Block diagram of processor (Harvard)
|
|
|
- Marshall Ward
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Block diagram of processor (Harvard) Register transfer view of Harvard architecture Separate busses for instruction memory and data memory Example: PIC 16 load path OP REG AC store path rd wr data Data Memory (16-bit words) N Z 16 addr Control FSM 16 OP IR PC data Inst Memory (8-bit words) addr 16 Microcontrollers 1
2 Block diagram of processor (Princeton) Register transfer view of Princeton / von Neumann architecture Single unified bus for instructions, data, and I/O Example: MSP load path OP REG 16 AC 16 store path rd wr data Data Memory (16-bit words) Control FSM N Z 16 8 addr MAR IR 16 PC 16 OP 16 Microcontrollers 2
3 MSP 430 Modular Architecture Microcontrollers 3
4 Digital I/O Independently programmable individual I/Os Port1 Port2 Port3 Port6 Function Select Register PxSEL yes yes Up to 6 ports (P1 P6) Each has 8 I/O pins Each pin can be configured as input or output P1. P2. P3. 7 Interrupt Edge Select Register PxIES Interrupt Enable Register PxIE Interrupt Flag Register PxIFG Direction Register PxDIR Output Register PxOUT Input Register PxIN yes yes yes yes yes yes no no no yes yes yes P1 and P2 pins can be configured to assert an interrupt request P4. P5. P6. Microcontrollers 4
5 Watchdog Timer WDT module performs a controlled system restart after a software problem occurs Can serve as an interval timer (generates interrupts) WDT Control register is password protected Note: Powers-up active Microcontrollers 5
6 Example 1: msp430x20x3_1.c // MSP430F20xx Demo - Software Toggle P1.0 #include <msp430x20x3.h> void main(void) { WDTCTL = WDTPW + WDTHOLD; // Stop watchdog timer P1DIR = 0x01; // Set P1.0 to output direction for (;;) { volatile unsigned int i; P1OUT ^= 0x01; // Toggle P1.0 using XOR i = 50000; // Delay do (i--); while (i!= 0); } } WDTCTL: Watch Dog Timer ConTroL WDTPW: WDT PassWord WTDHOLD: WDT Hold P1DIR: Port 1 DIRection P1OUT: Port 1 OUTput state Microcontrollers 6
7 Example 2: msp430x20x3p1_01.c // MSP430F20xx Demo - Software Poll P1.4, Set P1.0 if P1.4 = 1 // Desc: Poll P1.4 in a loop, if hi P1.0 is set, if low, P1.0 reset. // ACLK = n/a, MCLK = SMCLK = default DCO #include <msp430x20x3.h> void main(void) { WDTCTL = WDTPW + WDTHOLD; // Stop watchdog timer P1DIR = 0x01; // Set P1.0 to output direction while (1) // Test P1.4 { if ((0x10 & P1IN)) P1OUT = 0x01;// if P1.4 set, set P1.0 else P1OUT &= ~0x01; // else reset } } Microcontrollers 7
8 MSP430 Memory Model Not present in F2013 SFR: Special Function Registers Microcontrollers 8
9 Memory Organization Microcontrollers 9
10 MSP 430 Architecture: A Closer Look Microcontrollers 10
11 Basic Clock System Basic Clock Module provides the clocks for the MSP430 devices Or VLO (in MSP430F2xx) Subsystem Master CLocK Microcontrollers 11
12 Timer_A Timer_A is a 16-bit timer/counter with multiple capture/compare registers (2 in F2013) Capture external signals Compare PWM mode Microcontrollers 12
13 Example 3: msp430x20x3_ta_01.c // MSP430F20xx Demo - Timer_A, Toggle P1.0, CCR0 Cont. Mode ISR, DCO SMCLK // Description: Toggle P1.0 using software and TA_0 ISR. Toggles every // SMCLK cycles. SMCLK provides clock source for TACLK. // During the TA_0 ISR, P1.0 is toggled and clock cycles are added to // CCR0. TA_0 ISR is triggered every cycles. CPU is normally off and // used only during TA_ISR. // ACLK = n/a, MCLK = SMCLK = TACLK = default DCO #include <msp430x20x3.h> void main(void) { WDTCTL = WDTPW + WDTHOLD; // Stop WDT P1DIR = 0x01; // P1.0 output CCTL0 = CCIE; // CCR0 interrupt enabled CCR0 = 50000; TACTL = TASSEL_2 + MC_2; // SMCLK, contmode _BIS_SR(LPM0_bits + GIE); // Enter LPM0 w/ interrupt } // Timer A0 interrupt service routine #pragma vector=timera0_vector interrupt void Timer_A (void) { P1OUT ^= 0x01; // Toggle P1.0 CCR0 += 50000; // Add Offset to CCR0 } Microcontrollers 13
14 Comparator_A Comparator_A is an analog voltage comparator Supports precision slope analog-to-digital conversions Supply voltage supervision, and Monitoring of external analog signals. Microcontrollers 14
15 ADC12 High-performance 12-bit analog-todigital converter More than 200 Ksamples/sec Programmable sample& hold 8 external input channels Internal storage Microcontrollers 15
16 USART Serial Port The universal synchronous/ asynchronous receive/transmit (USART) peripheral interface supports two serial modes with one hardware module UART or SPI (Synchronous Peripheral Interface) modes Double-buffered Baud-rate generator Microcontrollers 16
17 End of lecture 2 Microcontrollers 17
18 MSP430 CPU Introduction RISC architecture with 27 instructions and 7 addressing modes. Orthogonal architecture with every instruction usable with every addressing mode. 16-bit address bus allows direct access and branching throughout entire memory range; no paging 16-bit data bus allows direct manipulation of word-wide arguments. Constant generator provides six most used immediate values and reduces code size. Direct memory-to-memory transfers without intermediate register holding. Word and byte addressing and instruction formats. Compact silicon 30% smaller than an 8051 saves power and cost Microcontrollers 18
19 MSP430 register properties Large 16-bit register file eliminates single accumulator bottleneck, reduces fetches to memory. Full register access including program counter, status registers, and stack pointer. Single-cycle register operations. Microcontrollers 19
20 MSP430 Registers Microcontrollers 20
21 Registers: PC (R0) Each instruction uses an even number of bytes (2, 4, or 6) PC is word aligned (the LSB is 0) Format: OP SRC, DST ; NB, a lot of processors use DST,SRC MOV #LABEL,PC ; Branch to address LABEL MOV LABEL,PC ; Branch to address contained in LABEL ; Branch indirect, indirect R14 Microcontrollers 21
22 Registers: SP (R1) Stack pointer for return addresses of subroutines and interrupts Stack is in general purpose RAM (unlike e.g. PIC) SP is word aligned (the LSB is 0) Pushing a single byte on the stack wastes a byte the byte at the wasted location is not modified by the push Contrast with single-byte register operations, which zero the unused byte SP points to most recently added word (not to next free word) Starts from top of memory (0x0280 in F2013) In assembly, you must initialize the SP yourself! Don t try to jump in to an initialization subroutine to set up the SP if the SP is not set up before the subroutine call, you won t return properly from the initialization subroutine! Microcontrollers 22
