Data and File Structures Laboratory
|
|
|
- Godwin Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Binary Trees Assistant Professor Machine Intelligence Unit Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata September, 2018
2 1 Basics 2 Implementation 3 Traversal
3 Basics of a tree A tree is recursively defined as a set of one or more nodes where a single node is designated as the root of the tree and all the remaining nodes can be partitioned into subtrees of the root. Note: Tree is a non-linear data structure (a data item can be linked to more than one data items).
4 Types of trees Trees can be of different types based on their use as data structures. Some of these are listed below. Forests: Disjoint union of trees. Binary trees: Trees having at most two subtrees per node. Binary search trees: Binary trees in which the nodes are arranged in an order (based on the data items that they keep). Expression trees: Trees that are used to store algebraic expressions. Tournament trees: Trees that are used to represent players using the leaf nodes and winners using the remaining nodes. Note: Trees are data structures that are mainly used to store data items (labels or keys on the nodes) hierarchically.
5 Binary trees Definition (Binary Tree) A binary tree T over a domain D is either an empty set (empty binary tree) or a recursively-defined triplet T 0, T 1, T 2 such that T 0 is a node over D (root), and T 1 and T 2 are binary trees over D (left and right subtree, respectively).
6 Terminologies in binary trees Left child: Left successor node of a node. Right child: Right successor node of a node. Parent: Ancestor node of a set of children. Sibling: Nodes that are at the same level and share the same parent. Degree of a node: Number of children of a node. Note: Every node other than the root node has a parent.
7 Extended binary trees A binary tree is turned into an extended binary tree by adding special nodes to those nodes, except the root node, which contain a null subtree (left or right) in the original tree. Note: The extended nodes are distinguishable from original nodes.
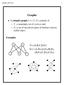
8 Full binary trees Definition (Full Binary Tree) A binary tree is said to be full binary tree (or 2-tree) if each node in the tree has either no child or exactly two children. Note: An extended binary tree becomes a full binary tree.
9 Complete binary trees Definition (Complete Binary Tree) A binary tree is said to be complete binary tree if it satisfies both of the following: Every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled. All nodes appear as far left as possible.
10 Complete binary trees Some properties: 1 A complete binary tree of height h comprises at least 2 h and at most 2 h+1 1 nodes. 2 The height of a complete binary tree having exactly n nodes is log 2 (n + 1). 3 The maximum possible number of parents with absent children in a complete binary tree having n nodes is (n + 1). 4 The number of internal nodes in a complete binary tree having n nodes is n/2.
11 Conventional implementation of binary trees Individual dynamic memory allocation per node. The allocated memories (to the nodes) may be scattered all over the heap area. typedef struct treenode{ DATA d; struct treenode *leftchild, *rightchild; struct treenode *parent; // This is optional }BTNODE; Note: The token DATA symbolizes the data type accommodated.
12 Conventional implementation of binary trees Adding a new node: BTNODE * addnode(int data){ BTNODE *node; if(null == (node = Malloc(1, BTNODE))) // PS: common.h ERR_MESG("out of memory"); node->d = data; // Initialize left and right child as NULL node->leftchild = NULL; node->rightchild = NULL; return(node); } Note: The new data is kept with NULL left and right pointers.
13 Conventional implementation of binary trees Creating the root node: int d1, d2, d3; BTNODE *root = addnode(d1); Adding nodes to the root node: root->left = addnode(d2); root->right = addnode(d3); Note: The root is NULL for an empty tree.
14 Conventional implementation An example
15 Alternative implementation of binary trees An initial dynamic memory allocation and successive reallocations as and when required. The allocated memories (to the nodes) are located within the same array. typedef struct treenode{ DATA d; int leftchild, rightchild; int parent; // This is optional }BTNODE; Note: The token DATA symbolizes the data type accommodated.
16 Alternative implementation An example Initially: root = NULL d leftchild rightchild free 0 1 NULL 1 2 NULL 2 3 NULL 3 4 NULL.... n 1 NULL NULL Note: The value NULL is treated as -1 during implementation.
