BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support
|
|
|
- Darrell Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in taking action against distributed denial of service (DDoS) mitigation by dropping the DDoS traffic or diverting it to an analyzer. BGP flow specification provides a mechanism to encode flow specification rules for traffic flows that can be distributed as BGP Network Layer Reachability Information (NLRI). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for, page 1 Information About, page 2 How to Configure, page 3 Configuration Examples for, page 10 Additional References for, page 11 Feature Information for, page 12 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to An account on Cisco.com is not required. Restrictions for In Cisco IOS 15.5(S) release, BGP flow specification is supported only on a route reflector. Mixing of address family matches and actions is not supported in flow spec rules. For example, IPv4 matches cannot be combined with IPv6 actions and vice versa. 1
2 Information About Information About Overview of Flowspec Flowspec specifies procedures for the distribution of flow specification rules as Border Gateway Protocol Network Layer Reachability Information (BGP NLRI) that can be used in any application. It also defines application for the purpose of packet filtering in order to mitigate distributed denial of service attacks. A flow specification rule consists of a matching part encoded in the BGP NLRI field and an action part encoded as BGP extended community as defined in the RFC A flow specification rule is a set of data (represented in an n-tuple) consisting of several matching criteria that can be applied to IP packet data. BGP flow specification rules are internally converted to equivalent Cisco Common Classification Policy Language (C3PL) representing corresponding match and action parameters. In Cisco IOS 15.5(S) release, Flowspec supports following functions for the BGP route reflector: Flowspec rules defined in RFC 5575 IPv6 extensions Redirect IP extensions BGP flowspec validation Matching Criteria The following table lists the various Flowspec tuples that are supported for BGP. BGP Flowspec NLRI Type QoS Matching Field (IPv6) QoS Matching Field (IPv4) Input Value Type 1 IPv6 destination address IPv4 destination address Prefix length Type 2 IPv6 source address IPv4 source address Prefix length Type 3 IPv6 next header IPv4 protocol Type 4 IPv6 source or destination port IPv4 source or destination port Type 5 IPv6 destination port IPv4 destination port Type 6 IPv6 source port IPv4 source port Type 7 IPv6 ICMP type IPv4 ICMP type Type 8 IPv6 ICMP code IPv4 ICMP code Type 9 IPv6 TCP flags IPv4 TCP flags (2 bytes include reserved bits) Bit mask 2
3 How to Configure BGP Flowspec NLRI Type QoS Matching Field (IPv6) QoS Matching Field (IPv4) Input Value Type 10 IPv6 packet length IPv4 packet length Type 11 IPv6 traffic class IPv4 DSCP Type 12 Reserved IPv4 fragment bits Bit mask Type 13 IPv6 flow label How to Configure Configuring Perform this task to configure BGP FlowSpec on a route reflector. This task specifies only the IPv4 address family but, other address families are also supported for BGP flow specifications. Before You Begin Configure a BGP route reflector. SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. router bgp autonomous-system-number 4. neighbor ip-address remote-as autonomous-system-number 5. address-family {ipv4 ipv6 vpnv4 vpnv6} flowspec 6. neighbor ip-address activate 7. neighbor ip-address route-reflector-client 8. end DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Device> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Device# configure terminal 3
4 Disabling BGP FlowSpec Validation Step 3 Step 4 Command or Action router bgp autonomous-system-number Device(config)# router bgp 1 neighbor ip-address remote-as autonomous-system-number Purpose Enters router configuration mode for the BGP routing process. Adds an entry to the BGP or multiprotocol BGP neighbor table. Step 5 Device(config-router)# neighbor remote-as 1 address-family {ipv4 ipv6 vpnv4 vpnv6} flowspec Device(config-router)# address-family ipv4 flowspec Specifies the address family and enters address family configuration mode. Flowspec is supported on IPv4, IPv6, VPNv4 and VPNv6 address families. Step 6 neighbor ip-address activate Enables the exchange of information with a BGP neighbor. Step 7 Step 8 Device(config-router-af)# neighbor activate neighbor ip-address route-reflector-client Device(config-router-af)# neighbor route-reflector-client end Device(config-router-af)# end Configures the router as a BGP route reflector and configures the specified neighbor as its client. (Optional) Exits address family configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. Disabling BGP FlowSpec Validation Perform this task if you want to disable the BGP flow specification validations for ebgp peers. The validations are enabled by default. To know more about BGP flow specification validations, see RFC 5575 (draft-ietf-idr-bgp-flowspec-oid-01-revised Validation Procedure for BGP Flow Specifications). 4
5 Verifying SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. router bgp autonomous-system-number 4. address-family {ipv4 ipv6 vpnv4 vpnv6} flowspec 5. neighbor ip-address validation off DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Device> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Step 3 Step 4 Device# configure terminal router bgp autonomous-system-number Device(config)# router bgp 1 address-family {ipv4 ipv6 vpnv4 vpnv6} flowspec Device(config-router)# address-family ipv4 flowspec Enters router configuration mode for the BGP routing process. Specifies the address family and enters address family configuration mode. Flowspec is supported on IPv4, IPv6, VPNv4 and VPNv6 address families. Step 5 neighbor ip-address validation off Disables validation of flow specification for ebgp peers. Device(config-router-af)# neighbor validation off Verifying The show commands can be entered in any order. Before You Begin Configure BGP FlowSec on a route reflector. 5
