Knowledge-based Systems for Industrial Applications - Propositional Logic
|
|
|
- Georgia Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Knowledge-based Systems for Industrial Applications - Propositional Logic P. Struss WS 16/17 WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 1
2 Logic 2A Logic und Knowledge Representation 2A.1 Propositional logic WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 2
3 Example: Problem with the Car ( [Reinfrank 91]) The engine of my car doesn t start What happens if you turn on the light? The light is on What do you hear if you try to start the engine? It sounds normal, but the engine doesn t start Then you probably forgot to buy gas Oh... (blushes) How did you know that? If the starter works fine, the battery is ok and there is enough gas, the engine would start. The noise shows, that the starter works fine and the battery has power. Hence, gas is missing. Can we use logic, to represent such knowledge and to draw proper conclusions? WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 3
4 Situations - Structures Specific situation described by aspects (features, objects properties, ) e.g. car problem: engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal Situation: represented by a structure (vector): Presence or absence of properties: e.g. a car situation engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal (F, F, T, T, F, F) WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 4
5 Situation Description Information about a specific situation: Constrains the set of vectors e.g. the problem situation engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal (F, *, *, *, T, T) (* means no constraints) Not all possible vectors characterize real situations e.g. all situations engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal (T, *, F, *, *, *) are impossible WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 5
6 Propositional Logic Atomic Formulas Knowledge: Constraint on the vector space Enumeration of all possible vectors impossible or unnecessary Description of sets of vectors with formulas of a symbolic language Symbolic names of elementary aspects, e.g. EngineStarts, BatteryOK Atomic Formulas e.g., the formula SoundNormal means: The starter sounds normal WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 6
7 Propositional Logic - Composite Formulas Composite formulas: consist of atomic formulas and/or composite formulas with logical relations (connectors) For instance: conjunction (AND) BatteryOK LightOn ( The battery is OK and the light is on ) For instance: Negation(NOT) ( BatteryOK LightOn) ( The battery is empty, and the light is on ) WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 7
8 Truth Value For each formula: true or false for a certain structure. Atomic formulas, p: Truth value directly given in structure S e.g. Val(LightON, S) = S (LightON) Composite formulas: Value (recursively) determined from the values of the parts dependent on the connectors e.g. Val( (BatteryOK LightOn), S) = T if Val(BatteryOK LightOn), S) = F = F if Val(BatteryOK LightOn), S) = T and Val (BatteryOK LightOn), S) = T if Val(BatteryOK, S) = T and Val(LightOn, S) = T = F else WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 8
9 Truth Tables Truth Values of different relations: p q q p q p q p q F F T F F T F T F F T T T F F T F T T T T T WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 9
10 Models Model of a formula p: A structure, S, for which p is true For instance, every structure engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal (*, F, *, *, T, *) is a model of the formula LightOn but no model of the formula ( BatteryOK LightOn) A structure, S, is a model of a set of formulas, if it is a model of every formula in the set. Tautology: formula, for which every structure is a model. Inconsistent: formula (or set of formulas) that has no model. WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 10
11 Models (Cont d) Models of a set of formulas: Intersection of the formulas model sets. For instance, a structure engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal (*, T, *, *, T, *) is a model of the set of formulas {LightOn, ( BatteryOK LightOn)} Basic Idea: Represent general knowledge about a domain and information about a particular situation by means of formulas and determine the models of this set of formulas. WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 11
12 Back to the Car Example Formulas and Models Information about the situation: ( 1 ) SoundNormal engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal (*, *, *, *, *, T) ( 2 ) MotorStarts (F, *, *, *, *, *) Knowledge about the domain : (K 1 ) SoundNormal ( StarterOK BatteryOK ) (*, T, *, T, *, T) (*, *, *, *, *, F) (K 2 ) (StarterOK BatteryOK Gasoline ) MotorStarts (T, T, T, T, *, *) (*, *, *, F, *, *) (*, *, F, *, *, *) (*, F, *, *, *, *) Intersection (F, T, F, T, *, T) that means: no gas! WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 12
13 Entailment A formula, p, which is true for all models of a set of formulas, {p 1,..., p k }, is entailed by {p 1,..., p k } : {p 1,..., p k } p Car example: gasoline is entailed by general knowledge and information about the situation: { 1, 2, K 1, K 2 } gasoline Task: Replace ( 1 ) and (K 1 ) with ( 1) LightOn (K 1) ( Batterie OK LightOn) Then { 1, 2, K 1, K 2 } ( Gasoline StarterOK) WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 13
14 Another Car Example Information about the situation: ( 1) LightOn engine battery gasoline starter light sound starts OK OK on normal (*, *, *, *, T, *) ( 2 ) MotorStarts (F, *, *, *, *, *) Knowledge about the domain : (K 1) ( BatteryOK LightOn) (*, T, *, *, *, *) (*, *, *, *, F, *) (K 2 ) (StarterOK BatteryOK Gasoline) MotorStarts (T, T, T, T, *, *) (*, *, *, F, *, *) (*, *, F, *, *, *) (*, F, *, *, *, *) Intersection: Diagnosis? WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 14
15 Inference Rules Determine all models to find the logical implications? impossible Basic Idea: transform formula sets directly and prove the logical consequences symbolically. Inference rules generate formulas from sets of formulas WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 15
16 Inference Rules - Examples Modus Ponens p, p q / q If p holds, and p q holds, then also q holds Because: p q p q F F T F T T T F F T T T Other inference rules: q, p q / p p, (p q) / q p, p q / q WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 16
17 Symbolic Proofs A proof of a formula, q, from a set of formulas, {p 1,..., p k }, is a sequence of execution of n inference rules q m1, q m2,..., q mj / q m, 1 m n, where for each q mi holds q mi {p 1,..., p k } or q mi = q j for j m 1 is valid and q m = q If such a proof exists, q is provable from {p 1,..., p k }: p 1,..., p k q WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 17
