Programming Languages
|
|
|
- Bertha Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Epressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Problem fun -> +1 Can functions only have a single parameter? A Solution: Simultaneous Binding Parameter (formal) Body Epr fun (,y) -> <y; (int * int) -> bool Can functions only have a single parameter? Another Solution Parameter (formal) Body Epr fun -> fun y-> <y; int -> (int -> bool) Whoa! A function can return a function # let lt = fun -> fn y -> < y ; val lt : int -> int -> bool = fn # let is5lt = lt 5; val is5lt : int -> bool = fn; # is5lt 10; val it : bool = true; # is5lt 2; val it : bool = false;
2 And how about Parameter (formal) Body Epr fun f -> fun -> not(f ); ( a ->bool) -> ( a -> bool) A function can also take a function argument # let neg = fun f -> fun -> not (f ); val lt : int -> int -> bool = fn # let is5gte = neg is5lt; val is5gte : int -> bool = fn # is5gte 10; val it : bool = false; # is5gte 2; val it : bool = true; (* odd, even *) A shorthand for function binding # let neg = fun f -> fun -> not (f ); # let neg f = not (f ); val neg : int -> int -> bool = fn # let is5gte = neg is5lt; val is5gte : int -> bool = fn; # is5gte 10; val it : bool = false; # is5gte 2; val it : bool = true; Put it together: a filter function If arg matches this pattern then use this Body Epr - let rec filter f l = match l with [] -> [] (h::t)-> if f h then h::(filter f t) else (filter f t) val filter : ( a->bool)-> a list-> a lisi) = fn # let list1 = [1;31;12;4;7;2;10] # filter is5lt list1 val it : int list = [31;12;7;10] # filter is5gte list1 val it : int list = [1;4;2] # filter even list1 val it : int list = [12;4;2;10] Put it together: a partition function # let partition f l = (filter f l, filter (neg f) l); val partition :( a->bool)-> a list-> a lisi * a list = fn # let list1 = [1,31,12,4,7,2,10]; - # partition is5lt list1 ; val it : (int list * int list) = ([31,12,7,10],[1,2,10] # partition even list1; val it : (int list * int list) = ([12,4,2,10],[1,31,7])
3 A little trick # 2 <= 3 val it : bool = true # ba <= ab val it : bool = false # let lt = (<) val it : a -> a -> bool = fn # lt 2 3 val it : bool = true; # lt ba ab val it : bool = false; Put it together: a quicksort function let rec sort s = match s with [] -> [] (h::t) -> let (l,r) = partition ((<) h) t in (sort l)@(h::(sort r)) # let is5lt = lt 5; val is5lt : int -> bool = fn; # is5lt 10; val it : bool = true; # is5lt 2; val it : bool = false; Now, lets begin at the beginning News PA 1 due 5pm tomorrow PA 2 out tomorrow Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. L checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules, L tries to find a unique type for the epression meaningful type for the epr 3. L evaluates epression to compute value Of the same type found in step 2
4 Base Type: int 2; 2 i i:int i i Base Type: float e r:float r r 2+3; 5 e1 + e2 e 1 :int e 2 :int e 1 +e 2 :int e1 v1 e2 v2 e1+e2 v1+v e1 +. e2 e 1 :float e 1 :float e 1 +.e 2 :float e1 v1 e2 v2 e1+.e2 v1+.v2 7-4; 3 e1 - e2 e 1 :int e 2 :int e 1 -e 2 :int e1 v1 e2 v2 e1-e2 v1-v e1 -. e2 e 1:float e 2 :float e 1 -.e 2 :float e1 v1 e2 v2 e1-.e2 v1-.v2 (2+3)*(7-4); 15 e1 * e2 e 1 :int e 2 :int e1 v1 e2 v2 e 1 * e 2 :int e1*e2 v1*v2 ( ) /. ( ) e1 /. e2 e 1:float e 2 :float e1 v1 e2 v2 e 1 /.e 2 :float e1/.e2 v1/.v2 Epressions built from sub-epressions Types computed from types of sub-epressions Values computed from values of sub-epressions Epressions built from sub-epressions Types computed from types of sub-epressions Values computed from values of sub-epressions Base Type: string ab ab s s:string s s Base Type: bool true true b b:bool b b 2 < 3 true e1 < e2 e 1 :T e 2 :T e 1 <e 2 : bool e1 v1 e2 v2 e1<e2 v1<v2 ab ^ cd abcd e1^e2 e 1 :string e 2 :string e 1^e 2 :string e1 v1 e2 v2 e1^e2 v1^v2 not(2<3) false not e ( ab = cd ) false e1 = e2 e : bool not e : bool e v not e not v e 1 :TT e 2 :T e1 v1 e2 v2 e 1 =e 2 : bool e1=e2 v1=v2 Epressions built from sub-epressions Types computed from types of sub-epressions Values computed from values of sub-epressions not (2<3) e false e1 && e2 1 :bool e 2 :bool e1 v1 e2 v2 && e 1 &&e 2 :bool e1&&e2 v1 && v2 ( ab = cd )
5 Base Type: bool Equality testing built-in in for all epr, values, types but compared epressions must have same type ecept for? Type Errors pq ^ 9; (2 + a ); e 1 :string e 2 :string e 1^e 2 :stringi e 1 :int e 2 :int e 1 + e 2 : int ( ab = cd ) false e1 = e2 e 1 :TT e 2 :T e1 v1 e2 v2 e 1 =e 2 : bool e1=e2 v1=v2 Epressions built from sub-epressions Types computed from types of sub-epression If a sub-epression is not well-typed then whole epression is not well-typed 0 * (2 + a ); Comple types: Tuples (2+2, 7>8); (4,false) int * bool Comple types: Tuples Can be of any fied size (9-3, ab ^ cd,7>8) (int * string * bool) (6, abcd, false) e1:t1 e2:t2 e1 v1 e2 v2 (e 1,e 2 ) : T1 * T2 (e1,e2) (v1,v2) e1:t1 e2:t2 en: Tn (e1,e2,,en) : T1 * T2* * Tn e1 v1 e2 v2 en vn (e1,e2,,en) (v1,v2,,vn) Elements can have different types Tuples can be nested in other tuples
6 Comple types: Records Comple types: Lists {name= ranjit ; age=31; pass=false} { name : string, age : int, pass : bool} [1+1;2+2;3+3;4+4] [2;4;6;8] int list [ a ; b ; c ^ d ]; [ a ; b ; cd ] string list Records are tuples with named elements [(1; a ^ b );(3+4, c )]; [(1, ab );(7, c )] (int*string) list {name= ranjit ;age=31;pass=false}.age 31 int [[1];[2;3];[4;5;6]]; [[1];[2;3];[4;5;6]]; (int list) list {age=31;name= ranjit ;pass=false}.age 31 int Unbounded size {age=31;name= ranjit ;pass=false}.pass false bool Can have lists of anything (e.g. lists of lists) Comple types: Lists Comple types: list..construct [] [e1;e2;e3; ] []: a list [] [] e1:t e2: T e3: T e1 v1 e2 v2 e3 v3 [e1;e2;e3; ] : T list [e1;e2; ] [v1;v2; ] 1 2 Cons operator e1:t e2: T list e1::e2 : T list 1::[2;3] [1;2;3] int list e1 v1 e2 v2 e1::e2 v1::v2 All elements have the same type [1; pq ] 1::[ b ; cd ]; Can only cons element to a list of same type
