Distributed Power Control Mechanisms for HSDPA Femtocells
|
|
|
- Jodie Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Distributed Power Control Mechanisms for HSDPA Femtocells Naveen Arulselvan, Vinod Ramachandran, Suresh Kalyanasundaram Guang Han Motorola India Private Limited, Bangalore Motorola Inc, USA Abstract Femtocells are low-cost, miniature basestations intended to improve indoor coverage in 3G networks and beyond. One of the main issues in adopting femtocells en masse is the surge in interference to the mobile users served by the macrocell arising from unplanned networks and private access. Therefore, distributed power control mechanisms for femtocells are essential to shield the existing users of the macrocell as well as to enable scalable femtocell deployments. This paper studies several such power control schemes that strike an effective balance between the throughput of the femto users and the degradation in macrocell performance. I. INTRODUCTION Recent years have witnessed price-wars among voice operators, and inspite of increasing number of subscribers, the average revenue per user (ARPU) for voice is declining [1]. Operators are starting to focus on home services, through bundled offerings with voice, television, data as the triple play, and mobile access adding a potential fourth dimension. But scarce spectrum has pushed 3G and 4G wireless technologies to operate at 2 GHz and above. This, in turn, will lead to spotty coverage for indoor users as signals tend to fade out faster at higher frequencies. Femtocells are low-cost cellular base-stations that can provide improved home coverage and increase the capacity for user traffic. Using an IP-based backhaul such as the user s existing DSL connection, femtocells can provide cost-effective high-bandwidth wireless services. In combination with a macrocellular network for coverage, femtocells can significantly reduce the total network costs [2]. For mobile operators, femtocells also provide an opportunity to compete directly with fixed-line and Voice-over-IP (VoIP) service providers. The two most important deployment characteristics of femtocells are related to (a) frequency of operation and (b) access privileges to the user [3]. Femtocells can share a carrier with the existing macro network, which is referred to as co-channel deployment, or operate in their own frequency band as in dedicated channel deployments. Femtocells could be deployed in a Closed Subscriber Group (CSG) fashion in private offices and homes, which implies that only registered users may establish connection with these femtocells. Alternatively, femtocells could have open access, where all subscribers of the operator can access these femtocells. Hot-spots such as cafes and hotel lobbies may opt for open-access deployments. Operating femtocells on a dedicated frequency and/or allowing open access remains a possibility; interference management is arguably simpler in such scenarios [4]. But co-channel operation with an existing macrocellular network is more rewarding for the operator due to increased spectral efficiency through frequency re-use. Moreover privacy issues of individual subscribers may preclude open access deployment at all times. As a result, we study the co-channel operation of femtocells with restricted access. Not only does this present more challenging problems, we also expect this to be the de facto deployment mode. Previous work in [5] and [6] have proposed methods where femtocells locally calibrate their DL transmission powers. Femtocell transmit power is computed so that minimum coverage is guaranteed for an imaginary macro user in the vicinity and the maximum data rate for a nearby femto user is fixed to control the interference to other femtocells. Such hard assumptions and errors in estimating physical locations will cause these calibration schemes to perform conservatively. In this work, we investigate two categories of power control algorithms for femtocells that can be performed locally with minimal network intervention. These power control schemes differ in their time-scale of operation. In the geo-static power control scheme, the transmit power of the femtocell is based on a simple function of the distance from the macrocell. The key idea behind the adaptive power control scheme is to adjust the transmit power of the femtocells so as to just achieve their target data rates. The target rate, in turn, is computed by the network to balance the degradation in macrocell performance and increase in femto user throughput. Using system-level simulations, we present coverage and capacity results for users served by both the macrocell and the femtocells /09/$ IEEE
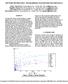
2 The paper is structured as follows. In section II, we study the effect of fixed transmit powers of femtocells on users in the macrocell. In section III, we discuss a class of power control schemes that operate on a slow time-scale. In section IV, we analyze a dynamic power control scheme. II. FIXED TRANSMIT POWER FOR FEMTOCELLS In this section, we investigate the adverse impact of fixed femtocell powers on the macro users capacity and coverage. We observe a near fifty-percent reduction in capacity of the macrocell for even nominal femtocell densities. The results also show that femtocells with unregulated transmit power are bound to cause large dead zones (i.e., out-of-coverage areas) for users served by the macrocell. We consider a High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) system deployed in a sub-urban environment with parameters indicated in Table I. Two tiers of neighboring macrocells are considered for modeling interference, but the statistics for the center-cell alone are considered for the results. We note that the results presented in this section can be easily extended to other advanced 4G systems. The macro users are all assumed to be outdoors, whereas the femtocells and the users they serve are indoors. Each femtocell is assumed to have one static user randomly placed in a cell radius of 15 meters. The center macrocell contains 50 users with full buffer FTP traffic, while the femtocells serve one mobile user each. The path-loss values for macrocell transmissions as a function of the distance d to the user is given by L M (d), and the path-loss values for femtocell transmissions are given by L i F (d) or L o F (d), depending on whether the mobile user is indoor or outdoor. The fraction of femtocell control channel power constituting total transmit power is generally higher than for macrocells to ensure better coverage. The macro users will experience interference from the transmissions of the neighboring femtocells and other macrocells. The macrocell employs a proportionallyfair scheduler. To study the impact of control channel power of femtocells on the macrocell performance, we model the activity level of femtocells via an activity factor. Active femtocells have data transmissions, while inactive femtocells simply transmit control channel power. A. Impact on Macrocell Capacity Consider 200 femtocells uniformly distributed in the center macrocell, each with an activity factor of 0.5. This corresponds to 100 effective femtocells transmitting at a fixed transmit power of P F and 100 other inactive femtocells transmitting only control signaling, which in turn is taken to be 0.25P F. Figure 1 gives the corresponding average macrocell Parameter Cell Layout TABLE I SYSTEM PARAMETERS Inter-site dist Carrier frequency/ Bandwidth Total Macro Tx power Control channel power Data channel power Femto total Tx power Femto control channel power Wall penetration loss (WP) Log-normal shadowing UE noise figure Speed Macro to indoor UE (L M ) Femto to outdoor UE (L o F ) Femto to indoor UE (L i F ) Scheduler Min inter-femto distance Min femto-macro UE distance Value Hexagonal grid 19 cell sites, 3 sectors/site 1732 m 2 GHz/ 5 MHz 20 W 2W 14 W P F 0.25P F 10 db σ=8db (towards macro) σ=10 db (towards femto) 9dB 3 km/h (for macro users only) log 10 d(km)+wp 7+56log 10 d(m)+wp log 10 d(m) Proportional fair 25 m 15 m and femtocell throughputs. We can observe that the macrocell throughput suffers significantly for even moderate femtocell transmit powers. On the other hand, femtocell throughputs are reasonably large even when their transmit power levels are low. Fig. 1. Effect of fixed femtocell power B. Impact on Macrocell Coverage Common Pilot Control Channel (CPICH) is a downlink channel broadcast by the macrocell with constant power and a known bit sequence. The macrocell s CPICH strength indicates the extent of macro UE coverage. In this section, we study the impact of femtocells on macro CPICH signal strength. The probability of a femtocell k being active is given by the activity factor
3 a k and the corresponding transmission power is P F,k. The inactive femtocells are assumed to transmit control channel power PF,k control. Then for a macro UE i, the CPICH signal-to-noise ratio Ec is given by E c N 0 = N P 0 cpich L M i N P M,n n=1 L M,n +, K a k P F,k +(1 a k )PF,k control k=1 L + W o F,k (1) where P cpich is the CPICH power, W is the noise power, and N and K are the number of macrocells and femtocells respectively. The total transmit power is taken to be 20 dbm for all the femtocells. The CDFs of CPICH E c /N 0 are shown in Figure 2 for different activity factors. Here the femtocells are assumed to switch off their control channels when inactive. Figure 3 gives the CDFs of CPICH E c /N o for the case where femtocells continue to transmit control channel power when inactive. As expected, the macrocell coverage further deteriorates and is almost independent of the activity factor. These results corroborate the fact that number of active femtocells and the control channel of femtocells have a strong negative impact on macrocell performance. Fig. 3. Macro signal strength CDF for different activity factors instead of scaling down both the control channel and the data channel powers by the same factor, we fix the femtocell control channel power and reduce the data channel power alone. This ensures optimum coverage for femto users and minimizes effect on macro users. Figure 4 shows the average macrocell and femtocell throughput when femtocells operate with a fixed control channel power of 25 mw while the data channel power is varied from 75 mw to 25 mw. We observe that this leads to approximately a ten percent improvement in the macrocell throughput. On the other hand, the femtocell throughput is large even with the reduced data channel power. Moreover, the femtocell coverage will not be impacted as the control channel power remains constant. Fig. 2. Macro signal strength CDF for different activity factors (No control channel) III. CALIBRATION TECHNIQUES In the next few sections, we propose several power control schemes that do not require the femtocells to change their transmit powers at a fast time-scale. A. Femtocells with Varying Data/Control Power Ratios Based on the results so far, it is evident that the femtocells are able to achieve a significantly larger throughput than the macrocell. However, they reduce the macrocell capacity, especially when operating at higher transmit powers. While reducing the transmit power of femtocells can help macro users, the femtocell coverage can be affected significantly. Therefore, Fig. 4. ratio Average cell throughput vs. femtocell data/control power B. Geo-static Transmit Power First, we study the geographic impact of femtocell transmit power on macro layer coverage by looking at the CPICH coverage. For a macro user i, thecpich SINR Ec/No takes the form as in (1) with activity factor a j =1for all j, i.e., all femtocells are active.
