2009 Shawn A. Bohner. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
|
|
|
- Anastasia Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2009 Shawn A. Bohner Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
2 GRASP II And Furthermore Polymorphism Indirection Pure Fabrication Protected Variations 2
3 Polymorphism Problem: How do we handle alternatives based on type? Chained ifs and lots of switch statements are a bad code smell new types require finding conditions and editing How do we create pluggable software components Pluggable components require swapping one module for another without changing surrounding design Solution: When related alternatives vary by type, assign responsibility to the types for which the behaviors varying. Use subtypes and polymorphic methods Eliminates lots of conditional logic based on type Corollary: Avoid instanceof tests
4 Polymorphism Example Bad: switch (square.gettype()) { case GO: case INCOME_TAX: case GO_TO_JAIL: default: }
5 Monopoly Polymorphism Example 5
6 Polymorphism Example (continued)
7 Monopoly Polymorphism Example 7
8 Monopoly Polymorphism Example 8
9 Monopoly Polymorphism Example 9
10 Monopoly Polymorphism Example 10
11 Polymorphism Observations Using polymorphism indicates that Piece class not needed since it s a proxy for the Player A design using Polymorphism can be easily extended for new variations When should supertype be an interface? Don t want to commit to a class hierarchy Need to reduce coupling Contraindication: Polymorphism can be over used speculative future-proofing
12 Team Polymorphism Working with your project team, identify a situation in your project where Polymorphism might be applicable. If no such situation exists, try to come up with an extension to your system that might use Polymorphism. What method(s) would behave differently for the different subtypes?
13 Pure Fabrication Problem: What object should have responsibility when solutions for low representation gap (like Info. Expert) lead us astray (i.e., into high coupling and low cohesion) Solution: Assign a cohesive set of responsibilities to an artificial (not in the domain model) class
14 Monopoly Pure Fabrication Example How do we model the player rolling the dice? If Player rolls dice, then dice rolling behavior not very reusable How do we provide something that would be more reusable? Die Player Cup 1 Cup Roll gettotal Dice * {ordered} Face Value Role getfv Pure Fabrication 14
15 Monopoly Pure Fabrication Example 15
16 Common Design Strategies Representational decomposition Lowering the representation gap (noun-based) Behavioral decomposition Centered around behaviors (verb-based)
17 Pure Fabrication Observations Benefits: Higher cohesion Greater potential for reuse Contraindications: Can be abused to create too many behavior objects Watch for data being passed to other objects for calculations
18 Cartoon of the Day
19 Indirection Problem: Where do we assign responsibility if we want to avoid direct coupling between two or more objects? Solution: Assign responsibility to an intermediate object to mediate between the other components
20 Indirection & Polymorphism Example 20
21 NexGen POS Indirection Example TaxMasterAdapter is a Pure Fabrication offering a level of Indirection Shields client (Sale) from variable server (proprietary tax calculator system) 21
22 Protected Variation Problem: How do we design objects and systems so that instability in them does not have undesirable effects on other elements? Solution: Identify points of predicted instability (variation) and assign responsibilities to create a stable interface around them
23 Protected Variation Pervasive in Computing Virtual machines and operating systems Data-driven designs (e.g., configuration files) Service lookup (URLs, DNS) Uniform access to methods/fields (Ada, Eiffel, C#, Objective-C, Ruby, ) Standard languages (SQL) Liskov Substitution Principle
24 Protected Variations: Observations When to use it? Variation point is a known area where clients need to be protected from variable servers Evolution point is an area where future variation may occur Should we invest in protecting against future variation? How likely is it to occur? If it is, then should probably use PV now If unlikely, then should probably defer using PV 24
25 Law of Demeter, or Don t Talk to Strangers Within a method, messages should only be sent to: this a parameter field of this element in collection of field of this new objects
26 Protected Variations Observations Benefits (if we guessed variation points correctly): Extensions easy to add Can plug in new implementations Lower coupling Lower cost of change Risk: watch out for speculative futureproofing
27 Protected Variations by Other Names Information hiding [Parnas72] We propose instead that one begins with a list of difficult design decisions which are likely to change. Each module is then designed to hide such a decision from the others. Open-Closed Principle [Meyer88] Modules should be both open (for extension ) and closed ( to modification[s] that affect clients)
28 Homework and Milestone Reminders Read Chapter 26 Homework 6 More GRASP on Video Store Design Due by 5:00pm Tuesday, January 26th, 2010 Milestone 4: Patterns and Detailed Design, with some Iteration 2 on the Side Due by 11:59pm Friday, January 29th,
Four More GRASP Principles CSSE 574: Session 5, Part 2
 Four More GRASP Principles CSSE 574: Session 5, Part 2 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu GRASP II And Furthermore Polymorphism Indirection
Four More GRASP Principles CSSE 574: Session 5, Part 2 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu GRASP II And Furthermore Polymorphism Indirection
GRASP 2. CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1
 GRASP 2 CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1 GRASP Patterns General Responsibility Assignment Software Patterns Describe fundamental principles of object design and responsibility assignment. Five GRASP
GRASP 2 CSC 440: Software Engineering Slide #1 GRASP Patterns General Responsibility Assignment Software Patterns Describe fundamental principles of object design and responsibility assignment. Five GRASP
CSSE 374: GRASP ing at the First Five Patterns Principles. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 CSSE 374: GRASP ing at the First Five Patterns Principles Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F22 Phone: (82) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify criteria
