How Insecure is Wireless LAN?
|
|
|
- Maurice Golden
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 7 How Insecure is Wireless LAN? Abstract Wireless LAN has gained popularity in the last few years due to its enormous benefits such as scalability, mobile access of the network, and reduced cost of ownership. Wireless LAN has vulnerable security and over the period of time many loopholes in the security have been identified. In this paper, we discuss in detail the security concerns of WLAN such as rouge access point, war-driving, MAC address spoofing, and denial of service attacks etc. The working and security leaks of the WEP are also a part of the paper. At the end of the paper, we will be suggesting a few techniques to ensure secure communication in WLANs. 1. Introduction Local Area Network (LAN) supplies networking capability to a group of computers in close proximity to each other, such as in an office building, a school, or a home. LAN facilitates sharing of resources and connectivity to the Internet. Traditionally the LAN was implemented as a wired network using Ethernet cable. WLAN is a data communication system that is implemented as an alternative or extension to wired LAN using electromagnetic waves instead of wires. The electromagnetic waves are referred as radio carriers, because of their functionality of delivering energy to a remote receiver. The information to be transmitted is modulated over the carrier and the modulated signal contains all the information. Multiple radio carriers can exist at the same time within a space, if they transmit on different radio frequencies. The receiver extracts the signal at the same frequency to which the signal was transmitted, while rejecting every thing at other frequencies. WLAN is built by attaching the access points to the edges of the wired network. Access point (AP) is a device that receives, buffers, and transmits data between the wired infrastructure and wireless LAN. Clients then communicate with the AP using a wireless network adapter similar to a traditional Ethernet adapter as shown in Figure 1. The WLAN adapters provide an interface between the client network operating system (NOS) and the airwaves via the antennas. The nature of the wireless connection is transparent to the NOS.
2 Page 2 of 7 Laptop computer with PC card adapter Tablet with PC card adapter Users can roam Laptop computer from one AP to Laptop computer another Handheld with PC card adapter Desktop System with PC card adapter Wireless Ethernet Access Point Cable Ethernet Access Point Wireless Ethernet Switch Cable Ethernet Switch Wired Network Backbone (Ethernet) Figure 1: Typical Wireless LAN setup. The range for WLAN varies from hundred to five hundred feet, it can also penetrate through walls and other surfaces because of its operation at radio frequency. The other devices, such as microwave oven, operating at the same frequency as that of WLAN may cause interference in the communication. WLANs from different vendors operating in the same vicinity may interfere with each other; using appropriate vendor s product solves this issue. Three popular standards have emerged since the inception of WLANs, a, b, and g. The comparison of these standards on the basis of some parameters is given in Table 1. Parameter a b g Frequency Band (GHz) , , Table 1: Comparison of a, b, g Number of Channels 12 or 4 in each band 3 non-overlapping 3 non-overlapping Data rate (Mbps) Modulation 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, and 54 Mbps Binary Shift Keying; Quad Phase Shift Keying 1, 2, 5.5 and 11 Differential Binary & Quad Phase Shift Keying 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48 and 54 Binary & Quad Phase Shift Keying; Diff Binary & Quad Phase Shift Keying WLAN provides mobility to the users; they can login from anywhere within network range, thus increasing productivity in the organizations. The installation is simple, fast. WLAN eliminates the need of pulling the cables through walls and ceilings; also the WLAN can be installed at the places where we
3 Page 3 of 7 cannot run the wires. WLANs are being implemented at hotels, airports, coffee shops, and in universities. With these benefits comes the security issue as well. The signals can be intercepted without physically accessing the network; this makes the WLAN security vulnerable. We discuss the WLANs with the security perspective in this survey paper. The following section is devoted to the features of the WLAN that make its security vulnerable. In section 3, we discuss the types of attacks and the security tools to protect WLAN. Section 4 describes overview and flaws of WEP. (To be continued in the final report) 2. How attackers gain access to WLAN? Wireless LAN access points (APs) announce their presence periodically by transmitting special format frames known as beacons. In this way the potential clients can find out the presence of the Wireless LAN and can link up to the services. This makes the access to the Wireless LAN very easy. The beacon frames are not protected by any privacy function, so any device with an card can access to the network and its parameters. War-driving is a method to locate the access points of an networks in the area. In war driving the attackers make use of high-gain antennas and drive around in the city to monitor the appearance of beacon frames being transmitted by the access points. They use software to log the presence of the beacon frames and record the coordinates of the AP location using the global positioning system (GPS). Hence they associate the located APs with the geographic locations in the AP maps. Tools like NetStumbler are available to assist the war-driving. Attackers share these AP maps on the Internet and those APs become the potential target of attack. AP maps of several cities with the thousands of AP locations are available on the Internet [1]. War-chalking is another way for marking the APs in the area, attacker marks the area with some specific symbols to pointing out that an AP is in the area. WiFi symbols can be accessed on the Internet as well [2]. Rogue Access Points: There are two cases of installation of rouge access points. First, one of the company s employees can deploy an AP onto the corporate network without authorization from the network administrator. This poses serious threat because user would not be able to implement security features properly and will provide a gateway to the intruders to access the network. Second, an intruder may physically place an AP on the network to gain remote access to the network via wireless. Once an attacker gains access to the wireless network through rouge access point, it can be a launch point of attacks. 3. Types of Attack Attacks can be categorized into two types: active attacks and passive attacks. Passive Attacks: Listening to the network traffic, with out interfering, to get information being transmitted, is known as passive attack. Passive attacks are of two types. First, the release of message content in which intruder tries to learn the content of the network traffic. Second type is traffic analysis, when eavesdropper captures the network traffic. However, even if the packets are encrypted still intruder can analyze the captured packets to make a guess about nature of the communication. Active Attacks:
4 Page 4 of 7 In active attacks, the intruder tries to modify the contents of the data stream of the victim network. Such attacks can be divided into four categories. First, when one entity pretends to be another entity, it is the masquerade attack. The attackers try to gain access to the resources by impersonating the entity, which has privilege to do so. Second, Replay is the extension of passive attack by retransmitting the captured packets to create an unauthorized effect. Third, Modification of the messages when a part of the legitimate message is altered, to create an unauthorized but attacker-desired effect. Forth, denial of service attack can be created by simply overloading the network with the bogus messages. This could result in the degraded performance or the unavailability of the network services because illegitimate traffic captures the frequencies, and legitimate traffic cannot get through. An attacker can configure its client to duplicate the IP or MAC address of a legitimate client causing the disruption on the network. Let us discuss some examples of active and passive attacks. 3.1 MAC Address spoofing networks do not authenticate frames. Access point caters all such frames, which have a valid MAC address. Some vendors provide the feature of MAC address filtering. Cisco s AP maintains a list of authorized MAC addresses and do not allow other users to connect, having MAC addresses other than the authorized one. The attacker can easily sniff the WLAN traffic. These packets contain all the information required to make an attack, which is MAC address and IP address. The attacker uses this information to mimic a valid MAC address and also use the IP address assigned to that MAC address. In spoofing the MAC address, attacker can spoof a MAC address by editing the registry. Attacker will set the value of the Network-Address key in the registry as the authorize MAC address. In the presence of a valid MAC and IP address intruder machine will be considered as a legitimate user of the network. Hence an attacker can gain direct access to the network resources. However, the attacker would not be able to access network until the valid system stops using the network. 3.2 Session Hijacking It is possible to inject false traffic into a connection. Attacker can issue commands on behalf of a legitimate user by injecting traffic and hijacking the victim session. 3.3 Base Station Clone (Evil Twin) Another security feature is server set identifier (SSID); it works like a shared password between base station and clients. This allows only those clients to communicate with base station, which are configured with the same SSID as that of base station. Most APs broadcast their SSID as part of the beacon frames to announce their presence. Tools like NetStumbler can capture these packets to find out the SSID. Now an attacker can use the valid SSID over the false AP to trick the clients to connect to it. Effectively SSID does not protect WLAN against the attacks; it is merely a mechanism to prevent wandering wireless devices in the area to get onto your network. A rouge access point, also known as honey pot, can pretend to be a valid access point by broadcasting the right SSID. The wireless clients of the network will connect to the attacker s false AP. The intruder can steal credentials by tricking the users with the false login prompts, and user gives away his/her password to the attacker in ignorance. Another way of stealing the credential is man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, where attacker places himself between the station and the AP relaying the packets from the AP to the station or vice versa. 3.4 Traffic Redirection Attackers can use spoofed frames to redirect traffic and to corrupt the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) tables in the switch on the wired network. The corrupted ARP tables cause the packets destined for a wired client to be routed to the attacking wireless client. 4. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Algorithm:
5 Page 5 of 7 The IEEE standard for wireless LAN communications introduced the Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol in an order to address the privacy issues. The WEP protocol protects the link level data during wireless transmission. It was an effort to bring the security level of wireless LAN closer to that of wired LAN. The working of WEP is described first, and then we will be discussing its weaknesses. WEP tries to achieve the security goals of the networks; such as confidentiality, access control, and data integrity. Wireless LAN transmissions are broadcasted over radio frequencies; anyone can intercept the information. WEP is implemented at MAC layer, and most of the radio network interface card and access point vendors support the protocol. The network interface card (NIC) encrypts the payload, which includes frame body and cyclic redundancy check (CRC). Then it transmits each frame using RC4 stream cipher. The receiving station, such as an access point or another radio NIC, performs decryption upon arrival of the frame. As a result, WEP only encrypts data between stations. Once the frame enters the wired side of the network, such as between access points, WEP no longer applies. The encryption process of WEP is based on a secret key shared between the communicating parties; the key protects the data being transmitted in the frame. First of all the integrity checksum of the message is calculated, and then concatenated with the message to form the plain text. The plain text is the data fed into the algorithm as the input for encryption. The plain text is encrypted using the famous encryption algorithm RC4. A 24-bit initialization vector (IV) is concatenated to the shared secret key supplied by the user of the sending station. The resulting block forms the seed that is input to pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) defined in RC4. The IV lengthens the life of the secret key because the station can change the IV for each frame transmission. Then the key stream is XOR-ed with the plain text to get the cipher text. This cipher text along with the IV is transmitted over the radio link as shown in the Figure 2. On the receiving end, the encryption process is reversed. With WEP, the receiving station must use the same secret key for decryption. Each radio NIC and access point, therefore, must be manually configured with the same secret key. First the recipient regenerates the key stream; then the key stream and the cipher text are XOR-ed to get back the initial plain text as shown in the Figure 2.
6 Page 6 of 7 Plain Text Decrypted Plain Text Message CRC Message CRC Key Stream = RC4 ( IV + key ) Key Stream = RC4 ( IV + key ) XOR XOR IV Cipher Text IV Cipher Text Transmitted Packet Received Packet Sender's End Receiver End Figure 2: Encryption and Decryption using WEP. The checksum is verified by recalculating the checksum and then matching that by the sent value, to check the integrity of the message. The receiver accepts the frames only with valid checksum. Note: In the final report we will discuss the WEP protocol flaws and the corresponding attacks. We will also discuss how we can build secure WLAN using different security tools to provide a shield against the attacks at multiple levels. References [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] M. Gast. Seven security problem of Wireless. [7] M. Gast. Wireless LAN security: A short history. [8] N. Borisov, I. Goldberg, and D. Wagner, Intercepting Mobile Communications: The Insecurity of [9] L.M.S.C. of the IEEE Computer Society. Wireless LAN medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications. IEEE standard 802.1, 1999 Edition, 1999.
