To design a 4-bit ALU To experimentally check the operation of the ALU
|
|
|
- Joleen Hudson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Experiment # 11 Design and Implementation of a 4 - bit ALU Objectives: The objectives of this lab are: To design a 4-bit ALU To experimentally check the operation of the ALU Overview An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a combinational circuit that performs logic and arithmetic micro-operations on a pair of n-bit operands (ex. A[3:0] and B[3:0]). The operations performed by an ALU are controlled by a set of function-select inputs. In this lab you will design a 4-bit ALU with 2 function-select inputs: Select S1 and S0 inputs. The functions performed by the ALU are specified in Table 1. Table 1: Functions of ALU S1 S0 C0 FUNCTION OPERATION A Transfer A A + 1 Increment A by A + B Add A and B A + B + 1 Increment the sum of A and B by A + B' A plus one's complement of B A B Subtract B from A (i.e. B' + A + 1) A' + B B plus one's complement of A B A B minus A (or A' + B + 1) A block diagram is given in Figure 1.
2 2 Figure 1: Block diagram of the 4-bit ALU. We will be using two s complement system of notation while dealing with arithmetic operations in our ALU. This has a number of advantages over the sign and magnitude representation such as easy addition or subtraction of mixed positive and negative numbers. Recall that the two s complement of a n-bit number N is defined as, 2 n - N = (2 n N) + 1 The last representation gives us an easy way to find two s complement: take the bit wise complement of the number and add 1 to it. As an example, to represent the number -5, we take two s complement of 5 (=0101) as follows, > (bit wise complement) (two s complement) Numbers represented in two s complement lie within the range - (2 n-1 ) to + (2 n-1-1). For a 4-bit number this means that the number is in the range of -8 to +7. There is a potential problem we still need to be aware of when working with two's complement, namely overflow and underflow as is illustrated in the examples below, (=carry Ci) = -7! also, (=carry Ci) = +7! Both calculations give the wrong results (-7 instead of +9 or +7 instead of -9) which is caused by the fact that the result +9 or -9 is out of the allowable range for a 4-bit
3 3 two s complement number. Whenever the result is larger than +7 or smaller than -8 there is an overflow or underflow and the result of the addition or subtraction is wrong. Overflow and underflow can be easily detected when the carry out of the most significant stage (i.e. C 4 ) is different from the carry out of the previous stage (i.e. C 3 ). In our lab, the inputs A and B have to be presented in two s complement to the inputs of the ALU. Design strategies When designing the ALU we will follow the principle "Divide and Conquer" in order to use a modular design that consists of smaller, more manageable blocks, some of which can be re-used. Instead of designing the 4-bit ALU as one circuit we will first design a one-bit ALU, also called a bit-slice. These bit-slices can then be put together to make a 4-bit ALU. There are different ways to design a bit-slice of the ALU. One method consists of writing the truth table for the one-bit ALU. This table has 5 inputs (S1, S0, C 0, A i and B i ) and two outputs F i and C i+1. Inputs One switch is used to define bits of the first operand (A) A second switch is used to define bits of the second operand (B) The bits of A & B are shifted one by one into 2 shift registers that will hold the two operands. A push button may be used as a clock for the 2 shift registers. A total of 4 clocks is required to input both operands (beware of bouncing problem). Selects, S0 and S1, and the C0 inputs will be defined by 3 other switches. Outputs The operands A and B should be displayed on the two leftmost 7-segment display digits as HEX digits. Thus an input of 1010 should be displayed as the character A, 1011 as b, 1100 as C, 1101 as d, 1110 as E, and 1111 as F. Another LED should display the overflow flag V. The result of arithmetic operation (2 s complement representation) is to be shown on the rightmost 7-segment display digit. An LED should be used to indicate the sign of the result. Another LED should display the carryout bit Cout. You need to time-multiplex the inputs of the 7-segment display digits such that all three digits (A, B & result) are displayed (in a manner similar to what was done to display the alarm clock time). Figure 3 shows a schematic of the overall system, consisting of the ALU, Decoder and Switching circuit, and Displays on the Digilab board.
4 4 Figure 2: Overall system, including the 4-bit ALU and display units. Pre Lab Do the following tasks prior to coming to the lab. Write the answers to all questions on a sheet prior to coming to the lab. You will also need to include answer to the prelab questions in your lab report. Read section 7-7 (the arithmetic/logic unit) of you text book (pp ). Design the HEX-to 7-segment display decoder. Derive the logic for the arithmetic overflow condition. ALU Unit Design. You have different choices to design and implement the ALU unit. A particularly attractive method is one that makes use of readily available modules such as Full Adders. The arithmetic unit basically performs additions on a set of inputs. By proper choice of the adder inputs, one can perform a range of operations. This approach is shown in Figure 3. The only blocks that need to be designed are the A Logic and B Logic circuits. You can make use of full adders available in the SPARTAN library. Figure 3: Schematic block diagram of the arithmetic unit. A. Give the truth tables for the Xi and Yi functions with inputs S1, S0 and Ai, and S1, S0 and Bi, respectively. Fill out the following tables. Notice that in definition table I of the ALU, the variable C 0 acts as the Carry input. Depending on the value of C 0, one performs the function on the odd or even entries of the definition table I. As an example the first entry is "transfer A" (for C 0 =0) while the second one is "A+1" (for C 0 =1); similarly for A + B and A + B + 1, etc.