6 Verifying SUMMARY STEPS 1. show bgp ipv4 flowspec 2. show bgp ipv4 flowspec detail 3. show bgp ipv4 flowspec summary 4. show bgp ipv6 flowspec 5. show bgp ipv6 flowspec detail 6. show bgp ipv6 flowspec summary 7. show bgp vpnv4 flowspec 8. show bgp vpnv4 flowspec all detail 9. show bgp vpnv6 flowspec 10. show bgp vpnv6 flowspec all detail DETAILED STEPS Step 1 show bgp ipv4 flowspec This command displays the IPv4 flowspec routes. Device# show bgp ipv4 flowspec BGP table version is 3, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i Dest: / i *>i Dest: / i Step 2 show bgp ipv4 flowspec detail This command displays the detailed information about IPv4 flowspec routes. Device# show bgp ipv4 flowspec detail BGP routing table entry for Dest: /24, version 2 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table IPv4-Flowspec-BGP-Table) Advertised to update-groups: 1 Refresh Epoch 1 Local, (Received from a RR-client) from ( ) Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best Extended Community: FLOWSPEC Redirect-IP:0x rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0 BGP routing table entry for Dest: /24, version 3 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table IPv4-Flowspec-BGP-Table) Advertised to update-groups: 1 Refresh Epoch 1 Local, (Received from a RR-client) 6
7 Verifying from ( ) Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0 Step 3 show bgp ipv4 flowspec summary This command displays the IPv4 flowspec neighbors. Device# show bgp ipv4 flowspec summary BGP router identifier , local AS number 239 BGP table version is 3, main routing table version 3 2 network entries using bytes of memory 2 path entries using 152 bytes of memory 2/2 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 304 bytes of memory 1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory 2 BGP extended community entries using 48 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using total bytes of memory BGP activity 18/0 prefixes, 18/0 paths, scan interval 15 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd :10: never Idle never Idle :10:53 Step 4 show bgp ipv6 flowspec This command displays the IPv6 flowspec routes. Device# show bgp ipv6 flowspec BGP table version is 2, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i Dest:3::/0-24,Source:4::/0-24 FEC0:: i Step 5 show bgp ipv6 flowspec detail This command displays the detailed information about IPv6 flowspec routes. Device# show bgp ipv6 flowspec detail BGP routing table entry for Dest:3::/0-24,Source:4::/0-24, version 2 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Global-Flowspecv6-Table) Advertised to update-groups: 2 Refresh Epoch 1 Local FEC0::1001 from FEC0::1001 ( ) 7
8 Verifying Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0 Step 6 show bgp ipv6 flowspec summary This command displays the IPv6 flowspec neighbors. Device# show bgp ipv6 flowspec summary BGP router identifier , local AS number 239 BGP table version is 3, main routing table version 3 2 network entries using bytes of memory 2 path entries using 152 bytes of memory 2/2 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 304 bytes of memory 1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory 2 BGP extended community entries using 48 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using total bytes of memory BGP activity 18/0 prefixes, 18/0 paths, scan interval 15 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd :10: never Idle never Idle :10:53 Step 7 show bgp vpnv4 flowspec This command displays the VPNv4 flowspec neighbors. Device# show bgp vpnv4 flowspec BGP table version is 2, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 200:200 *>i Dest: / i Step 8 show bgp vpnv4 flowspec all detail This command displays the VPNv4 flowspec details. Device# show bgp vpnv4 flowspec all detail Route Distinguisher: 200:200 BGP routing table entry for 200:200:Dest: /24, version 2 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table VPNv4-Flowspec-BGP-Table) Advertised to update-groups: 3 Refresh Epoch 1 Local (via default) from ( ) 8
9 Verifying Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best Extended Community: RT:100:100 rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0 Step 9 show bgp vpnv6 flowspec This command displays the VPNv6 flowspec neighbors. Device# show bgp vpnv6 flowspec BGP table version is 2, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 200:200 *>i SPort:=20640 FEC0:: i Step 10 show bgp vpnv6 flowspec all detail This command displays the VPNv6 flowspec details. Device# show bgp vpnv6 flowspec all detail Route Distinguisher: 200:200 BGP routing table entry for 200:200:SPort:=20640, version 2 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table VPNv6-Flowspec-BGP-Table) Advertised to update-groups: 3 Refresh Epoch 1 Local FEC0::1001 (via default) from FEC0::1001 ( ) Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, internal, best Extended Community: RT:100:100 rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0 9
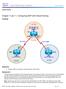
