Let!s go back to a course goal... Let!s go back to a course goal... Question? Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies
|
|
|
- Clinton Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Lecture 22 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies Let!s go back to a course goal... At the end of the semester, you should be able to......describe the fundamental components required in a single core of a modern microprocessor (Also, explain how they interact with each other, with main memory, and with external storage media...) Question? Let!s go back to a course goal... How much of a chip is memory? At the end of the semester, you should be able to... 10% 25% 50% 75%...describe the fundamental components required in a single core of a modern microprocessor (Also, explain how they interact with each other, with main memory, and with external storage media...) 85% Example How do on-chip memory, processor logic, main memory, disk interact?
2 5 Memory and Pipelining In our 5 stage pipe, we!ve constantly been assuming that we can access our operand from memory in 1 clock cycle We!d like this to be the case, and its is possible...but its also complicated We!ll discuss how this happens in the next several lectures We!ll talk about Memory Technology Memory Hierarchy Caches Memory Virtual Memory 6 If I say Memory what do you think of? Memory Comes in Many Flavors SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) ROM, Flash, etc. Disks, Tapes, etc. Difference in speed, price and size Fast is small and/or expensive Large is slow and/or expensive The search is on for a universal memory What!s a universal memory Fast and non-volatile. May be MRAM, PCRAM, etc. etc. Let!s start with DRAM. Its generally the largest piece of RAM. Performance Is there a problem with DRAM? 1 Processor-DRAM Memory Gap (latency) Why is this a problem? Moore!s Law Time CPU DRAM µproc 60%/yr. (2X/1.5yr) Processor-Memory Performance Gap: grows 50% / year DRAM 9%/yr. (2X/10yrs) More on DRAM DRAM takes about 100 ns... What if clock rate for our 5 stage pipeline was 1 GHZ? Would the memory and fetch stages stall for 100 cycles? Actually, yes... if only DRAM Caches come to the rescue As transistors have gotten smaller, its allowed us to put more (faster) memory closer to the processing logic The idea is to mask the latency of having to go off to main memory 8
3 9 The principle of locality says that most programs don!t access all code or data uniformly i.e. in a loop, small subset of instructions might be executed over and over again & a block of memory addresses might be accessed sequentially This has lead to memory hierarchies Some important things to note: Fast memory is expensive Levels of memory usually smaller/faster than previous Levels of memory usually subset one another All the stuff in a higher level is in some level below it Capacity Access Time Cost CPU Registers 100s Bytes <10s ns Cache K Bytes ns cents/bit Main Memory M Bytes 200ns- 500ns $ cents /bit Disk G Bytes, 10 ms (10,000,000 ns) cents/bit Tape infinite sec-min The Full Memory Hierarchy always reuse a good idea Our current focus Registers Cache Memory Disk Tape Instr. Operands Blocks Pages Files Staging Xfer Unit prog./compiler 1-8 bytes cache cntl bytes OS 4K-16K bytes user/operator Mbytes Upper Level faster Larger Lower Level Let!s talk about caches more on the chalkboard Accessing data in different levels of memory hierarchy: A performance perspective
4 13 Terminology Summary Hit: data appears in block in upper level (i.e. block X in cache) Hit Rate: fraction of memory access found in upper level Hit Time: time to access upper level which consists of RAM access time + Time to determine hit/miss Miss: data needs to be retrieved from a block in the lower level (i.e. block Y in memory) Miss Rate = 1 - (Hit Rate) Miss Penalty: Extra time to replace a block in the upper level + Time to deliver the block the processor Hit Time << Miss Penalty (500 instructions on 21264) 14 Average Memory Access Time AMAT = HitTime + (1 - h) x MissPenalty Hit time: basic time of every access. Hit rate (h): fraction of access that hit Miss penalty: extra time to fetch a block from lower level, including time to replace in CPU To Processor From Processor Upper Level Memory Blk X Lower Level Memory Blk Y A brief description of a cache Cache = next level of memory hierarchy up from register file All values in register file should be in cache Caches: Memory between registers and DRAM Cache entries usually referred to as blocks Block is minimum amount of information that can be in cache If we!re looking for item in a cache and find it, have a cache hit; it not a cache miss Cache miss rate = fraction of accesses not in the cache Miss penalty is # of clock cycles required b/c of the miss Mem. stall cycles = Inst. count x Mem. ref./inst. x Miss rate x Miss penalty
