Height (feet): 5 Height (inches): (meters) Weight (pounds): (kilograms) BMI: Exercise H: Hello World Run this HelloWorld.java program and see if you can figure out how it works. 1. What does the seed for Random do? 2. What does += mean for Strings? 3. What does the following do? (char)(rand.nextint(27) + '`') 4. Why was '`' chosen? 5. Why was 27 chosen? 6. Why were those specific seeds chosen? Exercise I: Write Program Write a program to use a Scanner to read the string, reading each number, " ControlType: " and print out as: building (522.0, 174.0)
9 hero (397.0, 287.0) fire (541.0, 387.0) using control type: 1 Exercise J: More Trace and Explain With your partner, trace and explain each of the following (also found in traceexplain2.txt ). Check your understanding using Java Visualizer. 15. String str = " r g h "; String.trim(); //Will this compile? str.trim(); //Will this remove leading and trailing whitespace from the string? //Is the trimmed string changed in place or returned? 16. int length = " strange looking".length(); //why does this work? System.out.println( length); 17. String str2 = "Careful reading will save " + " lots of time debugging."; System.out.println( str2.substring( str2.indexof('e') + 1, str2.indexof('o')).trim()); //What will be print out? Describe in your own words what the substring, indexof and trim methods do. 18. String str = "he" + (9+2) + 'o'; String str2 = str.touppercase(); System.out.println( str2); 19. int num = '1'; //will this data type conversion work? System.out.println( num); 20. Character ch = new Character('A'); System.out.println( ch.islowercase()); 21. Random numgenerator = new Random(); System.out.println( "number: " + Random.nextInt()); //What is wrong and how do you fix? 22. Random rand = new Random(); //remember to import java.util.random int num1 = rand.nextint(); int num2 = rand.nextint(); int num3 = rand.nextint(); //Will the nextint() method return the same value each time? //What is the range of possible values returned? //Each time you run this will the values returned be the same or different?
10 23. java.util.scanner stdin = new java.util.scanner( System.in); String str = stdin.nextline(); //what does this do, precisely? 24. //Will this compile? Scanner stdin = new Scanner( System.in); // remember to import java.util.scanner int num = stdin.nextdouble(); 25. Scanner input = new Scanner("one 1 2.0"); String str = input.next(); System.out.println( input.nextdouble()); 26. Scanner input = new Scanner("1 2 3\n 4 5 6"); String str = input.next(); System.out.println( input.next()); //str refers to what sequence of characters? 27. Scanner input = new Scanner("1 2 3\n 4 5 6"); String str = input.nextline(); System.out.println( input.nextint()); //str refers to what sequence of characters? Additional Learning Materials When you have mastered everything in this lab and previous labs, then you are welcome to learn from additional learning resources available on the web and beyond this course: Note: Due to programs and zybooks being individual work, it is Not appropriate to work on them during the Team Lab. Contributions by Marc Renault, Yien Xu Lab 2018 Jim Williams
Welcome to the Using Objects lab!
 Welcome to the Using Objects lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 3 terms. 2. Describe reference variables and compare with primitive data type variables. 3. Draw
Welcome to the Using Objects lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 3 terms. 2. Describe reference variables and compare with primitive data type variables. 3. Draw
Welcome to the Primitives and Expressions Lab!
 Welcome to the Primitives and Expressions Lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 2 terms. 2. Describe declarations, variables, literals and constants for primitive
Welcome to the Primitives and Expressions Lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 2 terms. 2. Describe declarations, variables, literals and constants for primitive
CS 200 Using Objects. Jim Williams, PhD
 CS 200 Using Objects Jim Williams, PhD This Week Notes By Friday Exam Conflict and Accommodations Install Eclipse (version 8) Help Queue Team Lab 2 Chap 2 Programs (P2): Due Thursday Hours Spent Week?
CS 200 Using Objects Jim Williams, PhD This Week Notes By Friday Exam Conflict and Accommodations Install Eclipse (version 8) Help Queue Team Lab 2 Chap 2 Programs (P2): Due Thursday Hours Spent Week?