10 Configuration Examples for Configuration Examples for BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support Configuring BGP FlowSpec on Route Reflector Configure BGP route reflector and inject flowspec in the route reflector. Figure 1: BGP Route Reflector Topology! Configure the topology!configure the interfaces on RR RR> enable RR# configure terminal RR(config)# interface E0/0 RR(config-if)# ip address RR(config-if)# no shutdown RR(config-if)# exit RR(config)# interface S2/0 RR(config-if)# ip address RR(config-if)# no shutdown RR(config-if)# exit RR(config)# interface S3/0 RR(config-if)# ip address RR(config-if)# no shutdown!configure RR as the route reflector with S2/0(R1) and S2/0 (R2) as the neighbors RR(config)# router bgp 333 RR(config-router)# no synchronization RR(config-router)# network mask RR(config-router)# network mask RR(config-router)# network mask RR(config-router)# neighbor remote-as 333 RR(config-router)# neighbor remote-as
11 Additional References for!configure flowspec on route reflector RR(config-router)# address-family ipv4 flowspec RR(configure-router-af)# neighbor activate RR(config-router)# neighbor route-reflector-client RR(configure-router-af)# neighbor activate RR(config-router)# neighbor route-reflector-client!verify the configuration RR> show bgp ipv4 flowspec Additional References for BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support Related Documents Related Topic Cisco IOS commands BGP commands Document Title Cisco IOS Master Command List, All Releases Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference Standards and RFCs Standard/RFC RFC 5575 Title Dissemination of Flow Specification Rules Technical Assistance Description The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. Link 11
12 Feature Information for Feature Information for The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to An account on Cisco.com is not required. Table 1: Feature Information for Feature Name BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support Releases 15.5(1)S Feature Information The BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support feature enables services providers to control traffic flows in their network and mitigate DDoS attack. The following command was introduced by this feature: address-family {ipv4 ipv6 vpnv4 vpnv6} flowspec. 12
Configuring IPv6 Provider Edge over MPLS (6PE)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
BGP Support for 4-byte ASN
 The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
BGP Dynamic Neighbors
 BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 This feature module describes the feature. This feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple ibgp paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed
This feature module describes the feature. This feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple ibgp paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed
BGP mvpn BGP safi IPv4
 The BGP mvpn BGP safi 129 IPv4 feature provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider s core IPv4 network This feature is needed to support BGP-based MVPNs BGP MVPN provides
The BGP mvpn BGP safi 129 IPv4 feature provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider s core IPv4 network This feature is needed to support BGP-based MVPNs BGP MVPN provides
BGP Link-State. Finding Feature Information. Overview of Link-State Information in BGP
 (LS) is an Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI) defined to carry interior gateway protocol (IGP) link-state database through BGP. BGP-LS delivers network topology information
(LS) is an Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI) defined to carry interior gateway protocol (IGP) link-state database through BGP. BGP-LS delivers network topology information
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for BGP Link Bandwidth
 The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
BGP Event-Based VPN Import
 The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
BGP AS-Override Split-Horizon
 The feature enables a Provider Edge (PE) device using split-horizon to avoid advertisement of routes propagated by a Customer Edge (CE) device to the same CE device. The BGP AS-Override Split-Horizon feature
The feature enables a Provider Edge (PE) device using split-horizon to avoid advertisement of routes propagated by a Customer Edge (CE) device to the same CE device. The BGP AS-Override Split-Horizon feature
Configuring a BGP Route Server
 BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP Best External. Finding Feature Information
 The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
Introduction to BGP. ISP Workshops. Last updated 30 October 2013
 Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
BGP Diverse Path Using a Diverse-Path Route Reflector
 BGP Diverse Path Using a Diverse-Path Route Reflector The feature allows Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to distribute an alternative path other than the best path between BGP speakers when route reflectors
BGP Diverse Path Using a Diverse-Path Route Reflector The feature allows Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to distribute an alternative path other than the best path between BGP speakers when route reflectors
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands
 Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
BGP Event-Based VPN Import
 BGP Event-Based VPN Import Last Updated: April 13, 2012 The BGP Event-Based VPN Import feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced
BGP Event-Based VPN Import Last Updated: April 13, 2012 The BGP Event-Based VPN Import feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for BGP Link Bandwidth
 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