7 Comple types: list construct Append operator [1;2;3;4] int list Comple types: list deconstruct Reading the elements of a list: Two operators : hd (head) and tl (tail) e1:t list e2: T list e1@e2 : T list e1 v1 e2 v2 e1@e2 v1@v2 [1;2;3;4;5] hd [1;2;3;4;5] 1 int tl [1;2;3;4;5] [2;3;4;5] int list 1@[ b ; cd ]; [ a ; b ; cd ] hd [ a ; b ; cd ] a string tl [ a ; b ; cd ] [ b ; cd ] string list [1]@[ b ; cd ]; Can only append lists of the same type [(1, a );(7, c )] hd [(1, a );(7, c )] 1 int [[];[1;2;3];[4;5]] hd [[];[1;2;3];4;5] 1 int list tl [(1, a );(7, c )] [(7; c ] (int * string) list tl [[];[1;2;3];4;5] [2;3;4;5] int list list List: Heads and Tails Recap Head e :T list hd e : T e v1::v2 hd e v1 Epressions (Synta) Eec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Tail e :T list tl e : T list e v1::v2 tl e v2 Compile-time Static Types (hd [[];[1;2;3]])[1 = (hd [[];[ a ]])[ int list e 1 :T e 2 :T e 1 =e 2 : bool string list 1. Programmer enters epression 2. L checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules, L tries to find a unique type for the epression meaningful type for the epr 3. L evaluates epression to compute value Of the same type found in step 2
8 Recap Integers: + -* floats: *. Booleans: =,<, &&,, not Strings: ^ Tuples (Records) Fied number of values, of dff different types Lists: ::,@,hd,tl,null Unbounded number of values, of same type If-then-else else epressions if (1 < 2) then 5 else 10 5 if (1 < 2) then [ ab, cd ] else [ ] If-then-else is also an epression! int [ ab, cd ] string ti list lit Can use any epression in then, else branch if e1 then e2 else e3 e1 : bool e2: T e3: T if e1 then e2 else e3 : T e1 true e2 v2 if e1 then e2 else e3 v2 e1 false e2 v3 if e1 then e2 else e3 v3 If-then-else else epressions if (1 < 2) then [1;2] else 5 if false then [1;2] else 5 then-subep, else-subep must have same type! which is the type of resulting epression e1 : bool e2: T e3: T if e1 then e2 else e3 : T If-then-else else epressions e1 : bool e2: T e3: T if e1 then e2 else e3 : T Then-subep, Else-subep must have same type! Equals type of resulting epression if 1>2 then [1,2] else [] [] int list if 1<2 then [] else [ a ] [] string list (if 1>2 then [1,2] else [])=(if 1<2 then [] else [ a ])
9 Net: Variables Variables and Bindings Q: How to use variables in L? Q: How to assign to a variable? # let = 2+2 val : int = 4 let = e Bind the value of epression e to the variable Variables and Bindings # let = 2+2 val : int = 4 # let y = * * val y : int = 64 # let z = [;y;+y] val z : int list = [4;64;68] Later declared epressions can use ost recent bound value used for evaluation Sounds like C/Java? NO! Environments ( Phone Book ) How L deals with variables Variables = names Values = phone number y z 4 : int 64 : int [4;64;68] : int list 8 : int
10 Environments and Evaluation L begins in a top-level environment Some names bound let = e L program = Sequence of variable bindings Program evaluated by evaluating bindings in order 1. Evaluate epr e in current env to get value v : t 2. Etend env to bind to v : t (Repeat with net binding) Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number 1. Evaluate: Find and use most recent value of variable 2. Etend: Add new binding at end of phone book Eample # let = 2+2 val : int = 4 # let y = * * val y : int = 64 y 4 : int 4 : int 64 : int # let z = [;y;+y] val z : int list = [4;64;68] 4 : int # let = + val : int = 8 New binding! y z y z 64 : int [4;64;68] : int list 4 : int 64 : int [4;64;68] : int list 8 : int Environments 1. Evaluate: Use most recent bound value of var 2. Etend: Add new binding at end How is this different from C/Java s store? # let = 2+2 val : int = 4 4 : int # let f = fun y -> + y; val f : int -> int = fn 4 : int f fn <code, >: int->int # let = + ; val : int = 8 # f 0; val it : int = 4 New binding: No change or mutation Old binding frozen in f
11 Environments 1. Evaluate: Use most recent bound value of var 2. Etend: Add new binding at end How is this different from C/Java s store? Environments 1. Evaluate: Use most recent bound value of var 2. Etend: Add new binding at end How is this different from C/Java s store? # let = 2+2; val : int = 4 4 : int # let f = fun y -> + y; val f : int -> int = fn 4 : int f fn <code, >: int->int # let = + ; val : int = 8; 4 : int # f 0; f fn <code, >: int->int val it : int = 4 8 : int # let = 2+2; val : int = 4 # let f = fun y -> + y val f : int -> int = fn Binding used to eval (f ) # let = + ; val : int = 8 4 : int f fn <code, >: int->int # f 0; 8 : int val it : int = 4 Binding for subsequent Cannot change the world Cannot assign to variables Can etend the env by adding a fresh binding Does not affect previous uses of variable Environment at fun declaration frozen inside fun value Frozen env used to evaluate application (f ) Q: Why is this a good thing? # let = 2+2 Binding used to eval (f ) val : int = 4 # let f = fun y -> + y val f : int -> int = fn # let = + val : int = 8; # f 0 val it : int = 4 4 : int f fn <code,, >: int->int 8 : int Binding for subsequent Cannot change the world Q: Why is this a good thing? A: Function behavior frozen at declaration Nothing entered afterwards affects function Same inputs always produce same outputs Localizes debugging Localizes reasoning about the program No sharing means no evil aliasing i