5 5 Table 2: Truth tables for the A and B logic circuits. S1 S0 Ai Xi (A Logic) S1 S0 Bi Yi (B Logic) B. Give the K-map for Xi and Yi functions. Find the minimum realization for Xi and Yi. C. Draw the logic diagram for Xi and Yi. D. Design the circuit that detects over- or underflow. E. BCD to Hex Decoder Design Design the switching circuit that is needed to use the seven-segment displays. In-lab: Your task is to design and implement the 4-bit ALU. Follow the guidelines of the prelab in designing the 4-bit ALU. You will create a project (see tasks below) with a toplevel schematic that will correspond to the one as shown in Figure-2. This top-level file will be instantiating several macros which are shown as black boxes in the Figure. These macros will have to be developed separately. Task 1: Design the input circuit using two 4 bits shift registers in order to shift-in inputs A and B serially. Task 2: Implement the 4-bit ALU. Design and add the circuit that detects overflow, V to your schematic. Simulate the full 4-bit ALU and verify that all operations function properly. Task 3: Inputs and outputs For the A and B inputs, use the two 4 bits shift register for inputs A and B and use switches SW1 and SW2
6 6 For the Select and CarryIn inputs (S1, S0 and Cin), you will need to use the general purpose switches SW3-SW5. The overflow and sign of the result is to be displayed using LEDs. Display the Hexadecimal values of the inputs A and B on the two leftmost 7- segment display digits and the result of the arithmetic operation on the rightmost 7-segment display digit. Specify the pin locations (using the constraint editor or on the schematic), implement and test the ALU. It will be instructive to do a timing simulation to get an idea about the overall speed of the circuit. Give the working demo to your lab instructor. Post Lab You have to hand in a lab report that contains the following: Section on the Pre-lab explaining the design of each block and giving the answers to each task. Section on the lab experiment: Brief description of the goals. b. Brief explanation of the design approach, the overall schematic and of each macro. Discussion of the results indicating that the circuit functions properly. Conclusion and discussion.
EGC221: Digital Logic Lab
 EGC221: Digital Logic Lab Experiment #7 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Schematic Implementation Student s Name: Student s Name: Reg. no.: Reg. no.: Semester: Spring 2017 Date: 04 April 2017 Assessment: Assessment
EGC221: Digital Logic Lab Experiment #7 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Schematic Implementation Student s Name: Student s Name: Reg. no.: Reg. no.: Semester: Spring 2017 Date: 04 April 2017 Assessment: Assessment
Basic Arithmetic (adding and subtracting)
 Basic Arithmetic (adding and subtracting) Digital logic to show add/subtract Boolean algebra abstraction of physical, analog circuit behavior 1 0 CPU components ALU logic circuits logic gates transistors
Basic Arithmetic (adding and subtracting) Digital logic to show add/subtract Boolean algebra abstraction of physical, analog circuit behavior 1 0 CPU components ALU logic circuits logic gates transistors
Number Systems. Readings: , Problem: Implement simple pocket calculator Need: Display, adders & subtractors, inputs
 Number Systems Readings: 3-3.3.3, 3.3.5 Problem: Implement simple pocket calculator Need: Display, adders & subtractors, inputs Display: Seven segment displays Inputs: Switches Missing: Way to implement
Number Systems Readings: 3-3.3.3, 3.3.5 Problem: Implement simple pocket calculator Need: Display, adders & subtractors, inputs Display: Seven segment displays Inputs: Switches Missing: Way to implement
Lab 7: RPN Calculator
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory Lab 7: RPN Calculator The purpose of this lab is: Purpose 1. To get familiar with the use
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory Lab 7: RPN Calculator The purpose of this lab is: Purpose 1. To get familiar with the use
Lab 3: Standard Combinational Components
 Lab 3: Standard Combinational Components Purpose In this lab you will implement several combinational circuits on the DE1 development board to test and verify their operations. Introduction Using a high-level
Lab 3: Standard Combinational Components Purpose In this lab you will implement several combinational circuits on the DE1 development board to test and verify their operations. Introduction Using a high-level
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501
 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Arithmetic Circuits. Nurul Hazlina Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit
 Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
Binary Addition. Add the binary numbers and and show the equivalent decimal addition.