CSSE 374: GRASP ing at the First Five Patterns Principles Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F22 Phone: (82) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify criteria
Object-Oriented Design II - GRASP
 Object-Oriented Design II - GRASP SWEN-610 Foundations of Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Controller Creator Indirection Information expert High
Object-Oriented Design II - GRASP SWEN-610 Foundations of Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Controller Creator Indirection Information expert High
Eliminate enterprise software design instability - protect variations! Nickolay Kofanov
 Eliminate enterprise software design instability - protect variations! Nickolay Kofanov Owning a hammer doesn't make one an architect. Responsibility-Driven-Design The way of thinking about the design
Eliminate enterprise software design instability - protect variations! Nickolay Kofanov Owning a hammer doesn't make one an architect. Responsibility-Driven-Design The way of thinking about the design
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 7 GRASP
 ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 7 GRASP Dave Clarke 1 TODAY S LECTURE We will discuss 7 of the GRASP design patterns cohesion and coupling were covered earlier. These provide principles for evaluating
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 7 GRASP Dave Clarke 1 TODAY S LECTURE We will discuss 7 of the GRASP design patterns cohesion and coupling were covered earlier. These provide principles for evaluating
GRASP: MORE PATTERNS FOR
 Chapter 22 GRASP: MORE PATTERNS FOR ASSIGNING RESPONSIBILITIES Luck is the residue of design. Branch Rickey Objectives Learn to apply the remaining GRASP patterns. Introduction Previously, we explored
Chapter 22 GRASP: MORE PATTERNS FOR ASSIGNING RESPONSIBILITIES Luck is the residue of design. Branch Rickey Objectives Learn to apply the remaining GRASP patterns. Introduction Previously, we explored
CSSE 374: UML Activity Diagrams. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 CSSE 374: UML Activity Diagrams Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify criteria for the design of a software
CSSE 374: UML Activity Diagrams Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify criteria for the design of a software
From Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object Oriented Software. Read the sections corresponding to patterns covered in the following slides.
 From Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object Oriented Software Read the sections corresponding to patterns covered in the following slides. DESIGN PRINCIPLES Modularity Cohesion Coupling Separation
From Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object Oriented Software Read the sections corresponding to patterns covered in the following slides. DESIGN PRINCIPLES Modularity Cohesion Coupling Separation
Object-Oriented Design
 Object-Oriented Design Department of Computer Engineering Lecture 12: Object-Oriented Principles Sharif University of Technology 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed
Object-Oriented Design Department of Computer Engineering Lecture 12: Object-Oriented Principles Sharif University of Technology 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed
Object-Oriented Design
 Object-Oriented Design Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 15: Object-Oriented Principles 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed for modification. OCP states that we should
Object-Oriented Design Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 15: Object-Oriented Principles 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed for modification. OCP states that we should
Last Time: Object Design. Comp435 Object-Oriented Design. Last Time: Responsibilities. Last Time: Creator. Last Time: The 9 GRASP Patterns
 Last Time: Object Design Comp435 Object-Oriented Design Week 7 Computer Science PSU HBG The main idea RDD: Responsibility-Driven Design Identify responsibilities Assign them to classes and objects Responsibilities
Last Time: Object Design Comp435 Object-Oriented Design Week 7 Computer Science PSU HBG The main idea RDD: Responsibility-Driven Design Identify responsibilities Assign them to classes and objects Responsibilities
PART 4 Elaboration Iteration 2 More Patterns
 PART 4 Elaboration Iteration 2 More Patterns development cycle iteration phase inc. elaboration construction transition Chapter 22 UML Tools and UML as Blueprint 1 Forward, Reverse, and Round-Trip Engineering
PART 4 Elaboration Iteration 2 More Patterns development cycle iteration phase inc. elaboration construction transition Chapter 22 UML Tools and UML as Blueprint 1 Forward, Reverse, and Round-Trip Engineering
CSSE 374: More Object Design with Gang of Four Design Patterns
 CSSE 374: More Object Design with Gang of Four Design Patterns Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Q1 Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify
CSSE 374: More Object Design with Gang of Four Design Patterns Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Q1 Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify
Object-Oriented Design I
 Object-Oriented Design I SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Single responsibility High cohesion Information expert Low coupling
Object-Oriented Design I SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Single responsibility High cohesion Information expert Low coupling
GRASP Design Patterns A.A. 2018/2019
 GRASP Design Patterns A.A. 2018/2019 Objectives Introducing design patterns Introduzione ai design pattern Designing objects and responsibilities GRASP design patterns A long corridor A passage room Does
GRASP Design Patterns A.A. 2018/2019 Objectives Introducing design patterns Introduzione ai design pattern Designing objects and responsibilities GRASP design patterns A long corridor A passage room Does
CSSE 374: Logical Architecture. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 CSSE 374: Logical Architecture Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu An Engineering Decision Learning Outcomes: O-O Design Demonstrate object-oriented
CSSE 374: Logical Architecture Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu An Engineering Decision Learning Outcomes: O-O Design Demonstrate object-oriented
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 4 GRASP. Dave Clarke
 ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 4 GRASP Dave Clarke TODAY S LECTURE We will discuss and apply the GRASP design patterns. These provide principles for evaluating and improving designs. friends User Name??