17 Alternative implementation An example Finally: d leftchild rightchild root NULL NULL NULL 4 11 NULL NULL 5 13 NULL NULL free 6 7 NULL.... n 1 NULL NULL Note: The value NULL is treated as -1 during implementation.
18 Sequential implementation of binary trees One time memory allocation for a one-dimensional array. The left and right child of the node at index i are at index 2i and 2i + 1, respectively. It might involve a lot of unused allocated memories. int h; // Keeps the height typedef struct treenode{ DATA d[power(2, h)]; // POWER(a, b) computes a^b }BTNODE; Note: A binary tree having height h can have at most (2 h 1) nodes.
19 Sequential implementation An example d 0 NULL root parent (at index i) NULL no left child (at index 2i) 7 13 right child (at index 2i + 1) Note: The value NULL is treated as -1 during implementation.
20 Traversal of a binary tree Pre-order traversal In-order traversal Post-order traversal Level-order traversal
21 Pre-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Visit the root node. 2 Traverse the left subtree. 3 Traverse the right subtree.
22 Pre-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Visit the root node. 2 Traverse the left subtree. 3 Traverse the right subtree. Order of visited nodes: 2, 3, 7, 11, 5, 13
23 Pre-order traversal int preorder(btnode *node){ if(null == node) // Reached a leaf node return 0; // Visit the node PRINT(node->d); preorder(node->leftchild); preorder(node->rightchild); }
24 In-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Traverse the left subtree. 2 Visit the root node. 3 Traverse the right subtree.
25 In-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Traverse the left subtree. 2 Visit the root node. 3 Traverse the right subtree. Order of visited nodes: 7, 3, 11, 2, 5, 13
26 In-order traversal int inorder(btnode *node){ if(null == node) // Reached a leaf node return 0; // Visit the node inorder(node->leftchild); PRINT(node->d); inorder(node->rightchild); return(node); }
27 Post-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Traverse the left subtree. 2 Traverse the right subtree. 3 Visit the root node.
28 Post-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Traverse the left subtree. 2 Traverse the right subtree. 3 Visit the root node. Order of visited nodes: 7, 11, 3, 13, 5, 2
29 Post-order traversal int postorder(btnode *node){ if(null == node) // Reached a leaf node return 0; // Visit the node postorder(node->leftchild); postorder(node->rightchild); PRINT(node->d); return(node); }
30 Level-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Visit the root node. 2 Traverse all the subtrees from left to right at the next level.
31 Level-order traversal Perform the following operations recursively at each node: 1 Visit the root node. 2 Traverse all the subtrees from left to right at the next level. Order of visited nodes: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13
32 Constructing binary trees from traversal results In-order traversal: 7, 3, 11, 2, 5, 13 Pre-order traversal: 2, 3, 7, 11, 5, 13 1 Consider the first data item visited in pre-order traversal as the root node. 2 Data items on the left and right side of the root node in the in-order traversal sequence form the left and right subtree of the root node, respectively. 3 Recursively select each data item from pre-order traversal sequence and create its left and right subtrees from the in-order traversal sequence.
33 Constructing binary trees from traversal results An example In-order traversal: 7, 3, 11, 2, 5, 13 Pre-order traversal: 2, 3, 7, 11, 5, 13 Step 1: Data item 2 is the root node (first in pre-order). Step 2: Left and right subtree of 2 comprises {7, 3, 11} and {5, 13}, respectively (items on the left and right of 2 in in-order). Step 3: 3 and 5 are the root nodes of the left and right subtree of 2 (first of those data items in pre-order). Step 4: Left and right subtree of 3 comprises {7} and {11}, respectively (items on the left and right of 3 in in-order). Step 5: Left and right subtree of 5 comprises and {13}, respectively (items on the left and right of 5 in in-order). Step 6: Subtrees of other nodes are.
34 Problems Day 14 1 Suppose a complete binary tree is represented with an array. In this array, the root node is placed at index 0. The left and right child of any arbitrary node at the index i is placed at the index 2i + 1 and 2(i + 1), respectively. Write a program to construct the tree hierarchically by taking its data items as an array from the user and print the pre-order traversal result. 2 In a tournament tree, each non-leaf node represents the winner of the match played between the players represented by its children nodes. Such trees are used to record the winner at each level up to the root (the overall winner). Given a binary tree, write a program to verify whether it is a tournament tree or not. 3 Write a program to construct a binary tree given (from the user) its pre-order and post-order traversal results. Note that, the constructed tree will not be unique.