7 Page 7 of 7 [10] William Stallings, Wireless Communications and Networks. Pearson Education Inc., [11] William Stallings, Data and Computer Communications 6 th Edition. Prentice Hall, 2000.
Wireless LAN Security (RM12/2002)
 Information Technology in Education Project Reference Materials Wireless LAN Security (RM12/2002) Infrastructure Division Education Department The Government of HKSAR www.ited.ed.gov.hk December 2002 For
Information Technology in Education Project Reference Materials Wireless LAN Security (RM12/2002) Infrastructure Division Education Department The Government of HKSAR www.ited.ed.gov.hk December 2002 For
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536)
 Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
CS-435 spring semester Network Technology & Programming Laboratory. Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis
 CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: WIRELESS ATTACKS
 CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: WIRELESS ATTACKS Wireless networks are everywhere, from the home to corporate data centres. They make our lives easier by avoiding bulky cables and related problems. But with these
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: WIRELESS ATTACKS Wireless networks are everywhere, from the home to corporate data centres. They make our lives easier by avoiding bulky cables and related problems. But with these
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures
 Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
What is Eavedropping?
 WLAN Security What is Eavedropping? War Driving War Driving refers to someone driving around with a laptop and an 802.11 client card looking for an 802.11 system to exploit. War Walking Someone walks
WLAN Security What is Eavedropping? War Driving War Driving refers to someone driving around with a laptop and an 802.11 client card looking for an 802.11 system to exploit. War Walking Someone walks
Wireless Security Security problems in Wireless Networks
 Wireless Security Security problems in Wireless Networks Security of Wireless Networks Wireless networks are everywhere more and more electronic devices are becoming wireless However, ensuring security
Wireless Security Security problems in Wireless Networks Security of Wireless Networks Wireless networks are everywhere more and more electronic devices are becoming wireless However, ensuring security
Outline : Wireless Networks Lecture 10: Management. Management and Control Services : Infrastructure Reminder.
 Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
CISNTWK-440. Chapter 4 Network Vulnerabilities and Attacks
 CISNTWK-440 Intro to Network Security Chapter 4 Network Vulnerabilities and Attacks Objectives Explain the types of network vulnerabilities List categories of network attacks Define different methods of
CISNTWK-440 Intro to Network Security Chapter 4 Network Vulnerabilities and Attacks Objectives Explain the types of network vulnerabilities List categories of network attacks Define different methods of
Securing Wireless Networks by By Joe Klemencic Mon. Apr
 http://www.cymru.com/ Securing Wireless Networks by By Joe Klemencic (faz@home.com) Mon. Apr 30 2001 Many companies make attempts to embrace new technologies, but unfortunately, many of these new technologies
http://www.cymru.com/ Securing Wireless Networks by By Joe Klemencic (faz@home.com) Mon. Apr 30 2001 Many companies make attempts to embrace new technologies, but unfortunately, many of these new technologies
Karthik Pinnamaneni COEN 150 Wireless Network Security Dr. Joan Holliday 5/21/03
 Karthik Pinnamaneni COEN 150 Wireless Network Security Dr. Joan Holliday 5/21/03 Introduction Although a variety of wireless network technologies have or will soon reach the general business market, wireless
Karthik Pinnamaneni COEN 150 Wireless Network Security Dr. Joan Holliday 5/21/03 Introduction Although a variety of wireless network technologies have or will soon reach the general business market, wireless
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
CITS3002 Networks and Security. The IEEE Wireless LAN protocol. 1 next CITS3002 help3002 CITS3002 schedule
 1 next CITS3002 help3002 CITS3002 schedule The IEEE-802.11 Wireless LAN protocol We'll next examine devices implementing the IEEE-802.11 family of wireless networking protocols, and get an appreciation
1 next CITS3002 help3002 CITS3002 schedule The IEEE-802.11 Wireless LAN protocol We'll next examine devices implementing the IEEE-802.11 family of wireless networking protocols, and get an appreciation
Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design. Artoré & Bizollon : Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design
 Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
NETWORK SECURITY. Ch. 3: Network Attacks
 NETWORK SECURITY Ch. 3: Network Attacks Contents 3.1 Network Vulnerabilities 3.1.1 Media-Based 3.1.2 Network Device 3.2 Categories of Attacks 3.3 Methods of Network Attacks 03 NETWORK ATTACKS 2 3.1 Network
NETWORK SECURITY Ch. 3: Network Attacks Contents 3.1 Network Vulnerabilities 3.1.1 Media-Based 3.1.2 Network Device 3.2 Categories of Attacks 3.3 Methods of Network Attacks 03 NETWORK ATTACKS 2 3.1 Network
LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY
 LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY Raúl Siles raul@taddong.com Founder and Security Analyst at Taddong Introduction to Wi Fi Network Security Wireless networks or Wi Fi networks IEEE 802.11 Standards Information
LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY Raúl Siles raul@taddong.com Founder and Security Analyst at Taddong Introduction to Wi Fi Network Security Wireless networks or Wi Fi networks IEEE 802.11 Standards Information
Analyzing Wireless Security in Columbia, Missouri
 Analyzing Wireless Security in Columbia, Missouri Matthew Chittum Clayton Harper John Mixon Johnathan Walton Abstract The current state of wireless security in most areas can be estimated based on trends
Analyzing Wireless Security in Columbia, Missouri Matthew Chittum Clayton Harper John Mixon Johnathan Walton Abstract The current state of wireless security in most areas can be estimated based on trends
Wireless Networking Basics. Ed Crowley
 Wireless Networking Basics Ed Crowley 2014 Today s Topics Wireless Networking Economic drivers and Vulnerabilities IEEE 802.11 Family WLAN Operational Modes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WPA and WPA2
Wireless Networking Basics Ed Crowley 2014 Today s Topics Wireless Networking Economic drivers and Vulnerabilities IEEE 802.11 Family WLAN Operational Modes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WPA and WPA2
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
What is a Wireless LAN? The wireless telegraph is not difficult to understand. The ordinary telegraph is like a very long cat. You pull the tail in Ne
 Introduction to Wireless Networking and Security Chino Information Technology Center Steve Siedschlag, Associate Professor What is a Wireless LAN? The wireless telegraph is not difficult to understand.