BGP Persistence. Restrictions for BGP Persistence. Information About BGP Persistence
 BGP persistence enables the router to retain routes that it has learnt from the configured neighbor even when the neighbor session is down. BGP persistence is also referred as long lived graceful restart
BGP persistence enables the router to retain routes that it has learnt from the configured neighbor even when the neighbor session is down. BGP persistence is also referred as long lived graceful restart
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP. BGP IPv4 Label Session
 MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
BGP-RT and VPN Distinguisher Attribute Rewrite Wildcard
 BGP-RT and VPN Distinguisher Attribute Rewrite Wildcard The BGP RT and VPN Distinguisher Attribute Rewrite Wildcard feature introduces the ability to set a range of route target (RT) community attributes
BGP-RT and VPN Distinguisher Attribute Rewrite Wildcard The BGP RT and VPN Distinguisher Attribute Rewrite Wildcard feature introduces the ability to set a range of route target (RT) community attributes
MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses
 MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN Inter-AS with Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses feature allows
MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN Inter-AS with Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses feature allows
Configuring a Basic BGP Network
 Configuring a Basic BGP Network This module describes the basic tasks to configure a basic Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network. BGP is an interdomain routing protocol that is designed to provide loop-free
Configuring a Basic BGP Network This module describes the basic tasks to configure a basic Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network. BGP is an interdomain routing protocol that is designed to provide loop-free
MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
 The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
BGP Graceful Shutdown
 The feature reduces or eliminates the loss of traffic along a link being shut down for maintenance. Routers always have a valid route available during the convergence process. This feature is used primarily
The feature reduces or eliminates the loss of traffic along a link being shut down for maintenance. Routers always have a valid route available during the convergence process. This feature is used primarily
BGP Enhancements for IPv6. ISP Training Workshops
 BGP Enhancements for IPv6 ISP Training Workshops Adding IPv6 to BGP RFC4760 Defines Multi-protocol Extensions for BGP4 Enables BGP to carry routing information of protocols other than IPv4 e.g. MPLS, IPv6,
BGP Enhancements for IPv6 ISP Training Workshops Adding IPv6 to BGP RFC4760 Defines Multi-protocol Extensions for BGP4 Enables BGP to carry routing information of protocols other than IPv4 e.g. MPLS, IPv6,
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Information About IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for. Multiprotocol BGP. Finding Feature Information
 IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP, page 1 How to Implement IPv6
IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP, page 1 How to Implement IPv6
BGP Cost Community. Prerequisites for the BGP Cost Community Feature
 The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature
 IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
BGP Route-Map Continue
 The feature introduces the continue clause to BGP route-map configuration. The continue clause allows for more programmable policy configuration and route filtering and introduces the capability to execute
The feature introduces the continue clause to BGP route-map configuration. The continue clause allows for more programmable policy configuration and route filtering and introduces the capability to execute
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
BGP Origin AS Validation
 The feature helps prevent network administrators from inadvertently advertising routes to networks they do not control. This feature uses a Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) server to authenticate
The feature helps prevent network administrators from inadvertently advertising routes to networks they do not control. This feature uses a Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) server to authenticate
BGP Next Hop Unchanged
 BGP Next Hop Unchanged Last Updated: September 8, 2011 In an external BGP (ebgp) session, by default, the router changes the next hop attribute of a BGP route (to its own address) when the router sends
BGP Next Hop Unchanged Last Updated: September 8, 2011 In an external BGP (ebgp) session, by default, the router changes the next hop attribute of a BGP route (to its own address) when the router sends
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies For OSPFv3
 Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies For OSPFv3
 Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Autoroute Announce and Forwarding The Autoroute Announce and Forwarding Adjacencies for OSPFv3 feature advertises IPv6 routes over MPLS/TE IPv4 tunnels. This module describes how to configure the Autoroute
Configuring Internal BGP Features
 This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics. 30 September :00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Revision: 2.0
 APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
Module 6 Implementing BGP
 Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
BGP Additional Paths. Finding Feature Information. Information About BGP Additional Paths. Problem That Additional Paths Can Solve
