(3 Hours) N.B. (1) Question No. 1 is compulsory. (2) Attempt any four from the remaining six questions. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
|
|
|
- Lester Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q. P. Code: (3 Hours) Total Marks: 0 N.B. (1) Question No. 1 is compulsory. (2) Attempt any four from the remaining six questions. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. Q.1 (a) What is flowchart? Explain its basic symbols with an example. [] (b) Explain the character set & basic data types in C language along the [] size in bytes of each type. Q.2 (a) What are control statements? Demonstrate usage of if-else construct [] through an example program. (b) Write a program in C to calculate factorial of a number. [] Q.3 (a) Explain break statement and continue statement with an example. [] (b) What are arrays? Write the syntax to declare, initialize and access two [] dimensional arrays. Q.4 (a) Clearly differentiate between function prototype, function definition [] and function call along with an example. (b) Explain getchar() & putchar() functions with examples. Differentiate [] between scanf() and gets() functions. Q. (a) Write a program in C to find the symmetry of the matrix. [] (b) Explain different modes of accessing a file. [] Q.6 (a) What is recursive function? Write a program to demonstrate recursive function. (b) Explain structures. Illustrate with an example structure initialization. Write the syntax for array of structures. Q.7 Write short Notes on: (Any four) a) Pointers b) File operations c) Unions d) Strings e) Static variables [] [] [20] *******************
2 Q. P. Code: (3 Hours) [Total Marks: 0] N.B.: (1) Question no. 1 is compulsory (2) Answer any four of the remaining six questions (3) All questions carry equal marks 1. (a) Explain Level 0 and level 1 DFD for an Online Food Ordering System (b) Explain SRS in detail with an example 2. (a)explain different types of Feasibility study. (b) Explain different Fact finding techniques 3. (a) Explain different types of software testing (b) Explain Warnier Orr Diagrams and HIPO chart 4. (a) What do you mean by Functional Technical Review? (b) Explain ER diagram with the help of an example. (a) Compare Iterative and Rad model (b) Explain structure chart in detail 6. (a)compare black box and white box testing methods (b) Explain the role and responsibilities of a System analyst 7. Write short notes on (any four):- 20 (a) CASE tools (b) Decision tree (c) Extreme programming (d)data dictionary (e) Spiral model ******************* Page 1 of 1
3 Q.P. CODE: (Time: 3 Hours) [Total marks: 0] Note (1) Question No. 1 is compulsory. (2) Attempt any four out of remaining six questions. (3) Answer to sub-questions should be grouped together. Q1. (a) Using K-Maps, simplify the following expression in four variables A, B, C, D. Draw logic diagram for the obtained solution. F(A,B,C,D) = Σ(0,1,2,,8,9,) (b) State major functions of control unit. (c) Draw the instruction cycle state diagram. (d) Explain the working of full adder. Q2. (a) Explain memory hierarchy. What is cache memory? Why is it needed? (b) What are flip-flops? Explain J-K flip flop in detail. Q3. (a) Discuss 8 to 1 multiplexer using truth table. Draw its implementation using the appropriate gates. (b) With reference to parallel processing explain SISD, SIMD, MISD and MIMD. What is their significance in practical parallel processing approaches? Q4. (a) Difference the following I. Sequential Vs Combinational circuits II. RISC Vs CISC (b) Explain six stage instruction pipelines. How would you deal with conditional branching? Q. (a) Discuss superscalar processors and instruction issue policies in detail. (b) Discuss various addressing modes with examples. Q6. (a) Compare programmed I/O with interrupt driven I/O. What technique would you suggest to overcome the drawback of Programmed I/O and Interrupt driven I/O. (b) What are shift registers? Explain different types of shift registers. Q7. Write short note on any two of the following 20 (a) Clusters (b) Bus interconnection structure (c) Asynchronous counters
4 Q.P. Code : [Time: 3 Hours] [ Marks: 0 N.B: Please check whether you have got the right question paper. 1. Question No. 1 is compulsory 2. Attempt any four out of remaining six questions 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks 1. (a) i) Obtain a principal disjunctive normal from of : ( P Q ) (P Q ) ii) Given A = {1,2,3,4,,6} and relation R is defied on A such that arb iff a+b =7. Draw digraph of the relation. (b) Determine whether the following set together with the binary operation is a semigroup, a monoid or neither. If its is a monoid, specify the identity. If it is a semigroup or a monoid determine whether it is commutative. Set S = {1,2,3,6,9,18} where a *b = L.C.M (a,b). 2. (a) i) Determine whether the following form is tautology or contradiction (P (Q R )) ((P Q ) (P R )) ii) What are quantifiers? Explain with examples. (b) Let A be a collection of subsets of a set S. Show that (A, ) is a poset, where represents the set inclusion. Draw the Hasse diagram when S = {a,b,c}. 3. (a) i) Using method of mathematical induction show that sum of the cubes of three consecutive integers is divisible by 9. ii) Show that the conclusion D follows from the premises (A B ) (A C ), (B C ), D A (b) i) Let P de otes is eve, Q de otes is a pri e u er a d R, de otes + is eve. The varia les a d represe t positive integers. Determine the truth values of the following: 1) x P ( x ) 2) x Q ( x ) 3) x y R ( x,y ) 4) x y R ( x,y ) ) x ( Q ( x )) ii) Find the particular solution of an-2an-1 = 3 2 n 4. (a) i) Use the method of homogeneous solutions to find a particular solution of recurrence relation an = 200an-1-0 with initial condition a0 = 1. ii) Let an = 0, 0 n 2 n 2, n 3 Find an, where denotes the forward difference. (b) Obtain the recurrence relation for the maximum number of regions of a plane when there are n lines in the plane. Give suitable initial condition(s). Solve the recurrence relation. TURN OVER
5 Q.P. Code : (a) i) Define f: (Z, ) ( Z, ) as f(x)=x, where Z = {n : n Z}. Verify that f is an isomorphism. ii) Let G = {,,,,,,, } e a group u der ultipli atio odulo Fi d the multiplication table of G. Find order of subgroups generated by 7. (b) i) Let H = be a parity check matrix. Determine the group code eh: ii) Consider the (2,) group encoding function defined by e(00) = 00000, e(01) = 011, e() = 011, e(11) = 111 Decode the word 011 using maximum likelihood decoding function. B 2 4 B 6. (a) i) Consider the (2,6) encoding function e defined by e(00) = e(01) = e() = e(11) = Let d be an associated maximum likelihood function. How many errors will (e,d) correct. ii) Let V = {v0, w, a, b, c}, S = {a, b, c} and let be the relation on V* given by 1. v 0 a w 2. w bbw 3. w c Consider the phase structure grammar G = (V, S, v, 0 ). Derive the sentence ab 4 c. Also draw the derivation tree. (b) Draw the diagram of the machine M = (S,I,F) whose state transition table is shown. Given S = {s0, s1, s2, s3}, I = {0,1} State Input 0 1 S0 S0 S1 S1 S0 S2 S2 S0 S0 S3 S2 S1 Also list the values of Fw where w = 111. TURN OVER
