NETWORK AND SYSTEM PROGRAMMING. I/O Multiplexing: select and poll function
|
|
|
- Baldwin Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NETWORK AND SYSTEM PROGRAMMING LAB 15 I/O Multiplexing: select and poll function 15.1 objectives What is a Concurrent server Use of Select System call Use of Poll System call 15.2 What is concurrent server? A server that can handle multiple clients at the same time is called concurrent server. It s necessary and very common to have single server that can serve multiple clients at the same time Select System call One traditional way to write network servers is to have the main server block on accept(), waiting for a connection. Once a connection comes in, the server fork()s, the child process handles the connection and the main server is able to service new incoming requests. With select(), instead of having a process for each request, there is usually only one process that "multi-plexes" all requests, servicing each request as much as it can. So one main advantage of using select() is that your server will only require a single process to handle all requests. Thus, your server will not need shared memory or synchronization primitives for different 'tasks' to communicate. int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
2 File Descriptors- readfds, writefds, exceptfds: Three independent sets of file descriptors are watched. Those listed in readfds will be watched to see if characters become available for reading (more precisely, to see if a read will not block; in particular, a file descriptor is also ready on end-of-file), those in writefds will be watched to see if a write will not block, and those in exceptfds will be watched for exceptions. On exit, the sets are modified in place to indicate which file descriptors actually changed status. Each of the three file descriptor sets may be specified as NULL if no file descriptors are to be watched for the corresponding class of events. nfds is the highest-numbered file descriptor in any of the three sets, plus 1. timeout is an upper bound on the amount of time elapsed before select() returns. If both fields of the timeval structure are zero, then select() returns immediately. (This is useful for polling.) If timeout is NULL (no timeout), select() can block indefinitely. Four macros are provided to manipulate the sets. void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set); FD_ZERO() clears a set. void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set); FD_SET() add a given file descriptor from a set. int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set); FD_ISSET() tests to see if a file descriptor is part of the set. This is useful after select() returns. void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set); FD_CLR() remove a given file descriptor from a set.
3 Example select() Concurrent Server: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/select.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <fcntl.h> #define MAXLINE 100 #define SERV_PORT int main(int argc, char **argv) int k, i, maxi, maxfd, listenfd, connfd, sockfd; int nready, client[fd_setsize]; ssize_t n; fd_set rset, allset; char line[maxline],buf[100]; socklen_t clilen; struct sockaddr_in cliaddr, servaddr; listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (listenfd < 0 ) perror("socket" ); exit(1); bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(inaddr_any); servaddr.sin_port = htons(serv_port); bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); listen(listenfd,5); maxfd = listenfd; /* initialize */ maxi = -1; /* index into client[] array */ for (i = 0; i < FD_SETSIZE; i++) client[i] = -1; /* -1 indicates available entry */ FD_ZERO(&allset); FD_SET(listenfd, &allset); /* end fig01 */
4 /* include fig02 */ for ( ; ; ) printf("server:i am waiting-----start of Main Loop\n"); rset = allset; /* structure assignment */ nready = select(maxfd+1, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL); if (FD_SET(listenfd, &rset)) /* new client connection */ clilen = sizeof(cliaddr); connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &cliaddr, &clilen); #ifdef NOTDEF printf("new client: %s, port %d\n", inet_ntop(af_inet, &cliaddr.sin_addr, buf, NULL), ntohs(cliaddr.sin_port)); #endif for (i = 0; i < FD_SETSIZE; i++) if (client[i] < 0) client[i] = connfd; /* save descriptor */ break; if (i == FD_SETSIZE) printf("too many clients"); exit(0); // FD_SET(connfd, &allset); /* add new descriptor to set */ if (connfd > maxfd) maxfd = connfd; /* for select */ if (i > maxi) maxi = i; /* max index in client[] array */ if (--nready <= 0) continue; /* no more readable descriptors */ for (i = 0; i <= maxi; i++) /* check all clients for data */ if ( (sockfd = client[i]) < 0) continue; // if (FD_ISSET(sockfd, &rset)) if ( (n = read(sockfd, line, MAXLINE)) == 0) /*4connection closed by client */ close(sockfd); FD_CLR(??); client[i] = -1; /* end fig02 */
5 /* include fig03 */ else printf("\n output at server\n"); for(k=0;line[k]!='\0';k++) printf("%c",toupper(line[k])); write(sockfd, line, n); if (--nready <= 0) break; /* no more readable descriptors */ /* end fig03 */ Program 15-1: Concurrent Server using Select() TASK 1: Compile and execute Program 15-1 as server and Program 15-2 as client. Remove the errors and find what is actually happening at server side.
6 Client Code: /* include fig01 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <fcntl.h> #define MAXBUFFER 1024 void sendstring(int, char *); int main( int C, char *V[] ) int sd,fd; char c; struct sockaddr_in serveraddress; char text[100]; int i=0; sd = socket( AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 ); if( sd < 0 ) perror( "socket" ); exit( 1 ); if (V[1] == NULL ) printf ("specify the server's IP Address \n"); exit(0); if (V[2] == NULL ) printf ("specify the server's Port No \n"); exit(0); memset( &serveraddress, 0, sizeof(serveraddress) ); serveraddress.sin_family = AF_INET; serveraddress.sin_port = htons(atoi(v[2]));//port NO serveraddress.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(v[1]);//address /* end fig01 */
7 /* include fig02 */ if (connect(sd,(struct sockaddr*)&serveraddress, sizeof(serveraddress))<0) printf("cannot Connect to server"); exit(1); printf("enter sentence to end enter #"); while(1) c=getchar(); if(c=='#') break; text[i++]=c; text[i]='\0'; sendstring(sd,text); close(sd); return 0; /*********************************************************************** * FUNCTION NAME:sendstring * DESCRIPTION: sends a string over the socket. * NOTES : No Error Checking is done. * RETURNS :void ***********************************************************************/ void sendstring( int sd, /*Socket Descriptor*/ char *fname) /*Array Containing the string */ /********************************************************************/ int n, byteswritten=0, written ; char buffer[maxbuffer]; strcpy(buffer, fname); n=strlen(buffer); while (byteswritten<n) written=write(sd, buffer+byteswritten,(n-byteswritten)); byteswritten+=written; printf("string : %s sent to server \n",buffer); /* end fig02 */ Program 15-2: Client Code
8 15.4 Poll System Call: #include <poll.h> int poll(struct pollfd fds[], nfds_t nfds, int timeout); struct pollfd int fd; /* descriptor to check */ short events; /* events of interest on fd */ short revents; /* events that occurred on fd */ ; The poll() function provides applications with a mechanism for multiplexing input/output over a set of file descriptors. For each member of the array pointed to by fds, poll() shall examine the given file descriptor for the event(s) specified in events. The number of pollfd structures in the fds array is specified by nfds. The poll() function shall identify those file descriptors on which an application can read or write data, or on which certain events have occurred. The fds argument specifies the file descriptors to be examined and the events of interest for each file descriptor. It is a pointer to an array with one member for each open file descriptor of interest. The array's members are pollfd structures within which fd specifies an open file descriptor and events and revents are bitmasks constructed by OR'ing a combination of the following event flags:
9 In each pollfd structure, poll() shall clear the revents member, except that where the application requested a report on a condition by setting one of the bits of events listed above, poll() shall set the corresponding bit in revents if the requested condition is true. In addition, poll() shall set the POLLHUP, POLLERR, and POLLNVAL flag in revents if the condition is true, even if the application did not set the corresponding bit in events. If none of the defined events have occurred on any selected file descriptor, poll() shall wait at least timeout milliseconds for an event to occur on any of the selected file descriptors. If the value of timeout is 0, poll() shall return immediately. If the value of timeout is -1, poll() shall block until a requested event occurs or until the call is interrupted. The poll() function shall not be affected by the O_NONBLOCK flag. The poll() function shall support regular files, terminal and pseudo-terminal devices, FIFOs, pipes, sockets and STREAMS-based files. The behavior of poll() on elements of fds that refer to other types of file is unspecified. Regular files shall always poll TRUE for reading and writing. A file descriptor for a socket that is listening for connections shall indicate that it is ready for reading, once connections are available. A file descriptor for a socket that is connecting asynchronously shall indicate that it is ready for writing, once a connection has been established.