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 4 GRASP Dave Clarke TODAY S LECTURE We will discuss and apply the GRASP design patterns. These provide principles for evaluating and improving designs. friends User Name??
GRASP ing at the First 5 Patterns Principles CSSE 574: Session 3, Part 4
 GRASP ing at the First 5 Patterns Principles CSSE 574: Session 3, Part 4 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu GRASP General Responsibility Assignment
GRASP ing at the First 5 Patterns Principles CSSE 574: Session 3, Part 4 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu GRASP General Responsibility Assignment
OODP OOAD Session 7a
 OODP OOAD Session 7a Session times PT group 1 Monday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 403 PT group 2 Thursday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 407 FT Tuesday 13:30 17:00 room: Malet 404 Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk Web Page:
OODP OOAD Session 7a Session times PT group 1 Monday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 403 PT group 2 Thursday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 407 FT Tuesday 13:30 17:00 room: Malet 404 Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk Web Page:
2009 Shawn A. Bohner. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 2009 Shawn A. Bohner Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Applying Patterns to NextGen POS Iteration 3 Local caching Used Adapter and Factory Failover
2009 Shawn A. Bohner Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Applying Patterns to NextGen POS Iteration 3 Local caching Used Adapter and Factory Failover
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Domain Engineering
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Domain Engineering Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Metamodels Design a metamodel
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Domain Engineering Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Metamodels Design a metamodel
Object-Oriented Design II
 Object-Oriented Design II SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Controller Pure fabrication Open/close Polymorphism Liskov substitution
Object-Oriented Design II SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Controller Pure fabrication Open/close Polymorphism Liskov substitution
We are at System Operation Contracts
 Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F22 Phone: (82) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu 2009 Shawn A. Bohner We are at System Operation Contracts 2 Where are the Operations in the SSD? Operation Contracts
Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F22 Phone: (82) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu 2009 Shawn A. Bohner We are at System Operation Contracts 2 Where are the Operations in the SSD? Operation Contracts
2009 Shawn A. Bohner. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 2009 Shawn A. Bohner Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Final Exam - Optional Monday, Feb. 22 nd, at 8am If you don t take the exam, we ll use your
2009 Shawn A. Bohner Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Final Exam - Optional Monday, Feb. 22 nd, at 8am If you don t take the exam, we ll use your
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Domain Specific Language Introduction
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Domain Specific Language Introduction Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Plan for the Day Introduction
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Domain Specific Language Introduction Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Plan for the Day Introduction
OODP Session 5a. Web Page: Visiting Hours: Tuesday 17:00 to 19:00
 OODP Session 5a Next week: Reading week Session times PT group 1 Monday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 403 PT group 2 Thursday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 407 FT Tuesday 13:30 17:00 room: Malet 404 Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk
OODP Session 5a Next week: Reading week Session times PT group 1 Monday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 403 PT group 2 Thursday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 407 FT Tuesday 13:30 17:00 room: Malet 404 Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk
CSSE 374: Even More Object Design with Gang of Four Design Patterns
 CSSE 374: Even More Object Design with Gang of Four Design Patterns Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Problem Solved Some engineer out there has
CSSE 374: Even More Object Design with Gang of Four Design Patterns Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Problem Solved Some engineer out there has
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems A formal design process Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Optional
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems A formal design process Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Optional
OODP Session 4. Web Page: Visiting Hours: Tuesday 17:00 to 19:00
 OODP Session 4 Session times PT group 1 Monday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 403 PT group 2 Thursday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 407 FT Tuesday 13:30 17:00 room: Malet 404 Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk Web Page: http://www.dcs.bbk.ac.uk/~oded
OODP Session 4 Session times PT group 1 Monday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 403 PT group 2 Thursday 18:00 21:00 room: Malet 407 FT Tuesday 13:30 17:00 room: Malet 404 Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk Web Page: http://www.dcs.bbk.ac.uk/~oded
Applying Some Gang of Four Design Patterns CSSE 574: Session 5, Part 3
 Applying Some Gang of Four Design Patterns CSSE 574: Session 5, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu Gang of Four (GoF) http://www.research.ibm.com/designpatterns/pubs/ddj-eip-award.htm
Applying Some Gang of Four Design Patterns CSSE 574: Session 5, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu Gang of Four (GoF) http://www.research.ibm.com/designpatterns/pubs/ddj-eip-award.htm
Final Exam CISC 475/675 Fall 2004
 True or False [2 pts each]: Final Exam CISC 475/675 Fall 2004 1. (True/False) All software development processes contain at least separate planning, testing, and documentation phases. 2. (True/False) The
True or False [2 pts each]: Final Exam CISC 475/675 Fall 2004 1. (True/False) All software development processes contain at least separate planning, testing, and documentation phases. 2. (True/False) The
Tecniche di Progettazione: Design Patterns