6 Q.P. Code : (a) Determine whether the relation R on a set A is reflective, irreflective, symmetric asymmetric, antisymmetric or transitive. Give necessary explanation to your answer. A = set of all positive integers, and arb iff a b + 1 (b) Perform the following. i) (.1)2 = (?) ii) (414)8 = (?) iii) (11)2-(01)2 = (?)2 iv) (01)2 (11)2 =? v) (0)2 (0)2 =? TURN OVER
7 N.B. 1) Question No. 1 is compulsory 2) Attempt any four from the remaining Questions No. 2 to No. 7. 3) Illustrate answers with proper example wherever necessary. Q. P. Code: 386 (3 Hours) Marks: 0 Q 1. a) Define Management. Explain various functions of Management? b) Explain Product Life Cycle in detail. Q 2. a) What is decision making? Explain its various steps. b) Explain Maslow s theory of motivation in detail Q 3. a) Briefly explain Steps/Stages in new product development process. b) Explain Marketing Mix with example. Q 4. a) What are assumptions of McGregor s theory X and theory Y b) What are advantages of management by objectives? Q. a) Describe the roles and responsibilities of an Economist. b) What is Performance Appraisal and Explain its Methods? Q 6. a) Define and explain law of Supply. b) Define and explain law of Demand. Q 7 Write short notes on: (Any 4) a) Features of Perfect and Imperfect Competition b) Demand Forecasting c) Internal Source of Recruitment d) Oligopoly e) Methods of Training f) HRM
8 Q. P. Code: 242
Object Oriented Programming
 Program Structure for Master of Computer Application (MCA) Mumbai University (With Effect from 2012-2013) Semester I Object Oriented Programming 1 C++ Fundamentals: Data types, Operators, Preprocessor
Program Structure for Master of Computer Application (MCA) Mumbai University (With Effect from 2012-2013) Semester I Object Oriented Programming 1 C++ Fundamentals: Data types, Operators, Preprocessor
GARDEN CITY UNIVERSITY. Bachelor of Computer Applications SEMESTER- I. Course: CONCEPTS OF PROGRAMMING USING C LANGUAGE CODE: 05ABCAR17111 CREDITS: 04
 GARDEN CITY UNIVERSITY Bachelor of Computer Applications SEMESTER- I Course: CONCEPTS OF PROGRAMMING USING C LANGUAGE CODE: 05ABCAR17111 CREDITS: 04 Unit 1 Programming Basics 1.1 Introduction to Programming
GARDEN CITY UNIVERSITY Bachelor of Computer Applications SEMESTER- I Course: CONCEPTS OF PROGRAMMING USING C LANGUAGE CODE: 05ABCAR17111 CREDITS: 04 Unit 1 Programming Basics 1.1 Introduction to Programming
Answer any Five Questions. All questions carry equal marks.
 PART I, PAPER I (Problem Solving and Programming) 1. What do you understand by function prototype? Differentiate between call by value and call by reference methods of parameters passing to a function
PART I, PAPER I (Problem Solving and Programming) 1. What do you understand by function prototype? Differentiate between call by value and call by reference methods of parameters passing to a function
Total No. of Questions : 18] [Total No. of Pages : 02. M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DEC First Year COMPUTER SCIENCE.
![Total No. of Questions : 18] [Total No. of Pages : 02. M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DEC First Year COMPUTER SCIENCE. Total No. of Questions : 18] [Total No. of Pages : 02. M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DEC First Year COMPUTER SCIENCE.](/thumbs/92/107951421.jpg) (DMCS01) Total No. of Questions : 18] [Total No. of Pages : 02 M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DEC. 2016 First Year COMPUTER SCIENCE Data Structures Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Section - A (3 x 15 = 45)
(DMCS01) Total No. of Questions : 18] [Total No. of Pages : 02 M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DEC. 2016 First Year COMPUTER SCIENCE Data Structures Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Section - A (3 x 15 = 45)
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE
 Page 1 1. Which register store the address of next instruction to be executed? A) PC B) AC C) SP D) NONE 2. How many bits are required to address the 128 words of memory? A) 7 B) 8 C) 9 D) NONE 3. is the
Page 1 1. Which register store the address of next instruction to be executed? A) PC B) AC C) SP D) NONE 2. How many bits are required to address the 128 words of memory? A) 7 B) 8 C) 9 D) NONE 3. is the
COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 1
 COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) Maximum Marks: 70 (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) Maximum Marks: 70 (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Code No: 07A3EC03 Set No. 1
 Code No: 07A3EC03 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering,
Code No: 07A3EC03 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering,
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER ARCHITECURE- III YEAR EEE-6 TH SEMESTER 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK UNIT-1
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER ARCHITECURE- III YEAR EEE-6 TH SEMESTER 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 Data representation: (CHAPTER-3) 1. Discuss in brief about Data types, (8marks)
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY COMPUTER ARCHITECURE- III YEAR EEE-6 TH SEMESTER 16 MARKS QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 Data representation: (CHAPTER-3) 1. Discuss in brief about Data types, (8marks)
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT-I
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : CO (16MC802) Year & Sem: I-MCA & I-Sem Course & Branch: MCA Regulation:
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : CO (16MC802) Year & Sem: I-MCA & I-Sem Course & Branch: MCA Regulation:
2. (a) Compare the characteristics of a floppy disk and a hard disk. (b) Discuss in detail memory interleaving. [8+7]
![2. (a) Compare the characteristics of a floppy disk and a hard disk. (b) Discuss in detail memory interleaving. [8+7] 2. (a) Compare the characteristics of a floppy disk and a hard disk. (b) Discuss in detail memory interleaving. [8+7]](/thumbs/96/127320205.jpg) Code No: A109211202 R09 Set No. 2 1. (a) Explain the purpose of the following registers: i. IR ii. PC iii. MDR iv. MAR. (b) Explain with an example the steps in subtraction of two n-digit unsigned numbers.