35 Problems Day 14 4 Given a binary tree with integer-valued nodes, and a target value, determine whether there exists a root-to-leaf path in the tree such that the sum of all node values along that path equals the target. Modify your program to consider all paths, not just root-to-leaf paths. 5 Given a binary tree stored in an array (using the alternative implementation), and the indices of two nodes in the tree, find the index of the node that is the lowest common ancestor of the given nodes.
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
BBM 201 Data structures
 BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 -
 Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park Basic Tree Concepts Logical structures Chap. 2~4 Chap. 5 Chap. 6 Linear list Tree Graph Linear structures Non-linear structures Linear Lists
Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park Basic Tree Concepts Logical structures Chap. 2~4 Chap. 5 Chap. 6 Linear list Tree Graph Linear structures Non-linear structures Linear Lists
Binary Trees. Examples:
 Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Trees. A tree is a directed graph with the property
 2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
Tree Data Structures CSC 221
 Tree Data Structures CSC 221 Specialized Trees Binary Tree: A restriction of trees such that the maximum degree of a node is 2. Order of nodes is now relevant May have zero nodes (emtpy tree) Formal Definition:
Tree Data Structures CSC 221 Specialized Trees Binary Tree: A restriction of trees such that the maximum degree of a node is 2. Order of nodes is now relevant May have zero nodes (emtpy tree) Formal Definition:
Bioinformatics Programming. EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang)
 Bioinformatics Programming EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang) 1 Tree 2 A Tree Structure A tree structure means that the data are organized so that items of information are related by branches 3 Definition
Bioinformatics Programming EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang) 1 Tree 2 A Tree Structure A tree structure means that the data are organized so that items of information are related by branches 3 Definition
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
Trees. Introduction & Terminology. February 05, 2018 Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1
 Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Binary Trees. Height 1
 Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
Lecture 32. No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions?
 Lecture 32 No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions? Friday, April 1 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 32 1 Outline Introduction
Lecture 32 No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions? Friday, April 1 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 32 1 Outline Introduction
A set of nodes (or vertices) with a single starting point
 Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Principles of Computer Science
 Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) Course 9 Lists / Graphs / Trees. Iulian Năstac
 Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) Course 9 Lists / Graphs / Trees Iulian Năstac Recapitulation It is considered the following type: typedef struct nod { ; struct nod *next; } NOD; 2 Circular
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) Course 9 Lists / Graphs / Trees Iulian Năstac Recapitulation It is considered the following type: typedef struct nod { ; struct nod *next; } NOD; 2 Circular
Topic Binary Trees (Non-Linear Data Structures)
 Topic Binary Trees (Non-Linear Data Structures) CIS210 1 Linear Data Structures Arrays Linked lists Skip lists Self-organizing lists CIS210 2 Non-Linear Data Structures Hierarchical representation? Trees
Topic Binary Trees (Non-Linear Data Structures) CIS210 1 Linear Data Structures Arrays Linked lists Skip lists Self-organizing lists CIS210 2 Non-Linear Data Structures Hierarchical representation? Trees
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
Binary Tree. Binary tree terminology. Binary tree terminology Definition and Applications of Binary Trees
 Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
COMP : Trees. COMP20012 Trees 219
 COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
8. Binary Search Tree
 8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson
 Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By
 CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Tree Structures. A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node
 Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Uses for Trees About Trees Binary Trees. Trees. Seth Long. January 31, 2010
 Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Module 04 Trees Contents
 Module 04 Trees Contents Chethan Raj C Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE 1. Trees Terminology 2. Binary Trees, Properties of Binary trees 3. Array and linked Representation of Binary Trees 4. Binary Tree
Module 04 Trees Contents Chethan Raj C Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE 1. Trees Terminology 2. Binary Trees, Properties of Binary trees 3. Array and linked Representation of Binary Trees 4. Binary Tree
Binary Tree. Preview. Binary Tree. Binary Tree. Binary Search Tree 10/2/2017. Binary Tree
 0/2/ Preview Binary Tree Tree Binary Tree Property functions In-order walk Pre-order walk Post-order walk Search Tree Insert an element to the Tree Delete an element form the Tree A binary tree is a tree
0/2/ Preview Binary Tree Tree Binary Tree Property functions In-order walk Pre-order walk Post-order walk Search Tree Insert an element to the Tree Delete an element form the Tree A binary tree is a tree
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