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
CS Week 5. Jim Williams, PhD
 CS 200 - Week 5 Jim Williams, PhD The Study Cycle Check Am I using study methods that are effective? Do I understand the material enough to teach it to others? http://students.lsu.edu/academicsuccess/studying/strategies/tests/studying
CS 200 - Week 5 Jim Williams, PhD The Study Cycle Check Am I using study methods that are effective? Do I understand the material enough to teach it to others? http://students.lsu.edu/academicsuccess/studying/strategies/tests/studying
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #2. Elementary Programming
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
Midterm Exam 2 Thursday, November 15th, points (15% of final grade) Instructors: Jim Williams and Marc Renault
 Computer Sciences 200 Midterm Exam 2 Thursday, November 15th, 2018 100 points (15% of final grade) Instructors: Jim Williams and Marc Renault (Family) Last Name: (Given) First Name: CS Login Name: NetID
Computer Sciences 200 Midterm Exam 2 Thursday, November 15th, 2018 100 points (15% of final grade) Instructors: Jim Williams and Marc Renault (Family) Last Name: (Given) First Name: CS Login Name: NetID
CS Programming I: Using Objects
 CS 200 - Programming I: Using Objects Marc Renault Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Spring 2018 TopHat Sec 3 (AM) Join Code: 427811 TopHat Sec 4 (PM) Join Code: 165455 Binary
CS 200 - Programming I: Using Objects Marc Renault Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Spring 2018 TopHat Sec 3 (AM) Join Code: 427811 TopHat Sec 4 (PM) Join Code: 165455 Binary
Reading Input from Text File
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Lab 5 Reading Input from Text File Eng. Mohammed Alokshiya November 2, 2014 The simplest
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Lab 5 Reading Input from Text File Eng. Mohammed Alokshiya November 2, 2014 The simplest
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
CS Programming I: Using Objects
 CS 200 - Programming I: Using Objects Marc Renault Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Fall 2017 TopHat Sec 3 (PM) Join Code: 719946 TopHat Sec 4 (AM) Join Code: 891624 Binary
CS 200 - Programming I: Using Objects Marc Renault Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Fall 2017 TopHat Sec 3 (PM) Join Code: 719946 TopHat Sec 4 (AM) Join Code: 891624 Binary
Tester vs. Controller. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Compile Time vs. Run Time
 Tester vs. Controller Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG For effective illustrations, code examples will mostly be written in the form of a tester
Tester vs. Controller Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG For effective illustrations, code examples will mostly be written in the form of a tester
Elementary Programming
 Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Learn ingredients of elementary programming: data types [numbers, characters, strings] literal
Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Learn ingredients of elementary programming: data types [numbers, characters, strings] literal
What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements
 Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Review Chapters 1 to 4. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Introduction to Java Applications
 2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
Lecture 6. Assignments. Java Scanner. User Input 1/29/18. Reading: 2.12, 2.13, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4
 Assignments Reading: 2.12, 2.13, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 Lecture 6 Complete for Lab 4, Project 1 Note: Slides 12 19 are summary slides for Chapter 2. They overview much of what we covered but are not complete.
Assignments Reading: 2.12, 2.13, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 Lecture 6 Complete for Lab 4, Project 1 Note: Slides 12 19 are summary slides for Chapter 2. They overview much of what we covered but are not complete.