Code No: A109211202 R09 Set No. 2 1. (a) Explain the purpose of the following registers: i. IR ii. PC iii. MDR iv. MAR. (b) Explain with an example the steps in subtraction of two n-digit unsigned numbers.
PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers.
![PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers. PART A (22 Marks) 2. a) Briefly write about r's complement and (r-1)'s complement. [8] b) Explain any two ways of adding decimal numbers.](/thumbs/96/128058841.jpg) Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, March - 2017 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE & ORGANIZATION (Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, March - 2017 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE & ORGANIZATION (Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
Digital Design with FPGAs. By Neeraj Kulkarni
 Digital Design with FPGAs By Neeraj Kulkarni Some Basic Electronics Basic Elements: Gates: And, Or, Nor, Nand, Xor.. Memory elements: Flip Flops, Registers.. Techniques to design a circuit using basic
Digital Design with FPGAs By Neeraj Kulkarni Some Basic Electronics Basic Elements: Gates: And, Or, Nor, Nand, Xor.. Memory elements: Flip Flops, Registers.. Techniques to design a circuit using basic
1. Draw general diagram of computer showing different logical components (3)
 Tutorial 1 1. Draw general diagram of computer showing different logical components (3) 2. List at least three input devices (1.5) 3. List any three output devices (1.5) 4. Fill the blank cells of the
Tutorial 1 1. Draw general diagram of computer showing different logical components (3) 2. List at least three input devices (1.5) 3. List any three output devices (1.5) 4. Fill the blank cells of the
ii) Do the following conversions: output is. (a) (101.10) 10 = (?) 2 i) Define X-NOR gate. (b) (10101) 2 = (?) Gray (2) /030832/31034
 No. of Printed Pages : 4 Roll No.... rd 3 Sem. / ECE Subject : Digital Electronics - I SECTION-A Note: Very Short Answer type questions. Attempt any 15 parts. (15x2=30) Q.1 a) Define analog signal. b)
No. of Printed Pages : 4 Roll No.... rd 3 Sem. / ECE Subject : Digital Electronics - I SECTION-A Note: Very Short Answer type questions. Attempt any 15 parts. (15x2=30) Q.1 a) Define analog signal. b)
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17333 13141 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17333 13141 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
COURSE DESCRIPTION. CS 232 Course Title Computer Organization. Course Coordinators
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Dept., Number Semester hours CS 232 Course Title Computer Organization 4 Course Coordinators Badii, Joseph, Nemes 2004-2006 Catalog Description Comparative study of the organization
COURSE DESCRIPTION Dept., Number Semester hours CS 232 Course Title Computer Organization 4 Course Coordinators Badii, Joseph, Nemes 2004-2006 Catalog Description Comparative study of the organization
END-TERM EXAMINATION
 (Please Write your Exam Roll No. immediately) END-TERM EXAMINATION DECEMBER 2006 Exam. Roll No... Exam Series code: 100919DEC06200963 Paper Code: MCA-103 Subject: Digital Electronics Time: 3 Hours Maximum
(Please Write your Exam Roll No. immediately) END-TERM EXAMINATION DECEMBER 2006 Exam. Roll No... Exam Series code: 100919DEC06200963 Paper Code: MCA-103 Subject: Digital Electronics Time: 3 Hours Maximum
COURSE STRUCTURE AND SYLLABUS APPROVED IN THE BOARD OF STUDIES MEETING HELD ON JULY TO BE EFFECTIVE FROM THE ACADEMIC YEAR
 COURSE STRUCTURE AND SYLLABUS APPROVED IN THE BOARD OF STUDIES MEETING HELD ON JULY- 2000 TO BE EFFECTIVE FROM THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2000-2001 MCA SEMESTER -1 Scheme of evaluation Max. Marks Min. Marks to
COURSE STRUCTURE AND SYLLABUS APPROVED IN THE BOARD OF STUDIES MEETING HELD ON JULY- 2000 TO BE EFFECTIVE FROM THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2000-2001 MCA SEMESTER -1 Scheme of evaluation Max. Marks Min. Marks to
Syllabus for Computer Science General Part I
 Distribution of Questions: Part I Q1. (Compulsory: 20 marks). Any ten questions to be answered out of fifteen questions, each carrying two marks (Group A 3 questions, Group B, Group C and Group D 4 questions
Distribution of Questions: Part I Q1. (Compulsory: 20 marks). Any ten questions to be answered out of fifteen questions, each carrying two marks (Group A 3 questions, Group B, Group C and Group D 4 questions
II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION. Discrete Mathematical Structures. Answer ONE question from each unit.