Trees 11/15/16. Chapter 11. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Outline. Preliminaries. Binary Trees Binary Search Trees. What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications
 Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree
![[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree [ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree](/thumbs/80/82537139.jpg) [ DATA STRUCTURES ] Chapter - 07 : Trees A Tree is a non-linear data structure in which items are arranged in a sorted sequence. It is used to represent hierarchical relationship existing amongst several
[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Chapter - 07 : Trees A Tree is a non-linear data structure in which items are arranged in a sorted sequence. It is used to represent hierarchical relationship existing amongst several
Lec 17 April 8. Topics: binary Trees expression trees. (Chapter 5 of text)
 Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Laboratory Module Trees
 Purpose: understand the notion of 2-3 trees to build, in C, a 2-3 tree 1 2-3 Trees 1.1 General Presentation Laboratory Module 7 2-3 Trees 2-3 Trees represent a the simplest type of multiway trees trees
Purpose: understand the notion of 2-3 trees to build, in C, a 2-3 tree 1 2-3 Trees 1.1 General Presentation Laboratory Module 7 2-3 Trees 2-3 Trees represent a the simplest type of multiway trees trees
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
Data Structure. IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017
 Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
CMPT 225. Binary Search Trees
 CMPT 225 Binary Search Trees Trees A set of nodes with a single starting point called the root Each node is connected by an edge to some other node A tree is a connected graph There is a path to every
CMPT 225 Binary Search Trees Trees A set of nodes with a single starting point called the root Each node is connected by an edge to some other node A tree is a connected graph There is a path to every
Successor/Predecessor Rules in Binary Trees
 Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Trees
 Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Advanced Set Representation Methods
 Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Why Do We Need Trees?
 CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))
![8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F)) 8. Write an example for expression tree. [A/M 10] (A+B)*((C-D)/(E^F))](/thumbs/89/97773603.jpg) DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT IV NONLINEAR DATA STRUCTURES Part A 1. Define Tree [N/D 08]
Operations on Heap Tree The major operations required to be performed on a heap tree are Insertion, Deletion, and Merging.
 Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington
 Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington 1 Trees Trees are a natural data structure for representing specific data. Family trees. Organizational
Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington 1 Trees Trees are a natural data structure for representing specific data. Family trees. Organizational
Data Structure. Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang. National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan
 Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2010 Spring Threaded Binary Tree Problem: There are more
Data Structure Chapter 5 Trees (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2010 Spring Threaded Binary Tree Problem: There are more
Chapter 4: Trees. 4.2 For node B :
 Chapter : Trees. (a) A. (b) G, H, I, L, M, and K.. For node B : (a) A. (b) D and E. (c) C. (d). (e).... There are N nodes. Each node has two pointers, so there are N pointers. Each node but the root has
Chapter : Trees. (a) A. (b) G, H, I, L, M, and K.. For node B : (a) A. (b) D and E. (c) C. (d). (e).... There are N nodes. Each node has two pointers, so there are N pointers. Each node but the root has
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees
 CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
Data Structures. Trees. By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini. M.A. Eljinini, PhD
 Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
Data Abstractions. National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 05/23/2012
 Data Abstractions National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 05/23/2012 Concept of Data Structures How do we store some conceptual structure in a linear memory? For example, an organization chart: 2/32
Data Abstractions National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 05/23/2012 Concept of Data Structures How do we store some conceptual structure in a linear memory? For example, an organization chart: 2/32
Binary Trees Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
BST Implementation. Data Structures. Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr University of Ain Shams
 Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees
 Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees The first part of this chapter takes a look at trees in general and unbalanced binary trees. The second part looks at various schemes to balance trees and/or make them more
Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees The first part of this chapter takes a look at trees in general and unbalanced binary trees. The second part looks at various schemes to balance trees and/or make them more
Search Trees. Data and File Structures Laboratory. DFS Lab (ISI) Search Trees 1 / 17
 Search Trees Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2017/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) Search Trees 1 / 17 Binary search trees. Definition. Binary tree in which following property
Search Trees Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2017/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) Search Trees 1 / 17 Binary search trees. Definition. Binary tree in which following property
Garbage Collection: recycling unused memory