 Binary Addition The rules for binary addition are 0 + 0 = 0 Sum = 0, carry = 0 0 + 1 = 0 Sum = 1, carry = 0 1 + 0 = 0 Sum = 1, carry = 0 1 + 1 = 10 Sum = 0, carry = 1 When an input carry = 1 due to a previous
Binary Addition The rules for binary addition are 0 + 0 = 0 Sum = 0, carry = 0 0 + 1 = 0 Sum = 1, carry = 0 1 + 0 = 0 Sum = 1, carry = 0 1 + 1 = 10 Sum = 0, carry = 1 When an input carry = 1 due to a previous
LECTURE 4. Logic Design
 LECTURE 4 Logic Design LOGIC DESIGN The language of the machine is binary that is, sequences of 1 s and 0 s. But why? At the hardware level, computers are streams of signals. These signals only have two
LECTURE 4 Logic Design LOGIC DESIGN The language of the machine is binary that is, sequences of 1 s and 0 s. But why? At the hardware level, computers are streams of signals. These signals only have two
ELEC 326: Class project
 ELEC 326: Class project Kartik Mohanram 1 Introduction For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers. In the
ELEC 326: Class project Kartik Mohanram 1 Introduction For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers. In the
ECE2029: Introduction to Digital Circuit Design Lab 3 Implementing a 4-bit Four Function ALU
 ECE2029: Introduction to Digital Circuit Design Lab 3 Implementing a 4-bit Four Function ALU Objective: Inside a computer's central processing unit (CPU) there is a sub-block called the arithmetic logic
ECE2029: Introduction to Digital Circuit Design Lab 3 Implementing a 4-bit Four Function ALU Objective: Inside a computer's central processing unit (CPU) there is a sub-block called the arithmetic logic
Experiment 7 Arithmetic Circuits Design and Implementation
 Experiment 7 Arithmetic Circuits Design and Implementation Introduction: Addition is just what you would expect in computers. Digits are added bit by bit from right to left, with carries passed to the
Experiment 7 Arithmetic Circuits Design and Implementation Introduction: Addition is just what you would expect in computers. Digits are added bit by bit from right to left, with carries passed to the
Elec 326: Digital Logic Design
 Elec 326: Digital Logic Design Project Requirements Fall 2005 For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers.
Elec 326: Digital Logic Design Project Requirements Fall 2005 For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers.
UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT
 UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital
 Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
5 Arithmetic Logic Unit
 Arithmetic Logic Unit, Muxes 5 Arithmetic Logic Unit I Overview An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) allows many pre-defined functions to be implemented on two binary inputs. We will look at a simple ALU that
Arithmetic Logic Unit, Muxes 5 Arithmetic Logic Unit I Overview An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) allows many pre-defined functions to be implemented on two binary inputs. We will look at a simple ALU that
REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS
 1 REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
1 REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
EXPERIMENT #8: BINARY ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
 EE 2 Lab Manual, EE Department, KFUPM EXPERIMENT #8: BINARY ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS OBJECTIVES: Design and implement a circuit that performs basic binary arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction,
EE 2 Lab Manual, EE Department, KFUPM EXPERIMENT #8: BINARY ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS OBJECTIVES: Design and implement a circuit that performs basic binary arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction,
CO Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL. Lecture 9
 CO20-320241 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 2017 A Four-bit Number Circle CAPL Fall 2017 2 / 38 Functional Parts of an ALU CAPL Fall 2017 3 / 38 Addition
CO20-320241 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 2017 A Four-bit Number Circle CAPL Fall 2017 2 / 38 Functional Parts of an ALU CAPL Fall 2017 3 / 38 Addition
CSCB58 - Lab 3. Prelab /3 Part I (in-lab) /2 Part II (in-lab) /2 TOTAL /8
 CSCB58 - Lab 3 Latches, Flip-flops, and Registers Learning Objectives The purpose of this exercise is to investigate the fundamental synchronous logic elements: latches, flip-flops, and registers. Prelab
CSCB58 - Lab 3 Latches, Flip-flops, and Registers Learning Objectives The purpose of this exercise is to investigate the fundamental synchronous logic elements: latches, flip-flops, and registers. Prelab
Register Transfer and Micro-operations
 Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus Memory Transfer Micro-operations Some Application of Logic Micro Operations Register Transfer and Micro-operations Learning Objectives After reading this
Real Digital Problem Set #6
 Real igital Problem et #6. (2 points) ketch a block diagram for a magnitude comparator bit-slice circuit. Create K-maps to define the bit-slice circuit, and use them to find optimal logic equations. ketch
Real igital Problem et #6. (2 points) ketch a block diagram for a magnitude comparator bit-slice circuit. Create K-maps to define the bit-slice circuit, and use them to find optimal logic equations. ketch
Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2)
 Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2) Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization 1 MICROOPERATIONS Computer system microoperations are of four types: Register transfer microoperations
Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2) Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization 1 MICROOPERATIONS Computer system microoperations are of four types: Register transfer microoperations
Digital Fundamentals. Lab 6 2 s Complement / Digital Calculator
 Richland College Engineering Technology Rev. 0. Donham Rev. 1 (7/2003) J. Horne Rev. 2 (1/2008) J. radbury Digital Fundamentals CETT 1425 Lab 6 2 s Complement / Digital Calculator Name: Date: Objectives:
Richland College Engineering Technology Rev. 0. Donham Rev. 1 (7/2003) J. Horne Rev. 2 (1/2008) J. radbury Digital Fundamentals CETT 1425 Lab 6 2 s Complement / Digital Calculator Name: Date: Objectives:
CSE140 L. Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 18,2006. CSE140L Course Info
 CSE4 L Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 8,26 CSE4L Course Info Lectures Wedesday :-:2AM, HSS33 Lab Assignment egins TA s JinHua Liu (jhliu@cs.ucsd.edu) Contact TAs if you re still looking for a lab