4 We declare a macro user is in x percent-outage if its CPICH Ec/No is below a threshold value t o for a fraction of time larger than x. Fort o and x values of - 25 db and 2%, respectively, Figure 5 shows macrocell mobiles that are in coverage and outage for femtocell transmit power settings of 0.1 mw and 100 mw (only extremes shown due to space constraints). The positions shown in green and red indicate mobiles that are in coverage and outage, respectively. The outage probability of a macro user is influenced by both the proximity to the serving macrocell as well as the distance to the nearest interfering femtocell. From the figure, we observe that (a) the coverage probability of macro users close to the serving macrocell is not influenced by presence of femtocells, even for high transmit powers of the femtocells, and (b) The coverage probability of macro users in the cell edge is sensitive to the distance to its nearest femtocell interferer. This coverage probability will deteriorate rapidly as the femtocell transmit power increases. The network can set the transmit power of the femtocells according to the geographical zone in which they lie. Because femtocell deployments will be unplanned, the power zones of the femtocell can be segregated simply based on the distance to the macrocell. The zone and the power level of the femtocells can be pre-configured and/or modified over the broadcast channel or the DSL backhaul. The power setting will not change, except in the case of rare events like macrocell-splitting or femtocell relocation. An example of such a power-zone division is shown in Figure 6. Macro users in outage will be much fewer than when all femtocells transmit at the maximum power level. Fig. 5. Femto transmit power vs User-outage positions Fig. 6. Power Zone segregation for Femtocells IV. ADAPTIVE TRANSMIT POWER CONTROL For a given macro user i, weassumetherearen macrocells and K femtocells. The downlink Signal to Interference and Noise ratio (SINR) for user i is then given by SINR i = N n=1 P i L M,i P M,n L M,n + K k=1 P F,k L + αpres o F,k L M,i + W, (2) where P i is the power in the shared data channel reserved for user i, P M,n is the power used by macrocell n, P F,k is the power used by femtocell k. Hereα is a factor that arises from non-orthogonality between different channelization codes in the HSDPA system and P res is the residual power of the serving cell after subtracting the power used for user i. The downlink bit-rate at time t is then given by the modified Shannon s equation [7]: R M (t) = log 2 ( SINR i ) bps/hz, (3) i S(t) where S(t) is the set of the users scheduled at time t and the factor of 0.5 is to account for the gap between the theoretical Shannon capacity and the capacity that can be achieved in practice with HSDPA. When all the femtocells use equal power, it is easy to see that SINR and hence macrocell throughput R M decreases with increasing femtocell density. The power allocation problem for multiple femtocells is similar to the non-cooperative game formulation studied in [8] for Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL). The authors developed an iterative algorithm with no centralized control and show that Nash Equilibrium (NE) is reached for the two-user case. We employ a similar approach where the network provides each femtocell k with a target bit-rate T k. The network may take into account factors such as macrocell load, number of active femtocells, distance of the femtocell to the macrocell, and fading environment to determine T k for a given femtocell. The femtocells collect the SINR measurements from the mobile users they serve and use this to schedule in each transmission opportunity.
5 The femtocells can determine the effective data rate RF k in the downlink using (3). Then the femtocells can regulate their transmit power so that their target bit-rates are just met. The power control algorithm executed in every femtocell k =1, 2,,K at every scheduling instant is as follows: Femtocell k checks to see if the DL bit-rate R k F is in the range [T k,t k + ɛ], for some constant ɛ If not, the femtocell adjusts its transmit power level P k accordingly The adjusted power level P k is then constrained to lie in the permissible range [P min,p max ]. For the numerical studies, we assume identical target rates are set for all femtocells. Figure 7 gives the relationship between the total macrocell throughput and the number of femtocells. Small target bit-rate settings for femtocell give as much as 15 % macrocell throughput enhancement even when the femtocell deployment is relatively sparse. This benefit increases to around 33% as femtocell deployments get denser. Figure 8 shows the throughput distribution of all macro users and the bottom 50% macro users for 300 femtocells and a fixed target bit rate, when (a) femtocells perform no power control, (b) femtocells perform the adaptive power control described, and (c) there are no femtocells. This demonstrates that adaptive power control benefits apply fairly to all macro users and not just users with good channel conditions. We also note that the total cell throughput (i.e., the sum of throughputs of all femtocells and the macrocell) increases linearly with the number of femtocells. This is because, inspite of power control, the femtocells operate at much higher spectral efficiencies than their macro counterpart. As a result, the contribution from macrocell to the total throughput is negligible. Fig. 7. Macrocell throughput vs Femtocell density Fig. 8. Macro user throughput distribution (300 femtocells) V. CONCLUSIONS We have studied the impact of femtocell interference on HSDPA macrocell capacity and coverage. We discussed the need for distributed transmit power control solutions for femtocells to enhance macro user performance and enable scalable deployments. We demonstrated the benefits of simply varying the ratio of femtocell data channel and control channel powers to improve macro users experience and maintain femtocell coverage. In the geo-static scheme, the transmit power of the femtocell is regulated as a function of its geographical location alone. In the adaptive power control scheme, femtocells locally achieve a target data rate that is centrally computed by the network. All these power control mechanisms provides efficient trade-offs between femtocell and macrocell performances, while varying in implementation complexity. VI. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to thank their colleague Rajeev Agrawal for several useful discussions. REFERENCES [1] E. Fox, North American ARPU growth outpaces the world: A look at wireless forecast drivers, Yankee group, March [2] H. Claussen, L. T. W. Ho, and L. G. Samuel, Financial Analysis of a Pico cellular home network deployment, in ICC, Nice, 2007, pp [3] 3GPP TR , 3G Home NodeB Study Item Technical report, July [4] H. Claussen, Performance of micro- and co-channel femtocells in hierarchical cell structure, in PIMRC, 2007, pp [5] Ericsson, R : Impact of Home NodeB with controlled output power on macro HSDPA capacity, in 3GPP RAN 4, April [6] Qualcomm Europe, R : Home NodeB and macro downlink performance with calibrated transmit power, in 3GPP RAN 4, June [7] Rysavy Research, EDGE, HSPA and LTE - the mobile broadband advantage, September [8] W. Yu, G. Ginis, and J. Cioffi, Distributed multiuser power control for digital subscriber lines, IEEE J. selected areas of comm., vol. 20, no. 5, pp , June 2002.