Lecture Notes. System.out.println( Circle radius: + radius + area: + area); radius radius area area value
 Lecture Notes 1. Comments a. /* */ b. // 2. Program Structures a. public class ComputeArea { public static void main(string[ ] args) { // input radius // compute area algorithm // output area Actions to
Lecture Notes 1. Comments a. /* */ b. // 2. Program Structures a. public class ComputeArea { public static void main(string[ ] args) { // input radius // compute area algorithm // output area Actions to
CHAPTER 4 MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS, CHARACTERS, STRINGS
 CHAPTER 4 MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS, CHARACTERS, STRINGS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS Java
CHAPTER 4 MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS, CHARACTERS, STRINGS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS Java
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types
 Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Using Java Classes Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
AP Computer Science A
 AP Computer Science A 1st Quarter Notes Table of Contents - section links Click on the date or topic below to jump to that section Date : 9/8/2017 Aim : Java Basics Objects and Classes Data types: Primitive
AP Computer Science A 1st Quarter Notes Table of Contents - section links Click on the date or topic below to jump to that section Date : 9/8/2017 Aim : Java Basics Objects and Classes Data types: Primitive
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
"Hello" " This " + "is String " + "concatenation"
 Strings About Strings Strings are objects, but there is a special syntax for writing String literals: "Hello" Strings, unlike most other objects, have a defined operation (as opposed to a method): " This
Strings About Strings Strings are objects, but there is a special syntax for writing String literals: "Hello" Strings, unlike most other objects, have a defined operation (as opposed to a method): " This
Assignment 2.4: Loops
 Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java
 Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Object Oriented Programming. Java-Lecture 1
 Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 1 Standard output System.out is known as the standard output object Methods to display text onto the standard output System.out.print prints text onto the screen
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
A variable is a name for a location in memory A variable must be declared
 Variables A variable is a name for a location in memory A variable must be declared, specifying the variable's name and the type of information that will be held in it data type variable name int total;
Variables A variable is a name for a location in memory A variable must be declared, specifying the variable's name and the type of information that will be held in it data type variable name int total;
Chapter 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING
 Chapter 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Objectives To write Java programs to perform simple
Chapter 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Objectives To write Java programs to perform simple
Program Fundamentals
 Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
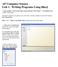 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Software Practice 1 - Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision
 Software Practice 1 - Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Hwansoo Han T.A. Minseop Jeong T.A. Wonseok Choi 1 Java Program //package details public class ClassName {
Software Practice 1 - Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Hwansoo Han T.A. Minseop Jeong T.A. Wonseok Choi 1 Java Program //package details public class ClassName {
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Strings, Strings and characters, String class methods. JAVA Standard Edition
 Strings, Strings and characters, String class methods JAVA Standard Edition Java - Character Class Normally, when we work with characters, we use primitive data types char. char ch = 'a'; // Unicode for
Strings, Strings and characters, String class methods JAVA Standard Edition Java - Character Class Normally, when we work with characters, we use primitive data types char. char ch = 'a'; // Unicode for
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
H212 Introduction to Software Systems Honors
 Introduction to Software Systems Honors Lecture #04: Fall 2015 1/20 Office hours Monday, Wednesday: 10:15 am to 12:00 noon Tuesday, Thursday: 2:00 to 3:45 pm Office: Lindley Hall, Room 401C 2/20 Printing
Introduction to Software Systems Honors Lecture #04: Fall 2015 1/20 Office hours Monday, Wednesday: 10:15 am to 12:00 noon Tuesday, Thursday: 2:00 to 3:45 pm Office: Lindley Hall, Room 401C 2/20 Printing
CSCI 2010 Principles of Computer Science. Data and Expressions 08/09/2013 CSCI
 CSCI 2010 Principles of Computer Science Data and Expressions 08/09/2013 CSCI 2010 1 Data Types, Variables and Expressions in Java We look at the primitive data types, strings and expressions that are
CSCI 2010 Principles of Computer Science Data and Expressions 08/09/2013 CSCI 2010 1 Data Types, Variables and Expressions in Java We look at the primitive data types, strings and expressions that are
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions
 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University April 21, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 53 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data Types
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University April 21, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 53 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data Types
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
Chapter 2 Elementary Programming
 Chapter 2 Elementary Programming Part I 1 Motivations In the preceding chapter, you learned how to create, compile, and run a Java program. Starting from this chapter, you will learn how to solve practical
Chapter 2 Elementary Programming Part I 1 Motivations In the preceding chapter, you learned how to create, compile, and run a Java program. Starting from this chapter, you will learn how to solve practical
Basic Computation. Chapter 2
 Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers and letters. Think of them
Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers and letters. Think of them
Java Foundations: Introduction to Program Design & Data Structures, 4e John Lewis, Peter DePasquale, Joseph Chase Test Bank: Chapter 2
 Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions
 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University January 15, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 1 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University January 15, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 1 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 24, Name: KEY 1
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
12/22/11. Java How to Program, 9/e. Help you get started with Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java Foundations: Unit 3. Parts of a Java Program
 Java Foundations: Unit 3 Parts of a Java Program class + name public class HelloWorld public static void main( String[] args ) System.out.println( Hello world! ); A class creates a new type, something
Java Foundations: Unit 3 Parts of a Java Program class + name public class HelloWorld public static void main( String[] args ) System.out.println( Hello world! ); A class creates a new type, something
Mr. Monroe s Guide to Mastering Java Syntax
 Mr. Monroe s Guide to Mastering Java Syntax Getting Started with Java 1. Download and install the official JDK (Java Development Kit). 2. Download an IDE (Integrated Development Environment), like BlueJ.