CSE4 L Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 8,26 CSE4L Course Info Lectures Wedesday :-:2AM, HSS33 Lab Assignment egins TA s JinHua Liu (jhliu@cs.ucsd.edu) Contact TAs if you re still looking for a lab
ECE 313 Computer Organization EXAM 2 November 11, 2000
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 50 minutes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. ALU Design / Logic Operations 20 Points The subset of
This exam is open book and open notes. You have 50 minutes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. ALU Design / Logic Operations 20 Points The subset of
EE 109 Unit 6 Binary Arithmetic
 EE 109 Unit 6 Binary Arithmetic 1 2 Semester Transition Point At this point we are going to start to transition in our class to look more at the hardware organization and the low-level software that is
EE 109 Unit 6 Binary Arithmetic 1 2 Semester Transition Point At this point we are going to start to transition in our class to look more at the hardware organization and the low-level software that is
Review. Steps to writing (stateless) circuits: Create a logic function (one per output)
 MIPS ALU Review Steps to writing (stateless) circuits: Create a truth table Go through all different combinations of inputs For each row, generate each output based on the problem description Create a
MIPS ALU Review Steps to writing (stateless) circuits: Create a truth table Go through all different combinations of inputs For each row, generate each output based on the problem description Create a
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE
 REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic
 Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic Counting to four billion two fingers at a time What do all those bits mean now? bits (011011011100010...01) instruction R-format I-format... integer data number text
Number Systems and Computer Arithmetic Counting to four billion two fingers at a time What do all those bits mean now? bits (011011011100010...01) instruction R-format I-format... integer data number text
Note that none of the above MAY be a VALID ANSWER.
 ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
ECE 2030B 1:00pm Computer Engineering Spring problems, 5 pages Exam Two 10 March 2010
 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Chapter 4. Combinational Logic
 Chapter 4. Combinational Logic Tong In Oh 1 4.1 Introduction Combinational logic: Logic gates Output determined from only the present combination of inputs Specified by a set of Boolean functions Sequential
Chapter 4. Combinational Logic Tong In Oh 1 4.1 Introduction Combinational logic: Logic gates Output determined from only the present combination of inputs Specified by a set of Boolean functions Sequential
Computer Organization (Autonomous)
 Computer Organization (Autonomous) UNIT I Sections - A & D Prepared by Anil Kumar Prathipati, Asst. Prof., Dept. of CSE. SYLLABUS Introduction: Types of Computers, Functional units of Basic Computer (Block
Computer Organization (Autonomous) UNIT I Sections - A & D Prepared by Anil Kumar Prathipati, Asst. Prof., Dept. of CSE. SYLLABUS Introduction: Types of Computers, Functional units of Basic Computer (Block
BUILDING BLOCKS OF A BASIC MICROPROCESSOR. Part 1 PowerPoint Format of Lecture 3 of Book
 BUILDING BLOCKS OF A BASIC MICROPROCESSOR Part PowerPoint Format of Lecture 3 of Book Decoder Tri-state device Full adder, full subtractor Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Memories Example showing how to write
BUILDING BLOCKS OF A BASIC MICROPROCESSOR Part PowerPoint Format of Lecture 3 of Book Decoder Tri-state device Full adder, full subtractor Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Memories Example showing how to write
Final Exam Solution Sunday, December 15, 10:05-12:05 PM
 Last (family) name: First (given) name: Student I.D. #: Circle section: Kim Hu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/CS 352 Digital System Fundamentals
Last (family) name: First (given) name: Student I.D. #: Circle section: Kim Hu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/CS 352 Digital System Fundamentals
CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations Outline Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations Outline Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations
CCE 3202 Advanced Digital System Design
 CCE 3202 Advanced Digital System Design Lab Exercise #2 Introduction You will use Xilinx Webpack v9.1 to allow the synthesis and creation of VHDLbased designs. This lab will outline the steps necessary
CCE 3202 Advanced Digital System Design Lab Exercise #2 Introduction You will use Xilinx Webpack v9.1 to allow the synthesis and creation of VHDLbased designs. This lab will outline the steps necessary
ECE468 Computer Organization & Architecture. The Design Process & ALU Design
 ECE6 Computer Organization & Architecture The Design Process & Design The Design Process "To Design Is To Represent" Design activity yields description/representation of an object -- Traditional craftsman
ECE6 Computer Organization & Architecture The Design Process & Design The Design Process "To Design Is To Represent" Design activity yields description/representation of an object -- Traditional craftsman
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H ) Next: continued. Consulting hours. Introduction to Sim. Milestone #1 (due 1/26)
 Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Consulting hours Introduction to Sim Milestone #1 (due 1/26) 2 1 Overview: Integer Operations Internal representation
Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Consulting hours Introduction to Sim Milestone #1 (due 1/26) 2 1 Overview: Integer Operations Internal representation
DLD VIDYA SAGAR P. potharajuvidyasagar.wordpress.com. Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology UNIT 3 DLD P VIDYA SAGAR
 DLD UNIT III Combinational Circuits (CC), Analysis procedure, Design Procedure, Combinational circuit for different code converters and other problems, Binary Adder- Subtractor, Decimal Adder, Binary Multiplier,
DLD UNIT III Combinational Circuits (CC), Analysis procedure, Design Procedure, Combinational circuit for different code converters and other problems, Binary Adder- Subtractor, Decimal Adder, Binary Multiplier,
For Example: P: LOAD 5 R0. The command given here is used to load a data 5 to the register R0.