A NOVEL RESOURCE ALLOCATION METHODOLOGY TO IMPROVE OVERALL NETWORK EFFICIENCY IN LTE HETEROGENEOUS FEMTOCELL NETWORKS
 A NOVEL RESOURCE ALLOCATION METHODOLOGY TO IMPROVE OVERALL NETWORK EFFICIENCY IN LTE HETEROGENEOUS FEMTOCELL NETWORKS MEGHANA ADUSUMILLI M.Tech Student (wireless and mobile communications), Department
A NOVEL RESOURCE ALLOCATION METHODOLOGY TO IMPROVE OVERALL NETWORK EFFICIENCY IN LTE HETEROGENEOUS FEMTOCELL NETWORKS MEGHANA ADUSUMILLI M.Tech Student (wireless and mobile communications), Department
Interference Mitigation Using Dynamic Frequency Re-use for Dense Femtocell Network Architectures
 Interference Mitigation Using Dynamic Frequency Re-use for Dense Femtocell Network Architectures Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury, Yeong Min Jang, and Zygmunt J. Haas * Department of Electronics Engineering, Kookmin
Interference Mitigation Using Dynamic Frequency Re-use for Dense Femtocell Network Architectures Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury, Yeong Min Jang, and Zygmunt J. Haas * Department of Electronics Engineering, Kookmin
LTE multi-cellular system in urban environment: inter-cell interference Impact on the Downlink radio transmission
 LTE multi-cellular system in urban environment: inter-cell interference Impact on the Downlink radio transmission Younes BALBOUL Signals, Systems and Components Lab Faculty of Science and Technology, Fez,
LTE multi-cellular system in urban environment: inter-cell interference Impact on the Downlink radio transmission Younes BALBOUL Signals, Systems and Components Lab Faculty of Science and Technology, Fez,
DYNAMIC POWER TUNING FOR DOWNLINK INTERFERENCE MITIGATION IN HETEROGENEOUS LTE NETWORK
 DYNAMIC POWER TUNING FOR DOWNLINK INTERFERENCE MITIGATION IN HETEROGENEOUS LTE NETWORK R. Sharanya, R. Gunasundari and K. Jayanthi Department of ECE, Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducherry, India
DYNAMIC POWER TUNING FOR DOWNLINK INTERFERENCE MITIGATION IN HETEROGENEOUS LTE NETWORK R. Sharanya, R. Gunasundari and K. Jayanthi Department of ECE, Pondicherry Engineering College, Puducherry, India
A Self-Organized Femtocell for IEEE e System
 A Self-Organized Femtocell for IEEE 80.16e System Young Jin Sang, Hae Gwang Hwang and Kwang Soon Kim School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Yonsei University 134, Shinchong-dong, Seodaemun-gu,
A Self-Organized Femtocell for IEEE 80.16e System Young Jin Sang, Hae Gwang Hwang and Kwang Soon Kim School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Yonsei University 134, Shinchong-dong, Seodaemun-gu,
Frequency and Time Resource Allocation for Enhanced Interference Management in a Heterogeneous Network based on the LTE-Advanced
 ICWMC 23 : The Ninth International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications Frequency and Time Resource Allocation for Enhanced Interference Management in a Heterogeneous Network based on the LTE-Advanced
ICWMC 23 : The Ninth International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications Frequency and Time Resource Allocation for Enhanced Interference Management in a Heterogeneous Network based on the LTE-Advanced
Performance Improvement in WIMAX Network with Femto Cells
 Performance Improvement in WIMAX Network with Femto Cells R. Elankavi 1, R. Udayakumar* 2, Kalaiprasath.R 3 Research Scholar, Bharath University, Chennai, India 1 Associate Professor, Department of Information
Performance Improvement in WIMAX Network with Femto Cells R. Elankavi 1, R. Udayakumar* 2, Kalaiprasath.R 3 Research Scholar, Bharath University, Chennai, India 1 Associate Professor, Department of Information
Power Control for Interference Avoidance in Femtocell Network
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(6): 416-422, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Power Control for Interference Avoidance in Femtocell Network 1 Mutieb I. Al-Hmoudi, 1 Rashid A. Saeed, 1 Aisha A. Hasan,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(6): 416-422, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Power Control for Interference Avoidance in Femtocell Network 1 Mutieb I. Al-Hmoudi, 1 Rashid A. Saeed, 1 Aisha A. Hasan,
Dynamic Resource Allocation in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks
 Dynamic Resource Allocation in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Jayant Thatte [jayantt@stanford.edu] 1 Introduction As the wireless technology and standards continue to evolve, wireless communication systems
Dynamic Resource Allocation in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Jayant Thatte [jayantt@stanford.edu] 1 Introduction As the wireless technology and standards continue to evolve, wireless communication systems
CHARACTERISATION OF SMALL CELLS NETWORKS DEPLOYMENT OPTIONS AND THEIR IMPACT UPON MACRO-CELULLAR NETWORKS
 CHARACTERISATION OF SMALL CELLS NETWORKS DEPLOYMENT OPTIONS AND THEIR IMPACT UPON MACRO-CELULLAR NETWORKS Cristian ANDRONE Tudor PALADE Communications Department, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, 6-8
CHARACTERISATION OF SMALL CELLS NETWORKS DEPLOYMENT OPTIONS AND THEIR IMPACT UPON MACRO-CELULLAR NETWORKS Cristian ANDRONE Tudor PALADE Communications Department, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, 6-8
HSPA+ R8. February 2009
 HSPA+ R8 February 2009 Disclaimer Nothing in this presentation is an offer to sell any of the parts referenced herein. This presentation may reference and/or show images of parts and/or devices utilizing
HSPA+ R8 February 2009 Disclaimer Nothing in this presentation is an offer to sell any of the parts referenced herein. This presentation may reference and/or show images of parts and/or devices utilizing
FEMTOCELL WITH RELAYS TO ENHANCE THE MACROCELL BACKHAUL BANDWIDTH
 FEMTOCELL WITH RELAYS TO ENHANCE THE MACROCELL BACKHAUL BANDWIDTH, Abstract In the future of Mobile networks it is important to implement a Femtocell at homes and to improve the domestic network. Even
FEMTOCELL WITH RELAYS TO ENHANCE THE MACROCELL BACKHAUL BANDWIDTH, Abstract In the future of Mobile networks it is important to implement a Femtocell at homes and to improve the domestic network. Even
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Spectral Efficiency Improvement By On Demand Channel Allocation In Femto And Macro Cell Networks
 ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Spectral Efficiency Improvement By On Demand Channel Allocation In Femto And Macro Cell Networks 1 G.K.Venkatesh
ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Spectral Efficiency Improvement By On Demand Channel Allocation In Femto And Macro Cell Networks 1 G.K.Venkatesh
Using TV White Space for Interference Mitigation in LTE Femtocell Networks
 Proceedings of ICCTA11 Using TV White Space for Interference Mitigation in LTE Femtocell Networks Fei Peng, Yue Gao, Yue Chen, K K Chai, Laurie Cuthbert Queen Mary University of London School of Electronic
Proceedings of ICCTA11 Using TV White Space for Interference Mitigation in LTE Femtocell Networks Fei Peng, Yue Gao, Yue Chen, K K Chai, Laurie Cuthbert Queen Mary University of London School of Electronic
IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 1, Issue 5, Oct-Nov, 2013 ISSN:
 Performance Improvement in WIMAX Network with Femto Cells A. S. Jadhav 1, R.V.Pawar 2 and R. S. Patil 3 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, BLDEA s Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology
Performance Improvement in WIMAX Network with Femto Cells A. S. Jadhav 1, R.V.Pawar 2 and R. S. Patil 3 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, BLDEA s Dr. P. G. Halakatti College of Engineering and Technology
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Innovative Engineering Volume I, Issue 5, May 2015 (ISSN: )
 International Journal of Emerging Technology and Innovative Engineering Volume I, Issue 5, May 2015 (ISSN: 2394 6598) LTE-A SHARING RELATIONSHIP IN MACROCELL AND FEMTOCELLS FOR SPECTRUM Jayaseelan.G [1],
International Journal of Emerging Technology and Innovative Engineering Volume I, Issue 5, May 2015 (ISSN: 2394 6598) LTE-A SHARING RELATIONSHIP IN MACROCELL AND FEMTOCELLS FOR SPECTRUM Jayaseelan.G [1],