5 17 Cache Basics Fast (but small) memory close to processor When data referenced If in cache, use cache instead of memory If not in cache, bring into cache (actually, bring entire block of data, too) Maybe have to kick something else out to do it! Important decisions Placement: where in the cache can a block go Identification: how do we find a block in cache Replacement: what to kick out to make room in cache Write policy: What do we do about writes 18 Cache Basics Cache consists of block-sized lines Line size typically power of two Typically 16 to 128 bytes in size Example Suppose block size is 128 bytes Lowest seven bits determine offset within block Read data at address A=0x7fffa3f4 Address begins to block with base address 0x7fffa Some initial questions to consider 20 Where can a block be placed in a cache? Where can a block be placed in an upper level of memory hierarchy (i.e. a cache)? How is a block found in an upper level of memory hierarchy? Which cache block should be replaced on a cache miss if entire cache is full and we want to bring in new data? What happens if a you want to write back to a memory location? Do you just write to the cache? Do you write somewhere else? 3 schemes for block placement in a cache: Direct mapped cache: Block (or data to be stored) can go to only 1 place in cache Usually: (Block address) MOD (# of blocks in the cache) Fully associative cache: Block can be placed anywhere in cache Set associative cache: Set = a group of blocks in the cache Block mapped onto a set & then block can be placed anywhere within that set Usually: (Block address) MOD (# of sets in the cache) If n blocks, we call it n-way set associative
6 21 Where can a block be placed in a cache? 22 Associativity Cache: Fully Associative Direct Mapped Set Associative Set 0Set 1Set 2Set 3 If you have associativity > 1 you have to have a replacement policy FIFO LRU Random Block 12 can go anywhere Block 12 can go only into Block 4 (12 mod 8) Memory: 12 Block 12 can go anywhere in set 0 (12 mod 4) Full or Full-map associativity means you check every tag in parallel and a memory block can go into any cache block Virtual memory is effectively fully associative (But don!t worry about virtual memory yet) 23 How is a block found in the cache? Cache!s have address tag on each block frame that provides block address Tag of every cache block that might have entry is examined against CPU address (in parallel! why?) Each entry usually has a valid bit Tells us if cache data is useful/not garbage If bit is not set, there can!t be a match How does address provided to CPU relate to entry in cache? Entry divided between block address & block offset and further divided between tag field & index field 24 How is a block found in the cache? Tag Block Address Index Block offset field selects data from block (i.e. address of desired data within block) Index field selects a specific set Tag field is compared against it for a hit Could we compare on more of address than the tag? Not necessary; checking index is redundant Used to select set to be checked Ex.: Address stored in set 0 must have 0 in index field Offset not necessary in comparison entire block is present or not and all block offsets must match Block Offset
7 25 Which block should be replaced on a cache miss? If we look something up in cache and entry not there, generally want to get data from memory and put it in cache B/c principle of locality says we!ll probably use it again Direct mapped caches have 1 choice of what block to replace Fully associative or set associative offer more choices Usually 2 strategies: Random pick any possible block and replace it LRU stands for Least Recently Used Why not throw out the block not used for the longest time Usually approximated, not much better than random i.e. 5.18% vs. 5.69% for 16KB 2-way set associative Caches: Replacement Policies What happens on a write? FYI most accesses to a cache are reads: Used to fetch instructions (reads) Most instructions don!t write to memory For MIPS only about 7% of memory traffic involve writes Translates to about 25% of cache data traffic Make common case fast! Optimize cache for reads! Actually pretty easy to do Can read block while comparing/reading tag Block read begins as soon as address available If a hit, address just passed right on to CPU Writes take longer. Any idea why? 28 What happens on a write? Generically, there are 2 kinds of write policies: Write through (or store through) With write through, information written to block in cache and to block in lower-level memory Write back (or copy back) With write back, information written only to cache. It will be written back to lower-level memory when cache block is replaced The dirty bit: Each cache entry usually has a bit that specifies if a write has occurred in that block or not Helps reduce frequency of writes to lower-level memory upon block replacement
8 29 What happens on a write? 30 What happens on a write? Write back versus write through: Write back advantageous because: Writes occur at the speed of cache and don!t incur delay of lower-level memory Multiple writes to cache block result in only 1 lower-level memory access Write through advantageous because: Lower-levels of memory have most recent copy of data If CPU has to wait for a write, we have write stall 1 way around this is a write buffer Ideally, CPU shouldn!t have to stall during a write Instead, data written to buffer which sends it to lowerlevels of memory hierarchy What if we want to write and block we want to write to isn!t in cache? There are 2 common policies: Write allocate: (or fetch on write) The block is loaded on a write miss The idea behind this is that subsequent writes will be captured by the cache (ideal for a write back