23 Registers: SP (R1) Example stack manipulations: MOV 2(SP),R6 ; Item I2 > R6 2(SP) means 2+SP MOV R7,0(SP) ; Overwrite TOS with R7 PUSH #0123h ; Put 0123h onto TOS POP R8 ; R8 = 0123h Highest RAM address is 0x0280 in F2013 TOS: Top Of Stack TOS is actually the lowest address in the stack! Microcontrollers 23
24 Registers: SR (R2) C: SR(0) Carry Z: SR(1) Zero N: SR(2) Negative (==msb of result) GIE: SR(3) Global interrupt enable CPUOff: SR(4) LPM control OSCOff: SR(5) LPM control SCG0: SR(6) System Clock Generator 0 LPM control SCG1: SR(7) System Clock Generator 0 LPM control V: SR(8) signed overflow Microcontrollers 24
25 Example: msp430x20x3_1.asm.cdecls C,LIST, "msp430x20x3.h" ; text ; Progam Start ; RESET mov.w #0280h,SP ; Initialize stackpointer StopWDT mov.w #WDTPW+WDTHOLD,&WDTCTL ; Stop WDT SetupP1 bis.b #001h,&P1DIR ; P1.0 output ; Mainloop xor.b #001h,&P1OUT ; Toggle P1.0 Wait mov.w #50000,R15 ; Delay to R15 L1 dec.w R15 ; Decrement R15 jnz L1 ; Delay over? jmp Mainloop ; Again ; ; ; Interrupt Vectors ; sect ".reset" ; MSP430 RESET Vector.short RESET ;.end Microcontrollers 25
26 Status bits NB: in MSP430, mov operations do not affect status register Microcontrollers 26
27 Demo interlude, including debugger! Microcontrollers 27
28 Constant Generators As source register addressing mode in the instruction word CPE/EE 421/521 Microcomputers 28
29 Constant generator examples Address Assembled instr Viewed in debugger ; Original user s asm code 0xF81C: 434F CLR.B R15 ; mov.b #0,R15 0xF81E: 435F MOV.B #1,R15 ; mov.b #1,R15 0xF820: 436F MOV.B #2,R15 ; mov.b #2,R15 0xF822: 407F 0003 MOV.B #0x0003,R15 ; mov.b #3,R15 0xF826: 426F MOV.B #4,R15 ; mov.b #4,R15 0xF828: 407F 0080 MOV.B #0x0080,R15 ; mov.b #80h,R15 0xF82C: 407F 007F MOV.B #0x007f,R15 ; mov.b #7Fh,R15 0xF830: 430F CLR.W R15 ; mov.w #0,R15 0xF832: 431F MOV.W #1,R15 ; mov.w #1,R15 0xF834: 432F MOV.W #2,R15 ; mov.w #2,R15 0xF836: 403F 0003 MOV.W #0x0003,R15 ; mov.w #3,R15 0xF83A: 422F MOV.W #4,R15 ; mov.w #4,R15 0xF83C: 403F 0080 MOV.W #0x0080,R15 ; mov.w #80h,R15 0xF840: 433F MOV.W #-1,R15 ; mov.w #0xFFFF,R15 Move operations that can use the constant generator assemble to 1 word Move operations that cannot use the constant generator assemble to 2 words Microcontrollers 29
30 CISC / RISC Instruction Set Good summary of MSP430 instructions: Microcontrollers 30
31 27 Core RISC Instructions Notes: -.b or.w: byte or word - add / addc: without/with carry - dadd: decimal add w/ carry ( bin. coded decimal math) swpb: swap bytes sxt: sign extend (copies sign bit from b7 to b15-b8 for converting signed byte into signed word) rra: Roll right rrc: Roll right, through carry Microcontrollers 31
32 Emulated Instructions Microcontrollers 32
33 51 Total Instructions Microcontrollers 33
34 Example 2: msp430x20x3_p1_01.asm ;*******************************************************************************.cdecls C,LIST, "msp430x20x3.h" ; text ; Program Start ; RESET mov.w #0280h,SP ; Initialize stackpointer StopWDT mov.w #WDTPW+WDTHOLD,&WDTCTL ; Stop WDT SetupP1 bis.b #001h,&P1DIR ; P1.0 output Mainloop bit.b #010h,&P1IN ; P1.4 hi/low? jc ON ; jmp--> P1.4 is set ; OFF bic.b #001h,&P1OUT ; P1.0 = 0 / LED OFF jmp Mainloop ; ON bis.b #001h,&P1OUT ; P1.0 = 1 / LED ON jmp Mainloop ; ; ; ; Interrupt Vectors ; sect ".reset" ; MSP430 RESET Vector.short RESET ;.end Microcontrollers 34
35 Double operand instructions Microcontrollers 35
36 Single Operand Instruction Microcontrollers 36
37 Jump Instructions Microcontrollers 37
38 3 Instruction Formats Microcontrollers 38
39 End of lecture 3 Microcontrollers 39
40 Addressing Modes Microcontrollers 40
41 Register Addressing Mode Microcontrollers 41
42 Register-Indexed Addressing Mode Useful for implementing arrays above, 100h is the base address of the source array, and the contents of R4 are the index of the source array. Difference between C and MSP430 assembly: in assembly bytes are indexed, even if we re dealing with an array of words of larger in C, the index counts the items, whatever size they are Microcontrollers 42
43 Symbolic Addressing Mode mov.w LoopCtr, R6 ; load word LoopCtr into R6, symbolic mode becomes mov.w X(PC),R6 ; load word LoopCtr into R6, symbolic mode Where X = LoopCtr PC --- calc done by assembler Could also be called PC relative Gives a relative addressing scheme that can be used to create positionindependent code. Less useful in flash-based systems than RAM-based (since moving code is very costly in time and energy for flash). Microcontrollers 43
44 Absolute Addressing Mode mov.b &P1IN,R6 ; load byte P1IN into R6, abs mode becomes mov.b P1IN(SR),R6 ; load byte P1IN into R6, abs mode SR returns 0 in this case a kind of constant generator fn Microcontrollers 44
45 SP-relative Not claimed as an addressing mode by TI some other manufacturers call this a distinct addressing mode mov.w 2(SP),R6 ; most recent word but one from stack Microcontrollers 45
46 Register Indirect Addressing Mode Memory at addr held in R4 is moved into R5 This mode can t be used for destination addresses, only source Instead, need to use indexed addressing for destination: Microcontrollers 46
47 Register Indirect Autoincrement Addressing Mode Inverse operation: mov.w R6,0(R5) ; store word from R6 into addr 0+(R5)=4 incd.w R5 ; R5 += 2 Microcontrollers 47
48 Immediate Addressing Mode Equivalent to ; load immediate word 1234h into R6 DW 1234h ; Microcontrollers 48
Microcontrollers. vs Microprocessors
 Microcontrollers vs Microprocessors Microprocessors Arbitrary computations Arbitrary control structures Arbitrary data structures Specify function at high-level and use compilers and debuggers Composed
Microcontrollers vs Microprocessors Microprocessors Arbitrary computations Arbitrary control structures Arbitrary data structures Specify function at high-level and use compilers and debuggers Composed
Alex Milenkovich 1. CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers: The MSP430 Introduction. Outline
 Outline CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers: The MSP430 Introduction Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Notes MSP430: An Introduction The MSP430 family Technology Roadmap Typical Applications The MSP430
Outline CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers: The MSP430 Introduction Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Notes MSP430: An Introduction The MSP430 family Technology Roadmap Typical Applications The MSP430
What is an Interrupt?
