2.3 Recursion 7/21/2014 5:12:34 PM
|
|
|
- Jasper Nathan Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3 Recursion Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright /21/2014 5:12:34 PM
2 Factorial The factorial of a positive integer N is computed as the product of N with all positive integers less than or equal to N. 4! = = 24 30! = =
3 Factorial - Iterative Implementation int b = factorial(5); static int factorial(int n) { int f = 1; for (int i=n; i>=1; i--) { f = f * i; Trace it.
4 5! = ! = ! = 5 4! N! = N (N-1)! Factorial can be defined in terms of itself
5 Recursion
6 Recursion
7 Overview What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking Powerful programming paradigm Many computations are naturally self-referential: Mergesort, FFT, gcd, depth-first search Linked data structures A folder contains files and other folders Closely related to mathematical induction Reproductive Parts M. C. Escher,
8 Factorial Recursive Implementation Trace it. int b = factorial(5); 9. static int factorial(int n) { else {
9 Last In First Out (LIFO) Stack of Plates
10 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function Call Stack
11 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function void main(string[] args){ int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); Call Stack
12 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function void main(string[] args){ int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); Call Stack main() a=10, Line=3
13 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=5) { else { Call Stack n=5, Line=1 main() a=10, Line=3
14 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=5) { else { Call Stack n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
15 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=4) { else { Call Stack n=4, Line=1 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
16 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=4) { else { Call Stack n=4, Line=5 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
17 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=3) { else { Call Stack n=3, Line=1 n=4, Line=5 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
18 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=3) { else { Call Stack n=3, Line=5 n=4, Line=5 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
19 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=2) { else { Call Stack n=2, Line=1 n=3, Line=5 n=4, Line=5 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
20 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=2) { else { Call Stack n=2, Line=5 n=3, Line=5 n=4, Line=5 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
21 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=1) { else { Call Stack n=1, Line=1 n=2, Line=5 n=3, Line=5 n=4, Line=5 a=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
22 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=1) { else { Call Stack n=1, Line=3 n=2, Line=5 n=3, Line=5 n=4, Line=5 a=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
23 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=2) { else { 1; Call Stack n=2, f=2, Line=6 n=3, Line=5 n=4, Line=5 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
24 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=3) { else { 2; Call Stack n=3, f=6, Line=6 n=4, Line=5 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
25 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=4) { else { 6; Call Stack n=4, f=24, Line=6 n=5, Line=5 main() a=10, Line=3
26 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function int factorial(int n=5) { else { 24; Call Stack n=5, f=120, Line=6 main() a=10, Line=3
27 Compiled Code public static void main (String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = factorial(5); System.out.println(b); static int factorial(int n) { else { Executing Function void main(string[] args){ int a = 10; int b = 120; System.out.println(b); Call Stack main() a=10, b=120, Line=4
28 The Call Stack keeps track of all functions that are suspended, in order the point in the function where execution should resume after the invoked subordinate function returns a snapshot of all variables and values within the scope of the suspended function so these can be restored upon continuing execution. When the subordinate function returns, we need this information in order to continue with computation. The concept of a call stack is not limited to recursion. The same thing happens even when function A calls function B.
29 Towers of Hanoi
30 Towers of Hanoi Move all the discs from the leftmost peg to the rightmost one. Only one disc may be moved at a time. A disc can be placed either on empty peg or on top of a larger disc. start finish Edouard Lucas (1883) 31
31 Towers of Hanoi Legend Q. Is world going to end (according to legend)? 64 golden discs on 3 diamond pegs. World ends when certain group of monks accomplish task. Q. Will computer algorithms help? 32
32 Towers of Hanoi: Recursive Solution Move n-1 smallest discs right. Move largest disc left. cyclic wrap-around Move n-1 smallest discs right. 33
33 Towers of Hanoi: Recursive Solution public class TowersOfHanoi { public static void moves(int n, boolean left) { if (n == 0) return; moves(n-1,!left); if (left) System.out.println(n + " left"); else System.out.println(n + " right"); moves(n-1,!left); public static void main(string[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); moves(n, true); moves(n, true) : move discs 1 to n one pole to the left moves(n, false): move discs 1 to n one pole to the right smallest disc 34
34 Towers of Hanoi: Recursive Solution % java TowersOfHanoi 3 left right left left left right left every other move is smallest disc So how long will it take the monks to finish their task?? % java TowersOfHanoi 4 right left right right right left right left right left right right right left right subdivisions of ruler 35
