CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
|
|
|
- Augustine Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam. No calculators, computers, or communication devices of any kind are permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will stop by. Since partial credit is possible, please write legibly and show your work. Problem Points Score Total 63 1
2 1. Loops, input (8 points). Consider the following program: public class Prob1 public static void main(string [] args) int i; for (i = 0; i < args.length - 1; i++) double val1 = Integer.parseInt(args[i]); double val2 = Integer.parseInt(args[i + 1]); if (val1 > val2) break; if (i == args.length - 1) System.out.println("yes"); System.out.println("no"); Give the output of Prob1 for each of the following commands. If the program would crash, write "error": Command Program output % java Prob "yes" % java Prob "no" % java Prob1 "no" % java Prob error % java Prob1 8 "yes" % java Prob "yes" 2
3 2. Multiple choice (10 points, 2 points each). Circle the best single answer. I. Consider the following code fragment: int i = 5 / 10; System.out.println(i); What is the output of the System.out.println? a) 0 b) 0.5 c) 1 d) none of the above II. Consider the following code fragment: int i = 2; i++; ++i; i = i + 1; System.out.println(i); What is the output of the System.out.println? a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 III. The private keyword when added to the declaration of an instance variable of a class helps enforce which of the following principles? a) data encapsulation b) immutability c) avoiding repeated code d) divide- and- conquer IV. The Fraction class we developed in class had a private helper method named reduce that reduced the fraction object to lowest terms. This was done for which of the following reasons? a) to allow sorting of Fraction objects b) to make the class immutable c) to avoid repeated code from appearing in multiple methods (e.g. in both add and substract). d) to serve as a base case for the recusion V. The this keyword can be used in an instance method to achieve which of the following? a) creating a new instance of the class b) specifying the use of an instance variable when there is an identically named local or parameter variable c) avoiding repeated code d) hiding implementation details from clients of the class 3
4 3. Objects, standard input, arrays (19 points). Consider the following class that represents a charged particle: public class Charge private double rx, ry; private double q; // position // charge public Charge(double x0, double y0, double q0) double rx = x0; double ry = y0; double q = q0; a) What is wrong with the above code? By declaring the type of the rx, ry, and q variables in the Charge constructor, we have created local instances with the same name as the instance variables. Thus the instance variables are not set by the constructor. This can be fixed by removing the double before each variable assignment statement. b) Assume you fixed the problem in part a. You are now developing a client program that reads via standard input a list of charged particles. Here is an example file 3charge.txt with a positively charged particle at (0.5, 0.7), a neutral particle at (1.0, 0.1), and a negative particle at (- 2.25, ): For now, the program just reads and stores all the charged particles in an array. Below is the skeleton of the client program. In the empty boxes, write the letter of the code fragments that combine to create a correct implementation. Not all letters will be used and each letter can only be used once. public class ChargeClient public static void main(string [] args) D = StdIn.readInt(); Charge [] particles = F ; Q ( A = 0; i < N; i++) double x = StdIn.readDouble(); double y = StdIn.readDouble(); double q = L ; particles[i] = I ; (continued on next page) 4 A. int i B. final int i C. String N D. final int N E. Charge[N] F. new Charge[N] G. new Charge() H. new Charge(N) I. new Charge(x, y, q) J. Charge(x, y, q) K. StdIn.readInt() L. StdIn.readDouble() M.!StdIn.isEmpty() N. Double.parseDouble(args[0]) O. Double.parseDouble(args[1]) P. while Q. for R. do while S. null
5 3. Objects, standard input, arrays (continued) c) In an effort to test your program from part b, you added the following line of code to the end of the loop: System.out.println(particles[i]); Unfortunately, you are getting strange looking output. Here is an example run using the example input file: % java ChargeClient < 3charge.txt Charge@128ef465 Charge@674f1c67 Charge@7ad1e32d What is the name of method you need to implement to get the above System.out.println to produce more sensible output? tostring() What class should this method be added to? Charge d) Match the description on the left with the signature of an instance method of Charge that would best provide the stated functionality. Each letter will be used exactly once. Return the net force exhibited on a given particle by a list of zero or more other particles. Return a new particle that has the same location and charge of an existing particle. Return a new particle that has a location and charge that is the average of two existing particles. Return a new particle with some default location and charge. Return the Euclidean distance between two particles. E G H F D A. public boolean foo1() B. public boolean foo2(double a) C. public boolean foo3(charge a) D. public double foo4(charge a) E. public double foo5(charge [] a) F. public Charge() G. public Charge(Charge a) H. public Charge(Charge a, Charge b) Determine whether two particles have the same charge. C Determine whether a particle is negatively charged. Determine whether a particle's position is within a given radius of the origin. A B 5