18 A Proof for Gasoline ( 1) SoundNormal (K1) SoundNormal ( StarterOK BatteryOK) p, p q / q (K2) (StarterOK BatteryOK Gasoline) MotorStarts ( 2) MotorStarts q, p q / p (StarterOK BatteryOK) (StarterOK BatteryOK Gasoline ) p, (p q) / q Gasoline WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 18
19 Symbolic Proofs - Properties Interesting are sets of inference rules, that are correct, i.e. if {p 1,..., p k } q, then {p 1,..., p k } q or even (correct and) complete, i.e. if {p 1,..., p k } q, then {p 1,..., p k } q WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 19
20 Another Example: Problem with the Car The engine of my car doesn t start What happens if you turn on the light? The light is on What do you hear if you try to start the engine? It sounds normal, but the engine doesn t start Then you probably forgot to buy gas My car is an electric car Oh (Blushes) Why does the reasoning fail this time? WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 20
21 Proof for Gasoline: Based on Assumptions about the Car ( 1) SoundNormal (K1) SoundNormal ( StarterOK BatteryOK) p, p q / q (K2) (StarterOK BatteryOK Gasoline) MotorStarts ( 2) MotorStarts q, p q / p (StarterOK BatteryOK) (StarterOK BatteryOK Gasoline ) p, (p q) / q Gasoline WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 21
22 A Different Approach to Diagnosis Required Rule base not re-usable Applicability implicit Needed: Explicit representation of the structure of the car Organize (diagnostic) knowledge around (types of) components Model-based diagnosis WS 16/17 KBSIA 2A - 22
Diagnosis through constrain propagation and dependency recording. 2 ATMS for dependency recording
 Diagnosis through constrain propagation and dependency recording 2 ATMS for dependency recording Fundamentals of Truth Maintenance Systems, TMS Motivation (de Kleer): for most search tasks, there is a
Diagnosis through constrain propagation and dependency recording 2 ATMS for dependency recording Fundamentals of Truth Maintenance Systems, TMS Motivation (de Kleer): for most search tasks, there is a
Declarative Programming. 2: theoretical backgrounds
 Declarative Programming 2: theoretical backgrounds 1 Logic Systems: structure and meta-theoretical properties logic system syntax semantics proof theory defines which sentences are legal in the logical
Declarative Programming 2: theoretical backgrounds 1 Logic Systems: structure and meta-theoretical properties logic system syntax semantics proof theory defines which sentences are legal in the logical
Revisiting Kalmar completeness metaproof
 Revisiting Kalmar completeness metaproof Angélica Olvera Badillo 1 Universidad de las Américas, Sta. Catarina Mártir, Cholula, Puebla, 72820 México angelica.olverabo@udlap.mx Abstract In this paper, I
Revisiting Kalmar completeness metaproof Angélica Olvera Badillo 1 Universidad de las Américas, Sta. Catarina Mártir, Cholula, Puebla, 72820 México angelica.olverabo@udlap.mx Abstract In this paper, I
STABILITY AND PARADOX IN ALGORITHMIC LOGIC
 STABILITY AND PARADOX IN ALGORITHMIC LOGIC WAYNE AITKEN, JEFFREY A. BARRETT Abstract. Algorithmic logic is the logic of basic statements concerning algorithms and the algorithmic rules of deduction between
STABILITY AND PARADOX IN ALGORITHMIC LOGIC WAYNE AITKEN, JEFFREY A. BARRETT Abstract. Algorithmic logic is the logic of basic statements concerning algorithms and the algorithmic rules of deduction between
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics
 Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
Propositional logic (Ch. 7)
 Propositional logic (Ch. 7) Announcements Writing 3 due Sunday - ideally use for project - if you haven't decided project by then, you will have to redo this work Logic: definitions We say that two sentences
Propositional logic (Ch. 7) Announcements Writing 3 due Sunday - ideally use for project - if you haven't decided project by then, you will have to redo this work Logic: definitions We say that two sentences
Chapter 2 & 3: Representations & Reasoning Systems (2.2)
 Chapter 2 & 3: A Representation & Reasoning System & Using Definite Knowledge Representations & Reasoning Systems (RRS) (2.2) Simplifying Assumptions of the Initial RRS (2.3) Datalog (2.4) Semantics (2.5)
Chapter 2 & 3: A Representation & Reasoning System & Using Definite Knowledge Representations & Reasoning Systems (RRS) (2.2) Simplifying Assumptions of the Initial RRS (2.3) Datalog (2.4) Semantics (2.5)
The Truth about Types. Bartosz Milewski
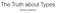 The Truth about Types Bartosz Milewski Truth Truth Logic Types Categories Truth intro Unit type Terminal object true I () : () Proofs Logic Types Categories Proof of proposition A Type A is inhabited Morphism
The Truth about Types Bartosz Milewski Truth Truth Logic Types Categories Truth intro Unit type Terminal object true I () : () Proofs Logic Types Categories Proof of proposition A Type A is inhabited Morphism
Proofs are Programs. Prof. Clarkson Fall Today s music: Proof by Paul Simon
 Proofs are Programs Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Proof by Paul Simon Review Previously in 3110: Functional programming in Coq Logic in Coq Today: A fundamental idea that goes by many names...
Proofs are Programs Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Proof by Paul Simon Review Previously in 3110: Functional programming in Coq Logic in Coq Today: A fundamental idea that goes by many names...
Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple. variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,
 CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 5 Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple, variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,, are all finite. 1 ( ) $ Pumping Lemma for
CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 5 Definition: A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4- tuple, variables = nonterminals, terminals, rules = productions,,, are all finite. 1 ( ) $ Pumping Lemma for
Propositional Logic. Part I
 Part I Propositional Logic 1 Classical Logic and the Material Conditional 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 The first purpose of this chapter is to review classical propositional logic, including semantic tableaux.
Part I Propositional Logic 1 Classical Logic and the Material Conditional 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 The first purpose of this chapter is to review classical propositional logic, including semantic tableaux.