Issues in Femtocell Deployment in Broadband OFDMA Networks : 3GPP LTE a case study
 Issues in Femtocell Deployment in Broadband OFDMA Networks : 3GPP LTE a case study Suvra Sekhar Das 1,2, Prabhu Chandhar 1, Soumen Mitra 1, Priyangshu Ghosh 1 1 G.S.Sanyal School of Telecommunications,
Issues in Femtocell Deployment in Broadband OFDMA Networks : 3GPP LTE a case study Suvra Sekhar Das 1,2, Prabhu Chandhar 1, Soumen Mitra 1, Priyangshu Ghosh 1 1 G.S.Sanyal School of Telecommunications,
Self-organized spectrum chunk selection algorithm for Local Area LTE-Advanced Kumar, Sanjay; Wang, Yuanye; Marchetti, Nicola
 Aalborg Universitet Self-organized spectrum chunk selection algorithm for Local Area LTE-Advanced Kumar, Sanjay; Wang, Yuanye; Marchetti, Nicola Published in: Proceedings from Kaleidoscope: Beyond the
Aalborg Universitet Self-organized spectrum chunk selection algorithm for Local Area LTE-Advanced Kumar, Sanjay; Wang, Yuanye; Marchetti, Nicola Published in: Proceedings from Kaleidoscope: Beyond the
Intercell Interference Mitigation in LTE-Advanced Heterogeneous Network
 Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 85 92 Intercell Interference Mitigation in LTE-Advanced Heterogeneous Network Prem Bahadur Chhetri 1, Sharad Kumar Ghimire 2 1, 2 Department of Electronics
Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 85 92 Intercell Interference Mitigation in LTE-Advanced Heterogeneous Network Prem Bahadur Chhetri 1, Sharad Kumar Ghimire 2 1, 2 Department of Electronics
A Review on Co-Tier Interference Reduction Techniques In Between LTE Femtocells
 A Review on Co-Tier Interference Reduction Techniques In Between LTE Femtocells Ninad M Belalekar 1, Shrikrishna D Patil 2 P.G. Student, ETC, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Andheri, Mumbai, India
A Review on Co-Tier Interference Reduction Techniques In Between LTE Femtocells Ninad M Belalekar 1, Shrikrishna D Patil 2 P.G. Student, ETC, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Andheri, Mumbai, India
Interference in Femtocell Networks. Roger Piqueras Jover ELEN E6951 Wireless & Mobile Networking II April 13th 2009
 Interference in Femtocell Networks Roger Piqueras Jover ELEN E6951 Wireless & Mobile Networking II April 13th 2009 Overview Wireless cellular networks Current challenges in cellular networks Femtocell
Interference in Femtocell Networks Roger Piqueras Jover ELEN E6951 Wireless & Mobile Networking II April 13th 2009 Overview Wireless cellular networks Current challenges in cellular networks Femtocell
Wireless Technologies Addressing the Too Much Data Paradox
 Wireless Technologies Addressing the Too Much Data Paradox May 25, 2011 Reinaldo A. Valenzuela Director, Wireless Communications Research Department Bell Labs, Alcatel-Lucent Reality The Ubiquitous Goal
Wireless Technologies Addressing the Too Much Data Paradox May 25, 2011 Reinaldo A. Valenzuela Director, Wireless Communications Research Department Bell Labs, Alcatel-Lucent Reality The Ubiquitous Goal
From always on to always available Energy saving possibilities and potential. Dr. Pål Frenger, Ericsson Research
 From always on to always available Energy saving possibilities and potential Dr. Pål Frenger, Ericsson Research Outline Why RAN energy performance? HetNet Energy efficiency P. Frenger, Y, Jading, and J.
From always on to always available Energy saving possibilities and potential Dr. Pål Frenger, Ericsson Research Outline Why RAN energy performance? HetNet Energy efficiency P. Frenger, Y, Jading, and J.
Small cells Contents. Overview & market drivers. Small cell and HetNet architecture. Deployment considerations. Introduction. Deployment scenarios
 Small cells Contents Introduction Overview & market drivers Small cell and HetNet architecture Deployment considerations Deployment scenarios Small cell site approach Macro scalability 20 UNIK4230 Mobile
Small cells Contents Introduction Overview & market drivers Small cell and HetNet architecture Deployment considerations Deployment scenarios Small cell site approach Macro scalability 20 UNIK4230 Mobile
Performance of Open Access Femtocells in 4G Macrocellular Networks *
 >WWRF2-WG4-5-JEFFRIES< Performance of Open Access Femtocells in 4G Macrocellular Networks * Steven R Hall, Member, IET, Andy W. Jeffries, Member, IET, Simon E. Avis and David D.N. Bevan, Member, IET Abstract
>WWRF2-WG4-5-JEFFRIES< Performance of Open Access Femtocells in 4G Macrocellular Networks * Steven R Hall, Member, IET, Andy W. Jeffries, Member, IET, Simon E. Avis and David D.N. Bevan, Member, IET Abstract
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: I E E E V T S Vehicular Technology Conference. Proceedings
 Aalborg Universitet A Site-specific Study of In-building Wireless Solutions Liu, Zhen; Sørensen, Troels Bundgaard; wigard, jeroen; Petri, Jolma; Kolding, Troels; Mogensen, Preben Elgaard Published in:
Aalborg Universitet A Site-specific Study of In-building Wireless Solutions Liu, Zhen; Sørensen, Troels Bundgaard; wigard, jeroen; Petri, Jolma; Kolding, Troels; Mogensen, Preben Elgaard Published in:
A Simulation Framework for LTE-A Systems with Femtocell Overlays
 A Simulation Framework for LTE-A Systems with Femtocell Overlays Christos Bouras Computer Technology Institute & Press Diophantus bouras@cti.gr Vasileios Kokkinos Computer Technology Institute & Press
A Simulation Framework for LTE-A Systems with Femtocell Overlays Christos Bouras Computer Technology Institute & Press Diophantus bouras@cti.gr Vasileios Kokkinos Computer Technology Institute & Press
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction. Harri Holma and Antti Toskala. 1.1 WCDMA technology and deployment status
 1 Introduction Harri Holma and Antti Toskala 1.1 WCDMA technology and deployment status The first Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) networks were
1 Introduction Harri Holma and Antti Toskala 1.1 WCDMA technology and deployment status The first Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) networks were
Small Cells- Innovation for Wireless networks
 Small Cells- Innovation for Wireless networks Dr. Malek Shahid Chairman, LTE Working Group Small Cell Forum (Alcatel-Lucent: Director, HetNet and network performance optimization) Latin American Spectrum
Small Cells- Innovation for Wireless networks Dr. Malek Shahid Chairman, LTE Working Group Small Cell Forum (Alcatel-Lucent: Director, HetNet and network performance optimization) Latin American Spectrum
Sensitivity of OFDMA-Based Macrocellular LTE Networks to Femtocell Deployment Density and Isolation
 Sensitivity of OFDMA-Based Macrocellular LTE Networks to Femtocell Deployment Density and Isolation Martin Taranetz, Josep Colom Ikuno, Markus Rupp Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Telecommunications
Sensitivity of OFDMA-Based Macrocellular LTE Networks to Femtocell Deployment Density and Isolation Martin Taranetz, Josep Colom Ikuno, Markus Rupp Vienna University of Technology, Institute of Telecommunications
3G Technical Evolution as an evolving broadband solution
 ITU-D Regional Development Forum for the Asia Pacific Region NGN and Broadband, Opportunities and Challenges Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 27 29 July 2009 3G Technical Evolution as an evolving broadband solution
ITU-D Regional Development Forum for the Asia Pacific Region NGN and Broadband, Opportunities and Challenges Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 27 29 July 2009 3G Technical Evolution as an evolving broadband solution
UNIK4230: Mobile Communications Spring Per Hjalmar Lehne Tel:
 UNIK4230: Mobile Communications Spring 2013 Per Hjalmar Lehne per-hjalmar.lehne@telenor.com Tel: 916 94 909 Small cells and HetNet 15.05.2014 Materials contribution: Nokia Siemens Networks 2 UNIK4230 Mobile
UNIK4230: Mobile Communications Spring 2013 Per Hjalmar Lehne per-hjalmar.lehne@telenor.com Tel: 916 94 909 Small cells and HetNet 15.05.2014 Materials contribution: Nokia Siemens Networks 2 UNIK4230 Mobile
Enterprise Multi-Femtocell Deployment Guidelines
 Enterprise Multi-Femtocell Deployment Guidelines Qualcomm Incorporated June 11 1 Contents 1.1 Table of Contents Enterprise Multi Femtocell Deployment GuidelinesError! Bookmark not defined. 1. Contents...