cache) No-write allocate: (or write around) Block modified in lower-level and not loaded into cache Usually used for write-through caches (subsequent writes still have to go to memory) 31 Memory access equations Using what we defined on previous slide, we can say: Memory stall clock cycles = Reads x Read miss rate x Read miss penalty + " Writes x Write miss rate x Write miss penalty Often, reads and writes are combined/averaged: Memory stall cycles = Memory access x Miss rate x Miss penalty (approximation) Also possible to factor in instruction count to get a complete formula: 32 Reducing cache misses Obviously, we want data accesses to result in cache hits, not misses this will optimize performance Start by looking at ways to increase % of hits. but first look at 3 kinds of misses! Compulsory misses: Very 1st access to cache block will not be a hit the data!s not there yet! Capacity misses: Cache is only so big. Won!t be able to store every block accessed in a program must swap out! Conflict misses: Result from set-associative or direct mapped caches Blocks discarded/retrieved if too many map to a location
Question?! Processor comparison!
 1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 5.1-5.2!! (Over the next 2 lectures)! Lecture 18" Introduction to Memory Hierarchies! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Question?!
Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" Why it s important " Fundamental lesson(s)" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter
 Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
Processor components" Multicore processors and programming" Processor comparison" vs." Lecture 17 Introduction to Memory Hierarchies" CSE 30321" Suggested reading:" (HP Chapter 5.1-5.2)" Writing more "
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. - Memory Hierarchies (I)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Hierarchies (I) Fall 2007 Slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05 Recap
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Hierarchies (I) Fall 2007 Slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05 Recap
Modern Computer Architecture
 Modern Computer Architecture Lecture3 Review of Memory Hierarchy Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Performance 1000 Recap: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor-DRAM Memory Gap
Modern Computer Architecture Lecture3 Review of Memory Hierarchy Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Performance 1000 Recap: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor-DRAM Memory Gap
Advanced Computer Architecture
 ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Some slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Some slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05
Performance! (1/latency)! 1000! 100! 10! Capacity Access Time Cost. CPU Registers 100s Bytes <10s ns. Cache K Bytes ns 1-0.
 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... EEL 5764: Graduate Computer Architecture Appendix C Hierarchy Review Ann Gordon-Ross Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Florida http://www.ann.ece.ufl.edu/
Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... EEL 5764: Graduate Computer Architecture Appendix C Hierarchy Review Ann Gordon-Ross Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Florida http://www.ann.ece.ufl.edu/
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 16 - Cache and virtual memory review
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Cache and virtual memory review Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Cache and virtual memory review Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
CPE 631 Lecture 04: CPU Caches
 Lecture 04 CPU Caches Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Outline Memory Hierarchy Four Questions for Memory Hierarchy Cache Performance 26/01/2004 UAH- 2 1 Processor-DR
Lecture 04 CPU Caches Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Outline Memory Hierarchy Four Questions for Memory Hierarchy Cache Performance 26/01/2004 UAH- 2 1 Processor-DR
Course Administration
 Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy
 Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy Outline Memory hierarchy Locality Cache design Virtual address spaces Page table layout TLB design options (MMU Sub-system) Conclusion 2012/11/7 2 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced
Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy Outline Memory hierarchy Locality Cache design Virtual address spaces Page table layout TLB design options (MMU Sub-system) Conclusion 2012/11/7 2 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced
Memory Hierarchy: Motivation
 Memory Hierarchy: Motivation The gap between CPU performance and main memory speed has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating performance bottlenecks for memory access instructions. The memory
Memory Hierarchy: Motivation The gap between CPU performance and main memory speed has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating performance bottlenecks for memory access instructions. The memory
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350):
 The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
Topics. Digital Systems Architecture EECE EECE Need More Cache?