Introduction to Wireless Networking and Security Chino Information Technology Center Steve Siedschlag, Associate Professor What is a Wireless LAN? The wireless telegraph is not difficult to understand.
Overview of Security
 Overview of 802.11 Security Bingdong Li Present for CPE 601 2/9/2011 Sources: 1 Jesse Walker (Intel) & 2. WinLab 1 Agenda Introduction 802.11 Basic Security Mechanisms What s Wrong? Major Risks Recommendations
Overview of 802.11 Security Bingdong Li Present for CPE 601 2/9/2011 Sources: 1 Jesse Walker (Intel) & 2. WinLab 1 Agenda Introduction 802.11 Basic Security Mechanisms What s Wrong? Major Risks Recommendations
Analysis of Security or Wired Equivalent Privacy Isn t. Nikita Borisov, Ian Goldberg, and David Wagner
 Analysis of 802.11 Security or Wired Equivalent Privacy Isn t Nikita Borisov, Ian Goldberg, and David Wagner WEP Protocol Wired Equivalent Privacy Part of the 802.11 Link-layer security protocol Security
Analysis of 802.11 Security or Wired Equivalent Privacy Isn t Nikita Borisov, Ian Goldberg, and David Wagner WEP Protocol Wired Equivalent Privacy Part of the 802.11 Link-layer security protocol Security
D. The bank s web server is using an X.509 certificate that is not signed by a root CA, causing the user ID and password to be sent unencrypted.
 Volume: 119 Questions Question No: 1 John Smith uses a coffee shop's Internet hot-spot (no authentication or encryption) to transfer funds between his checking and savings accounts at his bank's website.
Volume: 119 Questions Question No: 1 John Smith uses a coffee shop's Internet hot-spot (no authentication or encryption) to transfer funds between his checking and savings accounts at his bank's website.
Wireless Network Security Spring 2015
 Wireless Network Security Spring 2015 Patrick Tague Class #7 More WiFi Security 2015 Patrick Tague 1 Class #7 Continuation of WiFi security 2015 Patrick Tague 2 Device Private WiFi Networks AP Local AAA
Wireless Network Security Spring 2015 Patrick Tague Class #7 More WiFi Security 2015 Patrick Tague 1 Class #7 Continuation of WiFi security 2015 Patrick Tague 2 Device Private WiFi Networks AP Local AAA
Wireless Network Security Spring 2016
 Wireless Network Security Spring 2016 Patrick Tague Class #7 WiFi Security 1 Announcements Please do HW#2 in using the stable OMNET++ 4.6, not the beta version. Porting has proven difficult... Form project
Wireless Network Security Spring 2016 Patrick Tague Class #7 WiFi Security 1 Announcements Please do HW#2 in using the stable OMNET++ 4.6, not the beta version. Porting has proven difficult... Form project
Mobile Security Fall 2013
 Mobile Security 14-829 Fall 2013 Patrick Tague Class #6 More WiFi Security & Privacy Issues WiFi Security Issues A Scenario Internet Open AP SSID Network X Open OpenAP AP SSID Attacker Network X LaptopLaptop
Mobile Security 14-829 Fall 2013 Patrick Tague Class #6 More WiFi Security & Privacy Issues WiFi Security Issues A Scenario Internet Open AP SSID Network X Open OpenAP AP SSID Attacker Network X LaptopLaptop
Physical and Link Layer Attacks
 Physical and Link Layer Attacks CMSC 414 November 1, 2017 Attenuation Physical links are subject to attenuation Copper cables have internal resistance, which degrades signal over large distances Fiber
Physical and Link Layer Attacks CMSC 414 November 1, 2017 Attenuation Physical links are subject to attenuation Copper cables have internal resistance, which degrades signal over large distances Fiber
WLAN Security Performance Study
 WLAN Security Performance Study GHEORGHE MÜLEC *,. RADU VASIU *, FLAVIU M. FRIGURA-ILIASA **, DORU VATAU ** * Electronics and Telecommunication Faculty, ** Power and Electrical Engineering Faculty POLITEHNICA
WLAN Security Performance Study GHEORGHE MÜLEC *,. RADU VASIU *, FLAVIU M. FRIGURA-ILIASA **, DORU VATAU ** * Electronics and Telecommunication Faculty, ** Power and Electrical Engineering Faculty POLITEHNICA
Network Security. Dr. Ihsan Ullah. Department of Computer Science & IT University of Balochistan, Quetta Pakistan. June 18, 2015
 Network Security Dr. Ihsan Ullah Department of Computer Science & IT University of Balochistan, Quetta Pakistan June 18, 2015 1 / 19 ARP (Address resolution protocol) poisoning ARP is used to resolve 32-bit
Network Security Dr. Ihsan Ullah Department of Computer Science & IT University of Balochistan, Quetta Pakistan June 18, 2015 1 / 19 ARP (Address resolution protocol) poisoning ARP is used to resolve 32-bit
WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK SECURITY USING WPA2-PSK
 WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK SECURITY USING WPA2-PSK S.DEEPTHI 1 G.MARY SWARNALATHA 2 PAPARAO NALAJALA 3 Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Electronics &Communication Engineering at Institute of Aeronautical Engineering,
WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK SECURITY USING WPA2-PSK S.DEEPTHI 1 G.MARY SWARNALATHA 2 PAPARAO NALAJALA 3 Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Electronics &Communication Engineering at Institute of Aeronautical Engineering,
Network Encryption 3 4/20/17
 The Network Layer Network Encryption 3 CSC362, Information Security most of the security mechanisms we have surveyed were developed for application- specific needs electronic mail: PGP, S/MIME client/server
The Network Layer Network Encryption 3 CSC362, Information Security most of the security mechanisms we have surveyed were developed for application- specific needs electronic mail: PGP, S/MIME client/server
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security. Spring 2007 Lecture 8
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 8 Announcements Reminder: Project 1 is due on tonight by midnight. Midterm 1 will be held next Thursday, Feb. 8th. Example midterms
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 8 Announcements Reminder: Project 1 is due on tonight by midnight. Midterm 1 will be held next Thursday, Feb. 8th. Example midterms
 Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
1. INTRODUCTION. Wi-Fi 1
 Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
D-Link AirPlus G DWL-G700AP
 TM D-Link AirPlus G DWL-G700AP 2.4GHz Wireless Access Point Manual Building Networks for People Contents Package Contents...3 Introduction...4 Wireless Basics...6 Getting Started...8 Using the Configuration
TM D-Link AirPlus G DWL-G700AP 2.4GHz Wireless Access Point Manual Building Networks for People Contents Package Contents...3 Introduction...4 Wireless Basics...6 Getting Started...8 Using the Configuration