CSL105: Discrete Mathematical Structures. Ragesh Jaiswal, CSE, IIT Delhi
 is another way of showing that an argument is correct. Definitions: Literal: A variable or a negation of a variable is called a literal. Sum and Product: A disjunction of literals is called a sum and a
is another way of showing that an argument is correct. Definitions: Literal: A variable or a negation of a variable is called a literal. Sum and Product: A disjunction of literals is called a sum and a
Summary of Course Coverage
 CS-227, Discrete Structures I Spring 2006 Semester Summary of Course Coverage 1) Propositional Calculus a) Negation (logical NOT) b) Conjunction (logical AND) c) Disjunction (logical inclusive-or) d) Inequalities
CS-227, Discrete Structures I Spring 2006 Semester Summary of Course Coverage 1) Propositional Calculus a) Negation (logical NOT) b) Conjunction (logical AND) c) Disjunction (logical inclusive-or) d) Inequalities
Mathematics for Computer Scientists 2 (G52MC2)
 Mathematics for Computer Scientists 2 (G52MC2) L07 : Operations on sets School of Computer Science University of Nottingham October 29, 2009 Enumerations We construct finite sets by enumerating a list
Mathematics for Computer Scientists 2 (G52MC2) L07 : Operations on sets School of Computer Science University of Nottingham October 29, 2009 Enumerations We construct finite sets by enumerating a list
Knowledge Representation and Reasoning Logics for Artificial Intelligence
 Knowledge Representation and Reasoning Logics for Artificial Intelligence Stuart C. Shapiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering and Center for Cognitive Science University at Buffalo, The State
Knowledge Representation and Reasoning Logics for Artificial Intelligence Stuart C. Shapiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering and Center for Cognitive Science University at Buffalo, The State
Introduction to dependent types in Coq
 October 24, 2008 basic use of the Coq system In Coq, you can play with simple values and functions. The basic command is called Check, to verify if an expression is well-formed and learn what is its type.
October 24, 2008 basic use of the Coq system In Coq, you can play with simple values and functions. The basic command is called Check, to verify if an expression is well-formed and learn what is its type.
Propositional Logic Formal Syntax and Semantics. Computability and Logic
 Propositional Logic Formal Syntax and Semantics Computability and Logic Syntax and Semantics Syntax: The study of how expressions are structured (think: grammar) Semantics: The study of the relationship
Propositional Logic Formal Syntax and Semantics Computability and Logic Syntax and Semantics Syntax: The study of how expressions are structured (think: grammar) Semantics: The study of the relationship
Introduction to Logic Programming
 Introduction to Logic Programming York University CSE 3401 Vida Movahedi York University CSE 3401 V. Movahedi 1 Overview Programming Language Paradigms Logic Programming Functional Programming Brief review
Introduction to Logic Programming York University CSE 3401 Vida Movahedi York University CSE 3401 V. Movahedi 1 Overview Programming Language Paradigms Logic Programming Functional Programming Brief review
What's the difference between the entailment symbol with the equals vs the entailment symbol with one line? Single turnstile meaning
 Propositional connectives, satisfying values, Get expression from venn diagram Definitions (tautology, satisfiability, etc) and basic entailment and arrow rule 3-sat to 2-sat, turning a cnf into arrow
Propositional connectives, satisfying values, Get expression from venn diagram Definitions (tautology, satisfiability, etc) and basic entailment and arrow rule 3-sat to 2-sat, turning a cnf into arrow
[Ch 6] Set Theory. 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions. 400 lecture note #4. 1) Basics
![[Ch 6] Set Theory. 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions. 400 lecture note #4. 1) Basics [Ch 6] Set Theory. 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions. 400 lecture note #4. 1) Basics](/thumbs/82/86066673.jpg) 400 lecture note #4 [Ch 6] Set Theory 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions 1) Basics Element: ; A is a set consisting of elements x which is in a/another set S such that P(x) is true. Empty set: notated {
400 lecture note #4 [Ch 6] Set Theory 1. Basic Concepts and Definitions 1) Basics Element: ; A is a set consisting of elements x which is in a/another set S such that P(x) is true. Empty set: notated {
Knowledge-based systems in bioinformatics 1MB602. Exam
 Knowledge-based systems in bioinformatics MB602 Exam 2007-04-7 Contact under exam: Robin Andersson 08-47 66 86 Grading: 3: 20p 4: 27p 5: 36p Max: 45p General instructions:. Keep it short! 2. If anything
Knowledge-based systems in bioinformatics MB602 Exam 2007-04-7 Contact under exam: Robin Andersson 08-47 66 86 Grading: 3: 20p 4: 27p 5: 36p Max: 45p General instructions:. Keep it short! 2. If anything
For next Tuesday. Read chapter 8 No written homework Initial posts due Thursday 1pm and responses due by class time Tuesday
 For next Tuesday Read chapter 8 No written homework Initial posts due Thursday 1pm and responses due by class time Tuesday Any questions? Program 1 Imperfect Knowledge What issues arise when we don t know
For next Tuesday Read chapter 8 No written homework Initial posts due Thursday 1pm and responses due by class time Tuesday Any questions? Program 1 Imperfect Knowledge What issues arise when we don t know
Towards a Logical Reconstruction of Relational Database Theory
 Towards a Logical Reconstruction of Relational Database Theory On Conceptual Modelling, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 1984 Raymond Reiter Summary by C. Rey November 27, 2008-1 / 63 Foreword DB: 2
Towards a Logical Reconstruction of Relational Database Theory On Conceptual Modelling, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 1984 Raymond Reiter Summary by C. Rey November 27, 2008-1 / 63 Foreword DB: 2
(More) Propositional Logic and an Intro to Predicate Logic. CSCI 3202, Fall 2010
 (More) Propositional Logic and an Intro to Predicate Logic CSCI 3202, Fall 2010 Assignments Next week: Guest lectures (Jim Martin and Nikolaus Correll); Read Chapter 9 (but you can skip sections on logic
(More) Propositional Logic and an Intro to Predicate Logic CSCI 3202, Fall 2010 Assignments Next week: Guest lectures (Jim Martin and Nikolaus Correll); Read Chapter 9 (but you can skip sections on logic
ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF
 CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.6 Indirect Argument: Contradiction and Contraposition Copyright Cengage Learning. All
CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.6 Indirect Argument: Contradiction and Contraposition Copyright Cengage Learning. All
Automated Reasoning PROLOG and Automated Reasoning 13.4 Further Issues in Automated Reasoning 13.5 Epilogue and References 13.