 MSP430 Interrupts What is an Interrupt? Reaction to something in I/O (human, comm link) Usually asynchronous to processor activities interrupt handler or interrupt service routine (ISR) invoked to take
MSP430 Interrupts What is an Interrupt? Reaction to something in I/O (human, comm link) Usually asynchronous to processor activities interrupt handler or interrupt service routine (ISR) invoked to take
Interrupts CS4101 嵌入式系統概論. Prof. Chung-Ta King. Department of Computer Science National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 CS4101 嵌入式系統概論 Interrupts Prof. Chung-Ta King Department of Computer Science, Taiwan Materials from MSP430 Microcontroller Basics, John H. Davies, Newnes, 2008 Inside MSP430 (MSP430G2551) 1 Introduction
CS4101 嵌入式系統概論 Interrupts Prof. Chung-Ta King Department of Computer Science, Taiwan Materials from MSP430 Microcontroller Basics, John H. Davies, Newnes, 2008 Inside MSP430 (MSP430G2551) 1 Introduction
MSP430 Interrupts. Change value of internal variable (count) Read a data value (sensor, receive) Write a data value (actuator, send)
 MSP430 Interrupts What is an Interrupt? Reaction to something in I/O (human, comm link) Usually asynchronous to processor activities interrupt handler or interrupt service routine (ISR) invoked to take
MSP430 Interrupts What is an Interrupt? Reaction to something in I/O (human, comm link) Usually asynchronous to processor activities interrupt handler or interrupt service routine (ISR) invoked to take
Lecture 5: MSP430 Interrupt
 ECE342 Intro. to Embedded Systems Lecture 5: MSP430 Interrupt Ying Tang Electrical and Computer Engineering Rowan University 1 How A Computer React to Inputs? Polling: the processor regularly looks at
ECE342 Intro. to Embedded Systems Lecture 5: MSP430 Interrupt Ying Tang Electrical and Computer Engineering Rowan University 1 How A Computer React to Inputs? Polling: the processor regularly looks at
PHYS 319. Things to do before next week's lab Whirlwind tour of the MSP430 CPU and its assembly language Activity 1.
 PHYS 319 Things to do before next week's lab Whirlwind tour of the MSP430 CPU and its assembly language Activity 1. Before next week's lab: Read manual for Lab 2 and your OS setup guide then prepare your
PHYS 319 Things to do before next week's lab Whirlwind tour of the MSP430 CPU and its assembly language Activity 1. Before next week's lab: Read manual for Lab 2 and your OS setup guide then prepare your
MIDTERM#1. 2-(3pts) What is the difference between Von Neumann & Harvard processor architectures?
 CSE421-Microprocessors & Microcontrollers-Spring 2013 (March 26, 2013) NAME: MIDTERM#1 1- (2pts) What does MSP stand for in MSP430? Why? Mixed Signal Processor. It contains both analog and digital circuitry.
CSE421-Microprocessors & Microcontrollers-Spring 2013 (March 26, 2013) NAME: MIDTERM#1 1- (2pts) What does MSP stand for in MSP430? Why? Mixed Signal Processor. It contains both analog and digital circuitry.
CPE 323: MSP430 Timers
 CPE 323: MSP430 Timers Aleksandar Milenkovic Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Alabama in Huntsville milenka@ece.uah.edu http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Outline Watchdog Timer TimerA
CPE 323: MSP430 Timers Aleksandar Milenkovic Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Alabama in Huntsville milenka@ece.uah.edu http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Outline Watchdog Timer TimerA
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers
 CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Note S09 *Material used is in part developed by Dr. D. Raskovic and Dr. E. Jovanov CPE/EE 421/521 Microcomputers 1 Performance Outline
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Note S09 *Material used is in part developed by Dr. D. Raskovic and Dr. E. Jovanov CPE/EE 421/521 Microcomputers 1 Performance Outline
Before next weeks lab:
 Before next weeks lab: - To sign in to lab computers use student and Phys319. - read the lab manual for week two. - look at the tools installation guide for OS of your choice and/or lab computer guide,
Before next weeks lab: - To sign in to lab computers use student and Phys319. - read the lab manual for week two. - look at the tools installation guide for OS of your choice and/or lab computer guide,
Hacettepe University
 MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 3 Further into the MSP430 Hacettepe University Copyright 2009 Texas Instruments All Rights Reserved MSP430MtFaFbMc Mt: Memory Type C: ROM F: Flash P: OTP E: EPROM (for developmental
MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 3 Further into the MSP430 Hacettepe University Copyright 2009 Texas Instruments All Rights Reserved MSP430MtFaFbMc Mt: Memory Type C: ROM F: Flash P: OTP E: EPROM (for developmental
CPE 323 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems: MSP430 System Architecture An Overview
 CPE 323 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems: MSP430 System Architecture An Overview Aleksandar Milenkovic Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Alabama in Huntsville milenka@ece.uah.edu
CPE 323 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems: MSP430 System Architecture An Overview Aleksandar Milenkovic Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Alabama in Huntsville milenka@ece.uah.edu
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA)
 CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
Designing for Ultra-Low Power with MSP430
 Designing for Ultra-Low Power with MSP430 Christian Hernitscheck MSP430 FAE Europe Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda Introduction to Ultra-Low Power Looking for Ultra-Low Power
Designing for Ultra-Low Power with MSP430 Christian Hernitscheck MSP430 FAE Europe Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda Introduction to Ultra-Low Power Looking for Ultra-Low Power
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2019 Lecture #22: MSP430F5529 Operating Mode & the WDT
 ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2019 Lecture #22: MSP430F5529 Operating Mode & the WDT Reading for Today: User's Guide 1.4, Ch 16 Reading for Next Class: Review all since
