How much LTE traffic can be offloaded?
|
|
|
- Lionel Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How much LTE traffic can be offloaded? Souheir EIDO 1,2 and Annie GRAVEY 1,2 1 Telecom Bretagne, France firstname.lastname@telecom-bretagne.eu 2 IRISA, France Abstract. In this paper, we propose different offloading scenarios, which help operators controlling the ever increasing of mobile data volumes over the femto and the macro cellular networks. We consider the Selected IP traffic offload (SIPTO) approach in order to selectively offload mobile IP traffic in order to use servers deployed within the metro network at/above the RAN. A quantitative study is carried out to estimate the potential gains of bandwidth due to mobile traffic offload, both in the core and the metro networks, depending on the location of the servers accessed thanks to the offloading strategy. Keywords: Mobile Data Offloading, SIPTO, LIPA. 1 INTRODUCTION In the last few years, many fixed network operators have deployed multiple caches close to the end-users in order to limit the bandwidth requirements related to video streaming distribution in the downlink. Moreover, many cloud services can also rely on data centers that are distributed within the network in order to serve demands as close as possible to the users. In the present paper, we assess whether similar gains can be obtained for mobile traffic carried over an LTE access network. This is not obvious, since using distributed servers in LTE is not as simple as using distributed servers for fixed services, due to the mobile network specific architecture. Carrying on the same momentum that we have witnessed since the late of the 20th century, the mobile data traffic is expected to grow rapidly during the next decade. The compounded Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) will be close to 75% [1]. This is due to the increasing number of internet-based services such as online games and video services (streaming, conferencing, etc.). LTE routing is currently based on tunneling the traffic between the user equipment (UE) and the Packet-data-network Gateway (PGW) in both directions. The PGW is the gateway towards the IP backbone and the Internet. More precisely, the tunneling starts from the user equipment (UE) to the radio base station (enodeb), then from the enodeb to the Evolved Packed Core network (EPC), and thus to a Serving Gateway (SGW) which forwards it to a Packet-data-network Gateway (PGW). In particular, even if a video server or a datacenter is geographically close to a UE, the
2 requested content has to go through the EPC in order to enter the tunnel existing between the UE and the PGW. Mobile data offloading potentially allows a telecom operator to dynamically control the delivery of data originally targeted for mobile network using different available technologies such as: WiFi and Femtocells [2]. Each of these technologies proposes both EPC-routed and Non-EPC-routed traffic offloading solutions. EPC-routed Traffic offload is based on the network triggering the UE to use either femtocells (home base stations) or WiFi access instead of the macrocells. The traffic is then forwarded towards the EPC network. This solution allows alleviating the load on enodebs. Non-EPC-routed Traffic offload allows to alleviate the loads on SGW and PGW, and to balance load between available gateways. This is achieved by dynamically controlling routes used by the mobile traffic in the aggregation and core networks regardless of the technology used at the access network. Local IP Access (LIPA) and Selected IP Traffic Offload (SIPTO) are two 3GPP solutions that can be used for traffic offloading in the aggregation/core network. Assuming that these offloading techniques are actually implemented, what is the gain, in terms of offloaded traffic, that can be expected? The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the state of the art of different mobile data offloading techniques. Section 3 derives estimates of the amounts of offloaded traffic for each network portion and thus quantifies the potential bandwidth gains. Finally, Section 4 concludes the paper. 2 MOBILE DATA OFFLOADING Over the long term, telecom operators have noticed that with the dramatic increase of the mobile data traffic, the demand for bandwidth will continue to increase at every segment of the network (access, metro and backbone). Offloading mobile data is thus considered as one of the most promising technologies that help reducing the bandwidth demand on both aggregation and core networks. The present section reviews popular offloading approaches relying on femtocells. We first point out the benefits of the deployment of femtocells for telecom operators and its consequences. Next, we present the LIPA and SIPTO approaches that have been introduced by 3GPP. Finally, we outline the importance of mobile data offloading for the end-users as well as the operators. 2.1 Access Network Offloading Femtocells, also called Home enodebs (HeNB), are low power cellular base stations. They were first defined by 3GPP in order to offload the mobile traffic from the standard base stations (macro-cells) and thus improve the indoor voice and data coverage of mobile networks [3]. HeNBs transmit the mobile traffic using the same spec-
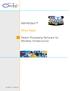
3 trum than macrocells [4]. Femtocells are connected to the cellular core network by the means of an IP home router, which uses a direct broadband connection such as: Fiber To The Home (FTTH) or Digital Subscriber Line (DSL). This connection replaces the backhaul infrastructure currently used for the macrocells. Wi-Fi access points located in Home Gateways can be used similarly. Besides the capacity, coverage and network performance s improvement, the deployment of femtocells helps operators reducing a significant part of capital expenditure (CAPEX) as well as operational expense (OPEX). According to Cisco [1], 33% of global mobile data traffic (GMDT) was offloaded onto the fixed network using femtocells and Wi-Fi in By 2017, the offloaded mobile data traffic is expected to reach 46% of the GMDT and thus, the use of femtocells and WiFi technologies to access the mobile core network will help saving 13% of CAPEX costs dedicated for macrocells deployment. Furthermore, considering the ongoing costs for running macro base stations, deploying and monitoring their backhaul as well as additional electricity, OPEX is reduced to only 200$ per year per femtocell down from 60,000 $ per year per macrocell [5]. However, due the fact that femtocells transmit on the same spectrum as macrocells, the following problems are still under study: Radio interferences Femtocell location detection Moreover, access network offloading does not help in solving the issue raised in Section 1, namely mobile traffic routing through the EPC. 2.2 Mobile aggregation/core network offloading 3GPP has extended the use of femtocells in order to limit the loads of both aggregation and core networks. Indeed, femtocells potentially allow a direct access to the public IP network via the fixed network. Hence, by adding local PDN gateway (L- PGW) which is either co-located with the femtocell or a standalone entity connected to the femtocell via a separate interface, mobile data traffic will bypass the mobile core network and thus reduce the load of the standard gateways (SGW and PGW) used in 3G/4G networks. The use of the local PDN gateways with the femtocells was initially proposed by 3GPP in Rel-10 [7]. LIPA and SIPTO, two solutions of traffic offloading, were also introduced in order to offload selected IP traffics from the mobile core network. LIPA and SIPTO both offer a direct connection between mobile users and the Home/Enterprise Local Access Network (LAN) devices. At the same time, a UE shall be able to have simultaneous access to the local IP network (using LIPA/SIPTO) and to the operator s core network through the normal path. These solutions were improved in 3GPP Rel-12 [7] by solving some of the mobility issues raised in their first version. Figure 1 illustrates the 3GPP regular data path as well as offloading architectures for both LIPA and SIPTO solutions.
4 Fig. 1. LIPA and SIPTO solutions for mobile data offloading LIPA is an offloading technique allowing a direct connection between the UE and the local IP network using a femtocell (HeNB) with a co-located or a standalone Local Gateway (LGW). The LGW must support limited PGW as well as SGW functionalities such as interconnecting with the external IP networks, UE s IP address allocation functionality, DL packet buffering, etc. [8]. However, LIPA is only intended to allow the UEs to access their own Private Local Access Network via a femtocell. Thus, UEs may not apply LIPA when connected through a macrocell. In particular, no service continuity is supported in case of mobility (e.g. whenever a UE moves away from the femtocell, all his sessions are terminated). SIPTO is an offloading mechanism defined by 3GPP to allow mobile operators to selectively breakout some of the user s IP data traffic: 1. At the local network using a femtocell with a co-located or a standalone LGW Similar to LIPA ; 2. At or above the RAN using a macrocell by selecting an SGW and PGW that are topologically/geographically closer to the radio network [9].