 Tecniche di Progettazione: Design Patterns Design principles 1 Plan of the lecture Your state of the art SOLID Grasp (to be continued next week) 2 Short summary of what you must know Few things on design
Tecniche di Progettazione: Design Patterns Design principles 1 Plan of the lecture Your state of the art SOLID Grasp (to be continued next week) 2 Short summary of what you must know Few things on design
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Cougaar Model-Driven Architecture Example
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Cougaar Model-Driven Architecture Example Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Cougaar Model-Driven Architecture Example Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline
17. GRASP: Designing Objects with Responsibilities
 17. GRASP: Designing Objects with Responsibilities Objectives Learn to apply five of the GRASP principles or patterns for OOD. Dr. Ziad Kobti School of Computer Science University of Windsor Understanding
17. GRASP: Designing Objects with Responsibilities Objectives Learn to apply five of the GRASP principles or patterns for OOD. Dr. Ziad Kobti School of Computer Science University of Windsor Understanding
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Introduction to Domain Engineering
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Introduction to Domain Engineering Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Metamodels Design
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Introduction to Domain Engineering Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Metamodels Design
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Software Factories
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Software Factories Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline Relate Model-Based
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Software Factories Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline Relate Model-Based
Model-Driven Architecture/ Development
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Shawn Bohner Model-Driven Architecture/ Development Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Transformations
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Shawn Bohner Model-Driven Architecture/ Development Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Transformations
Software Engineering
 Software Engineering 5. Software Design und Design Prinzipien Jonathan Brachthäuser Software Engineering Einordnung Problem Continuous Delivery & Feedback Lösung Anforderungsermittlung - (Nicht- )funktionale
Software Engineering 5. Software Design und Design Prinzipien Jonathan Brachthäuser Software Engineering Einordnung Problem Continuous Delivery & Feedback Lösung Anforderungsermittlung - (Nicht- )funktionale
Software Engineering
 Software Engineering 6. Design Patterns Jonathan Brachthäuser Software Engineering Einordnung Problem Continuous Delivery & Feedback Lösung Anforderungsermittlung - (Nicht- )funktionale Anf. - Anwendungsfälle
Software Engineering 6. Design Patterns Jonathan Brachthäuser Software Engineering Einordnung Problem Continuous Delivery & Feedback Lösung Anforderungsermittlung - (Nicht- )funktionale Anf. - Anwendungsfälle
Responsibilities. Using several specific design principles to guide OO design decisions.
 Designing Objects with Responsibilities Using several specific design principles to guide OO design decisions. Challenge Old-school advice on OOD After identifying i your requirements and creating a domain
Designing Objects with Responsibilities Using several specific design principles to guide OO design decisions. Challenge Old-school advice on OOD After identifying i your requirements and creating a domain
2 GRASP Patterns and basic OO Design. Roel Wuyts OASS
 2 GRASP Patterns and basic OO Design Roel Wuyts OASS1 2009-2010 Patterns 2 Bit of history... Christoffer Alexander The Timeless Way of Building, Christoffer Alexander, Oxford University Press, 1979, ISBN
2 GRASP Patterns and basic OO Design Roel Wuyts OASS1 2009-2010 Patterns 2 Bit of history... Christoffer Alexander The Timeless Way of Building, Christoffer Alexander, Oxford University Press, 1979, ISBN
Chapter 8: Class and Method Design
 Chapter 8: Class and Method Design Objectives Become familiar with coupling, cohesion, and connascence. Be able to specify, restructure, and optimize object designs. Be able to identify the reuse of predefined
Chapter 8: Class and Method Design Objectives Become familiar with coupling, cohesion, and connascence. Be able to specify, restructure, and optimize object designs. Be able to identify the reuse of predefined
Domain Analysis. SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering. Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology.
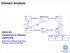 Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency. Object-Oriented Design: Assigning Responsibilities.
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency 15-214 toad Object-Oriented Design: Assigning Responsibilities Christian Kästner Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science With slides
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency 15-214 toad Object-Oriented Design: Assigning Responsibilities Christian Kästner Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science With slides
Topics. Software Process. Agile. Requirements. Basic Design. Modular Design. Design Patterns. Testing. Quality. Refactoring.
 CS310 - REVIEW Topics Process Agile Requirements Basic Design Modular Design Design Patterns Testing Quality Refactoring UI Design How these things relate Process describe benefits of using a software
CS310 - REVIEW Topics Process Agile Requirements Basic Design Modular Design Design Patterns Testing Quality Refactoring UI Design How these things relate Process describe benefits of using a software
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems Responsibility assignment Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Reading
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems Responsibility assignment Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Reading
Object Oriented. Analysis and Design
 OODP- OOAD Session 5 Object Oriented Analysis and Design Oded Lachish Department of Computer Science and Information Systems Birkbeck College, University of London Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk Web Page: http://www.dcs.bbk.ac.uk/~oded
OODP- OOAD Session 5 Object Oriented Analysis and Design Oded Lachish Department of Computer Science and Information Systems Birkbeck College, University of London Email: oded@dcs.bbk.ac.uk Web Page: http://www.dcs.bbk.ac.uk/~oded