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2019 Lecture #22: MSP430F5529 Operating Mode & the WDT Reading for Today: User's Guide 1.4, Ch 16 Reading for Next Class: Review all since
Lecture 2 MSP430 Architecture. Atul Lele Ramakrishna Reddy
 Lecture 2 MSP430 Architecture Atul Lele Ramakrishna Reddy About me Education B.E. in Electronics and Telecommunication, PICT, Pune (2000) Professional experience Working with Texas Instruments India Pvt
Lecture 2 MSP430 Architecture Atul Lele Ramakrishna Reddy About me Education B.E. in Electronics and Telecommunication, PICT, Pune (2000) Professional experience Working with Texas Instruments India Pvt
CONTENTS: Program 1 in C:
 CONTENTS: 1) Program 1 in C (Blink) 2) Program 2 in C (Interrupt ) 3) ADC example 4) Addressing Modes 5) Selected Assembly instructions 6) ADC10 register descriptions Program 1 in C: /* * PHYS319 Lab3
CONTENTS: 1) Program 1 in C (Blink) 2) Program 2 in C (Interrupt ) 3) ADC example 4) Addressing Modes 5) Selected Assembly instructions 6) ADC10 register descriptions Program 1 in C: /* * PHYS319 Lab3
Lab 4: Interrupt. CS4101 Introduction to Embedded Systems. Prof. Chung-Ta King. Department of Computer Science National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 CS4101 Introduction to Embedded Systems Lab 4: Interrupt Prof. Chung-Ta King Department of Computer Science, Taiwan Introduction In this lab, we will learn interrupts of MSP430 Handling interrupts in MSP430
CS4101 Introduction to Embedded Systems Lab 4: Interrupt Prof. Chung-Ta King Department of Computer Science, Taiwan Introduction In this lab, we will learn interrupts of MSP430 Handling interrupts in MSP430
Lecture test next week
 Lecture test next week Write a short program in Assembler doing. You will be given the print outs of all the assembler programs from the manual You can bring any notes you want Today: Announcements General
Lecture test next week Write a short program in Assembler doing. You will be given the print outs of all the assembler programs from the manual You can bring any notes you want Today: Announcements General
IV B.Tech. I Sem (R13) ECE : Embedded Systems : UNIT -2 1 UNIT 2
 IV B.Tech. I Sem (R13) ECE : Embedded Systems : UNIT -2 1 UNIT 2 1. Block diagram of MSP430x5xx series micro-controller --------------------- 1 2. CPU architecture of MSP430x5xx ------------------------------------------------
IV B.Tech. I Sem (R13) ECE : Embedded Systems : UNIT -2 1 UNIT 2 1. Block diagram of MSP430x5xx series micro-controller --------------------- 1 2. CPU architecture of MSP430x5xx ------------------------------------------------
Create and Add the Source File
 IAR Kickstart Procedure Create and Add the Source File 8. Create the Source File From the IAR Embedded Workbench menu bar, select File New File. In the untitled editor window that appears, type the following
IAR Kickstart Procedure Create and Add the Source File 8. Create the Source File From the IAR Embedded Workbench menu bar, select File New File. In the untitled editor window that appears, type the following
ECE PRACTICE EXAM #2 Clocks, Timers, and Digital I/O
 ECE2049 -- PRACTICE EXAM #2 Clocks, Timers, and Digital I/O Study HW3, Class Notes, Davies Ch 2.6, 5.8, 8, 9.2-3, 9.7, MSP43F5529 User's Guide Ch 5, 17, 28 Work all problems with your note sheet first
ECE2049 -- PRACTICE EXAM #2 Clocks, Timers, and Digital I/O Study HW3, Class Notes, Davies Ch 2.6, 5.8, 8, 9.2-3, 9.7, MSP43F5529 User's Guide Ch 5, 17, 28 Work all problems with your note sheet first
Timer Module Timer A. ReadMeFirst
 Timer Module Timer A ReadMeFirst Lab Folder Content 1) ReadMeFirst 2) TimerModule Lecture material 3) PinOutSummary 4) InterruptsVectorTable 5) Source code for screencast Interrupt Review Overview A Timer
Timer Module Timer A ReadMeFirst Lab Folder Content 1) ReadMeFirst 2) TimerModule Lecture material 3) PinOutSummary 4) InterruptsVectorTable 5) Source code for screencast Interrupt Review Overview A Timer
University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department. EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I.
 University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I Fall 2016 LAB 03 Low Power Mode and Port Interrupts Goals: Bonus: Pre Lab Questions:
University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I Fall 2016 LAB 03 Low Power Mode and Port Interrupts Goals: Bonus: Pre Lab Questions:
Interrupts, Low Power Modes
 Interrupts, Low Power Modes Registers Status Register Interrupts (Chapter 6 in text) A computer has 2 basic ways to react to inputs: 1) polling: The processor regularly looks at the input and reacts as
Interrupts, Low Power Modes Registers Status Register Interrupts (Chapter 6 in text) A computer has 2 basic ways to react to inputs: 1) polling: The processor regularly looks at the input and reacts as
CPE 325: Embedded Systems Laboratory Laboratory #7 Tutorial MSP430 Timers, Watchdog Timer, Timers A and B
 CPE 325: Embedded Systems Laboratory Laboratory #7 Tutorial MSP430 Timers, Watchdog Timer, Timers A and B Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective This
CPE 325: Embedded Systems Laboratory Laboratory #7 Tutorial MSP430 Timers, Watchdog Timer, Timers A and B Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective This
Today's plan: Announcements General Strategy Microcontroller programming concepts/last bits of assembly Activity 2
 Today's plan: Announcements General Strategy Microcontroller programming concepts/last bits of assembly Activity 2 Intro to programming in C time permitting Lab 1&2 Marking scheme: Announcements: Turn
Today's plan: Announcements General Strategy Microcontroller programming concepts/last bits of assembly Activity 2 Intro to programming in C time permitting Lab 1&2 Marking scheme: Announcements: Turn
Chapter 8 Architecture and Instruction Set
 Chapter 8 8-1 Introduction 8.1 Introduction The instruction set of the ultra low power-microcomputer MSP430 family differs strongly from the instruction sets used by other 8-bit and 16-bit microcomputers.
Chapter 8 8-1 Introduction 8.1 Introduction The instruction set of the ultra low power-microcomputer MSP430 family differs strongly from the instruction sets used by other 8-bit and 16-bit microcomputers.