5 Unlike LIPA, SIPTO can be used in both macrocells and femtocells. However, in SIPTO (as in LIPA) service continuity in case of mobility is not ensured although partial solutions have already been proposed to solve this issue (see for example [10] and [11]). Once this issue solved, the use of LIPA and SIPTO s offloading techniques is expected to allow significant benefits for both mobile operators (in terms of OPEX) as well as for the end-users (in terms of QoS) [12, 13]. In the present paper, we do not address potential enhancements to LIPA/SIPTO, which could solve the issue of session continuity in case of mobility. On the other hand, we want to assess the potential gain in terms of bandwidth, due to offloading the major part of mobile data into the metropolitan network at/above the RAN. Therefore, we chose to apply SIPTO technique to selectively offload a part of the mobile data traffic into the metro caching servers, assuming that session continuity is not an issue. 3 EVALUATION OF THE AMOUNT OF OFFLOADED MOBILE TRAFFIC In future years, mobile data traffic is expected to grow faster than fixed data traffic. Indeed, mobile data traffic is expected to double each year during the next five years. However, during the same period, fixed data traffic will remain significantly higher than mobile data traffic in volume. Table 1 shows the Cisco s forecast for the global IP traffic between 2012 and CAGR By Type (EB per Month) Total IP Traffic 43, ,643 23% Total Fixed Traffic 42, ,486 21% Total Mobile Traffic 0,885 11,157 66% Table 1. Global IP Traffic, Source Cisco VNI 2013 [15]. We see that during the time period, mobile data traffic will still remain significantly lower than fixed data traffic in absolute terms, growing from 2% in 2012 to slightly more than 9% in Considering the continuous growth of IP based traffic, telecom operators must increase the capacity of their networks. In that aim, actual deployments are based on distributing video servers and datacenters as close to the end-users as possible. 3.1 Distribution of services from the metro network There are currently two different video distribution architectures: IPTV and Internet Video.
6 In the first one, the Internet Service Provider (ISP) also distributes video; this service is known as IPTV. As the content provider controls the Digital Rights Management (DRM), and the access of the users to the various content, it is aware of all demands and can dynamically select the server, which shall serve each demand. In particular, IPTV operators distribute servers within the metro network in order to improve user s experience and network performance. There are a few main video servers (large servers) that contain the complete set of offered video content, and several smaller, secondary servers, operating often as caches, which only store the more popular content. A recent publication [15] shows that the file hit ratio in such secondary servers can be relatively small (less than 35%) while the byte hit ratio in those servers is quite large (75%), as popular content are requested very often compared to the mean request rate. In ``Internet Video, the Content Provider (CP) distributes the content over the Internet. Content distribution over the Internet relies on an overlay network linking multiple servers located at peering points. Popular content are present at multiple locations, while less popular are pulled on demand from central video servers. The Content Provider may directly distribute its own content (e.g. Google directly distributes YouTube content) or delegate content distribution to Content Distribution Networks (CDNs) such as Akamai and Limelight. CDN servers are located close to the peering points with the ISP and are controlled by the CP or the CDN. The ISP has a role neither in controlling the DRMs, nor in controlling the access to the content. As the ISP usually does not accept another provider to control servers within its own domain, there are no video caches in the metro network and the traffic cannot be offloaded. However, the video distribution ecosystem is constantly evolving, and strategic partnerships such as the one signed in 2012 between Akamai and Orange [16] may lead in the future to locating video caches used by Internet video services within ISPs domains. Although video is expected to be dominant in future traffic mixes, other services can also benefit from distributed servers. This is true for all cloud-based services such as e.g. on-line gaming and business services. 3.2 Gain of bandwidth at the core network Let us consider services offered to mobile users. These services can be achieved either in a centralized manner (relying on a central server located in the backbone), or in a distributed manner (relying on distributed servers located in the metro network). We now compare the respective amounts of traffic, generated by mobile services, over specific portions of the network, under different assumptions regarding the location of the distributed servers. A centralized LTE architecture relies on a very small number of PGWs, located high in the IP backbone, whereas a distributed LTE architecture relies on a larger number of PGWs (which we call LGWs in order to differentiate them from the standard PGWs). LGWs are located closer to the user, typically within the metro network.
7 Assuming that distributed servers and LGWs are conveniently co-located, the load reduction in the core network (CN) for the years 2012 and 2017 is now computed. Let X, Y, Z respectively represent the volumes in Total IP traffic, Total traffic generated by fixed services and Total traffic generated by the mobile services. Let also Xc, Yc and Zc respectively represent the volumes in Total IP traffic that crosses the CN, Total fixed network s traffic that crosses the CN and Total mobile network s traffic that crosses the CN. Gcm quantifies the potential gain of bandwidth in the core network due to mobile traffic offloading. Gcm is the percentage of traffic crossing the CN that can be diverted from the CN if mobile offloading is applied. The demands corresponding to this traffic are served from servers located in the metro network. Obviously: Xc=Yc+Zc (1) According to [17] we have with α=0.43 in 2012 and α=0.25 in Xc=α*X (2) In a centralized LTE architecture, none of the mobile traffic is offloaded, which yields Zc=Z and Yc=Xc-Z. The amount of fixed traffic, which is not offloaded from the CN, is then Yc=α*X Z (3) In a distributed LTE architecture, mobile traffic can be offloaded. We also assume that the proportions of traffic generated respectively by fixed services and mobile services, which can be served in the metro network, are identical: Zc/Z = Yc/Y (4) The amount of traffic crossing the CN, generated by mobile services and that can be offloaded is equal to Z*(1- Yc/Y) which finally yields Gcm Gcm=100*(1-Yc/Y)*Z/Xc (5) Table 2 applies the above derivation to the data given in Table 1 in order to assess the impact on the CN of distributing the LTE architecture. The obtained results imply that: In 2012, mobile traffic offloading allows to reduce the volume of traffic supported by the CN by less than 3%. This gain can be considered as negligible compared to the investment (in terms of LGW deployment) required to achieve it. In 2017, more than 30% of CN bandwidth can be offloaded if a distributed mobile LTE architecture is implemented. This significant gain can potentially justify the CAPEX increase due a distributed LTE architecture.
8 X Y Z Xc Yc Centralized LTE Distributed LTE Centralized LTE Distributed LTE Zc Gcm % % Table 2. Quantifying bandwidth gain in core network due to mobile traffic offloading 3.3 Gain of bandwidth at the metropolitan network As the gain in distributing the LTE architecture is not significant in 2012, we focus the following study to predictions relative to Regarding the traffic growth study presented in [17], two distribution models have been introduced: 1. Metro Centralized Caching: In this model, servers are centralized at the edge of the backbone network (fig.2, servers P3). 2. Metro Distributed Caching: In this model, servers are distributed within the metro network at the edges of the access/metro segment of the network (fig.2, servers P1) and at the edge of the metro/core segment of the network (fig.2, servers P2). Depending on the bandwidth demand statistics, operators may choose to implement either the first model or the second one. Moreover, operators can also implement a combination of both models. In order to estimate the gain of bandwidth in the metro network for 2017, we proposed three different scenarios. The first one assumes that a limited number of servers are located in the metro network (typically, at the edge of the CN). We also consider (arbitrary) distribution architectures, where servers are located deeper in the metro network.
9 Fig. 2. Locating servers in the metro and core networks Scenario 1: All the traffic that terminates in the metro network is offloaded at the centralized cache (fig.2, servers P3) at the edge of the backbone. Scenario 2: 50% of the total IP traffic is offloaded at the distributed cache (fig.2, servers P2) at the edge of the metro/core segment of the network. 25% of the total IP traffic is offloaded at the centralized cache (fig.2, servers P3) at the edge of the backbone. 25% of the total IP traffic traverses the backbone to the national IP server (fig.2, servers P4). Scenario 3: 30% of the total IP traffic is offloaded at the distributed cache (fig.2, servers P1) at the edge of the access/metro segment of the network 25% of the total IP traffic is offloaded at the distributed cache (fig.2, servers P2) at the edge of the metro/core segment of the network. 20% of the total IP traffic is offloaded at the centralized cache (fig.2, servers P3) at the edge of the backbone. 25% of the total IP traffic traverses the backbone to the national IP server (fig.2, servers P4). We can now apply similar methods as in the previous subsection to derive the gain on various portions of the metro network due to using different distributions of servers in the metro network. In scenario 1: the only gain of bandwidth is achieved at the CN (section 3.2). Thus, the gain of bandwidth at the metro network is 0% for the first scenario.
10 In scenario 2: the gain of bandwidth achieved at the metro network is: o 0% at the access/metro segment of the network. o 10% at the metro/core segment of the network. In scenario 3: the gain of bandwidth achieved at the metro network is: o 5% at the access/metro segment of the network. o 15% at the metro/core segment of the network. In addition, as the proportion of traffic generated by mobile services shall still be small in the near future compared to the proportion of traffic generated by fixed services, the cost of distributing servers for mobile services may be marginal as the same servers can potentially be used for fixed and mobile services. This type of consolidation is expected in the framework of fixed-mobile convergence (FMC). This in itself can be considered as a very significant gain for telecom operators. 4 CONCLUSION In the present paper, we have addressed the impact of distributing the LTE architecture on the amount of traffic generated by mobile services to be supported by different portions of the network. First, we briefly surveyed the various tools specified in the LTE architecture to offload mobile generated traffic. We then assumed that these tools were actually implemented (distributed LTE architecture), or not (centralized LTE architecture). Using well-accepted traffic prediction assumptions, we assessed the traffic reduction on the CN and on various portions of the metro network, due to mobile traffic offloading, under different server distribution assumptions. We have shown that the gain to be expected from server distribution for mobile traffic in the near future is small, but that in 5 year time, as much as 30% of backbone traffic can thus be offloaded. Smaller but significant gains can also be obtained in the metro network if servers are implemented deeper in the metro network, closer to the users. In the future, we intend to evaluate the anticipated costs due to offloading the mobile IP traffic. We shall also study SIPTO improved implementations that support session continuity in case of mobility. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community Seventh Framework Program FP7/ under grant agreement n COMBO project.