10 Example Poll(): #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <limits.h> /* for OPEN_MAX */ #include <errno.h> #define MAXLINE 100 //#define POLLRDNORM 5 #define INFTIM 5 #define OPEN_MAX 5 int main(int argc, char **argv) int k, i, maxi, listenfd, connfd, sockfd; int nready; ssize_t n; char line[maxline]; socklen_t clilen; struct pollfd client[open_max]; struct sockaddr_in cliaddr, servaddr; listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(inaddr_any); servaddr.sin_port = htons(serv_port); bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); listen(listenfd, 5); //31 client[0].fd = listenfd; //client[0].events = POLLRDNORM; for (i = 1; i < OPEN_MAX; i++) client[i].fd = -1; /* -1 indicates available entry */ maxi = 0; /* max index into client[] array */ /* end fig01 */
11 /* include fig02 */ for ( ; ; ) nready = poll(??, maxi+1, INFTIM); if (client[0].revents & POLLRDNORM) /* new client connection */ clilen = sizeof(cliaddr); connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &cliaddr, &clilen); #ifdef NOTDEF printf("new client: %s\n", sock_ntop((struct sockaddr *) &cliaddr, clilen)); #endif for (i = 1; i < OPEN_MAX; i++) if (client[i].fd < 0) client[i].fd = connfd; /* save descriptor */ break; if (i == OPEN_MAX) printf("too many clients"); exit(0); // client[i].events = POLLRDNORM; if (i > maxi) maxi = i; /* max index in client[] array */ */ if (--nready <= 0) continue; /* no more readable descriptors for (i = 1; i <= maxi; i++) /* check all clients for data */ if ( (sockfd = client[i].fd) < 0) continue; if (client[i].revents & (POLLRDNORM POLLERR)) if ( (n = read(sockfd, line, MAXLINE)) < 0) if (errno == ECONNRESET) /*4connection reset by client */ #ifdef NOTDEF printf("client[%d] aborted connection\n", i); #endif /* end fig02 */
12 /* include fig03 */ close(sockfd); client[i].fd = -1; else printf("readline error"); else if (n == 0) /*4connection closed by client */ #ifdef NOTDEF printf("client[%d] closed connection\n", i); #endif close(sockfd); client[i].fd = -1; else printf("\n data from client is \n"); k=strlen(line); printf(" length=%d data = %s\n", k,line); //write(sockfd, line, n); strcpy(line," "); if (--nready <= 0) break; /* no more readable descriptors */ /* end fig03 */ Program 15-3: I/O Multiplexing using Poll() TASK 2: Compile and execute Program 15-3 as server and Program 15-2 as client. Remove the errors and find what is actually happening at server side.
CONCURRENCY MODEL. UNIX Programming 2014 Fall by Euiseong Seo
 CONCURRENCY MODEL UNIX Programming 2014 Fall by Euiseong Seo Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero((char *)&saddr, sizeof(saddr));
CONCURRENCY MODEL UNIX Programming 2014 Fall by Euiseong Seo Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero((char *)&saddr, sizeof(saddr));
Introduction to Client-Server Model
 Preview Introduction to Client-Server Model Motivation of Client-Server Model Terminologies and Concepts in Client-Server Model Connectionless vs. Connection-Oriented Stateless vs. Stateful Server Identify
Preview Introduction to Client-Server Model Motivation of Client-Server Model Terminologies and Concepts in Client-Server Model Connectionless vs. Connection-Oriented Stateless vs. Stateful Server Identify
Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing
 Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing Στοεργαστήριοθαμελετηθούν: Server High Level View I/O Multiplexing Solutions for Concurrency nonblocking I/O Use alarm and signal handler to interrupt slow system calls. Use
Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing Στοεργαστήριοθαμελετηθούν: Server High Level View I/O Multiplexing Solutions for Concurrency nonblocking I/O Use alarm and signal handler to interrupt slow system calls. Use
CSC209H Lecture 10. Dan Zingaro. March 18, 2015
 CSC209H Lecture 10 Dan Zingaro March 18, 2015 Creating a Client To create a client that can connect to a server, call the following, in order: socket: create a communication endpoint This is the same as
CSC209H Lecture 10 Dan Zingaro March 18, 2015 Creating a Client To create a client that can connect to a server, call the following, in order: socket: create a communication endpoint This is the same as
I/O Models. Kartik Gopalan
 I/O Models Kartik Gopalan Types of Concurrency True Concurrency (multiple processes or threads) Multi-processor machines Child processes/threads execute in parallel. Multi-process (forking) servers If
I/O Models Kartik Gopalan Types of Concurrency True Concurrency (multiple processes or threads) Multi-processor machines Child processes/threads execute in parallel. Multi-process (forking) servers If
call connect call read call connect ret connect call fgets Client 2 blocks waiting to complete its connection request until after lunch!