The Design Patterns Matrix From Analysis to Implementation
 The Design Patterns Matrix From Analysis to Implementation This is an excerpt from Shalloway, Alan and James R. Trott. Design Patterns Explained: A New Perspective for Object-Oriented Design. Addison-Wesley
The Design Patterns Matrix From Analysis to Implementation This is an excerpt from Shalloway, Alan and James R. Trott. Design Patterns Explained: A New Perspective for Object-Oriented Design. Addison-Wesley
Object-Oriented Concepts and Design Principles
 Object-Oriented Concepts and Design Principles Signature Specifying an object operation or method involves declaring its name, the objects it takes as parameters and its return value. Known as an operation
Object-Oriented Concepts and Design Principles Signature Specifying an object operation or method involves declaring its name, the objects it takes as parameters and its return value. Known as an operation
Object-Oriented Design I - SOLID
 Object-Oriented Design I - SOLID SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Single responsibility Open/close Liskov substitution
Object-Oriented Design I - SOLID SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Single responsibility Open/close Liskov substitution
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: MDSD and Case Study
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: MDSD and Case Study Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline Relate Model-Based
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: MDSD and Case Study Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline Relate Model-Based
Introduction - SENG 330. Object-Oriented Analysis and Design
 Introduction - SENG 330 Object-Oriented Analysis and Design SENG 330 Fall 2006 Instructor: Alex Thomo Email: thomo@cs.uvic.ca Office hours: Office Hours: TWF 12:30-1:30 p.m. Location: ECS 556 Objective:
Introduction - SENG 330 Object-Oriented Analysis and Design SENG 330 Fall 2006 Instructor: Alex Thomo Email: thomo@cs.uvic.ca Office hours: Office Hours: TWF 12:30-1:30 p.m. Location: ECS 556 Objective:
CREATE YOUR CONTENT STRATEGY & LAUNCH PLAN Amanda Genther Inc. & Irresistible Offerings
 CREATE YOUR CONTENT STRATEGY & LAUNCH PLAN WHAT WE RE GOING TO TALK ABOUT» How to create content that entices your prospects to buy» How to create a content marketing plan that can be put on autopilot
CREATE YOUR CONTENT STRATEGY & LAUNCH PLAN WHAT WE RE GOING TO TALK ABOUT» How to create content that entices your prospects to buy» How to create a content marketing plan that can be put on autopilot
Domain Modeling. CSSE 574: Week 1, Part 3. Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) Cell (937)
 Domain Modeling CSSE 574: Week 1, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu s g Where we re going Sample UP Artifact Relationships date...
Domain Modeling CSSE 574: Week 1, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu s g Where we re going Sample UP Artifact Relationships date...
Index. Index. More information. block statements 66 y 107 Boolean 107 break 55, 68 built-in types 107
 A abbreviations 17 abstract class 105 abstract data types 105 abstract method 105 abstract types 105 abstraction 92, 105 access level 37 package 114 private 115 protected 115 public 115 accessors 24, 105
A abbreviations 17 abstract class 105 abstract data types 105 abstract method 105 abstract types 105 abstraction 92, 105 access level 37 package 114 private 115 protected 115 public 115 accessors 24, 105
References: Applying UML and patterns Craig Larman
 References: Applying UML and patterns Craig Larman 1 2 What are patterns? Principles and solutions codified in a structured format describing a problem and a solution A named problem/solution pair that
References: Applying UML and patterns Craig Larman 1 2 What are patterns? Principles and solutions codified in a structured format describing a problem and a solution A named problem/solution pair that
Summary of the course lectures
 Summary of the course lectures 1 Components and Interfaces Components: Compile-time: Packages, Classes, Methods, Run-time: Objects, Invocations, Interfaces: What the client needs to know: Syntactic and
Summary of the course lectures 1 Components and Interfaces Components: Compile-time: Packages, Classes, Methods, Run-time: Objects, Invocations, Interfaces: What the client needs to know: Syntactic and
CSSE 374: Design Class Diagrams. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 CSSE 374: Design Class Diagrams Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F22 Phone: (82) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu General solutions get you a 50% tip Plan for the Day Pre-break course evaluations
CSSE 374: Design Class Diagrams Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F22 Phone: (82) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu General solutions get you a 50% tip Plan for the Day Pre-break course evaluations
Design patterns. Jef De Smedt Beta VZW
 Design patterns Jef De Smedt Beta VZW Who Beta VZW www.betavzw.org Association founded in 1993 Computer training for the unemployed Computer training for employees (Cevora/Cefora) 9:00-12:30 13:00-16:00
Design patterns Jef De Smedt Beta VZW Who Beta VZW www.betavzw.org Association founded in 1993 Computer training for the unemployed Computer training for employees (Cevora/Cefora) 9:00-12:30 13:00-16:00
11/2/09. Code Critique. What goal are we designing to? What is the typical fix for code smells? Refactoring Liskov Substitution Principle
 Code Critique Identifying smells Refactoring Liskov Substitution Principle What goal are we designing to? What is the typical fix for code smells? What is a limitation of those fixes? How do we address
Code Critique Identifying smells Refactoring Liskov Substitution Principle What goal are we designing to? What is the typical fix for code smells? What is a limitation of those fixes? How do we address
CAS 703 Software Design
 Dr. Ridha Khedri Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University Canada L8S 4L7, Hamilton, Ontario Other 1 2 3 4 Other Principle of Least Privilege Principle of Fail-Safe Defaults Principle of
Dr. Ridha Khedri Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University Canada L8S 4L7, Hamilton, Ontario Other 1 2 3 4 Other Principle of Least Privilege Principle of Fail-Safe Defaults Principle of
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: More MBSD. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: More MBSD Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline Relate Model-Based Engineering