Overview of IEEE b Security
 Overview of IEEE 802.11b Security Sultan Weatherspoon, Network Communications Group, Intel Corporation Index words: 802.11b, wireless, WLAN, encryption, security ABSTRACT There is much regulatory and standards
Overview of IEEE 802.11b Security Sultan Weatherspoon, Network Communications Group, Intel Corporation Index words: 802.11b, wireless, WLAN, encryption, security ABSTRACT There is much regulatory and standards
WL-5420AP. User s Guide
 WL-5420AP User s Guide Table of contents INTRODUCTION... 1 About the Operation Modes...2 LED Indicators...5 Solid...5 Ports on the Rear Panel...7 GETTING CONNECTED... 8 WPA AP -CONFIGURATION VIA WEB...
WL-5420AP User s Guide Table of contents INTRODUCTION... 1 About the Operation Modes...2 LED Indicators...5 Solid...5 Ports on the Rear Panel...7 GETTING CONNECTED... 8 WPA AP -CONFIGURATION VIA WEB...
Wireless LAN Security. Gabriel Clothier
 Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 5: The 802.11 Standard October 7, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 All about 802.11 Today's Lecture CSMA/CD MAC and DCF WEP
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 5: The 802.11 Standard October 7, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 All about 802.11 Today's Lecture CSMA/CD MAC and DCF WEP
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
FAQ on Cisco Aironet Wireless Security
 FAQ on Cisco Aironet Wireless Security Document ID: 68583 Contents Introduction General FAQ Troubleshooting and Design FAQ Related Information Introduction This document provides information on the most
FAQ on Cisco Aironet Wireless Security Document ID: 68583 Contents Introduction General FAQ Troubleshooting and Design FAQ Related Information Introduction This document provides information on the most
TinySec: A Link Layer Security Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks. Presented by Paul Ruggieri
 TinySec: A Link Layer Security Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks Chris Karlof, Naveen Sastry,, David Wagner Presented by Paul Ruggieri 1 Introduction What is TinySec? Link-layer security architecture
TinySec: A Link Layer Security Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks Chris Karlof, Naveen Sastry,, David Wagner Presented by Paul Ruggieri 1 Introduction What is TinySec? Link-layer security architecture
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Managing Rogue Devices
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About Rogue Devices, page 1 How to Configure Rogue Detection, page 6 Monitoring Rogue Detection, page 8 Examples: Rogue Detection Configuration, page 9 Additional
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About Rogue Devices, page 1 How to Configure Rogue Detection, page 6 Monitoring Rogue Detection, page 8 Examples: Rogue Detection Configuration, page 9 Additional
The 8 th International Scientific Conference DEFENSE RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN THE 21st CENTURY Braşov, November 14 th 2013
 The 8 th International Scientific Conference DEFENSE RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN THE 21st CENTURY Braşov, November 14 th 2013 Florin OGÎGĂU-NEAMŢIU National Defense University of Romania "Carol I"/ The Regional
The 8 th International Scientific Conference DEFENSE RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN THE 21st CENTURY Braşov, November 14 th 2013 Florin OGÎGĂU-NEAMŢIU National Defense University of Romania "Carol I"/ The Regional
Managing and Securing Computer Networks. Guy Leduc. Chapter 7: Securing LANs. Chapter goals: security in practice: Security in the data link layer
 Managing and Securing Computer Networks Guy Leduc Chapter 7: Securing LANs Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 7 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2016. (section 8.8) Also
Managing and Securing Computer Networks Guy Leduc Chapter 7: Securing LANs Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 7 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2016. (section 8.8) Also
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems. Network Security Concepts
 CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Network Security Concepts Topics 1. Protocols and Layers 2. Layer 2 Network Concepts 3. MAC Spoofing 4. ARP 5. ARP Spoofing 6. Network Sniffing Protocols A protocol defines
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Network Security Concepts Topics 1. Protocols and Layers 2. Layer 2 Network Concepts 3. MAC Spoofing 4. ARP 5. ARP Spoofing 6. Network Sniffing Protocols A protocol defines
PMS 138 C Moto Black spine width spine width 100% 100%
 Series MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the US Patent & Trademark Office. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. 2009 Motorola, Inc. Table of
Series MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the US Patent & Trademark Office. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. 2009 Motorola, Inc. Table of
Vendor: HP. Exam Code: HP2-Z32. Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks. Version: Demo
 Vendor: HP Exam Code: HP2-Z32 Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 A network administrator deploys several HP MSM APs and an HP MSM Controller. The APs discover the
Vendor: HP Exam Code: HP2-Z32 Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 A network administrator deploys several HP MSM APs and an HP MSM Controller. The APs discover the
WiFi Networks: IEEE b Wireless LANs. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018
 WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
Wi-Fi Scanner. Glossary. LizardSystems
 Wi-Fi Scanner Glossary LizardSystems 2 Table of Contents 802 6 802.11 6 802.11a 6 802.11b 6 802.11d 6 802.11e 6 802.11g 6 802.11h 6 802.11i 6 802.11j 6 802.11n 7 802.1X 7 802.3 7 A 8 Ad-Hoc mode 8 AES
Wi-Fi Scanner Glossary LizardSystems 2 Table of Contents 802 6 802.11 6 802.11a 6 802.11b 6 802.11d 6 802.11e 6 802.11g 6 802.11h 6 802.11i 6 802.11j 6 802.11n 7 802.1X 7 802.3 7 A 8 Ad-Hoc mode 8 AES
2013 Summer Camp: Wireless LAN Security Exercises JMU Cyber Defense Boot Camp
 2013 Summer Camp: Wireless LAN Security Exercises 2013 JMU Cyber Defense Boot Camp Questions Have you used a wireless local area network before? At home? At work? Have you configured a wireless AP before?