 14CS IT302 November,2016 II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION Common for CSE & IT Discrete Mathematical Structures (4X12=48 Marks) 1. Answer all questions (1X12=12 Marks) a (Pv~P) is
14CS IT302 November,2016 II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION Common for CSE & IT Discrete Mathematical Structures (4X12=48 Marks) 1. Answer all questions (1X12=12 Marks) a (Pv~P) is
CS/IT DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 CS/IT 214 (CR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, DECEMBER- 2016 First Semester CS/IT DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Time: Three Hours 1. a) Flip-Flop Answer
CS/IT 214 (CR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, DECEMBER- 2016 First Semester CS/IT DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Time: Three Hours 1. a) Flip-Flop Answer
FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1
 FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1 Anurag Dwivedi Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Basic Block - Gates Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Gates -> Flip Flops Digital
FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1 Anurag Dwivedi Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Basic Block - Gates Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Gates -> Flip Flops Digital
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING. (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC1201 DIGITAL
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC1201 DIGITAL
(DMCA101) M.C.A. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY First Year INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
 (DMCA101) M.C.A. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY - 2017 First Year INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 SECTION - A (3 15 = 45) Answer any three of the following Q1) Discuss business pressures
(DMCA101) M.C.A. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY - 2017 First Year INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 SECTION - A (3 15 = 45) Answer any three of the following Q1) Discuss business pressures
Computer Science Paper 1 (Theory) Part I While working questions in this part, indicate briefly your working and reasoning wherever required.
 Computer Science Paper 1 (Theory) Part I While working questions in this part, indicate briefly your working and reasoning wherever required. Question 1. a) Using truth table, verify the following expression:
Computer Science Paper 1 (Theory) Part I While working questions in this part, indicate briefly your working and reasoning wherever required. Question 1. a) Using truth table, verify the following expression:
R10. II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May
 SET - 1 1. a) Convert the following decimal numbers into an equivalent binary numbers. i) 53.625 ii) 4097.188 iii) 167 iv) 0.4475 b) Add the following numbers using 2 s complement method. i) -48 and +31
SET - 1 1. a) Convert the following decimal numbers into an equivalent binary numbers. i) 53.625 ii) 4097.188 iii) 167 iv) 0.4475 b) Add the following numbers using 2 s complement method. i) -48 and +31
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science
Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science
COMPUTER SCIENCE. Paper 1
 COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
M.Sc. (Computer Science) I Year Assignments for May Paper I DATA STRUCTURES Assignment I
 Paper I DATA STRUCTURES (DMCS 01) 1. Explain in detail about the overview of Data structures. 2. Explain circular linked list and double-linked list. 3. Explain CPU scheduling in Multiprogramming Environment.
Paper I DATA STRUCTURES (DMCS 01) 1. Explain in detail about the overview of Data structures. 2. Explain circular linked list and double-linked list. 3. Explain CPU scheduling in Multiprogramming Environment.
Scheme G. Sample Test Paper-I
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Times:1 Hour 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. Assume suitable
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Times:1 Hour 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. Assume suitable
COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1
 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Maximum Marks: 70) (Time allowed: Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.)
COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Maximum Marks: 70) (Time allowed: Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.)
HANSABA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (098) SUBJECT: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS ( ) Assignment
 Assignment 1. What is multiplexer? With logic circuit and function table explain the working of 4 to 1 line multiplexer. 2. Implement following Boolean function using 8: 1 multiplexer. F(A,B,C,D) = (2,3,5,7,8,9,12,13,14,15)
Assignment 1. What is multiplexer? With logic circuit and function table explain the working of 4 to 1 line multiplexer. 2. Implement following Boolean function using 8: 1 multiplexer. F(A,B,C,D) = (2,3,5,7,8,9,12,13,14,15)
DE Solution Set QP Code : 00904
 DE Solution Set QP Code : 00904 1. Attempt any three of the following: 15 a. Define digital signal. (1M) With respect to digital signal explain the terms digits and bits.(2m) Also discuss active high and
DE Solution Set QP Code : 00904 1. Attempt any three of the following: 15 a. Define digital signal. (1M) With respect to digital signal explain the terms digits and bits.(2m) Also discuss active high and
Computer organization by G. Naveen kumar, Asst Prof, C.S.E Department 1
 Pipelining and Vector Processing Parallel Processing: The term parallel processing indicates that the system is able to perform several operations in a single time. Now we will elaborate the scenario,
Pipelining and Vector Processing Parallel Processing: The term parallel processing indicates that the system is able to perform several operations in a single time. Now we will elaborate the scenario,
Course Description: This course includes concepts of instruction set architecture,
 Computer Architecture Course Title: Computer Architecture Full Marks: 60+ 20+20 Course No: CSC208 Pass Marks: 24+8+8 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Credit Hrs: 3 Course Description: This course includes
Computer Architecture Course Title: Computer Architecture Full Marks: 60+ 20+20 Course No: CSC208 Pass Marks: 24+8+8 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Credit Hrs: 3 Course Description: This course includes
CS6303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE UNIT I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS PART A
 CS6303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE UNIT I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS 1. Define Computer Architecture 2. Define Computer H/W 3. What are the functions of control unit? 4. 4.Define Interrupt 5. What are the uses
CS6303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE UNIT I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS 1. Define Computer Architecture 2. Define Computer H/W 3. What are the functions of control unit? 4. 4.Define Interrupt 5. What are the uses
Rizvi College of Arts, Science & Commerce Bandra (W), Mumbai Teaching Plan Academic Year
 Academic Year 17-18 Subject: Communication Skills Faculty: SHABANA ANSARI Class : F.Y.B.Sc. (IT) SEM-1 JUNE The Seven Cs of Effective Communication: Completeness, Conciseness, Consideration, Concreteness,
Academic Year 17-18 Subject: Communication Skills Faculty: SHABANA ANSARI Class : F.Y.B.Sc. (IT) SEM-1 JUNE The Seven Cs of Effective Communication: Completeness, Conciseness, Consideration, Concreteness,
Digital Logic Design Exercises. Assignment 1
 Assignment 1 For Exercises 1-5, match the following numbers with their definition A Number Natural number C Integer number D Negative number E Rational number 1 A unit of an abstract mathematical system
Assignment 1 For Exercises 1-5, match the following numbers with their definition A Number Natural number C Integer number D Negative number E Rational number 1 A unit of an abstract mathematical system
2c. Content of Computer systems (Component 01)
 c. Content of Computer systems (Component 01) This component will introduce learners to the internal workings of the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the exchange of data and will also look at software development,
c. Content of Computer systems (Component 01) This component will introduce learners to the internal workings of the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the exchange of data and will also look at software development,
Injntu.com Injntu.com Injntu.com R16
 1. a) What are the three methods of obtaining the 2 s complement of a given binary (3M) number? b) What do you mean by K-map? Name it advantages and disadvantages. (3M) c) Distinguish between a half-adder
1. a) What are the three methods of obtaining the 2 s complement of a given binary (3M) number? b) What do you mean by K-map? Name it advantages and disadvantages. (3M) c) Distinguish between a half-adder
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science & Systems
Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science & Systems
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ADITYA SILVER OAK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 BE - SEMESTER III MID SEMESTER-I EXAMINATION WINTER 2017 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT (2130004) (CE/IT/EC/EE) DATE: 04/08/2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS:40 Instructions: 1.