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers December 4, 2001 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers December 4, 2001 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent
Unix Network Programming Chapter 4. Elementary TCP Sockets 광운대학교컴퓨터과학과 정보통신연구실 석사과정안중현
 Unix Network Programming Chapter 4. Elementary TCP Sockets 광운대학교컴퓨터과학과 정보통신연구실 석사과정안중현 4.1 Introduction A Time line of the typical scenario that takes place between a TCP client and server. Describes the
Unix Network Programming Chapter 4. Elementary TCP Sockets 광운대학교컴퓨터과학과 정보통신연구실 석사과정안중현 4.1 Introduction A Time line of the typical scenario that takes place between a TCP client and server. Describes the
Concurrent Programming. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Concurrent Programming Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet,
Concurrent Programming Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet,
Sockets. Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University Embedded Software Lab.
 1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Echo Client (1) 2 #include #include #include #include
1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Echo Client (1) 2 #include #include #include #include
Piotr Mielecki Ph. D.
 Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://mielecki.ristel.pl/ piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Building blocks of client-server applications: Client, Server, Middleware. Simple client-server application:
Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://mielecki.ristel.pl/ piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Building blocks of client-server applications: Client, Server, Middleware. Simple client-server application:
UNIT IV - SOCKET OPTIONS, ELEMENTARY UDP SOCKETS
 UNIT IV - SOCKET OPTIONS, ELEMENTARY UDP SOCKETS Socket options getsocket and setsocket functions generic socket options IP socket options ICMP socket options TCP socket options Elementary UDP sockets
UNIT IV - SOCKET OPTIONS, ELEMENTARY UDP SOCKETS Socket options getsocket and setsocket functions generic socket options IP socket options ICMP socket options TCP socket options Elementary UDP sockets
UNIT III - APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT. TCP Echo Server
 UNIT III - APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT TCP Echo Server TCP Echo Client Posix Signal handling Server with multiple clients boundary conditions: Server process Crashes, Server host Crashes, Server Crashes and
UNIT III - APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT TCP Echo Server TCP Echo Client Posix Signal handling Server with multiple clients boundary conditions: Server process Crashes, Server host Crashes, Server Crashes and
Inter-Process Communication. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1
 Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
/* * porting from BSD to SVR4 */ #ifdef USE_BSD # include <machine/param.h> #endif
 * This is a free program sample that may be reproduced in any form. * The author's information should be retained to preserve its identity. * * Date written: January 1, 2002 * Written by: Peraphon Sophatsathit
* This is a free program sample that may be reproduced in any form. * The author's information should be retained to preserve its identity. * * Date written: January 1, 2002 * Written by: Peraphon Sophatsathit
Sockets. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Sockets Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Internet Connections (1) Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of
Sockets Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Internet Connections (1) Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of
CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING. Lecture 5
 CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING Lecture 5 Last lecture TCP I/O RIO: buffered I/O. Unix IO Question: difference between send() and write()? MSG_DONTWAIT, MSG_NOSIGNAL 2 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human
CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING Lecture 5 Last lecture TCP I/O RIO: buffered I/O. Unix IO Question: difference between send() and write()? MSG_DONTWAIT, MSG_NOSIGNAL 2 Concurrent Programming is Hard! The human
Hyo-bong Son Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Sockets Hyo-bong Son (proshb@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Client-Server Model Most network application is based on the client-server model: A server
Sockets Hyo-bong Son (proshb@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Client-Server Model Most network application is based on the client-server model: A server
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering. Spring 2018
 ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Inter-process Communication (IPC) Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Recall Process vs. Thread A process is
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Inter-process Communication (IPC) Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Recall Process vs. Thread A process is
The BSD UNIX Socket Interface (CS 640 Lecture) Assignment 1. Interprocess Communication (IPC) Work Individually (no groups)
 The BSD UNIX Socket Interface (CS 640 Lecture) Assignment 1 Work Individually (no groups) Due Date: in class, Monday, September 19 Robert T Olsen olsen@cswiscedu 7390CS Office Hours: 3-5T, 11-12F - exception
The BSD UNIX Socket Interface (CS 640 Lecture) Assignment 1 Work Individually (no groups) Due Date: in class, Monday, September 19 Robert T Olsen olsen@cswiscedu 7390CS Office Hours: 3-5T, 11-12F - exception
PA #2 Reviews. set_name, get_name, del_name. Questions? Will be modified after PA #4 ~
 Sockets Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Dong-Yun Lee(dylee@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu PA #2 Reviews set_name, get_name, del_name Will
Sockets Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Dong-Yun Lee(dylee@csl.skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu PA #2 Reviews set_name, get_name, del_name Will
Network Programming in C: The Berkeley Sockets API. Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions
 Network Programming in C: The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available
Network Programming in C: The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available
CS307 Operating Systems Processes
 CS307 Processes Fan Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Spring 2018 Process Concept Process a program in execution An operating system executes a variety of
CS307 Processes Fan Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Spring 2018 Process Concept Process a program in execution An operating system executes a variety of
Processes. Process Concept. The Process. The Process (Cont.) Process Control Block (PCB) Process State
 CS307 Process Concept Process a program in execution Processes An operating system executes a variety of programs: Batch system jobs Time-shared systems user programs or tasks All these activities are
CS307 Process Concept Process a program in execution Processes An operating system executes a variety of programs: Batch system jobs Time-shared systems user programs or tasks All these activities are
Lecture 3 Overview! Last Lecture! TCP/UDP and Sockets introduction!
 Lecture 3 Overview! Last Lecture! TCP/UDP and Sockets introduction! This Lecture! Elementary TCP sockets! TCP Client-Server example! Source: Stevens book(chapters 4,5), Comer s book (Chapters 20, 21)!
Lecture 3 Overview! Last Lecture! TCP/UDP and Sockets introduction! This Lecture! Elementary TCP sockets! TCP Client-Server example! Source: Stevens book(chapters 4,5), Comer s book (Chapters 20, 21)!
Semester 2, Computer Communication 352 Module 4
 Page 4.1; CRICOS Number: 00301J MODULE 4 References: 1. Stevens, Fenner, Rudoff, UNIX Network Programming, vol. 1, Chapter 5. OBJECTIVE Provide detail description on TCP Client-Server Example. Discuss
Page 4.1; CRICOS Number: 00301J MODULE 4 References: 1. Stevens, Fenner, Rudoff, UNIX Network Programming, vol. 1, Chapter 5. OBJECTIVE Provide detail description on TCP Client-Server Example. Discuss
Network Programming Worksheet 2. Simple TCP Clients and Servers on *nix with C.