6 4. Static methods (16 points). Consider the following library containing a number of static methods: public class NumHelpers public static int foo(int a, int b) a = a + b; return a; public static boolean foo(int n) return (n % 2 == 0); public static int foo(int a, int b, int c) return Math.max(a, Math.max(b, c)); public static int foo(int target, int [] vals) int result = 0; for (int i = 0; i < vals.length; i++) if (vals[i] == target) result++; System.out.printf("TRACE %d %d %d %d\n", i, vals[i], target, result); return result; a) Assume you are developing code a program Calculator.java that makes use of the NumHelpers library. Mark whether each of the following lines is valid (i.e. compiles) or invalid (i.e. causes a compile error). Code Valid Invalid boolean r1 = NumHelpers.foo(20); boolean r2 = foo(20); int r3 = NumHelpers.foo(10.0, 20.0); boolean r4 = (NumHelpers.foo(- 5, 23, 928) > 5.0); int r5 = NumHelpers.foo(Integer.parseInt("2"), Integer.parseInt("3")); int r6 = NumHelpers.foo(1, 2, 3, 4); (continued on next page) 6
7 4. Static methods (continued) b) For each of methods in NumHelpers implemented on the previous page, briefly describe what it does (i.e. given its input what does the output of the method represent). public static int foo(int a, int b) Adds a and b and returns the sum public static boolean foo(int n) Determines if n is an even number public static int foo(int a, int b, int c) Returns the maximum of the three numbers a, b and c public static int foo(int target, int [] vals) Counts the number of items in the vals array that are equal to the target value c) The following code fragment makes use of the first method in NumHelpers. What does it output? int a = 5; int b = NumHelpers.foo(1, 2); System.out.println("a = " + a + ", b = " + b); "a = 5, b = 3" d) The following code fragment makes use of the last method in NumHelpers. Fill in the table giving the values output by the TRACE System.out.printf statement in the method (you may not need all rows). As the printf outputs 4 values, fill out the table cells showing these values for each loop iteration on the given input. int [] data = 1, 4, 8, 4; NumHelpers.foo(4, data); TRACE TRACE TRACE TRACE TRACE TRACE 7
8 5. Recursive drawing (10 points). Label each StdDraw output with the letter of the recursive method that generated it, each image was generated by exactly one of the methods. Each method was initially called with the same parameters: draw(n, 0.5, 0.5, 0.25); One of the recursive methods generates a stack overflow due to unbounded recursion, circle this method. _A D B C_ static void drawa(int n, double x, double y, double s) if (n <= 0) return; if (n % 2 == 0) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED); StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLUE); StdDraw.filledSquare(x, y, s); drawa(n - 1, x - s, y - s, s / 2.0); drawa(n - 1, x + s, y - s, s / 2.0); static void drawb(int n, double x, double y, double s) if (n % 2 == 0) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED); StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLUE); StdDraw.filledSquare(x, y, s); drawb(n - 1, x - s, y + s, s / 2.0); drawb(n - 1, x + s, y + s, s / 2.0); static void drawc(int n, double x, double y, double s) if (n <= 0) return; if (n % 2 == 0) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED); StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLUE); StdDraw.filledSquare(x, y, s); drawc(n - 1, x - s, y + s, s / 2.0); drawc(n - 1, x + s, y + s, s / 2.0); drawc(n - 1, x - s, y - s, s / 2.0); drawc(n - 1, x + s, y - s, s / 2.0); static void drawd(int n, double x, double y, double s) if (n <= 0) return; if (n % 2 == 0) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED); StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLUE); StdDraw.filledSquare(x, y, s); drawd(n - 1, x - s, y + s, s / 4.0); drawd(n - 1, x + s, y + s, s / 2.0); 8
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012
 CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014
 CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014 Name: This exam consists of 8 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2014 Name: This exam consists of 8 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-sided handwritten 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-sided handwritten 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-side hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-side hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011
 CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011 Name: This exam consists of 12 problems on the following 11 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011 Name: This exam consists of 12 problems on the following 11 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. February 29, 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
More on inheritance CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014
 More on inheritance CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Object hierarchies Overview Several classes inheriting from same base class Concrete versus abstract classes
More on inheritance CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Object hierarchies Overview Several classes inheriting from same base class Concrete versus abstract classes
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2012
 Name:!! Login ID:!!! Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2012 is test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. e exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page single-sided
Name:!! Login ID:!!! Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2012 is test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. e exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page single-sided
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
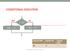 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Question: Total Points: Score:
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 001 Fall 2014 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 001 Fall 2014 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2014
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2014 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2014 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CIS Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key. Miscellaneous
 CIS 110-001 1 CIS 110-001 Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
CIS 110-001 1 CIS 110-001 Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
Selected Questions from by Nageshwara Rao
 Selected Questions from http://way2java.com by Nageshwara Rao Swaminathan J Amrita University swaminathanj@am.amrita.edu November 24, 2016 Swaminathan J (Amrita University) way2java.com (Nageshwara Rao)
Selected Questions from http://way2java.com by Nageshwara Rao Swaminathan J Amrita University swaminathanj@am.amrita.edu November 24, 2016 Swaminathan J (Amrita University) way2java.com (Nageshwara Rao)
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2011
 NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2011 This test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2011 This test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
Birkbeck (University of London) Software and Programming 1 In-class Test Mar 2018
 Birkbeck (University of London) Software and Programming 1 In-class Test 2.1 22 Mar 2018 Student Name Student Number Answer ALL Questions 1. What output is produced when the following Java program fragment
Birkbeck (University of London) Software and Programming 1 In-class Test 2.1 22 Mar 2018 Student Name Student Number Answer ALL Questions 1. What output is produced when the following Java program fragment
CIS Introduction to Computer Programming. 5 October 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110-001 Introduction to Computer Programming 5 October 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110-001 Introduction to Computer Programming 5 October 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I
 Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science. Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007 Supplementary Examination Question
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007 Supplementary Examination Question
More on methods and variables. Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen
 More on methods and variables Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Terminology of a method Goal: helper method than can draw a random integer between start and end (inclusive) access modifier
More on methods and variables Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Terminology of a method Goal: helper method than can draw a random integer between start and end (inclusive) access modifier
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming. February 29, 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CSCI 135 Final Fall Problem Points Score Total 100
 CSCI 135 Final Fall 2011 Name: This exams consists of 11 problems on the following 14 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam. No calculators, computers, or
CSCI 135 Final Fall 2011 Name: This exams consists of 11 problems on the following 14 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam. No calculators, computers, or
CS 113 PRACTICE FINAL
 CS 113 PRACTICE FINAL There are 13 questions on this test. The value of each question is: 1-10 multiple choice (4 pt) 11-13 coding problems (20 pt) You may get partial credit for questions 11-13. If you
CS 113 PRACTICE FINAL There are 13 questions on this test. The value of each question is: 1-10 multiple choice (4 pt) 11-13 coding problems (20 pt) You may get partial credit for questions 11-13. If you
I pledge by honor that I will not discuss this exam with anyone until my instructor reviews the exam in the class.