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: More MBSD Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: MBE Discipline Relate Model-Based Engineering
Software Engineering Principles
 1 / 19 Software Engineering Principles Miaoqing Huang University of Arkansas Spring 2010 2 / 19 Outline 1 2 3 Compiler Construction 3 / 19 Outline 1 2 3 Compiler Construction Principles, Methodologies,
1 / 19 Software Engineering Principles Miaoqing Huang University of Arkansas Spring 2010 2 / 19 Outline 1 2 3 Compiler Construction 3 / 19 Outline 1 2 3 Compiler Construction Principles, Methodologies,
PROCESS DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGY The development process of an API fits the most fundamental iterative code development
 INTRODUCING API DESIGN PRINCIPLES IN CS2 Jaime Niño Computer Science, University of New Orleans New Orleans, LA 70148 504-280-7362 jaime@cs.uno.edu ABSTRACT CS2 provides a great opportunity to teach an
INTRODUCING API DESIGN PRINCIPLES IN CS2 Jaime Niño Computer Science, University of New Orleans New Orleans, LA 70148 504-280-7362 jaime@cs.uno.edu ABSTRACT CS2 provides a great opportunity to teach an
Setting the stage... Key Design Issues. Main purpose - Manage software system complexity by improving software quality factors
 Setting the stage... Dr. Radu Marinescu 1 1946 Key Design Issues Main purpose - Manage software system complexity by...... improving software quality factors... facilitating systematic reuse Dr. Radu Marinescu
Setting the stage... Dr. Radu Marinescu 1 1946 Key Design Issues Main purpose - Manage software system complexity by...... improving software quality factors... facilitating systematic reuse Dr. Radu Marinescu
Avancier Methods. Very basic design patterns. It is illegal to copy, share or show this document
 Methods Very basic design patterns It is illegal to copy, share or show this document (or other document published at http://avancier.co.uk) without the written permission of the copyright holder Copyright
Methods Very basic design patterns It is illegal to copy, share or show this document (or other document published at http://avancier.co.uk) without the written permission of the copyright holder Copyright
Modularity Guidelines for design in any programming language
 Modularity Guidelines for design in any programming language 14-1 Modular Software Software constructed as assemblies of small pieces» Each piece encompasses the data and operations necessary to do one
Modularity Guidelines for design in any programming language 14-1 Modular Software Software constructed as assemblies of small pieces» Each piece encompasses the data and operations necessary to do one
Assigning Responsibilities
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency (Part 2: Designing (Sub-)Systems) Assigning Responsibilities Christian Kästner Bogdan Vasilescu School of Computer Science 1 2 2 Learning
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency (Part 2: Designing (Sub-)Systems) Assigning Responsibilities Christian Kästner Bogdan Vasilescu School of Computer Science 1 2 2 Learning
COMP 6471 Software Design Methodologies
 COMP 647 Software Design Methodologies Fall 20 Dr Greg Butler http://www.cs.concordia.ca/~gregb/home/comp647-fall20.html Course Introduction Course People Course Components What the course is What the
COMP 647 Software Design Methodologies Fall 20 Dr Greg Butler http://www.cs.concordia.ca/~gregb/home/comp647-fall20.html Course Introduction Course People Course Components What the course is What the
18.1 Definitions and General OO Principles
 Chapter 18: Design Patterns Design patterns are elegant, adaptable, and reusable solutions to everyday software development problems. Each pattern includes a description of a commonly occuring type of
Chapter 18: Design Patterns Design patterns are elegant, adaptable, and reusable solutions to everyday software development problems. Each pattern includes a description of a commonly occuring type of
Object Analysis & Design in the textbook. Introduction to GRASP: Assigning Responsibilities to Objects. Responsibility-Driven Design
 Object Analysis & Design in the textbook Chapter 2 Object Oriented Design Process Introduction to GRASP: Assigning Responsibilities to Objects CS 4354 Summer II 2016 Jill Seaman Much of the material in
Object Analysis & Design in the textbook Chapter 2 Object Oriented Design Process Introduction to GRASP: Assigning Responsibilities to Objects CS 4354 Summer II 2016 Jill Seaman Much of the material in
Modularity!! Guidelines for design! in any programming language!
 Modularity!! Guidelines for design! in any programming language! 14-1! Modular Software! Software constructed as assemblies of small pieces! 14-2! Modular Software 2! Software constructed as assemblies
Modularity!! Guidelines for design! in any programming language! 14-1! Modular Software! Software constructed as assemblies of small pieces! 14-2! Modular Software 2! Software constructed as assemblies
The following topics will be covered in this course (not necessarily in this order).
 The following topics will be covered in this course (not necessarily in this order). Introduction The course focuses on systematic design of larger object-oriented programs. We will introduce the appropriate
The following topics will be covered in this course (not necessarily in this order). Introduction The course focuses on systematic design of larger object-oriented programs. We will introduce the appropriate
be used for more than one use case (for instance, for use cases Create User and Delete User, one can have one UserController, instead of two separate
 UNIT 4 GRASP GRASP: Designing objects with responsibilities Creator Information expert Low Coupling Controller High Cohesion Designing for visibility - Applying GoF design patterns adapter, singleton,
UNIT 4 GRASP GRASP: Designing objects with responsibilities Creator Information expert Low Coupling Controller High Cohesion Designing for visibility - Applying GoF design patterns adapter, singleton,
Information Expert (or Expert)
 Page 2 Page 3 Pattern or Principle? Information Expert (or Expert) Class Responsibility Sale Knows Sale total SalesLineItem Knows line item total ProductDescription Knows product price The GRASP patterns
Page 2 Page 3 Pattern or Principle? Information Expert (or Expert) Class Responsibility Sale Knows Sale total SalesLineItem Knows line item total ProductDescription Knows product price The GRASP patterns
A4 Explain how the Visitor design pattern works (4 marks)
 COMP61532 exam Performance feedback Original marking scheme in bold, additional comments in bold italic. Section A In general the level of English was poor, spelling and grammar was a problem in most cases.