 The feature allows the advertisement of multiple paths through the same peering session for the same prefix without the new paths implicitly replacing any previous paths. This behavior promotes path diversity
The feature allows the advertisement of multiple paths through the same peering session for the same prefix without the new paths implicitly replacing any previous paths. This behavior promotes path diversity
MPLS VPN over mgre. Finding Feature Information. Last Updated: November 1, 2012
 MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
BGP Policy Accounting
 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) policy accounting measures and classifies IP traffic that is sent to, or received from, different peers. Policy accounting is enabled on an input interface, and counters based
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) policy accounting measures and classifies IP traffic that is sent to, or received from, different peers. Policy accounting is enabled on an input interface, and counters based
Add Path Support in EIGRP
 The feature enables hubs in a single Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) domain to advertise multiple best paths to connected spokes when the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is the routing
The feature enables hubs in a single Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) domain to advertise multiple best paths to connected spokes when the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is the routing
BGP-MVPN SAFI 129 IPv6
 Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI) 129, known as VPN Multicast SAFI, provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider's core IPv6 network. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI) 129, known as VPN Multicast SAFI, provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider's core IPv6 network. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Configuring BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution
 Configuring BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution is a feature that can be used by service providers in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 VPNs to reduce
Configuring BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution is a feature that can be used by service providers in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 VPNs to reduce
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
Restrictions for Disabling Flow Cache Entries in NAT and NAT64
 The feature allows you to disable flow cache entries for dynamic and static Network Address Translation (NAT) translations. Disabling flow cache entries for dynamic and static translations saves memory
The feature allows you to disable flow cache entries for dynamic and static Network Address Translation (NAT) translations. Disabling flow cache entries for dynamic and static translations saves memory
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
EIGRP Route Tag Enhancements
 The feature enables you to specify and display route tags in dotted-decimal format, filter routes using the route tag value with wildcard mask, and set a default route tag for all internal Enhanced Interior
The feature enables you to specify and display route tags in dotted-decimal format, filter routes using the route tag value with wildcard mask, and set a default route tag for all internal Enhanced Interior
BGP NSF Awareness. Finding Feature Information
 Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) awareness allows a device to assist NSF-capable neighbors to continue forwarding packets during a Stateful Switchover (SSO) operation. The feature allows an NSF-aware device that
Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) awareness allows a device to assist NSF-capable neighbors to continue forwarding packets during a Stateful Switchover (SSO) operation. The feature allows an NSF-aware device that
BGP on IOS: Getting Started
 BGP on IOS: Getting Started ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 IOS Good Practices p ISPs should start off with the following BGP commands as a basic template: router bgp 64511 bgp deterministic-med
BGP on IOS: Getting Started ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 IOS Good Practices p ISPs should start off with the following BGP commands as a basic template: router bgp 64511 bgp deterministic-med
BGP Policy Accounting Output Interface Accounting
 BGP Policy Accounting Output Interface Accounting Last Updated: November 2, 2011 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) policy accounting (PA) measures and classifies IP traffic that is sent to, or received from,
BGP Policy Accounting Output Interface Accounting Last Updated: November 2, 2011 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) policy accounting (PA) measures and classifies IP traffic that is sent to, or received from,
BGP Table Version. Contents. Introduction. Network Diagram. Best Path
 BGP Table Version Document ID: 116511 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Sep 30, 2013 Contents Introduction Network Diagram Best Path Types of Table Versions Initial Table Version Number
BGP Table Version Document ID: 116511 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Sep 30, 2013 Contents Introduction Network Diagram Best Path Types of Table Versions Initial Table Version Number
BGP Monitoring Protocol
 The (BMP) feature supports the following functionality to monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) neighbors, also called BMP clients: Configure devices to function as BMP servers, and set up parameters on