 Name: Covers Chapters 1-3 50 mins CSCI 1301 Introduction to Programming Armstrong Atlantic State University Instructor: Dr. Y. Daniel Liang I pledge by honor that I will not discuss this exam with anyone
Name: Covers Chapters 1-3 50 mins CSCI 1301 Introduction to Programming Armstrong Atlantic State University Instructor: Dr. Y. Daniel Liang I pledge by honor that I will not discuss this exam with anyone
CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall Exam 1
 COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2005 Exam 1 This test has 9 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2005 Exam 1 This test has 9 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
Arrays. COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science. Christopher Conway 10 June 2003
 Arrays COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 10 June 2003 Arrays An array is a list of values. In Java, the components of an array can be of any type, basic or object. An array
Arrays COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 10 June 2003 Arrays An array is a list of values. In Java, the components of an array can be of any type, basic or object. An array
10. Creating Data Types
 COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 10. Creating Data Types Section 3.2 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 10. Creating Data Types Overview Point
COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 10. Creating Data Types Section 3.2 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E 10. Creating Data Types Overview Point
CS101 Part 2: Practice Questions Algorithms on Arrays, Classes and Objects, String Class, Stack Class
 CS1 Part 2: Algorithms on Arrays, Classes and Objects, String Class, Stack Class 1. Write a method that, given two sorted arrays of integers, merges the two arrays into a single sorted array that is returned.
CS1 Part 2: Algorithms on Arrays, Classes and Objects, String Class, Stack Class 1. Write a method that, given two sorted arrays of integers, merges the two arrays into a single sorted array that is returned.
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1
 McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
Chapter 6 Introduction to Defining Classes
 Introduction to Defining Classes Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives Design and implement a simple class from user requirements. Organize a program in terms of
Introduction to Defining Classes Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives Design and implement a simple class from user requirements. Organize a program in terms of
University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science. Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007 Final Examination Question Max
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007 Final Examination Question Max
CSE 131 Introduction to Computer Science Fall Exam II
 CSE 131 Introduction to Computer Science Fall 2013 Given: 6 November 2013 Exam II Due: End of session This exam is closed-book, closed-notes, no electronic devices allowed. The exception is the cheat sheet
CSE 131 Introduction to Computer Science Fall 2013 Given: 6 November 2013 Exam II Due: End of session This exam is closed-book, closed-notes, no electronic devices allowed. The exception is the cheat sheet
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Final Exam Solution
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Final Exam Solution
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Final Exam Solution
About this exam review
 Final Exam Review About this exam review I ve prepared an outline of the material covered in class May not be totally complete! Exam may ask about things that were covered in class but not in this review
Final Exam Review About this exam review I ve prepared an outline of the material covered in class May not be totally complete! Exam may ask about things that were covered in class but not in this review
3.2 Creating Data Types
 1 3.2 Creating Data Types Data Types Data type. Set of values and operations on those values. Basic types. Data Type boolean int String Set of Values true, false -2 31 to 2 31-1 sequence of Unicode characters
1 3.2 Creating Data Types Data Types Data type. Set of values and operations on those values. Basic types. Data Type boolean int String Set of Values true, false -2 31 to 2 31-1 sequence of Unicode characters
COMP 401 Spring 2014 Midterm 1
 COMP 401 Spring 2014 Midterm 1 I have not received nor given any unauthorized assistance in completing this exam. Signature: Name: PID: Please be sure to put your PID at the top of each page. This page
