ECE 645: Lecture 1. Basic Adders and Counters. Implementation of Adders in FPGAs
|
|
|
- Evan Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECE 645: Lecture Basic Adders and Counters Implementation of Adders in FPGAs
2 Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 5, Basic Addition and Counting, Sections , pp
3 Required Reading Spartan-3 Generation FPGA User Guide Chapter 9, Using Carry and Arithmetic Logic
4 Half-adder c s HA x y 2 x + y = ( c s ) 2 x y c s
5 Half-adder Alternative implementations () a) c = xy s = x y b) c = x + y s = xy + xy
6 Half-adder Alternative implementations (2) c) c = xy s = xc + yc = xc yc
7 Full-adder x y c out s FA x + y + c in = ( c out s ) 2 2 x y c out s c in c in
8 a) Full-adder Alternative implementations (2) c out = xy + xc in + yc in s = x y c in = xyc in + xyc in + xyc in + xyc in
9 Full-adder Alternative implementations () b) s = (x y) c in c out = xy + c in (x y) c c s
10 Full-adder Alternative implementations (3) c) x y c out s c in c in c in c in c in c in
11 Full-adder Alternative implementations (4) Implementation used to generate fast carry logic in Xilinx FPGAs x y c out y c in c in y p = x y g = y x y A2 A XOR D p g C out C in S s= p c in = x y c in
12
13
14
15 Latency of a k-bit ripple-carry adder d RCA (k) = d FA (x,y c out ) + + (k-2) d FA (c in c out ) + + d FA (c in s) Latency = a k + b
16
17 Unsigned addition vs. signed addition weight carry + = X Y S Machine Unsigned mind Programmer Signed mind x 7 y 7 x 6 y 6 x 5 y 5 x 4 y 4 x 3 y 3 x 2 y 2 x y x y c 8 FA c 7 FA c 6 FA c 5 FA c 4 FA c 3 FA c 2 FA c FA s 7 s 6 s 5 s 4 s 3 s 2 s s
18 Out of range flags Carry flag - C out-of-range for unsigned numbers C = if result > MAX_UNSIGNED or result < otherwise where MAX_UNSIGNED = for 8-bit operands for 6-bit operands Overflow flag - V out-of-range for signed numbers V = if result > MAX_SIGNED or result < MIN_SIGNED otherwise where MAX_SIGNED = for 8-bit operands for 6-bit operands MIN_SIGNED = -2 7 for 8-bit operands -2 5 for 6-bit operands
19 Overflow for signed numbers Indication of overflow Positive + Positive = Negative Negative + Negative = Positive Formulas Overflow 2 s complement = x k- y k- s k- + x k- y k- s k-
20 Addition of Signed and Unsigned Numbers C= and V= C= and V=
21 Addition of Signed and Unsigned Numbers C= and V= C= and V=
22 Two s complement representation of signed integers
23
24 Overflow for signed numbers () Indication of overflow Positive + Positive = Negative Negative + Negative = Positive Formulas Overflow 2 s complement = x k- y k- s k- + x k- y k- s k- = = c k c k-
25 Overflow for signed numbers (2) x k- y k- c k- c k s k- overflow c k c k-
26 Implementation of Adders in FPGAs
27 Xilinx FPGA Devices Technology Low- cost High- performance 22 nm Spartan II Virtex 2/5 nm Virtex II, II Pro 9 nm Spartan 3 Virtex 4 65 nm Virtex 5 45 nm Spartan 6 4 nm Virtex 6 28 nm Ar<x 7 Virtex 7
28 Altera FPGA Devices Technology Low- cost Mid- range High- performance 3 nm Cyclone Stra<x 9 nm Cyclone II Stra<x II 65 nm Cyclone III Arria I Stra<x III 4 nm Cyclone IV Arria II Stra<x IV 28 nm Cyclone V Arria V Stra<x V
29 General structure of an FPGA Programmable interconnect Programmable logic blocks The Design Warrior s Guide to FPGAs Devices, Tools, and Flows. ISBN Copyright 24 Mentor Graphics Corp. ( 29
30 3
31 Xilinx Spartan 3 FPGAs Configurable logic block (CLB) Slice Slice CLB CLB Logic cell Logic cell Logic cell Logic cell Slice Slice CLB CLB Logic cell Logic cell Logic cell Logic cell The Design Warrior s Guide to FPGAs Devices, Tools, and Flows. ISBN Copyright 24 Mentor Graphics Corp. ( 3
32 CLB Slice Structure Each slice contains two sets of the following: Four-input LUT Any 4-input logic function, or 6-bit x sync RAM (SLICEM only) or 6-bit shift register (SLICEM only) Carry & Control Fast arithmetic logic Multiplier logic Multiplexer logic Storage element Latch or flip-flop Set and reset True or inverted inputs Sync. or async. control 32
33 33 COUT D Q CK S R EC D Q CK R EC O G4 G3 G2 G Look-Up Table Carry & Control Logic O YB Y F4 F3 F2 F XB X Look-Up Table F5IN BY SR S Carry & Control Logic CIN CLK CE SLICE Carry & Control Logic
34 Carry & Control Logic in Xilinx FPGAs x y COUT y CIN CIN y x y Propagate = x y Generate = y Sum= Propagate CIN = x y CIN
35 Carry & Control Logic in Spartan 3 FPGAs x y LUT Hardwired (fast) logic
36 x y Simplified View of Spartan-3 FPGA Carry and Arithmetic Logic in One Logic Cell
37 Simplified View of Carry Logic in One Spartan 3 Slice
38
39 Critical Path for an Adder Implemented Using Xilinx Spartan 3 FPGAs
40 Number and Length of Carry Chains for Spartan 3 FPGAs
41 Bottom Operand Input to Carry Out Delay T OPCYF.9 ns for Spartan 3
42 .2 ns for Spartan 3 Carry Propagation Delay t BYP
43 Carry Input to Top Sum Combinational Output Delay T CINY.2 ns for Spartan 3
44 Critical Path Delays and Maximum Clock Frequencies (taking into account surrounding registers)
45 Major Differences between Xilinx Families Look-Up Tables Spartan 3 Virtex 4 4-input Virtex 5, Virtex 6, Spartan 6 6-input Number of CLB slices per CLB Number of LUTs per CLB slice Number of adder stages per CLB slice
46 Altera Cyclone III Logic Element (LE) Normal Mode
47 Altera Cyclone III Logic Element (LE) Arithmetic Mode
48 Altera Stratix III, Stratix IV Adaptive Logic Modules (ALM) Normal Mode
49 Altera Stratix III, Stratix IV Adaptive Logic Modules (ALM) Arithmetic Mode
50 Addition of a Constant
51 Addition of a constant () + x k- x k-2... x x y k- y k-2... y y s k- s k-2... s s variable constant + x k- x k-2... x h+ x h x h-... x y k- y k-2... y h+... variable constant s k- s k-2... s h+ x h x h-... x
52 Addition of a constant (2) x k- x k-2... x h+2 x h+ x h x h-... x c k HA/ MHA HA/ MHA.. HA/ MHA HA/ MHA... s k- s k s h+2 s h+ x h x h- x If y i = y i = Half-adder (HA) Modified half-adder (MHA)
53 Modified half-adder c s MHA x y 2 x + y + = ( c s ) 2 x y c s
54 Incrementer x k- x k-2... x 2 x x c k HA HA.. HA HA Decrementer s k- s k-2... s 2 s x x k- x k-2... x 2 x x c k MHA MHA.. MHA MHA s k- s k-2... s 2 s x
55
56
57 Bit-Serial & Digit-Serial Adders
58
59 x i y i c i+ Bit-serial adder c start clk s i
60 x i y i d d c i+ Digit-serial adder c start clk d s i
61 Asynchronous Adders
62 Possible solutions to the carry propagate problem. Detect the end of propagation rather than wait for the worst-case time 2. Speed-up propagation via look-ahead carry skip carry select, etc 3. Limit carry propagation to within a small number of bits 4. Eliminate carry propagation through the redundant number representation
63
64 Analysis of carry propagation Probability of carry generation = (x i y i = ) 4 Probability of carry propagation = (x i y i = or ) 2 Probability of carry anihilation = (x i y i = or ) 2 j j i+ i or or Probability of carry propagating from position i to position j = 2 j i probability of propagation 2 = probability of anihilation 2 j i
65 Expected length of the carry chain that starts at position i () Expected length(i, k) = j k = i ( j + i) 2 j i + ( k i) 2 k i Length of the carry chain Probability of the given length Distance till the end of adder Probability of propagation till the end of adder
66 Expected length of the carry chain that starts at position i (2) Expected length(i, k) = 2 2 ( k i ) For i << k Expected length of the carry propagation is 2
Lecture 3: Basic Adders and Counters
 Lecture 3: Basic Adders and Counters ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic /5/8 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Revisiting Addition and Overflow Rounding Techniques Basic Adders and Counters Required
Lecture 3: Basic Adders and Counters ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic /5/8 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Revisiting Addition and Overflow Rounding Techniques Basic Adders and Counters Required
ECE 545 Lecture 12. FPGA Resources. George Mason University
 ECE 545 Lecture 2 FPGA Resources George Mason University Recommended reading 7 Series FPGAs Configurable Logic Block: User Guide Overview Functional Details 2 What is an FPGA? Configurable Logic Blocks
ECE 545 Lecture 2 FPGA Resources George Mason University Recommended reading 7 Series FPGAs Configurable Logic Block: User Guide Overview Functional Details 2 What is an FPGA? Configurable Logic Blocks
INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE
 3/3/25 INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN (BASIC TECHNIQUES) a b a y 2input Black Box y b Functional Schematic a b y a b y a b y 2 Truth Table (AND) Truth Table (OR) Truth Table (XOR)
3/3/25 INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN (BASIC TECHNIQUES) a b a y 2input Black Box y b Functional Schematic a b y a b y a b y 2 Truth Table (AND) Truth Table (OR) Truth Table (XOR)
ECE 448 Lecture 5. FPGA Devices
 ECE 448 Lecture 5 FPGA Devices George Mason University Required reading Spartan-6 FPGA Configurable Logic Block: User Guide CLB Overview Slice Description 2 Recommended reading Highly recommended for the
ECE 448 Lecture 5 FPGA Devices George Mason University Required reading Spartan-6 FPGA Configurable Logic Block: User Guide CLB Overview Slice Description 2 Recommended reading Highly recommended for the
Xilinx ASMBL Architecture
 FPGA Structure Xilinx ASMBL Architecture Design Flow Synthesis: HDL to FPGA primitives Translate: FPGA Primitives to FPGA Slice components Map: Packing of Slice components into Slices, placement of Slices
FPGA Structure Xilinx ASMBL Architecture Design Flow Synthesis: HDL to FPGA primitives Translate: FPGA Primitives to FPGA Slice components Map: Packing of Slice components into Slices, placement of Slices
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN
 11-1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN Purpose Extend the design of the basic four bit adder to include other arithmetic and logic functions. References Wakerly: Section 5.1 Materials Required
11-1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN Purpose Extend the design of the basic four bit adder to include other arithmetic and logic functions. References Wakerly: Section 5.1 Materials Required
Topics. Midterm Finish Chapter 7
 Lecture 9 Topics Midterm Finish Chapter 7 Xilinx FPGAs Chapter 7 Spartan 3E Architecture Source: Spartan-3E FPGA Family Datasheet CLB Configurable Logic Blocks Each CLB contains four slices Each slice
Lecture 9 Topics Midterm Finish Chapter 7 Xilinx FPGAs Chapter 7 Spartan 3E Architecture Source: Spartan-3E FPGA Family Datasheet CLB Configurable Logic Blocks Each CLB contains four slices Each slice
! Program logic functions, interconnect using SRAM. ! Advantages: ! Re-programmable; ! dynamically reconfigurable; ! uses standard processes.
 Topics! SRAM-based FPGA fabrics:! Xilinx.! Altera. SRAM-based FPGAs! Program logic functions, using SRAM.! Advantages:! Re-programmable;! dynamically reconfigurable;! uses standard processes.! isadvantages:!
Topics! SRAM-based FPGA fabrics:! Xilinx.! Altera. SRAM-based FPGAs! Program logic functions, using SRAM.! Advantages:! Re-programmable;! dynamically reconfigurable;! uses standard processes.! isadvantages:!
FPGA for Complex System Implementation. National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 04/14/2011
 FPGA for Complex System Implementation National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 04/14/2011 About FPGA FPGA was invented by Ross Freeman in 1989 SRAM-based FPGA properties Standard parts Allowing multi-level
FPGA for Complex System Implementation National Chiao Tung University Chun-Jen Tsai 04/14/2011 About FPGA FPGA was invented by Ross Freeman in 1989 SRAM-based FPGA properties Standard parts Allowing multi-level
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H ) Next: continued. Consulting hours. Introduction to Sim. Milestone #1 (due 1/26)
 Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Consulting hours Introduction to Sim Milestone #1 (due 1/26) 2 1 Overview: Integer Operations Internal representation
Lecture Topics Today: Integer Arithmetic (P&H 3.1-3.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Consulting hours Introduction to Sim Milestone #1 (due 1/26) 2 1 Overview: Integer Operations Internal representation
Topics. Midterm Finish Chapter 7
 Lecture 9 Topics Midterm Finish Chapter 7 ROM (review) Memory device in which permanent binary information is stored. Example: 32 x 8 ROM Five input lines (2 5 = 32) 32 outputs, each representing a memory
Lecture 9 Topics Midterm Finish Chapter 7 ROM (review) Memory device in which permanent binary information is stored. Example: 32 x 8 ROM Five input lines (2 5 = 32) 32 outputs, each representing a memory
FPGA architecture and design technology
 CE 435 Embedded Systems Spring 2017 FPGA architecture and design technology Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly 1 FPGA fabric A generic island-style FPGA
CE 435 Embedded Systems Spring 2017 FPGA architecture and design technology Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly 1 FPGA fabric A generic island-style FPGA
ECE 448 Lecture 5. FPGA Devices
 E 448 Lecture 5 FPGA evices E 448 FPGA and ASIC esign with VHL George Mason University Required reading 7 Series FPGAs Configurable Logic Block: User Guide Overview Functional etails 2 What is an FPGA?
E 448 Lecture 5 FPGA evices E 448 FPGA and ASIC esign with VHL George Mason University Required reading 7 Series FPGAs Configurable Logic Block: User Guide Overview Functional etails 2 What is an FPGA?
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 9: Binary Addition & Multiplication Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Pop Quiz! Using 4 bits signed integer notation:
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 9: Binary Addition & Multiplication Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Pop Quiz! Using 4 bits signed integer notation:
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Digital Logic & Computer Design CS Professor Dan Moldovan Spring 2010
 Digital Logic & Computer Design CS 434 Professor Dan Moldovan Spring 2 Copyright 27 Elsevier 5- Chapter 5 :: Digital Building Blocks Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah
Digital Logic & Computer Design CS 434 Professor Dan Moldovan Spring 2 Copyright 27 Elsevier 5- Chapter 5 :: Digital Building Blocks Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah
ECE 699: Lecture 9. Programmable Logic Memories
 ECE 699: Lecture 9 Programmable Logic Memories Recommended reading XST User Guide for Virtex-6, Spartan-6, and 7 Series Devices Chapter 7, HDL Coding Techniques Sections: RAM HDL Coding Techniques ROM
ECE 699: Lecture 9 Programmable Logic Memories Recommended reading XST User Guide for Virtex-6, Spartan-6, and 7 Series Devices Chapter 7, HDL Coding Techniques Sections: RAM HDL Coding Techniques ROM
Lecture 7. Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits. Hardware Description Language)
 Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits Hardware Description Language) 1 Standard ICs PLD: Programmable Logic Device CPLD: Complex PLD FPGA: Field Programmable
Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits Hardware Description Language) 1 Standard ICs PLD: Programmable Logic Device CPLD: Complex PLD FPGA: Field Programmable
Basic FPGA Architectures. Actel FPGAs. PLD Technologies: Antifuse. 3 Digital Systems Implementation Programmable Logic Devices
 3 Digital Systems Implementation Programmable Logic Devices Basic FPGA Architectures Why Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs)? Low cost, low risk way of implementing digital circuits as application specific
3 Digital Systems Implementation Programmable Logic Devices Basic FPGA Architectures Why Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs)? Low cost, low risk way of implementing digital circuits as application specific
Digital Circuit Design and Language. Datapath Design. Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University
 Digital Circuit Design and Language Datapath Design Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University Typical Synchronous Design + Control Section : Finite State Machine + Data Section: Adder, Multiplier, Shift Register
Digital Circuit Design and Language Datapath Design Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University Typical Synchronous Design + Control Section : Finite State Machine + Data Section: Adder, Multiplier, Shift Register
Real Digital Problem Set #6
 Real igital Problem et #6. (2 points) ketch a block diagram for a magnitude comparator bit-slice circuit. Create K-maps to define the bit-slice circuit, and use them to find optimal logic equations. ketch
Real igital Problem et #6. (2 points) ketch a block diagram for a magnitude comparator bit-slice circuit. Create K-maps to define the bit-slice circuit, and use them to find optimal logic equations. ketch
Lecture 11 Memories in Xilinx FPGAs
 Lecture 11 Memories in Xilinx FPGAs ECE 448 FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL Recommended reading XAPP463 Using Block RAM in Spartan-3 Generation FPGAs Google search: XAPP463 XAPP464 Using Look-Up Tables
Lecture 11 Memories in Xilinx FPGAs ECE 448 FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL Recommended reading XAPP463 Using Block RAM in Spartan-3 Generation FPGAs Google search: XAPP463 XAPP464 Using Look-Up Tables
Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction
 Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction Iterative combinational circuits Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple carry and carry lookahead adders Binary subtraction Binary adder-subtractors Signed binary
Chapter 3: part 3 Binary Subtraction Iterative combinational circuits Binary adders Half and full adders Ripple carry and carry lookahead adders Binary subtraction Binary adder-subtractors Signed binary
Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)
 Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Lecturer: Krébesz, Tamas 1 FPGA in general Reprogrammable Si chip Invented in 1985 by Ross Freeman (Xilinx inc.) Combines the advantages of ASIC and uc-based systems
Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Lecturer: Krébesz, Tamas 1 FPGA in general Reprogrammable Si chip Invented in 1985 by Ross Freeman (Xilinx inc.) Combines the advantages of ASIC and uc-based systems
ECE 545: Lecture 11. Programmable Logic Memories
 ECE 545: Lecture 11 Programmable Logic Memories Recommended reading Vivado Design Suite User Guide: Synthesis Chapter 4 RAM HDL Coding Techniques Initializing RAM Contents 7 Series FPGAs Memory Resources:
ECE 545: Lecture 11 Programmable Logic Memories Recommended reading Vivado Design Suite User Guide: Synthesis Chapter 4 RAM HDL Coding Techniques Initializing RAM Contents 7 Series FPGAs Memory Resources:
ECE 545: Lecture 11. Programmable Logic Memories. Recommended reading. Memory Types. Memory Types. Memory Types specific to Xilinx FPGAs
 ECE 545: Lecture 11 Programmable Logic Memories Recommended reading Vivado Design Suite User Guide: Synthesis Chapter 4 RAM HDL Coding Techniques Initializing RAM Contents 7 Series FPGAs Resources: User
ECE 545: Lecture 11 Programmable Logic Memories Recommended reading Vivado Design Suite User Guide: Synthesis Chapter 4 RAM HDL Coding Techniques Initializing RAM Contents 7 Series FPGAs Resources: User
Microcomputers. Outline. Number Systems and Digital Logic Review
 Microcomputers Number Systems and Digital Logic Review Lecture 1-1 Outline Number systems and formats Common number systems Base Conversion Integer representation Signed integer representation Binary coded
Microcomputers Number Systems and Digital Logic Review Lecture 1-1 Outline Number systems and formats Common number systems Base Conversion Integer representation Signed integer representation Binary coded
Basic FPGA Architecture Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Basic FPGA Architecture 2005 Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved Objectives After completing this module, you will be able to: Identify the basic architectural resources of the Virtex -II FPGA List the differences
Basic FPGA Architecture 2005 Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved Objectives After completing this module, you will be able to: Identify the basic architectural resources of the Virtex -II FPGA List the differences
The Virtex FPGA and Introduction to design techniques
 The Virtex FPGA and Introduction to design techniques SM098 Computation Structures Lecture 6 Simple Programmable Logic evices Programmable Array Logic (PAL) AN-OR arrays are common blocks in SPL and CPL
The Virtex FPGA and Introduction to design techniques SM098 Computation Structures Lecture 6 Simple Programmable Logic evices Programmable Array Logic (PAL) AN-OR arrays are common blocks in SPL and CPL
Programmable Logic. Simple Programmable Logic Devices
 Programmable Logic SM098 Computation Structures - Programmable Logic Simple Programmable Logic evices Programmable Array Logic (PAL) AN-OR arrays are common blocks in SPL and CPL architectures Implements
Programmable Logic SM098 Computation Structures - Programmable Logic Simple Programmable Logic evices Programmable Array Logic (PAL) AN-OR arrays are common blocks in SPL and CPL architectures Implements
ECE 545 Lecture 17 RAM. George Mason University
 ECE 545 Lecture 17 RAM George Mason University Recommended reading XST User Guide for Virtex-6, Spartan-6, and 7 Series Devices Chapter 7, HDL Coding Techniques [ UG687 (v 14.5) March 20, 2013 ] Sections:
ECE 545 Lecture 17 RAM George Mason University Recommended reading XST User Guide for Virtex-6, Spartan-6, and 7 Series Devices Chapter 7, HDL Coding Techniques [ UG687 (v 14.5) March 20, 2013 ] Sections:
UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents Memory: Introduction, Random-Access memory, Memory decoding, ROM, Programmable Logic Array, Programmable Array Logic, Sequential programmable
UNIT - V MEMORY P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents Memory: Introduction, Random-Access memory, Memory decoding, ROM, Programmable Logic Array, Programmable Array Logic, Sequential programmable
Today. Comments about assignment Max 1/T (skew = 0) Max clock skew? Comments about assignment 3 ASICs and Programmable logic Others courses
 Today Comments about assignment 3-43 Comments about assignment 3 ASICs and Programmable logic Others courses octor Per should show up in the end of the lecture Mealy machines can not be coded in a single
Today Comments about assignment 3-43 Comments about assignment 3 ASICs and Programmable logic Others courses octor Per should show up in the end of the lecture Mealy machines can not be coded in a single
Computer Architecture and Organization: L04: Micro-operations
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
Computer Architecture and Organization: L4: Micro-operations By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 Outlines 1. Arithmetic microoperation 2.
UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT
 UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
ECE 636. Reconfigurable Computing. Lecture 2. Field Programmable Gate Arrays I
 ECE 636 Reconfigurable Computing Lecture 2 Field Programmable Gate Arrays I Overview Anti-fuse and EEPROM-based devices Contemporary SRAM devices - Wiring - Embedded New trends - Single-driver wiring -
ECE 636 Reconfigurable Computing Lecture 2 Field Programmable Gate Arrays I Overview Anti-fuse and EEPROM-based devices Contemporary SRAM devices - Wiring - Embedded New trends - Single-driver wiring -
4DM4 Lab. #1 A: Introduction to VHDL and FPGAs B: An Unbuffered Crossbar Switch (posted Thursday, Sept 19, 2013)
 1 4DM4 Lab. #1 A: Introduction to VHDL and FPGAs B: An Unbuffered Crossbar Switch (posted Thursday, Sept 19, 2013) Lab #1: ITB Room 157, Thurs. and Fridays, 2:30-5:20, EOW Demos to TA: Thurs, Fri, Sept.
1 4DM4 Lab. #1 A: Introduction to VHDL and FPGAs B: An Unbuffered Crossbar Switch (posted Thursday, Sept 19, 2013) Lab #1: ITB Room 157, Thurs. and Fridays, 2:30-5:20, EOW Demos to TA: Thurs, Fri, Sept.
EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
 EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Introduction to FPGA design Rakesh Gangarajaiah Rakesh.gangarajaiah@eit.lth.se Slides from Chenxin Zhang and Steffan Malkowsky WWW.FPGA What is FPGA? Field
EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Introduction to FPGA design Rakesh Gangarajaiah Rakesh.gangarajaiah@eit.lth.se Slides from Chenxin Zhang and Steffan Malkowsky WWW.FPGA What is FPGA? Field
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 90 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a)
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 90 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a)
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec06-FPGA Page 1 Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec06-FPGA Page 1 Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history
EE178 Lecture Module 2. Eric Crabill SJSU / Xilinx Fall 2007
 EE178 Lecture Module 2 Eric Crabill SJSU / Xilinx Fall 2007 Lecture #4 Agenda Survey of implementation technologies. Implementation Technologies Small scale and medium scale integration. Up to about 200
EE178 Lecture Module 2 Eric Crabill SJSU / Xilinx Fall 2007 Lecture #4 Agenda Survey of implementation technologies. Implementation Technologies Small scale and medium scale integration. Up to about 200
ECE 448 Lecture 13. FPGA Memories. George Mason University
 ECE 448 Lecture 13 FPGA Memories George Mason University Recommended reading Spartan-6 FPGA Block RAM Resources: User Guide Google search: UG383 Spartan-6 FPGA Configurable Logic Block: User Guide Google
ECE 448 Lecture 13 FPGA Memories George Mason University Recommended reading Spartan-6 FPGA Block RAM Resources: User Guide Google search: UG383 Spartan-6 FPGA Configurable Logic Block: User Guide Google
Outline. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) FPGA Overview. Why FPGAs?
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history lesson). FPGA variations Internal logic
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history lesson). FPGA variations Internal logic
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE
 REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
Altera FLEX 8000 Block Diagram
 Altera FLEX 8000 Block Diagram Figure from Altera technical literature FLEX 8000 chip contains 26 162 LABs Each LAB contains 8 Logic Elements (LEs), so a chip contains 208 1296 LEs, totaling 2,500 16,000
Altera FLEX 8000 Block Diagram Figure from Altera technical literature FLEX 8000 chip contains 26 162 LABs Each LAB contains 8 Logic Elements (LEs), so a chip contains 208 1296 LEs, totaling 2,500 16,000
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 1/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Historical introduction.
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 1/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Historical introduction.
Arithmetic Logic Unit. Digital Computer Design
 Arithmetic Logic Unit Digital Computer Design Arithmetic Circuits Arithmetic circuits are the central building blocks of computers. Computers and digital logic perform many arithmetic functions: addition,
Arithmetic Logic Unit Digital Computer Design Arithmetic Circuits Arithmetic circuits are the central building blocks of computers. Computers and digital logic perform many arithmetic functions: addition,
Virtex-II Architecture
 Virtex-II Architecture Block SelectRAM resource I/O Blocks (IOBs) edicated multipliers Programmable interconnect Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs) Virtex -II architecture s core voltage operates at 1.5V
Virtex-II Architecture Block SelectRAM resource I/O Blocks (IOBs) edicated multipliers Programmable interconnect Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs) Virtex -II architecture s core voltage operates at 1.5V
TSEA44 - Design for FPGAs
 2015-11-24 Now for something else... Adapting designs to FPGAs Why? Clock frequency Area Power Target FPGA architecture: Xilinx FPGAs with 4 input LUTs (such as Virtex-II) Determining the maximum frequency
2015-11-24 Now for something else... Adapting designs to FPGAs Why? Clock frequency Area Power Target FPGA architecture: Xilinx FPGAs with 4 input LUTs (such as Virtex-II) Determining the maximum frequency
1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4]
![1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4] 1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4]](/thumbs/81/83055464.jpg) HW 3 Answer Key 1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4] You can build a NAND gate from tri-state buffers and inverters and thus you
HW 3 Answer Key 1. Prove that if you have tri-state buffers and inverters, you can build any combinational logic circuit. [4] You can build a NAND gate from tri-state buffers and inverters and thus you
Review from last time. CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 6. Verilog (finish) Multiply, Divide, Shift
 Review from last time CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 6 Verilog (finish) Multiply, Divide, Shift February 11, 2004 John Kubiatowicz (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~kubitron) lecture slides: http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/
Review from last time CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 6 Verilog (finish) Multiply, Divide, Shift February 11, 2004 John Kubiatowicz (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~kubitron) lecture slides: http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/
DSP Resources. Main features: 1 adder-subtractor, 1 multiplier, 1 add/sub/logic ALU, 1 comparator, several pipeline stages
 DSP Resources Specialized FPGA columns for complex arithmetic functionality DSP48 Tile: two DSP48 slices, interconnect Each DSP48 is a self-contained arithmeticlogical unit with add/sub/multiply/logic
DSP Resources Specialized FPGA columns for complex arithmetic functionality DSP48 Tile: two DSP48 slices, interconnect Each DSP48 is a self-contained arithmeticlogical unit with add/sub/multiply/logic
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2-2. Digital System Design DATAPATH COMPONENTS
 2-2. 2-2.2 Learning Outcomes piral 2-2 Arithmetic Components and Their Efficient Implementations I understand the control inputs to counters I can design logic to control the inputs of counters to create
2-2. 2-2.2 Learning Outcomes piral 2-2 Arithmetic Components and Their Efficient Implementations I understand the control inputs to counters I can design logic to control the inputs of counters to create
Final Exam Solution Sunday, December 15, 10:05-12:05 PM
 Last (family) name: First (given) name: Student I.D. #: Circle section: Kim Hu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/CS 352 Digital System Fundamentals
Last (family) name: First (given) name: Student I.D. #: Circle section: Kim Hu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/CS 352 Digital System Fundamentals
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 15: Midterm 1 Review Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Basics Midterm to cover Book Sections (inclusive) 1.1 1.5
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 15: Midterm 1 Review Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Basics Midterm to cover Book Sections (inclusive) 1.1 1.5
ELCT 501: Digital System Design
 ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 4: CAD tools (Continued) Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Basic VHDL Concept Via an Example Problem: write VHDL code for 1-bit adder 4-bit adder 2 1-bit adder Inputs: A (1 bit)
ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 4: CAD tools (Continued) Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Basic VHDL Concept Via an Example Problem: write VHDL code for 1-bit adder 4-bit adder 2 1-bit adder Inputs: A (1 bit)
register:a group of binary cells suitable for holding binary information flip-flops + gates
 9 차시 1 Ch. 6 Registers and Counters 6.1 Registers register:a group of binary cells suitable for holding binary information flip-flops + gates control when and how new information is transferred into the
9 차시 1 Ch. 6 Registers and Counters 6.1 Registers register:a group of binary cells suitable for holding binary information flip-flops + gates control when and how new information is transferred into the
An Efficient Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier
 An Efficient Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Mohamed Al-Ashrafy Mentor Graphics Mohamed_Samy@Mentor.com Ashraf Salem Mentor Graphics Ashraf_Salem@Mentor.com Wagdy Anis Communications and Electronics
An Efficient Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Mohamed Al-Ashrafy Mentor Graphics Mohamed_Samy@Mentor.com Ashraf Salem Mentor Graphics Ashraf_Salem@Mentor.com Wagdy Anis Communications and Electronics
CHAPTER 4. DIGITAL DOWNCONVERTER FOR WiMAX SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 4 IMPLEMENTATION OF DIGITAL UPCONVERTER AND DIGITAL DOWNCONVERTER FOR WiMAX SYSTEM 4.1 Introduction FPGAs provide an ideal implementation platform for developing broadband wireless systems such
CHAPTER 4 IMPLEMENTATION OF DIGITAL UPCONVERTER AND DIGITAL DOWNCONVERTER FOR WiMAX SYSTEM 4.1 Introduction FPGAs provide an ideal implementation platform for developing broadband wireless systems such
CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment. Description
 CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment To design a 16-bit ALU which will be used in the datapath of the microprocessor. This ALU must support two s complement arithmetic and the instructions in the baseline
CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment To design a 16-bit ALU which will be used in the datapath of the microprocessor. This ALU must support two s complement arithmetic and the instructions in the baseline
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Israel Koren Fall 2010 ECE666/Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Israel Koren Fall 2010 ECE666/Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers
2015 Paper E2.1: Digital Electronics II
 s 2015 Paper E2.1: Digital Electronics II Answer ALL questions. There are THREE questions on the paper. Question ONE counts for 40% of the marks, other questions 30% Time allowed: 2 hours (Not to be removed
s 2015 Paper E2.1: Digital Electronics II Answer ALL questions. There are THREE questions on the paper. Question ONE counts for 40% of the marks, other questions 30% Time allowed: 2 hours (Not to be removed
An FPGA based Implementation of Floating-point Multiplier
 An FPGA based Implementation of Floating-point Multiplier L. Rajesh, Prashant.V. Joshi and Dr.S.S. Manvi Abstract In this paper we describe the parameterization, implementation and evaluation of floating-point
An FPGA based Implementation of Floating-point Multiplier L. Rajesh, Prashant.V. Joshi and Dr.S.S. Manvi Abstract In this paper we describe the parameterization, implementation and evaluation of floating-point
University, Patiala, Punjab, India 1 2
 1102 Design and Implementation of Efficient Adder based Floating Point Multiplier LOKESH BHARDWAJ 1, SAKSHI BAJAJ 2 1 Student, M.tech, VLSI, 2 Assistant Professor,Electronics and Communication Engineering
1102 Design and Implementation of Efficient Adder based Floating Point Multiplier LOKESH BHARDWAJ 1, SAKSHI BAJAJ 2 1 Student, M.tech, VLSI, 2 Assistant Professor,Electronics and Communication Engineering
CS Digital Systems Project Laboratory
 CS 194- igital Systems Project Laboratory Lecture 1 Virtex-5 Microarchitecture Not a professor. John is OK. 2008-9- John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) And also, an introduction to the project.
CS 194- igital Systems Project Laboratory Lecture 1 Virtex-5 Microarchitecture Not a professor. John is OK. 2008-9- John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) And also, an introduction to the project.
Pipelined FPGA Adders
 010 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications Pipelined FPGA Adders Florent de Dinechin, Hong Diep Nguyen, Bogdan Pasca LIP, projet Arénaire ENS de Lyon 6 allée d Italie, 6936
010 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications Pipelined FPGA Adders Florent de Dinechin, Hong Diep Nguyen, Bogdan Pasca LIP, projet Arénaire ENS de Lyon 6 allée d Italie, 6936
Parallel logic circuits
 Computer Mathematics Week 9 Parallel logic circuits College of Information cience and Engineering Ritsumeikan University last week the mathematics of logic circuits the foundation of all digital design
Computer Mathematics Week 9 Parallel logic circuits College of Information cience and Engineering Ritsumeikan University last week the mathematics of logic circuits the foundation of all digital design
Lecture 12 VHDL Synthesis
 CPE 487: Digital System Design Spring 2018 Lecture 12 VHDL Synthesis Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ 07030 1 What is Synthesis?
CPE 487: Digital System Design Spring 2018 Lecture 12 VHDL Synthesis Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken, NJ 07030 1 What is Synthesis?
Adders, Subtracters and Accumulators in XC3000
 s, ubtracters and Accumulators in XC3000 XAPP 022.000 Application Note By PETER ALFKE and BERNIE NEW ummary This Application Note surveys the different adder techniques that are available for XC3000 designs.
s, ubtracters and Accumulators in XC3000 XAPP 022.000 Application Note By PETER ALFKE and BERNIE NEW ummary This Application Note surveys the different adder techniques that are available for XC3000 designs.
Verilog Sequential Logic. Verilog for Synthesis Rev C (module 3 and 4)
 Verilog Sequential Logic Verilog for Synthesis Rev C (module 3 and 4) Jim Duckworth, WPI 1 Sequential Logic Module 3 Latches and Flip-Flops Implemented by using signals in always statements with edge-triggered
Verilog Sequential Logic Verilog for Synthesis Rev C (module 3 and 4) Jim Duckworth, WPI 1 Sequential Logic Module 3 Latches and Flip-Flops Implemented by using signals in always statements with edge-triggered
ECE 545 Lecture 12. FPGA Embedded Resources 12/8/11. Resources. Recommended reading. Use of Embedded FPGA Resources in SHA-3 Candidates
 ECE 545 Lecture 12 FPGA Embedded Resources Resources FPGA Embedded Resources web page available from the course web page George Mason University 2 Recommended reading XAPP463 Using Block RAM in Spartan-3
ECE 545 Lecture 12 FPGA Embedded Resources Resources FPGA Embedded Resources web page available from the course web page George Mason University 2 Recommended reading XAPP463 Using Block RAM in Spartan-3
Experiment 3. Digital Circuit Prototyping Using FPGAs
 Experiment 3. Digital Circuit Prototyping Using FPGAs Masud ul Hasan Muhammad Elrabaa Ahmad Khayyat Version 151, 11 September 2015 Table of Contents 1. Objectives 2. Materials Required 3. Background 3.1.
Experiment 3. Digital Circuit Prototyping Using FPGAs Masud ul Hasan Muhammad Elrabaa Ahmad Khayyat Version 151, 11 September 2015 Table of Contents 1. Objectives 2. Materials Required 3. Background 3.1.
Stratix II vs. Virtex-4 Performance Comparison
 White Paper Stratix II vs. Virtex-4 Performance Comparison Altera Stratix II devices use a new and innovative logic structure called the adaptive logic module () to make Stratix II devices the industry
White Paper Stratix II vs. Virtex-4 Performance Comparison Altera Stratix II devices use a new and innovative logic structure called the adaptive logic module () to make Stratix II devices the industry
Note that none of the above MAY be a VALID ANSWER.
 ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm
 Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm Abstract: Floating point multiplication is the most usefull in all the computation application like in Arithematic operation, DSP application.
Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm Abstract: Floating point multiplication is the most usefull in all the computation application like in Arithematic operation, DSP application.
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI. Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing
 EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Spring 2017 Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers The two basic operations - generation
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6c High-Speed Multiplication - III Spring 2017 Koren Part.6c.1 Array Multipliers The two basic operations - generation
Chapter 8 FPGA Basics
 Chapter 8 FPGA Basics NCHU EE Yin-Tsung Hwang YT Hwang VLSI SP 1 What are PLs? YT Hwang VLSI SP 2 Programmable Logic evices A pre-fabricated ASIC capable of performing any logic subject to user programming
Chapter 8 FPGA Basics NCHU EE Yin-Tsung Hwang YT Hwang VLSI SP 1 What are PLs? YT Hwang VLSI SP 2 Programmable Logic evices A pre-fabricated ASIC capable of performing any logic subject to user programming
EECS 150 Homework 7 Solutions Fall (a) 4.3 The functions for the 7 segment display decoder given in Section 4.3 are:
 Problem 1: CLD2 Problems. (a) 4.3 The functions for the 7 segment display decoder given in Section 4.3 are: C 0 = A + BD + C + BD C 1 = A + CD + CD + B C 2 = A + B + C + D C 3 = BD + CD + BCD + BC C 4
Problem 1: CLD2 Problems. (a) 4.3 The functions for the 7 segment display decoder given in Section 4.3 are: C 0 = A + BD + C + BD C 1 = A + CD + CD + B C 2 = A + B + C + D C 3 = BD + CD + BCD + BC C 4
Field Programmable Gate Array
 Field Programmable Gate Array System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) What is FPGA? System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) 2 FPGA Programmable (= reconfigurable) Digital System Component Basic components Combinational
Field Programmable Gate Array System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) What is FPGA? System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) 2 FPGA Programmable (= reconfigurable) Digital System Component Basic components Combinational
Readings: Storage unit. Can hold an n-bit value Composed of a group of n flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores 1 bit of information.
 Registers Readings: 5.8-5.9.3 Storage unit. Can hold an n-bit value Composed of a group of n flip-flops Each flip-flop stores 1 bit of information ff ff ff ff 178 Controlled Register Reset Load Action
Registers Readings: 5.8-5.9.3 Storage unit. Can hold an n-bit value Composed of a group of n flip-flops Each flip-flop stores 1 bit of information ff ff ff ff 178 Controlled Register Reset Load Action
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
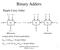 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Use of Embedded FPGA Resources in Implementa:ons of 14 Round 2 SHA- 3 Candidates
 Use of Embedded FPGA Resources in Implementa:ons of 14 Round 2 SHA- 3 Candidates Kris Gaj, Rabia Shahid, Malik Umar Sharif, and Marcin Rogawski George Mason University U.S.A. Co-Authors Rabia Shahid Malik
Use of Embedded FPGA Resources in Implementa:ons of 14 Round 2 SHA- 3 Candidates Kris Gaj, Rabia Shahid, Malik Umar Sharif, and Marcin Rogawski George Mason University U.S.A. Co-Authors Rabia Shahid Malik
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science & Systems
Code No: R059210504 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN ( Common to Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology and Computer Science & Systems
A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm
 455 A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm B. Jeevan, Asst. Professor, Dept. of E&IE, KITS, Warangal. jeevanbs776@gmail.com S. Narender, M.Tech (VLSI&ES), KITS, Warangal. narender.s446@gmail.com
455 A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm B. Jeevan, Asst. Professor, Dept. of E&IE, KITS, Warangal. jeevanbs776@gmail.com S. Narender, M.Tech (VLSI&ES), KITS, Warangal. narender.s446@gmail.com
Overview. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 16 Arithmetic II (Multiplication) Computer Number Systems.
 Overview EE 15 - omponents and Design Techniques for Digital ystems Lec 16 Arithmetic II (Multiplication) Review of Addition Overflow Multiplication Further adder optimizations for multiplication LA in
Overview EE 15 - omponents and Design Techniques for Digital ystems Lec 16 Arithmetic II (Multiplication) Review of Addition Overflow Multiplication Further adder optimizations for multiplication LA in
Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 4 Arithmetic Functions Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Iterative combinational
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2 2. Digital System Design DATAPATH COMPONENTS
 2-2. 2-2.2 Learning Outcomes piral 2 2 Arithmetic Components and Their Efficient Implementations I know how to combine overflow and subtraction results to determine comparison results of both signed and
2-2. 2-2.2 Learning Outcomes piral 2 2 Arithmetic Components and Their Efficient Implementations I know how to combine overflow and subtraction results to determine comparison results of both signed and
*Instruction Matters: Purdue Academic Course Transformation. Introduction to Digital System Design. Module 4 Arithmetic and Computer Logic Circuits
 Purdue IM:PACT* Fall 2018 Edition *Instruction Matters: Purdue Academic Course Transformation Introduction to Digital System Design Module 4 Arithmetic and Computer Logic Circuits Glossary of Common Terms
Purdue IM:PACT* Fall 2018 Edition *Instruction Matters: Purdue Academic Course Transformation Introduction to Digital System Design Module 4 Arithmetic and Computer Logic Circuits Glossary of Common Terms
Parallel FIR Filters. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
Pipelining & Verilog. Sequential Divider. Verilog divider.v. Math Functions in Coregen. Lab #3 due tonight, LPSet 8 Thurs 10/11
 Lab #3 due tonight, LPSet 8 Thurs 0/ Pipelining & Verilog Latency & Throughput Pipelining to increase throughput Retiming Verilog Math Functions Debugging Hints Sequential Divider Assume the Divid (A)
Lab #3 due tonight, LPSet 8 Thurs 0/ Pipelining & Verilog Latency & Throughput Pipelining to increase throughput Retiming Verilog Math Functions Debugging Hints Sequential Divider Assume the Divid (A)
FYSE420 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS. Lecture 7
 FYSE420 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS Lecture 7 1 [1] [2] [3] DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & DESIGN Nelson, Nagle, Irvin, Carrol ISBN 0-13-463894-8 DIGITAL DESIGN Morris Mano Fourth edition ISBN 0-13-198924-3
FYSE420 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS Lecture 7 1 [1] [2] [3] DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & DESIGN Nelson, Nagle, Irvin, Carrol ISBN 0-13-463894-8 DIGITAL DESIGN Morris Mano Fourth edition ISBN 0-13-198924-3
FPGA Architecture Overview. Generic FPGA Architecture (1) FPGA Architecture
 FPGA Architecture Overview dr chris dick dsp chief architect wireless and signal processing group xilinx inc. Generic FPGA Architecture () Generic FPGA architecture consists of an array of logic tiles
FPGA Architecture Overview dr chris dick dsp chief architect wireless and signal processing group xilinx inc. Generic FPGA Architecture () Generic FPGA architecture consists of an array of logic tiles
CSE140 L. Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 18,2006. CSE140L Course Info
 CSE4 L Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 8,26 CSE4L Course Info Lectures Wedesday :-:2AM, HSS33 Lab Assignment egins TA s JinHua Liu (jhliu@cs.ucsd.edu) Contact TAs if you re still looking for a lab
CSE4 L Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 8,26 CSE4L Course Info Lectures Wedesday :-:2AM, HSS33 Lab Assignment egins TA s JinHua Liu (jhliu@cs.ucsd.edu) Contact TAs if you re still looking for a lab
Programmable Logic Devices FPGA Architectures II CMPE 415. Overview This set of notes introduces many of the features available in the FPGAs of today.
 Overview This set of notes introduces many of the features available in the FPGAs of today. The majority use SRAM based configuration cells, which allows fast reconfiguation. Allows new design ideas to
Overview This set of notes introduces many of the features available in the FPGAs of today. The majority use SRAM based configuration cells, which allows fast reconfiguation. Allows new design ideas to
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501
 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Lecture 3: Modeling in VHDL. EE 3610 Digital Systems
 EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Lecture 3: Modeling in VHDL VHDL: Overview 2 VHDL VHSIC Hardware Description Language VHSIC=Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Programming language for modelling of hardware
EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Lecture 3: Modeling in VHDL VHDL: Overview 2 VHDL VHSIC Hardware Description Language VHSIC=Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Programming language for modelling of hardware
Arithmetic Circuits. Nurul Hazlina Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit
 Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
Nurul Hazlina 1 1. Adder 2. Multiplier 3. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) 4. HDL for Arithmetic Circuit Nurul Hazlina 2 Introduction 1. Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations 2. Fundamental
Lecture 19: Arithmetic Modules 14-1
 Lecture 19: Arithmetic Modules 14-1 Syllabus Objectives Addition and subtraction Multiplication Division Arithmetic and logic unit 14-2 Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe
Lecture 19: Arithmetic Modules 14-1 Syllabus Objectives Addition and subtraction Multiplication Division Arithmetic and logic unit 14-2 Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI. Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing
 EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6b High-Speed Multiplication - II Spring 2017 Koren Part.6b.1 Accumulating the Partial Products After generating partial
EE878 Special Topics in VLSI Computer Arithmetic for Digital Signal Processing Part 6b High-Speed Multiplication - II Spring 2017 Koren Part.6b.1 Accumulating the Partial Products After generating partial