COMP61532 exam Performance feedback Original marking scheme in bold, additional comments in bold italic. Section A In general the level of English was poor, spelling and grammar was a problem in most cases.
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Transformational Programming
 CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Transformational Programming Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Transformations Define
CSSE 490 Model-Based Software Engineering: Transformational Programming Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Transformations Define
Design and Information Hiding
 Design and Information Hiding 15-214: Foundations of Software Engineering Jonathan Aldrich Related Reading: D. L. Parnas. On the Criteria To Be Used in Decomposing Systems into Modules. CACM 15(12):1053-1058,
Design and Information Hiding 15-214: Foundations of Software Engineering Jonathan Aldrich Related Reading: D. L. Parnas. On the Criteria To Be Used in Decomposing Systems into Modules. CACM 15(12):1053-1058,
Department of Computer Science Undergraduate Events
 Events this week Public Speaking 101 Date: Mon., Jan 25 Time: 5 6 pm Location: DMP 101 CS Co op Info Session Date: Wed., Jan 27 Time: 5:00 6:30 pm Location: DMP 201 OR Date: Thurs., Jan 28 Time: 12:30
Events this week Public Speaking 101 Date: Mon., Jan 25 Time: 5 6 pm Location: DMP 101 CS Co op Info Session Date: Wed., Jan 27 Time: 5:00 6:30 pm Location: DMP 201 OR Date: Thurs., Jan 28 Time: 12:30
Applying Design Patterns to accelerate development of reusable, configurable and portable UVCs. Accellera Systems Initiative 1
 Applying Design Patterns to accelerate development of reusable, configurable and portable UVCs. Accellera Systems Initiative 1 About the presenter Paul Kaunds Paul Kaunds is a Verification Consultant at
Applying Design Patterns to accelerate development of reusable, configurable and portable UVCs. Accellera Systems Initiative 1 About the presenter Paul Kaunds Paul Kaunds is a Verification Consultant at
Assigning Responsibilities (Patterns of Responsibility Assignment Principles: GRASP)
 Subsystem design basics Assigning Responsibilities (Patterns of Responsibility Assignment Principles: GRASP) Dept. of Computer Science Baylor University Focus on modeling how subsystems accomplish goals
Subsystem design basics Assigning Responsibilities (Patterns of Responsibility Assignment Principles: GRASP) Dept. of Computer Science Baylor University Focus on modeling how subsystems accomplish goals
CSE 70 Final Exam Fall 2009
 Signature cs70f Name Student ID CSE 70 Final Exam Fall 2009 Page 1 (10 points) Page 2 (16 points) Page 3 (22 points) Page 4 (13 points) Page 5 (15 points) Page 6 (20 points) Page 7 (9 points) Page 8 (15
Signature cs70f Name Student ID CSE 70 Final Exam Fall 2009 Page 1 (10 points) Page 2 (16 points) Page 3 (22 points) Page 4 (13 points) Page 5 (15 points) Page 6 (20 points) Page 7 (9 points) Page 8 (15
1 Software Architecture
 Some buzzwords and acronyms for today Software architecture Design pattern Separation of concerns Single responsibility principle Keep it simple, stupid (KISS) Don t repeat yourself (DRY) Don t talk to
Some buzzwords and acronyms for today Software architecture Design pattern Separation of concerns Single responsibility principle Keep it simple, stupid (KISS) Don t repeat yourself (DRY) Don t talk to
Lecture: Modular Design
 Software Engineering Lecture: Modular Design Thomas Fritz Many thanks to Philippe Beaudoin, Gail Murphy, David Shepherd, Neil Ernst and Meghan Allen Reading! For next lecture: (all required) Composite
Software Engineering Lecture: Modular Design Thomas Fritz Many thanks to Philippe Beaudoin, Gail Murphy, David Shepherd, Neil Ernst and Meghan Allen Reading! For next lecture: (all required) Composite
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency A formal design process Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod Darya Melicher 1 Administrivia Homework 2 feedback in your GitHub repository Homework
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency A formal design process Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod Darya Melicher 1 Administrivia Homework 2 feedback in your GitHub repository Homework
Patterns and Testing
 and Lecture # 7 Department of Computer Science and Technology University of Bedfordshire Written by David Goodwin, based on the lectures of Marc Conrad and Dayou Li and on the book Applying UML and (3
and Lecture # 7 Department of Computer Science and Technology University of Bedfordshire Written by David Goodwin, based on the lectures of Marc Conrad and Dayou Li and on the book Applying UML and (3
Plan. Design principles: laughing in the face of change. What kind of change? What are we trying to achieve?