BE - SEMESTER III MID SEMESTER-I EXAMINATION WINTER 2017 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT (2130004) (CE/IT/EC/EE) DATE: 04/08/2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS:40 Instructions: 1.
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4. Harper Langston New York University
 Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INDEX
 INDEX Absorption law, 31, 38 Acyclic graph, 35 tree, 36 Addition operators, in VHDL (VHSIC hardware description language), 192 Algebraic division, 105 AND gate, 48 49 Antisymmetric, 34 Applicable input
INDEX Absorption law, 31, 38 Acyclic graph, 35 tree, 36 Addition operators, in VHDL (VHSIC hardware description language), 192 Algebraic division, 105 AND gate, 48 49 Antisymmetric, 34 Applicable input
1. What is y-chart? ans: The y- chart consists of three domains:- behavioral, structural and geometrical.
 SECTION- A Short questions: (each 2 marks) 1. What is y-chart? ans: The y- chart consists of three domains:- behavioral, structural and geometrical. 2. What is fabrication? ans: It is the process used
SECTION- A Short questions: (each 2 marks) 1. What is y-chart? ans: The y- chart consists of three domains:- behavioral, structural and geometrical. 2. What is fabrication? ans: It is the process used
R07. Code No: V0423. II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April - 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April - 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Assignment For Fresh (Session ) admitted students of Odd Semester PGDCA/M.Sc Computer Science/ MCA (Through Distance Education)
 Assignment For Fresh (Session 2018-2019) admitted students of Odd Semester PGDCA/M.Sc Computer Science/ MCA (Through Distance Education) For session 2018-2019 Directorate of Distance Education Guru Jambeshwar
Assignment For Fresh (Session 2018-2019) admitted students of Odd Semester PGDCA/M.Sc Computer Science/ MCA (Through Distance Education) For session 2018-2019 Directorate of Distance Education Guru Jambeshwar
5 Computer Organization
 5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science ã Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: q List the three subsystems of a computer. q Describe
5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science ã Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: q List the three subsystems of a computer. q Describe
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Regular Examinations December 2014 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 B.Tech II Year I Semester () Regular Examinations December 2014 (Common to IT and CSE) (a) If 1010 2 + 10 2 = X 10, then X is ----- Write the first 9 decimal digits in base 3. (c) What is meant by don
B.Tech II Year I Semester () Regular Examinations December 2014 (Common to IT and CSE) (a) If 1010 2 + 10 2 = X 10, then X is ----- Write the first 9 decimal digits in base 3. (c) What is meant by don
Summary of Course Coverage
 CS-227, Discrete Structures I Spring 2006 Semester Summary of Course Coverage 1) Propositional Calculus a) Negation (logical NOT) b) Conjunction (logical AND) c) Disjunction (logical inclusive-or) d) Inequalities
CS-227, Discrete Structures I Spring 2006 Semester Summary of Course Coverage 1) Propositional Calculus a) Negation (logical NOT) b) Conjunction (logical AND) c) Disjunction (logical inclusive-or) d) Inequalities
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: Digital Design Using Verilog Hdl Class : ECE-II Group A (Short Answer Questions) UNIT-I 1 Define verilog HDL? 2 List levels of
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: Digital Design Using Verilog Hdl Class : ECE-II Group A (Short Answer Questions) UNIT-I 1 Define verilog HDL? 2 List levels of
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE)
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : STLD(16EC402) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : STLD(16EC402) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
Propositional Calculus. Math Foundations of Computer Science
 Propositional Calculus Math Foundations of Computer Science Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus so that they can use it to
Propositional Calculus Math Foundations of Computer Science Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus so that they can use it to
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Winter
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday March 18 8am-11am. Lecture A will take the exam in GH 242 Lecture B will take the exam
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday March 18 8am-11am. Lecture A will take the exam in GH 242 Lecture B will take the exam
Honorary Professor Supercomputer Education and Research Centre Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE V. Rajaraman Honorary Professor Supercomputer Education and Research Centre Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore T. Radhakrishnan Professor of Computer Science
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE V. Rajaraman Honorary Professor Supercomputer Education and Research Centre Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore T. Radhakrishnan Professor of Computer Science
About the Tutorial. Audience. Prerequisites. Copyright & Disclaimer. Discrete Mathematics
 About the Tutorial Discrete Mathematics is a branch of mathematics involving discrete elements that uses algebra and arithmetic. It is increasingly being applied in the practical fields of mathematics
About the Tutorial Discrete Mathematics is a branch of mathematics involving discrete elements that uses algebra and arithmetic. It is increasingly being applied in the practical fields of mathematics
ISC 2010 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY
 ISC 2010 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY Question 1. a) If X=A BC + AB C + ABC + A BC then find the value of X when A=1; B=0; C=1 b) Verify if, P.(~P+Q )=(P Q) using truth table. c) Draw the logic circuit
ISC 2010 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY Question 1. a) If X=A BC + AB C + ABC + A BC then find the value of X when A=1; B=0; C=1 b) Verify if, P.(~P+Q )=(P Q) using truth table. c) Draw the logic circuit
5 Computer Organization
 5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer. Describe the
5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer. Describe the
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2006 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science & Systems
Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2006 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science & Systems
(l) Represent each of the sets A, B and C using bit strings. Then, use bit string representation and bitwise logical operations to find
 Fall 2004 Ahmed Elgammal CS 205: Sample Final Exam December 6th, 2004 1. [10 points] Let A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}, C = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}, D = {1, 2, 3} and let the universal set be U = {1,