11 References 1. Cisco Visual Networking Index: Global Mobile Data Traffic Forecast Update, , White Paper, CISCO GPP Service requirements for Home Node B (HNB) and Home enode B (HeNB), TS , June D. N. Knisely, T. Yoshizawa and F. Favichia, Standardization of Femtocells in 3GPP, IEEE Communications Magazine, September Cisco 3G Femtocell, CISCO Public Information document, V. Chandrasekhar, J. Andrews, and A. Gatherer, Femtocell networks: a survey, Communications Magazine, IEEE, June GPP Local IP Access and Selected IP Traffic Offload (LIPA-SIPTO), TS , Mars GPP LIPA Mobility and SIPTO at Local Network (LIMONET), TR , April GPP Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN), Stage 2, TS , Mars C. Sankaran, Data offloading techniques in 3gpp rel-10 networks: A tutorial, Communications Magazine, IEEE, June T. Taleb, K. Samdanis, and S. Schmid, Dns-based solution for operator control of select-ed ip traffic offload, in IEEE ICC, June T. Taleb, Y. Hadjadj-Aoul and K. Samdanis, Efficient Solutions for Enhancing Data Traffic Management in 3GPP Networks, in IEEE Systems Journal, November NEC s Femtocell Solutions, and_solutions/prod_femtocell/benefits/. 13. Mobile Traffic Offload: NEC s Cloud Centric Approach to Future Mobile Networks, White Paper, NEC Cisco Visual Networking Index: Forecast and Methodology, , White Paper, CISCO A. Gravey, F. Guillemin, and S. Moteau, Last Mile Caching of Video Content by an ISP, ETS 2013 : 2nd European Teletraffic Seminar, October J. Young, T. Wright, and N. Temple, Orange and Akamai form Content Delivery Strategic Alliance, November Bell Labs Metro Network Traffic Growth: An architecture impact study, White Paper, Alcatel-Lucent 2013.
LTE CONVERGED GATEWAY IP FLOW MOBILITY SOLUTION
 LTE CONVERGED GATEWAY FLOW MOBILITY SOLUTION John Cartmell InterDigital Melville, New York, USA john.cartmell@interdigital.com ABSTRACT Flow Mobility (IFOM) is a feature defined in the 3GPP standards.
LTE CONVERGED GATEWAY FLOW MOBILITY SOLUTION John Cartmell InterDigital Melville, New York, USA john.cartmell@interdigital.com ABSTRACT Flow Mobility (IFOM) is a feature defined in the 3GPP standards.
Unified Access and Aggregation Network Allowing Fixed and Mobile Networks to Converge: The COMBO project
 Unified Access and Aggregation Network Allowing Fixed and Mobile Networks to Converge: The COMBO project P. Chanclou, S. Gosselin, T. Mamouni, D. Breuer, E. Weis, J. Torrijos 1 Agenda 2 COMBO project Key
Unified Access and Aggregation Network Allowing Fixed and Mobile Networks to Converge: The COMBO project P. Chanclou, S. Gosselin, T. Mamouni, D. Breuer, E. Weis, J. Torrijos 1 Agenda 2 COMBO project Key
Handover between Macrocell and Femtocell for UMTS based Networks
 Handover between Macrocell and Femtocell for UMTS based Networks Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury, Won Ryu, Eunjun Rhee, and Yeong Min Jang Kookmin University, Korea Electronic and Telecommunications Research Institute
Handover between Macrocell and Femtocell for UMTS based Networks Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury, Won Ryu, Eunjun Rhee, and Yeong Min Jang Kookmin University, Korea Electronic and Telecommunications Research Institute
Very Tight Coupling between LTE and WiFi: a Practical Analysis
 Very Tight Coupling between LTE and WiFi: a Practical Analysis Younes Khadraoui, Xavier Lagrange, Annie Gravey To cite this version: Younes Khadraoui, Xavier Lagrange, Annie Gravey. Very Tight Coupling
Very Tight Coupling between LTE and WiFi: a Practical Analysis Younes Khadraoui, Xavier Lagrange, Annie Gravey To cite this version: Younes Khadraoui, Xavier Lagrange, Annie Gravey. Very Tight Coupling
FEMTOCELL WITH RELAYS TO ENHANCE THE MACROCELL BACKHAUL BANDWIDTH
 FEMTOCELL WITH RELAYS TO ENHANCE THE MACROCELL BACKHAUL BANDWIDTH, Abstract In the future of Mobile networks it is important to implement a Femtocell at homes and to improve the domestic network. Even
FEMTOCELL WITH RELAYS TO ENHANCE THE MACROCELL BACKHAUL BANDWIDTH, Abstract In the future of Mobile networks it is important to implement a Femtocell at homes and to improve the domestic network. Even
INTRODUCTION TO LTE. ECE MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018
 INTRODUCTION TO LTE ECE 2526 - MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018 1 WHAT IS LTE? 1. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and it was started as a project in 2004 by the Third Generation Partnership
INTRODUCTION TO LTE ECE 2526 - MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018 1 WHAT IS LTE? 1. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and it was started as a project in 2004 by the Third Generation Partnership
Fiber in the backhaul : Powering mobile Broadband
 Fiber in the backhaul : Powering mobile Broadband Gamal Hegazi / Lead Architect Founding Board member FTTH Council Members and Mission MENA council members are from the main FTTH industry players of the
Fiber in the backhaul : Powering mobile Broadband Gamal Hegazi / Lead Architect Founding Board member FTTH Council Members and Mission MENA council members are from the main FTTH industry players of the
Over-The-Top (OTT) Aggregation Solutions
 Over-The-Top (OTT) Aggregation Solutions Omkar Dharmadhikari, Wireless Architect odharmadhikari@cablelabscom CableLabs February 12, 2019 Agenda Introduction Why aggregation is important? Traditional Aggregation
Over-The-Top (OTT) Aggregation Solutions Omkar Dharmadhikari, Wireless Architect odharmadhikari@cablelabscom CableLabs February 12, 2019 Agenda Introduction Why aggregation is important? Traditional Aggregation
Naresh Soni CTO, InterDigital
 March 5, 2012 WTC 2012 Challenges and Innovations in LTE Deployment Naresh Soni CTO, InterDigital Agenda InterDigital Overview Key Trends Key Challenges in LTE Innovative Solutions for LTE Deployment Summary
March 5, 2012 WTC 2012 Challenges and Innovations in LTE Deployment Naresh Soni CTO, InterDigital Agenda InterDigital Overview Key Trends Key Challenges in LTE Innovative Solutions for LTE Deployment Summary
SMALL CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION Strategic White Paper
 SMALL CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION Strategic White Paper Small cells is an umbrella term for a genre of low-powered wireless access points capable of using both licensed and unlicensed spectrum. Small cells
SMALL CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION Strategic White Paper Small cells is an umbrella term for a genre of low-powered wireless access points capable of using both licensed and unlicensed spectrum. Small cells
Next Generation Core Networks Summit 2011 Standardisation and Developments within SAE
 Next Generation Core Networks Summit 2011 Standardisation and Developments within SAE Frédéric Firmin (frederic.firmin@3gpp.org) 3GPP Technical Officer Mobile World Congress, 19 th February 2009 1 Terminology
Next Generation Core Networks Summit 2011 Standardisation and Developments within SAE Frédéric Firmin (frederic.firmin@3gpp.org) 3GPP Technical Officer Mobile World Congress, 19 th February 2009 1 Terminology
IXP economic aspect and benefits
 IXP economic aspect and benefits M. Sall modou.sall@orange-sonatel.com Slide 1 ITU IXP Workshop September 28 th, 2015 Copyright Sonatel. All rights reserved Outline Context Content Distribution and Hosting
IXP economic aspect and benefits M. Sall modou.sall@orange-sonatel.com Slide 1 ITU IXP Workshop September 28 th, 2015 Copyright Sonatel. All rights reserved Outline Context Content Distribution and Hosting
virtual Evolved Packet Core as a Service (vepcaas) BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING MARCH 3, 2016