 Simple TCP Clients and Servers on *nix with C. Aims. This worksheet introduces a simple client and a simple server to experiment with a daytime service. It shows how telnet can be used to test the server.
Simple TCP Clients and Servers on *nix with C. Aims. This worksheet introduces a simple client and a simple server to experiment with a daytime service. It shows how telnet can be used to test the server.
Concurrent Servers Dec 2, 2009"
 Concurrent Servers Dec 2, 2009" Administrivia" 2! Iterative Servers" client 1! server! client 2! call connect ret connect call read ret read close call accept" ret accept" write close call accept" ret
Concurrent Servers Dec 2, 2009" Administrivia" 2! Iterative Servers" client 1! server! client 2! call connect ret connect call read ret read close call accept" ret accept" write close call accept" ret
Any of the descriptors in the set {1, 4} have an exception condition pending
 Page 1 of 6 6.3 select Function This function allows the process to instruct the kernel to wait for any one of multiple events to occur and to wake up the process only when one or more of these events
Page 1 of 6 6.3 select Function This function allows the process to instruct the kernel to wait for any one of multiple events to occur and to wake up the process only when one or more of these events
socketservertcl a Tcl extension for using SCM_RIGHTS By Shannon Noe - FlightAware
 socketservertcl a Tcl extension for using SCM_RIGHTS By Shannon Noe - FlightAware Presented at the 24th annual Tcl/Tk conference, Houston Texas, October 2017 Abstract: Horizontal scaling is used to distribute
socketservertcl a Tcl extension for using SCM_RIGHTS By Shannon Noe - FlightAware Presented at the 24th annual Tcl/Tk conference, Houston Texas, October 2017 Abstract: Horizontal scaling is used to distribute
Review. Preview. Closing a TCP Connection. Closing a TCP Connection. Port Numbers 11/27/2017. Packet Exchange for TCP Connection
 Review Preview Algorithms and Issues in Client Software Design Client Architecture Identifying the Location of a Parsing an Address Argument Looking Up a Domain Name Looking Up a Well-Known Port by Name
Review Preview Algorithms and Issues in Client Software Design Client Architecture Identifying the Location of a Parsing an Address Argument Looking Up a Domain Name Looking Up a Well-Known Port by Name
CSCE 313 Introduction to Computer Systems. Instructor: Dezhen Song
 CSCE 313 Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Dezhen Song UNIX I/O Files and File Representation Basic operations: Reading / Writing Caching: File Open / Close Multiplexing: Select / Poll File
CSCE 313 Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Dezhen Song UNIX I/O Files and File Representation Basic operations: Reading / Writing Caching: File Open / Close Multiplexing: Select / Poll File
MSc Integrated Electronics Networks Assignment. Investigation of TCP/IP Sockets and Ports. Gavin Cameron
 MSc Integrated Electronics Networks Assignment Investigation of TCP/IP Sockets and Ports Gavin Cameron Introduction TCP and IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) are two protocols from
MSc Integrated Electronics Networks Assignment Investigation of TCP/IP Sockets and Ports Gavin Cameron Introduction TCP and IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) are two protocols from
UNIX Network Programming. Overview of Socket API Network Programming Basics
 UNIX Network Programming Overview of Socket API Network Programming Basics 1 Client-Server Model Client Machine A Network Server Machine B Web browser and server FTP client and server Telnet client and
UNIX Network Programming Overview of Socket API Network Programming Basics 1 Client-Server Model Client Machine A Network Server Machine B Web browser and server FTP client and server Telnet client and
ISA 563: Fundamentals of Systems Programming
 ISA 563: Fundamentals of Systems Programming Advanced IO April 9, 2012 Non-blocking IO Data processing can be much faster than data access Waiting for IO to finish can be time consuming, and may not even
ISA 563: Fundamentals of Systems Programming Advanced IO April 9, 2012 Non-blocking IO Data processing can be much faster than data access Waiting for IO to finish can be time consuming, and may not even
CISC2200 Threads Spring 2015
 CISC2200 Threads Spring 2015 Process We learn the concept of process A program in execution A process owns some resources A process executes a program => execution state, PC, We learn that bash creates
CISC2200 Threads Spring 2015 Process We learn the concept of process A program in execution A process owns some resources A process executes a program => execution state, PC, We learn that bash creates
9/13/2007. Motivations for Sockets What s in a Socket? Working g with Sockets Concurrent Network Applications Software Engineering for Project 1
 Daniel Spangenberger 15 441 Computer Networks, Fall 2007 Goal of Networking: Communication Share data Pass Messages Say I want to talk to a friend in Singapore How can I do this? What applications and
Daniel Spangenberger 15 441 Computer Networks, Fall 2007 Goal of Networking: Communication Share data Pass Messages Say I want to talk to a friend in Singapore How can I do this? What applications and
COMP/ELEC 429/556 Introduction to Computer Networks
 COMP/ELEC 429/556 Introduction to Computer Networks Creating a Network Application Some slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang 1 How to Programmatically
COMP/ELEC 429/556 Introduction to Computer Networks Creating a Network Application Some slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang 1 How to Programmatically
The Berkeley Sockets API. Networked Systems Architecture 3 Lecture 4
 The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems Architecture 3 Lecture 4 The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available on most platforms: Linux,
The Berkeley Sockets API Networked Systems Architecture 3 Lecture 4 The Berkeley Sockets API Widely used low-level C networking API First introduced in 4.3BSD Unix Now available on most platforms: Linux,
Three Basic Mechanisms for Creating Concurrent Flows. Systemprogrammering 2009 Föreläsning 10 Concurrent Servers. Process-Based Concurrent Server
 Systemprogrammering 2009 Föreläsning 10 Concurrent Servers Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent servers Three
Systemprogrammering 2009 Föreläsning 10 Concurrent Servers Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent servers Three
CS321: Computer Networks Socket Programming
 CS321: Computer Networks Socket Programming Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Socket Programming It shows how the network application programs
CS321: Computer Networks Socket Programming Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Socket Programming It shows how the network application programs
Network programming(ii) Lenuta Alboaie