// Conditions for 9600/4=2400 Baud SW UART, SMCLK = 1MHz #define Bitime_5 0x05*4 // ~ 0.5 bit length + small adjustment #define Bitime 13*4//0x0D
 /****************************************************************************** * * * 1. Device starts up in LPM3 + blinking LED to indicate device is alive * + Upon first button press, device transitions
/****************************************************************************** * * * 1. Device starts up in LPM3 + blinking LED to indicate device is alive * + Upon first button press, device transitions
LECTURE - 4 Programming MSP430 using Code Composer Studio(CCS)
 LECTURE - 4 Programming MSP430 using Code Composer Studio(CCS) Atul Lele, Ramakrishna Reddy K, MSP430 Design, Texas Instruments India Pvt Ltd. 2/16/2012 1 Outline of today s session What have we learnt
LECTURE - 4 Programming MSP430 using Code Composer Studio(CCS) Atul Lele, Ramakrishna Reddy K, MSP430 Design, Texas Instruments India Pvt Ltd. 2/16/2012 1 Outline of today s session What have we learnt
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
 Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) Operating Systems M. Schölzel Operating System Tasks Traditional OS Controlling and protecting access to resources (memory, I/O, computing resources) managing their allocation
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) Operating Systems M. Schölzel Operating System Tasks Traditional OS Controlling and protecting access to resources (memory, I/O, computing resources) managing their allocation
Timers and Clocks CS4101 嵌入式系統概論. Prof. Chung-Ta King. Department of Computer Science National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 CS4101 嵌入式系統概論 Timers and Clocks Prof. Chung-Ta King Department of Computer Science, Taiwan Materials from MSP430 Microcontroller Basics, John H. Davies, Newnes, 2008 Recall the Container Thermometer Container
CS4101 嵌入式系統概論 Timers and Clocks Prof. Chung-Ta King Department of Computer Science, Taiwan Materials from MSP430 Microcontroller Basics, John H. Davies, Newnes, 2008 Recall the Container Thermometer Container
CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART
 General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
Microcontrollers. Microcontroller
 Microcontrollers Microcontroller A microprocessor on a single integrated circuit intended to operate as an embedded system. As well as a CPU, a microcontroller typically includes small amounts of RAM and
Microcontrollers Microcontroller A microprocessor on a single integrated circuit intended to operate as an embedded system. As well as a CPU, a microcontroller typically includes small amounts of RAM and
Texas Instruments Mixed Signal Processor Tutorial Abstract
 Texas Instruments Mixed Signal Processor Tutorial Abstract This tutorial goes through the process of writing a program that uses buttons to manipulate LEDs. One LED will be hard connected to the output
Texas Instruments Mixed Signal Processor Tutorial Abstract This tutorial goes through the process of writing a program that uses buttons to manipulate LEDs. One LED will be hard connected to the output
Chapter 1 MSP430 Microcontroller Family
 Chapter 1 1-1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction The MSP430 is a 16-bit microcontroller that has a number of special features not commonly available with other microcontrollers: Complete system on-a-chip includes
Chapter 1 1-1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction The MSP430 is a 16-bit microcontroller that has a number of special features not commonly available with other microcontrollers: Complete system on-a-chip includes
Lab 4 Interrupts ReadMeFirst
 Lab 4 Interrupts ReadMeFirst Lab Folder Content 1) ReadMeFirst 2) Interrupt Vector Table 3) Pin out Summary Objectives Understand how interrupts work Learn to program Interrupt Service Routines in C Language
Lab 4 Interrupts ReadMeFirst Lab Folder Content 1) ReadMeFirst 2) Interrupt Vector Table 3) Pin out Summary Objectives Understand how interrupts work Learn to program Interrupt Service Routines in C Language
Basic System Memory Architecture View (Functional)
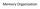 Memory Organization Basic System Memory Architecture View (Functional) Notation: [FFFE]=27h FFFE: 27 Basic Characteristics (1/3) Memory cell registers are one byte wide Memory Word is the contents of the
Memory Organization Basic System Memory Architecture View (Functional) Notation: [FFFE]=27h FFFE: 27 Basic Characteristics (1/3) Memory cell registers are one byte wide Memory Word is the contents of the
2002 Mixed Signal Products SLAU056B
 User s Guide 22 Mixed Signal Products SLAU56B IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
User s Guide 22 Mixed Signal Products SLAU56B IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
Befehle des MSP430. ADC Add carry to destination. ADD Add source to destination. ADDC[ Add source and carry to destination
 Befehle des MSP430 ADC ADC ADC.B Add carry to destination Add carry to destination ADC dst or ADC.W dst ADC.B dst dst + C > dst The carry bit (C) is added to the destination operand. The previous contents
Befehle des MSP430 ADC ADC ADC.B Add carry to destination Add carry to destination ADC dst or ADC.W dst ADC.B dst dst + C > dst The carry bit (C) is added to the destination operand. The previous contents
6. General purpose Input/Output
 Chapter 6 6. General purpose Input/Output This chapter starts with a description of one of the simplest integrated peripherals of the MSP430 the General Purpose 8-bit Input Output (GPIO). The Input/Output
Chapter 6 6. General purpose Input/Output This chapter starts with a description of one of the simplest integrated peripherals of the MSP430 the General Purpose 8-bit Input Output (GPIO). The Input/Output
Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP
 Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP DB805C-FSM 805 Microcontroller FSM Finite State Machine General Description The Digital Blocks DB805C-FSM IP Core contains Digital Blocks compact DB805C CPU Core & GPIO
Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP DB805C-FSM 805 Microcontroller FSM Finite State Machine General Description The Digital Blocks DB805C-FSM IP Core contains Digital Blocks compact DB805C CPU Core & GPIO
DERTS Design Requirements (1): Microcontroller Architecture & Programming
 Lecture (5) DERTS Design Requirements (1): Microcontroller Architecture & Programming Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University 1 Lecture Outline: Features of microcomputers and microcontrollers.
Lecture (5) DERTS Design Requirements (1): Microcontroller Architecture & Programming Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University 1 Lecture Outline: Features of microcomputers and microcontrollers.
Organization in Memory
 in 16 addresses for sub-routines Is written once prior to initialization, however it can be changed in chunks of 512 bytes during operation two small blocks programmed via scatt.-fl. only 2kB fast RAM
in 16 addresses for sub-routines Is written once prior to initialization, however it can be changed in chunks of 512 bytes during operation two small blocks programmed via scatt.-fl. only 2kB fast RAM
University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department. EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I.
 University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I Fall 2016 LAB 04 Timer Interrupts Goals: Learn about Timer Interrupts. Learn how to
University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I Fall 2016 LAB 04 Timer Interrupts Goals: Learn about Timer Interrupts. Learn how to
Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices,
 Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices, CISC and RISC processors etc. Knows the architecture and
Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices, CISC and RISC processors etc. Knows the architecture and
Microcomputer Architecture and Programming
 IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP
 805 SFR Bus Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP 805 Microcontroller Configurable Peripherals General Description The Digital Blocks (Configurable Peripherals) Microcontroller Verilog IP Core is complaint with
805 SFR Bus Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP 805 Microcontroller Configurable Peripherals General Description The Digital Blocks (Configurable Peripherals) Microcontroller Verilog IP Core is complaint with
Question Bank Microprocessor and Microcontroller
 QUESTION BANK - 2 PART A 1. What is cycle stealing? (K1-CO3) During any given bus cycle, one of the system components connected to the system bus is given control of the bus. This component is said to
QUESTION BANK - 2 PART A 1. What is cycle stealing? (K1-CO3) During any given bus cycle, one of the system components connected to the system bus is given control of the bus. This component is said to
Hacettepe University
 www.msp430.ubi.pt MSP430 Teaching Materials Introductory Overview Week2 Hacettepe University Outline Microcontrollers Versus Microprocessors Central Processing Unit System Buses Memory Organization I/O
www.msp430.ubi.pt MSP430 Teaching Materials Introductory Overview Week2 Hacettepe University Outline Microcontrollers Versus Microprocessors Central Processing Unit System Buses Memory Organization I/O
MSP430. More on MSP430
 MSP430 More on MSP430 CodeComposer TI recently launched Code Composer Essentials v3. This IDE s latest version (version 3) supports all available MSP430 devices. The new features of CCE v3 include: - Free
MSP430 More on MSP430 CodeComposer TI recently launched Code Composer Essentials v3. This IDE s latest version (version 3) supports all available MSP430 devices. The new features of CCE v3 include: - Free
Lab 1: I/O, timers, interrupts on the ez430-rf2500
 Lab 1: I/O, timers, interrupts on the ez430-rf2500 UC Berkeley - EE 290Q Thomas Watteyne January 25, 2010 1 The ez430-rf2500 and its Components 1.1 Crash Course on the MSP430f2274 The heart of this platform
Lab 1: I/O, timers, interrupts on the ez430-rf2500 UC Berkeley - EE 290Q Thomas Watteyne January 25, 2010 1 The ez430-rf2500 and its Components 1.1 Crash Course on the MSP430f2274 The heart of this platform
Network Embedded Systems Sensor Networks Fall Hardware. Marcus Chang,
 Network Embedded Systems Sensor Networks Fall 2013 Hardware Marcus Chang, mchang@cs.jhu.edu 1 Embedded Systems Designed to do one or a few dedicated and/or specific functions Embedded as part of a complete
Network Embedded Systems Sensor Networks Fall 2013 Hardware Marcus Chang, mchang@cs.jhu.edu 1 Embedded Systems Designed to do one or a few dedicated and/or specific functions Embedded as part of a complete
Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP
 Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP 805 Microcontroller General Description The Digital Blocks Microcontroller Verilog IP Core is complaint with the MCS 5 Instruction Set and contains standard 805 MCU peripherals,
Digital Blocks Semiconductor IP 805 Microcontroller General Description The Digital Blocks Microcontroller Verilog IP Core is complaint with the MCS 5 Instruction Set and contains standard 805 MCU peripherals,
Copyright 2009 Texas Instruments All Rights Reserved
 MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 3 Further into the MSP430 Hacettepe University Anatomy of a Typical Small Microcontroller Central processing unit Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs computation.
MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 3 Further into the MSP430 Hacettepe University Anatomy of a Typical Small Microcontroller Central processing unit Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs computation.
MICROPROCESSOR BASED SYSTEM DESIGN
 MICROPROCESSOR BASED SYSTEM DESIGN Lecture 5 Xmega 128 B1: Architecture MUHAMMAD AMIR YOUSAF VON NEUMAN ARCHITECTURE CPU Memory Execution unit ALU Registers Both data and instructions at the same system
MICROPROCESSOR BASED SYSTEM DESIGN Lecture 5 Xmega 128 B1: Architecture MUHAMMAD AMIR YOUSAF VON NEUMAN ARCHITECTURE CPU Memory Execution unit ALU Registers Both data and instructions at the same system
Alex Milenkovich 1. CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers. Course Administration. Review: Outline. Getting Started with EasyWeb2. Review: MSP bit RISC
 CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Note S12 Course Administration Instructor: URL: TA: Labs: Test I: Text: Review: Today: Aleksandar Milenkovic milenka@ece.uah.edu www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Note S12 Course Administration Instructor: URL: TA: Labs: Test I: Text: Review: Today: Aleksandar Milenkovic milenka@ece.uah.edu www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka
Week 4: Embedded Programming Using C
 Week 4: Embedded Programming Using C The C language evolved from BCPL (1967) and B (1970), both of which were type-less languages. C was developed as a strongly-typed language by DennisRitchie in 1972,
Week 4: Embedded Programming Using C The C language evolved from BCPL (1967) and B (1970), both of which were type-less languages. C was developed as a strongly-typed language by DennisRitchie in 1972,
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring Lecture #11: More Clocks and Timers
 ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2018 Lecture #11: More Clocks and Timers Reading for Today: Davie's Ch 8.3-8.4, 8.9-8.10, User's Guide Ch. 17 Reading for Next Class: User's
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2018 Lecture #11: More Clocks and Timers Reading for Today: Davie's Ch 8.3-8.4, 8.9-8.10, User's Guide Ch. 17 Reading for Next Class: User's
Architecture & Instruction set of 8085 Microprocessor and 8051 Micro Controller
 of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
Have difficulty identifying any products Not incorporating embedded processor FPGA or CPLD In one form or another
 Introduction Embedded systems Continue pervasive expansion into Vast variety of electronic systems and products Aircraft and automobiles games and medical equipment Have difficulty identifying any products
Introduction Embedded systems Continue pervasive expansion into Vast variety of electronic systems and products Aircraft and automobiles games and medical equipment Have difficulty identifying any products
Embedded Systems. 3. Hardware Software Interface. Lothar Thiele. Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory
 Embedded Systems 3. Hardware Software Interface Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory Do you Remember? 3 2 3 3 High Level Physical View 3 4 High Level Physical View 3 5 What you will
Embedded Systems 3. Hardware Software Interface Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory Do you Remember? 3 2 3 3 High Level Physical View 3 4 High Level Physical View 3 5 What you will
Physics 319 Spring 2015: Introduction to the Programming and Use of Microprocessors
 Physics 319 Spring 2015: Introduction to the Programming and Use of Microprocessors Sing Chow, Andrzej Kotlicki, Ryan Wicks, and Carl Michal December 2014 This lab is going to introduce you to the world
Physics 319 Spring 2015: Introduction to the Programming and Use of Microprocessors Sing Chow, Andrzej Kotlicki, Ryan Wicks, and Carl Michal December 2014 This lab is going to introduce you to the world
ECE2049 Homework #2 The MSP430 Architecture & Basic Digital IO (DUE Friday 9/8/17 at 4 pm in class)
 ECE2049 Homework #2 The MSP430 Architecture & Basic Digital IO (DUE Friday 9/8/17 at 4 pm in class) Your homework should be neat and professional looking. You will loose points if your HW is not properly
ECE2049 Homework #2 The MSP430 Architecture & Basic Digital IO (DUE Friday 9/8/17 at 4 pm in class) Your homework should be neat and professional looking. You will loose points if your HW is not properly
AVR Microcontrollers Architecture
 ก ก There are two fundamental architectures to access memory 1. Von Neumann Architecture 2. Harvard Architecture 2 1 Harvard Architecture The term originated from the Harvard Mark 1 relay-based computer,
ก ก There are two fundamental architectures to access memory 1. Von Neumann Architecture 2. Harvard Architecture 2 1 Harvard Architecture The term originated from the Harvard Mark 1 relay-based computer,
Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Question Bank
 www.examquestionpaper.in Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Question Bank SUBJECT CODE / NAME: ET7102 / MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEM DESIGN BRANCH : M.E. (C&I) YEAR / SEM : I / I
www.examquestionpaper.in Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Question Bank SUBJECT CODE / NAME: ET7102 / MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEM DESIGN BRANCH : M.E. (C&I) YEAR / SEM : I / I
CPE/EE 323 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems Homework V
 CPE/EE 323 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems Homework V 1(15) 2(15) 3(25) 4(25) 5(20) Total Problem #1 (15 points) Power, Low power systems A sensor platform features a microcontroller, a sensor,
CPE/EE 323 Introduction to Embedded Computer Systems Homework V 1(15) 2(15) 3(25) 4(25) 5(20) Total Problem #1 (15 points) Power, Low power systems A sensor platform features a microcontroller, a sensor,
8051 Overview and Instruction Set
 8051 Overview and Instruction Set Curtis A. Nelson Engr 355 1 Microprocessors vs. Microcontrollers Microprocessors are single-chip CPUs used in microcomputers Microcontrollers and microprocessors are different
8051 Overview and Instruction Set Curtis A. Nelson Engr 355 1 Microprocessors vs. Microcontrollers Microprocessors are single-chip CPUs used in microcomputers Microcontrollers and microprocessors are different
Embedded Controller Programming
 Embedded Controller Programming Counters, Timers and I/O in Assembly Language Ken Arnold Copyright 2000-2004 Ken Arnold 1 Outline Timer/Counters Serial Port More 8051 Instructions Examples Copyright 2000-2004
Embedded Controller Programming Counters, Timers and I/O in Assembly Language Ken Arnold Copyright 2000-2004 Ken Arnold 1 Outline Timer/Counters Serial Port More 8051 Instructions Examples Copyright 2000-2004
FIFTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLOGY-MARCH 2014 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS (Common for CT,CM) [Time: 3 hours] (Maximum marks : 100)
![FIFTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLOGY-MARCH 2014 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS (Common for CT,CM) [Time: 3 hours] (Maximum marks : 100) FIFTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLOGY-MARCH 2014 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS (Common for CT,CM) [Time: 3 hours] (Maximum marks : 100)](/thumbs/76/73351884.jpg) (Revision-10) FIFTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLOGY-MARCH 2014 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS (Common for CT,CM) [Time: 3 hours] (Maximum marks : 100) PART-A (Maximum marks : 10) I. Answer all
(Revision-10) FIFTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLOGY-MARCH 2014 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS (Common for CT,CM) [Time: 3 hours] (Maximum marks : 100) PART-A (Maximum marks : 10) I. Answer all
Hacettepe University
 MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 3 Further into the MSP430 Hacettepe University Anatomy of a Typical Small Microcontroller Central processing unit Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs computation.
MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 3 Further into the MSP430 Hacettepe University Anatomy of a Typical Small Microcontroller Central processing unit Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs computation.
@databasescaling Wednesday, 18 th April 2013
 andyjpb@ashurst.eu.org @databasescaling Wednesday, 18 th April 2013 OSHUG #24 1 / 56 Writing C For Constrained Systems a@jpb.li @databasescaling Wednesday, 18 th April 2013 OSHUG #24 2 / 56 Writing C For
andyjpb@ashurst.eu.org @databasescaling Wednesday, 18 th April 2013 OSHUG #24 1 / 56 Writing C For Constrained Systems a@jpb.li @databasescaling Wednesday, 18 th April 2013 OSHUG #24 2 / 56 Writing C For
Using peripherals on the MSP430 (if time)
 Today's Plan: Announcements Review Activities 1&2 Programming in C Using peripherals on the MSP430 (if time) Activity 3 Announcements: Midterm coming on Feb 9. Will need to write simple programs in C and/or
Today's Plan: Announcements Review Activities 1&2 Programming in C Using peripherals on the MSP430 (if time) Activity 3 Announcements: Midterm coming on Feb 9. Will need to write simple programs in C and/or
063[[[0LFURFRQWUROOHUV /RZ3RZHU0RGHV &3($GYDQFHG0LFURFRPSXWHU7HFKQLTXHV 'U(PLO-RYDQRY /RZ3RZHU. Power: A First-Class Architectural Design Constraint
 063[[[0LFURFRQWUROOHUV /RZ3RZHU0RGHV &3($GYDQFHG0LFURFRPSXWHU7HFKQLTXHV 'U(PLO-RYDQRY MSP430 low power concepts 1 /RZ3RZHU Power: A First-Class Architectural Design Constraint Trevor Mudge, IEEE Computer,
063[[[0LFURFRQWUROOHUV /RZ3RZHU0RGHV &3($GYDQFHG0LFURFRPSXWHU7HFKQLTXHV 'U(PLO-RYDQRY MSP430 low power concepts 1 /RZ3RZHU Power: A First-Class Architectural Design Constraint Trevor Mudge, IEEE Computer,
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers
 CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Note S11 MSP430 Documentation MSP430 home page (TI) www.ti.com/msp430 User s manual http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka/cpe421-05s/manuals/slau049c.pdf
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Note S11 MSP430 Documentation MSP430 home page (TI) www.ti.com/msp430 User s manual http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka/cpe421-05s/manuals/slau049c.pdf
COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs2121 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session 2, 2017 1 Contents Memory models Registers Data types Instructions
COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs2121 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session 2, 2017 1 Contents Memory models Registers Data types Instructions
Computer Hardware Requirements for ERTSs: Microprocessors & Microcontrollers
 Lecture (4) Computer Hardware Requirements for ERTSs: Microprocessors & Microcontrollers Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University-Jordan DERTS-MSc, 2015 Prof. Kasim Al-Aubidy 1 Lecture Outline:
Lecture (4) Computer Hardware Requirements for ERTSs: Microprocessors & Microcontrollers Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University-Jordan DERTS-MSc, 2015 Prof. Kasim Al-Aubidy 1 Lecture Outline:
Hacettepe University
 MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF INTERFACING AND TIMERS for MSP430 Hacettepe University Elements in Basic MCU Interface Power Source Feeds CPU and peripherals Clock Oscillators System synchronization
MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF INTERFACING AND TIMERS for MSP430 Hacettepe University Elements in Basic MCU Interface Power Source Feeds CPU and peripherals Clock Oscillators System synchronization
MSP430 instruction set *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m23503 1 MSP430 instruction set * Pedro Dinis António Espírito Santo Bruno Ribeiro This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m23503 1 MSP430 instruction set * Pedro Dinis António Espírito Santo Bruno Ribeiro This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
 Contents 8051 Instruction Set BY D. BALAKRISHNA, Research Assistant, IIIT-H Chapter I : Control Transfer Instructions Lesson (a): Loop Lesson (b): Jump (i) Conditional Lesson (c): Lesson (d): Lesson (e):
Contents 8051 Instruction Set BY D. BALAKRISHNA, Research Assistant, IIIT-H Chapter I : Control Transfer Instructions Lesson (a): Loop Lesson (b): Jump (i) Conditional Lesson (c): Lesson (d): Lesson (e):
Hacettepe University
 MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF INTERFACING AND TIMERS for MSP430 Hacettepe University Elements in Basic MCU Interface Power Source Feeds CPU and peripherals Clock Oscillators System synchronization
MSP430 Teaching Materials Week 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF INTERFACING AND TIMERS for MSP430 Hacettepe University Elements in Basic MCU Interface Power Source Feeds CPU and peripherals Clock Oscillators System synchronization
Designing for Ultra-Low Power with MSP430
 Designing for Ultra-Low Power with MSP430 Christian Hernitscheck MSP430 FAE Europe Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda Introduction to Ultra-Low Power Looking for Ultra-Low Power
Designing for Ultra-Low Power with MSP430 Christian Hernitscheck MSP430 FAE Europe Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda Introduction to Ultra-Low Power Looking for Ultra-Low Power
Module Contents of the Module Hours COs
 Microcontrollers (EE45): Syllabus: Module Contents of the Module Hours COs 1 8051 MICROCONTROLLER ARCHITECTURE: Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers, the 8051 Architecture, 08 1 and pin
Microcontrollers (EE45): Syllabus: Module Contents of the Module Hours COs 1 8051 MICROCONTROLLER ARCHITECTURE: Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers, the 8051 Architecture, 08 1 and pin
Introduction to the Texas Instruments ez430. By: Naren Anand
 Introduction to the Texas Instruments ez430 By: Naren Anand Introduction to the Texas Instruments ez430 By: Naren Anand Online: C O N N E X I O N S Rice University,
Introduction to the Texas Instruments ez430 By: Naren Anand Introduction to the Texas Instruments ez430 By: Naren Anand Online: C O N N E X I O N S Rice University,
2006 Mixed Signal Products SLAU049F
 User s Guide 2006 Mixed Signal Products SLAU049F Related Documentation From Texas Instruments Preface About This Manual This manual discusses modules and peripherals of the MSP430x1xx family of devices.