35 Towers of Hanoi: Recursion Tree n, left 3, true , false , true left 2, false , true right , true 1, true left 21 3 left left right left 36
36 Recursive Graphics
37 L-systems
38 L-systems
39 L-systems void drawtree(int x, int y, double angle, int depth) { // base case (x + cos(angle) * length, y + sin(angle) * length) // compute end coordinate (x2, y2) // (with length = depth * scalefactor) // draw tree recursively angle (x,y) leftδangle angle (x,y) rightδangle
40 L-systems void drawtree(int x, int y, double angle, int depth) { // base case (x + cos(angle) * length, y + sin(angle) * length) // compute end coordinate (x2, y2) // (with length = depth * scalefactor) // draw tree recursively line (x, y, x2, y2) drawtree(x2, y2, angle leftδangle, depth 1); drawtree(x2, y2, angle + rightδangle, depth 1); angle (x,y) leftδangle angle (x,y) rightδangle
41 L-systems static double scale = 0; static double leftdeltaangle = 15; static double rightdeltaangle = 15; static int recursivedepth = 10; static void drawtree(int x, int y, double angle, int depth) { // base case if (depth == 0) return; (x + cos(angle) * length, y + sin(angle) * length) angle (x,y) // compute end coordinate double angleradians = Math.toRadians(angle); int x2 = x + (int) (Math.cos(angleRadians) * depth * scale); int y2 = y + (int) (Math.sin(angleRadians) * depth * scale); leftδangle // draw tree recursively StdDraw.line(x, y, x2, y2); drawtree(x2, y2, angle - leftdeltaangle, depth - 1); drawtree(x2, y2, angle + rightdeltaangle, depth - 1); angle (x,y) rightδangle
42 L-systems static double scale = 0; static double leftdeltaangle = 15; static double rightdeltaangle = 15; static int recursivedepth = 10; static void drawtree(int x, int y, double angle, int depth) { // base case if (depth == 0) return; public static void setup() { StdDraw.setXscale(0,100); StdDraw.setYscale(0,100); // compute end coordinate double angleradians = Math.toRadians(angle); int x2 = x + (int) (Math.cos(angleRadians) * depth * scale); int y2 = y + (int) (Math.sin(angleRadians) * depth * scale); // draw one frame of animation public static void draw() { drawtree(50, 0, 90, recursivedepth); // draw tree recursively StdDraw.line(x, y, x2, y2); drawtree(x2, y2, angle - leftdeltaangle, depth - 1); drawtree(x2, y2, angle + rightdeltaangle, depth - 1);
43 Htree H-tree of order n. and half the size Draw an H. Recursively draw 4 H-trees of order n-1, one connected to each tip. tip size order 1 order 2 order 3 54
44 55
45 Taplin Auditorium Ventilation System 56
46 Animated H-tree Animated H-tree. Pause for 1 second after drawing each H. 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 57
47 Htree in Java public class Htree { public static void draw(int n, double sz, double x, double y) { if (n == 0) return; double x0 = x - sz/2, x1 = x + sz/2; double y0 = y - sz/2, y1 = y + sz/2; StdDraw.line(x0, y, x1, y); StdDraw.line(x0, y0, x0, y1); StdDraw.line(x1, y0, x1, y1); draw the H, centered on (x, y) draw(n-1, draw(n-1, draw(n-1, draw(n-1, recursively draw 4 half-size Hs sz/2, sz/2, sz/2, sz/2, x0, x0, x1, x1, y0); y1); y0); y1); public static void main(string[] args) { int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); draw(n,.5,.5,.5); 58
48 Fractional Brownian Motion
49 Fractional Brownian Motion Physical process which models many natural and artificial phenomenon. Price of stocks. Dispersion of ink flowing in water. Rugged shapes of mountains and clouds. Fractal landscapes and textures for computer graphics. 70
50 Simulating Brownian Motion Midpoint displacement method. Maintain an interval with endpoints (x0, y0) and (x1, y1). Divide the interval in half. Choose at random from Gaussian distribution. Set xm = (x0 + x1)/2 and ym = (y0 + y1)/2 +. Recur on the left and right intervals. 71
51 Simulating Brownian Motion: Java Implementation Midpoint displacement method. Maintain an interval with endpoints (x0, y0) and (x1, y1). Divide the interval in half. Choose at random from Gaussian distribution. Set xm = (x0 + x1)/2 and ym = (y0 + y1)/2 +. Recur on the left and right intervals. public static void curve(double x0, double y0, double x1, double y1, double var) { if (x1 - x0 < 0.01) { StdDraw.line(x0, y0, x1, y1); return; double xm = (x0 + x1) / 2; double ym = (y0 + y1) / 2; ym += StdRandom.gaussian(0, Math.sqrt(var)); curve(x0, y0, xm, ym, var/2); variance halves at each level; curve(xm, ym, x1, y1, var/2); change factor to get different shapes 72
52 Plasma Cloud Plasma cloud centered at (x, y) of size s. Each corner labeled with some grayscale value. Divide square into four quadrants. The grayscale of each new corner is the average of others. center: average of the four corners + random displacement others: average of two original corners Recur on the four quadrants. c c 1 c1 2 c2 2 c1 c3 2 c2 c4 2 (c1 c 2 c 3 c 4 ) 4 c3 c3 c4 2 c4 73
53 Plasma Cloud 74
54 Brownian Island 75
55 Brownian Landscape Reference: 76
2.3 Recursion 7/23/2015 3:06:35 PM
 3 Recursion Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 7/23/2015 3:06:35 PM Factorial The factorial of a positive integer N
3 Recursion Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 7/23/2015 3:06:35 PM Factorial The factorial of a positive integer N
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #13: Recursion Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements: some
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #13: Recursion Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements: some
26 Feb Recursion. Overview. Greatest Common Divisor. Greatest Common Divisor. Greatest Common Divisor. Greatest Common Divisor
 Overview.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview. What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly.