12 Eamples of no sharing Remember: No addresses, no sharing. Each variable is bound to a fresh instance of a value Tuples, Lists Efficient implementation without sharing? There is sharing and pointers but hidden from you Compiler s job is to optimize code Efficiently implement these no-sharing semantics Your job is to use the simplified semantics Write correct, cleaner, readable, etendable systems Function bindings Functions are values, can bind using val let fname = fun -> e Problem: Can t define recursive functions! fname is bound after computing rhs value no (or old ) binding for occurences of fname inside id e let rec fname = e Occurences of fname inside e bound to this definition let rec fac = if <=1 then 1 else *fac (-1) Local bindings So far: global bindings (Remain till a re-binding) Net: local variables Useful inside functions Avoid repeating computations ake functions more readable Local bindings let = e1 in e2 Let-in is an epression! Evaluating let-in in env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 in env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] to evaluate e2
13 Local bindings Evaluating let-in in env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 in env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] to evaluate e2 let in = 10 * 10 : int Let-in is an epression! Evaluating let-in in env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 in env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] to evaluate e2 let y = let = 10 in * y 100 : int 10 : int Nested bindings Evaluating let-in in env E: 1. Evaluate epr e1 in env E to get value v : t 2. Use etended E [ a v : t] to evaluate e2 let = 10 in (let y = 20 in * y) + 10 : int y 10 : int 10 : int 20 : int Nested bindings let = 10 in let in y = 20 * y let = 10 in let y = 20 in * y Correct Formatting
14 Eample Nested function bindings let rec filter (f,l) = if l = [] then [] else let h = hd l in let t = filter (f, tl l) in if (f h) then h::t else t let a = 20 let f = let y = 10 in let g z = y + z in a + (g ) f 0; Env frozen with function Used to evaluate fun application Values in application are those frozen in env at definition Recap Recap Variables are names for values Environment: dictionary/phonebook ost recent binding used Entries never changed, new entries added Build comple epressions with local bindings let-in epression The let-binding is visible (in scope) inside in-epression Elsewhere the binding is not visible Environment frozen at fun definition Re-binding vars cannot change function behavior Same I/O behavior at every call
15 Static/Leical Scoping Net: Functions For each occurrence of a variable, there is a unique place in program tet where the variable was defined ost recent binding in environment Static/Leical: Determined from the program tet Without eecuting the programy Epressions Types Values Very useful for readability, debugging: Don t have to figure out where a variable got assigned Unique, statically known definition for each occurrence Q: What s the value of a function?
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Epressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 1 due (net) Fri 10/10 5pm PA 2 out today or tomorrow Office hours posted on Webpage: Held in
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Epressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 1 due (net) Fri 10/10 5pm PA 2 out today or tomorrow Office hours posted on Webpage: Held in
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course Ctd, Expressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A shorthand for function binding # let neg = fun f -> fun x -> not (f x); # let
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course Ctd, Expressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A shorthand for function binding # let neg = fun f -> fun x -> not (f x); # let
Side note: Tail Recursion. Begin at the beginning. Side note: Tail Recursion. Base Types. Base Type: int. Base Type: int
 Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Tail Recursion: Factorial. Begin at the beginning. How does it execute? Tail recursion. Tail recursive factorial. Tail recursive factorial
 Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Begin at the beginning
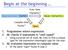 Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
Variables and Bindings
 Net: Variables Variables and Bindings Q: How to use variables in ML? Q: How to assign to a variable? # let = 2+2;; val : int = 4 let = e;; Bind the value of epression e to the variable Variables and Bindings
Net: Variables Variables and Bindings Q: How to use variables in ML? Q: How to assign to a variable? # let = 2+2;; val : int = 4 let = e;; Bind the value of epression e to the variable Variables and Bindings
Recap. Recap. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions
 Recap Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types (Semantics) Recap Integers: +,-,* floats: +,-,* Booleans: =,
Recap Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types (Semantics) Recap Integers: +,-,* floats: +,-,* Booleans: =,
News. Programming Languages. Complex types: Lists. Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. CSE 130: Spring 2012
 News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
News. CSE 130: Programming Languages. Environments & Closures. Functions are first-class values. Recap: Functions as first-class values
 CSE 130: Programming Languages Environments & Closures News PA 3 due THIS Friday (5/1) Midterm NEXT Friday (5/8) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values,
CSE 130: Programming Languages Environments & Closures News PA 3 due THIS Friday (5/1) Midterm NEXT Friday (5/8) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values,
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programmg Languages Lecture 4: Variables, Environments, Scope News PA 1 due Frida 5pm PA 2 out esterda (due net Fi) Fri) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Variables and Bdgs Q: How to use variables
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programmg Languages Lecture 4: Variables, Environments, Scope News PA 1 due Frida 5pm PA 2 out esterda (due net Fi) Fri) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Variables and Bdgs Q: How to use variables
OCaml. ML Flow. Complex types: Lists. Complex types: Lists. The PL for the discerning hacker. All elements must have same type.
 OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward. 2. Rewind. 3. Slow motion. Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml. Go over the pieces individually
 Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Rewind 3. Slow motion Go over the pieces individually History, Variants Meta Language Designed by Robin Milner @ Edinburgh Language
Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Rewind 3. Slow motion Go over the pieces individually History, Variants Meta Language Designed by Robin Milner @ Edinburgh Language
Recap from last time. Programming Languages. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 3: Data Types. Put it together: a filter function
 CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
OCaml. History, Variants. ML s holy trinity. Interacting with ML. Base type: Integers. Base type: Strings. *Notes from Sorin Lerner at UCSD*
 OCaml 1. Introduction Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Focus on Features Individually as Needed as Semester Progresses *Notes from Sorin Lerner at UCSD* History, Variants Meta Language Designed
OCaml 1. Introduction Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Focus on Features Individually as Needed as Semester Progresses *Notes from Sorin Lerner at UCSD* History, Variants Meta Language Designed
Recap: Functions as first-class values
 Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values, bindings What are the benefits? Parameterized, similar functions (e.g. Testers) Creating, (Returning) Functions Iterator, Accumul, Reuse
Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values, bindings What are the benefits? Parameterized, similar functions (e.g. Testers) Creating, (Returning) Functions Iterator, Accumul, Reuse
Any questions. Say hello to OCaml. Say hello to OCaml. Why readability matters. History, Variants. Plan (next 4 weeks)
 Any questions Say hello to OCaml? void sort(int arr[], int beg, int end){ if (end > beg + 1){ int piv = arr[beg]; int l = beg + 1; int r = end; while (l!= r-1){ if(arr[l]
Any questions Say hello to OCaml? void sort(int arr[], int beg, int end){ if (end > beg + 1){ int piv = arr[beg]; int l = beg + 1; int r = end; while (l!= r-1){ if(arr[l]
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
News. Programming Languages. Recap. Recap: Environments. Functions. of functions: Closures. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes
 CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
So what does studying PL buy me?
 So what does studying PL buy me? Enables you to better choose the right language but isn t that decided by libraries, standards, and my boss? Yes. Chicken-and-egg. My goal: educate tomorrow s tech leaders
So what does studying PL buy me? Enables you to better choose the right language but isn t that decided by libraries, standards, and my boss? Yes. Chicken-and-egg. My goal: educate tomorrow s tech leaders
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
sum: tree -> int sum_leaf: tree -> int sum_leaf: tree -> int Representing Trees Next: Lets get cosy with Recursion Sum up the leaf values. E.g.
 Representing Trees Node Next: Lets get cosy with Recursion 1 2 3 1 Node 2 3 Node(Node( 1, 2), 3) sum: tree -> int Next: Lets get cosy with Recursion Sum up the leaf values. E.g. # let t0 = sum Node(Node(
Representing Trees Node Next: Lets get cosy with Recursion 1 2 3 1 Node 2 3 Node(Node( 1, 2), 3) sum: tree -> int Next: Lets get cosy with Recursion Sum up the leaf values. E.g. # let t0 = sum Node(Node(
CSE 130 Programming Languages. Lecture 3: Datatypes. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? PA #2 (coming tonight) Ocaml-top issues? Pleas post questions to Piazza Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax)
CSE 130 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? PA #2 (coming tonight) Ocaml-top issues? Pleas post questions to Piazza Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax)
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. Story So Far... CSE 130 Programming Languages. Datatypes. A function is a value! Next: functions, but remember.
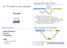 CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages. Datatypes. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130 Programming Languages Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages
![CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages](/thumbs/85/92581372.jpg) CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages Introduction to OCaml (Continued) Ravi Chugh! Jan 14 Announcements HW #1 due Mon Jan 20 Post questions/discussion to Piazza Check Piazza for TA/Tutor lab hours
CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages Introduction to OCaml (Continued) Ravi Chugh! Jan 14 Announcements HW #1 due Mon Jan 20 Post questions/discussion to Piazza Check Piazza for TA/Tutor lab hours
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity
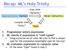 Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Today s Plan. Programming Languages. Example : Factorial. Recursion. CSE 130 : Spring Lecture 6: Higher-Order Functions
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Higher-Order Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan A little more practice with recursion Base Pattern -> Base Expression Induction Pattern -> Induction
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Higher-Order Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan A little more practice with recursion Base Pattern -> Base Expression Induction Pattern -> Induction
Programming Languages. Tail Recursion. CSE 130: Winter Lecture 8: NOT TR. last thing function does is a recursive call
 CSE 130: Winter 2010 News Programming Languages Lecture 8: Higher-Order Od Functions Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan Finish Static Scoping Tail Recursion last thing function does is a recursive
CSE 130: Winter 2010 News Programming Languages Lecture 8: Higher-Order Od Functions Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today s Plan Finish Static Scoping Tail Recursion last thing function does is a recursive
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Functional Programming with Lists
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Datatypes t and Recursion Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 2 Due Fri (and PA3 up) PA3 is a bit difficult, but do it yourself, or repent in the final
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Datatypes t and Recursion Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 2 Due Fri (and PA3 up) PA3 is a bit difficult, but do it yourself, or repent in the final
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Functional Programming with Lists
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as a linked data structure
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as a linked data structure
A Programming Language. A different language g is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Fall Two variables. L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1 L2:
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1 L2:
A Programming Language. A different language g is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Spring Two variables. L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?
 CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1
CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1
Programming Languages Lecture 14: Sum, Product, Recursive Types
 CSE 230: Winter 200 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Sum, Product, Recursive Types The end is nigh HW 3 No HW 4 (= Final) Project (Meeting + Talk) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap Goal: Relate
CSE 230: Winter 200 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Sum, Product, Recursive Types The end is nigh HW 3 No HW 4 (= Final) Project (Meeting + Talk) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap Goal: Relate
CVO103: Programming Languages. Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions
 CVO103: Programming Languages Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions Hakjoo Oh 2018 Spring Hakjoo Oh CVO103 2018 Spring, Lecture 5 April 3, 2018 1 / 23 Plan Part 1 (Preliminaries):
CVO103: Programming Languages Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions Hakjoo Oh 2018 Spring Hakjoo Oh CVO103 2018 Spring, Lecture 5 April 3, 2018 1 / 23 Plan Part 1 (Preliminaries):
CSE 341: Programming Languages
 CSE 341: Programming Languages Hal Perkins Spring 2011 Lecture 2 Functions, pairs, and lists Hal Perkins CSE341 Spring 2011, Lecture 2 1 What is a programming language? Here are separable concepts for
CSE 341: Programming Languages Hal Perkins Spring 2011 Lecture 2 Functions, pairs, and lists Hal Perkins CSE341 Spring 2011, Lecture 2 1 What is a programming language? Here are separable concepts for
Function definitions. CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists. Example, extended. Some gotchas. Zach Tatlock Winter 2018
 Function definitions CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
Function definitions CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists. Zach Tatlock Winter 2018
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Function definitions Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Function definitions Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
Programming Languages. So why study PL? A Programming Language. A different language is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Spring 2015
 CSE 130 : Spring 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++;
CSE 130 : Spring 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++;
Programming Languages. So why study PL? A Programming Language. A different language is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Fall 2015
 CSE 130 : Fall 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World! Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--;
CSE 130 : Fall 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World! Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--;
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists. Dan Grossman Fall 2011
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Dan Grossman Fall 2011 Review Building up SML one construct at a time via precise definitions Constructs have syntax, type-checking rules,
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Dan Grossman Fall 2011 Review Building up SML one construct at a time via precise definitions Constructs have syntax, type-checking rules,
Programming Languages
 What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
Typical workflow. CSE341: Programming Languages. Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures. Reality more complicated
 Typical workflow concrete synta (string) "(fn => + ) 4" Parsing CSE341: Programming Languages abstract synta (tree) Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Function Constant + 4 Var Var Type
Typical workflow concrete synta (string) "(fn => + ) 4" Parsing CSE341: Programming Languages abstract synta (tree) Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Function Constant + 4 Var Var Type
CSE 341 Section 5. Winter 2018
 CSE 341 Section 5 Winter 2018 Midterm Review! Variable Bindings, Shadowing, Let Expressions Boolean, Comparison and Arithmetic Operations Equality Types Types, Datatypes, Type synonyms Tuples, Records
CSE 341 Section 5 Winter 2018 Midterm Review! Variable Bindings, Shadowing, Let Expressions Boolean, Comparison and Arithmetic Operations Equality Types Types, Datatypes, Type synonyms Tuples, Records
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Next: What s in a name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Next: What s in a name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really
CSE 130: Programming Languages. Polymorphism. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130: Programming Languages Polymorphism Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Q: What is the value of res? let f g = let x = 0 in g 2 let x = 100 let h y = x + y let res = f h (a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 100 (d) 102 (e) 12
CSE 130: Programming Languages Polymorphism Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Q: What is the value of res? let f g = let x = 0 in g 2 let x = 100 let h y = x + y let res = f h (a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 100 (d) 102 (e) 12
CPSC W1 University of British Columbia
 Definition of Programming Languages CPSC 311 2016W1 University of British Columbia Practice Midterm Eamination 26 October 2016, 19:00 21:00 Joshua Dunfield Student Name: Signature: Student Number: CS userid:
Definition of Programming Languages CPSC 311 2016W1 University of British Columbia Practice Midterm Eamination 26 October 2016, 19:00 21:00 Joshua Dunfield Student Name: Signature: Student Number: CS userid:
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 13: Whats in a name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego f = open( foo.txt, read ) f.readlines() for l in f.readlines(): f.close ou now know enough to do PA5
CSE 130 : Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 13: Whats in a name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego f = open( foo.txt, read ) f.readlines() for l in f.readlines(): f.close ou now know enough to do PA5
CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter
 Due: Thurs October 27, 10:00pm CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter Note: This is a much longer assignment than anything we ve seen up until now. You are given two weeks to complete
Due: Thurs October 27, 10:00pm CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter Note: This is a much longer assignment than anything we ve seen up until now. You are given two weeks to complete
Next: What s in a name? Programming Languages. Data model in functional PL. What s in a name? CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 13: What s in a Name?