 virtual Evolved Packet Core as a Service (vepcaas) BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING MARCH 3, 2016 3GPP Evolved Packet Core (EPC) The 3GPP Evolved Packet Core (EPC) is an increasingly complex platform
virtual Evolved Packet Core as a Service (vepcaas) BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING MARCH 3, 2016 3GPP Evolved Packet Core (EPC) The 3GPP Evolved Packet Core (EPC) is an increasingly complex platform
It s Time to Aim Lower Zero Latency at the Edge
 #DATACENTERWORLD #CPEXPO CHANNELPARTNERSCONFERENCE.COM DATACENTERWORLD.COM It s Time to Aim Lower Zero Latency at the Edge Anton Kapela, CTO, EdgeMicro #DATACENTERWORLD DATACENTERWORLD.COM Data Center
#DATACENTERWORLD #CPEXPO CHANNELPARTNERSCONFERENCE.COM DATACENTERWORLD.COM It s Time to Aim Lower Zero Latency at the Edge Anton Kapela, CTO, EdgeMicro #DATACENTERWORLD DATACENTERWORLD.COM Data Center
Business Case for the Cisco ASR 5500 Mobile Multimedia Core Solution
 Business Case for the Cisco ASR 5500 Mobile Multimedia Core Solution Executive Summary The scale, use and technologies of mobile broadband networks are changing rapidly. Mobile broadband growth continues
Business Case for the Cisco ASR 5500 Mobile Multimedia Core Solution Executive Summary The scale, use and technologies of mobile broadband networks are changing rapidly. Mobile broadband growth continues
Open ContEnt Aware Networks
 Open ContEnt Aware Networks Nathalie Amann, Yann Levené Orange Labs Workshop "Optimization of Network Resources for Content Access and Delivery September 6 th, 2012 www.ict-ocean.eu V.2004-10-01 Agenda
Open ContEnt Aware Networks Nathalie Amann, Yann Levené Orange Labs Workshop "Optimization of Network Resources for Content Access and Delivery September 6 th, 2012 www.ict-ocean.eu V.2004-10-01 Agenda
Towards Multitechnology
 Towards Multitechnology seamless access for 5G: a first approach with very tight coupling IMT 5G Workshop, 7 sep 2015 X. Lagrange, Y. Khadraoui, A. Gravey Outline Introduction : Fixed Mobile Convergence
Towards Multitechnology seamless access for 5G: a first approach with very tight coupling IMT 5G Workshop, 7 sep 2015 X. Lagrange, Y. Khadraoui, A. Gravey Outline Introduction : Fixed Mobile Convergence
Addressing Current and Future Wireless Demand
 Addressing Current and Future Wireless Demand Dave Wolter Executive Director Radio Technology AT&T Architecture and Planning Rising Demand and The Need to Innovate in the Network 6,732% growth over 13
Addressing Current and Future Wireless Demand Dave Wolter Executive Director Radio Technology AT&T Architecture and Planning Rising Demand and The Need to Innovate in the Network 6,732% growth over 13
Multi-Domain Service Optimization
 Multi-Domain Service Optimization 1. High-level summary New solutions need to be fifth-generation (5G)- and service-ready while covering the entire network along with individual network slice instances
Multi-Domain Service Optimization 1. High-level summary New solutions need to be fifth-generation (5G)- and service-ready while covering the entire network along with individual network slice instances
IPv6 migration strategies for mobile networks
 migration strategies for mobile s White paper To cope with the increasing demand for IP addresses, most mobile operators (MNOs) have deployed Carrier Grade Network Address Translation (CG-NAT). Introducing
migration strategies for mobile s White paper To cope with the increasing demand for IP addresses, most mobile operators (MNOs) have deployed Carrier Grade Network Address Translation (CG-NAT). Introducing
Wireless Wireline Convergence. Tod Sizer, Director Broadband and Wireless Research Center Bell Laboratories
 Wireless Wireline Convergence Tod Sizer, Director Broadband and Wireless Research Center Bell Laboratories Wireless Wireline Convergence The past decade has seen unprecedented growth in both Wireless and
Wireless Wireline Convergence Tod Sizer, Director Broadband and Wireless Research Center Bell Laboratories Wireless Wireline Convergence The past decade has seen unprecedented growth in both Wireless and
Small Cells as a Service rethinking the mobile operator business
 Small Cells as a Service rethinking the mobile operator business Mats Eriksson, CEO Arctos Labs Scandinavia AB -02-18 1 Executive summary Mobile operators (MNOs) face a huge challenge in meeting the data
Small Cells as a Service rethinking the mobile operator business Mats Eriksson, CEO Arctos Labs Scandinavia AB -02-18 1 Executive summary Mobile operators (MNOs) face a huge challenge in meeting the data
Virtual Evolved Packet Core (VEPC) Placement in the Metro Core- Backhual-Aggregation Ring BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING OCTOBER 20, 2017
 Virtual Evolved Packet Core (VEPC) Placement in the Metro Core- Backhual-Aggregation Ring BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING OCTOBER 20, 2017 LTE: All-IP, simplified network architecture [1] Introduction
Virtual Evolved Packet Core (VEPC) Placement in the Metro Core- Backhual-Aggregation Ring BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING OCTOBER 20, 2017 LTE: All-IP, simplified network architecture [1] Introduction
5G voice network evolution aspects. Voice over NR in a 5G System and migration from Evolved Packet System Fallback. Paper 3
 5G voice network evolution aspects Voice over NR in a 5G System and migration from Evolved Packet System Fallback Paper 3 2 Ericsson 5G voice network evolution aspects Abstract This document is part of
5G voice network evolution aspects Voice over NR in a 5G System and migration from Evolved Packet System Fallback Paper 3 2 Ericsson 5G voice network evolution aspects Abstract This document is part of
Novel design of embms based on Femtocell
 Novel design of embms based on Femtocell Otgonbayar Bataa a, Young-il Kim b, Erdenetuya Dorj c, Bat-Enkh Oyunbileg d, Khishigjargal Gonchigsumlaa e, Oyu Chuluun f, Tulga Orosoo g a, f, g Wireless Communication
Novel design of embms based on Femtocell Otgonbayar Bataa a, Young-il Kim b, Erdenetuya Dorj c, Bat-Enkh Oyunbileg d, Khishigjargal Gonchigsumlaa e, Oyu Chuluun f, Tulga Orosoo g a, f, g Wireless Communication
EU ICT COMBO Project: Fixed Mobile Convergence Solution. Ricardo Martínez ONA, IP Tech. & Engineering Unit
 EU ICT COMBO Project: Fixed Mobile Convergence Solution Ricardo Martínez ONA, IP Tech. & Engineering Unit Outline Project details Scope Challenges and Concept Targets Workplan CTTC participation 2 Project
EU ICT COMBO Project: Fixed Mobile Convergence Solution Ricardo Martínez ONA, IP Tech. & Engineering Unit Outline Project details Scope Challenges and Concept Targets Workplan CTTC participation 2 Project
Optimized Handover Algorithm for Two-tier Macro-Femto Cellular LTE Networks
 2013 IEEE 9th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob) Optimized Handover Algorithm for Two-tier Macro-Femto Cellular LTE Networks Ahlam Ben Cheikh
2013 IEEE 9th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob) Optimized Handover Algorithm for Two-tier Macro-Femto Cellular LTE Networks Ahlam Ben Cheikh
Business Case Studies with STEM
 ITU-D/ ITU-T T Seminar on Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks for the Arab Region 29 April 2 May 2007, Manama, Barhain with STEM Oscar González Soto ITU Consultant Expert Strategic
ITU-D/ ITU-T T Seminar on Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks for the Arab Region 29 April 2 May 2007, Manama, Barhain with STEM Oscar González Soto ITU Consultant Expert Strategic
A Flow Label Based QoS Scheme for End-to-End Mobile Services
 A Flow Label Based QoS Scheme for End-to-End Mobile Services Tao Zheng, Lan Wang, Daqing Gu Orange Labs Beijing France Telecom Group Beijing, China e-mail: {tao.zheng; lan.wang; daqing.gu}@orange.com Abstract