Fall 2004 Ahmed Elgammal CS 205: Sample Final Exam December 6th, 2004 1. [10 points] Let A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}, C = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}, D = {1, 2, 3} and let the universal set be U = {1,
DC57 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION JUNE 2013
 Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
Q2 (a) How do various factors like Hardware design, Instruction set, Compiler related to the performance of a computer? The most important measure of a computer is how quickly it can execute programs.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE. SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC6302 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur-603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC6302 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS YEAR / SEMESTER: II / III ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (ODD
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur-603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC6302 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS YEAR / SEMESTER: II / III ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (ODD
BCA Part-1 Examination, 2007 Computer Fundamentals
 Computer Fundamentals 1. (a) What are the advantages of computers? Explain with examples the major applications of computers. (b) What are the main characteristics of a digital computer? 2. (a) Describe
Computer Fundamentals 1. (a) What are the advantages of computers? Explain with examples the major applications of computers. (b) What are the main characteristics of a digital computer? 2. (a) Describe
Fundamental of I.T. (c) Application of computer *************
 Paper I Fundamental of I.T 1. What is an output device? Discuss the type of output device used in computer. 2. What is Secondary memory? Discuss the type of secondary memory used in computer. 3. Explain
Paper I Fundamental of I.T 1. What is an output device? Discuss the type of output device used in computer. 2. What is Secondary memory? Discuss the type of secondary memory used in computer. 3. Explain
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION FOR B.Sc.(COMPUTER SCIENCE) SEMESTER SYSTEM (Regular Course) w.e.f Scheme for B.Sc.-I. Semester-I. Internal Assessment
 SCHEME OF EXAMINATION FOR B.Sc.(COMPUTER SCIENCE) SEMESTER SYSTEM (Regular Course) w.e.f. 2013-14 Scheme for B.Sc.-I Sr. No. Paper 1 Paper-I Computer And Programming Fundamentals Semester-I Internal Assessment
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION FOR B.Sc.(COMPUTER SCIENCE) SEMESTER SYSTEM (Regular Course) w.e.f. 2013-14 Scheme for B.Sc.-I Sr. No. Paper 1 Paper-I Computer And Programming Fundamentals Semester-I Internal Assessment
ISC 2011 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY
 ISC 2011 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY Question 1. a) State the two absorption laws. Verify any one of them using truth table. b) Reduce the following expression : F(A,B,C)= (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7) Also find
ISC 2011 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY Question 1. a) State the two absorption laws. Verify any one of them using truth table. b) Reduce the following expression : F(A,B,C)= (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7) Also find
INTELLIGENCE PLUS CHARACTER - THAT IS THE GOAL OF TRUE EDUCATION UNIT-I
 UNIT-I 1. List and explain the functional units of a computer with a neat diagram 2. Explain the computer levels of programming languages 3. a) Explain about instruction formats b) Evaluate the arithmetic
UNIT-I 1. List and explain the functional units of a computer with a neat diagram 2. Explain the computer levels of programming languages 3. a) Explain about instruction formats b) Evaluate the arithmetic
RISC Processors and Parallel Processing. Section and 3.3.6
 RISC Processors and Parallel Processing Section 3.3.5 and 3.3.6 The Control Unit When a program is being executed it is actually the CPU receiving and executing a sequence of machine code instructions.
RISC Processors and Parallel Processing Section 3.3.5 and 3.3.6 The Control Unit When a program is being executed it is actually the CPU receiving and executing a sequence of machine code instructions.
Computer Systems. Binary Representation. Binary Representation. Logical Computation: Boolean Algebra
 Binary Representation Computer Systems Information is represented as a sequence of binary digits: Bits What the actual bits represent depends on the context: Seminar 3 Numerical value (integer, floating
Binary Representation Computer Systems Information is represented as a sequence of binary digits: Bits What the actual bits represent depends on the context: Seminar 3 Numerical value (integer, floating
Structure of Computer Systems
 288 between this new matrix and the initial collision matrix M A, because the original forbidden latencies for functional unit A still have to be considered in later initiations. Figure 5.37. State diagram
288 between this new matrix and the initial collision matrix M A, because the original forbidden latencies for functional unit A still have to be considered in later initiations. Figure 5.37. State diagram
COMPUTER APPLICATION
 Total No. of Printed Pages 16 HS/XII/A.Sc.Com/CAP/14 2 0 1 4 COMPUTER APPLICATION ( Science / Arts / Commerce ) ( Theory ) Full Marks : 70 Time : 3 hours The figures in the margin indicate full marks for
Total No. of Printed Pages 16 HS/XII/A.Sc.Com/CAP/14 2 0 1 4 COMPUTER APPLICATION ( Science / Arts / Commerce ) ( Theory ) Full Marks : 70 Time : 3 hours The figures in the margin indicate full marks for
(DMTCS 01) Answer Question No.1 is compulsory (15) Answer One question from each unit (4 15=60) 1) a) State whether the following is True/False:
 (DMTCS 01) M.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER - 2015 (Examination at the end of First Year) COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper - I : Data structures Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 75 Answer Question No.1 is compulsory
(DMTCS 01) M.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER - 2015 (Examination at the end of First Year) COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper - I : Data structures Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 75 Answer Question No.1 is compulsory
Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING. Fifth Semester. Subject: VHDL Programming
 Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Fifth Semester Subject: VHDL Programming Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester : 64 CONTENTS No. Of
Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Fifth Semester Subject: VHDL Programming Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester : 64 CONTENTS No. Of
Old Question Papers of PGDCA 1 st Semester H.K. Hi-Tech (College of IT & Management) H.K. Hi-Tech College of IT & Management
 () Q.1 (a) What is a computer system? What are the various components of a CPU? Also explain its working. (b) What are the things that computers can do? Also explain the various characteristics of computers?