 1 2.3 Recursion Overview What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
1 2.3 Recursion Overview What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson Closely related to mathematical induction.
 2/6/12 Overview CS 112 Introduction to Programming What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. (Spring 2012) Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming
2/6/12 Overview CS 112 Introduction to Programming What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. (Spring 2012) Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming
Recursion LOGO STYLE GUIDE Schools within the University 19
 2.3 Recursion LOGO STYLE GUIDE Schools within the University Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 10/3/16 11:41 AM Recursion
2.3 Recursion LOGO STYLE GUIDE Schools within the University Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 10/3/16 11:41 AM Recursion
2.3 Recursion. Overview. Greatest Common Divisor. Greatest Common Divisor. What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly.
 Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
2.3 Recursion. Overview. Greatest Common Divisor. Greatest Common Divisor. What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly.
 Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
! New mode of thinking. ! Powerful programming paradigm. ! Mergesort, FFT, gcd. ! Linked data structures.
 Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
Overview 2.3 Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations are naturally
2.3 Recursion. Overview. Mathematical Induction. What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly.
 2.3 Recursion Overview Mathematical Induction What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations
2.3 Recursion Overview Mathematical Induction What is recursion? When one function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? New mode of thinking. Powerful programming paradigm. Many computations
More recursion, Divide and conquer
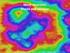 More recursion, Divide and conquer CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 More recursion Overview Recursion + randomness = pretty pictures Example 1: Brownian motion
More recursion, Divide and conquer CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 More recursion Overview Recursion + randomness = pretty pictures Example 1: Brownian motion
CMSC 150 LECTURE 7 RECURSION
 CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: AN INTERDISCIPLINARY APPROACH, SEDGEWICK AND WAYNE (PEARSON ADDISON-WESLEY
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: AN INTERDISCIPLINARY APPROACH, SEDGEWICK AND WAYNE (PEARSON ADDISON-WESLEY
COMPUTER SCIENCE. Computer Science. 6. Recursion. Computer Science. An Interdisciplinary Approach. Section 2.3.
 COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E PA R T I : P R O G R A M M I N G I N J AVA Computer Science Computer Science An Interdisciplinary Approach Section 2.3 ROBERT SEDGEWICK K E V I N WAY N E
COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E PA R T I : P R O G R A M M I N G I N J AVA Computer Science Computer Science An Interdisciplinary Approach Section 2.3 ROBERT SEDGEWICK K E V I N WAY N E
Lecture P6: Recursion
 Overview Lecture P6: Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls ITSELF directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? Powerful programming tool to solve a problem by breaking it up into one (or
Overview Lecture P6: Recursion What is recursion? When one function calls ITSELF directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion? Powerful programming tool to solve a problem by breaking it up into one (or
8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE. Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE. Revisit search and sorting using recursion. Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO?
 8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Revisit search and sorting using recursion Binary search Merge sort Lecture 8 Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO? A function is recursive
8/5/10 TODAY'S OUTLINE Recursion COMP 10 EXPLORING COMPUTER SCIENCE Revisit search and sorting using recursion Binary search Merge sort Lecture 8 Recursion WHAT DOES THIS CODE DO? A function is recursive
UNIT 5A Recursion: Basics. Recursion
 UNIT 5A Recursion: Basics 1 Recursion A recursive operation is an operation that is defined in terms of itself. Sierpinski's Gasket http://fusionanomaly.net/recursion.jpg 2 1 Recursive Definitions Every
UNIT 5A Recursion: Basics 1 Recursion A recursive operation is an operation that is defined in terms of itself. Sierpinski's Gasket http://fusionanomaly.net/recursion.jpg 2 1 Recursive Definitions Every
Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011
 Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Recursion A method calling itself Overview A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming
Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Recursion A method calling itself Overview A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming
Recursion. Overview. Mathematical induction. Hello recursion. Recursion. Example applications. Goal: Compute factorial N! = 1 * 2 * 3...