A Flow Label Based QoS Scheme for End-to-End Mobile Services Tao Zheng, Lan Wang, Daqing Gu Orange Labs Beijing France Telecom Group Beijing, China e-mail: {tao.zheng; lan.wang; daqing.gu}@orange.com Abstract
Distributed Mobility Management: Current Practices and Gap Analysis
 Distributed Mobility Management: Current Practices and Gap Analysis draft-ietf-dmm-best-practices-gap-analysis-02 Juan Carlos Zuniga (Editor) Presenting Dapeng Liu (Editor) CJ. Bernardos Pierrick Seite
Distributed Mobility Management: Current Practices and Gap Analysis draft-ietf-dmm-best-practices-gap-analysis-02 Juan Carlos Zuniga (Editor) Presenting Dapeng Liu (Editor) CJ. Bernardos Pierrick Seite
Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING NOVEMBER 17, 2017
 Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING NOVEMBER 17, 2017 Motivation Volume of data to be transported in across a mobile network keeps increasing Proprietary
Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING NOVEMBER 17, 2017 Motivation Volume of data to be transported in across a mobile network keeps increasing Proprietary
Femtocells as a Tool for Data Off-Load November 18 th 2010 CDG-Femto Forum Live Webinar: How Femtocells are Enhancing CDMA Networks
 Femtocells as a Tool for Data Off-Load November 18 th 2010 CDG-Femto Forum Live Webinar: How Femtocells are Enhancing CDMA Networks Sameer Lalwani, Staff Manager, Qualcomm 1 Maximize End-User Value and
Femtocells as a Tool for Data Off-Load November 18 th 2010 CDG-Femto Forum Live Webinar: How Femtocells are Enhancing CDMA Networks Sameer Lalwani, Staff Manager, Qualcomm 1 Maximize End-User Value and
Things You Can Do Today to Build a 5G Ready Network. Building the Mobile Edge
 Things You Can Do Today to Build a 5G Ready Network Building the Mobile Edge Opinion Paper Things You Can Do Today to Build a 5G Ready Network Building the Mobile Edge Summary While 5G network standards
Things You Can Do Today to Build a 5G Ready Network Building the Mobile Edge Opinion Paper Things You Can Do Today to Build a 5G Ready Network Building the Mobile Edge Summary While 5G network standards
RAN Sharing NEC s Approach towards Active Radio Access Network Sharing
 White Paper RAN Sharing NEC s Approach towards Active Radio Access Network Sharing NEC Corporation Executive Summary The volume of data carried by wireless networks is expected to increase rapidly in the
White Paper RAN Sharing NEC s Approach towards Active Radio Access Network Sharing NEC Corporation Executive Summary The volume of data carried by wireless networks is expected to increase rapidly in the
VOLTE and the IP/MPLS Cell Site Evolution
 AVIAT NETWORKS VOLTE and the IP/MPLS Cell Site Evolution By Eduardo J. Sánchez, Aviat Networks Technical Marketing TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 PROBLEM: DEPLOYING VOLTE FOR RELIABLE VOICE AND VIDEO...3
AVIAT NETWORKS VOLTE and the IP/MPLS Cell Site Evolution By Eduardo J. Sánchez, Aviat Networks Technical Marketing TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 PROBLEM: DEPLOYING VOLTE FOR RELIABLE VOICE AND VIDEO...3
LTE Backhaul Considerations. June 25,
 LTE Backhaul Considerations June 25, 2012 1 AGENDA LTE Requirements and Backhaul Considerations Backhaul Framework and Architecture How to Manage the Network Evolution 2 LTE Business model challenge imperatives:
LTE Backhaul Considerations June 25, 2012 1 AGENDA LTE Requirements and Backhaul Considerations Backhaul Framework and Architecture How to Manage the Network Evolution 2 LTE Business model challenge imperatives:
kt 3G to LTE Strategy Global Service Delivery UNIT
 kt 3G to LTE Strategy Global Service Delivery UNIT 2013.12 Contents 1 LTE Strategy and Considerations 2 KT s Network Evolution and Vision 3 KT LTE WARP 1 LTE Strategy and Considerations 2 KT s Network
kt 3G to LTE Strategy Global Service Delivery UNIT 2013.12 Contents 1 LTE Strategy and Considerations 2 KT s Network Evolution and Vision 3 KT LTE WARP 1 LTE Strategy and Considerations 2 KT s Network
Leverage SDN Principles in LTE to Meet Future Network Demands
 Leverage SDN Principles in LTE to Meet Future Network Demands PLATFORM FOR PROFITABLE GROWTH The Role of SDN in LTE Networks SDN refers to specific technologies considered promising for mobile network
Leverage SDN Principles in LTE to Meet Future Network Demands PLATFORM FOR PROFITABLE GROWTH The Role of SDN in LTE Networks SDN refers to specific technologies considered promising for mobile network
Satellite-Based Cellular Backhaul in the Era of LTE
 Satellite-Based Cellular Backhaul in the Era of LTE Introduction 3 Essential Technologies for 3G/LTE Backhauling over Satellite 6 Gilat s Solution SkyEdge II-c Capricorn 7 Why Ultra-fast TDMA is the Only
Satellite-Based Cellular Backhaul in the Era of LTE Introduction 3 Essential Technologies for 3G/LTE Backhauling over Satellite 6 Gilat s Solution SkyEdge II-c Capricorn 7 Why Ultra-fast TDMA is the Only
An Architecture. What the MEC? for 5G
 An Architecture What the MEC? for 5G What the MEC? An architecture for 5G As we stated in the first e-book in this series, the evolution from LTE to 5G will be the most profound transformation on the wireless
An Architecture What the MEC? for 5G What the MEC? An architecture for 5G As we stated in the first e-book in this series, the evolution from LTE to 5G will be the most profound transformation on the wireless
Self-Organizing Networks in LTE and Quantification of Economic Benefits Amit Mukhopadhyay, Ph. D. Director, Network Modeling & Optimization -
 Self-Organizing Networks in LTE and Quantification of Economic Benefits Amit Mukhopadhyay, Ph. D. Director, Network Modeling & Optimization - Wireless Bell Labs 1 Agenda Self Organizing Networks (SON)
Self-Organizing Networks in LTE and Quantification of Economic Benefits Amit Mukhopadhyay, Ph. D. Director, Network Modeling & Optimization - Wireless Bell Labs 1 Agenda Self Organizing Networks (SON)
Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING JANUARY 5, 2018
 Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING JANUARY 5, 2018 Motivation Volume of data to be transported across a mobile network keeps increasing Traditional EPC
Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING JANUARY 5, 2018 Motivation Volume of data to be transported across a mobile network keeps increasing Traditional EPC
Tellabs End of Profit study executive summary
 Tellabs End of Profit study executive summary Executive summary Between November 2010 and January 2011, Tellabs created a study that analysed revenue and cost trends for carriers in Western Europe, North
Tellabs End of Profit study executive summary Executive summary Between November 2010 and January 2011, Tellabs created a study that analysed revenue and cost trends for carriers in Western Europe, North
Cisco Access Policy Server
 Data Sheet Cisco Access Policy Server The Cisco Access Policy Server is a fully virtualized, carrier-grade network discovery, selection, and authentication solution. It uses the Cisco Policy Suite policy,
Data Sheet Cisco Access Policy Server The Cisco Access Policy Server is a fully virtualized, carrier-grade network discovery, selection, and authentication solution. It uses the Cisco Policy Suite policy,
NC-CELL: Network Coding-based Content Distribution in Cellular Networks for Cloud Applications
 -CELL: Network Coding-based Content Distribution Introduction Results Mobile cloud applications is one of the fastest growing markets: Mobile data traffic will rise up to 15 EB per month by 218 By 217
-CELL: Network Coding-based Content Distribution Introduction Results Mobile cloud applications is one of the fastest growing markets: Mobile data traffic will rise up to 15 EB per month by 218 By 217
GVF Connectivity 2017 Serving the next generation customers, extending the demarcation Comtech EF Data Corp.
 GVF Connectivity 2017 Serving the next generation customers, extending the demarcation 2015 Comtech EF Data Corp. The Challenge (Cisco VNI Mobile Traffic Feb. 2017) MEA mobile data traffic grew 96% in
GVF Connectivity 2017 Serving the next generation customers, extending the demarcation 2015 Comtech EF Data Corp. The Challenge (Cisco VNI Mobile Traffic Feb. 2017) MEA mobile data traffic grew 96% in
IPTV Bandwidth Demands in Metropolitan Area Networks
 IPTV Bandwidth Demands in Metropolitan Area Networks LANMAN 27 Jesse Simsarian and Marcus Duelk Bell Laboratories, Alcatel-Lucent, Holmdel, NJ 7733, email: jesses@alcatel-lucent.com June 11, 27 Introduction
IPTV Bandwidth Demands in Metropolitan Area Networks LANMAN 27 Jesse Simsarian and Marcus Duelk Bell Laboratories, Alcatel-Lucent, Holmdel, NJ 7733, email: jesses@alcatel-lucent.com June 11, 27 Introduction
Enabling Agile Service Chaining with Service Based Routing
 Enabling Agile Service Chaining with Service Based Routing Contents Abstract...1 1. Introduction...1 2. Huawei s SBR Solution for Agile Service Chaining...3 2.1. Architecture Overview...3 2.2. Multi-Dimensional
Enabling Agile Service Chaining with Service Based Routing Contents Abstract...1 1. Introduction...1 2. Huawei s SBR Solution for Agile Service Chaining...3 2.1. Architecture Overview...3 2.2. Multi-Dimensional
Intercell Interference Coordination (ICIC) for LTE small cells: A practical solution Node-H GmbH St.-Martin-Str. 57, Munich, Germany
 Intercell Interference Coordination (ICIC) for LTE small cells: A practical solution Node-H GmbH St.-Martin-Str. 57, Munich, Germany Copyright 2016 Node-H GmbH. All rights reserved. Contents Executive
Intercell Interference Coordination (ICIC) for LTE small cells: A practical solution Node-H GmbH St.-Martin-Str. 57, Munich, Germany Copyright 2016 Node-H GmbH. All rights reserved. Contents Executive
Interference in Femtocell Networks. Roger Piqueras Jover ELEN E6951 Wireless & Mobile Networking II April 13th 2009
 Interference in Femtocell Networks Roger Piqueras Jover ELEN E6951 Wireless & Mobile Networking II April 13th 2009 Overview Wireless cellular networks Current challenges in cellular networks Femtocell
Interference in Femtocell Networks Roger Piqueras Jover ELEN E6951 Wireless & Mobile Networking II April 13th 2009 Overview Wireless cellular networks Current challenges in cellular networks Femtocell
Path to 5G: A Control Plane Perspective
 Path to 5G: A Control Plane Perspective Erik Guttman 1 and Irfan Ali 2 1 Chairman of 3GPP TSG-SA, Samsung Electronics, Germany 2 Senior 5G architect at Cisco Systems, USA E-mail: erik.guttman@samsung.com;
Path to 5G: A Control Plane Perspective Erik Guttman 1 and Irfan Ali 2 1 Chairman of 3GPP TSG-SA, Samsung Electronics, Germany 2 Senior 5G architect at Cisco Systems, USA E-mail: erik.guttman@samsung.com;
Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks. Presenter: S. Vasudevan, Technical Manager, Advanced Technology Standards
 Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Presenter: S. Vasudevan, Technical Manager, Advanced Technology Standards What are Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Integrated Networks supporting a range of cell sizes
Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Presenter: S. Vasudevan, Technical Manager, Advanced Technology Standards What are Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Integrated Networks supporting a range of cell sizes
CHALLENGES TO LTE PROGRESS. The Evolution of Mobile Broadband and Regulatory Policy
 CHALLENGES TO LTE PROGRESS The Evolution of Mobile Broadband and Regulatory Policy LTE North America, Dallas, Texas, November 21-22, 2013 4G Americas Board of Governors Exabytes per Month Traffic Growth
CHALLENGES TO LTE PROGRESS The Evolution of Mobile Broadband and Regulatory Policy LTE North America, Dallas, Texas, November 21-22, 2013 4G Americas Board of Governors Exabytes per Month Traffic Growth
Small Cells Management Strategic White Paper
 Small Cells Management Strategic White Paper As small cells are introduced into the network, operations and maintenance becomes much more critical. There has to be some sense of total integration between
Small Cells Management Strategic White Paper As small cells are introduced into the network, operations and maintenance becomes much more critical. There has to be some sense of total integration between
Virtual residential gateways: Architecture and performance
 Virtual residential gateways: Architecture and performance Younes Khadraoui Email: younes.khadraoui@telecom-bretagne.eu Xavier Lagrange Email: xavier.lagrange@telecom-bretagne.eu Abstract With the increase
Virtual residential gateways: Architecture and performance Younes Khadraoui Email: younes.khadraoui@telecom-bretagne.eu Xavier Lagrange Email: xavier.lagrange@telecom-bretagne.eu Abstract With the increase
07/08/2016. Sami TABBANE. I. Introduction II. Evolved Packet Core III. Core network Dimensioning IV. Summary
 Core network and transmission dimensioning Sami TABBANE 1 CONTENTS I. Introduction II. Evolved Packet Core III. Core network Dimensioning IV. Summary 2 1 CONTENTS I. Introduction 3 Introduction LTE Commercialization
Core network and transmission dimensioning Sami TABBANE 1 CONTENTS I. Introduction II. Evolved Packet Core III. Core network Dimensioning IV. Summary 2 1 CONTENTS I. Introduction 3 Introduction LTE Commercialization
Lowering Cost per Bit With 40G ATCA
 White Paper Lowering Cost per Bit With 40G ATCA Prepared by Simon Stanley Analyst at Large, Heavy Reading www.heavyreading.com sponsored by www.radisys.com June 2012 Executive Summary Expanding network
White Paper Lowering Cost per Bit With 40G ATCA Prepared by Simon Stanley Analyst at Large, Heavy Reading www.heavyreading.com sponsored by www.radisys.com June 2012 Executive Summary Expanding network
DOCSIS FOR LTE SMALL CELL BACKHAUL ADDRESSING PERFORMANCE AND THROUGHPUT REQUIREMENTS FOR MOBILE BACKHAUL
 DOCSIS FOR LTE SMALL CELL BACKHAUL ADDRESSING PERFORMANCE AND THROUGHPUT REQUIREMENTS FOR MOBILE BACKHAUL WHITE PAPER Small cells can be used to increase wireless network capacity, provide coverage in
DOCSIS FOR LTE SMALL CELL BACKHAUL ADDRESSING PERFORMANCE AND THROUGHPUT REQUIREMENTS FOR MOBILE BACKHAUL WHITE PAPER Small cells can be used to increase wireless network capacity, provide coverage in
Header Compression Capacity Calculations for Wireless Networks
 Header Compression Capacity Calculations for Wireless Networks Abstract Deployment of wireless transport in a data-centric world calls for a fresh network planning approach, requiring a balance between
Header Compression Capacity Calculations for Wireless Networks Abstract Deployment of wireless transport in a data-centric world calls for a fresh network planning approach, requiring a balance between
SECURING ULTRA-BROADBAND MOBILE ACCESS Deploying the Alcatel-Lucent Security
 SECURING ULTRA-BROADBAND MOBILE ACCESS Deploying the Alcatel-Lucent Security Gateway to address the challenges of a flatter IP network architecture Application Note Abstract Traffic volumes are increasing
SECURING ULTRA-BROADBAND MOBILE ACCESS Deploying the Alcatel-Lucent Security Gateway to address the challenges of a flatter IP network architecture Application Note Abstract Traffic volumes are increasing
INTRODUCTION OUR SERVICES
 INTRODUCTION OUR SERVICES Conduct aims to revolutionise the South African telecommunications market by building a trusted, open-access, optical network in the last mile. We deploy carrier neutral, dark
INTRODUCTION OUR SERVICES Conduct aims to revolutionise the South African telecommunications market by building a trusted, open-access, optical network in the last mile. We deploy carrier neutral, dark
SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS
 SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS Erik L. Org (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA; erik@bitwave.com ); Russell J. Cyr (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA;
SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS Erik L. Org (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA; erik@bitwave.com ); Russell J. Cyr (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA;
90 % of WAN decision makers cite their
 WHITEPAPER So many ways to WAN How the most essential technology for distributed enterprises has evolved and where it s headed One of the most critical components to the success of any growth-oriented
WHITEPAPER So many ways to WAN How the most essential technology for distributed enterprises has evolved and where it s headed One of the most critical components to the success of any growth-oriented
Wi-Fi PROFESSIONAL SERVICES SPEED TIME TO MARKET FOR CARRIER Wi-Fi NETWORKS