 Next: What s in a name? CSE 13 : Fall 211 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really mean? Ranjit Jhala UC San
Next: What s in a name? CSE 13 : Fall 211 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really mean? Ranjit Jhala UC San
Programming Languages
 CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Ocaml/HW #3 Q-A Session Push deadline = Mar 10 Session Mon 3pm? Lecture 15: Type Systems Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Why Typed Languages? Development
CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Ocaml/HW #3 Q-A Session Push deadline = Mar 10 Session Mon 3pm? Lecture 15: Type Systems Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Why Typed Languages? Development
Lists. Prof. Clarkson Fall Today s music: "Blank Space" by Taylor Swift
 Lists Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: "Blank Space" by Taylor Swift I could show you incredible things // Magic, madness, heaven, sin So it's gonna be forever // Or it's gonna go down in flames
Lists Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: "Blank Space" by Taylor Swift I could show you incredible things // Magic, madness, heaven, sin So it's gonna be forever // Or it's gonna go down in flames
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. OCaml Imperative Programming
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory
A Second Look At ML. Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1
 A Second Look At ML Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline Patterns Local variable definitions A sorting example Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 2 Two Patterns
A Second Look At ML Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline Patterns Local variable definitions A sorting example Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 2 Two Patterns
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. OCaml Expressions and Functions
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Expressions and Functions CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lecture Presentation Style Our focus: semantics and idioms for OCaml Semantics is what the language
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Expressions and Functions CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lecture Presentation Style Our focus: semantics and idioms for OCaml Semantics is what the language
CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages
![CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages](/thumbs/84/89705892.jpg) CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages Course Introduction! Ravi Chugh! Filling in today for Ranjit Jhala Apr 01 A Programming Language Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- L1: x++; y--; L2:!
CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages Course Introduction! Ravi Chugh! Filling in today for Ranjit Jhala Apr 01 A Programming Language Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- L1: x++; y--; L2:!
SML A F unctional Functional Language Language Lecture 19
 SML A Functional Language Lecture 19 Introduction to SML SML is a functional programming language and acronym for Standard d Meta Language. SML has basic data objects as expressions, functions and list
SML A Functional Language Lecture 19 Introduction to SML SML is a functional programming language and acronym for Standard d Meta Language. SML has basic data objects as expressions, functions and list
Programming Language Concepts, cs2104 Lecture 04 ( )
 Programming Language Concepts, cs2104 Lecture 04 (2003-08-29) Seif Haridi Department of Computer Science, NUS haridi@comp.nus.edu.sg 2003-09-05 S. Haridi, CS2104, L04 (slides: C. Schulte, S. Haridi) 1
Programming Language Concepts, cs2104 Lecture 04 (2003-08-29) Seif Haridi Department of Computer Science, NUS haridi@comp.nus.edu.sg 2003-09-05 S. Haridi, CS2104, L04 (slides: C. Schulte, S. Haridi) 1
Fall Lecture 3 September 4. Stephen Brookes
 15-150 Fall 2018 Lecture 3 September 4 Stephen Brookes Today A brief remark about equality types Using patterns Specifying what a function does equality in ML e1 = e2 Only for expressions whose type is
15-150 Fall 2018 Lecture 3 September 4 Stephen Brookes Today A brief remark about equality types Using patterns Specifying what a function does equality in ML e1 = e2 Only for expressions whose type is
Lambda Calculus. Concepts in Programming Languages Recitation 6:
 Concepts in Programming Languages Recitation 6: Lambda Calculus Oded Padon & Mooly Sagiv (original slides by Kathleen Fisher, John Mitchell, Shachar Itzhaky, S. Tanimoto ) Reference: Types and Programming
Concepts in Programming Languages Recitation 6: Lambda Calculus Oded Padon & Mooly Sagiv (original slides by Kathleen Fisher, John Mitchell, Shachar Itzhaky, S. Tanimoto ) Reference: Types and Programming
CMSC 336: Type Systems for Programming Languages Lecture 4: Programming in the Lambda Calculus Acar & Ahmed 22 January 2008.
 CMSC 336: Type Systems for Programming Languages Lecture 4: Programming in the Lambda Calculus Acar & Ahmed 22 January 2008 Contents 1 Announcements 1 2 Solution to the Eercise 1 3 Introduction 1 4 Multiple
CMSC 336: Type Systems for Programming Languages Lecture 4: Programming in the Lambda Calculus Acar & Ahmed 22 January 2008 Contents 1 Announcements 1 2 Solution to the Eercise 1 3 Introduction 1 4 Multiple
Dialects of ML. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Dialects of ML (cont.) Features of ML. Functional Languages. Features of ML (cont.
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 1 Functional Programming Dialects of ML ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh,1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 1 Functional Programming Dialects of ML ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh,1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
F28PL1 Programming Languages. Lecture 14: Standard ML 4
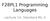 F28PL1 Programming Languages Lecture 14: Standard ML 4 Polymorphic list operations length of list base case: [] ==> 0 recursion case: (h::t) => 1 more than length of t - fun length [] = 0 length (_::t)
F28PL1 Programming Languages Lecture 14: Standard ML 4 Polymorphic list operations length of list base case: [] ==> 0 recursion case: (h::t) => 1 more than length of t - fun length [] = 0 length (_::t)
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. OCaml Imperative Programming
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Fall 2017 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory All
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Fall 2017 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory All
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 11 Type Inference. Dan Grossman Spring 2016
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 11 Type Inference Dan Grossman Spring 2016 Type-checking (Static) type-checking can reject a program before it runs to prevent the possibility of some errors A feature
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 11 Type Inference Dan Grossman Spring 2016 Type-checking (Static) type-checking can reject a program before it runs to prevent the possibility of some errors A feature
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 12: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A crash course in Python Interpreted, imperative, OO Language g Everything is an object Dynamic Typing
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 12: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A crash course in Python Interpreted, imperative, OO Language g Everything is an object Dynamic Typing
Tuples. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Examples With Tuples. Another Example
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 2 Higher Order Functions Tuples Constructed using (e1,..., en) Deconstructed using pattern matching Patterns involve parens and commas, e.g., (p1,p2,
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 2 Higher Order Functions Tuples Constructed using (e1,..., en) Deconstructed using pattern matching Patterns involve parens and commas, e.g., (p1,p2,
Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping
 CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? Formalize first-order type systems Simple types (integers and booleans)
CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? Formalize first-order type systems Simple types (integers and booleans)
Lecture #23: Conversion and Type Inference
 Lecture #23: Conversion and Type Inference Administrivia. Due date for Project #2 moved to midnight tonight. Midterm mean 20, median 21 (my expectation: 17.5). Last modified: Fri Oct 20 10:46:40 2006 CS164:
Lecture #23: Conversion and Type Inference Administrivia. Due date for Project #2 moved to midnight tonight. Midterm mean 20, median 21 (my expectation: 17.5). Last modified: Fri Oct 20 10:46:40 2006 CS164:
Background. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Useful Information on OCaml language. Dialects of ML. ML (Meta Language) Standard ML
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with OCaml 1 Background ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh, 1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with OCaml 1 Background ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh, 1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
Conversion vs. Subtyping. Lecture #23: Conversion and Type Inference. Integer Conversions. Conversions: Implicit vs. Explicit. Object x = "Hello";
 Lecture #23: Conversion and Type Inference Administrivia. Due date for Project #2 moved to midnight tonight. Midterm mean 20, median 21 (my expectation: 17.5). In Java, this is legal: Object x = "Hello";
Lecture #23: Conversion and Type Inference Administrivia. Due date for Project #2 moved to midnight tonight. Midterm mean 20, median 21 (my expectation: 17.5). In Java, this is legal: Object x = "Hello";
Exercises on ML. Programming Languages. Chanseok Oh
 Exercises on ML Programming Languages Chanseok Oh chanseok@cs.nyu.edu Dejected by an arcane type error? - foldr; val it = fn : ('a * 'b -> 'b) -> 'b -> 'a list -> 'b - foldr (fn x=> fn y => fn z => (max
Exercises on ML Programming Languages Chanseok Oh chanseok@cs.nyu.edu Dejected by an arcane type error? - foldr; val it = fn : ('a * 'b -> 'b) -> 'b -> 'a list -> 'b - foldr (fn x=> fn y => fn z => (max
Programming Languages. Example 5. Example 4. CSE 130 : Fall type, can reuse code for all types! let rec cat l = match l with
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 9: s and Signatures Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Previously: Polymorphism enables Reuse Can reuse generic functions: map : a * b b * a filter: ( a bool *
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 9: s and Signatures Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Previously: Polymorphism enables Reuse Can reuse generic functions: map : a * b b * a filter: ( a bool *
FOFL and FOBS: First-Order Functions
 CS251 Programming Languages Handout # 35 Prof. Lyn Turbak April 14, 2005 Wellesley College Revised April 24, 2005 FOFL and FOBS: First-Order Functions Revisions: Apr 24 : In the interpreters for Fofl and
CS251 Programming Languages Handout # 35 Prof. Lyn Turbak April 14, 2005 Wellesley College Revised April 24, 2005 FOFL and FOBS: First-Order Functions Revisions: Apr 24 : In the interpreters for Fofl and
CSE341 Autumn 2017, Final Examination December 12, 2017
 CSE341 Autumn 2017, Final Examination December 12, 2017 Please do not turn the page until 2:30. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, etc. except for both sides of one 8.5x11in piece of paper. Please
CSE341 Autumn 2017, Final Examination December 12, 2017 Please do not turn the page until 2:30. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, etc. except for both sides of one 8.5x11in piece of paper. Please
Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421)
 Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421) #3: Closures, evaluation of function applications, order of evaluation #4: Evaluation and Application rules using symbolic rewriting Madhusudan Parthasarathy
Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421) #3: Closures, evaluation of function applications, order of evaluation #4: Evaluation and Application rules using symbolic rewriting Madhusudan Parthasarathy
02157 Functional Programming. Michael R. Ha. Lecture 2: Functions, Types and Lists. Michael R. Hansen
 Lecture 2: Functions, Types and Lists nsen 1 DTU Compute, Technical University of Denmark Lecture 2: Functions, Types and Lists MRH 13/09/2018 Outline Functions as first-class citizens Types, polymorphism
Lecture 2: Functions, Types and Lists nsen 1 DTU Compute, Technical University of Denmark Lecture 2: Functions, Types and Lists MRH 13/09/2018 Outline Functions as first-class citizens Types, polymorphism
Program Flow. Instructions and Memory. Why are these 16 bits? C code. Memory. a = b + c. Machine Code. Memory. Assembly Code.
 Instructions and Memory C code Why are these 16 bits? a = b + c Assembly Code ldr r0, [sp, #4] ldr adds r1, [sp] r0, r0, r1 str r0, [sp, #8] Machine Code 09801 09900 01840 09002 Memory 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Instructions and Memory C code Why are these 16 bits? a = b + c Assembly Code ldr r0, [sp, #4] ldr adds r1, [sp] r0, r0, r1 str r0, [sp, #8] Machine Code 09801 09900 01840 09002 Memory 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Operational Semantics CMSC 330 Summer 2018 1 Formal Semantics of a Prog. Lang. Mathematical description of the meaning of programs written in that language
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Operational Semantics CMSC 330 Summer 2018 1 Formal Semantics of a Prog. Lang. Mathematical description of the meaning of programs written in that language
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Lets, Tuples, Records
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lets, Tuples, Records CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Let Expressions Enable binding variables in other expressions These are different from the let definitions we
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lets, Tuples, Records CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Let Expressions Enable binding variables in other expressions These are different from the let definitions we
Functional Programming. Pure Functional Programming
 Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 6 Nested Patterns Exceptions Tail Recursion. Zach Tatlock Winter 2018
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 6 Nested Patterns Exceptions Tail Recursion Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Nested patterns We can nest patterns as deep as we want Just like we can nest expressions as deep
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 6 Nested Patterns Exceptions Tail Recursion Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Nested patterns We can nest patterns as deep as we want Just like we can nest expressions as deep
CSE 413 Midterm, May 6, 2011 Sample Solution Page 1 of 8
 Question 1. (12 points) For each of the following, what value is printed? (Assume that each group of statements is executed independently in a newly reset Scheme environment.) (a) (define x 1) (define
Question 1. (12 points) For each of the following, what value is printed? (Assume that each group of statements is executed independently in a newly reset Scheme environment.) (a) (define x 1) (define
Cunning Plan. One-Slide Summary. Functional Programming. Functional Programming. Introduction to COOL #1. Classroom Object-Oriented Language
 Functional Programming Introduction to COOL #1 Cunning Plan Functional Programming Types Pattern Matching Higher-Order Functions Classroom Object-Oriented Language Methods Attributes Inheritance Method
Functional Programming Introduction to COOL #1 Cunning Plan Functional Programming Types Pattern Matching Higher-Order Functions Classroom Object-Oriented Language Methods Attributes Inheritance Method
Lecture 11: Subprograms & their implementation. Subprograms. Parameters
 Lecture 11: Subprograms & their implementation Subprograms Parameter passing Activation records The run-time stack Implementation of static and dynamic scope rules Subprograms A subprogram is a piece of
Lecture 11: Subprograms & their implementation Subprograms Parameter passing Activation records The run-time stack Implementation of static and dynamic scope rules Subprograms A subprogram is a piece of
Metaprogramming assignment 3
 Metaprogramming assignment 3 Optimising embedded languages Due at noon on Thursday 29th November 2018 This exercise uses the BER MetaOCaml compiler, which you can install via opam. The end of this document
Metaprogramming assignment 3 Optimising embedded languages Due at noon on Thursday 29th November 2018 This exercise uses the BER MetaOCaml compiler, which you can install via opam. The end of this document
Redefinition of an identifier is OK, but this is redefinition not assignment; Thus
 Redefinition of an identifier is OK, but this is redefinition not assignment; Thus val x = 100; val x = (x=100); is fine; there is no type error even though the first x is an integer and then it is a boolean.