 Register Transfer Language Computers are the electronic devices which have several sets of digital hardware which are inter connected to exchange data. Digital hardware comprises of VLSI Chips which are
Register Transfer Language Computers are the electronic devices which have several sets of digital hardware which are inter connected to exchange data. Digital hardware comprises of VLSI Chips which are
REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS
 REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
Computer Architecture and Organization: L04: Micro-operations
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
CHW 261: Logic Design
 CHW 261: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed14 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby14# Slide 1 Slide 2 Slide 3 Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER
CHW 261: Logic Design Instructors: Prof. Hala Zayed Dr. Ahmed Shalaby http://www.bu.edu.eg/staff/halazayed14 http://bu.edu.eg/staff/ahmedshalaby14# Slide 1 Slide 2 Slide 3 Digital Fundamentals CHAPTER
CHAPTER 9 MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES
 CHAPTER 9 MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Multiplexers 9.3 Three-State Buffers 9.4 Decoders and Encoders
CHAPTER 9 MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Multiplexers 9.3 Three-State Buffers 9.4 Decoders and Encoders
Lab Assignment 1. Developing and Using Testbenches
 Lab Assignment 1 Developing and Using Testbenches Task 1 Develop a testbench in VHDL to test and verify the operation of an ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. The ALU
Lab Assignment 1 Developing and Using Testbenches Task 1 Develop a testbench in VHDL to test and verify the operation of an ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. The ALU
11/22/1999 7pm - 9pm. Name: Login Name: Preceptor Name: Precept Number:
 Login Preceptor Precept Number: Computer Science 126 Second Midterm Exam 11/22/1999 7pm - 9pm This exam has 10 questions. The weight of each question is printed in the table below and next to each question.
Login Preceptor Precept Number: Computer Science 126 Second Midterm Exam 11/22/1999 7pm - 9pm This exam has 10 questions. The weight of each question is printed in the table below and next to each question.
ECE 2030D Computer Engineering Spring problems, 5 pages Exam Two 8 March 2012
 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
IA Digital Electronics - Supervision I
 IA Digital Electronics - Supervision I Nandor Licker Due noon two days before the supervision 1 Overview The goal of this exercise is to design an 8-digit calculator capable of adding
IA Digital Electronics - Supervision I Nandor Licker Due noon two days before the supervision 1 Overview The goal of this exercise is to design an 8-digit calculator capable of adding
Chapter 1. Digital Systems and Binary Numbers
 Chapter 1. Digital Systems and Binary Numbers Tong In Oh 1 1.1 Digital Systems Digital age Characteristic of digital system Generality and flexibility Represent and manipulate discrete elements of information
Chapter 1. Digital Systems and Binary Numbers Tong In Oh 1 1.1 Digital Systems Digital age Characteristic of digital system Generality and flexibility Represent and manipulate discrete elements of information
Decimal & Binary Representation Systems. Decimal & Binary Representation Systems
 Decimal & Binary Representation Systems Decimal & binary are positional representation systems each position has a value: d*base i for example: 321 10 = 3*10 2 + 2*10 1 + 1*10 0 for example: 101000001
Decimal & Binary Representation Systems Decimal & binary are positional representation systems each position has a value: d*base i for example: 321 10 = 3*10 2 + 2*10 1 + 1*10 0 for example: 101000001
ECE2029: Introduction to Digital Circuit Design. Lab 2 Implementing Combinational Functional Blocks
 ECE2029: Introduction to Digital Circuit Design Lab 2 Implementing Combinational Functional Blocks Objective: In this lab exercise you will simulate, test, and download various digital circuits which implement
ECE2029: Introduction to Digital Circuit Design Lab 2 Implementing Combinational Functional Blocks Objective: In this lab exercise you will simulate, test, and download various digital circuits which implement
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
Keywords: Soft Core Processor, Arithmetic and Logical Unit, Back End Implementation and Front End Implementation.
 ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.32 October-2014, Pages:6436-6440 www.ijsetr.com Design and Modeling of Arithmetic and Logical Unit with the Platform of VLSI N. AMRUTHA BINDU 1, M. SAILAJA 2 1 Dept of ECE,
ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.32 October-2014, Pages:6436-6440 www.ijsetr.com Design and Modeling of Arithmetic and Logical Unit with the Platform of VLSI N. AMRUTHA BINDU 1, M. SAILAJA 2 1 Dept of ECE,
Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Chapter 4. Operations on Data
 Chapter 4 Operations on Data 1 OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, the reader should be able to: List the three categories of operations performed on data. Perform unary and binary logic operations
Chapter 4 Operations on Data 1 OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, the reader should be able to: List the three categories of operations performed on data. Perform unary and binary logic operations
Lab Manual for COE 203: Digital Design Lab
 Lab Manual for COE 203: Digital Design Lab 1 Table of Contents 1. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using Discrete Components...3 2. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using EEPROMs...9 3. Introduction to FPGA
Lab Manual for COE 203: Digital Design Lab 1 Table of Contents 1. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using Discrete Components...3 2. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using EEPROMs...9 3. Introduction to FPGA
EE 231 Fall EE 231 Lab 3. Decoders and Multiplexers. Figure 1: 7-Segment Display. Memory: where the program is stored.