() Q.1 (a) What is a computer system? What are the various components of a CPU? Also explain its working. (b) What are the things that computers can do? Also explain the various characteristics of computers?
SECTION A. (i) The Boolean function in sum of products form where K-map is given below (figure) is:
 SECTION A 1. Fill in the blanks: (i) The Boolean function in sum of products form where K-map is given below (figure) is: C B 0 1 0 1 0 1 A A (ii) Consider a 3-bit error detection and 1-bit error correction
SECTION A 1. Fill in the blanks: (i) The Boolean function in sum of products form where K-map is given below (figure) is: C B 0 1 0 1 0 1 A A (ii) Consider a 3-bit error detection and 1-bit error correction
NADAR SARASWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Vadapudupatti, Theni
 NADAR SARASWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Vadapudupatti, Theni-625531 Question Bank for the Units I to V SEMESTER BRANCH SUB CODE 3rd Semester B.E. / B.Tech. Electrical and Electronics Engineering
NADAR SARASWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Vadapudupatti, Theni-625531 Question Bank for the Units I to V SEMESTER BRANCH SUB CODE 3rd Semester B.E. / B.Tech. Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Computer Organization
 A Text Book of Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. JATINDER SINGH Director, GGI, Dhaliwal Er. AMARDEEP SINGH M.Tech (IT) AP&HOD, Deptt.of CSE, SVIET, Banur Er. GURJEET SINGH M.Tech (CSE) Head,
A Text Book of Computer Organization and Architecture Prof. JATINDER SINGH Director, GGI, Dhaliwal Er. AMARDEEP SINGH M.Tech (IT) AP&HOD, Deptt.of CSE, SVIET, Banur Er. GURJEET SINGH M.Tech (CSE) Head,
Principles of Digital Techniques PDT (17320) Assignment No State advantages of digital system over analog system.
 Assignment No. 1 1. State advantages of digital system over analog system. 2. Convert following numbers a. (138.56) 10 = (?) 2 = (?) 8 = (?) 16 b. (1110011.011) 2 = (?) 10 = (?) 8 = (?) 16 c. (3004.06)
Assignment No. 1 1. State advantages of digital system over analog system. 2. Convert following numbers a. (138.56) 10 = (?) 2 = (?) 8 = (?) 16 b. (1110011.011) 2 = (?) 10 = (?) 8 = (?) 16 c. (3004.06)
 www.vidyarthiplus.com Question Paper Code : 31298 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 2202/CS 34/EC 1206 A/10144 CS 303/080230012--DIGITAL
www.vidyarthiplus.com Question Paper Code : 31298 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 2202/CS 34/EC 1206 A/10144 CS 303/080230012--DIGITAL
Computer Organization
 Objectives 5.1 Chapter 5 Computer Organization Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning 5.2 After studying this chapter, students should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer.
Objectives 5.1 Chapter 5 Computer Organization Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning 5.2 After studying this chapter, students should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer.
Digital logic fundamentals. Question Bank. Unit I
 Digital logic fundamentals Question Bank Subject Name : Digital Logic Fundamentals Subject code: CA102T Staff Name: R.Roseline Unit I 1. What is Number system? 2. Define binary logic. 3. Show how negative
Digital logic fundamentals Question Bank Subject Name : Digital Logic Fundamentals Subject code: CA102T Staff Name: R.Roseline Unit I 1. What is Number system? 2. Define binary logic. 3. Show how negative
What Is A Relation? Example. is a relation from A to B.
 3.3 Relations What Is A Relation? Let A and B be nonempty sets. A relation R from A to B is a subset of the Cartesian product A B. If R A B and if (a, b) R, we say that a is related to b by R and we write
3.3 Relations What Is A Relation? Let A and B be nonempty sets. A relation R from A to B is a subset of the Cartesian product A B. If R A B and if (a, b) R, we say that a is related to b by R and we write
mrrj izns k jktf kz V.Mu eqdr fo ofo ky;]bykgkckn
![mrrj izns k jktf kz V.Mu eqdr fo ofo ky;]bykgkckn mrrj izns k jktf kz V.Mu eqdr fo ofo ky;]bykgkckn](/thumbs/94/121751516.jpg) dk;zdze vf/ku;kl सत र 2018-19 Course Code: PGDCA-01 Discrete Mathematics 1. Answer the following: a. Out of 7 consonants and 4 vowels, how many words of 3 consonants and 2 vowels can be formed? b. In a
dk;zdze vf/ku;kl सत र 2018-19 Course Code: PGDCA-01 Discrete Mathematics 1. Answer the following: a. Out of 7 consonants and 4 vowels, how many words of 3 consonants and 2 vowels can be formed? b. In a
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1
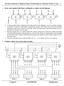 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : DIGITAL DESIGN USING VERILOG HDL Course Code : A00 Class : II - B.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : DIGITAL DESIGN USING VERILOG HDL Course Code : A00 Class : II - B.
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2018/2019 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 03/01/2019
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2018/2019 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 03/01/2019
ISC 2009 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY PART I Answer all questions in this part
 ISC 2009 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY PART I Answer all questions in this part Question 1. a) Obtain the truth table to verify the following expression: X(Y+Z) = XY + XZ. Also name the law stated above.