COMP 401 Spring 2014 Midterm 1 I have not received nor given any unauthorized assistance in completing this exam. Signature: Name: PID: Please be sure to put your PID at the top of each page. This page
Questions Answer Key Questions Answer Key Questions Answer Key
 Benha University Term: 2 nd (2013/2014) Class: 2 nd Year Students Subject: Object Oriented Programming Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: 26/4/2014 Time: 1 hours Exam: Mid-Term (A) Name:. Status:
Benha University Term: 2 nd (2013/2014) Class: 2 nd Year Students Subject: Object Oriented Programming Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: 26/4/2014 Time: 1 hours Exam: Mid-Term (A) Name:. Status:
Summer Session 2004 Prelim I July 12, CUID: NetID:
 COM S / ENGRD 211 Computers and Programming Summer Session 2004 Prelim I July 12, 2004 Name: CUID: NetID: You have one hour and fifteen minutes to do this exam. All programs must be written in Java. Where
COM S / ENGRD 211 Computers and Programming Summer Session 2004 Prelim I July 12, 2004 Name: CUID: NetID: You have one hour and fifteen minutes to do this exam. All programs must be written in Java. Where
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java 1. Q: When you compile your program, you receive an error as follows: 2. 3. %javac Welcome.java 4. javac not found 5. 6. What is wrong? 7. A: Two
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java 1. Q: When you compile your program, you receive an error as follows: 2. 3. %javac Welcome.java 4. javac not found 5. 6. What is wrong? 7. A: Two
Final Exam CS 152, Computer Programming Fundamentals December 5, 2014
 Final Exam CS 152, Computer Programming Fundamentals December 5, 2014 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
Final Exam CS 152, Computer Programming Fundamentals December 5, 2014 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
COMP 401 Spring 2013 Midterm 1
 COMP 401 Spring 2013 Midterm 1 I have not received nor given any unauthorized assistance in completing this exam. Signature: Name: PID: Please be sure to put your PID at the top of each page. This page
COMP 401 Spring 2013 Midterm 1 I have not received nor given any unauthorized assistance in completing this exam. Signature: Name: PID: Please be sure to put your PID at the top of each page. This page
CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2010 Sample mid-term exam Answer key
 Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2010 Sample mid-term exam Answer key 1. [Question:] (15 points) Consider the code fragment below. Mark each location where an automatic cast will occur. Also find
Introduction to Computer Science I Spring 2010 Sample mid-term exam Answer key 1. [Question:] (15 points) Consider the code fragment below. Mark each location where an automatic cast will occur. Also find
CMPS 12A Winter 2006 Prof. Scott A. Brandt Final Exam, March 21, Name:
 CMPS 12A Winter 2006 Prof. Scott A. Brandt Final Exam, March 21, 2006 Name: Email: This is a closed note, closed book exam. There are II sections worth a total of 200 points. Plan your time accordingly.
CMPS 12A Winter 2006 Prof. Scott A. Brandt Final Exam, March 21, 2006 Name: Email: This is a closed note, closed book exam. There are II sections worth a total of 200 points. Plan your time accordingly.
CSE 11 Midterm Fall 2012
 Signature cs11f Name Student ID CSE 11 Midterm Fall 2012 Page 1 (20 points) Page 2 (17 points) Page 3 (31 points) Page 4 (15 points) Page 5 (8 points) Page 6 (20 points) Total (111 points = 105 base points
Signature cs11f Name Student ID CSE 11 Midterm Fall 2012 Page 1 (20 points) Page 2 (17 points) Page 3 (31 points) Page 4 (15 points) Page 5 (8 points) Page 6 (20 points) Total (111 points = 105 base points
Computer Science. 9. Creating Data Types. Computer Science COMPUTER SCIENCE. Section 3.2.
 COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E PA R T I : P R O G R A M M I N G I N J AVA Computer Science Computer Science An Interdisciplinary Approach Section 3.2 ROBERT SEDGEWICK K E V I N WAY N E
COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E PA R T I : P R O G R A M M I N G I N J AVA Computer Science Computer Science An Interdisciplinary Approach Section 3.2 ROBERT SEDGEWICK K E V I N WAY N E
CS 113 MIDTERM EXAM 2 SPRING 2013
 CS 113 MIDTERM EXAM 2 SPRING 2013 There are 18 questions on this test. The value of each question is: 1-15 multiple choice (3 pts) 17 coding problem (15 pts) 16, 18 coding problems (20 pts) You may get
CS 113 MIDTERM EXAM 2 SPRING 2013 There are 18 questions on this test. The value of each question is: 1-15 multiple choice (3 pts) 17 coding problem (15 pts) 16, 18 coding problems (20 pts) You may get
Java Object Oriented Design. CSC207 Fall 2014
 Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!)
 CS 161 Exam 2: FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!) True (A)/False(B) (2 pts each): 1. Recursive algorithms tend to be less efficient than iterative algorithms. 2. A recursive function
CS 161 Exam 2: FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!) True (A)/False(B) (2 pts each): 1. Recursive algorithms tend to be less efficient than iterative algorithms. 2. A recursive function
Computer Science E-119 Fall Problem Set 1. Due before lecture on Wednesday, September 26
 Due before lecture on Wednesday, September 26 Getting Started Before starting this assignment, make sure that you have completed Problem Set 0, which can be found on the assignments page of the course
Due before lecture on Wednesday, September 26 Getting Started Before starting this assignment, make sure that you have completed Problem Set 0, which can be found on the assignments page of the course
1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4'
 Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2013
 NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2013 qüáë= íéëí= Ü~ë= U= èìéëíáçåëi= ïéáöüíéç= ~ë= áåçáå~íéçk= qüé= Éñ~ã= áë= ÅäçëÉÇ= ÄççâI=ÉñÅÉéí=íÜ~í= óçì= ~êé= ~ääçïéç= íç= ìëé= ~= çåé=
NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2013 qüáë= íéëí= Ü~ë= U= èìéëíáçåëi= ïéáöüíéç= ~ë= áåçáå~íéçk= qüé= Éñ~ã= áë= ÅäçëÉÇ= ÄççâI=ÉñÅÉéí=íÜ~í= óçì= ~êé= ~ääçïéç= íç= ìëé= ~= çåé=
Final Exam Practice. Partial credit will be awarded.
 Please note that this problem set is intended for practice, and does not fully represent the entire scope covered in the final exam, neither the range of the types of problems that may be included in the
Please note that this problem set is intended for practice, and does not fully represent the entire scope covered in the final exam, neither the range of the types of problems that may be included in the
10. Creating Data Types
 Overview Point charges Turtle graphics Complex numbers Section 3.2 Object-oriented programming (OOP) Implementing a data type Object-oriented programming (OOP). To create a data type, you need provide
Overview Point charges Turtle graphics Complex numbers Section 3.2 Object-oriented programming (OOP) Implementing a data type Object-oriented programming (OOP). To create a data type, you need provide
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall Exam 1
 COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2008 Exam 1 This test has 11 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2008 Exam 1 This test has 11 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2014!
 NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2014 This test has 9 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2014 This test has 9 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
CO Java SE 8: Fundamentals
 CO-83527 Java SE 8: Fundamentals Summary Duration 5 Days Audience Application Developer, Developer, Project Manager, Systems Administrator, Technical Administrator, Technical Consultant and Web Administrator
CO-83527 Java SE 8: Fundamentals Summary Duration 5 Days Audience Application Developer, Developer, Project Manager, Systems Administrator, Technical Administrator, Technical Consultant and Web Administrator
CSCI 201L Written Exam #1 - SOLUTION Fall % of course grade
 CSCI 201L Written Exam #1 - SOLUTION Fall 2016 10% of course grade The exam is closed book, closed note, but one 8.5 x11 double-sided paper of handwritten notes is allowed. One hour and 50 minutes will
CSCI 201L Written Exam #1 - SOLUTION Fall 2016 10% of course grade The exam is closed book, closed note, but one 8.5 x11 double-sided paper of handwritten notes is allowed. One hour and 50 minutes will
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Lecture 3 Fall 2017 Instructors: Bill & Bill
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 3 Fall 2017 Instructors: Bill & Bill Administrative Details Lab today in TCL 216 (217a is available, too) Lab is due by 11pm Sunday Copy your folder
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 3 Fall 2017 Instructors: Bill & Bill Administrative Details Lab today in TCL 216 (217a is available, too) Lab is due by 11pm Sunday Copy your folder
CS 307 Midterm 1 Spring 2009
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Spring 2009 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Todd Guhan Xiuming(aka David) Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell phones.
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Spring 2009 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Todd Guhan Xiuming(aka David) Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell phones.