The (BMP) feature supports the following functionality to monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) neighbors, also called BMP clients: Configure devices to function as BMP servers, and set up parameters on
Stateful Network Address Translation 64
 The feature provides a translation mechanism that translates IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets and vice versa. The stateful NAT64 translator algorithmically translates the IPv4 addresses of IPv4 hosts to
The feature provides a translation mechanism that translates IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets and vice versa. The stateful NAT64 translator algorithmically translates the IPv4 addresses of IPv4 hosts to
MPLS over GRE. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for MPLS VPN L3VPN over GRE
 The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
Rev External BGP
 Rev. 00.. External BGP c c n a c o o k b o o k. c o m C O N C E P T S AS (Autonomous System) A network under a single administrative control, like a single company or a single ISP. ASN (AS Number) used
Rev. 00.. External BGP c c n a c o o k b o o k. c o m C O N C E P T S AS (Autonomous System) A network under a single administrative control, like a single company or a single ISP. ASN (AS Number) used
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) What Is BGP?
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
BGP Support for IP Prefix Export from a VRF Table into the Global Table
 BGP Support for IP Prefix Export from a VRF Table into the Global Table This feature allows a network administrator to export IP prefixes from a VRF table into the global routing table. Finding Feature
BGP Support for IP Prefix Export from a VRF Table into the Global Table This feature allows a network administrator to export IP prefixes from a VRF table into the global routing table. Finding Feature
BGP Named Community Lists
 The feature allows the network operator to assign meaningful names to community lists and increases the number of community lists that can be configured. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information
The feature allows the network operator to assign meaningful names to community lists and increases the number of community lists that can be configured. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information
The information in this document is based on Cisco IOS Software Release 15.4 version.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
BGP Enhanced Route Refresh
 The feature provides a way for Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to find route inconsistencies, and in that unlikely event, to synchronize BGP peers without a hard reset. The feature is enabled by default;
The feature provides a way for Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to find route inconsistencies, and in that unlikely event, to synchronize BGP peers without a hard reset. The feature is enabled by default;
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
EIGRP Over the Top. Finding Feature Information. Information About EIGRP Over the Top. EIGRP Over the Top Overview
 The feature enables a single end-to-end routing domain between two or more Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) sites that are connected using a private or a public WAN connection. This module
The feature enables a single end-to-end routing domain between two or more Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) sites that are connected using a private or a public WAN connection. This module
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
VRF-Aware Cloud Web Security
 The feature adds virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) support to the Cisco Cloud Web Security configuration. VRF instances in IP-based networks enable a device to have multiple instances of the routing
The feature adds virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) support to the Cisco Cloud Web Security configuration. VRF instances in IP-based networks enable a device to have multiple instances of the routing
Introduction to BGP. ISP/IXP Workshops
 Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Implementing DCI VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway
 This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Release Modification Release 5.3.2 This feature
This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Release Modification Release 5.3.2 This feature
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed
 EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed EVPN-VPWS single homed is a BGP control plane solution for point-to-point services. It has the ability to forward traffic from or to one network to
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed EVPN-VPWS single homed is a BGP control plane solution for point-to-point services. It has the ability to forward traffic from or to one network to
IS-IS Inbound Filtering
 The Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Inbound Filtering feature prevents unwanted IS-IS routes from being installed in a routing table. A user can deny or permit a route from being installed
The Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Inbound Filtering feature prevents unwanted IS-IS routes from being installed in a routing table. A user can deny or permit a route from being installed
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed
 EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed Effective Release Cisco IOS XE 3.18, this feature is now supported on Cisco ASR 920 Series Aggregation Services Router, EVPN-VPWS single homed is a