Enterprise Multi-Femtocell Deployment Guidelines Qualcomm Incorporated June 11 1 Contents 1.1 Table of Contents Enterprise Multi Femtocell Deployment GuidelinesError! Bookmark not defined. 1. Contents...
Hetergeneous Networks HETNET IMPROVE DENSIFY ADD
 Hetergeneous Networks HETNET IMPROVE DENSIFY ADD Why and what HetNet is About End User Experience Coverage Coverage is taken for granted But is bitrate dependent Capacity Data and voice volume capacity
Hetergeneous Networks HETNET IMPROVE DENSIFY ADD Why and what HetNet is About End User Experience Coverage Coverage is taken for granted But is bitrate dependent Capacity Data and voice volume capacity
Femtocell Interference Alleviation using Cluster-based Frequency Reuse Technique
 Femtocell Interference Alleviation using Cluster-based Frequency Reuse Technique Kanchan Dhuri, Sheetal Bhujade 2 Electronics and Telecommunication, Mumbai University, SCOE, Kharghar, India 2 Electronics
Femtocell Interference Alleviation using Cluster-based Frequency Reuse Technique Kanchan Dhuri, Sheetal Bhujade 2 Electronics and Telecommunication, Mumbai University, SCOE, Kharghar, India 2 Electronics
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 4, April ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 4, April-2015 213 SSR Improvement in OFDMA Femtocell Networks Sandhya Y. A. M.Tech Student, KU Mar Baselios College of Engineering
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 4, April-2015 213 SSR Improvement in OFDMA Femtocell Networks Sandhya Y. A. M.Tech Student, KU Mar Baselios College of Engineering
Comparison between Static and Dynamic Modeling Approaches for Heterogeneous Cellular Networks
 Comparison between Static and Dynamic Modeling Approaches for Heterogeneous Cellular Networks by Dariush Fooladivanda A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement
Comparison between Static and Dynamic Modeling Approaches for Heterogeneous Cellular Networks by Dariush Fooladivanda A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement
Analyzing the performance of WiMAX zone handover in the presence of relay node Qualnet6.1
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May - Jun. 2014), PP 49-53 Analyzing the performance of WiMAX zone
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May - Jun. 2014), PP 49-53 Analyzing the performance of WiMAX zone
Femtocells Coordination in Future Hybrid Access Deployments
 Femtocells Coordination in Future Hybrid Access Deployments Christos Bouras 1,2, Georgios Diles 1,2, Vasileios Kokkinos 2, Andreas Papazois 1,2 1 Computer Technology Institute & Press Diophantus, Patras,
Femtocells Coordination in Future Hybrid Access Deployments Christos Bouras 1,2, Georgios Diles 1,2, Vasileios Kokkinos 2, Andreas Papazois 1,2 1 Computer Technology Institute & Press Diophantus, Patras,
Asia pacific analyst forum. Beijing 15 september 2011
 Asia pacific analyst forum Beijing 15 september 2011 SAFE HARBOR THIS PRESENTATION MAY CONTAIN FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS. SUCH STATEMENTS ARE BASED ON OUR CURRENT EXPECTATIONS AND ARE SUBJECT TO CERTAIN
Asia pacific analyst forum Beijing 15 september 2011 SAFE HARBOR THIS PRESENTATION MAY CONTAIN FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS. SUCH STATEMENTS ARE BASED ON OUR CURRENT EXPECTATIONS AND ARE SUBJECT TO CERTAIN
Naresh Soni CTO, InterDigital
 March 5, 2012 WTC 2012 Challenges and Innovations in LTE Deployment Naresh Soni CTO, InterDigital Agenda InterDigital Overview Key Trends Key Challenges in LTE Innovative Solutions for LTE Deployment Summary
March 5, 2012 WTC 2012 Challenges and Innovations in LTE Deployment Naresh Soni CTO, InterDigital Agenda InterDigital Overview Key Trends Key Challenges in LTE Innovative Solutions for LTE Deployment Summary
Imagining Tomorrow's Wireless Landscape
 Imagining Tomorrow's Wireless Landscape Wireless Broadband Evolution Rasmus Hellberg, PhD Director, Technical Marketing Qualcomm Wireless Broadband Evolution 3G offers excellent mobile broadband today
Imagining Tomorrow's Wireless Landscape Wireless Broadband Evolution Rasmus Hellberg, PhD Director, Technical Marketing Qualcomm Wireless Broadband Evolution 3G offers excellent mobile broadband today
Combining D2D and content caching for mobile network offload
 Combining and content caching for mobile network offload Salah Eddine Elayoubi Orange Labs & IRT SystemX Joint work with Antonia Masucci and Berna Sayrac 07/09/2015 Key 5G technologies Ultra-dense networks
Combining and content caching for mobile network offload Salah Eddine Elayoubi Orange Labs & IRT SystemX Joint work with Antonia Masucci and Berna Sayrac 07/09/2015 Key 5G technologies Ultra-dense networks
A Power Management Algorithm For Green Femtocell Networks
 2011 The 10th IFIP Annual Mediterranean Ad Hoc Networking Workshop A Power Management Algorithm For Green Femtocell Networks Fadoua.Mhiri 1, 2, Kaouthar Sethom Ben Reguiga 1, Ridha Bouallegue 1 and Guy
2011 The 10th IFIP Annual Mediterranean Ad Hoc Networking Workshop A Power Management Algorithm For Green Femtocell Networks Fadoua.Mhiri 1, 2, Kaouthar Sethom Ben Reguiga 1, Ridha Bouallegue 1 and Guy
SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS
 SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS Erik L. Org (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA; erik@bitwave.com ); Russell J. Cyr (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA;
SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS Erik L. Org (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA; erik@bitwave.com ); Russell J. Cyr (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA;
Mobile Broadband Spectrum Considerations
 Mobile Broadband Spectrum Considerations Peter Rysavy Rysavy Research http://www.rysavy.com Given at the Wireless Spectrum R&D Workshop at MIT April 23, 2013 1 Copyright 2013 Rysavy Research Data Explosion
Mobile Broadband Spectrum Considerations Peter Rysavy Rysavy Research http://www.rysavy.com Given at the Wireless Spectrum R&D Workshop at MIT April 23, 2013 1 Copyright 2013 Rysavy Research Data Explosion
INTRODUCTION TO LTE. ECE MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018
 INTRODUCTION TO LTE ECE 2526 - MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018 1 WHAT IS LTE? 1. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and it was started as a project in 2004 by the Third Generation Partnership
INTRODUCTION TO LTE ECE 2526 - MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018 1 WHAT IS LTE? 1. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and it was started as a project in 2004 by the Third Generation Partnership
From heterogeneous wireless networks to sustainable efficient ICT infrastructures: How antenna and propagation simulation tools can help?