 Network programming(ii) Lenuta Alboaie adria@info.uaic.ro 1 Content let s remember: iterative TCP client/server UDP client/server model I/O primitives Advanced programming aspects in Internet socket API
Network programming(ii) Lenuta Alboaie adria@info.uaic.ro 1 Content let s remember: iterative TCP client/server UDP client/server model I/O primitives Advanced programming aspects in Internet socket API
04 Elementary. Client/Server. CEN 463 Network Programming. Dr. Mostafa Hassan Dahshan. King Saud University
 CEN 463 Network Programming 04 Elementary TCP Sockets Dr. Mostafa Hassan Dahshan College of Computer and Information Sciences King Saud University Elementary TCP Client/Server 2 socket Function First function
CEN 463 Network Programming 04 Elementary TCP Sockets Dr. Mostafa Hassan Dahshan College of Computer and Information Sciences King Saud University Elementary TCP Client/Server 2 socket Function First function
CS 3516: Computer Networks
 Welcome to CS 3516: Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: AK219 Fall 2018 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook Computer Networking: A Top
Welcome to CS 3516: Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: AK219 Fall 2018 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook Computer Networking: A Top
chat.h #ifndef _CHAT_H #define _CHAT_H #define LBUFFSIZE 128 #define CBUFFSIZE 331
 chat.h #ifndef _CHAT_H #define _CHAT_H #define LBUFFSIZE 128 #define CBUFFSIZE 331 #define INCRSLOT(V) { \ ++(V) ; \ if ((V) >= CBUFFSIZE) \ (V) = 0 ; \ enum Lstates {UNUSED, MESSAGE ; struct linebuff
chat.h #ifndef _CHAT_H #define _CHAT_H #define LBUFFSIZE 128 #define CBUFFSIZE 331 #define INCRSLOT(V) { \ ++(V) ; \ if ((V) >= CBUFFSIZE) \ (V) = 0 ; \ enum Lstates {UNUSED, MESSAGE ; struct linebuff
Group-A Assignment No. 6
 Group-A Assignment No. 6 R N Oral Total Dated Sign (2) (5) (3) (10) Title : File Transfer using TCP Socket Problem Definition: Use Python for Socket Programming to connect two or more PCs to share a text
Group-A Assignment No. 6 R N Oral Total Dated Sign (2) (5) (3) (10) Title : File Transfer using TCP Socket Problem Definition: Use Python for Socket Programming to connect two or more PCs to share a text
Announcement (1) Due date for PA3 is changed (~ next week) PA4 will also be started in the next class. Not submitted. Not scored
 Announcement (1) Due date for PA3 is changed (~ next week) PA4 will also be started in the next class Not submitted Not scored 1 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Sanghoon
Announcement (1) Due date for PA3 is changed (~ next week) PA4 will also be started in the next class Not submitted Not scored 1 Concurrent Programming Prof. Jin-Soo Kim( jinsookim@skku.edu) TA Sanghoon
Network Programming in C. Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions and Problem Sets
 Network Programming in C Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions and Problem Sets Lab Timetable, Aims, and Objectives Teaching Week Activity 14 Introduction 15 Warm-up exercise 16 17 Web client 18 19 20
Network Programming in C Networked Systems 3 Laboratory Sessions and Problem Sets Lab Timetable, Aims, and Objectives Teaching Week Activity 14 Introduction 15 Warm-up exercise 16 17 Web client 18 19 20
1 /* client.c - adapted from code for example client program that uses TCP */ 2 /*Modified by Vincent Chu, Winter
 1 /* client.c - adapted from code for example client program that uses TCP */ 2 /*Modified by Vincent Chu, Winter 2004. 3 http://www.sfu.ca/~vwchu 4 chuvincent (at) gmail (dot) com 5 */ 6 7 #define closesocket
1 /* client.c - adapted from code for example client program that uses TCP */ 2 /*Modified by Vincent Chu, Winter 2004. 3 http://www.sfu.ca/~vwchu 4 chuvincent (at) gmail (dot) com 5 */ 6 7 #define closesocket
CSC209H Lecture 9. Dan Zingaro. March 11, 2015
 CSC209H Lecture 9 Dan Zingaro March 11, 2015 Socket Programming (Kerrisk Ch 56, 57, 59) Pipes and signals are only useful for processes communicating on the same machine Sockets are a general interprocess
CSC209H Lecture 9 Dan Zingaro March 11, 2015 Socket Programming (Kerrisk Ch 56, 57, 59) Pipes and signals are only useful for processes communicating on the same machine Sockets are a general interprocess
A Socket Example. Haris Andrianakis & Angelos Stavrou George Mason University
 A Socket Example & George Mason University Everything is a file descriptor Most socket system calls operate on file descriptors Server - Quick view socket() bind() listen() accept() send(), recv() close()
A Socket Example & George Mason University Everything is a file descriptor Most socket system calls operate on file descriptors Server - Quick view socket() bind() listen() accept() send(), recv() close()
CS118 Discussion Week 2. Taqi
 CS118 Discussion Week 2 Taqi Outline Any Questions for Course Project 1? Socket Programming: Non-blocking mode Lecture Review: Application Layer Much of the other related stuff we will only discuss during
CS118 Discussion Week 2 Taqi Outline Any Questions for Course Project 1? Socket Programming: Non-blocking mode Lecture Review: Application Layer Much of the other related stuff we will only discuss during
Iterative Servers The course that gives CMU its Zip! Iterative servers process one request at a time. Concurrent Servers
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers Dec 3, 2002 Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Servers Dec 3, 2002 Topics! Limitations of iterative servers! Process-based concurrent servers! Event-based concurrent servers! Threads-based concurrent
Concurrent Programming April 21, 2005
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Programming April 21, 2005 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Concurrent Programming April 21, 2005 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent
Inter-Process Communication. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1
 Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
Inter-Process Communication Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 Today Inter-Process Communication (IPC) What is it? What IPC mechanisms are available? 2 Inter-Process
CS321: Computer Networks Introduction to Application Layer
 CS321: Computer Networks Introduction to Application Layer Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Basic Application layer provides services to the
CS321: Computer Networks Introduction to Application Layer Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Basic Application layer provides services to the
Concurrent Programming November 28, 2007
 15-213 Concurrent Programming November 28, 2007 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers class25.ppt Concurrent
15-213 Concurrent Programming November 28, 2007 Topics Limitations of iterative servers Process-based concurrent servers Event-based concurrent servers Threads-based concurrent servers class25.ppt Concurrent
More Network Programming
 More Network Programming More Network Programming HTTP push server Request framing and server push concepts Demo Useful API s select/poll and advanced sockets tidbits threads HTTP push server code Components