CMPS 134: Computer Science I Fall 2011 Test #1 October 5 Name Dr. McCloskey
 CMPS 134: Computer Science I Fall 2011 Test #1 October 5 Name Dr. McCloskey 1. For each statement, circle the response (or write its letter on the underscore) that best completes that statement. (i) is
CMPS 134: Computer Science I Fall 2011 Test #1 October 5 Name Dr. McCloskey 1. For each statement, circle the response (or write its letter on the underscore) that best completes that statement. (i) is
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide
 AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
Place your name tag here
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 001 Spring 2015 Name: Place your name tag here Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 001 Spring 2015 Name: Place your name tag here Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with
Static methods. Not actually a valid Java static method. Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen
 Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
Announcements. PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6. Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am
 Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
Object Oriented Modeling
 Object Oriented Modeling Object oriented modeling is a method that models the characteristics of real or abstract objects from application domain using classes and objects. Objects Software objects are
Object Oriented Modeling Object oriented modeling is a method that models the characteristics of real or abstract objects from application domain using classes and objects. Objects Software objects are
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 CI101 / CI177. Programming
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 CI101 / CI177 Programming Time allowed: THREE hours: Answer: ALL questions Items permitted: Items supplied: There is
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 CI101 / CI177 Programming Time allowed: THREE hours: Answer: ALL questions Items permitted: Items supplied: There is
Midterm I - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total.
 Midterm I - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total. Name: ID: Problem 1) (8 points) For the following code segment, what are the values of i, j, k, and d, after the segment
Midterm I - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total. Name: ID: Problem 1) (8 points) For the following code segment, what are the values of i, j, k, and d, after the segment
Exam Duration: 2hrs and 30min Software Design
 Exam Duration: 2hrs and 30min. 433-254 Software Design Section A Multiple Choice (This sample paper has less questions than the exam paper The exam paper will have 25 Multiple Choice questions.) 1. Which
Exam Duration: 2hrs and 30min. 433-254 Software Design Section A Multiple Choice (This sample paper has less questions than the exam paper The exam paper will have 25 Multiple Choice questions.) 1. Which
Final Exam COMP Fall 2004 Dec 16, 2004
 1. Closed book and closed notes. Final Exam COMP 14-062 Fall 2004 Dec 16, 2004 2. Write all scratch work and answers on the exam itself. If you need extra space, let me know. Indicate your final answer
1. Closed book and closed notes. Final Exam COMP 14-062 Fall 2004 Dec 16, 2004 2. Write all scratch work and answers on the exam itself. If you need extra space, let me know. Indicate your final answer
Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Prelim 1. CS 2110, October 1, 2015, 5:30 PM Total Question Name True Short Testing Strings Recursion
 Prelim 1 CS 2110, October 1, 2015, 5:30 PM 0 1 2 3 4 5 Total Question Name True Short Testing Strings Recursion False Answer Max 1 20 36 16 15 12 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes.
Prelim 1 CS 2110, October 1, 2015, 5:30 PM 0 1 2 3 4 5 Total Question Name True Short Testing Strings Recursion False Answer Max 1 20 36 16 15 12 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes.
CMP 326 Midterm Fall 2015
 CMP 326 Midterm Fall 2015 Name: 1) (30 points; 5 points each) Write the output of each piece of code. If the code gives an error, write any output that would happen before the error, and then write ERROR.
CMP 326 Midterm Fall 2015 Name: 1) (30 points; 5 points each) Write the output of each piece of code. If the code gives an error, write any output that would happen before the error, and then write ERROR.
ECE264 Fall 2013 Exam 1, September 24, 2013
 ECE264 Fall 2013 Exam 1, September 24, 2013 In signing this statement, I hereby certify that the work on this exam is my own and that I have not copied the work of any other student while completing it.
ECE264 Fall 2013 Exam 1, September 24, 2013 In signing this statement, I hereby certify that the work on this exam is my own and that I have not copied the work of any other student while completing it.
Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue
 Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue General Loops in Java Look at other loop constructions Very common while loop: do a loop a fixed number of times (MAX in the example) int
Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue General Loops in Java Look at other loop constructions Very common while loop: do a loop a fixed number of times (MAX in the example) int
Midterm Exam CS 251, Intermediate Programming October 8, 2014
 Midterm Exam CS 251, Intermediate Programming October 8, 2014 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
Midterm Exam CS 251, Intermediate Programming October 8, 2014 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
MACS 261J Final Exam. Question: Total Points: Score:
 MACS 261J Final Exam May 5, 2008 Name: Question: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Total Points: 15 10 15 5 10 5 20 8 12 100 Score: Question 1............................................................. (15 points) (a)
MACS 261J Final Exam May 5, 2008 Name: Question: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Total Points: 15 10 15 5 10 5 20 8 12 100 Score: Question 1............................................................. (15 points) (a)
CMPS 12A - Winter 2002 Midterm 2 March 5, Name: ID:
 CMPS 12A - Winter 2002 Midterm 2 March 5, 2002 Name: ID: This is a closed note, closed book exam. Any place where you are asked to write code, you must declare all variables that you use. However, I just
CMPS 12A - Winter 2002 Midterm 2 March 5, 2002 Name: ID: This is a closed note, closed book exam. Any place where you are asked to write code, you must declare all variables that you use. However, I just
Final Exam. COMP Summer I June 26, points
 Final Exam COMP 14-090 Summer I 2000 June 26, 2000 200 points 1. Closed book and closed notes. No outside material allowed. 2. Write all answers on the test itself. Do not write any answers in a blue book
Final Exam COMP 14-090 Summer I 2000 June 26, 2000 200 points 1. Closed book and closed notes. No outside material allowed. 2. Write all answers on the test itself. Do not write any answers in a blue book
CIS 120 Midterm II November 8, Name (printed): Pennkey (login id):
 CIS 120 Midterm II November 8, 2013 Name (printed): Pennkey (login id): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic Integrity in completing
CIS 120 Midterm II November 8, 2013 Name (printed): Pennkey (login id): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic Integrity in completing
Question: Total Points: Score:
 CS 170 Exam 2 Section 001 Fall 2014 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 2 Section 001 Fall 2014 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 1331 Exam 1 ANSWER KEY
 CS 1331 Exam 1 Fall 2016 ANSWER KEY Failure to properly fill in the information on this page will result in a deduction of up to 5 points from your exam score. Signing signifies you are aware of and in
CS 1331 Exam 1 Fall 2016 ANSWER KEY Failure to properly fill in the information on this page will result in a deduction of up to 5 points from your exam score. Signing signifies you are aware of and in
CSCI 355 Lab #2 Spring 2007
 CSCI 355 Lab #2 Spring 2007 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
CSCI 355 Lab #2 Spring 2007 More Java Objectives: 1. To explore several Unix commands for displaying information about processes. 2. To explore some differences between Java and C++. 3. To write Java applications
CSI 1100 / 1500 Fall 2004 Introduction to Computer Science I Final Examination
 CSI 1100 / 1500 Final Examination Page 1 of 13 CSI 1100 / 1500 Fall 2004 Introduction to Computer Science I Final Examination Duration : 3 hours 09:30 December 9, 2004 Professors: Alan Williams, Daniel
CSI 1100 / 1500 Final Examination Page 1 of 13 CSI 1100 / 1500 Fall 2004 Introduction to Computer Science I Final Examination Duration : 3 hours 09:30 December 9, 2004 Professors: Alan Williams, Daniel
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Lecture 3 Fall 2018 Instructors: Bill & Bill
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 3 Fall 2018 Instructors: Bill & Bill Administrative Details Lab today in TCL 217a (and 216) Lab is due by 11pm Sunday Lab 1 design doc is due at
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 3 Fall 2018 Instructors: Bill & Bill Administrative Details Lab today in TCL 217a (and 216) Lab is due by 11pm Sunday Lab 1 design doc is due at
3. Convert 2E from hexadecimal to decimal. 4. Convert from binary to hexadecimal
 APCS A Midterm Review You will have a copy of the one page Java Quick Reference sheet. This is the same reference that will be available to you when you take the AP Computer Science exam. 1. n bits can
APCS A Midterm Review You will have a copy of the one page Java Quick Reference sheet. This is the same reference that will be available to you when you take the AP Computer Science exam. 1. n bits can
CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016
![CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016 CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016](/thumbs/77/76167327.jpg) Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016 There are 5 problems on the exam, with 56 points total available. There are 10 pages to the exam (5 pages
Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016 There are 5 problems on the exam, with 56 points total available. There are 10 pages to the exam (5 pages
Midterm Exam CS 251, Intermediate Programming March 12, 2014
 Midterm Exam CS 251, Intermediate Programming March 12, 2014 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
Midterm Exam CS 251, Intermediate Programming March 12, 2014 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