 From heterogeneous wireless networks to sustainable efficient ICT infrastructures: How antenna and propagation simulation tools can help? Yves Lostanlen SIRADEL April 9 th 2013, Gothenburg, Sweden EUCAP
From heterogeneous wireless networks to sustainable efficient ICT infrastructures: How antenna and propagation simulation tools can help? Yves Lostanlen SIRADEL April 9 th 2013, Gothenburg, Sweden EUCAP
BushLAN Distributed Wireless:
 Australian National University BushLAN Distributed Wireless: Spectrum efficient long range wireless extension of broadband infrastructure to remote areas July 24, 2014 1 1 Abstract BushLAN is a distributed
Australian National University BushLAN Distributed Wireless: Spectrum efficient long range wireless extension of broadband infrastructure to remote areas July 24, 2014 1 1 Abstract BushLAN is a distributed
Annex 10 - Summary of analysis of differences between frequencies
 Annex 10 - Summary of analysis of differences between frequencies Introduction A10.1 This Annex summarises our refined analysis of the differences that may arise after liberalisation between operators
Annex 10 - Summary of analysis of differences between frequencies Introduction A10.1 This Annex summarises our refined analysis of the differences that may arise after liberalisation between operators
CCNC 2016 A System-level Assessment of Uplink CoMP in LTE-A Heterogeneous Networks. Mohamad Tavakoli, Claudio Casetti
 CCNC 2016 A System-level Assessment of Uplink CoMP in LTE-A Heterogeneous Networks Mohamad Tavakoli, Claudio Casetti LTE-A and CoMP LTE-Advanced: higher capacity and bitrates in a cost-efficient way Increased
CCNC 2016 A System-level Assessment of Uplink CoMP in LTE-A Heterogeneous Networks Mohamad Tavakoli, Claudio Casetti LTE-A and CoMP LTE-Advanced: higher capacity and bitrates in a cost-efficient way Increased
Building Better Small Cell Solutions
 Building Better Small Cell Solutions Mobile traffic is expected to increase 18-fold by 2016. The demand for high-speed wireless access driven by tablets, smart phones and bandwidth intensive applications
Building Better Small Cell Solutions Mobile traffic is expected to increase 18-fold by 2016. The demand for high-speed wireless access driven by tablets, smart phones and bandwidth intensive applications
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 2, February ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 2, February-2016 161 Enhanced CoMP technique for interference cancellation in HETNets of LTE K.S.R.S. Jyothsna 1, T. Aravinda
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 2, February-2016 161 Enhanced CoMP technique for interference cancellation in HETNets of LTE K.S.R.S. Jyothsna 1, T. Aravinda
Deployment of LTE In-Band Relay and Micro Base Stations in a Realistic Metropolitan Scenario Coletti, Claudio; Mogensen, Preben Elgaard; Irmer, Ralf
 Aalborg Universitet Deployment of LTE In-Band Relay and Micro Base Stations in a Realistic Metropolitan Scenario Coletti, Claudio; Mogensen, Preben Elgaard; Irmer, Ralf Published in: I E E E V T S Vehicular
Aalborg Universitet Deployment of LTE In-Band Relay and Micro Base Stations in a Realistic Metropolitan Scenario Coletti, Claudio; Mogensen, Preben Elgaard; Irmer, Ralf Published in: I E E E V T S Vehicular
HSPA evolution. ericsson White paper July beyond 3gpp release 10
 ericsson White paper 284 23-3156 July 2011 HSPA evolution HSPA evolution beyond 3gpp release 10 Many mobile operators around the world have HSPA technology to thank for their mobile broadband success.
ericsson White paper 284 23-3156 July 2011 HSPA evolution HSPA evolution beyond 3gpp release 10 Many mobile operators around the world have HSPA technology to thank for their mobile broadband success.
Progress Report of NTT DOCOMO LTE Trials January 26, 2009 Takehiro Nakamura NTT DOCOMO
 ATIS-3GPP LTE Conference January 26, 2009 Progress Report of NTT DOCOMO LTE Trials January 26, 2009 NTT DOCOMO LTE History and Status in 3GPP 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3
ATIS-3GPP LTE Conference January 26, 2009 Progress Report of NTT DOCOMO LTE Trials January 26, 2009 NTT DOCOMO LTE History and Status in 3GPP 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3
DOWNLINK PACKET SCHEDULING IN LTE-ADVANCED HETEROGENEOUS NETWORKS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 2286-3540 DOWNLINK PACKET SCHEDULING IN LTE-ADVANCED HETEROGENEOUS NETWORKS Alexandru VULPE 1, Octavian FRATU 2, Simona HALUNGA 3 In order to increase
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 2286-3540 DOWNLINK PACKET SCHEDULING IN LTE-ADVANCED HETEROGENEOUS NETWORKS Alexandru VULPE 1, Octavian FRATU 2, Simona HALUNGA 3 In order to increase
Transfer Learning Based Diagnosis for Configuration Troubleshooting in Self-Organizing Femtocell Networks
 Transfer Learning Based Diagnosis for Configuration Troubleshooting in Self-Organizing Femtocell Networks Wei Wang, Jin Zhang, Qian Zhang Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Hong Kong University
Transfer Learning Based Diagnosis for Configuration Troubleshooting in Self-Organizing Femtocell Networks Wei Wang, Jin Zhang, Qian Zhang Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Hong Kong University
Business Drivers for Selecting LTE Technology. HSPA+ & LTE Executive Briefing, Jan 27, 2009 Hank Kafka, Vice President, Network Architecture, AT&T
 Business Drivers for Selecting LTE Technology HSPA+ & LTE Executive Briefing, Jan 27, 2009 Hank Kafka, Vice President, Network Architecture, AT&T Why LTE? HSPA, HSPA+ provides great data speeds with impressive
Business Drivers for Selecting LTE Technology HSPA+ & LTE Executive Briefing, Jan 27, 2009 Hank Kafka, Vice President, Network Architecture, AT&T Why LTE? HSPA, HSPA+ provides great data speeds with impressive
PERFORMANCE OF HYBRID NETWORK IN FRACTIONAL FREQUENCY REUSE AND FEMTOCELL POWER CONTROL SCHEMES
 PERFORMANCE OF HYBRID NETWORK IN FRACTIONAL FREQUENCY REUSE AND FEMTOCELL POWER CONTROL SCHEMES Jing Huey Lim 1, R. Badlishah 2, M. Jusoh 2 and T. Sabapathy 2 1 IEEE, School of Computer and Communication
PERFORMANCE OF HYBRID NETWORK IN FRACTIONAL FREQUENCY REUSE AND FEMTOCELL POWER CONTROL SCHEMES Jing Huey Lim 1, R. Badlishah 2, M. Jusoh 2 and T. Sabapathy 2 1 IEEE, School of Computer and Communication
NTT DOCOMO s Views on 5G
 NTT DOCOMO s Views on 5G NTT DOCOMO, INC. NTT DOCOMO, INC., Copyright 2014, All rights reserved. 1 Network/Communication Society in 2020 and Beyond Everything Connected by Wireless Monitor/collect information
NTT DOCOMO s Views on 5G NTT DOCOMO, INC. NTT DOCOMO, INC., Copyright 2014, All rights reserved. 1 Network/Communication Society in 2020 and Beyond Everything Connected by Wireless Monitor/collect information
Aalborg Universitet. Dual-Cell HSDPA for Network Energy Saving Micallef, Gilbert
 Aalborg Universitet Dual-Cell HSDPA for Network Energy Saving Micallef, Gilbert Published in: I E E E V T S Vehicular Technology Conference. Proceedings DOI (link to publication from Publisher): 10.1109/VETECS.2010.5494049
Aalborg Universitet Dual-Cell HSDPA for Network Energy Saving Micallef, Gilbert Published in: I E E E V T S Vehicular Technology Conference. Proceedings DOI (link to publication from Publisher): 10.1109/VETECS.2010.5494049
HSPA+ Advanced Smart Networks: Multipoint Transmission
 Qualcomm Incorporated February 2011 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Multipoint HSPA Description... 2 Single Frequency Multipoint HSPA... 2 Dual Frequency Multipoint HSPA... 3 3. Advantages...
Qualcomm Incorporated February 2011 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Multipoint HSPA Description... 2 Single Frequency Multipoint HSPA... 2 Dual Frequency Multipoint HSPA... 3 3. Advantages...
Dr. Evaldas Stankevičius, Regulatory and Security Expert.