 Wi-Fi PROFESSIONAL SERVICES SPEED TIME TO MARKET FOR CARRIER Wi-Fi NETWORKS Application Note Table of contents Introduction / 1 New revenue opportunities with lightradio Wi-Fi / 2 Simplify evolution with
Wi-Fi PROFESSIONAL SERVICES SPEED TIME TO MARKET FOR CARRIER Wi-Fi NETWORKS Application Note Table of contents Introduction / 1 New revenue opportunities with lightradio Wi-Fi / 2 Simplify evolution with
Hierarchical Video Caching in Wireless Cloud: Approaches and Algorithms
 Realizing Advanced Video Optimized Wireless Networks Hierarchical Video Caching in Wireless Cloud: Approaches and Algorithms Hasti Ahlehagh and Sujit Dey Mobile System Design Lab, Dept. of Electrical and
Realizing Advanced Video Optimized Wireless Networks Hierarchical Video Caching in Wireless Cloud: Approaches and Algorithms Hasti Ahlehagh and Sujit Dey Mobile System Design Lab, Dept. of Electrical and
Fujitsu Femtocell Solutions Supporting ideal in-building communications environments. shaping tomorrow with you
 Supporting ideal in-building communications environments shaping tomorrow with you Increase Coverage and Capacity with a Superior End-user Experience The Fujitsu in-building solution enhances residential
Supporting ideal in-building communications environments shaping tomorrow with you Increase Coverage and Capacity with a Superior End-user Experience The Fujitsu in-building solution enhances residential
Interference Mitigation Using Dynamic Frequency Re-use for Dense Femtocell Network Architectures
 Interference Mitigation Using Dynamic Frequency Re-use for Dense Femtocell Network Architectures Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury, Yeong Min Jang, and Zygmunt J. Haas * Department of Electronics Engineering, Kookmin
Interference Mitigation Using Dynamic Frequency Re-use for Dense Femtocell Network Architectures Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury, Yeong Min Jang, and Zygmunt J. Haas * Department of Electronics Engineering, Kookmin
HSS Resiliency Surviving attach storms in the networks of today and tomorrow
 HSS Resiliency Surviving attach storms in the networks of today and tomorrow Strategic White Paper Mobile service providers are taking advantage of the lower operational costs associated with Long Term
HSS Resiliency Surviving attach storms in the networks of today and tomorrow Strategic White Paper Mobile service providers are taking advantage of the lower operational costs associated with Long Term
Traffic Types and Growth in Backbone Networks
 Traffic Types and Growth in Backbone Networks Alexandre Gerber, Robert Doverspike AT&T Labs Research Outline Overview of a US carrier inter-city backbone optical network: Services running on ROADMs Breakdown
Traffic Types and Growth in Backbone Networks Alexandre Gerber, Robert Doverspike AT&T Labs Research Outline Overview of a US carrier inter-city backbone optical network: Services running on ROADMs Breakdown
7/27/2010 LTE-WIMAX BLOG HARISHVADADA.WORDPRESS.COM. QOS over 4G networks Harish Vadada
 7/27/2010 HARISHVADADA.WORDPRESS.COM LTE-WIMAX BLOG QOS over 4G networks Harish Vadada Cellular network operators across the world have seen an explosive growth of mobile broadband usage. Traffic volume
7/27/2010 HARISHVADADA.WORDPRESS.COM LTE-WIMAX BLOG QOS over 4G networks Harish Vadada Cellular network operators across the world have seen an explosive growth of mobile broadband usage. Traffic volume
INICTEL-UNI 15/11/2010. Tecnología de Banda Ancha Inalámbrica LTE
 INICTEL-UNI 15/11/2010 Tecnología de Banda Ancha Inalámbrica LTE 1 2Market Overview 2 LTE Presentation / Alcatel-Lucent. Title January 2008 Market Trends iphone (Apple) and G1 (Google) are bandwidth drivers
INICTEL-UNI 15/11/2010 Tecnología de Banda Ancha Inalámbrica LTE 1 2Market Overview 2 LTE Presentation / Alcatel-Lucent. Title January 2008 Market Trends iphone (Apple) and G1 (Google) are bandwidth drivers
When ICN Meets C-RAN for HetNets: An SDN Approach C H E N C H E N Y A N G, Z H I Y O N G C H E N, B I N X I A, A N D J I A N G Z H O U W A N G
 When ICN Meets C-RAN for HetNets: An SDN Approach C H E N C H E N Y A N G, Z H I Y O N G C H E N, B I N X I A, A N D J I A N G Z H O U W A N G Motivation Mobile Internet and explosion of its applications,
When ICN Meets C-RAN for HetNets: An SDN Approach C H E N C H E N Y A N G, Z H I Y O N G C H E N, B I N X I A, A N D J I A N G Z H O U W A N G Motivation Mobile Internet and explosion of its applications,
Wireless Network Infrastructure Market (2G, 3G, LTE, WiMAX, WiFi):
 Wireless Network Infrastructure Market (2G, 3G, LTE, WiMAX, WiFi): 2012 2017 November 2012 Overview: The wireless network infrastructure market will grow by nearly 8% between 2012 and 2013, representing
Wireless Network Infrastructure Market (2G, 3G, LTE, WiMAX, WiFi): 2012 2017 November 2012 Overview: The wireless network infrastructure market will grow by nearly 8% between 2012 and 2013, representing
Access CDN - Novel Architecture for Highly Distributed CDN Network Lab
 Access CDN - Novel Architecture for Highly Distributed CDN 2012 Network Lab Outline Bring CDN to the Edge Access CDN - Novel Architecture for Highly Distributed CDN A Healthier Ecosystem with Access CDN
Access CDN - Novel Architecture for Highly Distributed CDN 2012 Network Lab Outline Bring CDN to the Edge Access CDN - Novel Architecture for Highly Distributed CDN A Healthier Ecosystem with Access CDN
System Enhancements for Accessing Broadcast Services in All-IP Networks. Motivation
 System Enhancements for ing Broadcast Services in All-IP Networks Patrick Stupar, Krishna Pandit, and Wolfgang Granzow Qualcomm CDMA Technologies GmbH Motivation 54.2 % 18.0 % 23.1 % 36.4 % Over 4 billion
System Enhancements for ing Broadcast Services in All-IP Networks Patrick Stupar, Krishna Pandit, and Wolfgang Granzow Qualcomm CDMA Technologies GmbH Motivation 54.2 % 18.0 % 23.1 % 36.4 % Over 4 billion
LTE multi-cellular system in urban environment: inter-cell interference Impact on the Downlink radio transmission
 LTE multi-cellular system in urban environment: inter-cell interference Impact on the Downlink radio transmission Younes BALBOUL Signals, Systems and Components Lab Faculty of Science and Technology, Fez,
LTE multi-cellular system in urban environment: inter-cell interference Impact on the Downlink radio transmission Younes BALBOUL Signals, Systems and Components Lab Faculty of Science and Technology, Fez,
Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (ETSI Markets)
 Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (ETSI Markets) The Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (MPR) provides cost-effective IP transformation for seamless microwave transport of TDM, ATM, IP
Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (ETSI Markets) The Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (MPR) provides cost-effective IP transformation for seamless microwave transport of TDM, ATM, IP
Addressing Unique M2M Challenges with Converged Gateways
 October 19-20, 2010 Addressing Unique M2M Challenges with Converged Gateways Paul L. Russell, Jr. Paul.Russell@InterDigital.com ETSI TC M2M Workshop 19-20 October 2010, Sophia Antipolis, France Where are
October 19-20, 2010 Addressing Unique M2M Challenges with Converged Gateways Paul L. Russell, Jr. Paul.Russell@InterDigital.com ETSI TC M2M Workshop 19-20 October 2010, Sophia Antipolis, France Where are
Network Coding-based Content Distribution in Cellular Access Networks
 IEEE ICC 2016 Network Coding-based Content Distribution in Cellular Access Networks Claudio Fiandrino Dzmitry Kliazovich Pascal Bouvry Albert Y. Zomaya University of Luxembourg University of Sydney May
IEEE ICC 2016 Network Coding-based Content Distribution in Cellular Access Networks Claudio Fiandrino Dzmitry Kliazovich Pascal Bouvry Albert Y. Zomaya University of Luxembourg University of Sydney May
Author Version. Double-NAT Based Mobility Management for Future LTE Networks
 Double- Based Mobility Management for Future LTE Networks Morteza Karimzadeh 1, Luca Valtulina 1, Aiko Pras 1, Hans van den Berg 1,2, Ricardo de O. Schmidt 1 1 University of Twente, 2 TNO, The Netherlands
Double- Based Mobility Management for Future LTE Networks Morteza Karimzadeh 1, Luca Valtulina 1, Aiko Pras 1, Hans van den Berg 1,2, Ricardo de O. Schmidt 1 1 University of Twente, 2 TNO, The Netherlands
LTE Access Controller (LAC) for Small Cell Tool Design and Technology
 LTE Access Controller (LAC) for Small Cell Tool Design and Technology http://parallelwireless.com/products/lte-access-controller/ 1 Team Expertise Came Together to Reimagine the RAN Core Access Networking,
LTE Access Controller (LAC) for Small Cell Tool Design and Technology http://parallelwireless.com/products/lte-access-controller/ 1 Team Expertise Came Together to Reimagine the RAN Core Access Networking,
Cisco ASR 5000 Series Small Cell Gateway