 Recursion Recursion Overview A method calling itself A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming paradigm Related to mathematical induction Example applications Factorial
Recursion Recursion Overview A method calling itself A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming paradigm Related to mathematical induction Example applications Factorial
3/30/16. Program Structure. Drawing/Anima+on. Read input and create data objects. Basic Plots 50-99
 Drawing/Anima+on Coordinate modifica.on No variables in the shape coordinates variables added to x and y trigs involving angle variable added to x and y scale factor mul.plied to x and y Transforma.ons
Drawing/Anima+on Coordinate modifica.on No variables in the shape coordinates variables added to x and y trigs involving angle variable added to x and y scale factor mul.plied to x and y Transforma.ons
Recursive Definitions
 Recursion Objectives Explain the underlying concepts of recursion Examine recursive methods and unravel their processing steps Explain when recursion should and should not be used Demonstrate the use of
Recursion Objectives Explain the underlying concepts of recursion Examine recursive methods and unravel their processing steps Explain when recursion should and should not be used Demonstrate the use of
Recursion Chapter 17. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Recursion Chapter 17 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Introduction to Recursion: The concept of recursion Recursive methods Infinite recursion When to use (and
Recursion Chapter 17 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Introduction to Recursion: The concept of recursion Recursive methods Infinite recursion When to use (and
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Recursion. Chapter 5
 Recursion Chapter 5 Chapter Objectives To understand how to think recursively To learn how to trace a recursive method To learn how to write recursive algorithms and methods for searching arrays To learn
Recursion Chapter 5 Chapter Objectives To understand how to think recursively To learn how to trace a recursive method To learn how to write recursive algorithms and methods for searching arrays To learn
CSE 214 Computer Science II Recursion
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Recursion Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction Basic design technique
CSE 214 Computer Science II Recursion Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction Basic design technique
Chapter 15: Recursion
 Chapter 15: Recursion Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 15 discusses the following main topics: Introduction to Recursion
Chapter 15: Recursion Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 15 discusses the following main topics: Introduction to Recursion
Unit 5: Recursive Thinking
 AP Computer Science Mr. Haytock Unit 5: Recursive Thinking Topics: I. Recursion II. Computational limits III. Recursion in graphics Materials: I. Hein ch. 3.2 II. Rawlins: Towers of Hanoi III. Lewis &
AP Computer Science Mr. Haytock Unit 5: Recursive Thinking Topics: I. Recursion II. Computational limits III. Recursion in graphics Materials: I. Hein ch. 3.2 II. Rawlins: Towers of Hanoi III. Lewis &
Recursion. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Recursion Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Recursion A method calling itself All good recursion must come to an end A powerful tool in computer science Allows writing elegant and easy to understand
Recursion Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Recursion A method calling itself All good recursion must come to an end A powerful tool in computer science Allows writing elegant and easy to understand
Recursion. Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science
 Recursion Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Recursion Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Principle: Reduce a complex problem into a simpler instance of the same problem Recursion
Recursion Jordi Cortadella Department of Computer Science Recursion Introduction to Programming Dept. CS, UPC 2 Principle: Reduce a complex problem into a simpler instance of the same problem Recursion
UNIT 5A Recursion: Basics. Recursion
 UNIT 5A Recursion: Basics 1 Recursion A recursive function is one that calls itself. Infinite loop? Not necessarily. 2 1 Recursive Definitions Every recursive definition includes two parts: Base case (non
UNIT 5A Recursion: Basics 1 Recursion A recursive function is one that calls itself. Infinite loop? Not necessarily. 2 1 Recursive Definitions Every recursive definition includes two parts: Base case (non
COMP-202. Recursion. COMP Recursion, 2013 Jörg Kienzle and others
 COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II. Recursive Algorithms. Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Recursive Algorithms Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Recursion Recursion is a strategy for solving problems A procedure that
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Recursive Algorithms Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Recursion Recursion is a strategy for solving problems A procedure that
2.4 Modular Programming
 Percolation 2.4 Modular Programming Percolation. Pour liquid on top of some porous material. Will liquid reach the bottom? Applications. [Chemistry, materials science]! Chromatography.! Natural gas through
Percolation 2.4 Modular Programming Percolation. Pour liquid on top of some porous material. Will liquid reach the bottom? Applications. [Chemistry, materials science]! Chromatography.! Natural gas through
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015
 CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #9 John Ridgway February 26, 2015 1 Recursive Definitions, Algorithms, and Programs Recursion in General In mathematics and computer science
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #9 John Ridgway February 26, 2015 1 Recursive Definitions, Algorithms, and Programs Recursion in General In mathematics and computer science
Recursion. CSCI 112: Programming in C
 Recursion CSCI 112: Programming in C 1 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem as a bunch of smaller versions of the same problem. 2 2 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem
Recursion CSCI 112: Programming in C 1 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem as a bunch of smaller versions of the same problem. 2 2 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem
CS200: Recursion and induction (recap from cs161)
 CS200: Recursion and induction (recap from cs161) Prichard Ch. 6.1 & 6.3 1 2 Backtracking n Problem solving technique that involves moves: guesses at a solution. n Depth First Search: in case of failure
CS200: Recursion and induction (recap from cs161) Prichard Ch. 6.1 & 6.3 1 2 Backtracking n Problem solving technique that involves moves: guesses at a solution. n Depth First Search: in case of failure
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture #15: Thinking Recursively David Mix Barrington 10 October 2012
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #15: Thinking Recursively David Mix Barrington 10 October 2012 Thinking Recursively Recursive Definitions, Algorithms, and Programs Computing Factorials
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #15: Thinking Recursively David Mix Barrington 10 October 2012 Thinking Recursively Recursive Definitions, Algorithms, and Programs Computing Factorials
Combinatorial Search. permutations backtracking counting subsets paths in a graph. Overview
 Overview Exhaustive search. Iterate through all elements of a search space. Combinatorial Search Backtracking. Systematic method for examining feasible solutions to a problem, by systematically eliminating
Overview Exhaustive search. Iterate through all elements of a search space. Combinatorial Search Backtracking. Systematic method for examining feasible solutions to a problem, by systematically eliminating
Chapter 10: Recursive Problem Solving
 2400 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR INTERNATIONAL ENGINEERS Chapter 0: Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition Be able to use recursion in
2400 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR INTERNATIONAL ENGINEERS Chapter 0: Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition Be able to use recursion in
Recursion. EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
1.7 Recursion. Department of CSE
 1.7 Recursion 1 Department of CSE Objectives To learn the concept and usage of Recursion in C Examples of Recursion in C 2 Department of CSE What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem
1.7 Recursion 1 Department of CSE Objectives To learn the concept and usage of Recursion in C Examples of Recursion in C 2 Department of CSE What is recursion? Sometimes, the best way to solve a problem
Reduction & Recursion Overview
 Reduction & Recursion Overview Reduction definition Reduction techniques Recursion definition Recursive thinking (Many) recursion examples Indirect recursion Runtime stack Factorial isnumericstring add
Reduction & Recursion Overview Reduction definition Reduction techniques Recursion definition Recursive thinking (Many) recursion examples Indirect recursion Runtime stack Factorial isnumericstring add
COMP-202. Recursion. COMP Recursion, 2011 Jörg Kienzle and others
 COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
COMP-202 Recursion Recursion Recursive Definitions Run-time Stacks Recursive Programming Recursion vs. Iteration Indirect Recursion Lecture Outline 2 Recursive Definitions (1) A recursive definition is
ENGG1811 Computing for Engineers Week 10 Recursion, External Application Interfacing
 ENGG1811 Computing for Engineers Week 10 Recursion, External Application Interfacing ENGG1811 UNSW, CRICOS Provider No: 00098G W10 slide 1 This Week Wednesday am: Will include discussion about assignment
ENGG1811 Computing for Engineers Week 10 Recursion, External Application Interfacing ENGG1811 UNSW, CRICOS Provider No: 00098G W10 slide 1 This Week Wednesday am: Will include discussion about assignment
COMP 202 Recursion. CONTENTS: Recursion. COMP Recursion 1
 COMP 202 Recursion CONTENTS: Recursion COMP 202 - Recursion 1 Recursive Thinking A recursive definition is one which uses the word or concept being defined in the definition itself COMP 202 - Recursion
COMP 202 Recursion CONTENTS: Recursion COMP 202 - Recursion 1 Recursive Thinking A recursive definition is one which uses the word or concept being defined in the definition itself COMP 202 - Recursion
11/2/2017 RECURSION. Chapter 5. Recursive Thinking. Section 5.1
 RECURSION Chapter 5 Recursive Thinking Section 5.1 1 Recursive Thinking Recursion is a problem-solving approach that can be used to generate simple solutions to certain kinds of problems that are difficult
RECURSION Chapter 5 Recursive Thinking Section 5.1 1 Recursive Thinking Recursion is a problem-solving approach that can be used to generate simple solutions to certain kinds of problems that are difficult
Recursion. Thinking Recursively. Tracing the Recursive Definition of List. CMPT 126: Lecture 10. Recursion
 Recursion CMPT 126: Lecture 10 Recursion Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 25, 2007 Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of
Recursion CMPT 126: Lecture 10 Recursion Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 25, 2007 Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of
Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5. Mr. Dave Clausen La Cañada High School
 Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5 La Cañada High School Recursion: Definitions Recursion The process of a subprogram (method) calling itself. A clearly defined stopping state must exist. The
Chapter 12 Supplement: Recursion with Java 1.5 La Cañada High School Recursion: Definitions Recursion The process of a subprogram (method) calling itself. A clearly defined stopping state must exist. The
mith College Computer Science Week 13 CSC111 Spring 2018 Dominique Thiébaut
 mith College Computer Science Week 13 CSC111 Spring 2018 Dominique Thiébaut dthiebaut@smith.edu Recursion Continued Visiting a Maze Start Exit How do we represent a maze in Python? mazetext = """ #########################...#
mith College Computer Science Week 13 CSC111 Spring 2018 Dominique Thiébaut dthiebaut@smith.edu Recursion Continued Visiting a Maze Start Exit How do we represent a maze in Python? mazetext = """ #########################...#
Recursive Thinking. Chapter 8: Recursion. Recursive Definitions. Recursion. Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science A 2nd Edition