More Network Programming More Network Programming HTTP push server Request framing and server push concepts Demo Useful API s select/poll and advanced sockets tidbits threads HTTP push server code Components
NETWORK PROGRAMMING. Instructor: Junaid Tariq, Lecturer, Department of Computer Science
 NETWORK PROGRAMMING CSC- 341 25 Instructor: Junaid Tariq, Lecturer, Department of Computer Science 26 9 Lecture Sockets as means for inter-process communication (IPC) application layer Client Process Socket
NETWORK PROGRAMMING CSC- 341 25 Instructor: Junaid Tariq, Lecturer, Department of Computer Science 26 9 Lecture Sockets as means for inter-process communication (IPC) application layer Client Process Socket
A GENERALIZED FRAMEWORK FOR CATV TRANSMISSION ON FUTURE BISDN
 A GENERALIZED FRAMEWORK FOR CATV TRANSMISSION ON FUTURE BISDN Geng-Sheng (G.S.) Kuo Department of Information Management, National Central University Chung-Li, Taiwan 32054, R.O.C. TEL: +886 3 4263086
A GENERALIZED FRAMEWORK FOR CATV TRANSMISSION ON FUTURE BISDN Geng-Sheng (G.S.) Kuo Department of Information Management, National Central University Chung-Li, Taiwan 32054, R.O.C. TEL: +886 3 4263086
B TCP/IP programming
 308-435B TCP/IP programming Juan de Lara, Hans Vangheluwe McGill University Winter Term 2001 Resources 1 Request For Comments (RFC): 2 man pages: 3 books: structured overview TCP/IP related RFCs: http://wwwwebzonenet/machadospage/rfchtml
308-435B TCP/IP programming Juan de Lara, Hans Vangheluwe McGill University Winter Term 2001 Resources 1 Request For Comments (RFC): 2 man pages: 3 books: structured overview TCP/IP related RFCs: http://wwwwebzonenet/machadospage/rfchtml
Assignment 2 Group 5 Simon Gerber Systems Group Dept. Computer Science ETH Zurich - Switzerland
 Assignment 2 Group 5 Simon Gerber Systems Group Dept. Computer Science ETH Zurich - Switzerland t Your task Write a simple file server Client has to be implemented in Java Server has to be implemented
Assignment 2 Group 5 Simon Gerber Systems Group Dept. Computer Science ETH Zurich - Switzerland t Your task Write a simple file server Client has to be implemented in Java Server has to be implemented
Experiential Learning Workshop on Basics of Socket Programming
 Experiential Learning Workshop on Basics of Socket June 28, 2018 Dr. Ram P Rustagi Professor, CSE Dept KSIT, Bangalore rprustagi@ksit.edu.in Resources https://rprustagi.com/elnt/experiential- Learning.html
Experiential Learning Workshop on Basics of Socket June 28, 2018 Dr. Ram P Rustagi Professor, CSE Dept KSIT, Bangalore rprustagi@ksit.edu.in Resources https://rprustagi.com/elnt/experiential- Learning.html
Programming with TCP/IP. Ram Dantu
 1 Programming with TCP/IP Ram Dantu 2 Client Server Computing Although the Internet provides a basic communication service, the protocol software cannot initiate contact with, or accept contact from, a
1 Programming with TCP/IP Ram Dantu 2 Client Server Computing Although the Internet provides a basic communication service, the protocol software cannot initiate contact with, or accept contact from, a
Introduction to Socket Programming
 Introduction to Socket Programming (Advanced Computer Networks) By Priyank Shah NET ID : pss160530 A Simple Question What are Sockets? Sockets are communication points on the same or different computers
Introduction to Socket Programming (Advanced Computer Networks) By Priyank Shah NET ID : pss160530 A Simple Question What are Sockets? Sockets are communication points on the same or different computers
6950 Enterprise Gateway Server USER S GUIDE PN:
 6950 Enterprise Gateway Server USER S GUIDE PN: 961-047-091 Acknowledgments CAUTION: Intermec Technologies Corporation suggests you buy cables from us to connect with other devices. Our cables are safe,
6950 Enterprise Gateway Server USER S GUIDE PN: 961-047-091 Acknowledgments CAUTION: Intermec Technologies Corporation suggests you buy cables from us to connect with other devices. Our cables are safe,
Today: VM wrap-up Select (if time) Course wrap-up Final Evaluations
 Today: VM wrap-up Select (if time) Course wrap-up Final Evaluations Program structure int A[1024][1024] ; Each row is stored in one page Ignore code page in this example One frame allocated Program 1 for
Today: VM wrap-up Select (if time) Course wrap-up Final Evaluations Program structure int A[1024][1024] ; Each row is stored in one page Ignore code page in this example One frame allocated Program 1 for
Inter-process Communication using Pipes
 Inter-process Communication using Pipes Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering 1 Pipes A pipe is a one-way communication channel that couples one process to another. Used only between processes that have
Inter-process Communication using Pipes Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering 1 Pipes A pipe is a one-way communication channel that couples one process to another. Used only between processes that have
Operating Systems. Lecture 06. System Calls (Exec, Open, Read, Write) Inter-process Communication in Unix/Linux (PIPE), Use of PIPE on command line
 Operating Systems Lecture 06 System Calls (Exec, Open, Read, Write) Inter-process Communication in Unix/Linux (PIPE), Use of PIPE on command line March 04, 2013 exec() Typically the exec system call is
Operating Systems Lecture 06 System Calls (Exec, Open, Read, Write) Inter-process Communication in Unix/Linux (PIPE), Use of PIPE on command line March 04, 2013 exec() Typically the exec system call is
Sockets. Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University Embedded Software Lab.
 1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Internet Connections (1) 2 Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of bytes over
1 Sockets Dong-kun Shin Embedded Software Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://nyx.skku.ac.kr Internet Connections (1) 2 Connection Clients and servers communicate by sending streams of bytes over
How to write a Measurement Telnet Server
 How to write a Measurement Telnet Server A measurement Telnet server allows you to access remote I/Os with a standard Telnet client program. The following samples shows a way to set the LEDs of a DNP/EVA1
How to write a Measurement Telnet Server A measurement Telnet server allows you to access remote I/Os with a standard Telnet client program. The following samples shows a way to set the LEDs of a DNP/EVA1
l27 handout.txt buggy server.c Printed by Michael Walfish Apr 29, 10 13:41 Page 1/1 Apr 29, 10 11:51 Page 1/1
 Apr 29, 10 13:41 Page 1/1 1 Handout for CS 372H 2 Class 27 3 29 April 2010 4 5 1. Introduction to buffer overflow attacks 6 7 There are many ways to attack computers. Today we study the 8 "classic" method.
Apr 29, 10 13:41 Page 1/1 1 Handout for CS 372H 2 Class 27 3 29 April 2010 4 5 1. Introduction to buffer overflow attacks 6 7 There are many ways to attack computers. Today we study the 8 "classic" method.