 EE 231 Lab 3 Decoders and Multiplexers Decoders and multiplexers are important combinational circuits in many logic designs. Decoders convert n inputs to a maximum of unique 2 n outputs. A special case
EE 231 Lab 3 Decoders and Multiplexers Decoders and multiplexers are important combinational circuits in many logic designs. Decoders convert n inputs to a maximum of unique 2 n outputs. A special case
ECE 331: N0. Professor Andrew Mason Michigan State University. Opening Remarks
 ECE 331: N0 ECE230 Review Professor Andrew Mason Michigan State University Spring 2013 1.1 Announcements Opening Remarks HW1 due next Mon Labs begin in week 4 No class next-next Mon MLK Day ECE230 Review
ECE 331: N0 ECE230 Review Professor Andrew Mason Michigan State University Spring 2013 1.1 Announcements Opening Remarks HW1 due next Mon Labs begin in week 4 No class next-next Mon MLK Day ECE230 Review
CPE 335 Computer Organization. MIPS Arithmetic Part I. Content from Chapter 3 and Appendix B
 CPE 335 Computer Organization MIPS Arithmetic Part I Content from Chapter 3 and Appendix B Dr. Iyad Jafar Adatped from Dr. Gheith Abandah Slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s08/index.html
CPE 335 Computer Organization MIPS Arithmetic Part I Content from Chapter 3 and Appendix B Dr. Iyad Jafar Adatped from Dr. Gheith Abandah Slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s08/index.html
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic
 Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Lab #12: ArithmeticLogic Unit
 Lab #12: ArithmeticLogic Unit Zack Mattis Lab: 3/27/17 Report: 4/8/17 Partner: Brendan Schuster Purpose In this lab, a fully functioning 4-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) was designed and fully implemented
Lab #12: ArithmeticLogic Unit Zack Mattis Lab: 3/27/17 Report: 4/8/17 Partner: Brendan Schuster Purpose In this lab, a fully functioning 4-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) was designed and fully implemented
EE 231 Fall EE 231 Lab 3
 EE 231 Lab 3 Decoders and Multiplexers Decoders and multiplexers are important combinational circuits in many logic designs. Decoders convert n inputs to a maximum of unique 2 n outputs. A special case
EE 231 Lab 3 Decoders and Multiplexers Decoders and multiplexers are important combinational circuits in many logic designs. Decoders convert n inputs to a maximum of unique 2 n outputs. A special case
DIGITAL ARITHMETIC: OPERATIONS AND CIRCUITS
 C H A P T E R 6 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC: OPERATIONS AND CIRCUITS OUTLINE 6- Binary Addition 6-2 Representing Signed Numbers 6-3 Addition in the 2 s- Complement System 6-4 Subtraction in the 2 s- Complement
C H A P T E R 6 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC: OPERATIONS AND CIRCUITS OUTLINE 6- Binary Addition 6-2 Representing Signed Numbers 6-3 Addition in the 2 s- Complement System 6-4 Subtraction in the 2 s- Complement
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN
 11-1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN Purpose Extend the design of the basic four bit adder to include other arithmetic and logic functions. References Wakerly: Section 5.1 Materials Required
11-1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN Purpose Extend the design of the basic four bit adder to include other arithmetic and logic functions. References Wakerly: Section 5.1 Materials Required
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual
 ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Modified Fall 2017 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission)
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Modified Fall 2017 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission)
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 3. Arithmetic for Computers Implementation
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
Date Performed: Marks Obtained: /10. Group Members (ID):. Experiment # 09 MULTIPLEXERS
 Name: Instructor: Engr. Date Performed: Marks Obtained: /10 Group Members (ID):. Checked By: Date: Experiment # 09 MULTIPLEXERS OBJECTIVES: To experimentally verify the proper operation of a multiplexer.
Name: Instructor: Engr. Date Performed: Marks Obtained: /10 Group Members (ID):. Checked By: Date: Experiment # 09 MULTIPLEXERS OBJECTIVES: To experimentally verify the proper operation of a multiplexer.
Digital Fundamentals
 Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter 2 2009 Pearson Education, Upper 2008 Pearson Saddle River, Education NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Decimal Numbers The position of each digit in a weighted
Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter 2 2009 Pearson Education, Upper 2008 Pearson Saddle River, Education NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Decimal Numbers The position of each digit in a weighted
Digital Systems. John SUM Institute of Technology Management National Chung Hsing University Taichung, ROC. December 6, 2012
 Digital Systems John SUM Institute of Technology Management National Chung Hsing University Taichung, ROC December 6, 2012 Contents 1 Logic Gates 3 1.1 Logic Gate............................. 3 1.2 Truth
Digital Systems John SUM Institute of Technology Management National Chung Hsing University Taichung, ROC December 6, 2012 Contents 1 Logic Gates 3 1.1 Logic Gate............................. 3 1.2 Truth
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS Arithmetic (a) The four possible cases Carry (b) Truth table x y
 Arithmetic A basic operation in all digital computers is the addition and subtraction of two numbers They are implemented, along with the basic logic functions such as AND,OR, NOT,EX- OR in the ALU subsystem
Arithmetic A basic operation in all digital computers is the addition and subtraction of two numbers They are implemented, along with the basic logic functions such as AND,OR, NOT,EX- OR in the ALU subsystem
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS II Fall 1999
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS II Fall 1999 Lab 7-10: Micro-processor Design: Minimal Instruction Set Processor (MISP) Objective:
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS II Fall 1999 Lab 7-10: Micro-processor Design: Minimal Instruction Set Processor (MISP) Objective:
Chapter 1. Microprocessor architecture ECE Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud.