 Plan Design principles: laughing in the face of change Perdita Stevens School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are we trying to achieve? Review: Design principles you know from Inf2C-SE Going
Plan Design principles: laughing in the face of change Perdita Stevens School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are we trying to achieve? Review: Design principles you know from Inf2C-SE Going
Originality is Overrated: OO Design Principles
 Originality is Overrated: OO Design Principles Kenneth M. Anderson University of Colorado, Boulder CSCI 4448/6448 Lecture 13 10/09/2007 University of Colorado, 2007 1 Lecture Goals Review material from
Originality is Overrated: OO Design Principles Kenneth M. Anderson University of Colorado, Boulder CSCI 4448/6448 Lecture 13 10/09/2007 University of Colorado, 2007 1 Lecture Goals Review material from
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency. Assigning Responsibilities to Objects. toad. Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Assigning Responsibilities to Objects toad Fall 2014 Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science Key concepts from Thursday
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Assigning Responsibilities to Objects toad Fall 2014 Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science Key concepts from Thursday
Object-Oriented Analysis and Design
 0. Object Orientation: An Subject/Topic/Focus: over this lecture Summary: Lecturer, lecture, rooms, assistants, lab classes, credit points... Need for systems analysis and software engineers Literature
0. Object Orientation: An Subject/Topic/Focus: over this lecture Summary: Lecturer, lecture, rooms, assistants, lab classes, credit points... Need for systems analysis and software engineers Literature
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 4 SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
 ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 4 SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE Dave Clarke 1 THIS LECTURE At the end of this lecture you will know notations for expressing software architecture the design principles of cohesion
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 4 SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE Dave Clarke 1 THIS LECTURE At the end of this lecture you will know notations for expressing software architecture the design principles of cohesion
Application Architectures, Design Patterns
 Application Architectures, Design Patterns Martin Ledvinka martin.ledvinka@fel.cvut.cz Winter Term 2017 Martin Ledvinka (martin.ledvinka@fel.cvut.cz) Application Architectures, Design Patterns Winter Term
Application Architectures, Design Patterns Martin Ledvinka martin.ledvinka@fel.cvut.cz Winter Term 2017 Martin Ledvinka (martin.ledvinka@fel.cvut.cz) Application Architectures, Design Patterns Winter Term
Cross-platform software development in practice. Object-Oriented approach.
 Cross-platform software development in practice. Object-Oriented approach. Vitaly Repin Maemo Devices, Nokia Maemo March 25, 2010 (Maemo) Cross-platform software development. March 25, 2010 1 / 37 Outline
Cross-platform software development in practice. Object-Oriented approach. Vitaly Repin Maemo Devices, Nokia Maemo March 25, 2010 (Maemo) Cross-platform software development. March 25, 2010 1 / 37 Outline
Lecture 17: Patterns Potpourri. Copyright W. Howden 1
 Lecture 17: Patterns Potpourri Copyright W. Howden 1 GOF Patterns GOF: Gamma, Helm, Johnson, Vlissides Design Patterns, Addison Wesley, 1995 Patterns we have seen so far Creational Patterns e.g. Factory,
Lecture 17: Patterns Potpourri Copyright W. Howden 1 GOF Patterns GOF: Gamma, Helm, Johnson, Vlissides Design Patterns, Addison Wesley, 1995 Patterns we have seen so far Creational Patterns e.g. Factory,
CSCD01 Engineering Large Software Systems. Design Patterns. Joe Bettridge. Winter With thanks to Anya Tafliovich
 CSCD01 Engineering Large Software Systems Design Patterns Joe Bettridge Winter 2018 With thanks to Anya Tafliovich Design Patterns Design patterns take the problems consistently found in software, and
CSCD01 Engineering Large Software Systems Design Patterns Joe Bettridge Winter 2018 With thanks to Anya Tafliovich Design Patterns Design patterns take the problems consistently found in software, and
Object Oriented Programming
 Object Oriented Programming Comp-361 : O.O. Programming Lecture 4 Alexandre Denault Original notes by Jörg Kienzle and Hans Vangheluwe Computer Science McGill University Winter 2008 On my desk You should
Object Oriented Programming Comp-361 : O.O. Programming Lecture 4 Alexandre Denault Original notes by Jörg Kienzle and Hans Vangheluwe Computer Science McGill University Winter 2008 On my desk You should
Schedule(3/3) March 18th 13:00 Unified Process and Usecase-Driven Approach. (problem definition, use case model)
 Schedule(3/3) March 18th 13:00 Unified Process and Usecase-Driven Approach 14:30 Case Study of Elevator Control System (problem definition, use case model) March 19th 13:00 Case Study of Elevator Control
Schedule(3/3) March 18th 13:00 Unified Process and Usecase-Driven Approach 14:30 Case Study of Elevator Control System (problem definition, use case model) March 19th 13:00 Case Study of Elevator Control
17.11 Bean Rules persistent
 17.10 Java Beans Java beans are a framework for creating components in Java. AWT and Swing packages are built within this framework Made to fit in with graphic development environments such as Jbuilder
17.10 Java Beans Java beans are a framework for creating components in Java. AWT and Swing packages are built within this framework Made to fit in with graphic development environments such as Jbuilder
1: Introduction to Object (1)
 1: Introduction to Object (1) 김동원 2003.01.20 Overview (1) The progress of abstraction Smalltalk Class & Object Interface The hidden implementation Reusing the implementation Inheritance: Reusing the interface
1: Introduction to Object (1) 김동원 2003.01.20 Overview (1) The progress of abstraction Smalltalk Class & Object Interface The hidden implementation Reusing the implementation Inheritance: Reusing the interface