 13 Automated Reasoning 13.0 Introduction to Weak Methods in Theorem Proving 13.1 The General Problem Solver and Difference Tables 13.2 Resolution Theorem Proving 13.3 PROLOG and Automated Reasoning 13.4
13 Automated Reasoning 13.0 Introduction to Weak Methods in Theorem Proving 13.1 The General Problem Solver and Difference Tables 13.2 Resolution Theorem Proving 13.3 PROLOG and Automated Reasoning 13.4
On Agda JAIST/AIST WS CVS/AIST Yoshiki Kinoshita, Yoriyuki Yamagata. Agenda
 On Agda 2009.3.12 JAIST/AIST WS CVS/AIST Yoshiki Kinoshita, Yoriyuki Yamagata Agenda On Agda Agda as a programming language Agda as a proof system Further information. 2 1 Agenda On Agda Agda as a programming
On Agda 2009.3.12 JAIST/AIST WS CVS/AIST Yoshiki Kinoshita, Yoriyuki Yamagata Agenda On Agda Agda as a programming language Agda as a proof system Further information. 2 1 Agenda On Agda Agda as a programming
Hoare Logic. COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering. Rajeev Goré
 Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
Section 2.4: Arguments with Quantified Statements
 Section 2.4: Arguments with Quantified Statements In this section, we shall generalize the ideas we developed in Section 1.3 to arguments which involve quantified statements. Most of the concepts we shall
Section 2.4: Arguments with Quantified Statements In this section, we shall generalize the ideas we developed in Section 1.3 to arguments which involve quantified statements. Most of the concepts we shall
CSE 311: Foundations of Computing. Lecture 8: Predicate Logic Proofs
 CSE 311: Foundations of Computing Lecture 8: Predicate Logic Proofs Last class: Propositional Inference Rules Two inference rules per binary connective, one to eliminate it and one to introduce it Elim
CSE 311: Foundations of Computing Lecture 8: Predicate Logic Proofs Last class: Propositional Inference Rules Two inference rules per binary connective, one to eliminate it and one to introduce it Elim
CS 416, Artificial Intelligence Midterm Examination Fall 2004
 CS 416, Artificial Intelligence Midterm Examination Fall 2004 Name: This is a closed book, closed note exam. All questions and subquestions are equally weighted. Introductory Material 1) True or False:
CS 416, Artificial Intelligence Midterm Examination Fall 2004 Name: This is a closed book, closed note exam. All questions and subquestions are equally weighted. Introductory Material 1) True or False:
Lecture 17 of 41. Clausal (Conjunctive Normal) Form and Resolution Techniques
 Lecture 17 of 41 Clausal (Conjunctive Normal) Form and Resolution Techniques Wednesday, 29 September 2004 William H. Hsu, KSU http://www.kddresearch.org http://www.cis.ksu.edu/~bhsu Reading: Chapter 9,
Lecture 17 of 41 Clausal (Conjunctive Normal) Form and Resolution Techniques Wednesday, 29 September 2004 William H. Hsu, KSU http://www.kddresearch.org http://www.cis.ksu.edu/~bhsu Reading: Chapter 9,
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2)
 #1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember: just do the counterexample guided abstraction refinement part of DPLL(T). If you notice any other errors, those are good
#1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember: just do the counterexample guided abstraction refinement part of DPLL(T). If you notice any other errors, those are good
A deterministic action is a partial function from states to states. It is partial because not every action can be carried out in every state
 CmSc310 Artificial Intelligence Classical Planning 1. Introduction Planning is about how an agent achieves its goals. To achieve anything but the simplest goals, an agent must reason about its future.
CmSc310 Artificial Intelligence Classical Planning 1. Introduction Planning is about how an agent achieves its goals. To achieve anything but the simplest goals, an agent must reason about its future.
1. Define admissibility and suggest an admissible heuristic functions for the Rubik s cube. (half-twist is counted as a single move).
 1. Define admissibility and suggest an admissible heuristic functions for the Rubik s cube. (half-twist is counted as a single move). (5p) 2. Prove that A* never terminates with the suboptimal goal G 2
1. Define admissibility and suggest an admissible heuristic functions for the Rubik s cube. (half-twist is counted as a single move). (5p) 2. Prove that A* never terminates with the suboptimal goal G 2
Answer Key #1 Phil 414 JL Shaheen Fall 2010
 Answer Key #1 Phil 414 JL Shaheen Fall 2010 1. 1.42(a) B is equivalent to B, and so also to C, where C is a DNF formula equivalent to B. (By Prop 1.5, there is such a C.) Negated DNF meets de Morgan s
Answer Key #1 Phil 414 JL Shaheen Fall 2010 1. 1.42(a) B is equivalent to B, and so also to C, where C is a DNF formula equivalent to B. (By Prop 1.5, there is such a C.) Negated DNF meets de Morgan s
CS 380/480 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Winter 2007 Assignment 2 Solutions to Selected Problems
 CS 380/480 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Winter 2007 Assignment 2 Solutions to Selected Problems 1. Search trees for the state-space graph given below: We only show the search trees corresponding
CS 380/480 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Winter 2007 Assignment 2 Solutions to Selected Problems 1. Search trees for the state-space graph given below: We only show the search trees corresponding
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages. Lecture 16
 CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 16 Zheng Zhang Department of Computer Science Rutgers University Friday 28 th October, 2016 Zheng Zhang 1 CS@Rutgers University Class Information Reminder:
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 16 Zheng Zhang Department of Computer Science Rutgers University Friday 28 th October, 2016 Zheng Zhang 1 CS@Rutgers University Class Information Reminder:
Software Engineering Lecture Notes
 Software Engineering Lecture Notes Paul C. Attie August 30, 2013 c Paul C. Attie. All rights reserved. 2 Contents I Hoare Logic 11 1 Propositional Logic 13 1.1 Introduction and Overview..............................