2013 Summer Camp: Wireless LAN Security Exercises 2013 JMU Cyber Defense Boot Camp Questions Have you used a wireless local area network before? At home? At work? Have you configured a wireless AP before?
Security Setup CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to set up your bridge s security features. This chapter contains the following sections: Security Overview, page 8-2 Setting Up WEP, page 8-7 Enabling Additional WEP
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to set up your bridge s security features. This chapter contains the following sections: Security Overview, page 8-2 Setting Up WEP, page 8-7 Enabling Additional WEP
NETWORK INTRUSION. Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program. Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006
 NETWORK INTRUSION Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006 1 Learning Objectives Students should be able to: Recognize different
NETWORK INTRUSION Information Security in Systems & Networks Public Development Program Sanjay Goel University at Albany, SUNY Fall 2006 1 Learning Objectives Students should be able to: Recognize different
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Attacking Networks. Joshua Wright LightReading LIVE! October 1, 2003
 Attacking 802.11 Networks Joshua Wright Joshua.Wright@jwu.edu LightReading LIVE! October 1, 2003 Attention The material presented here reflects the personal experience and opinions of the author, and not
Attacking 802.11 Networks Joshua Wright Joshua.Wright@jwu.edu LightReading LIVE! October 1, 2003 Attention The material presented here reflects the personal experience and opinions of the author, and not
CHAPTER 8 SECURING INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 8 SECURING INFORMATION SYSTEMS BY: S. SABRAZ NAWAZ SENIOR LECTURER IN MANAGEMENT & IT SEUSL Learning Objectives Why are information systems vulnerable to destruction, error, and abuse? What is
CHAPTER 8 SECURING INFORMATION SYSTEMS BY: S. SABRAZ NAWAZ SENIOR LECTURER IN MANAGEMENT & IT SEUSL Learning Objectives Why are information systems vulnerable to destruction, error, and abuse? What is
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks
 A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
06/02/ Local & Metropolitan Area Networks. 0. Overview. Terminology ACOE322. Lecture 8 Network Security
 1 Local & Metropolitan Area Networks ACOE322 Lecture 8 Network Security Dr. L. Christofi 1 0. Overview As the knowledge of computer networking and protocols has become more widespread, so the threat of
1 Local & Metropolitan Area Networks ACOE322 Lecture 8 Network Security Dr. L. Christofi 1 0. Overview As the knowledge of computer networking and protocols has become more widespread, so the threat of
Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371
 Article ID: 5072 Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371 Objective Virtual Access Points (VAPs) segment the wireless LAN into multiple broadcast domains that are the wireless equivalent of
Article ID: 5072 Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371 Objective Virtual Access Points (VAPs) segment the wireless LAN into multiple broadcast domains that are the wireless equivalent of
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking
 CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
Securing a Wireless LAN
 Securing a Wireless LAN This module describes how to apply strong wireless security mechanisms on a Cisco 800, 1800, 2800, or 3800 series integrated services router, hereafter referred to as an access
Securing a Wireless LAN This module describes how to apply strong wireless security mechanisms on a Cisco 800, 1800, 2800, or 3800 series integrated services router, hereafter referred to as an access
Wireless Network Security Spring 2011
 Wireless Network Security 14-814 Spring 2011 Patrick Tague Feb 8, 2011 Class #9 Link/MAC layer security Announcements HW #1 is due on Thursday 2/10 If anyone would like Android phones for their course
Wireless Network Security 14-814 Spring 2011 Patrick Tague Feb 8, 2011 Class #9 Link/MAC layer security Announcements HW #1 is due on Thursday 2/10 If anyone would like Android phones for their course
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment:
 Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Managing Rogue Devices
 Information About Rogue Devices, page 1 Configuring Rogue Detection (GUI), page 5 Configuring Rogue Detection (CLI), page 8 Information About Rogue Devices Rogue access points can disrupt wireless LAN
Information About Rogue Devices, page 1 Configuring Rogue Detection (GUI), page 5 Configuring Rogue Detection (CLI), page 8 Information About Rogue Devices Rogue access points can disrupt wireless LAN
Viewing Status and Statistics
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter explains how to use ADU to view the client adapter s status and its transmit and receive statistics. The following topics are covered in this chapter: Overview of ADU and Statistics
CHAPTER 7 This chapter explains how to use ADU to view the client adapter s status and its transmit and receive statistics. The following topics are covered in this chapter: Overview of ADU and Statistics
PRODUCT GUIDE Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems
 PRODUCT GUIDE Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems The Need for Wireless INTRUSION PREVENTION SYSTEMS A Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) is designed to address two classes of challenges facing
PRODUCT GUIDE Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems The Need for Wireless INTRUSION PREVENTION SYSTEMS A Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) is designed to address two classes of challenges facing
Configuring Security Solutions
 3 CHAPTER This chapter describes the security solutions for wireless LANs. It contains the following sections: Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Security, page 3-1 Interpreting the Security Tab,
3 CHAPTER This chapter describes the security solutions for wireless LANs. It contains the following sections: Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Security, page 3-1 Interpreting the Security Tab,