 Data Sheet Cisco ASR 5000 Series Small Cell Gateway Mobile subscribers want access to the network at home, work, hotspots, and everywhere in between. This requires mobile operators to expand their service
Data Sheet Cisco ASR 5000 Series Small Cell Gateway Mobile subscribers want access to the network at home, work, hotspots, and everywhere in between. This requires mobile operators to expand their service
ECE 257A. Communication Networks
 ECE 257A. Communication Networks Lecture 01. Introduction and Overview Prof. Xinyu Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California San Diego Today s agenda Course logistics
ECE 257A. Communication Networks Lecture 01. Introduction and Overview Prof. Xinyu Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California San Diego Today s agenda Course logistics
Investor Presentation. February 2016
 Investor Presentation February 2016 Disclaimer Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended,
Investor Presentation February 2016 Disclaimer Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended,
Energy-aware Traffic Allocation to Optical Lightpaths in Multilayer Core Networks
 Telecommunication Networks and integrated Services (TNS) Laboratory Department of Digital Systems University of Piraeus Research Center (UPRC) University of Piraeus Energy-aware Traffic Allocation to Optical
Telecommunication Networks and integrated Services (TNS) Laboratory Department of Digital Systems University of Piraeus Research Center (UPRC) University of Piraeus Energy-aware Traffic Allocation to Optical
Voice over Long Term Evolution Migration Strategies
 White Paper Voice over Long Term Evolution Migration Strategies What You Will Learn The evolution of mobile networks to the Voice over Long Term Evolution (VoLTE) all-ip technology standard has generated
White Paper Voice over Long Term Evolution Migration Strategies What You Will Learn The evolution of mobile networks to the Voice over Long Term Evolution (VoLTE) all-ip technology standard has generated
Axyom Ultra-Broadband Software Framework
 Axyom Ultra-Broadband Software Framework MULTI-SERVICE ACCESS AND CORE SOLUTIONS Expanding Quantity and Variety of Broadband Network Connections The Internet of Things (IoT), high-definition everything,
Axyom Ultra-Broadband Software Framework MULTI-SERVICE ACCESS AND CORE SOLUTIONS Expanding Quantity and Variety of Broadband Network Connections The Internet of Things (IoT), high-definition everything,
Converged fixed and mobile broadband networks based on Next Generation Point of Presence
 Converged fixed and mobile broadband networks based on Next Generation Point of Presence Stéphane GOSSELIN, Tahar MAMOUNI, Philippe BERTIN, Jose TORRIJOS, Dirk BREUER, Erik WEIS, Jean-Charles POINT Orange,
Converged fixed and mobile broadband networks based on Next Generation Point of Presence Stéphane GOSSELIN, Tahar MAMOUNI, Philippe BERTIN, Jose TORRIJOS, Dirk BREUER, Erik WEIS, Jean-Charles POINT Orange,
Enablers for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access
 Enablers for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Dorin Odiaţiu, Marketing Director 20 th October 2009 Broadband Wireless Access Enablers solutions for the development of mobile BWA - regulatory perspective
Enablers for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Dorin Odiaţiu, Marketing Director 20 th October 2009 Broadband Wireless Access Enablers solutions for the development of mobile BWA - regulatory perspective
Overview of the Juniper Networks Mobile Cloud Architecture
 Overview of the Juniper Networks Mobile Cloud Architecture Laying the Foundation for a Next-Generation Secure Distributed Telco Cloud White Paper June 2017 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale,
Overview of the Juniper Networks Mobile Cloud Architecture Laying the Foundation for a Next-Generation Secure Distributed Telco Cloud White Paper June 2017 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale,
Simplifying the Branch Network
 Simplifying the Branch Network By: Lee Doyle, Principal Analyst at Doyle Research Sponsored by Aruba, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company Executive Summary A majority of IT organizations are experiencing
Simplifying the Branch Network By: Lee Doyle, Principal Analyst at Doyle Research Sponsored by Aruba, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company Executive Summary A majority of IT organizations are experiencing
MPLS/RSVP-TE-BASED FUTURE UMTS RADIO ACCESS NETWORK
 12th GI/ITG CONFERENCE ON MEASURING, MODELLING AND EVALUATION OF COMPUTER AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 3rd POLISH-GERMAN TELETRAFFIC SYMPOSIUM MPLS/RSVP-TE-BASED FUTURE UMTS RADIO ACCESS NETWORK René Böringer*,
12th GI/ITG CONFERENCE ON MEASURING, MODELLING AND EVALUATION OF COMPUTER AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 3rd POLISH-GERMAN TELETRAFFIC SYMPOSIUM MPLS/RSVP-TE-BASED FUTURE UMTS RADIO ACCESS NETWORK René Böringer*,
The 5G Infrastructure Public-Private Partnership
 The 5G Infrastructure Public-Private Partnership Francesco Mauro (TIM) From Research To Standardization (ETSI), Sophia Antipolis (France), 2016 May 11th 1 C-RAN and the Virtualization path toward The drivers
The 5G Infrastructure Public-Private Partnership Francesco Mauro (TIM) From Research To Standardization (ETSI), Sophia Antipolis (France), 2016 May 11th 1 C-RAN and the Virtualization path toward The drivers
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION WIDE AREA MOBILE DATA (WAMD)
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION WIDE AREA MOBILE DATA (WAMD) V1.0 April 2018 Contents INTRODUCTION 2 SERVICE OVERVIEW 3 HIGH LEVEL DESIGN 4 SCOPE OF SERVICES 6 4G CPE (CUSTOMER PREMISES EQUIPMENT) 7 HEATHROW 4G
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION WIDE AREA MOBILE DATA (WAMD) V1.0 April 2018 Contents INTRODUCTION 2 SERVICE OVERVIEW 3 HIGH LEVEL DESIGN 4 SCOPE OF SERVICES 6 4G CPE (CUSTOMER PREMISES EQUIPMENT) 7 HEATHROW 4G
SENZA FILI. Is cooperation better than competition? CONSULTING. A closer look at the Sprint and Clearwire deal
 Is cooperation better than competition? A closer look at the Sprint and Clearwire deal Monica Paolini Senza Fili Consulting September 2007 SENZA FILI CONSULTING Many operators worldwide have begun planning
Is cooperation better than competition? A closer look at the Sprint and Clearwire deal Monica Paolini Senza Fili Consulting September 2007 SENZA FILI CONSULTING Many operators worldwide have begun planning
Metering Re-ECN: Performance Evaluation and its Applicability in
 Metering Re-ECN: Performance Evaluation and its Applicability in Cellular Networks Ying Zhang, Ingemar Johansson, Howard Green, Mallik Tatipamula Ericsson Research Resource allocation and usage accountability
Metering Re-ECN: Performance Evaluation and its Applicability in Cellular Networks Ying Zhang, Ingemar Johansson, Howard Green, Mallik Tatipamula Ericsson Research Resource allocation and usage accountability
6WINDGate. White Paper. Packet Processing Software for Wireless Infrastructure
 Packet Processing Software for Wireless Infrastructure Last Update: v1.0 - January 2011 Performance Challenges for Wireless Networks As advanced services proliferate and video consumes an ever-increasing
Packet Processing Software for Wireless Infrastructure Last Update: v1.0 - January 2011 Performance Challenges for Wireless Networks As advanced services proliferate and video consumes an ever-increasing
Small Cells- Innovation for Wireless networks
 Small Cells- Innovation for Wireless networks Dr. Malek Shahid Chairman, LTE Working Group Small Cell Forum (Alcatel-Lucent: Director, HetNet and network performance optimization) Latin American Spectrum
Small Cells- Innovation for Wireless networks Dr. Malek Shahid Chairman, LTE Working Group Small Cell Forum (Alcatel-Lucent: Director, HetNet and network performance optimization) Latin American Spectrum
A quick guide: modern point-to-multipoint microwave networks
 A quick guide: modern point-to-multipoint microwave networks Understanding how point-to-multipoint wireless backhaul and access solutions improve telecommunication network capacity and efficiency VectaStar
A quick guide: modern point-to-multipoint microwave networks Understanding how point-to-multipoint wireless backhaul and access solutions improve telecommunication network capacity and efficiency VectaStar
Interference Control Technology for Heterogeneous Networks
 Interference Control Technology for Heterogeneous Networks Junsik Kim junsik@etri.re.kr Byunghan Ryu rubh@etri.re.kr Kyongtak Cho ktcho@etri.re.kr Namhoon Park nhpark@etri.re.kr Abstract To eliminate dead
Interference Control Technology for Heterogeneous Networks Junsik Kim junsik@etri.re.kr Byunghan Ryu rubh@etri.re.kr Kyongtak Cho ktcho@etri.re.kr Namhoon Park nhpark@etri.re.kr Abstract To eliminate dead