Redefinition of an identifier is OK, but this is redefinition not assignment; Thus val x = 100; val x = (x=100); is fine; there is no type error even though the first x is an integer and then it is a boolean.
Introduction to ML. Mooly Sagiv. Cornell CS 3110 Data Structures and Functional Programming
 Introduction to ML Mooly Sagiv Cornell CS 3110 Data Structures and Functional Programming Typed Lambda Calculus Chapter 9 Benjamin Pierce Types and Programming Languages Call-by-value Operational Semantics
Introduction to ML Mooly Sagiv Cornell CS 3110 Data Structures and Functional Programming Typed Lambda Calculus Chapter 9 Benjamin Pierce Types and Programming Languages Call-by-value Operational Semantics
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Formal Semantics of a Prog. Lang. Specifying Syntax, Semantics
 Recall Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Source Scanner Parser Static Analyzer Operational Semantics Intermediate Representation Front End Back End
Recall Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Source Scanner Parser Static Analyzer Operational Semantics Intermediate Representation Front End Back End
Lecture 7: Type Systems and Symbol Tables. CS 540 George Mason University
 Lecture 7: Type Systems and Symbol Tables CS 540 George Mason University Static Analysis Compilers examine code to find semantic problems. Easy: undeclared variables, tag matching Difficult: preventing
Lecture 7: Type Systems and Symbol Tables CS 540 George Mason University Static Analysis Compilers examine code to find semantic problems. Easy: undeclared variables, tag matching Difficult: preventing
To figure this out we need a more precise understanding of how ML works
 Announcements: What are the following numbers: 74/2/70/17 (2:30,2:30,3:35,7:30) PS2 due Thursday 9/20 11:59PM Guest lecture on Tuesday 9/25 o No RDZ office hours next Friday, I am on travel A brief comment
Announcements: What are the following numbers: 74/2/70/17 (2:30,2:30,3:35,7:30) PS2 due Thursday 9/20 11:59PM Guest lecture on Tuesday 9/25 o No RDZ office hours next Friday, I am on travel A brief comment
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 3 September 18, 2017 1 / 44 Why learn ML? Learning ML is a good way of
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 3 September 18, 2017 1 / 44 Why learn ML? Learning ML is a good way of
CMSC 330, Fall 2013, Practice Problem 3 Solutions
 CMSC 330, Fall 2013, Practice Problem 3 Solutions 1. OCaml and Functional Programming a. Define functional programming Programs are expression evaluations b. Define imperative programming Programs change
CMSC 330, Fall 2013, Practice Problem 3 Solutions 1. OCaml and Functional Programming a. Define functional programming Programs are expression evaluations b. Define imperative programming Programs change
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages News PA 4 is up (Due Fri, 5pm) Lecture 12: Crash course in Python Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego MidtermGeneral Statistics Total of 80 points < 20 9 people Mean:
CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages News PA 4 is up (Due Fri, 5pm) Lecture 12: Crash course in Python Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego MidtermGeneral Statistics Total of 80 points < 20 9 people Mean:
CPS 506 Comparative Programming Languages. Programming Language Paradigm
 CPS 506 Comparative Programming Languages Functional Programming Language Paradigm Topics Introduction Mathematical Functions Fundamentals of Functional Programming Languages The First Functional Programming
CPS 506 Comparative Programming Languages Functional Programming Language Paradigm Topics Introduction Mathematical Functions Fundamentals of Functional Programming Languages The First Functional Programming
Computer Science 21b (Spring Term, 2015) Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs. Lexical addressing
 Computer Science 21b (Spring Term, 2015) Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Lexical addressing The difference between a interpreter and a compiler is really two points on a spectrum of possible
Computer Science 21b (Spring Term, 2015) Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Lexical addressing The difference between a interpreter and a compiler is really two points on a spectrum of possible
Introduction to OCaml
 Introduction to OCaml Jed Liu Department of Computer Science Cornell University CS 6110 Lecture 26 January 2009 Based on CS 3110 course notes and an SML tutorial by Mike George Jed Liu Introduction to
Introduction to OCaml Jed Liu Department of Computer Science Cornell University CS 6110 Lecture 26 January 2009 Based on CS 3110 course notes and an SML tutorial by Mike George Jed Liu Introduction to