Elementary TCP Sockets
 Elementary TCP Sockets Chapter 4 UNIX Network Programming Vol. 1, Second Ed. Stevens Distributed Computer Systems 1 socket interface Application 1 Application 2 socket interface user kernel user kernel
Elementary TCP Sockets Chapter 4 UNIX Network Programming Vol. 1, Second Ed. Stevens Distributed Computer Systems 1 socket interface Application 1 Application 2 socket interface user kernel user kernel
Ά η η 1 (30%): Sockets. socket () bind () listen () accept () connect () read () write () close ()
 ΗΜΥ 316 - Ε α η ια ή Ά η η 5 Υ ο οίη η Π ω ο ό ο α η αι α α ο ή sockets Ά η η 1 (30%): Sockets π α α α α α π πα π α α ω sockets Unix/Linux. Γ α α α π π α π α Server α Client π π π α έ Α π, α α απ π ω.
ΗΜΥ 316 - Ε α η ια ή Ά η η 5 Υ ο οίη η Π ω ο ό ο α η αι α α ο ή sockets Ά η η 1 (30%): Sockets π α α α α α π πα π α α ω sockets Unix/Linux. Γ α α α π π α π α Server α Client π π π α έ Α π, α α απ π ω.
ECE322 Systems Programming Project 2: Networking with Matrix Multiplication in C Grant Kimes 12/16/15
 ECE322 Systems Programming Project 2: Networking with Matrix Multiplication in C Grant Kimes 12/16/15 This project take two inputted matrices of a given size to multiply. The client sends the data to a
ECE322 Systems Programming Project 2: Networking with Matrix Multiplication in C Grant Kimes 12/16/15 This project take two inputted matrices of a given size to multiply. The client sends the data to a
Network Games Part II. Architecture of Network Game
 Network Games Part II Doron Nussbaum Network Games Part II COMP 5900 1 Architecture of Network Game Client Server Peer to Peer Player 1 Player 2 Player 1 Player 2 Server Player 5 Player 3 Player 5 Player
Network Games Part II Doron Nussbaum Network Games Part II COMP 5900 1 Architecture of Network Game Client Server Peer to Peer Player 1 Player 2 Player 1 Player 2 Server Player 5 Player 3 Player 5 Player
CS118 Discussion 1A, Week 3. Zengwen Yuan Dodd Hall 78, Friday 10:00 11:50 a.m.
 CS118 Discussion 1A, Week 3 Zengwen Yuan Dodd Hall 78, Friday 10:00 11:50 a.m. 1 Outline Application Layer Protocol: DNS, CDN, P2P Transport Layer Protocol: UDP, principles of reliable transport protocol
CS118 Discussion 1A, Week 3 Zengwen Yuan Dodd Hall 78, Friday 10:00 11:50 a.m. 1 Outline Application Layer Protocol: DNS, CDN, P2P Transport Layer Protocol: UDP, principles of reliable transport protocol
Example Questions for Midterm EE122, Fall 2008 EECS Berkeley
 Example Questions for Midterm EE122, Fall 2008 EECS Berkeley Note: The midterm exam will have six problems or more. The five problems below represent around 60-70% of the workload you should expect at
Example Questions for Midterm EE122, Fall 2008 EECS Berkeley Note: The midterm exam will have six problems or more. The five problems below represent around 60-70% of the workload you should expect at
Global Employee Location Server
 S4516 HELP Session 1 Global Employee Location Server Jeff Zhou jeffz@cs.wpi.edu 3/19/2011 Modified based on S4514 B05 slides Objective: Description To implement a simple concurrent server that has four
S4516 HELP Session 1 Global Employee Location Server Jeff Zhou jeffz@cs.wpi.edu 3/19/2011 Modified based on S4514 B05 slides Objective: Description To implement a simple concurrent server that has four
Ports under 1024 are often considered special, and usually require special OS privileges to use.
 1 2 Turns out that besides an IP address (used by the IP layer), there is another address that is used by TCP (stream sockets) and, coincidentally, by UDP (datagram sockets). It is the port number. It's
1 2 Turns out that besides an IP address (used by the IP layer), there is another address that is used by TCP (stream sockets) and, coincidentally, by UDP (datagram sockets). It is the port number. It's
serverbase.txt (1) Server Client1 (3) (2) Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB.
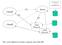 serverbase.txt Client1 (3) (1) (2) Server Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB. Client APP Layer Server APP Layer NW Layer NW Layer DLL DLL PHL
serverbase.txt Client1 (3) (1) (2) Server Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB. Client APP Layer Server APP Layer NW Layer NW Layer DLL DLL PHL
Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Concurrent Programming Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero((char
Concurrent Programming Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Echo Server Revisited int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {... listenfd = socket(af_inet, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero((char
CS4514 HELP Session 3. Concurrent Server (in APP) Using Go-Back-N (in DLL)
 CS4514 HELP Session 3 Concurrent Server (in APP) Using Go-Back-N (in DLL) Description! You are supposed to implement a simple concurrent server on top of an emulated network protocol stack (NWL, DLL, PHL).
CS4514 HELP Session 3 Concurrent Server (in APP) Using Go-Back-N (in DLL) Description! You are supposed to implement a simple concurrent server on top of an emulated network protocol stack (NWL, DLL, PHL).
Concurrent Programming
 CHAPTER 12 Concurrent Programming 121 Concurrent Programming with Processes 935 122 Concurrent Programming with I/O Multiplexing 939 123 Concurrent Programming with Threads 947 124 Shared Variables in
CHAPTER 12 Concurrent Programming 121 Concurrent Programming with Processes 935 122 Concurrent Programming with I/O Multiplexing 939 123 Concurrent Programming with Threads 947 124 Shared Variables in
Embedded System Design
 Embedded System Design Lecture 9 Jaeyong Chung Robust Systems Laboratory Incheon National University Inter-process Commnucation (IPC) Chung EPC6071 2 Inter-process Commnucation (IPC) A set of methods for
Embedded System Design Lecture 9 Jaeyong Chung Robust Systems Laboratory Incheon National University Inter-process Commnucation (IPC) Chung EPC6071 2 Inter-process Commnucation (IPC) A set of methods for
10. I/O System Library
 10. I/O System Library Header File #include // Found in C:\Nburn\include General File Descriptor Functions close --- Close open file descriptors read --- Read data from a file descriptor ReadWithTimeout
10. I/O System Library Header File #include // Found in C:\Nburn\include General File Descriptor Functions close --- Close open file descriptors read --- Read data from a file descriptor ReadWithTimeout
Application Programming Interfaces
 Application Programming Interfaces Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2018 SYSTEM CALLS Machine 1 Machine 2 Application 1 Application 3 Application 4 Application 5 Application 2 API (system functions) API (system
Application Programming Interfaces Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2018 SYSTEM CALLS Machine 1 Machine 2 Application 1 Application 3 Application 4 Application 5 Application 2 API (system functions) API (system
CSE 333 SECTION 7. Client-Side Network Programming
 CSE 333 SECTION 7 Client-Side Network Programming Overview Domain Name Service (DNS) Client side network programming steps and calls dig and ncat tools Network programming for the client side Recall the
CSE 333 SECTION 7 Client-Side Network Programming Overview Domain Name Service (DNS) Client side network programming steps and calls dig and ncat tools Network programming for the client side Recall the
CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networking
 CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networking Prof. Alan Mislove Lecture 3: Crash course in socket programming September 10th, 2009 Project 0 Goal: Familiarize you with socket programming in C Implement
CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networking Prof. Alan Mislove Lecture 3: Crash course in socket programming September 10th, 2009 Project 0 Goal: Familiarize you with socket programming in C Implement
Networks. Practical Investigation of TCP/IP Ports and Sockets. Gavin Cameron
 Networks Practical Investigation of TCP/IP Ports and Sockets Gavin Cameron MSc/PGD Networks and Data Communication May 9, 1999 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS.........................................................