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed Effective Release Cisco IOS XE 3.18, this feature is now supported on Cisco ASR 920 Series Aggregation Services Router, EVPN-VPWS single homed is a
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF
 MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF Last Updated: December 15, 2011 The MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF feature provides a Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) option to display a subset of the running configuration
MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF Last Updated: December 15, 2011 The MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF feature provides a Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) option to display a subset of the running configuration
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Contents. BGP commands 1
 Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Configurable Number of Simultaneous Packets per Flow
 Configurable Number of Simultaneous Packets per Flow In zone-based policy firewalls, the number of simultaneous packets per flow is restricted to 25 and packets that exceed the limit are dropped. The dropping
Configurable Number of Simultaneous Packets per Flow In zone-based policy firewalls, the number of simultaneous packets per flow is restricted to 25 and packets that exceed the limit are dropped. The dropping
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks
 Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
EIGRP Support for Route Map Filtering
 The feature enables Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to interoperate with other protocols to leverage additional routing functionality by filtering inbound and outbound traffic based
The feature enables Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to interoperate with other protocols to leverage additional routing functionality by filtering inbound and outbound traffic based
IPv6 Routing: RIP for IPv6
 IPv6 Routing Information Protocol (RIP) functions the same and offers the same benefits as IPv4 RIP. RIP enhancements for IPv6, detailed in RFC 2080, include support for IPv6 addresses and prefixes and
IPv6 Routing Information Protocol (RIP) functions the same and offers the same benefits as IPv4 RIP. RIP enhancements for IPv6, detailed in RFC 2080, include support for IPv6 addresses and prefixes and
QoS Policy Propagation via BGP
 The feature allows you to classify packets by IP precedence based on the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) community lists, BGP autonomous system paths, and access lists. After packets have been classified,
The feature allows you to classify packets by IP precedence based on the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) community lists, BGP autonomous system paths, and access lists. After packets have been classified,
BGP-VPN Distinguisher Attribute
 The BGP VPN Distinguisher Attribute feature allows a network administrator to keep source route targets (RTs) private from an Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) in a destination autonomous system.
The BGP VPN Distinguisher Attribute feature allows a network administrator to keep source route targets (RTs) private from an Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) in a destination autonomous system.
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Object Tracking: IPv6 Route Tracking
 The feature expands the Enhanced Object Tracking (EOT) functionality to allow the tracking of IPv6 routes. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for, page 1 Information About, page 2 How to
The feature expands the Enhanced Object Tracking (EOT) functionality to allow the tracking of IPv6 routes. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for, page 1 Information About, page 2 How to
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support
 Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN
 Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) and VPLS BGP-Based Autodiscovery
 Configuring Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) and VPLS BGP-Based Autodiscovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring VPLS, page 1 Configuring VPLS BGP-based Autodiscovery, page 17 Finding Feature
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) and VPLS BGP-Based Autodiscovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring VPLS, page 1 Configuring VPLS BGP-based Autodiscovery, page 17 Finding Feature
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
 Feature History Release Modification 12.2(8)T This feature was introduced. This module describes how to configure and use a sham-link to connect Virtual Private Network (VPN) client sites that run the
Feature History Release Modification 12.2(8)T This feature was introduced. This module describes how to configure and use a sham-link to connect Virtual Private Network (VPN) client sites that run the
BGP Attributes and Path Selection
 BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
Configuration and Management of Networks 2012
 Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Multi-VRF Support. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Multi-VRF Support
 The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
 The feature allows different flows of traffic over a Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) interface to be identified based on the packet header and then mapped to the different member links of the port channel.
The feature allows different flows of traffic over a Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) interface to be identified based on the packet header and then mapped to the different member links of the port channel.