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3130 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud The slides are copyright protected. It is not permissible to use them without a permission from Dr Mahmoud http://www.cae.tntech.edu/~mmahmoud/
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3130 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud The slides are copyright protected. It is not permissible to use them without a permission from Dr Mahmoud http://www.cae.tntech.edu/~mmahmoud/
Number representations
 Number representations Number bases Three number bases are of interest: Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal. We look briefly at conversions among them and between each of them and decimal. Binary Base-two, or
Number representations Number bases Three number bases are of interest: Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal. We look briefly at conversions among them and between each of them and decimal. Binary Base-two, or
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1
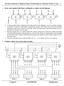 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Chapter 4 Arithmetic
 Computer Eng 1 (ECE290) Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits HOANG Trang Reference: 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture note of Prof.Donna J.Brown Overview Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple
Computer Eng 1 (ECE290) Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits HOANG Trang Reference: 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture note of Prof.Donna J.Brown Overview Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple
Lab Assignment 2. Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL
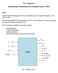 Lab Assignment 2 Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL Task 1 Draw a detailed block diagram of the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. Then develop
Lab Assignment 2 Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL Task 1 Draw a detailed block diagram of the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. Then develop
1010 2?= ?= CS 64 Lecture 2 Data Representation. Decimal Numbers: Base 10. Reading: FLD Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
 CS 64 Lecture 2 Data Representation Reading: FLD 1.2-1.4 Decimal Numbers: Base 10 Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Example: 3271 = (3x10 3 ) + (2x10 2 ) + (7x10 1 ) + (1x10 0 ) 1010 10?= 1010 2?= 1
CS 64 Lecture 2 Data Representation Reading: FLD 1.2-1.4 Decimal Numbers: Base 10 Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Example: 3271 = (3x10 3 ) + (2x10 2 ) + (7x10 1 ) + (1x10 0 ) 1010 10?= 1010 2?= 1
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison. ECE/CS 352 Digital System Fundamentals.
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/C 352 Digital ystem Fundamentals Quiz #2 Thursday, March 7, 22, 7:15--8:3PM 1. (15 points) (a) (5 points) NAND, NOR
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/C 352 Digital ystem Fundamentals Quiz #2 Thursday, March 7, 22, 7:15--8:3PM 1. (15 points) (a) (5 points) NAND, NOR
Arithmetic Logic Unit. Digital Computer Design
 Arithmetic Logic Unit Digital Computer Design Arithmetic Circuits Arithmetic circuits are the central building blocks of computers. Computers and digital logic perform many arithmetic functions: addition,
Arithmetic Logic Unit Digital Computer Design Arithmetic Circuits Arithmetic circuits are the central building blocks of computers. Computers and digital logic perform many arithmetic functions: addition,
Introduction to Computer Science-103. Midterm
 Introduction to Computer Science-103 Midterm 1. Convert the following hexadecimal and octal numbers to decimal without using a calculator, showing your work. (6%) a. (ABC.D) 16 2748.8125 b. (411) 8 265
Introduction to Computer Science-103 Midterm 1. Convert the following hexadecimal and octal numbers to decimal without using a calculator, showing your work. (6%) a. (ABC.D) 16 2748.8125 b. (411) 8 265
Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE
 Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE 1 Features It is a 16-bit μp. 8086 has a 20 bit address bus can access up to 2 20 memory locations (1 MB). It can support up to 64K I/O ports. It provides 14, 16
Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE 1 Features It is a 16-bit μp. 8086 has a 20 bit address bus can access up to 2 20 memory locations (1 MB). It can support up to 64K I/O ports. It provides 14, 16
COMPUTER ARITHMETIC (Part 1)
 Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture COMPUTER ARITHMETIC (Part 1) Introduction The two principal concerns for computer arithmetic
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture COMPUTER ARITHMETIC (Part 1) Introduction The two principal concerns for computer arithmetic
Combinational and sequential circuits (learned in Chapters 1 and 2) can be used to create simple digital systems.
 REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers
 Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers 1 Arithmetic Where we've been: Abstractions: Instruction Set Architecture Assembly Language and Machine Language What's up ahead: Implementing the Architecture operation
Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers 1 Arithmetic Where we've been: Abstractions: Instruction Set Architecture Assembly Language and Machine Language What's up ahead: Implementing the Architecture operation
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual
 ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Version 1.1 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission) 1
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Version 1.1 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission) 1
UNIT - I: COMPUTER ARITHMETIC, REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE & MICROOPERATIONS
 UNIT - I: COMPUTER ARITHMETIC, REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE & MICROOPERATIONS (09 periods) Computer Arithmetic: Data Representation, Fixed Point Representation, Floating Point Representation, Addition and
UNIT - I: COMPUTER ARITHMETIC, REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE & MICROOPERATIONS (09 periods) Computer Arithmetic: Data Representation, Fixed Point Representation, Floating Point Representation, Addition and
Semester Transition Point. EE 109 Unit 11 Binary Arithmetic. Binary Arithmetic ARITHMETIC
 1 2 Semester Transition Point EE 109 Unit 11 Binary Arithmetic At this point we are going to start to transition in our class to look more at the hardware organization and the low-level software that is
1 2 Semester Transition Point EE 109 Unit 11 Binary Arithmetic At this point we are going to start to transition in our class to look more at the hardware organization and the low-level software that is
EC2303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION
 EC2303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION QUESTION BANK UNIT-II 1. What are the disadvantages in using a ripple carry adder? (NOV/DEC 2006) The main disadvantage using ripple carry adder is time delay.
EC2303-COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION QUESTION BANK UNIT-II 1. What are the disadvantages in using a ripple carry adder? (NOV/DEC 2006) The main disadvantage using ripple carry adder is time delay.
Exp#8: Designing a Programmable Sequence Detector
 Exp#8: Designing a Programmable Sequence Detector Objectives Learning how to partition a system into data-path and control unit. Integrating Schematics and Verilog code together Overview In this lab you
Exp#8: Designing a Programmable Sequence Detector Objectives Learning how to partition a system into data-path and control unit. Integrating Schematics and Verilog code together Overview In this lab you
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 9: Binary Addition & Multiplication Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Pop Quiz! Using 4 bits signed integer notation:
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 9: Binary Addition & Multiplication Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Pop Quiz! Using 4 bits signed integer notation:
Floating Point Arithmetic
 Floating Point Arithmetic Floating point numbers are frequently used in many applications. Implementation of arithmetic units such as adder, multiplier, etc for Floating point numbers are more complex
Floating Point Arithmetic Floating point numbers are frequently used in many applications. Implementation of arithmetic units such as adder, multiplier, etc for Floating point numbers are more complex
BINARY SYSTEM. Binary system is used in digital systems because it is:
 CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER CONTENTS 2.1 Binary System 2.2 Binary Arithmetic Operation 2.3 Signed & Unsigned Numbers 2.4 Arithmetic Operations of Signed Numbers 2.5 Hexadecimal Number System 2.6 Octal Number System
CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER CONTENTS 2.1 Binary System 2.2 Binary Arithmetic Operation 2.3 Signed & Unsigned Numbers 2.4 Arithmetic Operations of Signed Numbers 2.5 Hexadecimal Number System 2.6 Octal Number System
CS Computer Architecture. 1. Explain Carry Look Ahead adders in detail
 1. Explain Carry Look Ahead adders in detail A carry-look ahead adder (CLA) is a type of adder used in digital logic. A carry-look ahead adder improves speed by reducing the amount of time required to
1. Explain Carry Look Ahead adders in detail A carry-look ahead adder (CLA) is a type of adder used in digital logic. A carry-look ahead adder improves speed by reducing the amount of time required to
CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment. Description
 CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment To design a 16-bit ALU which will be used in the datapath of the microprocessor. This ALU must support two s complement arithmetic and the instructions in the baseline
CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment To design a 16-bit ALU which will be used in the datapath of the microprocessor. This ALU must support two s complement arithmetic and the instructions in the baseline
8/26/2010. Introduction to 8085 BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL Introduction to Introduction to Three Units of 8085
 BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL 8085 GURSHARAN SINGH TATLA Introduction to 8085 It was introduced in 1977. It is 8-bit microprocessor. Its actual name is 8085 A. It is single NMOS device. It contains 6200 transistors
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL 8085 GURSHARAN SINGH TATLA Introduction to 8085 It was introduced in 1977. It is 8-bit microprocessor. Its actual name is 8085 A. It is single NMOS device. It contains 6200 transistors
Experiment 18 Full Adder and Parallel Binary Adder
 Objectives Experiment 18 Full Adder and Parallel Binary Adder Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, you should be able to: Create and simulate a full adder in VHDL, assign pins to the design, and
Objectives Experiment 18 Full Adder and Parallel Binary Adder Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, you should be able to: Create and simulate a full adder in VHDL, assign pins to the design, and
Lecture 21: Combinational Circuits. Integrated Circuits. Integrated Circuits, cont. Integrated Circuits Combinational Circuits
 Lecture 21: Combinational Circuits Integrated Circuits Combinational Circuits Multiplexer Demultiplexer Decoder Adders ALU Integrated Circuits Circuits use modules that contain multiple gates packaged
Lecture 21: Combinational Circuits Integrated Circuits Combinational Circuits Multiplexer Demultiplexer Decoder Adders ALU Integrated Circuits Circuits use modules that contain multiple gates packaged
Chapter 4. The Processor. Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler. We will examine two MIPS implementations
 Chapter 4 The Processor Part I Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations
Chapter 4 The Processor Part I Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations
