Generating String Attack Inputs Using Constrained Symbolic Execution. presented by Kinga Dobolyi
|
|
|
- Lee Delilah Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Generating String Attack Inputs Using Constrained Symbolic Execution presented by Kinga Dobolyi
2 What is a String Attack? Web applications are 3 tiered Vulnerabilities in the application layer Buffer overruns, cross-site scripting, code injection Command injection allow a malicious user direct access to the back end database In 2006 they made up 14% of reported vulnerabilities (second most common)
3 Outline SQL command injections Motivating example Algorithm to detect Generating grammars Generating strings Concatenation Intersection Summary
4 Background What is an SQL command injection? Query commands are passed to the DB, usually some sort of business logic A bad command could return secret information or corrupt the database
5 An Example Attack $DB->query("SELECT * from news where newsid= 5 "); $DB->query("SELECT * from news where newsid= 5 OR 1=1; DROP news ");
6 How can we avoid this? Dynamic taint analyses expensive Static analyses Undecidable approximate
7 Static Analysis
8 Motivation Static analyses will result in false positives Even if we flag vulnerable points in the code, it would be better if we could generate test cases automatically that demonstrate them How could we generate test cases with a test input and a viable path to the error?
9 Algorithm Create a Context Free Grammar to represent all possible bad String variable values in the program Identify a set of locations (from the grammar) that we must pass through to get a specific bad String Find the exact path Use static analysis to find the inputs that will demonstrate the fault along that path to the location
10 Inputs The program as a control flow graph The location that represents the defect A policy: a regular expression describing illegal string arguments ( to the query function)
11 Algorithm
12 Step 1: the grammar Construct an annotated grammar that soundly approximates the values possible at a location We want a Context Free Grammar that represents all possible values that String variables in the program might take at runtime Not precise, but it always terminates We are interested in variables that the user might have an effect on We need to encode locations in the program
13 Step 1: the grammar Each String variable is associated with a sub-grammar from the program Context Free Grammar The variable is a terminal For each production, add conditionals that had to be true for the program to get there from the Control Flow Graph
14 Step 1: the grammar
15 Step 1: the grammar
16 Step 1: the grammar
17 Step 1: the grammar
18 Step 1: the grammar
19 Step 1: the grammar
20 Step 1: the grammar
21 Step 1: the grammar Now we have a way of representing the values that a particular variable may take at runtime
22 Step 1: String generation Use the potential runtime values of the variable (from the grammar), together with our policy to generate violating String instances Intersect the grammar with the policy If == Ø, we are safe (good programmer filtering) If!= Ø, we have a violation (bad programmer filtering = defect)
23 What next? The grammar doesn t match the Control Flow Graph exactly, to give a precise path We enumerate a String in our grammar, keeping track of the productions used From this set of productions, we obtain a set of constraints on program variables and a set of locations that must be visited Check for internal consistency of the constraints
24 Algorithm
25 Step 2: get a path Step 2: Use backwards reachability analysis from the location to the start of the program to enumerate paths that demonstrate the defect
26 Step 3: user inputs Step 3: We want to find user inputs for the path Given a path that lead to a location with some vulnerability, what was the user input? How do we build the defective String for the query? We need to concatenate Strings along the path of execution but there can be so many! So unclear!
27 Dependency Graph We have a set of locations in the Control Flow Graph that we must pass through to demonstrate the defect, and we are trying to get to the start from the location We can build a dependency graph of program statements
28 Dependency Graph: example 1 $p = getuserinput(); 2 if ($p == ab ) //t0 3 exit(); 4 $querystring = $q.$p; 5 $DB->query($queryString); For line 5, if our policy says querystring is Σ*cab, let akcab be a bad String
29 Dependency Graph Perform a topological sort of the graph to generate a sequence of operations But how does this work when we have so many possibilities? Use concatenationintersection to generate the Strings
30 Concatenation-intersection Problem statement: Given 3 regular languages L 1, L 2, L 3 Generate a set of elements <L i, L i >
31 How do we solve the CI problem? Use the NFA that recognizes L 5 = (L 1 L 2 ) L 3 We need to construct M 5 to extract a solution, assuming that there is a single start state and a single final state
32 Constructing M 5 First construct M 4 for L 4 = (L 1 L 2 ) Use a single ε-transition between the final state of M 1 and the start state of M 2 Next construct the cross product of L 4 and L 3 such that L 5 = L 4 L 3 = (L 1 L 2 ) L 3
33 Continuing the previous example We now have a finite state machine that represents all possible Strings that would lead to the defect Enumerate over Strings in this language to generate the test cases Breadth first search of the DFA
34 Victory Now we can use these test cases to show the defect, and for regression testing
35 Summary We have an algorithm that is able to produce test cases for command injections in vulnerable code We did this by modeling the variables String variables could take on in the code We found the path through the code to the defect We generated user inputs to demonstrate the defect
Outline STRANGER. Background
 Outline Malicious Code Analysis II : An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP 1 Mitchell Adair 2 November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 2 Credit: [: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP] Background
Outline Malicious Code Analysis II : An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP 1 Mitchell Adair 2 November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 2 Credit: [: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP] Background
Malicious Code Analysis II
 Malicious Code Analysis II STRANGER: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP Mitchell Adair November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 STRANGER Credit: [STRANGER: An Automata-based
Malicious Code Analysis II STRANGER: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP Mitchell Adair November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 STRANGER Credit: [STRANGER: An Automata-based
Generating String Inputs using Constrained Symbolic Execution
 Generating String Inputs using Constrained Symbolic Execution A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the School of Engineering and Applied Science University of Virginia in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Generating String Inputs using Constrained Symbolic Execution A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the School of Engineering and Applied Science University of Virginia in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Midterm Exam II CIS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Spring 2006, day section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama
 Midterm Exam II CIS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Spring 2006, day section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama Print family (or last) name: Print given (or first) name: I have read and understand all of
Midterm Exam II CIS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Spring 2006, day section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama Print family (or last) name: Print given (or first) name: I have read and understand all of
Automata Based String Analysis for Vulnerability Detection
 Automata Based String Analysis for Vulnerability Detection 1 Automata-based String Analysis Finite State Automata can be used to characterize sets of string values Automata based string analysis Associate
Automata Based String Analysis for Vulnerability Detection 1 Automata-based String Analysis Finite State Automata can be used to characterize sets of string values Automata based string analysis Associate
Static Vulnerability Analysis
 Static Vulnerability Analysis Static Vulnerability Detection helps in finding vulnerabilities in code that can be extracted by malicious input. There are different static analysis tools for different kinds
Static Vulnerability Analysis Static Vulnerability Detection helps in finding vulnerabilities in code that can be extracted by malicious input. There are different static analysis tools for different kinds
HW due tonight Time for guest lecture on Friday Projects
 HW due tonight Time for guest lecture on Friday Projects Web servers accessible by outside world Web apps developed with security as an afterthought Example: Target breach Year Total Web-related Percentage
HW due tonight Time for guest lecture on Friday Projects Web servers accessible by outside world Web apps developed with security as an afterthought Example: Target breach Year Total Web-related Percentage
Security Analyses For The Lazy Superhero
 #1 Security Analyses For The Lazy Superhero #2 One-Slide Summary We can statically detect buffer overruns in programs by modeling the space allocated for a buffer and the space used for a buffer. We cannot
#1 Security Analyses For The Lazy Superhero #2 One-Slide Summary We can statically detect buffer overruns in programs by modeling the space allocated for a buffer and the space used for a buffer. We cannot
OWASP 5/07/09. The OWASP Foundation OWASP Static Analysis (SA) Track Session 1: Intro to Static Analysis
 Static Analysis (SA) Track Session 1: Intro to Static Analysis Eric Dalci Cigital edalci at cigital dot com 5/07/09 Copyright The Foundation Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this
Static Analysis (SA) Track Session 1: Intro to Static Analysis Eric Dalci Cigital edalci at cigital dot com 5/07/09 Copyright The Foundation Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this
Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions Version of June 6, 2008
 Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions Version of June 6, 2008 This is a collection of sample theory bridge exam questions. This is just to get some idea of the format of the bridge exam and the level of
Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions Version of June 6, 2008 This is a collection of sample theory bridge exam questions. This is just to get some idea of the format of the bridge exam and the level of
Securing Software Applications Using Dynamic Dataflow Analysis. OWASP June 16, The OWASP Foundation
 Securing Software Applications Using Dynamic Dataflow Analysis Steve Cook OWASP June 16, 2010 0 Southwest Research Institute scook@swri.org (210) 522-6322 Copyright The OWASP Foundation Permission is granted
Securing Software Applications Using Dynamic Dataflow Analysis Steve Cook OWASP June 16, 2010 0 Southwest Research Institute scook@swri.org (210) 522-6322 Copyright The OWASP Foundation Permission is granted
14.1 Encoding for different models of computation
 Lecture 14 Decidable languages In the previous lecture we discussed some examples of encoding schemes, through which various objects can be represented by strings over a given alphabet. We will begin this
Lecture 14 Decidable languages In the previous lecture we discussed some examples of encoding schemes, through which various objects can be represented by strings over a given alphabet. We will begin this
CS 432 Fall Mike Lam, Professor. Finite Automata Conversions and Lexing
 CS 432 Fall 2017 Mike Lam, Professor Finite Automata Conversions and Lexing Finite Automata Key result: all of the following have the same expressive power (i.e., they all describe regular languages):
CS 432 Fall 2017 Mike Lam, Professor Finite Automata Conversions and Lexing Finite Automata Key result: all of the following have the same expressive power (i.e., they all describe regular languages):
Command-form Coverage for Testing DB Applications
 Command-form Coverage for Testing DB Applications Alessandro Orso William G.J. Halfond Georgia Institute of Technology Supported by NSF awards CCR- 0205422 and CCR-0306372 to GA Tech and by DHS and US
Command-form Coverage for Testing DB Applications Alessandro Orso William G.J. Halfond Georgia Institute of Technology Supported by NSF awards CCR- 0205422 and CCR-0306372 to GA Tech and by DHS and US
Applications. Cloud. See voting example (DC Internet voting pilot) Select * from userinfo WHERE id = %%% (variable)
 Software Security Requirements General Methodologies Hardware Firmware Software Protocols Procedure s Applications OS Cloud Attack Trees is one of the inside requirement 1. Attacks 2. Evaluation 3. Mitigation
Software Security Requirements General Methodologies Hardware Firmware Software Protocols Procedure s Applications OS Cloud Attack Trees is one of the inside requirement 1. Attacks 2. Evaluation 3. Mitigation
Sandboxing Untrusted Code: Software-Based Fault Isolation (SFI)
 Sandboxing Untrusted Code: Software-Based Fault Isolation (SFI) Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS GZ03 / M030 9 th December 2011 Motivation: Vulnerabilities in C Seen dangers of vulnerabilities: injection
Sandboxing Untrusted Code: Software-Based Fault Isolation (SFI) Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS GZ03 / M030 9 th December 2011 Motivation: Vulnerabilities in C Seen dangers of vulnerabilities: injection
Multiple Choice Questions
 Techno India Batanagar Computer Science and Engineering Model Questions Subject Name: Formal Language and Automata Theory Subject Code: CS 402 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The basic limitation of an FSM
Techno India Batanagar Computer Science and Engineering Model Questions Subject Name: Formal Language and Automata Theory Subject Code: CS 402 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The basic limitation of an FSM
Static Analysis. Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Static Analysis Trent
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Static Analysis Trent
Lexical Analysis - 2
 Lexical Analysis - 2 More regular expressions Finite Automata NFAs and DFAs Scanners JLex - a scanner generator 1 Regular Expressions in JLex Symbol - Meaning. Matches a single character (not newline)
Lexical Analysis - 2 More regular expressions Finite Automata NFAs and DFAs Scanners JLex - a scanner generator 1 Regular Expressions in JLex Symbol - Meaning. Matches a single character (not newline)
Data Flow Analysis. CSCE Lecture 9-02/15/2018
 Data Flow Analysis CSCE 747 - Lecture 9-02/15/2018 Data Flow Another view - program statements compute and transform data So, look at how that data is passed through the program. Reason about data dependence
Data Flow Analysis CSCE 747 - Lecture 9-02/15/2018 Data Flow Another view - program statements compute and transform data So, look at how that data is passed through the program. Reason about data dependence
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 1.2, 1.3 Design NFA recognizing a given language Convert an NFA (with or without
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 1.2, 1.3 Design NFA recognizing a given language Convert an NFA (with or without
A Decision Procedure for Subset Constraints over Regular Languages
 A Decision Procedure for Subset Constraints over Regular Languages Pieter Hooimeijer and Westley Weimer University of Virginia {pieter, weimer}@cs.virginia.edu Abstract Reasoning about string variables,
A Decision Procedure for Subset Constraints over Regular Languages Pieter Hooimeijer and Westley Weimer University of Virginia {pieter, weimer}@cs.virginia.edu Abstract Reasoning about string variables,
Converting a DFA to a Regular Expression JP
 Converting a DFA to a Regular Expression JP Prerequisite knowledge: Regular Languages Deterministic Finite Automata Nondeterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Conversion of Regular Expression
Converting a DFA to a Regular Expression JP Prerequisite knowledge: Regular Languages Deterministic Finite Automata Nondeterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Conversion of Regular Expression
String Abstractions for String Verification
 String Abstractions for String Verification Fang Yu 1, Tevfik Bultan 2, and Ben Hardekopf 2 1 Department of Management Information Systems National Chengchi University, Taipei, Taiwan yuf@nccu.edu.tw 2
String Abstractions for String Verification Fang Yu 1, Tevfik Bultan 2, and Ben Hardekopf 2 1 Department of Management Information Systems National Chengchi University, Taipei, Taiwan yuf@nccu.edu.tw 2
QUESTION BANK. Formal Languages and Automata Theory(10CS56)
 QUESTION BANK Formal Languages and Automata Theory(10CS56) Chapter 1 1. Define the following terms & explain with examples. i) Grammar ii) Language 2. Mention the difference between DFA, NFA and εnfa.
QUESTION BANK Formal Languages and Automata Theory(10CS56) Chapter 1 1. Define the following terms & explain with examples. i) Grammar ii) Language 2. Mention the difference between DFA, NFA and εnfa.
Symbolic String Verification: An Automata-based Approach
 : An Automata-based Approach Fang Yu Tevfik Bultan Marco Cova Oscar H. Ibarra Dept. of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, USA {yuf, bultan, marco, ibarra}@cs.ucsb.edu August 11, 2008
: An Automata-based Approach Fang Yu Tevfik Bultan Marco Cova Oscar H. Ibarra Dept. of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, USA {yuf, bultan, marco, ibarra}@cs.ucsb.edu August 11, 2008
Finding Vulnerabilities in Web Applications
 Finding Vulnerabilities in Web Applications Christopher Kruegel, Technical University Vienna Evolving Networks, Evolving Threats The past few years have witnessed a significant increase in the number of
Finding Vulnerabilities in Web Applications Christopher Kruegel, Technical University Vienna Evolving Networks, Evolving Threats The past few years have witnessed a significant increase in the number of
Static analysis of PHP applications
 Static analysis of PHP applications Ondřej Šerý DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS RESEARCH GROUP http://dsrg.mff.cuni.cz CHARLES UNIVERSITY PRAGUE Faculty of Mathematics and Physics References G. Wassermann, Z. Su:
Static analysis of PHP applications Ondřej Šerý DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS RESEARCH GROUP http://dsrg.mff.cuni.cz CHARLES UNIVERSITY PRAGUE Faculty of Mathematics and Physics References G. Wassermann, Z. Su:
Automata Theory TEST 1 Answers Max points: 156 Grade basis: 150 Median grade: 81%
 Automata Theory TEST 1 Answers Max points: 156 Grade basis: 150 Median grade: 81% 1. (2 pts) See text. You can t be sloppy defining terms like this. You must show a bijection between the natural numbers
Automata Theory TEST 1 Answers Max points: 156 Grade basis: 150 Median grade: 81% 1. (2 pts) See text. You can t be sloppy defining terms like this. You must show a bijection between the natural numbers
Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis
 Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis Host Based Attacks Pavel Laskov Wilhelm Schickard Institute for Computer Science Software security threats Modification of program code viruses and self-replicating
Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis Host Based Attacks Pavel Laskov Wilhelm Schickard Institute for Computer Science Software security threats Modification of program code viruses and self-replicating
Limitations of Algorithmic Solvability In this Chapter we investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems Some can be solved algorithmically and
 Computer Language Theory Chapter 4: Decidability 1 Limitations of Algorithmic Solvability In this Chapter we investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems Some can be solved algorithmically and
Computer Language Theory Chapter 4: Decidability 1 Limitations of Algorithmic Solvability In this Chapter we investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems Some can be solved algorithmically and
CSE450. Translation of Programming Languages. Lecture 20: Automata and Regular Expressions
 CSE45 Translation of Programming Languages Lecture 2: Automata and Regular Expressions Finite Automata Regular Expression = Specification Finite Automata = Implementation A finite automaton consists of:
CSE45 Translation of Programming Languages Lecture 2: Automata and Regular Expressions Finite Automata Regular Expression = Specification Finite Automata = Implementation A finite automaton consists of:
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
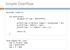 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Static Analysis in Practice
 in Practice 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 Quick Poll Who is familiar and comfortable with design patterns? e.g. what is a Factory and why use it? 2 1 Outline: in Practice
in Practice 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 Quick Poll Who is familiar and comfortable with design patterns? e.g. what is a Factory and why use it? 2 1 Outline: in Practice
Lexical Analysis. Implementation: Finite Automata
 Lexical Analysis Implementation: Finite Automata Outline Specifying lexical structure using regular expressions Finite automata Deterministic Finite Automata (DFAs) Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFAs)
Lexical Analysis Implementation: Finite Automata Outline Specifying lexical structure using regular expressions Finite automata Deterministic Finite Automata (DFAs) Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFAs)
Lecture 4 September Required reading materials for this class
 EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice
 Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Secure Development After Security Bugs
 Secure Development After Security Bugs Jeremy Epstein Program Manager Presentation to 1 st IEEE Cybersecurity Development Conference (SecDev) 11/03/16 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release:
Secure Development After Security Bugs Jeremy Epstein Program Manager Presentation to 1 st IEEE Cybersecurity Development Conference (SecDev) 11/03/16 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release:
CSE 431S Scanning. Washington University Spring 2013
 CSE 431S Scanning Washington University Spring 2013 Regular Languages Three ways to describe regular languages FSA Right-linear grammars Regular expressions Regular Expressions A regular expression is
CSE 431S Scanning Washington University Spring 2013 Regular Languages Three ways to describe regular languages FSA Right-linear grammars Regular expressions Regular Expressions A regular expression is
CMPSC 497: Static Analysis
 CMPSC 497: Static Analysis Trent Jaeger Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security (SIIS) Lab Computer Science and Engineering Department Pennsylvania State University Page 1 Our Goal In this course,
CMPSC 497: Static Analysis Trent Jaeger Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security (SIIS) Lab Computer Science and Engineering Department Pennsylvania State University Page 1 Our Goal In this course,
1. (10 points) Draw the state diagram of the DFA that recognizes the language over Σ = {0, 1}
 CSE 5 Homework 2 Due: Monday October 6, 27 Instructions Upload a single file to Gradescope for each group. should be on each page of the submission. All group members names and PIDs Your assignments in
CSE 5 Homework 2 Due: Monday October 6, 27 Instructions Upload a single file to Gradescope for each group. should be on each page of the submission. All group members names and PIDs Your assignments in
Whatever it takes. Fixing SQLIA and XSS in the process. Diploma Thesis Outline Presentation, Florian Thiel
 Whatever it takes Fixing SQLIA and XSS in the process Diploma Thesis Outline Presentation, Florian Thiel Seminar Beiträge zum Software Engineering, FU Berlin, 11/06/2008 OWASP Top 10 2007 1. XSS 2. Injection
Whatever it takes Fixing SQLIA and XSS in the process Diploma Thesis Outline Presentation, Florian Thiel Seminar Beiträge zum Software Engineering, FU Berlin, 11/06/2008 OWASP Top 10 2007 1. XSS 2. Injection
Theory of Computations Spring 2016 Practice Final Exam Solutions
 1 of 8 Theory of Computations Spring 2016 Practice Final Exam Solutions Name: Directions: Answer the questions as well as you can. Partial credit will be given, so show your work where appropriate. Try
1 of 8 Theory of Computations Spring 2016 Practice Final Exam Solutions Name: Directions: Answer the questions as well as you can. Partial credit will be given, so show your work where appropriate. Try
Secure Software Programming and Vulnerability Analysis
 Secure Software Programming and Vulnerability Analysis Christopher Kruegel chris@auto.tuwien.ac.at http://www.auto.tuwien.ac.at/~chris Race Conditions Secure Software Programming 2 Overview Parallel execution
Secure Software Programming and Vulnerability Analysis Christopher Kruegel chris@auto.tuwien.ac.at http://www.auto.tuwien.ac.at/~chris Race Conditions Secure Software Programming 2 Overview Parallel execution
Monitoring Standards for the Producers of Web Services Alexander Quang Truong
 Monitoring Standards for the Producers of Web Services 02-21-2017 Alexander Quang Truong Contents 1. Summary... 2 2. Metrics... 2 3. Benefits and Explanations of Metrics... 2 4. Tools for Monitoring...
Monitoring Standards for the Producers of Web Services 02-21-2017 Alexander Quang Truong Contents 1. Summary... 2 2. Metrics... 2 3. Benefits and Explanations of Metrics... 2 4. Tools for Monitoring...
Theory of Computation, Homework 3 Sample Solution
 Theory of Computation, Homework 3 Sample Solution 3.8 b.) The following machine M will do: M = "On input string : 1. Scan the tape and mark the first 1 which has not been marked. If no unmarked 1 is found,
Theory of Computation, Homework 3 Sample Solution 3.8 b.) The following machine M will do: M = "On input string : 1. Scan the tape and mark the first 1 which has not been marked. If no unmarked 1 is found,
Secure Coding, some simple steps help. OWASP EU Tour 2013
 Secure Coding, some simple steps help. OWASP EU Tour 2013 About Me Steven van der Baan - Dutch - 7Safe, part of PA Consulting Group - Developer - Pentester - Consultant - CISSP, OSCP It's amazing how
Secure Coding, some simple steps help. OWASP EU Tour 2013 About Me Steven van der Baan - Dutch - 7Safe, part of PA Consulting Group - Developer - Pentester - Consultant - CISSP, OSCP It's amazing how
Input Validation For Free Text Fields
 Input Validation For Free Text Fields User Manual Project Members: Hagar Offer & Ran Mor Academic Advisor: Dr Gera Weiss Technical Advisors: Raffi Lipkin & Nadav Attias 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...
Input Validation For Free Text Fields User Manual Project Members: Hagar Offer & Ran Mor Academic Advisor: Dr Gera Weiss Technical Advisors: Raffi Lipkin & Nadav Attias 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...
Last lecture CMSC330. This lecture. Finite Automata: States. Finite Automata. Implementing Regular Expressions. Languages. Regular expressions
 Last lecture CMSC330 Finite Automata Languages Sets of strings Operations on languages Regular expressions Constants Operators Precedence 1 2 Finite automata States Transitions Examples Types This lecture
Last lecture CMSC330 Finite Automata Languages Sets of strings Operations on languages Regular expressions Constants Operators Precedence 1 2 Finite automata States Transitions Examples Types This lecture
COS 320. Compiling Techniques
 Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
CHAPTER 8 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE ENHANCEMENTS
 180 CHAPTER 8 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE ENHANCEMENTS 8.1 SUMMARY This research has focused on developing a Web Applications Secure System from Code Injection Vulnerabilities through Web Services (WAPS-CIVS),
180 CHAPTER 8 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE ENHANCEMENTS 8.1 SUMMARY This research has focused on developing a Web Applications Secure System from Code Injection Vulnerabilities through Web Services (WAPS-CIVS),
CSE509 Spring 2007 Midterm Exam. Electronic devices, including calculators, cell phones, mp3 players, and laptops are all prohibited.
 CSE509 Spring 2007 Midterm Exam Name: You may not use any reference materials during this exam. Electronic devices, including calculators, cell phones, mp3 players, and laptops are all prohibited. You
CSE509 Spring 2007 Midterm Exam Name: You may not use any reference materials during this exam. Electronic devices, including calculators, cell phones, mp3 players, and laptops are all prohibited. You
Application vulnerabilities and defences
 Application vulnerabilities and defences In this lecture We examine the following : SQL injection XSS CSRF SQL injection SQL injection is a basic attack used to either gain unauthorized access to a database
Application vulnerabilities and defences In this lecture We examine the following : SQL injection XSS CSRF SQL injection SQL injection is a basic attack used to either gain unauthorized access to a database
Theory of Computation Dr. Weiss Extra Practice Exam Solutions
 Name: of 7 Theory of Computation Dr. Weiss Extra Practice Exam Solutions Directions: Answer the questions as well as you can. Partial credit will be given, so show your work where appropriate. Try to be
Name: of 7 Theory of Computation Dr. Weiss Extra Practice Exam Solutions Directions: Answer the questions as well as you can. Partial credit will be given, so show your work where appropriate. Try to be
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study. Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU
 Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
CSE450. Translation of Programming Languages. Automata, Simple Language Design Principles
 CSE45 Translation of Programming Languages Automata, Simple Language Design Principles Finite Automata State Graphs A state: The start state: An accepting state: A transition: a A Simple Example A finite
CSE45 Translation of Programming Languages Automata, Simple Language Design Principles Finite Automata State Graphs A state: The start state: An accepting state: A transition: a A Simple Example A finite
Module: Future of Secure Programming
 Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Database Management System Fall Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102
 Database Management System Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Outline What a database is, the individuals who use them, and how databases evolved Important database
Database Management System Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Outline What a database is, the individuals who use them, and how databases evolved Important database
Code Generation for network software with formal safety guarantees
 R. Sisto Cisco Tech Talk July 24th, 2009 1 Code Generation for network software with formal safety guarantees Riccardo Sisto Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Politecnico di Torino R. Sisto Cisco
R. Sisto Cisco Tech Talk July 24th, 2009 1 Code Generation for network software with formal safety guarantees Riccardo Sisto Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Politecnico di Torino R. Sisto Cisco
Front End: Lexical Analysis. The Structure of a Compiler
 Front End: Lexical Analysis The Structure of a Compiler Constructing a Lexical Analyser By hand: Identify lexemes in input and return tokens Automatically: Lexical-Analyser generator We will learn about
Front End: Lexical Analysis The Structure of a Compiler Constructing a Lexical Analyser By hand: Identify lexemes in input and return tokens Automatically: Lexical-Analyser generator We will learn about
(DMTCS 01) Answer Question No.1 is compulsory (15) Answer One question from each unit (4 15=60) 1) a) State whether the following is True/False:
 (DMTCS 01) M.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER - 2015 (Examination at the end of First Year) COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper - I : Data structures Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 75 Answer Question No.1 is compulsory
(DMTCS 01) M.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER - 2015 (Examination at the end of First Year) COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper - I : Data structures Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 75 Answer Question No.1 is compulsory
SHIFTLEFT OCULAR THE CODE PROPERTY GRAPH
 SHIFTLEFT OCULAR INTRODUCTION ShiftLeft Ocular offers code auditors the full range of capabilities of ShiftLeft s best-in-class static code analysis 1, ShiftLeft Inspect. Ocular enables code auditors to
SHIFTLEFT OCULAR INTRODUCTION ShiftLeft Ocular offers code auditors the full range of capabilities of ShiftLeft s best-in-class static code analysis 1, ShiftLeft Inspect. Ocular enables code auditors to
NET 311 INFORMATION SECURITY
 NET 311 INFORMATION SECURITY Networks and Communication Department Lec12: Software Security / Vulnerabilities lecture contents: o Vulnerabilities in programs Buffer Overflow Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
NET 311 INFORMATION SECURITY Networks and Communication Department Lec12: Software Security / Vulnerabilities lecture contents: o Vulnerabilities in programs Buffer Overflow Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
Security Fusion: A New Security Architecture for Resource-Constrained Environments
 11 Security Fusion: A New Security Architecture for Resource-Constrained Environments Suku Nair, Subil Abraham, Omar Al Ibrahim HACNet Labs, Southern Methodist University Resource-Constrained Devices Alien
11 Security Fusion: A New Security Architecture for Resource-Constrained Environments Suku Nair, Subil Abraham, Omar Al Ibrahim HACNet Labs, Southern Methodist University Resource-Constrained Devices Alien
Excerpts of Web Application Security focusing on Data Validation. adapted for F.I.S.T. 2004, Frankfurt
 Excerpts of Web Application Security focusing on Data Validation adapted for F.I.S.T. 2004, Frankfurt by fs Purpose of this course: 1. Relate to WA s and get a basic understanding of them 2. Understand
Excerpts of Web Application Security focusing on Data Validation adapted for F.I.S.T. 2004, Frankfurt by fs Purpose of this course: 1. Relate to WA s and get a basic understanding of them 2. Understand
Chapter 11 Outline. A Simple PHP Example Overview of Basic Features of PHP Overview of PHP Database Programming. Slide 11-2
 Chapter 11 Outline A Simple PHP Example Overview of Basic Features of PHP Overview of PHP Database Programming Slide 11-2 1 Web Database Programming Using PHP Techniques for programming dynamic features
Chapter 11 Outline A Simple PHP Example Overview of Basic Features of PHP Overview of PHP Database Programming Slide 11-2 1 Web Database Programming Using PHP Techniques for programming dynamic features
CS 181 EXAM #1 NAME. You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. You may state without proof any fact taught in class or assigned as homework.
 CS 8 EXAM # NAME FALL 206 UCLA ID You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. You may state without proof any fact taught in class or assigned as homework. Give a simple verbal description of the language
CS 8 EXAM # NAME FALL 206 UCLA ID You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. You may state without proof any fact taught in class or assigned as homework. Give a simple verbal description of the language
Static Analysis in Practice
 in Practice 15-313: Foundations of Software Engineering Jonathan Aldrich 1 Outline: in Practice Case study: Analysis at ebay Case study: Analysis at Microsoft Analysis Results and Process Example: Standard
in Practice 15-313: Foundations of Software Engineering Jonathan Aldrich 1 Outline: in Practice Case study: Analysis at ebay Case study: Analysis at Microsoft Analysis Results and Process Example: Standard
A Typed Lambda Calculus for Input Sanitation
 A Typed Lambda Calculus for Input Sanitation Nathan Fulton Carthage College nfulton@carthage.edu April 11, 2013 Abstract Programmers often wish to validate or sanitize user input. One common approach to
A Typed Lambda Calculus for Input Sanitation Nathan Fulton Carthage College nfulton@carthage.edu April 11, 2013 Abstract Programmers often wish to validate or sanitize user input. One common approach to
lec3:nondeterministic finite state automata
 lec3:nondeterministic finite state automata 1 1.introduction Nondeterminism is a useful concept that has great impact on the theory of computation. When the machine is in a given state and reads the next
lec3:nondeterministic finite state automata 1 1.introduction Nondeterminism is a useful concept that has great impact on the theory of computation. When the machine is in a given state and reads the next
Module: Future of Secure Programming
 Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
I have read and understand all of the instructions below, and I will obey the Academic Honor Code.
 Midterm Exam CS 341-451: Foundations of Computer Science II Fall 2014, elearning section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama Print family (or last) name: Print given (or first) name: I have read and understand all
Midterm Exam CS 341-451: Foundations of Computer Science II Fall 2014, elearning section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama Print family (or last) name: Print given (or first) name: I have read and understand all
Automation Framework for Large-Scale Regular Expression Matching on FPGA. Thilan Ganegedara, Yi-Hua E. Yang, Viktor K. Prasanna
 Automation Framework for Large-Scale Regular Expression Matching on FPGA Thilan Ganegedara, Yi-Hua E. Yang, Viktor K. Prasanna Ming-Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California
Automation Framework for Large-Scale Regular Expression Matching on FPGA Thilan Ganegedara, Yi-Hua E. Yang, Viktor K. Prasanna Ming-Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California
CS 181 B&C EXAM #1 NAME. You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. You may assume without proof any statement proved in class.
 CS 8 B&C EXAM # NAME SPRING 204 UCLA ID You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. You may assume without proof any statement proved in class. Give a simple verbal description of the language recognized
CS 8 B&C EXAM # NAME SPRING 204 UCLA ID You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. You may assume without proof any statement proved in class. Give a simple verbal description of the language recognized
Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input
 Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input Sathish Kuppuswamy & Yufei Fu Department of computer Science University of Texas at Dallas March 21 st, 2012 Outline Bouncer Existing Techniques Bouncer
Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input Sathish Kuppuswamy & Yufei Fu Department of computer Science University of Texas at Dallas March 21 st, 2012 Outline Bouncer Existing Techniques Bouncer
Recursively Enumerable Languages, Turing Machines, and Decidability
 Recursively Enumerable Languages, Turing Machines, and Decidability 1 Problem Reduction: Basic Concepts and Analogies The concept of problem reduction is simple at a high level. You simply take an algorithm
Recursively Enumerable Languages, Turing Machines, and Decidability 1 Problem Reduction: Basic Concepts and Analogies The concept of problem reduction is simple at a high level. You simply take an algorithm
SLR parsers. LR(0) items
 SLR parsers LR(0) items As we have seen, in order to make shift-reduce parsing practical, we need a reasonable way to identify viable prefixes (and so, possible handles). Up to now, it has not been clear
SLR parsers LR(0) items As we have seen, in order to make shift-reduce parsing practical, we need a reasonable way to identify viable prefixes (and so, possible handles). Up to now, it has not been clear
One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline. Language Security
 Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
Automotive Software Security Testing
 Detecting and Addressing Cybersecurity Issues V1.1 2018-03-05 Code ahead! 2 Automated vulnerability detection and triage + = 3 How did we get here? Vector was engaged with a large, US Tier 1 and we were
Detecting and Addressing Cybersecurity Issues V1.1 2018-03-05 Code ahead! 2 Automated vulnerability detection and triage + = 3 How did we get here? Vector was engaged with a large, US Tier 1 and we were
Bottom-Up Parsing LR Parsing
 Bottom-Up Parsing LR Parsing Maryam Siahbani 2/19/2016 1 What we need for LR parsing LR0) states: Describe all possible states in which parser can be Parsing table ransition between LR0) states Actions
Bottom-Up Parsing LR Parsing Maryam Siahbani 2/19/2016 1 What we need for LR parsing LR0) states: Describe all possible states in which parser can be Parsing table ransition between LR0) states Actions
Symbolic String Verification: Combining String Analysis and Size Analysis
 Symbolic String Verification: Combining String Analysis and Size Analysis Fang Yu Tevfik Bultan Oscar H. Ibarra Deptartment of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, USA {yuf, bultan,
Symbolic String Verification: Combining String Analysis and Size Analysis Fang Yu Tevfik Bultan Oscar H. Ibarra Deptartment of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, USA {yuf, bultan,
CMSC330 Fall 2016 Midterm #2 2:00pm/3:30pm
 CMSC330 Fall 2016 Midterm #2 2:00pm/3:30pm Gradescope ID: (Gradescope ID is the First letter of your last name and last 5 digits of your UID) (If you write your name on the test, or your gradescope ID
CMSC330 Fall 2016 Midterm #2 2:00pm/3:30pm Gradescope ID: (Gradescope ID is the First letter of your last name and last 5 digits of your UID) (If you write your name on the test, or your gradescope ID
Detecting and exploiting integer overflows
 Detecting and exploiting integer overflows Guillaume TOURON Laboratoire Verimag, Ensimag - Grenoble INP Marie-Laure Potet, Laurent Mounier 20/05/11 1 / 18 Context Binary representation Integers misinterpretation
Detecting and exploiting integer overflows Guillaume TOURON Laboratoire Verimag, Ensimag - Grenoble INP Marie-Laure Potet, Laurent Mounier 20/05/11 1 / 18 Context Binary representation Integers misinterpretation
EC500. Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware. Lecture 1 & 2
 EC500 Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware Lecture 1 & 2 Mark Karpovsky January 17 th, 2013 1 Security Errors injected by the attacker (active attacks) Reliability Errors injected by random sources e.g.
EC500 Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware Lecture 1 & 2 Mark Karpovsky January 17 th, 2013 1 Security Errors injected by the attacker (active attacks) Reliability Errors injected by random sources e.g.
2010: Compilers REVIEW: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS HOW TO USE REGULAR EXPRESSIONS
 2010: Compilers Lexical Analysis: Finite State Automata Dr. Licia Capra UCL/CS REVIEW: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS a Character in A Empty string R S Alternation (either R or S) RS Concatenation (R followed by
2010: Compilers Lexical Analysis: Finite State Automata Dr. Licia Capra UCL/CS REVIEW: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS a Character in A Empty string R S Alternation (either R or S) RS Concatenation (R followed by
The Devils Behind Web Application Vulnerabilities
 The Devils Behind Web Application Vulnerabilities Defending against Web Application Vulnerabilities IEEE Computer, February 2012 Nuno Antunes, Marco Vieira {nmsa, mvieira}@dei.uc.pt Postgrad Colloquium
The Devils Behind Web Application Vulnerabilities Defending against Web Application Vulnerabilities IEEE Computer, February 2012 Nuno Antunes, Marco Vieira {nmsa, mvieira}@dei.uc.pt Postgrad Colloquium
Operating System Security
 Operating System Security Operating Systems Defined Hardware: I/o...Memory.CPU Operating Systems: Windows or Android, etc Applications run on operating system Operating Systems Makes it easier to use resources.
Operating System Security Operating Systems Defined Hardware: I/o...Memory.CPU Operating Systems: Windows or Android, etc Applications run on operating system Operating Systems Makes it easier to use resources.