 Digital Systems Architecture EECE 33-0 EECE 9-0 Need More Cache? Dr. William H. Robinson March, 00 http://eecs.vanderbilt.edu/courses/eece33/ Topics Cache: a safe place for hiding or storing things. Webster
Digital Systems Architecture EECE 33-0 EECE 9-0 Need More Cache? Dr. William H. Robinson March, 00 http://eecs.vanderbilt.edu/courses/eece33/ Topics Cache: a safe place for hiding or storing things. Webster
Memory Hierarchy: The motivation
 Memory Hierarchy: The motivation The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating performance bottlenecks for memory access instructions. The memory
Memory Hierarchy: The motivation The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating performance bottlenecks for memory access instructions. The memory
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17: Cache System
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver. Lecture 19: Caches EE141
 EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
1/19/2009. Data Locality. Exploiting Locality: Caches
 Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Administrivia. CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 8 Basic Pipelining, cont., & Memory Hierarchy. SPEC92 benchmarks
 Administrivia CMSC 4 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 8 Basic Pipelining, cont., & Memory Hierarchy Alan Sussman als@cs.umd.edu Homework # returned today solutions posted on password protected web
Administrivia CMSC 4 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 8 Basic Pipelining, cont., & Memory Hierarchy Alan Sussman als@cs.umd.edu Homework # returned today solutions posted on password protected web
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Virtual Memory
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Virtual Memory ECE468 vm.1 Review: The Principle of Locality Probability of reference 0 Address Space 2 The Principle of Locality: Program access a relatively
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Virtual Memory ECE468 vm.1 Review: The Principle of Locality Probability of reference 0 Address Space 2 The Principle of Locality: Program access a relatively
CSC Memory System. A. A Hierarchy and Driving Forces
 CSC1016 1. System A. A Hierarchy and Driving Forces 1A_1 The Big Picture: The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Input Control Datapath Output Topics: Motivation for Hierarchy View of Hierarchy
CSC1016 1. System A. A Hierarchy and Driving Forces 1A_1 The Big Picture: The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Input Control Datapath Output Topics: Motivation for Hierarchy View of Hierarchy
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory
 1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
ECE4680 Computer Organization and Architecture. Virtual Memory
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Virtual Memory If I can see it and I can touch it, it s real. If I can t see it but I can touch it, it s invisible. If I can see it but I can t touch it, it
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Virtual Memory If I can see it and I can touch it, it s real. If I can t see it but I can touch it, it s invisible. If I can see it but I can t touch it, it
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache
 Removing The Ideal Memory Assumption: The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory
Removing The Ideal Memory Assumption: The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Memory Hierarchy
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
3Introduction. Memory Hierarchy. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
LECTURE 11. Memory Hierarchy
 LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Lecture 29 Review" CPU time: the best metric" Be sure you understand CC, clock period" Common (and good) performance metrics"
 Be sure you understand CC, clock period Lecture 29 Review Suggested reading: Everything Q1: D[8] = D[8] + RF[1] + RF[4] I[15]: Add R2, R1, R4 RF[1] = 4 I[16]: MOV R3, 8 RF[4] = 5 I[17]: Add R2, R2, R3
Be sure you understand CC, clock period Lecture 29 Review Suggested reading: Everything Q1: D[8] = D[8] + RF[1] + RF[4] I[15]: Add R2, R1, R4 RF[1] = 4 I[16]: MOV R3, 8 RF[4] = 5 I[17]: Add R2, R2, R3
Memory Hierarchy Technology. The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer
 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Datapath Today s Topics: technologies Technology trends Impact on performance Hierarchy The principle of locality
The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Datapath Today s Topics: technologies Technology trends Impact on performance Hierarchy The principle of locality