 2018-08-23 Dr. Evaldas Stankevičius, Regulatory and Security Expert Email: evaldas.stankevicius@tele2.com 1G: purely analog system. 2G: voice and SMS. 3G: packet switching communication. 4G: enhanced mobile
2018-08-23 Dr. Evaldas Stankevičius, Regulatory and Security Expert Email: evaldas.stankevicius@tele2.com 1G: purely analog system. 2G: voice and SMS. 3G: packet switching communication. 4G: enhanced mobile
Load Balancing in Downlink LTE Self- Optimizing Networks
 FP7 ICT-SOCRATES Load Balancing in Downlink LTE Self- Optimizing Networks TD ()7 COST 2, th MCM Athens, Greece February 3 rd 5 th NSN, Wroclaw, Poland NSN, Munich, Germany TUBS, Braunschweig, Germany IBBT,
FP7 ICT-SOCRATES Load Balancing in Downlink LTE Self- Optimizing Networks TD ()7 COST 2, th MCM Athens, Greece February 3 rd 5 th NSN, Wroclaw, Poland NSN, Munich, Germany TUBS, Braunschweig, Germany IBBT,
Femto-Matching: Efficient Traffic Offloading in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks
 Femto-Matching: Efficient Traffic Offloading in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks Wei Wang, Xiaobing Wu, Lei Xie and Sanglu Lu Nanjing University April 28, 2015 1/1 Heterogeneous Cellular Networks femto-cell
Femto-Matching: Efficient Traffic Offloading in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks Wei Wang, Xiaobing Wu, Lei Xie and Sanglu Lu Nanjing University April 28, 2015 1/1 Heterogeneous Cellular Networks femto-cell
New Same-Band Combining Technology Improves LTE Deployment
 White Paper New Same-Band Combining Technology Improves LTE Deployment Juan Irola, Engineer Principal, Electrical www.commscope.com Contents New same-band combining technology improves LTE deployment 3
White Paper New Same-Band Combining Technology Improves LTE Deployment Juan Irola, Engineer Principal, Electrical www.commscope.com Contents New same-band combining technology improves LTE deployment 3
Enablers for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access
 Enablers for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Dorin Odiaţiu, Marketing Director 20 th October 2009 Broadband Wireless Access Enablers solutions for the development of mobile BWA - regulatory perspective
Enablers for Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Dorin Odiaţiu, Marketing Director 20 th October 2009 Broadband Wireless Access Enablers solutions for the development of mobile BWA - regulatory perspective
CHALLENGES TO LTE PROGRESS. The Evolution of Mobile Broadband and Regulatory Policy
 CHALLENGES TO LTE PROGRESS The Evolution of Mobile Broadband and Regulatory Policy LTE North America, Dallas, Texas, November 21-22, 2013 4G Americas Board of Governors Exabytes per Month Traffic Growth
CHALLENGES TO LTE PROGRESS The Evolution of Mobile Broadband and Regulatory Policy LTE North America, Dallas, Texas, November 21-22, 2013 4G Americas Board of Governors Exabytes per Month Traffic Growth
Traffic Management Strategies for Operators
 Traffic Management Strategies for Operators QUALCOMM, Incorporated January 2011 For more information on Qualcomm innovations: http://www.qualcomm.com/innovation/research/feature_project/femtocells.html
Traffic Management Strategies for Operators QUALCOMM, Incorporated January 2011 For more information on Qualcomm innovations: http://www.qualcomm.com/innovation/research/feature_project/femtocells.html
Alcatel-Lucent Public Safety 700 MHz Broadband Solution
 Alcatel-Lucent Public Safety 700 MHz Broadband Solution Deployed Today, Evolving with the Future Kenneth C. Budka, Ph.D. Bell Labs June, 2007 Alcatel-Lucent Market Leader and Innovator in Network Infrastructure
Alcatel-Lucent Public Safety 700 MHz Broadband Solution Deployed Today, Evolving with the Future Kenneth C. Budka, Ph.D. Bell Labs June, 2007 Alcatel-Lucent Market Leader and Innovator in Network Infrastructure
Joint Channel Allocation and User Association for Heterogeneous Wireless Cellular Networks
 Joint Channel Allocation and User Association for Heterogeneous Wireless Cellular Networks Dariush Fooladivanda, Ashraf Al Daoud and Catherine Rosenberg Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Joint Channel Allocation and User Association for Heterogeneous Wireless Cellular Networks Dariush Fooladivanda, Ashraf Al Daoud and Catherine Rosenberg Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
4G Mobil-szélessáv: Hogyan jutunk 4-ről az 5-re. Novák Csaba Ericsson Magyarország. LTE Subscriptions
 4G Mobil-szélessáv: Hogyan jutunk 4-ről az 5-re Novák Csaba Ericsson Magyarország LTE Subscriptions 1H 2014 298 012 134 Wireless-access generations 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 The foundation of mobile telephony
4G Mobil-szélessáv: Hogyan jutunk 4-ről az 5-re Novák Csaba Ericsson Magyarország LTE Subscriptions 1H 2014 298 012 134 Wireless-access generations 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 The foundation of mobile telephony
An efficient trigger to improve intra-wifi handover performance
 An efficient trigger to improve intra-wifi handover performance Roberta Fracchia, Guillaume Vivier Motorola Labs, Parc les Algorithmes, Saint-Aubin, 91193 Gif-sur-Yvette, France Abstract Seamless mobility
An efficient trigger to improve intra-wifi handover performance Roberta Fracchia, Guillaume Vivier Motorola Labs, Parc les Algorithmes, Saint-Aubin, 91193 Gif-sur-Yvette, France Abstract Seamless mobility
QoS and System Capacity Optimization in WiMAX Multi-hop Relay Using Flexible Tiered Control Technique
 2009 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications IPCSIT vol.2 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS and System Capacity Optimization in WiMAX Multi-hop Relay Using Flexible Tiered
2009 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications IPCSIT vol.2 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS and System Capacity Optimization in WiMAX Multi-hop Relay Using Flexible Tiered
Performance Evaluation of Sectorized Fractional Frequency Reuse Techniques Using Novel Metric
 2016 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communication (ISCC) Performance Evaluation of Sectorized Fractional Frequency Reuse Techniques Using Novel Metric Uttara Sawant Department of Computer Science and
2016 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communication (ISCC) Performance Evaluation of Sectorized Fractional Frequency Reuse Techniques Using Novel Metric Uttara Sawant Department of Computer Science and
Corporate R&D: Excellence in Wireless Innovation. September
 Corporate R&D: Excellence in Wireless Innovation September 2011 www.qualcomm.com/research State of the Art Capabilities Fostering Innovation Human Resources Complete Development Labs 30% of engineers with
Corporate R&D: Excellence in Wireless Innovation September 2011 www.qualcomm.com/research State of the Art Capabilities Fostering Innovation Human Resources Complete Development Labs 30% of engineers with
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH SCIENCE & MANAGEMENT
 MOBILE OFFLOADING USING POWER BASED DECISION IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION M.Nivethamani 1*, Soma Prathinha 2 1* PG Scholar, Student Member, IEEE, Sri Sairam Engineering College, Chennai 2 Associate Professor,
MOBILE OFFLOADING USING POWER BASED DECISION IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION M.Nivethamani 1*, Soma Prathinha 2 1* PG Scholar, Student Member, IEEE, Sri Sairam Engineering College, Chennai 2 Associate Professor,
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology
 LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
LS100 Series Residential Femtocell
 shaping tomorrow with you LS100 Series Residential Femtocell The LS100 series residential femtocell delivers fieldproven, interoperable 4G/. Already widely deployed, this femtocell also offers unparalleled
shaping tomorrow with you LS100 Series Residential Femtocell The LS100 series residential femtocell delivers fieldproven, interoperable 4G/. Already widely deployed, this femtocell also offers unparalleled
The challenges, opportunities and setting the framework for 5G EMF and Health
 The challenges, opportunities and setting the framework for 5G EMF and Health 5G, EMF & Health 5 December 2017, Warsaw, Poland Mike Wood - General Manager Telstra EME Strategy, Governance and Risk Management
The challenges, opportunities and setting the framework for 5G EMF and Health 5G, EMF & Health 5 December 2017, Warsaw, Poland Mike Wood - General Manager Telstra EME Strategy, Governance and Risk Management
Cluster based OFDMA Resource Allocation in Femtocell Networks
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-83,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume, Issue 5, Ver. III (Sep.-Oct.), PP - www.iosrjournals.org Cluster based OFDMA Resource Allocation
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 78-83,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume, Issue 5, Ver. III (Sep.-Oct.), PP - www.iosrjournals.org Cluster based OFDMA Resource Allocation
Interference Management Scheme for Wireless Sensor Network
 , pp.64-69 http://dx.doi.org/0.4257/astl.204.46.5 Interference Management Scheme for Wireless Sensor Network Sangmi Moon, Saransh Malik, Bora Kim, Hun Choi, Jinsul Kim, Cheolhong Kim, and Intae Hwang Dept.
, pp.64-69 http://dx.doi.org/0.4257/astl.204.46.5 Interference Management Scheme for Wireless Sensor Network Sangmi Moon, Saransh Malik, Bora Kim, Hun Choi, Jinsul Kim, Cheolhong Kim, and Intae Hwang Dept.