Software Engineering Lecture Notes Paul C. Attie August 30, 2013 c Paul C. Attie. All rights reserved. 2 Contents I Hoare Logic 11 1 Propositional Logic 13 1.1 Introduction and Overview..............................
Module 6. Knowledge Representation and Logic (First Order Logic) Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 6 Knowledge Representation and Logic (First Order Logic) Lesson 15 Inference in FOL - I 6.2.8 Resolution We have introduced the inference rule Modus Ponens. Now we introduce another inference rule
Module 6 Knowledge Representation and Logic (First Order Logic) Lesson 15 Inference in FOL - I 6.2.8 Resolution We have introduced the inference rule Modus Ponens. Now we introduce another inference rule
Warm-Up Problem. 1. What is the definition of a Hoare triple satisfying partial correctness? 2. Recall the rule for assignment: x (assignment)
 Warm-Up Problem 1 What is the definition of a Hoare triple satisfying partial correctness? 2 Recall the rule for assignment: x (assignment) Why is this the correct rule and not the following rule? x (assignment)
Warm-Up Problem 1 What is the definition of a Hoare triple satisfying partial correctness? 2 Recall the rule for assignment: x (assignment) Why is this the correct rule and not the following rule? x (assignment)
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Fall
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday December 16 11:30am-2:30pm. Lecture A will take the exam in Lecture B will take the exam
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday December 16 11:30am-2:30pm. Lecture A will take the exam in Lecture B will take the exam
Propositional Calculus: Boolean Algebra and Simplification. CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson
 Propositional Calculus: Boolean Algebra and Simplification CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson Propositional Calculus Topics Motivation: Simplifying Conditional Expressions
Propositional Calculus: Boolean Algebra and Simplification CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson Propositional Calculus Topics Motivation: Simplifying Conditional Expressions
Introduction & Review
 Introduction & Review York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 Why this course? Overview Programming Language Paradigms Brief review of Logic Propositional logic Predicate logic
Introduction & Review York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 Why this course? Overview Programming Language Paradigms Brief review of Logic Propositional logic Predicate logic
Proofs are Programs. Prof. Clarkson Fall Today s music: Two Sides to Every Story by Dyan Cannon and Willie Nelson
 Proofs are Programs Prof. Clarkson Fall 2016 Today s music: Two Sides to Every Story by Dyan Cannon and Willie Nelson Review Currently in 3110: Advanced topics Futures Monads Today: An idea that goes by
Proofs are Programs Prof. Clarkson Fall 2016 Today s music: Two Sides to Every Story by Dyan Cannon and Willie Nelson Review Currently in 3110: Advanced topics Futures Monads Today: An idea that goes by
Resolution (14A) Young W. Lim 6/14/14
 Copyright (c) 2013-2014. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free
Copyright (c) 2013-2014. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free
System Correctness. EEC 421/521: Software Engineering. System Correctness. The Problem at Hand. A system is correct when it meets its requirements
 System Correctness EEC 421/521: Software Engineering A Whirlwind Intro to Software Model Checking A system is correct when it meets its requirements a design without requirements cannot be right or wrong,
System Correctness EEC 421/521: Software Engineering A Whirlwind Intro to Software Model Checking A system is correct when it meets its requirements a design without requirements cannot be right or wrong,
Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421)
 Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421) Elsa L Gunter 2112 SC, UIUC http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs421 Based in part on slides by Mattox Beckman, as updated by Vikram Adve and Gul Agha 10/3/17
Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421) Elsa L Gunter 2112 SC, UIUC http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs421 Based in part on slides by Mattox Beckman, as updated by Vikram Adve and Gul Agha 10/3/17
AXIOMS OF AN IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE PARTIAL CORRECTNESS WEAK AND STRONG CONDITIONS. THE AXIOM FOR nop
 AXIOMS OF AN IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE We will use the same language, with the same abstract syntax that we used for operational semantics. However, we will only be concerned with the commands, since the language
AXIOMS OF AN IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE We will use the same language, with the same abstract syntax that we used for operational semantics. However, we will only be concerned with the commands, since the language
Integrity Constraints (Chapter 7.3) Overview. Bottom-Up. Top-Down. Integrity Constraint. Disjunctive & Negative Knowledge. Proof by Refutation
 CSE560 Class 10: 1 c P. Heeman, 2010 Integrity Constraints Overview Disjunctive & Negative Knowledge Resolution Rule Bottom-Up Proof by Refutation Top-Down CSE560 Class 10: 2 c P. Heeman, 2010 Integrity
CSE560 Class 10: 1 c P. Heeman, 2010 Integrity Constraints Overview Disjunctive & Negative Knowledge Resolution Rule Bottom-Up Proof by Refutation Top-Down CSE560 Class 10: 2 c P. Heeman, 2010 Integrity
Formal Predicate Calculus. Michael Meyling
 Formal Predicate Calculus Michael Meyling May 24, 2013 2 The source for this document can be found here: http://www.qedeq.org/0_04_07/doc/math/qedeq_formal_logic_v1.xml Copyright by the authors. All rights
Formal Predicate Calculus Michael Meyling May 24, 2013 2 The source for this document can be found here: http://www.qedeq.org/0_04_07/doc/math/qedeq_formal_logic_v1.xml Copyright by the authors. All rights
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS WITH APPLICATIONS THIRD EDITION SUSANNA S. EPP DePaul University THOIVISON * BROOKS/COLE Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CONTENTS Chapter 1 The
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS WITH APPLICATIONS THIRD EDITION SUSANNA S. EPP DePaul University THOIVISON * BROOKS/COLE Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CONTENTS Chapter 1 The
PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC (2)
 PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC (2) based on Huth & Ruan Logic in Computer Science: Modelling and Reasoning about Systems Cambridge University Press, 2004 Russell & Norvig Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach
PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC (2) based on Huth & Ruan Logic in Computer Science: Modelling and Reasoning about Systems Cambridge University Press, 2004 Russell & Norvig Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach
Typed Lambda Calculus for Syntacticians
 Department of Linguistics Ohio State University January 12, 2012 The Two Sides of Typed Lambda Calculus A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a