 Chapter 8: Recursion Presentation slides for Recursive Thinking Recursion is a programming technique in which a method can call itself to solve a problem Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science
Chapter 8: Recursion Presentation slides for Recursive Thinking Recursion is a programming technique in which a method can call itself to solve a problem Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science
Introduction to Computers & Programming
 16.070 Introduction to Computers & Programming Ada: Recursion Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Recursion Recursion means writing procedures and functions which call themselves. Recursion
16.070 Introduction to Computers & Programming Ada: Recursion Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Recursion Recursion means writing procedures and functions which call themselves. Recursion
This Week. Trapezoidal Rule, theory. Warmup Example: Numeric Integration. Trapezoidal Rule, pseudocode. Trapezoidal Rule, implementation
 This Week ENGG8 Computing for Engineers Week 9 Recursion, External Application Interfacing Monday: numeric integration example, then first part of the material Wednesday 9am: rest of the new material Wednesday
This Week ENGG8 Computing for Engineers Week 9 Recursion, External Application Interfacing Monday: numeric integration example, then first part of the material Wednesday 9am: rest of the new material Wednesday
Recursion: Factorial (1) Recursion. Recursion: Principle. Recursion: Factorial (2) Recall the formal definition of calculating the n factorial:
 Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Factorial (1) Recall the formal definition of calculating the n factorial: 1 if n = 0 n! = n (n 1) (n 2) 3 2
Recursion EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Factorial (1) Recall the formal definition of calculating the n factorial: 1 if n = 0 n! = n (n 1) (n 2) 3 2
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
Summary. csci 210: Data Structures Recursion. Recursive algorithms. Recursion. Topics READING:
 Summary csci 210: Data Structures Recursion Topics recursion overview simple eamples Sierpinski gasket counting blobs in a grid Hanoi towers READING: LC tetbook chapter 7 Recursion Recursive algorithms
Summary csci 210: Data Structures Recursion Topics recursion overview simple eamples Sierpinski gasket counting blobs in a grid Hanoi towers READING: LC tetbook chapter 7 Recursion Recursive algorithms
csci 210: Data Structures Recursion
 csci 210: Data Structures Recursion Summary Topics recursion overview simple eamples Sierpinski gasket counting blobs in a grid Hanoi towers READING: LC tetbook chapter 7 Recursion A method of defining
csci 210: Data Structures Recursion Summary Topics recursion overview simple eamples Sierpinski gasket counting blobs in a grid Hanoi towers READING: LC tetbook chapter 7 Recursion A method of defining
11. Recursion. n (n 1)!, otherwise. Mathematical Recursion. Recursion in Java: Infinite Recursion. 1, if n 1. n! =
 Mathematical Recursion 11. Recursion Mathematical Recursion, Termination, Call Stack, Examples, Recursion vs. Iteration, Lindenmayer Systems Many mathematical functions can be naturally defined recursively.
Mathematical Recursion 11. Recursion Mathematical Recursion, Termination, Call Stack, Examples, Recursion vs. Iteration, Lindenmayer Systems Many mathematical functions can be naturally defined recursively.
12. Recursion. n (n 1)!, otherwise. Educational Objectives. Mathematical Recursion. Recursion in Java: 1, if n 1. n! =
 Educational Objectives You understand how a solution to a recursive problem can be implemented in Java. You understand how methods are being executed in an execution stack. 12. Recursion Mathematical Recursion,
Educational Objectives You understand how a solution to a recursive problem can be implemented in Java. You understand how methods are being executed in an execution stack. 12. Recursion Mathematical Recursion,
Taking Stock. IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 5. The Towers of Hanoi. Divide and Conquer
 Taking Stock IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 5 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University January 24, 2007 Last Time In-Place, Out-of-Place Count
Taking Stock IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 5 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University January 24, 2007 Last Time In-Place, Out-of-Place Count
Functions. x y z. f (x, y, z) Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing)
 2.1 Functions Functions Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing) Return one output value Input Arguments x y z f Return Value f (x, y, z)
2.1 Functions Functions Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing) Return one output value Input Arguments x y z f Return Value f (x, y, z)
Lecture 24 Tao Wang 1
 Lecture 24 Tao Wang 1 Objectives Introduction of recursion How recursion works How recursion ends Infinite recursion Recursion vs. Iteration Recursion that Returns a Value Edition 2 Introduction If we
Lecture 24 Tao Wang 1 Objectives Introduction of recursion How recursion works How recursion ends Infinite recursion Recursion vs. Iteration Recursion that Returns a Value Edition 2 Introduction If we
C22a: Problem Solving using Recursion
 CISC 3115 TY3 C22a: Problem Solving using Recursion Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/6/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Characteristics of recursion Recursion
CISC 3115 TY3 C22a: Problem Solving using Recursion Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/6/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Characteristics of recursion Recursion
CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Recursion
 CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Recursion Professor Henry Carter Spring 2018 Recap Stacks provide a LIFO ordered data structure Implementation tradeoffs between arrays and linked lists typically
CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Recursion Professor Henry Carter Spring 2018 Recap Stacks provide a LIFO ordered data structure Implementation tradeoffs between arrays and linked lists typically
A Foundation for Programming
 2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
Recursion. Tracing Method Calls via a Stack. Beyond this lecture...