Building the Business Case for Mobile Broadband The HSPA Evolution Path
 MIKE WRIGHT Executive Director Wireless Engineering & Operations Building the Business Case for Mobile Broadband The HSPA Evolution Path Broadband World Forum 2009 Australia a wireless snapshot >100% mobile
MIKE WRIGHT Executive Director Wireless Engineering & Operations Building the Business Case for Mobile Broadband The HSPA Evolution Path Broadband World Forum 2009 Australia a wireless snapshot >100% mobile
Enabling Hyper-Dense Small Cell Deployments with UltraSON TM
 Enabling Hyper-Dense Small Cell Deployments with UltraSON TM February 8, 2014 Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. Not to be used, copied, reproduced, or modified in whole or in part, nor its contents revealed
Enabling Hyper-Dense Small Cell Deployments with UltraSON TM February 8, 2014 Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. Not to be used, copied, reproduced, or modified in whole or in part, nor its contents revealed
802.11n in the Outdoor Environment
 POSITION PAPER 802.11n in the Outdoor Environment How Motorola is transforming outdoor mesh networks to leverage full n advantages Municipalities and large enterprise customers are deploying mesh networks
POSITION PAPER 802.11n in the Outdoor Environment How Motorola is transforming outdoor mesh networks to leverage full n advantages Municipalities and large enterprise customers are deploying mesh networks
Cost of Ownership: CDMA 2000 Competitive Advantage. Paul Edwards Chairman Starcomms, Nigeria
 Cost of Ownership: CDMA 2000 Competitive Advantage Paul Edwards Chairman Starcomms, Nigeria Teledensity Facts & Figures > Teledensity & Internet Penetration has a direct positive impact on levels of economic
Cost of Ownership: CDMA 2000 Competitive Advantage Paul Edwards Chairman Starcomms, Nigeria Teledensity Facts & Figures > Teledensity & Internet Penetration has a direct positive impact on levels of economic
Frugal 5G : Next Generation Wireless Systems!
 Frugal 5G : Next Generation Wireless Systems! Abhay Karandikar Dean (Faculty Affairs) Institute Chair Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India
Frugal 5G : Next Generation Wireless Systems! Abhay Karandikar Dean (Faculty Affairs) Institute Chair Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India
John E. Smee, Ph.D. Sr. Director, Engineering Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. May QUALCOMM Technologies, Inc. and/or its affiliates.
 John E. Smee, Ph.D. Sr. Director, Engineering Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. May 2015 This presentation addresses potential use cases and views on characteristics of 5G technology and is not intended to reflect
John E. Smee, Ph.D. Sr. Director, Engineering Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. May 2015 This presentation addresses potential use cases and views on characteristics of 5G technology and is not intended to reflect
Dynamic Fractional Frequency Reuse Method for Self-Organizing Smallcell Network
 Dynamic Fractional Frequency Reuse Method for Self-Organizing Smallcell Network Daniel H. Chae, Nicholas H. Kim, Yibeltal F. Alem, Salman Durrani, Rodney A. Kennedy SK Telecom, South Korea Juni Australia
Dynamic Fractional Frequency Reuse Method for Self-Organizing Smallcell Network Daniel H. Chae, Nicholas H. Kim, Yibeltal F. Alem, Salman Durrani, Rodney A. Kennedy SK Telecom, South Korea Juni Australia
Intercell Interference Coordination (ICIC) for LTE small cells: A practical solution Node-H GmbH St.-Martin-Str. 57, Munich, Germany
 Intercell Interference Coordination (ICIC) for LTE small cells: A practical solution Node-H GmbH St.-Martin-Str. 57, Munich, Germany Copyright 2016 Node-H GmbH. All rights reserved. Contents Executive
Intercell Interference Coordination (ICIC) for LTE small cells: A practical solution Node-H GmbH St.-Martin-Str. 57, Munich, Germany Copyright 2016 Node-H GmbH. All rights reserved. Contents Executive
ENERGY-EFFICIENT WIRELESS IN-HOME: THE NEED FOR INTERFERENCE-CONTROLLED FEMTOCELLS
 ACCEPTED FROM O PEN C ALL ENERGY-EFFICIENT WIRELESS IN-HOME: THE NEED FOR INTERFERENCE-CONTROLLED FEMTOCELLS KAN ZHENG, YUYU WANG, AND WENBO WANG, BEIJING UNIVERSITY OF POSTS & TELECOMMUNICATION MISCHA
ACCEPTED FROM O PEN C ALL ENERGY-EFFICIENT WIRELESS IN-HOME: THE NEED FOR INTERFERENCE-CONTROLLED FEMTOCELLS KAN ZHENG, YUYU WANG, AND WENBO WANG, BEIJING UNIVERSITY OF POSTS & TELECOMMUNICATION MISCHA
Macro Cell Muting Coordination for Non-Uniform Topologies in LTE-A HetNets Alvarez, Beatriz Soret; Pedersen, Klaus I.
 Aalborg Universitet Macro Cell Muting Coordination for Non-Uniform Topologies in LTE-A HetNets Alvarez, Beatriz Soret; Pedersen, Klaus I. Published in: Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), 213 IEEE
Aalborg Universitet Macro Cell Muting Coordination for Non-Uniform Topologies in LTE-A HetNets Alvarez, Beatriz Soret; Pedersen, Klaus I. Published in: Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), 213 IEEE
Coordinated carrier aggregation for campus of home base stations
 2015 IEEE 2015 International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), Brussels (Belgium), Aug. 2015 DOI: 10.1109/ISWCS.2015.7454390 Coordinated carrier aggregation for campus of home base stations
2015 IEEE 2015 International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), Brussels (Belgium), Aug. 2015 DOI: 10.1109/ISWCS.2015.7454390 Coordinated carrier aggregation for campus of home base stations
Questions & Answers From Thursday, September 16 Webinar Alternatives Case Examples Frequency and Spectrum Planning Security WiMAX Capabilities
 Questions & Answers From Thursday, September 16 Webinar Alternatives Case Examples Frequency and Spectrum Planning Security WiMAX Capabilities Alternatives Q: How about PLC? Is it a viable alternative
Questions & Answers From Thursday, September 16 Webinar Alternatives Case Examples Frequency and Spectrum Planning Security WiMAX Capabilities Alternatives Q: How about PLC? Is it a viable alternative
A Review on Soft Handover Schemes in LTE Cellular Networks
 http:// A Review on Soft Handover Schemes in LTE Cellular Networks Shreedhar K V M Department of Computer Science and Engineering R V College of Engineering Bengaluru, India - 560095 Abstract - Long Term
http:// A Review on Soft Handover Schemes in LTE Cellular Networks Shreedhar K V M Department of Computer Science and Engineering R V College of Engineering Bengaluru, India - 560095 Abstract - Long Term
Real-World Experience with a Mobile Broadband Network
 Real-World Experience with a Mobile Broadband Network Dr. Jin Yang Verizon Wireless jin.yang@ieee.org September 23, 2004 IEEE Communications Society Oakland-East Bay Chapter, CA Outline Introduction Overview
Real-World Experience with a Mobile Broadband Network Dr. Jin Yang Verizon Wireless jin.yang@ieee.org September 23, 2004 IEEE Communications Society Oakland-East Bay Chapter, CA Outline Introduction Overview
SENZA FILI. Is cooperation better than competition? CONSULTING. A closer look at the Sprint and Clearwire deal
 Is cooperation better than competition? A closer look at the Sprint and Clearwire deal Monica Paolini Senza Fili Consulting September 2007 SENZA FILI CONSULTING Many operators worldwide have begun planning
Is cooperation better than competition? A closer look at the Sprint and Clearwire deal Monica Paolini Senza Fili Consulting September 2007 SENZA FILI CONSULTING Many operators worldwide have begun planning
The Power of MulteFire
 The Power of MulteFire LTE-like performance with Wi-Fi-like deployment simplicity LTE-based technology for small cells operating solely in unlicensed spectrum Brings enhanced data and voice services to
The Power of MulteFire LTE-like performance with Wi-Fi-like deployment simplicity LTE-based technology for small cells operating solely in unlicensed spectrum Brings enhanced data and voice services to
Interference Control Technology for Heterogeneous Networks
 Interference Control Technology for Heterogeneous Networks Junsik Kim junsik@etri.re.kr Byunghan Ryu rubh@etri.re.kr Kyongtak Cho ktcho@etri.re.kr Namhoon Park nhpark@etri.re.kr Abstract To eliminate dead
Interference Control Technology for Heterogeneous Networks Junsik Kim junsik@etri.re.kr Byunghan Ryu rubh@etri.re.kr Kyongtak Cho ktcho@etri.re.kr Namhoon Park nhpark@etri.re.kr Abstract To eliminate dead