Department of Linguistics Ohio State University January 12, 2012 The Two Sides of Typed Lambda Calculus A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a
Typed Lambda Calculus
 Department of Linguistics Ohio State University Sept. 8, 2016 The Two Sides of A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a system of notation for functions
Department of Linguistics Ohio State University Sept. 8, 2016 The Two Sides of A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a system of notation for functions
Chapter 3: Propositional Languages
 Chapter 3: Propositional Languages We define here a general notion of a propositional language. We show how to obtain, as specific cases, various languages for propositional classical logic and some non-classical
Chapter 3: Propositional Languages We define here a general notion of a propositional language. We show how to obtain, as specific cases, various languages for propositional classical logic and some non-classical
Program Verification. Program Verification 307/434
 Program Verification Program Verification 307/434 Outline Introduction: What and Why? Pre- and Postconditions Conditionals while-loops and Total Correctness Arrays Program Verification Introduction 308/434
Program Verification Program Verification 307/434 Outline Introduction: What and Why? Pre- and Postconditions Conditionals while-loops and Total Correctness Arrays Program Verification Introduction 308/434
Deduction Rule System vs Production Rule System. Prof. Bob Berwick. Rules Rule
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.034 Artificial Intelligence, Fall 2003 Recitation 2, September 11/12 Rules Rule Prof. Bob Berwick Agenda
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.034 Artificial Intelligence, Fall 2003 Recitation 2, September 11/12 Rules Rule Prof. Bob Berwick Agenda
INF5390 Kunstig intelligens. First-Order Logic. Roar Fjellheim
 INF5390 Kunstig intelligens First-Order Logic Roar Fjellheim Outline Logical commitments First-order logic First-order inference Resolution rule Reasoning systems Summary Extracts from AIMA Chapter 8:
INF5390 Kunstig intelligens First-Order Logic Roar Fjellheim Outline Logical commitments First-order logic First-order inference Resolution rule Reasoning systems Summary Extracts from AIMA Chapter 8:
Propositional Calculus. Math Foundations of Computer Science
 Propositional Calculus Math Foundations of Computer Science Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus so that they can use it to
Propositional Calculus Math Foundations of Computer Science Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus so that they can use it to
THE LOGIC OF QUANTIFIED STATEMENTS
 CHAPTER 3 THE LOGIC OF QUANTIFIED STATEMENTS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 3.4 Arguments with Quantified Statements Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Arguments
CHAPTER 3 THE LOGIC OF QUANTIFIED STATEMENTS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 3.4 Arguments with Quantified Statements Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Arguments
Programming Languages Third Edition
 Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Computer Science Technical Report
 Computer Science Technical Report Feasibility of Stepwise Addition of Multitolerance to High Atomicity Programs Ali Ebnenasir and Sandeep S. Kulkarni Michigan Technological University Computer Science
Computer Science Technical Report Feasibility of Stepwise Addition of Multitolerance to High Atomicity Programs Ali Ebnenasir and Sandeep S. Kulkarni Michigan Technological University Computer Science
6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions
 6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions Program Verification ETH Zurich, Spring Semester 07 Alexander J. Summers 30 Program Correctness There are many notions of correctness properties for a given program
6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions Program Verification ETH Zurich, Spring Semester 07 Alexander J. Summers 30 Program Correctness There are many notions of correctness properties for a given program
Propositional Theories are Strongly Equivalent to Logic Programs
 Under consideration for publication in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming 1 Propositional Theories are Strongly Equivalent to Logic Programs Pedro Cabalar Department of Computer Science, University
Under consideration for publication in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming 1 Propositional Theories are Strongly Equivalent to Logic Programs Pedro Cabalar Department of Computer Science, University
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics
 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2)
 #1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember that you can t just define a meaning function in terms of itself you must use some fixed point machinery. #2 #3 Observations
#1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember that you can t just define a meaning function in terms of itself you must use some fixed point machinery. #2 #3 Observations
Avoiding Fake Boundaries in Set Interval Computing
 Journal of Uncertain Systems Vol.11, No.2, pp.137-148, 2017 Online at: www.jus.org.uk Avoiding Fake Boundaries in Set Interval Computing Anthony Welte 1, Luc Jaulin 1, Martine Ceberio 2, Vladik Kreinovich
Journal of Uncertain Systems Vol.11, No.2, pp.137-148, 2017 Online at: www.jus.org.uk Avoiding Fake Boundaries in Set Interval Computing Anthony Welte 1, Luc Jaulin 1, Martine Ceberio 2, Vladik Kreinovich
== is a decent equivalence
 Table of standard equiences 30/57 372 TABLES FOR PART I Propositional Logic Lecture 2 (Chapter 7) September 9, 2016 Equiences for connectives Commutativity: Associativity: P Q == Q P, (P Q) R == P (Q R),
Table of standard equiences 30/57 372 TABLES FOR PART I Propositional Logic Lecture 2 (Chapter 7) September 9, 2016 Equiences for connectives Commutativity: Associativity: P Q == Q P, (P Q) R == P (Q R),
Type Checking. Outline. General properties of type systems. Types in programming languages. Notation for type rules.
 Outline Type Checking General properties of type systems Types in programming languages Notation for type rules Logical rules of inference Common type rules 2 Static Checking Refers to the compile-time
Outline Type Checking General properties of type systems Types in programming languages Notation for type rules Logical rules of inference Common type rules 2 Static Checking Refers to the compile-time
1.3. Conditional expressions To express case distinctions like
 Introduction Much of the theory developed in the underlying course Logic II can be implemented in a proof assistant. In the present setting this is interesting, since we can then machine extract from a
Introduction Much of the theory developed in the underlying course Logic II can be implemented in a proof assistant. In the present setting this is interesting, since we can then machine extract from a
RESULTS ON TRANSLATING DEFAULTS TO CIRCUMSCRIPTION. Tomasz Imielinski. Computer Science Department Rutgers University New Brunswick, N.