Mr. Monroe s Guide to Mastering Java Syntax Getting Started with Java 1. Download and install the official JDK (Java Development Kit). 2. Download an IDE (Integrated Development Environment), like BlueJ.
String. Other languages that implement strings as character arrays
 1. length() 2. tostring() 3. charat() 4. getchars() 5. getbytes() 6. tochararray() 7. equals() 8. equalsignorecase() 9. regionmatches() 10. startswith() 11. endswith() 12. compareto() 13. indexof() 14.
1. length() 2. tostring() 3. charat() 4. getchars() 5. getbytes() 6. tochararray() 7. equals() 8. equalsignorecase() 9. regionmatches() 10. startswith() 11. endswith() 12. compareto() 13. indexof() 14.
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination October 11, Name: KEY
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 11, 2018 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 11, 2018 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make
Fall 2017 CISC124 9/16/2017
 CISC124 Labs start this week in JEFF 155: Meet your TA. Check out the course web site, if you have not already done so. Watch lecture videos if you need to review anything we have already done. Problems
CISC124 Labs start this week in JEFF 155: Meet your TA. Check out the course web site, if you have not already done so. Watch lecture videos if you need to review anything we have already done. Problems
Basic Computation. Chapter 2
 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers
Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
First Java Program - Output to the Screen
 First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
CEN 414 Java Programming
 CEN 414 Java Programming Instructor: H. Esin ÜNAL SPRING 2017 Slides are modified from original slides of Y. Daniel Liang WEEK 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING 2 Computing the Area of a Circle public class ComputeArea
CEN 414 Java Programming Instructor: H. Esin ÜNAL SPRING 2017 Slides are modified from original slides of Y. Daniel Liang WEEK 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING 2 Computing the Area of a Circle public class ComputeArea
CSCI 355 LAB #2 Spring 2004
 CSCI 355 LAB #2 Spring 2004 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
CSCI 355 LAB #2 Spring 2004 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
Exam 1. Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik. Total Marks: 45 Obtained Marks:
 كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 1 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: October 18, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 45 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 1 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: October 18, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 45 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #5. Strings & Text Files Input
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #5
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #5
Software Practice 1 Basic Grammar
 Software Practice 1 Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Joonwon Lee T.A. Jaehyun Song Jongseok Kim (42) T.A. Sujin Oh Junseong Lee (43) 1 2 Java Program //package details
Software Practice 1 Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Joonwon Lee T.A. Jaehyun Song Jongseok Kim (42) T.A. Sujin Oh Junseong Lee (43) 1 2 Java Program //package details
CS Week 2. Jim Williams
 CS 302 - Week 2 Jim Williams This Week Team Labs Lecture: Scanner, data types, conditionals Team Labs First meeting this week. 1350 cs and 1370 cs Expect an Ice Breaker, be assigned a partner and do the
CS 302 - Week 2 Jim Williams This Week Team Labs Lecture: Scanner, data types, conditionals Team Labs First meeting this week. 1350 cs and 1370 cs Expect an Ice Breaker, be assigned a partner and do the
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Math Functions, Characters and Strings (Part II)
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Math Functions, Characters and Strings (Part II) Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs How to generate
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Math Functions, Characters and Strings (Part II) Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs How to generate
CSCI 355 Lab #2 Spring 2007
 CSCI 355 Lab #2 Spring 2007 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
CSCI 355 Lab #2 Spring 2007 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing. Objectives: Examples: Text-printing program. CSC 209 JAVA I
 AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
AP Computer Science A Unit 2. Exercises
 AP Computer Science A Unit 2. Exercises A common standard is 24-bit color where 8 bits are used to represent the amount of red light, 8 bits for green light, and 8 bits for blue light. It is the combination
AP Computer Science A Unit 2. Exercises A common standard is 24-bit color where 8 bits are used to represent the amount of red light, 8 bits for green light, and 8 bits for blue light. It is the combination
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Introduction to Java. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods
 Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Università degli Studi di Bologna Facoltà di Ingegneria. Principles, Models, and Applications for Distributed Systems M