Networks Practical Investigation of TCP/IP Ports and Sockets Gavin Cameron MSc/PGD Networks and Data Communication May 9, 1999 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS.........................................................
Azblink API for Sending XMPP Messages via HTTP POST
 Azblink API for Sending XMPP Messages via HTTP POST Abstract: This document is to describe the API of Azblink SBC for sending XMPP messages via HTTP POST. This is intended for the systems or the devices
Azblink API for Sending XMPP Messages via HTTP POST Abstract: This document is to describe the API of Azblink SBC for sending XMPP messages via HTTP POST. This is intended for the systems or the devices
CS 471 Operating Systems. Spring 2016 Midterm Exam Time 2 & 1/2 hours. Open Book & Notes
 CS 471 Operating Systems Spring 2016 Midterm Exam Time 2 & 1/2 hours Open Book & Notes Name: Unix Login: Question 1 (20 points) A. What is the output of the following program if executed as: % Q1A Q1A.c
CS 471 Operating Systems Spring 2016 Midterm Exam Time 2 & 1/2 hours Open Book & Notes Name: Unix Login: Question 1 (20 points) A. What is the output of the following program if executed as: % Q1A Q1A.c
Message passing systems are popular because they support client-server interactions, where: clients send messages to servers requesting a server.
 Client-Server Model Message passing systems are popular because they support client-server interactions, where: clients send messages to servers requesting a server. servers provide services requested
Client-Server Model Message passing systems are popular because they support client-server interactions, where: clients send messages to servers requesting a server. servers provide services requested
Introduction to Berkeley Sockets
 INF1060: Introduction to Operating Systems and Data Communication Data Communication: Introduction to Berkeley Sockets Michael Welzl (revised by Hans Petter Taugbøl Kragset 2015) (adapted from lectures
INF1060: Introduction to Operating Systems and Data Communication Data Communication: Introduction to Berkeley Sockets Michael Welzl (revised by Hans Petter Taugbøl Kragset 2015) (adapted from lectures
CSE 333 SECTION 7. C++ Virtual Functions and Client-Side Network Programming
 CSE 333 SECTION 7 C++ Virtual Functions and Client-Side Network Programming Overview Virtual functions summary and worksheet Domain Name Service (DNS) Client side network programming steps and calls dig
CSE 333 SECTION 7 C++ Virtual Functions and Client-Side Network Programming Overview Virtual functions summary and worksheet Domain Name Service (DNS) Client side network programming steps and calls dig
Networking Endterm. Below 6 netmasks are shown in both binary and dotted-quad form
 Networking Endterm Below 6 netmasks are shown in both binary and dotted-quad form. Binary Dotted-quad 11111111 11111111 11111111 10000000-255.255.255.128 11111111 11111111 11111111 11000000-255.255.255.192
Networking Endterm Below 6 netmasks are shown in both binary and dotted-quad form. Binary Dotted-quad 11111111 11111111 11111111 10000000-255.255.255.128 11111111 11111111 11111111 11000000-255.255.255.192
Introduction to Berkeley Sockets
 INF1060: Introduction to Operating Systems and Data Communication Data Communication: Introduction to Berkeley Sockets Michael Welzl (adapted from lectures by Pål Halvorsen, Carsten Griwodz & Olav Lysne)
INF1060: Introduction to Operating Systems and Data Communication Data Communication: Introduction to Berkeley Sockets Michael Welzl (adapted from lectures by Pål Halvorsen, Carsten Griwodz & Olav Lysne)
CSE 333 SECTION 8. Sockets, Network Programming
 CSE 333 SECTION 8 Sockets, Network Programming Overview Domain Name Service (DNS) Client side network programming steps and calls Server side network programming steps and calls dig and ncat tools Network
CSE 333 SECTION 8 Sockets, Network Programming Overview Domain Name Service (DNS) Client side network programming steps and calls Server side network programming steps and calls dig and ncat tools Network
2
 Reseaux Informatiques I Jean-Yves Le Boudec ICA Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne 2 Tu aimeras les reseaux Les noms de modeles en couche Ne te seront plus farouches TCP/IP, ISO Loin des ares des
Reseaux Informatiques I Jean-Yves Le Boudec ICA Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne 2 Tu aimeras les reseaux Les noms de modeles en couche Ne te seront plus farouches TCP/IP, ISO Loin des ares des
Preview. Interprocess Communication with Pipe. Pipe from the Parent to the child Pipe from the child to the parent FIFO popen() with r Popen() with w
 Preview Interprocess Communication with Pipe Pipe from the Parent to the child Pipe from the child to the parent FIFO popen() with r Popen() with w COCS 350 System Software, Fall 2015 1 Interprocess Communication
Preview Interprocess Communication with Pipe Pipe from the Parent to the child Pipe from the child to the parent FIFO popen() with r Popen() with w COCS 350 System Software, Fall 2015 1 Interprocess Communication
Defending Computer Networks Lecture 2: Vulnerabili0es. Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science
 Defending Computer Networks Lecture 2: Vulnerabili0es Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science Logis;cs S;ll space in class Restric;on to CS M.Eng will be libed shortly HW1 probably given
Defending Computer Networks Lecture 2: Vulnerabili0es Stuart Staniford Adjunct Professor of Computer Science Logis;cs S;ll space in class Restric;on to CS M.Eng will be libed shortly HW1 probably given