ISC 2009 COMPUTER SCIENCE PAPER 1 THEORY PART I Answer all questions in this part Question 1. a) Obtain the truth table to verify the following expression: X(Y+Z) = XY + XZ. Also name the law stated above.
STUDENT NUMBER: MATH Final Exam. Lakehead University. April 13, Dr. Adam Van Tuyl
 Page 1 of 13 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MATH 1281 - Final Exam Lakehead University April 13, 2011 Dr. Adam Van Tuyl Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided. If you need more room, answer on
Page 1 of 13 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: MATH 1281 - Final Exam Lakehead University April 13, 2011 Dr. Adam Van Tuyl Instructions: Answer all questions in the space provided. If you need more room, answer on
Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs)
 Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs) 212: Digital Design I, week 13 PLDs basically store binary information in a volatile/nonvolatile device. Data is specified by designer and physically inserted (Programmed)
Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs) 212: Digital Design I, week 13 PLDs basically store binary information in a volatile/nonvolatile device. Data is specified by designer and physically inserted (Programmed)
10EC33: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS QUESTION BANK
 10EC33: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS Faculty: Dr.Bajarangbali E Examination QuestionS QUESTION BANK 1. Discuss canonical & standard forms of Boolean functions with an example. 2. Convert the following Boolean function
10EC33: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS Faculty: Dr.Bajarangbali E Examination QuestionS QUESTION BANK 1. Discuss canonical & standard forms of Boolean functions with an example. 2. Convert the following Boolean function
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. Spring 2010 May 10, 2010
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 J. Wawrzynek Spring 2010 May 10, 2010 Final Exam Name: ID number: This is
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 J. Wawrzynek Spring 2010 May 10, 2010 Final Exam Name: ID number: This is
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
Unit wise Question Bank UNIT-II
 Academic year: 2017-18 Program: B Tech Course Title: Microprocessor & Microcontrollers Unit wise Question Bank Year/Semester: III/I Section: A, B & C Branch: ECE UNIT-I 1. Draw the functional pin diagram
Academic year: 2017-18 Program: B Tech Course Title: Microprocessor & Microcontrollers Unit wise Question Bank Year/Semester: III/I Section: A, B & C Branch: ECE UNIT-I 1. Draw the functional pin diagram
CS 101 Advanced Computer System Architecture 100 ( ) CS 102 Operating System 100 ( )
 Syllabus for M.Sc. Computer Science Programme Semester I External/ Internal CS 101 Advanced Computer System Architecture 100 ( 75 + 25 ) CS 102 Operating System 100 ( 75 + 25 ) CS 103 Mathematical Foundation
Syllabus for M.Sc. Computer Science Programme Semester I External/ Internal CS 101 Advanced Computer System Architecture 100 ( 75 + 25 ) CS 102 Operating System 100 ( 75 + 25 ) CS 103 Mathematical Foundation
(ii) Simplify and implement the following SOP function using NOR gates:
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EE6301 DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS UNIT I NUMBER SYSTEMS AND DIGITAL LOGIC FAMILIES PART A 1. How can an OR gate be
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EE6301 DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS UNIT I NUMBER SYSTEMS AND DIGITAL LOGIC FAMILIES PART A 1. How can an OR gate be
Sample Exam I PAC II ANSWERS
 Sample Exam I PAC II ANSWERS Please answer questions 1 and 2 on this paper and put all other answers in the blue book. 1. True/False. Please circle the correct response. a. T In the C and assembly calling
Sample Exam I PAC II ANSWERS Please answer questions 1 and 2 on this paper and put all other answers in the blue book. 1. True/False. Please circle the correct response. a. T In the C and assembly calling
MLR Institute of Technology
 MLR Institute of Technology Laxma Reddy Avenue, Dundigal, Quthbullapur (M), Hyderabad 500 043 Course Name Course Code Class Branch ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : DIGITAL DESIGN
MLR Institute of Technology Laxma Reddy Avenue, Dundigal, Quthbullapur (M), Hyderabad 500 043 Course Name Course Code Class Branch ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : DIGITAL DESIGN
MC 302 GRAPH THEORY 10/1/13 Solutions to HW #2 50 points + 6 XC points
 MC 0 GRAPH THEORY 0// Solutions to HW # 0 points + XC points ) [CH] p.,..7. This problem introduces an important class of graphs called the hypercubes or k-cubes, Q, Q, Q, etc. I suggest that before you
MC 0 GRAPH THEORY 0// Solutions to HW # 0 points + XC points ) [CH] p.,..7. This problem introduces an important class of graphs called the hypercubes or k-cubes, Q, Q, Q, etc. I suggest that before you
[Ch 6] Set Theory. 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions. 400 lecture note #4. 1) Basics
![[Ch 6] Set Theory. 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions. 400 lecture note #4. 1) Basics [Ch 6] Set Theory. 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions. 400 lecture note #4. 1) Basics](/thumbs/82/86066673.jpg) 400 lecture note #4 [Ch 6] Set Theory 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions 1) Basics Element: ; A is a set consisting of elements x which is in a/another set S such that P(x) is true. Empty set: notated {
400 lecture note #4 [Ch 6] Set Theory 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions 1) Basics Element: ; A is a set consisting of elements x which is in a/another set S such that P(x) is true. Empty set: notated {
MULTIPLE OPERAND ADDITION. Multioperand Addition
 MULTIPLE OPERAND ADDITION Chapter 3 Multioperand Addition Add up a bunch of numbers Used in several algorithms Multiplication, recurrences, transforms, and filters Signed (two s comp) and unsigned Don
MULTIPLE OPERAND ADDITION Chapter 3 Multioperand Addition Add up a bunch of numbers Used in several algorithms Multiplication, recurrences, transforms, and filters Signed (two s comp) and unsigned Don