 Recursion EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
Recursion EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Recursion: Principle Recursion is useful in expressing solutions to problems that can be recursively defined: Base Cases:
Solutions to Problem 1 of Homework 3 (10 (+6) Points)
 Solutions to Problem 1 of Homework 3 (10 (+6) Points) Sometimes, computing extra information can lead to more efficient divide-and-conquer algorithms. As an example, we will improve on the solution to
Solutions to Problem 1 of Homework 3 (10 (+6) Points) Sometimes, computing extra information can lead to more efficient divide-and-conquer algorithms. As an example, we will improve on the solution to
Functions. CS10001: Programming & Data Structures. Sudeshna Sarkar Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc. & Engg., Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
 Functions CS10001: Programming & Data Structures Sudeshna Sarkar Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc. & Engg., Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur 1 Recursion A process by which a function calls itself
Functions CS10001: Programming & Data Structures Sudeshna Sarkar Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc. & Engg., Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur 1 Recursion A process by which a function calls itself
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 15/1/2013 22:16:24 A Foundation for Programming any program
1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 15/1/2013 22:16:24 A Foundation for Programming any program
Recursion Chapter 4 Self-Reference. Recursive Definitions Inductive Proofs Implementing Recursion
 Recursion Chapter 4 Self-Reference Recursive Definitions Inductive Proofs Implementing Recursion Imperative Algorithms Based on a basic abstract machine model - linear execution model - storage - control
Recursion Chapter 4 Self-Reference Recursive Definitions Inductive Proofs Implementing Recursion Imperative Algorithms Based on a basic abstract machine model - linear execution model - storage - control
Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures Recursion and Stacks. By: Jonas Öberg
 Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures Recursion and Stacks M1 By: Jonas Öberg What is recursion? Quick answer: A recursive function is a function which uses itself Example We define by the use of f( n
Logic, Algorithms and Data Structures Recursion and Stacks M1 By: Jonas Öberg What is recursion? Quick answer: A recursive function is a function which uses itself Example We define by the use of f( n
Recursion. Chapter 7. Copyright 2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
 Recursion Chapter 7 Contents What Is Recursion? Tracing a Recursive Method Recursive Methods That Return a Value Recursively Processing an Array Recursively Processing a Linked Chain The Time Efficiency
Recursion Chapter 7 Contents What Is Recursion? Tracing a Recursive Method Recursive Methods That Return a Value Recursively Processing an Array Recursively Processing a Linked Chain The Time Efficiency
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1. Recursion 2018W A. Ferscha (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz)
 SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1 Recursion 2018W (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz) PRINCIPLE OF SELF-REFERENCE Recursion: Describing something in a self-similar way. An elegant, powerful and simple way
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT 1 Recursion 2018W (Institute of Pervasive Computing, JKU Linz) PRINCIPLE OF SELF-REFERENCE Recursion: Describing something in a self-similar way. An elegant, powerful and simple way
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
Programming with Recursion. What Is Recursion?
 Chapter 7 Programming with Recursion Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 1 What Is Recursion? How is recursion like a set of Russian dolls? Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 2 What Is Recursion? Recursive call A method
Chapter 7 Programming with Recursion Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 1 What Is Recursion? How is recursion like a set of Russian dolls? Fall 2017 Yanjun Li CS2200 2 What Is Recursion? Recursive call A method
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 9 (Part II) Recursion MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 9 (Part II) Recursion MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
APCS-AB: Java. Recursion in Java December 12, week14 1
 APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
Recursion. Let s start by looking at some problems that are nicely solved using recursion. First, let s look at generating The Fibonacci series.
 Recursion The programs we have discussed so far have been primarily iterative and procedural. Code calls other methods in a hierarchical manner. For some problems, it is very useful to have the methods
Recursion The programs we have discussed so far have been primarily iterative and procedural. Code calls other methods in a hierarchical manner. For some problems, it is very useful to have the methods
Recursive Methods and Problem Solving. Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms
 Recursive Methods and Problem Solving Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Review: Calling Methods int x(int n) { int m = 0; n = n + m + 1; return n; int y(int
Recursive Methods and Problem Solving Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Review: Calling Methods int x(int n) { int m = 0; n = n + m + 1; return n; int y(int
Recursion (Rosen, 6 th edition, Section 4.3, 4.4)
 Recursion (Rosen, 6 th edition, Section 4.3, 4.4) Carol Zander For recursion, the focus is mostly on recursive algorithms. While recursive definitions will sometimes be used in definitions (you already
Recursion (Rosen, 6 th edition, Section 4.3, 4.4) Carol Zander For recursion, the focus is mostly on recursive algorithms. While recursive definitions will sometimes be used in definitions (you already
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 .3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 04, 2008 0:00 AM A Foundation for Programming A Foundation
.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 04, 2008 0:00 AM A Foundation for Programming A Foundation
OVERVIEW. Recursion is an algorithmic technique where a function calls itself directly or indirectly. Why learn recursion?