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Direct Mapped Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
ECE ECE4680
 ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Computer Architecture ECE 568/668
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Computer Architecture ECE 568/668 Part 11 Memory Hierarchy - I Israel Koren ECE568/Koren Part.11.1 ECE568/Koren Part.11.2 Ideal Memory
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Computer Architecture ECE 568/668 Part 11 Memory Hierarchy - I Israel Koren ECE568/Koren Part.11.1 ECE568/Koren Part.11.2 Ideal Memory
CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/76/74076691.jpg) CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches. Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky
 Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky Review Hazards reduce effectiveness of pipelining Cause stalls/bubbles Structural Hazards Conflict in use of datapath component Data
Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky Review Hazards reduce effectiveness of pipelining Cause stalls/bubbles Structural Hazards Conflict in use of datapath component Data
CS61C : Machine Structures
 CS C L.. Cache I () Design Principles for Hardware CSC : Machine Structures Lecture.. Cache I -- Kurt Meinz inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~csc. Simplicity favors regularity Every instruction has operands, opcode
CS C L.. Cache I () Design Principles for Hardware CSC : Machine Structures Lecture.. Cache I -- Kurt Meinz inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~csc. Simplicity favors regularity Every instruction has operands, opcode
Memory hierarchy review. ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov
 Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Cache performance Opteron example Processor-DRAM gap in latency Q1. How to deal
Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Cache performance Opteron example Processor-DRAM gap in latency Q1. How to deal
Page 1. Memory Hierarchies (Part 2)
 Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Computer Architecture Spring 2016
 Computer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 02: Introduction II Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Pipeline Hazards Major hurdle to pipelining: hazards prevent the
Computer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 02: Introduction II Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Pipeline Hazards Major hurdle to pipelining: hazards prevent the
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
Topics. Computer Organization CS Improving Performance. Opportunity for (Easy) Points. Three Generic Data Hazards
 Computer Organization CS 231-01 Improving Performance Dr. William H. Robinson November 8, 2004 Topics Money's only important when you don't have any. Sting Cache Scoreboarding http://eecs.vanderbilt.edu/courses/cs231/
Computer Organization CS 231-01 Improving Performance Dr. William H. Robinson November 8, 2004 Topics Money's only important when you don't have any. Sting Cache Scoreboarding http://eecs.vanderbilt.edu/courses/cs231/
Caches Part 1. Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger. School of Information Science and Technology SIST
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
Lecture 12. Memory Design & Caches, part 2. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
CPS101 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13: The Memory System. Outline of Today s Lecture. The Big Picture: Where are We Now?
 cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
Memory Hierarchy. ENG3380 Computer Organization and Architecture Cache Memory Part II. Topics. References. Memory Hierarchy
 ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1
 CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
Cache Memory COE 403. Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar. Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals
 Cache Memory COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline The Need for Cache Memory The Basics
Cache Memory COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline The Need for Cache Memory The Basics
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems. Cache $$$$$
 CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
Review: Performance Latency vs. Throughput. Time (seconds/program) is performance measure Instructions Clock cycles Seconds.
 Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Fall 2017
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Memory System Design Part II. Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore.