Wireless Terms. Uses a Chipping Sequence to Provide Reliable Higher Speed Data Communications Than FHSS
 How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
Wireless KRACK attack client side workaround and detection
 Wireless KRACK attack client side workaround and detection Contents Introduction Components used Requirements EAPoL Attack protections Why this works Possible impact How to identify if a client is deleted
Wireless KRACK attack client side workaround and detection Contents Introduction Components used Requirements EAPoL Attack protections Why this works Possible impact How to identify if a client is deleted
Configuring Cipher Suites and WEP
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the cipher suites required to use WPA authenticated key management, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), and broadcast
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the cipher suites required to use WPA authenticated key management, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), and broadcast
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide
 Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
Wireless Network Security
 Wireless Network Security Why wireless? Wifi, which is short for wireless fi something, allows your computer to connect to the Internet using magic. -Motel 6 commercial 2 but it comes at a price Wireless
Wireless Network Security Why wireless? Wifi, which is short for wireless fi something, allows your computer to connect to the Internet using magic. -Motel 6 commercial 2 but it comes at a price Wireless
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security
 Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
Table of Contents 1 WLAN Service Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 WLAN Service Configuration 1-1 WLAN Service Overview 1-1 Terminology 1-1 Wireless Client Access 1-2 802.11 Overview 1-4 WLAN Topologies 1-5 Single BSS 1-5 Multi-ESS 1-5 Single ESS Multiple
Table of Contents 1 WLAN Service Configuration 1-1 WLAN Service Overview 1-1 Terminology 1-1 Wireless Client Access 1-2 802.11 Overview 1-4 WLAN Topologies 1-5 Single BSS 1-5 Multi-ESS 1-5 Single ESS Multiple
CE Advanced Network Security Wireless Security
 CE 817 - Advanced Network Security Wireless Security Lecture 23 Mehdi Kharrazi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Acknowledgments: Some of the slides are fully or partially
CE 817 - Advanced Network Security Wireless Security Lecture 23 Mehdi Kharrazi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Acknowledgments: Some of the slides are fully or partially
Today s challenge on Wireless Networking. David Leung, CISM Solution Consultant, Security Datacraft China/Hong Kong Ltd.
 Today s challenge on Wireless Networking David Leung, CISM Solution Consultant, Security Datacraft China/Hong Kong Ltd. Agenda How Popular is Wireless Network? Threats Associated with Wireless Networking
Today s challenge on Wireless Networking David Leung, CISM Solution Consultant, Security Datacraft China/Hong Kong Ltd. Agenda How Popular is Wireless Network? Threats Associated with Wireless Networking
Multi-Layered Security Framework for Metro-Scale Wi-Fi Networks
 Multi-Layered Security Framework for Metro-Scale Wi-Fi Networks A Security Whitepaper January, 2004 Photo courtesy of NASA Image exchange. Image use in no way implies endorsement by NASA of any of the
Multi-Layered Security Framework for Metro-Scale Wi-Fi Networks A Security Whitepaper January, 2004 Photo courtesy of NASA Image exchange. Image use in no way implies endorsement by NASA of any of the
Advanced Security and Mobile Networks
 Advanced Security and Mobile Networks W.Buchanan (1) 9. GSM/3G Unit 7: Mobile Networks. Wireless. Security. Mobile IP. Mobile Agents. Spread spectrum. Military/Emergency Networks 8. Ad-hoc 7. Mobile Networks
Advanced Security and Mobile Networks W.Buchanan (1) 9. GSM/3G Unit 7: Mobile Networks. Wireless. Security. Mobile IP. Mobile Agents. Spread spectrum. Military/Emergency Networks 8. Ad-hoc 7. Mobile Networks
How can you bring. Trust and Security. to Wireless LAN solutions? November 2002
 How can you bring Trust and Security to Wireless LAN solutions? November 2002 1 Today s Topics Entrust Introduction Brief overview of the 802.11b technology/security Top vulnerabilities Analysis and attack
How can you bring Trust and Security to Wireless LAN solutions? November 2002 1 Today s Topics Entrust Introduction Brief overview of the 802.11b technology/security Top vulnerabilities Analysis and attack
Networking interview questions
 Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Frequently Asked Questions WPA2 Vulnerability (KRACK)
 Frequently Asked Questions WPA2 Vulnerability (KRACK) Release Date: October 20, 2017 Document version: 1.0 What is the issue? A research paper disclosed serious vulnerabilities in the WPA and WPA2 key
Frequently Asked Questions WPA2 Vulnerability (KRACK) Release Date: October 20, 2017 Document version: 1.0 What is the issue? A research paper disclosed serious vulnerabilities in the WPA and WPA2 key
Selection of EAP Authentication Method for use in a Public WLAN: Implementation Environment Based Approach
 Selection of EAP Authentication Method for use in a Public WLAN: Implementation Environment Based Approach David Gitonga Mwathi * William Okello-Odongo Elisha Opiyo Department of Computer Science and ICT
Selection of EAP Authentication Method for use in a Public WLAN: Implementation Environment Based Approach David Gitonga Mwathi * William Okello-Odongo Elisha Opiyo Department of Computer Science and ICT
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics
 Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
Wireless Router at Home
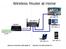 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
School of Computer Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Pulau Pinang
 School of Computer Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Pulau Pinang Information Security & Assurance Assignment 2 White Paper Virtual Private Network (VPN) By Lim Teck Boon (107593) Page 1 Table of Content