 CH. 5 RECURSION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OVERVIEW Recursion is an algorithmic
CH. 5 RECURSION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OVERVIEW Recursion is an algorithmic
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #5: Conditionals and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #5: Conditionals and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
Lecture Notes 4 More C++ and recursion CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson
 Lecture Notes 4 More C++ and recursion CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading for this lecture: Carrano, Chapter 2 Copy constructor, destructor, operator=
Lecture Notes 4 More C++ and recursion CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading for this lecture: Carrano, Chapter 2 Copy constructor, destructor, operator=
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2019 Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2019 Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to
CS/CE 2336 Computer Science II
 S/E 2336 omputer Science II UT D Session 10 Recursion dapted from D Liang s Introduction to Java Programming, 8 th Ed 2 factorial(0) = 1; omputing Factorial factorial(n) = n*factorial(n-1); n! = n * (n-1)!
S/E 2336 omputer Science II UT D Session 10 Recursion dapted from D Liang s Introduction to Java Programming, 8 th Ed 2 factorial(0) = 1; omputing Factorial factorial(n) = n*factorial(n-1); n! = n * (n-1)!
EE 368. Weeks 4 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 4 (Notes) 1 Read Chapter 3 Recursion and Backtracking Recursion - Recursive Definition - Some Examples - Pros and Cons A Class of Recursive Algorithms (steps or mechanics about performing
EE 368 Weeks 4 (Notes) 1 Read Chapter 3 Recursion and Backtracking Recursion - Recursive Definition - Some Examples - Pros and Cons A Class of Recursive Algorithms (steps or mechanics about performing
Recursive Problem Solving
 Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should: Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition. Be able to use recursion in Java to solve problems. 2 Recursive Problem Solving How to solve
Recursive Problem Solving Objectives Students should: Be able to explain the concept of recursive definition. Be able to use recursion in Java to solve problems. 2 Recursive Problem Solving How to solve
Recursion. Dr. Jürgen Eckerle FS Recursive Functions
 Recursion Dr. Jürgen Eckerle FS 2008 Recursive Functions Recursion, in mathematics and computer science, is a method of defining functions in which the function being defined is applied within its own
Recursion Dr. Jürgen Eckerle FS 2008 Recursive Functions Recursion, in mathematics and computer science, is a method of defining functions in which the function being defined is applied within its own
CSC 148 Lecture 3. Dynamic Typing, Scoping, and Namespaces. Recursion
 CSC 148 Lecture 3 Dynamic Typing, Scoping, and Namespaces Recursion Announcements Python Ramp Up Session Monday June 1st, 1 5pm. BA3195 This will be a more detailed introduction to the Python language
CSC 148 Lecture 3 Dynamic Typing, Scoping, and Namespaces Recursion Announcements Python Ramp Up Session Monday June 1st, 1 5pm. BA3195 This will be a more detailed introduction to the Python language
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring
 Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Notes - Recursion. A geeky definition of recursion is as follows: Recursion see Recursion.
 Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
We cover recursion in 150. Why do it again in 151?
 Recursion We cover recursion in 150. Why do it again in 151? First, good solutions to problems are often recursive. Here is a quick way to sort a list of objects: split the list in half, recursively sort
Recursion We cover recursion in 150. Why do it again in 151? First, good solutions to problems are often recursive. Here is a quick way to sort a list of objects: split the list in half, recursively sort
Module 10. Recursion. Adapted from Absolute Java, Rose Williams, Binghamton University
 Module 10 Recursion Adapted from Absolute Java, Rose Williams, Binghamton University Recursive void Methods A recursive method is a method that includes a call to itself Recursion is based on the general
Module 10 Recursion Adapted from Absolute Java, Rose Williams, Binghamton University Recursive void Methods A recursive method is a method that includes a call to itself Recursion is based on the general
Lecture 3: Loops. While Loops. While Loops: Newton-Raphson Method. While Loops: Powers of Two
 While Loops Lecture 3: Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
While Loops Lecture 3: Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
Opening Problem. Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
 Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
q To develop recursive methods for recursive mathematical functions ( ).
 Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem? There
Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem? There
Lecture 3: Loops. While Loops. While Loops: Powers of Two. While Loops: Newton-Raphson Method
 While Loops Lecture : Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
While Loops Lecture : Loops The while loop is a common repetition structure. Check loop-continuation condition. Execute a sequence of statements. Repeat. while (boolean expression) statement; while loop
q To develop recursive methods for recursive mathematical functions ( ).
 /2/8 Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem?
/2/8 Chapter 8 Recursion CS: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations Suppose you want to find all the files under a directory that contains a particular word. How do you solve this problem?
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 10 Recursion and Search MOUNA KACEM Recursion: General Overview 2 Recursion in Algorithms Recursion is the use of recursive algorithms to solve a problem A recursive algorithm
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
A Foundation for Programming 1.3 Conditionals and Loops any program you might want to write objects functions and modules graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and loops Math primitive data
Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