 Università degli Studi di Bologna Facoltà di Ingegneria Principles, Models, and Applications for Distributed Systems M tutor Isam M. Al Jawarneh, PhD student isam.aljawarneh3@unibo.it Mobile Middleware
Università degli Studi di Bologna Facoltà di Ingegneria Principles, Models, and Applications for Distributed Systems M tutor Isam M. Al Jawarneh, PhD student isam.aljawarneh3@unibo.it Mobile Middleware
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
Mid Term Exam 1. Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: Sunday November 3, 2013 Total Marks: 50 Obtained Marks:
 Mid Term Exam 1 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: Sunday November 3, 2013 Student Name: Total Marks: 50 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this exam booklet until you
Mid Term Exam 1 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: Sunday November 3, 2013 Student Name: Total Marks: 50 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this exam booklet until you
CS 302: Introduction to Programming
 CS 302: Introduction to Programming Lectures 2-3 CS302 Summer 2012 1 Review What is a computer? What is a computer program? Why do we have high-level programming languages? How does a high-level program
CS 302: Introduction to Programming Lectures 2-3 CS302 Summer 2012 1 Review What is a computer? What is a computer program? Why do we have high-level programming languages? How does a high-level program
Data and Expressions. Outline. Data and Expressions 12/18/2010. Let's explore some other fundamental programming concepts. Chapter 2 focuses on:
 Data and Expressions Data and Expressions Let's explore some other fundamental programming concepts Chapter 2 focuses on: Character Strings Primitive Data The Declaration And Use Of Variables Expressions
Data and Expressions Data and Expressions Let's explore some other fundamental programming concepts Chapter 2 focuses on: Character Strings Primitive Data The Declaration And Use Of Variables Expressions
String is one of mostly used Object in Java. And this is the reason why String has unique handling in Java(String Pool). The String class represents
 String is one of mostly used Object in Java. And this is the reason why String has unique handling in Java(String Pool). The String class represents character strings. All string literals in Java programs,
String is one of mostly used Object in Java. And this is the reason why String has unique handling in Java(String Pool). The String class represents character strings. All string literals in Java programs,
Data and Variables. Data Types Expressions. String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators. Operators Precedence
 Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations. Objectives
 Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Prerequisites for Part I Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs,
Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Prerequisites for Part I Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs,
Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators
 www.thestudycampus.com Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.3 Modifying Your First Java Program 2.4 Displaying
www.thestudycampus.com Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.3 Modifying Your First Java Program 2.4 Displaying
Data Types. 1 You cannot change the type of the variable after declaration. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 52 / 87
 Data Types Java is a strongly-typed 1 programming language. Every variable has a type. Also, every (mathematical) expression has a type. There are two categories of data types: primitive data types, and
Data Types Java is a strongly-typed 1 programming language. Every variable has a type. Also, every (mathematical) expression has a type. There are two categories of data types: primitive data types, and
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Compile Time vs. Run Time. Learning Outcomes
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will be defined within the
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will be defined within the
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #4. Mathematical Functions & Characters
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #4
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #4
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
CS Week 2. Jim Williams, PhD
 CS 200 - Week 2 Jim Williams, PhD Society of Women Engineers "Not just for women and not just for engineers; all students are welcome. We are especially looking for more computer science students!" - Emile
CS 200 - Week 2 Jim Williams, PhD Society of Women Engineers "Not just for women and not just for engineers; all students are welcome. We are especially looking for more computer science students!" - Emile
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Chapter 2: Using Data
 Chapter 2: Using Data TRUE/FALSE 1. A variable can hold more than one value at a time. F PTS: 1 REF: 52 2. The legal integer values are -2 31 through 2 31-1. These are the highest and lowest values that
Chapter 2: Using Data TRUE/FALSE 1. A variable can hold more than one value at a time. F PTS: 1 REF: 52 2. The legal integer values are -2 31 through 2 31-1. These are the highest and lowest values that
Final Exam Practice. Partial credit will be awarded.