School of Computer Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Pulau Pinang Information Security & Assurance Assignment 2 White Paper Virtual Private Network (VPN) By Lim Teck Boon (107593) Page 1 Table of Content
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
CSC 6575: Internet Security Fall Attacks on Different OSI Layer Protocols OSI Layer Basic Attacks at Lower Layers
 CSC 6575: Internet Security Fall 2017 Attacks on Different OSI Layer Protocols OSI Layer Basic Attacks at Lower Layers Mohammad Ashiqur Rahman Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Tennessee
CSC 6575: Internet Security Fall 2017 Attacks on Different OSI Layer Protocols OSI Layer Basic Attacks at Lower Layers Mohammad Ashiqur Rahman Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Tennessee
CIS 5373 Systems Security
 CIS 5373 Systems Security Topic 4.1: Network Security Basics Endadul Hoque Slide Acknowledgment Contents are based on slides from Cristina Nita-Rotaru (Northeastern) 2 Network Security INTRODUCTION 3 What
CIS 5373 Systems Security Topic 4.1: Network Security Basics Endadul Hoque Slide Acknowledgment Contents are based on slides from Cristina Nita-Rotaru (Northeastern) 2 Network Security INTRODUCTION 3 What
Chapter 1 Describing Regulatory Compliance
 [ 2 ] Chapter 1 Describing Regulatory Compliance Failure to secure a WLAN makes it vulnerable to attack. To properly secure your network, you must be able to identify common threats to wireless and know
[ 2 ] Chapter 1 Describing Regulatory Compliance Failure to secure a WLAN makes it vulnerable to attack. To properly secure your network, you must be able to identify common threats to wireless and know
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide
 Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
A Visualization Tool for Wireless Network Attacks
 A Visualization Tool for Wireless Network Attacks Xiaohong YUAN, Ricky L. ARCHER, Jinsheng XU, Huiming YU Department of Computer Science, North Carolina A&T State University Greensboro, NC 27411, USA ABSTRACT
A Visualization Tool for Wireless Network Attacks Xiaohong YUAN, Ricky L. ARCHER, Jinsheng XU, Huiming YU Department of Computer Science, North Carolina A&T State University Greensboro, NC 27411, USA ABSTRACT
CompTIA Security+ Malware. Threats and Vulnerabilities Vulnerability Management
 CompTIA Security+ Lecture Six Threats and Vulnerabilities Vulnerability Management Copyright 2011 - VTC Malware Malicious code refers to software threats to network and systems, including viruses, Trojan
CompTIA Security+ Lecture Six Threats and Vulnerabilities Vulnerability Management Copyright 2011 - VTC Malware Malicious code refers to software threats to network and systems, including viruses, Trojan
On completing this chapter, you will be able to Explain the different WLAN configurations Explain how WLANs work Describe the risks of open wireless
 On completing this chapter, you will be able to Explain the different WLAN configurations Explain how WLANs work Describe the risks of open wireless ports Describe SAFE WLAN design techniques C H A P T
On completing this chapter, you will be able to Explain the different WLAN configurations Explain how WLANs work Describe the risks of open wireless ports Describe SAFE WLAN design techniques C H A P T
Interworking Evaluation of current security mechanisms and lacks in wireless and Bluetooth networks ...
 Interworking 2006 Evaluation of current security mechanisms and lacks in wireless and Bluetooth networks Interworking Conference, 15th - 17th of January 2007 Dr-Ing Kai-Oliver Detken Business URL: http://wwwdecoitde
Interworking 2006 Evaluation of current security mechanisms and lacks in wireless and Bluetooth networks Interworking Conference, 15th - 17th of January 2007 Dr-Ing Kai-Oliver Detken Business URL: http://wwwdecoitde
CS 393/682 Network Security
 CS 393/682 Network Security Nasir Memon Polytechnic University Module 9 Wireless LAN Security Course Logistics Start working on HW 6 Final homework. To be posted today. HW6 - Points for defending and attacking.
CS 393/682 Network Security Nasir Memon Polytechnic University Module 9 Wireless LAN Security Course Logistics Start working on HW 6 Final homework. To be posted today. HW6 - Points for defending and attacking.
NWD2705. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter. Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012
 NWD2705 Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL Communications Corporation IMPORTANT! READ CAREFULLY BEFORE
NWD2705 Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL Communications Corporation IMPORTANT! READ CAREFULLY BEFORE
Digital Entertainment. Networking Made Easy
 Digital Entertainment 2003 by TiVo Inc. Reproduction in whole or in part without written permission is prohibited. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. TiVo, TiVo Central, and TiVolution are registered
Digital Entertainment 2003 by TiVo Inc. Reproduction in whole or in part without written permission is prohibited. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. TiVo, TiVo Central, and TiVolution are registered
Define information security Define security as process, not point product.
 CSA 223 Network and Web Security Chapter One What is information security. Look at: Define information security Define security as process, not point product. Define information security Information is
CSA 223 Network and Web Security Chapter One What is information security. Look at: Define information security Define security as process, not point product. Define information security Information is
Configuring Security Solutions
 3 CHAPTER This chapter describes the security solutions for wireless LANs. It contains the following sections: Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Security, page 3-1 Interpreting the Security Dashboard,
3 CHAPTER This chapter describes the security solutions for wireless LANs. It contains the following sections: Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Security, page 3-1 Interpreting the Security Dashboard,