 Outline backtracking garbage collection trees binary search trees tree traversal binary search tree algorithms: add, remove, traverse binary node class 1 Backtracking finding a path through a maze is an
Outline backtracking garbage collection trees binary search trees tree traversal binary search tree algorithms: add, remove, traverse binary node class 1 Backtracking finding a path through a maze is an
Tree Structures. Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest
 Tree Structures Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest o A tree is a connected digraph with these properties: There is exactly one node (Root)
Tree Structures Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest o A tree is a connected digraph with these properties: There is exactly one node (Root)
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 8/15 Hua Lu
 Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 8/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Trees Basics Rooted trees Binary trees Binary tree ADT Tree traversal
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 8/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Trees Basics Rooted trees Binary trees Binary tree ADT Tree traversal
CISC 235 Topic 3. General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
EE 368. Weeks 5 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 5 (Notes) 1 Chapter 5: Trees Skip pages 273-281, Section 5.6 - If A is the root of a tree and B is the root of a subtree of that tree, then A is B s parent (or father or mother) and B is A
EE 368 Weeks 5 (Notes) 1 Chapter 5: Trees Skip pages 273-281, Section 5.6 - If A is the root of a tree and B is the root of a subtree of that tree, then A is B s parent (or father or mother) and B is A
CSI 402 Spring 2014 Programming Assignment I 1 / 15
 CSI 402 Spring 2014 Programming Assignment I 1 / 15 Administrative Information Deadline: 11 PM, Friday, Feb. 14, 2014. Cutoff: 11 PM, Sunday, Feb. 16, 2014. The program must have three or more C source
CSI 402 Spring 2014 Programming Assignment I 1 / 15 Administrative Information Deadline: 11 PM, Friday, Feb. 14, 2014. Cutoff: 11 PM, Sunday, Feb. 16, 2014. The program must have three or more C source
An undirected graph is a tree if and only of there is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices.
 Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
binary tree empty root subtrees Node Children Edge Parent Ancestor Descendant Path Depth Height Level Leaf Node Internal Node Subtree
 Binary Trees A binary tree is made up of a finite set of nodes that is either empty or consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left and right subtrees which are disjoint
Binary Trees A binary tree is made up of a finite set of nodes that is either empty or consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left and right subtrees which are disjoint
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections
 Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree is an instance of a particular type (e.g. binary, and later heap, etc.) Describe
Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree is an instance of a particular type (e.g. binary, and later heap, etc.) Describe
Binary Trees. College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University. CPCS-204 Data Structures I
 Binary Trees College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Outline Tree Stuff Trees Binary Trees Implementation of a Binary Tree Tree Traversals Depth
Binary Trees College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Outline Tree Stuff Trees Binary Trees Implementation of a Binary Tree Tree Traversals Depth
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree
 CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
CMSC 341 Leftist Heaps
 CMSC 341 Leftist Heaps Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Review of Min Heaps Introduction of Left-ist Heaps Merge Operation Heap Operations Review of Heaps Min Binary
CMSC 341 Leftist Heaps Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Review of Min Heaps Introduction of Left-ist Heaps Merge Operation Heap Operations Review of Heaps Min Binary
Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Organizing Spatial Data
 Organizing Spatial Data Spatial data records include a sense of location as an attribute. Typically location is represented by coordinate data (in 2D or 3D). 1 If we are to search spatial data using the
Organizing Spatial Data Spatial data records include a sense of location as an attribute. Typically location is represented by coordinate data (in 2D or 3D). 1 If we are to search spatial data using the
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
Trees CONTENTS. Hours: 8. Marks: 12. Anuradha Bhatia 1
 Trees CONTENTS 6.1 Introduction 1. Terminologies: tree,degree of a node, degree of a tree, level of a node, leaf node, Depth / Height of a tree, In-degree & out- Degree, Directed edge, Path, Ancestor &
Trees CONTENTS 6.1 Introduction 1. Terminologies: tree,degree of a node, degree of a tree, level of a node, leaf node, Depth / Height of a tree, In-degree & out- Degree, Directed edge, Path, Ancestor &
Tree traversals and binary trees
 Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Concept Question
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
11 TREES DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IMPLEMENTATION & APPLICATIONS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS 11 TREES IMPLEMENTATION & APPLICATIONS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM LECTURES ADAPTED FROM: DANIEL KANE, NEIL RHODES DEPARTMENT
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS 11 TREES IMPLEMENTATION & APPLICATIONS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM LECTURES ADAPTED FROM: DANIEL KANE, NEIL RHODES DEPARTMENT
Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees.
 Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees. Chapter 6 Definition of graphs (I) A directed graph or digraph is a pair G = (V,E) s.t.: V is a finite set called the set of vertices of G. E V
Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees. Chapter 6 Definition of graphs (I) A directed graph or digraph is a pair G = (V,E) s.t.: V is a finite set called the set of vertices of G. E V
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections. 2501ICT Logan
 Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Logan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Queues and Stacks Queues and Stacks
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Logan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Queues and Stacks Queues and Stacks
Introduction to Binary Trees
 Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees
 COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Data Structure and Algorithm Homework #3 Due: 2:20pm, Tuesday, April 9, 2013 TA === Homework submission instructions ===
 Data Structure and Algorithm Homework #3 Due: 2:20pm, Tuesday, April 9, 2013 TA email: dsa1@csientuedutw === Homework submission instructions === For Problem 1, submit your source code, a Makefile to compile
Data Structure and Algorithm Homework #3 Due: 2:20pm, Tuesday, April 9, 2013 TA email: dsa1@csientuedutw === Homework submission instructions === For Problem 1, submit your source code, a Makefile to compile
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms and Data Structures CS-CO-412
 Algorithms and Data Structures CS-CO-412 David Vernon Professor of Informatics University of Skövde Sweden david@vernon.eu www.vernon.eu Algorithms and Data Structures 1 Copyright D. Vernon 2014 Trees
Algorithms and Data Structures CS-CO-412 David Vernon Professor of Informatics University of Skövde Sweden david@vernon.eu www.vernon.eu Algorithms and Data Structures 1 Copyright D. Vernon 2014 Trees
CHAPTER 5. Trees CHAPTER 5 1/70
 CHAPTER 5 Trees All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C /2nd Edition, Silicon Press, 2008. CHAPTER 5
CHAPTER 5 Trees All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C /2nd Edition, Silicon Press, 2008. CHAPTER 5
Tree Travsersals and BST Iterators
 Tree Travsersals and BST Iterators PIC 10B May 25, 2016 PIC 10B Tree Travsersals and BST Iterators May 25, 2016 1 / 17 Overview of Lecture 1 Sorting a BST 2 In-Order Travsersal 3 Pre-Order Traversal 4
Tree Travsersals and BST Iterators PIC 10B May 25, 2016 PIC 10B Tree Travsersals and BST Iterators May 25, 2016 1 / 17 Overview of Lecture 1 Sorting a BST 2 In-Order Travsersal 3 Pre-Order Traversal 4
We have the pointers reference the next node in an inorder traversal; called threads
 Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Threaded Binary Tree Introduction: Threaded Binary Tree is also a binary tree in which all left child pointers that are NULL (in Linked
Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Threaded Binary Tree Introduction: Threaded Binary Tree is also a binary tree in which all left child pointers that are NULL (in Linked
Module 6: Binary Trees
 Module : Binary Trees Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 327 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Tree All the data structures we have seen
Module : Binary Trees Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 327 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Tree All the data structures we have seen
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