Using Threat Modeling To Find Design Flaws
 Using Threat Modeling To Find Design Flaws Introduction Jim DelGrosso Run Cigital's Architecture Analysis practice 20+ years in software development in many different domains ~15 years focusing on software
Using Threat Modeling To Find Design Flaws Introduction Jim DelGrosso Run Cigital's Architecture Analysis practice 20+ years in software development in many different domains ~15 years focusing on software
Webapps Vulnerability Report
 Webapps Vulnerability Report Tuesday, January 12, 2010 Introduction This report provides detailed information of every vulnerability that was found and successfully exploited by CORE IMPACT during this
Webapps Vulnerability Report Tuesday, January 12, 2010 Introduction This report provides detailed information of every vulnerability that was found and successfully exploited by CORE IMPACT during this
LOCAL STRUCTURE AND DETERMINISM IN PROBABILISTIC DATABASES. Theodoros Rekatsinas, Amol Deshpande, Lise Getoor
 LOCAL STRUCTURE AND DETERMINISM IN PROBABILISTIC DATABASES Theodoros Rekatsinas, Amol Deshpande, Lise Getoor Motivation Probabilistic databases store, manage and query uncertain data Numerous applications
LOCAL STRUCTURE AND DETERMINISM IN PROBABILISTIC DATABASES Theodoros Rekatsinas, Amol Deshpande, Lise Getoor Motivation Probabilistic databases store, manage and query uncertain data Numerous applications
Understanding and Automatically Preventing Injection Attacks on Node.js
 Understanding and Automatically Preventing Injection Attacks on Node.js Michael Pradel TU Darmstadt Joint work with Cristian Staicu (TU Darmstadt) and Ben Livshits (Microsoft Research, Redmond) 1 Why JavaScript?
Understanding and Automatically Preventing Injection Attacks on Node.js Michael Pradel TU Darmstadt Joint work with Cristian Staicu (TU Darmstadt) and Ben Livshits (Microsoft Research, Redmond) 1 Why JavaScript?
Checking System Rules Using System-Specific, Programmer- Written Compiler Extensions
 Motivation for using Checking System Rules Using System-Specific, Programmer- Written Compiler Extensions Dawson Engler Benjamin Chelf Andy Chou Seth Hallem 1 Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University
Motivation for using Checking System Rules Using System-Specific, Programmer- Written Compiler Extensions Dawson Engler Benjamin Chelf Andy Chou Seth Hallem 1 Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University
Secure Programming Lecture 15: Information Leakage
 Secure Programming Lecture 15: Information Leakage David Aspinall 21st March 2017 Outline Overview Language Based Security Taint tracking Information flow security by type-checking Summary Recap We have
Secure Programming Lecture 15: Information Leakage David Aspinall 21st March 2017 Outline Overview Language Based Security Taint tracking Information flow security by type-checking Summary Recap We have
Introduction to Lexical Analysis
 Introduction to Lexical Analysis Outline Informal sketch of lexical analysis Identifies tokens in input string Issues in lexical analysis Lookahead Ambiguities Specifying lexical analyzers (lexers) Regular
Introduction to Lexical Analysis Outline Informal sketch of lexical analysis Identifies tokens in input string Issues in lexical analysis Lookahead Ambiguities Specifying lexical analyzers (lexers) Regular
Web Security. Outline
 Security CS 161/194-1 Anthony D. Joseph November 21, 2005 s Outline Static and Dynamic Content Firewall review Adding a DMZ Secure Topologies 2 1 Polls How many people have set up a personal web server?
Security CS 161/194-1 Anthony D. Joseph November 21, 2005 s Outline Static and Dynamic Content Firewall review Adding a DMZ Secure Topologies 2 1 Polls How many people have set up a personal web server?
R10 SET a) Construct a DFA that accepts an identifier of a C programming language. b) Differentiate between NFA and DFA?
 R1 SET - 1 1. a) Construct a DFA that accepts an identifier of a C programming language. b) Differentiate between NFA and DFA? 2. a) Design a DFA that accepts the language over = {, 1} of all strings that
R1 SET - 1 1. a) Construct a DFA that accepts an identifier of a C programming language. b) Differentiate between NFA and DFA? 2. a) Design a DFA that accepts the language over = {, 1} of all strings that
Security. CSC309 TA: Sukwon Oh
 Security CSC309 TA: Sukwon Oh Outline SQL Injection NoSQL Injection (MongoDB) Same Origin Policy XSSI XSS CSRF (XSRF) SQL Injection What is SQLI? Malicious user input is injected into SQL statements and
Security CSC309 TA: Sukwon Oh Outline SQL Injection NoSQL Injection (MongoDB) Same Origin Policy XSSI XSS CSRF (XSRF) SQL Injection What is SQLI? Malicious user input is injected into SQL statements and
Chapter Seven: Regular Expressions
 Chapter Seven: Regular Expressions Regular Expressions We have seen that DFAs and NFAs have equal definitional power. It turns out that regular expressions also have exactly that same definitional power:
Chapter Seven: Regular Expressions Regular Expressions We have seen that DFAs and NFAs have equal definitional power. It turns out that regular expressions also have exactly that same definitional power:
Implementation of Lexical Analysis
 Implementation of Lexical Analysis Outline Specifying lexical structure using regular expressions Finite automata Deterministic Finite Automata (DFAs) Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFAs) Implementation
Implementation of Lexical Analysis Outline Specifying lexical structure using regular expressions Finite automata Deterministic Finite Automata (DFAs) Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFAs) Implementation
Protect your apps and your customers against application layer attacks
 Protect your apps and your customers against application layer attacks Development 1 IT Operations VULNERABILITY DETECTION Bots, hackers, and other bad actors will find and exploit vulnerabilities in web
Protect your apps and your customers against application layer attacks Development 1 IT Operations VULNERABILITY DETECTION Bots, hackers, and other bad actors will find and exploit vulnerabilities in web