 RESULTS ON TRANSLATING DEFAULTS TO CIRCUMSCRIPTION Tomasz Imielinski Computer Science Department Rutgers University New Brunswick, N.J 08905 ABSTRACT In this paper we define different concepts, of translating
RESULTS ON TRANSLATING DEFAULTS TO CIRCUMSCRIPTION Tomasz Imielinski Computer Science Department Rutgers University New Brunswick, N.J 08905 ABSTRACT In this paper we define different concepts, of translating
Chapter 3. Set Theory. 3.1 What is a Set?
 Chapter 3 Set Theory 3.1 What is a Set? A set is a well-defined collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Here, well-defined means accurately and unambiguously stated or described. Any
Chapter 3 Set Theory 3.1 What is a Set? A set is a well-defined collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Here, well-defined means accurately and unambiguously stated or described. Any
Mathematics for Computer Scientists 2 (G52MC2)
 Mathematics for Computer Scientists 2 (G52MC2) L03 : More Coq, Classical Logic School of Computer Science University of Nottingham October 8, 2009 The cut rule Sometimes we want to prove a goal Q via an
Mathematics for Computer Scientists 2 (G52MC2) L03 : More Coq, Classical Logic School of Computer Science University of Nottingham October 8, 2009 The cut rule Sometimes we want to prove a goal Q via an
Outline. General properties of type systems. Types in programming languages. Notation for type rules. Common type rules. Logical rules of inference
 Type Checking Outline General properties of type systems Types in programming languages Notation for type rules Logical rules of inference Common type rules 2 Static Checking Refers to the compile-time
Type Checking Outline General properties of type systems Types in programming languages Notation for type rules Logical rules of inference Common type rules 2 Static Checking Refers to the compile-time
(a) (4 pts) Prove that if a and b are rational, then ab is rational. Since a and b are rational they can be written as the ratio of integers a 1
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2000 Wagner MT1 Sol Solutions to Midterm 1 1. (16 pts.) Theorems and proofs (a) (4 pts) Prove that if a and b are rational, then ab is rational. Since a and b are
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2000 Wagner MT1 Sol Solutions to Midterm 1 1. (16 pts.) Theorems and proofs (a) (4 pts) Prove that if a and b are rational, then ab is rational. Since a and b are
Symbolic Methods. The finite-state case. Martin Fränzle. Carl von Ossietzky Universität FK II, Dpt. Informatik Abt.
 Symbolic Methods The finite-state case Part I Martin Fränzle Carl von Ossietzky Universität FK II, Dpt. Informatik Abt. Hybride Systeme 02917: Symbolic Methods p.1/34 What you ll learn How to use and manipulate
Symbolic Methods The finite-state case Part I Martin Fränzle Carl von Ossietzky Universität FK II, Dpt. Informatik Abt. Hybride Systeme 02917: Symbolic Methods p.1/34 What you ll learn How to use and manipulate
Introductory logic and sets for Computer scientists
 Introductory logic and sets for Computer scientists Nimal Nissanke University of Reading ADDISON WESLEY LONGMAN Harlow, England II Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California New York Don Mills, Ontario
Introductory logic and sets for Computer scientists Nimal Nissanke University of Reading ADDISON WESLEY LONGMAN Harlow, England II Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California New York Don Mills, Ontario
Knowledge Representation. CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Knowledge Representation CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 1 Outline Knowledge-based agents Logics in general Propositional Logic& Reasoning First Order Logic 2 Introduction So far we
Knowledge Representation CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 1 Outline Knowledge-based agents Logics in general Propositional Logic& Reasoning First Order Logic 2 Introduction So far we
Data Integration: Logic Query Languages
 Data Integration: Logic Query Languages Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Datalog Datalog A logic language Datalog programs consist of logical facts and rules Datalog is a subset of Prolog (no data structures)
Data Integration: Logic Query Languages Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Datalog Datalog A logic language Datalog programs consist of logical facts and rules Datalog is a subset of Prolog (no data structures)
Solutions to Problem Set 1
 CSCI-GA.3520-001 Honors Analysis of Algorithms Solutions to Problem Set 1 Problem 1 An O(n) algorithm that finds the kth integer in an array a = (a 1,..., a n ) of n distinct integers. Basic Idea Using
CSCI-GA.3520-001 Honors Analysis of Algorithms Solutions to Problem Set 1 Problem 1 An O(n) algorithm that finds the kth integer in an array a = (a 1,..., a n ) of n distinct integers. Basic Idea Using
SC/MATH Boolean Formulae. Ref: G. Tourlakis, Mathematical Logic, John Wiley & Sons, York University
 SC/MATH 1090 1- Boolean Formulae Ref: G. Tourlakis, Mathematical Logic, John Wiley & Sons, 2008. York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering York University- MATH 1090 01-Boolean 1 Overview
SC/MATH 1090 1- Boolean Formulae Ref: G. Tourlakis, Mathematical Logic, John Wiley & Sons, 2008. York University Department of Computer Science and Engineering York University- MATH 1090 01-Boolean 1 Overview
Classical logic, truth tables. Types, Propositions and Problems. Heyting. Brouwer. Conjunction A B A & B T T T T F F F T F F F F.