User s Guide 2006 Mixed Signal Products SLAU049F Related Documentation From Texas Instruments Preface About This Manual This manual discusses modules and peripherals of the MSP430x1xx family of devices.
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. MSP430F11x2/12x2 Device Erratasheet Current Version Devices MSP430F1122
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. MSP430F11x2/12x2 Device Erratasheet Current Version Devices MSP430F1122
MSP430FG4618 Programming Reference Revision 3
 MSP430FG4618/F2013 Experimenter Board MSP430FG4618 Programming Reference Revision 3 George Mason University 1. CPU Registers The CPU incorporates sixteen 20-bit registers. R0, R1, R2 and R3 have dedicated
MSP430FG4618/F2013 Experimenter Board MSP430FG4618 Programming Reference Revision 3 George Mason University 1. CPU Registers The CPU incorporates sixteen 20-bit registers. R0, R1, R2 and R3 have dedicated
Getting Started with the MSP430 IAR Assembly
 Getting Started with the MSP430 IAR Assembly by Alex Milenkovich, milenkovic@computer.org Objectives: This tutorial will help you get started with the MSP30 IAR Assembly program development. You will learn
Getting Started with the MSP430 IAR Assembly by Alex Milenkovich, milenkovic@computer.org Objectives: This tutorial will help you get started with the MSP30 IAR Assembly program development. You will learn
Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
 Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 2 Processor Core Architecture Computes things > ALU (Arithmetic Logic
Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 2 Processor Core Architecture Computes things > ALU (Arithmetic Logic
CPE 323 MSP430 MSP430 Assembly Language Programming
 CPE 323 MSP430 MSP430 Assembly Language Programming Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective: Introduce MSP430 assembly language Contents Contents...
CPE 323 MSP430 MSP430 Assembly Language Programming Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective: Introduce MSP430 assembly language Contents Contents...
AVR XMEGA Product Line Introduction AVR XMEGA TM. Product Introduction.
 AVR XMEGA TM Product Introduction 32-bit AVR UC3 AVR Flash Microcontrollers The highest performance AVR in the world 8/16-bit AVR XMEGA Peripheral Performance 8-bit megaavr The world s most successful
AVR XMEGA TM Product Introduction 32-bit AVR UC3 AVR Flash Microcontrollers The highest performance AVR in the world 8/16-bit AVR XMEGA Peripheral Performance 8-bit megaavr The world s most successful
5xx Active & Low Power Mode Operation
 5xx Active & Low Power Mode Operation 38 Lab 2: ULP Operation Lab Goals Learn ULP Best Practices Learn & understand how to configure two key modules of the 5xx to achieve ultra-low power operation. Power
5xx Active & Low Power Mode Operation 38 Lab 2: ULP Operation Lab Goals Learn ULP Best Practices Learn & understand how to configure two key modules of the 5xx to achieve ultra-low power operation. Power
Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set]
![Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set] Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set]](/thumbs/82/86620819.jpg) Microcontroller Intel 8051 [Instruction Set] Structure of Assembly Language [ label: ] mnemonic [operands] [ ;comment ] Example: MOV R1, #25H ; load data 25H into R1 2 8051 Assembly Language Registers
Microcontroller Intel 8051 [Instruction Set] Structure of Assembly Language [ label: ] mnemonic [operands] [ ;comment ] Example: MOV R1, #25H ; load data 25H into R1 2 8051 Assembly Language Registers
These three counters can be programmed for either binary or BCD count.
 S5 KTU 1 PROGRAMMABLE TIMER 8254/8253 The Intel 8253 and 8254 are Programmable Interval Timers (PTIs) designed for microprocessors to perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit registers.
S5 KTU 1 PROGRAMMABLE TIMER 8254/8253 The Intel 8253 and 8254 are Programmable Interval Timers (PTIs) designed for microprocessors to perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit registers.
Microcontroller systems Lec 2 PIC18LF8722 Microcontroller s s core
 TKT-3500 Microcontroller systems Lec 2 PIC18LF8722 Microcontroller s s core Erno Salminen Copyright notice Some figures by Robert Reese, from supplementary CD of the course book from PIC18F8722 Family
TKT-3500 Microcontroller systems Lec 2 PIC18LF8722 Microcontroller s s core Erno Salminen Copyright notice Some figures by Robert Reese, from supplementary CD of the course book from PIC18F8722 Family
8051 microcontrollers
 8051 microcontrollers Presented by: Deepak Kumar Rout Synergy Institute of Engineering and Technology, Dhenkanal Chapter 2 Introduction Intel MCS-51 family of microcontrollers consists of various devices
8051 microcontrollers Presented by: Deepak Kumar Rout Synergy Institute of Engineering and Technology, Dhenkanal Chapter 2 Introduction Intel MCS-51 family of microcontrollers consists of various devices
Course Introduction. Purpose: Objectives: Content: 27 pages 4 questions. Learning Time: 20 minutes
 Course Introduction Purpose: This course provides an overview of the Direct Memory Access Controller and the Interrupt Controller on the SH-2 and SH-2A families of 32-bit RISC microcontrollers, which are
Course Introduction Purpose: This course provides an overview of the Direct Memory Access Controller and the Interrupt Controller on the SH-2 and SH-2A families of 32-bit RISC microcontrollers, which are
FIFTH SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION MODEL TEST QUESTION PAPER, NOVEMBER CS 305: Microprocessor and Microcontrollers PART A
 Reg No Name FIFTH SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION MODEL TEST QUESTION PAPER, NOVEMBER 2017 CS 305: Microprocessor and Microcontrollers Max. Marks: 100 Duration: 3 Hours PART A Answer all questions.
Reg No Name FIFTH SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION MODEL TEST QUESTION PAPER, NOVEMBER 2017 CS 305: Microprocessor and Microcontrollers Max. Marks: 100 Duration: 3 Hours PART A Answer all questions.
Highlights. FP51 (FPGA based 1T 8051 core)
 Copyright 2017 PulseRain Technology, LLC. FP51 (FPGA based 1T 8051 core) 10555 Scripps Trl, San Diego, CA 92131 858-877-3485 858-408-9550 http://www.pulserain.com Highlights 1T 8051 Core Intel MCS-51 Compatible
Copyright 2017 PulseRain Technology, LLC. FP51 (FPGA based 1T 8051 core) 10555 Scripps Trl, San Diego, CA 92131 858-877-3485 858-408-9550 http://www.pulserain.com Highlights 1T 8051 Core Intel MCS-51 Compatible