 Please note that this problem set is intended for practice, and does not fully represent the entire scope covered in the final exam, neither the range of the types of problems that may be included in the
Please note that this problem set is intended for practice, and does not fully represent the entire scope covered in the final exam, neither the range of the types of problems that may be included in the
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba. (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Eng. Mohammed Abdualal
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 4 Characters
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 4 Characters
The Irving K. Barber School of Arts and Sciences COSC 111 Final Exam Winter Term II Instructor: Dr. Bowen Hui. Tuesday, April 19, 2016
 First Name (Print): Last Name (Print): Student Number: The Irving K. Barber School of Arts and Sciences COSC 111 Final Exam Winter Term II 2016 Instructor: Dr. Bowen Hui Tuesday, April 19, 2016 Time: 6:00pm
First Name (Print): Last Name (Print): Student Number: The Irving K. Barber School of Arts and Sciences COSC 111 Final Exam Winter Term II 2016 Instructor: Dr. Bowen Hui Tuesday, April 19, 2016 Time: 6:00pm
Lecture 2. COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall M. Jason Hinek Carleton University
 Lecture 2 COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall 2013 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda a quick look back (last Thursday) assignment 0 is posted and is due this Friday at 2pm Java compiling
Lecture 2 COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall 2013 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda a quick look back (last Thursday) assignment 0 is posted and is due this Friday at 2pm Java compiling
Chapter 02: Using Data
 True / False 1. A variable can hold more than one value at a time. ANSWER: False REFERENCES: 54 2. The int data type is the most commonly used integer type. ANSWER: True REFERENCES: 64 3. Multiplication,
True / False 1. A variable can hold more than one value at a time. ANSWER: False REFERENCES: 54 2. The int data type is the most commonly used integer type. ANSWER: True REFERENCES: 64 3. Multiplication,
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Java characters Lecture 8
 Java characters Lecture 8 Waterford Institute of Technology January 31, 2016 John Fitzgerald Waterford Institute of Technology, Java characters Lecture 8 1/33 Presentation outline Estimated duration presentation
Java characters Lecture 8 Waterford Institute of Technology January 31, 2016 John Fitzgerald Waterford Institute of Technology, Java characters Lecture 8 1/33 Presentation outline Estimated duration presentation
We now start exploring some key elements of the Java programming language and ways of performing I/O
 We now start exploring some key elements of the Java programming language and ways of performing I/O This week we focus on: Introduction to objects The String class String concatenation Creating objects
We now start exploring some key elements of the Java programming language and ways of performing I/O This week we focus on: Introduction to objects The String class String concatenation Creating objects
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING LAB WEEK 3 STANDARD IO FORMATTING OUTPUT SCANNER REDIRECTING
 CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING LAB WEEK 3 STANDARD IO FORMATTING OUTPUT SCANNER REDIRECTING INPUT AND OUTPUT Input devices Keyboard Mouse Hard drive Network Digital camera Microphone Output devices.
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING LAB WEEK 3 STANDARD IO FORMATTING OUTPUT SCANNER REDIRECTING INPUT AND OUTPUT Input devices Keyboard Mouse Hard drive Network Digital camera Microphone Output devices.
Java Programming Language. 0 A history
 Java Programming Language 0 A history How java works What you ll do in Java JVM API Java Features 0Platform Independence. 0Object Oriented. 0Compiler/Interpreter 0 Good Performance 0Robust. 0Security 0
Java Programming Language 0 A history How java works What you ll do in Java JVM API Java Features 0Platform Independence. 0Object Oriented. 0Compiler/Interpreter 0 Good Performance 0Robust. 0Security 0
Lec 3. Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables
 Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Supplementary Test 1
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Supplementary Test 1 Question
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Supplementary Test 1 Question
Question: Total Points: Score:
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 000 Spring 2014 Name (print):. Instructions Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 000 Spring 2014 Name (print):. Instructions Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CSE1710. Big Picture. Tuesday, Dec 02 is designated as a study day. No classes. Thursday, Dec 04 is last lecture.
 CSE1710 Click to edit Master Week text 12, styles Lecture 22 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2014 Tuesday, Nov 25, 2014 1 Big Picture Tuesday, Dec 02 is designated as a study day.
CSE1710 Click to edit Master Week text 12, styles Lecture 22 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2014 Tuesday, Nov 25, 2014 1 Big Picture Tuesday, Dec 02 is designated as a study day.