 Memory System Design Part II Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore. References: Outline Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, Hennessy & Patterson Topics Memory hierarchy Cache Multi-core
Memory System Design Part II Bharadwaj Amrutur ECE Dept. IISc Bangalore. References: Outline Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, Hennessy & Patterson Topics Memory hierarchy Cache Multi-core
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
Page 1. Review: Address Segmentation " Review: Address Segmentation " Review: Address Segmentation "
 Review Address Segmentation " CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 23, 2011! Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! 1111 0000" 1110 000" Seg #"
Review Address Segmentation " CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 23, 2011! Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! 1111 0000" 1110 000" Seg #"
COSC4201. Chapter 5. Memory Hierarchy Design. Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University
 COSC4201 Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University 1 Memory Hierarchy The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating
COSC4201 Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University 1 Memory Hierarchy The gap between CPU performance and main memory has been widening with higher performance CPUs creating
V. Primary & Secondary Memory!
 V. Primary & Secondary Memory! Computer Architecture and Operating Systems & Operating Systems: 725G84 Ahmed Rezine 1 Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
V. Primary & Secondary Memory! Computer Architecture and Operating Systems & Operating Systems: 725G84 Ahmed Rezine 1 Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring
 Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
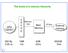 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs.
 The Hierarchical Memory System The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy:
The Hierarchical Memory System The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy:
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 35 Caches IV / VM I 2004-11-19 Andy Carle inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c-ta Google strikes back against recent encroachments into the Search
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 35 Caches IV / VM I 2004-11-19 Andy Carle inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c-ta Google strikes back against recent encroachments into the Search
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Cache Review. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
Review : Pipelining. Memory Hierarchy
 CS61C L11 Caches (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Review : Pipelining The Big Picture Lecture #11 Caches 2009-07-29 Jeremy Huddleston!! Pipeline challenge is hazards "! Forwarding helps w/many data hazards
CS61C L11 Caches (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Review : Pipelining The Big Picture Lecture #11 Caches 2009-07-29 Jeremy Huddleston!! Pipeline challenge is hazards "! Forwarding helps w/many data hazards
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Improving Cache Performance. Administrative. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. Review: Principle of Locality
 Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Memory - I. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Memory - I Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 Outline q Why Memory Hierarchy q How Memory Hierarchy? SRAM (Cache) & DRAM (main memory) Memory System
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Memory - I Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 Outline q Why Memory Hierarchy q How Memory Hierarchy? SRAM (Cache) & DRAM (main memory) Memory System
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19. Cache
 COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19 Cache Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Cache Topics 3 Cache Hardware Cost How many total bits are required
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19 Cache Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Cache Topics 3 Cache Hardware Cost How many total bits are required
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]
![ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]](/thumbs/72/68075397.jpg) ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
Caches. Samira Khan March 23, 2017
 Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
CHAPTER 6 Memory. CMPS375 Class Notes Page 1/ 16 by Kuo-pao Yang
 CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 233 6.2 Types of Memory 233 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 235 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 237 6.4 Cache Memory 237 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 239 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 247
CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 233 6.2 Types of Memory 233 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 235 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 237 6.4 Cache Memory 237 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 239 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 247
CHAPTER 6 Memory. CMPS375 Class Notes (Chap06) Page 1 / 20 Dr. Kuo-pao Yang
 CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 341 6.2 Types of Memory 341 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 343 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 346 6.4 Cache Memory 347 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 349 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 365
CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 341 6.2 Types of Memory 341 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 343 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 346 6.4 Cache Memory 347 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 349 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 365
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
CS 31: Intro to Systems Caching. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 2015
 CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, Textbook web site:
 Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, 2003 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org 1 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org Laboratory Hardware 2 Topics 14:332:331
Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, 2003 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org 1 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org Laboratory Hardware 2 Topics 14:332:331
Memory Hierarchy Motivation, Definitions, Four Questions about Memory Hierarchy
 Memory Hierarchy Motivation, Definitions, Four Questions about Memory Hierarchy Soner Onder Michigan Technological University Randy Katz & David A. Patterson University of California, Berkeley Levels in
Memory Hierarchy Motivation, Definitions, Four Questions about Memory Hierarchy Soner Onder Michigan Technological University Randy Katz & David A. Patterson University of California, Berkeley Levels in
CS 136: Advanced Architecture. Review of Caches
 1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
Memory. Lecture 22 CS301
 Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory
 Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Chapter Seven. Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
10/19/17. You Are Here! Review: Direct-Mapped Cache. Typical Memory Hierarchy
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
CS3350B Computer Architecture
 CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