 lassical logic, truth tables Types, Propositions and Problems an introduction to type theoretical ideas engt Nordström omputing Science, halmers and University of Göteborg Types Summer School, Hisingen,
lassical logic, truth tables Types, Propositions and Problems an introduction to type theoretical ideas engt Nordström omputing Science, halmers and University of Göteborg Types Summer School, Hisingen,
Proving the Correctness of Distributed Algorithms using TLA
 Proving the Correctness of Distributed Algorithms using TLA Khushboo Kanjani, khush@cs.tamu.edu, Texas A & M University 11 May 2007 Abstract This work is a summary of the Temporal Logic of Actions(TLA)
Proving the Correctness of Distributed Algorithms using TLA Khushboo Kanjani, khush@cs.tamu.edu, Texas A & M University 11 May 2007 Abstract This work is a summary of the Temporal Logic of Actions(TLA)
CSI30. Chapter 1. The Foundations: Logic and Proofs Rules of inference with quantifiers Logic and bit operations Specification consistency
 Chapter 1. The Foundations: Logic and Proofs 1.13 Rules of inference with quantifiers Logic and bit operations Specification consistency 1.13 Rules of inference with quantifiers universal instantiation
Chapter 1. The Foundations: Logic and Proofs 1.13 Rules of inference with quantifiers Logic and bit operations Specification consistency 1.13 Rules of inference with quantifiers universal instantiation
Knowledge Representation
 Knowledge Representation References Rich and Knight, Artificial Intelligence, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill, 1991 Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 Outline
Knowledge Representation References Rich and Knight, Artificial Intelligence, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill, 1991 Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 Outline
Please try all of the TRY THIS problems throughout this document. When done, do the following:
 AP Computer Science Summer Assignment Dr. Rabadi-Room 1315 New Rochelle High School nrabadi@nredlearn.org One great resource for any course is YouTube. Please watch videos to help you with any of the summer
AP Computer Science Summer Assignment Dr. Rabadi-Room 1315 New Rochelle High School nrabadi@nredlearn.org One great resource for any course is YouTube. Please watch videos to help you with any of the summer
Interpretations and Models. Chapter Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry
 Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Interpretations and Models Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Axiomatic Systems and Incidence Geometry Axiomatic Systems in Mathematics The gold standard for rigor in an area of mathematics Not fully achieved in most areas
Lambda Calculus and Type Inference
 Lambda Calculus and Type Inference Björn Lisper Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University bjorn.lisper@mdh.se http://www.idt.mdh.se/ blr/ October 13, 2004 Lambda Calculus and Type
Lambda Calculus and Type Inference Björn Lisper Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University bjorn.lisper@mdh.se http://www.idt.mdh.se/ blr/ October 13, 2004 Lambda Calculus and Type
CS61A Lecture 38. Robert Huang UC Berkeley April 17, 2013
 CS61A Lecture 38 Robert Huang UC Berkeley April 17, 2013 Announcements HW12 due Wednesday Scheme project, contest out Review: Program Generator A computer program is just a sequence of bits It is possible
CS61A Lecture 38 Robert Huang UC Berkeley April 17, 2013 Announcements HW12 due Wednesday Scheme project, contest out Review: Program Generator A computer program is just a sequence of bits It is possible
Logic and its Applications
 Logic and its Applications Edmund Burke and Eric Foxley PRENTICE HALL London New York Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore Madrid Mexico City Munich Contents Preface xiii Propositional logic 1 1.1 Informal introduction
Logic and its Applications Edmund Burke and Eric Foxley PRENTICE HALL London New York Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore Madrid Mexico City Munich Contents Preface xiii Propositional logic 1 1.1 Informal introduction
The Rule of Constancy(Derived Frame Rule)
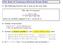 The Rule of Constancy(Derived Frame Rule) The following derived rule is used on the next slide The rule of constancy {P } C {Q} {P R} C {Q R} where no variable assigned to in C occurs in R Outline of derivation
The Rule of Constancy(Derived Frame Rule) The following derived rule is used on the next slide The rule of constancy {P } C {Q} {P R} C {Q R} where no variable assigned to in C occurs in R Outline of derivation
Inf2D 12: Resolution-Based Inference
 School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh 09/02/18 Slide Credits: Jacques Fleuriot, Michael Rovatsos, Michael Herrmann Last time Unification: Given α and β, find θ such that αθ = βθ Most general unifier
School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh 09/02/18 Slide Credits: Jacques Fleuriot, Michael Rovatsos, Michael Herrmann Last time Unification: Given α and β, find θ such that αθ = βθ Most general unifier
Incompatibility Dimensions and Integration of Atomic Commit Protocols
 The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 5, No. 4, October 2008 381 Incompatibility Dimensions and Integration of Atomic Commit Protocols Yousef Al-Houmaily Department of Computer
The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 5, No. 4, October 2008 381 Incompatibility Dimensions and Integration of Atomic Commit Protocols Yousef Al-Houmaily Department of Computer
Lecture 14: Lower Bounds for Tree Resolution
 IAS/PCMI Summer Session 2000 Clay Mathematics Undergraduate Program Advanced Course on Computational Complexity Lecture 14: Lower Bounds for Tree Resolution David Mix Barrington and Alexis Maciel August
IAS/PCMI Summer Session 2000 Clay Mathematics Undergraduate Program Advanced Course on Computational Complexity Lecture 14: Lower Bounds for Tree Resolution David Mix Barrington and Alexis Maciel August
Constraint Solving. Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Constraint Solving Systems
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Constraint Solving Systems
The Resolution Principle
 Summary Introduction [Chang-Lee Ch. 5.1] for Propositional Logic [Chang-Lee Ch. 5.2] Herbrand's orem and refutation procedures Satisability procedures We can build refutation procedures building on Herbrand's
Summary Introduction [Chang-Lee Ch. 5.1] for Propositional Logic [Chang-Lee Ch. 5.2] Herbrand's orem and refutation procedures Satisability procedures We can build refutation procedures building on Herbrand's
CSC242: Intro to AI. Lecture 10. Tuesday, February 26, 13
 CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 10 No Quiz Propositional Logic Propositional Logic Fly Problem-solving state Transition Model World state Action Arad Sibiu Timosoara Zerind Rimnicu Vilcea Arad Arad Lugoj
CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 10 No Quiz Propositional Logic Propositional Logic Fly Problem-solving state Transition Model World state Action Arad Sibiu Timosoara Zerind Rimnicu Vilcea Arad Arad Lugoj
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages
 CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 17: Functional Programming Zheng (Eddy Zhang Rutgers University April 4, 2018 Class Information Homework 6 will be posted later today. All test cases
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 17: Functional Programming Zheng (Eddy Zhang Rutgers University April 4, 2018 Class Information Homework 6 will be posted later today. All test cases
The DPL (Decisive Plausible Logic) Tool
 The DPL (Decisive Plausible Logic) Tool Andrew Rock November 25 2013 Abstract This documents the DPL tool which implements the Decisive Plausible Logic of David Billington. 1 Plausible Logic in short A
The DPL (Decisive Plausible Logic) Tool Andrew Rock November 25 2013 Abstract This documents the DPL tool which implements the Decisive Plausible Logic of David Billington. 1 Plausible Logic in short A
