Catalyst Switch Operations. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 6-1
|
|
|
- Brianna Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Catalyst Switch Operations 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 6-1
2 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Describe Layer 2 switching (bridging) operations Describe the Catalyst 1900 switch operations Describe the Catalyst 1900 switch default configuration Configure Catalyst 1900 switch Use show commands to verify Catalyst 1900 switch configuration and operations 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-2
3 Switcing /bridging at OSI The layer of the OSI reference model at which bridging and switching technologies operate 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-3
4 Three Switch Functions Address learning Forward/filter decision Loop avoidance 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-4
5 How Switches Learn Host Locations Initial MAC address table is empty 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-5
6 How Switches Learn Hosts Locations Station A sends a frame to Station C Switch caches station A MAC address to port E0 by learning the source address of data frames The frame from station A to station C is flooded out to all ports except port E0 (unknown unicasts are flooded) 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-6
7 How Switches Learn Host Locations Station D sends a frame to station C Switch caches station D MAC address to port E3 by learning the source Address of data frames The frame from station D to station C is flooded out to all ports except port E3 (unknown unicasts are flooded) 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-7
8 How Switches Filter Frames Station C sends a frame to station A Destination is known, frame is not flooded 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-8
9 Forward/Filter Process Destination is known, frame is not flooded 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-9
10 Broadcast and Multicast Frames Station D sends a broadcast or multicast frame Broadcast and multicast frames are flooded to all ports other than the originating port 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-10
11 Forward/Filter Process Example of Forward/Filter Process 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-11
12 Redundant Topology Server/host X Router Y Segment 1 Segment 2 Redundant topology eliminates single points of failure Redundant topology causes broadcast storms, multiple frame copies, and MAC address table instability problems 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-12
13 Broadcast Storms Server/host X Router Y Segment 1 Broadcast Switch A Switch B Segment 2 Host X sends a Broadcast 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-13
14 Broadcast Storms Server/host X Router Y Broadcast Segment 1 Switch A Switch B Segment 2 Host X sends a Broadcast 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-14
15 Broadcast Storms Server/host X Router Y Segment 1 Switch A Broadcast Switch B Segment 2 Switches continue to propagate broadcast traffic over and over 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-15
16 Multiple Frame Copies Host X sends an unicast frame to router Y Router Y MAC address has not been learned by either switch yet 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-16
17 Multiple Frame Copies Host X sends an unicast frame to Router Y Router Y MAC Address has not been learned by either Switch yet Router Y will receive two copies of the same frame 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-17
18 MAC Database Instability Host X sends an unicast frame to Router Y Router Y MAC Address has not been learned by either Switch yet Switch A and B learn Host X MAC address on port , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-18
19 MAC Database Instability Host X sends an unicast frame to Router Y Router Y MAC Address has not been learned by either Switch yet Switch A and B learn Host X MAC address on port 0 Frame to Router Y is flooded Switch A and B incorrectly learn Host X MAC address on port , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-19
20 Multiple Loop Problems Complex topology can cause multiple loops to occur Layer 2 has no mechanism to stop the loop 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-20
21 Solution: Spanning-Tree Protocol x Block Provides a loop free redundant network topology by placing certain ports in the blocking state 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-21
22 Spanning-Tree Operations One root bridge per network One root port per nonroot bridge One designated port per segment 100baseT Root bridge Designated port (F) Root port (F) SW X SW Y Designated port (F) Nondesignated port (B) x Nonroot bridge 10baseT 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-22
23 Spanning-Tree Protocol Root Bridge Selection Switch X Default priority (8000 hex) MAC 0c BPDU Switch Y Default priority (8000 hex) MAC 0c BPDU = Bridge protocol data unit (default = sent every 2 seconds) Root bridge = Bridge with the lowest bridge ID Bridge ID = Bridge priority + bridge MAC address In the example, which switch has the lowest bridge ID? 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-23
24 Spanning-Tree Protocol Port States 100baseT Switch X Default priority MAC 0c Designated port (F) Port 0 Port 0 Root bridge Port 1 Port 1 Designated port (F) x Root port (F) Switch Y Default priority MAC 0c Nondesignated port (B) 10baseT 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-24
25 Spanning-Tree Protocol Path Cost Link Speed Cost (reratify IEEE spec) Cost (previous IEEE spec) Gbps Gbps Mbps Mbps , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-25
26 Spanning-Tree: Port 0 Switch Z Mac 0c Default priority Port 0 Switch X MAC 0c Default priority Port 1 100baseT 100baseT Port 0 Port 1 Switch Y MAC 0c Default priority Can you figure out: What is the root bridge? What are the designated, nondesignated, and root ports? Which are the forwarding and blocking ports? 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-26
27 Spanning-Tree: Port 0 Switch Z Mac 0c Default priority Designated port (F) Port 0 Switch X MAC 0c Default priority Port 1 100baseT Root port (F) Port 0 Port 1 Designated port (F) 100baseT Root port (F) Switch Y MAC 0c Default priority Nondesignated port (BLK) Can you figure out: What is the root bridge? What are the designated, nondesignated, and root parts? Which are the forwarding and blocking ports? 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-27
28 Spanning-Tree Port States Spanning-tree transitions each port through several different state: Blocking (20 sec) Listening (15 sec) Learning (15 sec) Forwarding 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-28
29 Spanning-Tree Recalculation 100baseT Switch X MAC 0c Default priority Designated port Port 0 Root Bridge Port 1 Designated port Port 0 Port 1 x Root port (F) Switch Y MAC 0c Default priority Nondesignated port (BLK) 10baseT 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-29
30 Spanning-Tree Recalculation 100baseT Switch X MAC 0c Default priority Designated port Port 0 x Root Bridge Port 1 Designated port MAXAGE x BPDU Port 0 Port 1 x Root port (F) Switch Y MAC 0c Default priority Nondesignated port (BLK) 10baseT 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-30
31 Key Issue: Time to Convergence Convergence occurs when all the switch and bridge ports have transitioned to either the forwarding or blocking state When network topology changes, switches and bridges must recompute the Spanning-Tree Protocol, which disrupts user traffic 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-31
32 Bridging Compared to LAN Switching Bridging Primarily software based One spanning-tree instance per bridge Usually up to 16 ports per bridge LAN Switching Primarily hardware based (ASIC) Many spanning-tree instances per switch More ports on a switch 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-32
33 Transmitting Frames Through a Switch Cut-through Switch checks destination address and immediately begins forwarding frame 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-33
34 Transmitting Frames through a Switch Cut-through Switch checks destination address and immediately begins forwarding frame Store and forward Complete frame is received and checked before forwarding 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-34
35 Transmitting Frames through a Switch Cut-through Store and forward Fragment free (modified cut-through) Cat1900 Default Switch checks the first 64 bytes then Immediately begins forwarding frame 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-35
36 Duplex Overview Half duplex (CSMA/CD) Unidirectional data flow Higher potential for collison Hubs connectivity Switch Hub 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-36
37 Duplex Overview Half duplex (CSMA/CD) Unidirectional data flow Higher potential for collison Hubs connectivity Switch Hub Full duplex Point-to-point only Attached to dedicated switched port Requires full-duplex support on both ends Collision free Collision detect circuit disabled 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-37
38 Configuring the Switch Catalyst 1900 Menu driven interface Web-based VSM (Visual Switch Manager) IOS CLI (command-line interface) 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-38
39 Catalyst 1900 Default Configurations IP address: CDP: Enabled Switching mode: fragment free 100baseT port: Auto-negotiate duplex mode 10baseT port: Half duplex Spanning Tree: Enabled Console password: none 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-39
40 Ports on the Catalyst 1900 Cat1912 Cat baseT ports AUI port 100baseT uplink ports e0/1 to e0/12 e0/1 to e0/24 e0/25 e0/25 fa0/26 (port A) fa0/27 (port B) fa0/26 (port A) fa0/27 (port B) 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-40
41 Ports on the Catalyst 1900 wg_sw_d#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration:!! interface Ethernet 0/1! interface Ethernet 0/2 wg_sw_d#sh span Port Ethernet 0/1 of VLAN1 is Forwarding Port path cost 100, Port priority 128 Designated root has priority 32768, address Designated bridge has priority 32768, address Designated port is Ethernet 0/1, path cost 0 Timers: message age 20, forward delay 15, hold 1 wg_sw_a#show vlan-membership Port VLAN Membership Type Port VLAN Membership Type Static 13 1 Static 2 1 Static 14 1 Static 3 1 Static 15 1 Static 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-41
42 Configuring the Switch Configuration Modes Global configuration mode wg_sw_a# conf term wg_sw_a(config)# Interface configuration mode wg_sw_a(config)# interface e0/1 wg_sw_a(config-if)# 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-42
43 Configuring the Switch IP Address wg_sw_a(config)# ip address {ip address} {mask} 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-43
44 Configuring the Switch IP Address wg_sw_a(config)# ip address {ip address} {mask} wg_sw_a(config)#ip address , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-44
45 Configuring the Switch Default Gateway wg_sw_a(config)# ip default-gateway {ip address} 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-45
46 Configuring the Switch Default Gateway wg_sw_a(config)# ip default-gateway {ip address} wg_sw_a(config)#ip default-gateway , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-46
47 Showing the Switch IP Address wg_sw_a#show ip IP address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Management VLAN: 1 Domain name: Name server 1: Name server 2: HTTP server: Enabled HTTP port: 80 RIP: Enabled wg_sw_a# 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-47
48 Speed and Duplex Options wg_sw_a(config)#interface e0/1 wg_sw_a(config-if)# duplex {auto full full-flow-control half} 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-48
49 Setting Duplex Options wg_sw_a(config)#interface e0/1 wg_sw_a(config-if)# duplex {auto full full-flow-control half} wg_sw_a(config-if)#duplex half 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-49
50 Showing Duplex Options wg _sw_a#sh interfaces Ethernet 0/1 is Enabled Hardware is Built-in 10Base-T Address is MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbits 802.1d STP State: Forwardi ng Forward Transitions: 1 Port monitoring: Disabled Unknown unicast flooding: Enabled Unregistered multicast flooding: Enabled Description: Duplex setting: Half duplex Back pressure: Disabled Receive Statistics Transmit Statistics Total good frames Total frames Total octets Total octets Broadcast/multicast frames Broadcast/multicast frames Broadcast/multicast octets Broadcast/multicast octets Good frames forwarded Deferrals 0 Frames filtered 9 Single collisions 0 Runt frames 0 Multiple collisions 0 No buffer discards 0 Excessive collisions 0 Queue full discards 0 Errors: Errors: FCS errors 0 Late collisions 0 Alignment errors 0 Excessive deferrals 0 Giant frames 0 Jabber errors 0 Address violations 0 Other transmit errors , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-50
51 Duplex Mismatches The manually set duplex parameter differs between connected ports The switch port is in autonegotiate and the attached port is set to full duplex with no auto-negotiation capability causing the switch port to be in half-duplex mode 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-51
52 FCS and Late Collision wg _sw_a#show interfaces Errors Ethernet 0/1 is Enabled Hardware is Built-in 10Base-T Address is MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbits 802.1d STP State: Forwardi ng Forward Transitions: 1 Port monitoring: Disabled Unknown unicast flooding: Enabled Unregistered multicast flooding: Enabled Description: Duplex setting: Half duplex Back pressure: Disabled Receive Statistics Transmit Statistics Total good frames Total frames Total octets Total octets Broadcast/multicast frames Broadcast/multicast frames Broadcast/multicast octets Broadcast/multicast octets Good frames forwarded Deferrals 0 Frames filtered 9 Single collisions 0 Runt frames 0 Mul tiple collisions 0 No buffer discards 0 Excessive collisions 0 Queue full discards 0 Errors: Errors: FCS errors 0 Late collisions 0 Alignment errors 0 Excessive deferrals 0 Giant frames 0 Jabber errors 0 Address violations 0 Other transmit errors , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-52
53 Managing Mac Address Table wg_sw_a#show mac-address-table 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-53
54 Managing Mac Address Table wg_sw_a#show mac-address-table wg_sw_a#sh mac-address-table Number of permanent addresses : 0 Number of restricted static addresses : 0 Number of dynamic addresses : 6 Address Dest Interface Type Source Interface List E0.1E5D.AE2F Ethernet 0/2 Dynamic All 00D0.588F.B604 FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All 00E0.1E5D.AE2B FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All B.87A4 FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All 00D0.588F.B600 FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All 00D C4 FastEthernet 0/27 Dynamic All 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-54
55 Setting Permanent MAC Address wg_sw_a(config)# mac-address-table permanent {mac-address type module/port} 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-55
56 Setting Permanent MAC Address wg_sw_a(config)# mac-address-table permanent {mac-address type module/port} wg_sw_a(config)#mac-address-table permanent ethernet 0/3 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-56
57 Setting Permanent MAC Address wg_sw_a(config)# mac-address-table permanent {mac-address type module/port} wg_sw_a(config)#mac-address-table permanent ethernet 0/3 wg_sw_a#sh mac-address-table Number of permanent addresses : 1 Number of restricted static addresses : 0 Number of dynamic addresses : 4 Address Dest Interface Type Source Interface List E0.1E5D.AE2F Ethernet 0/2 Dynamic All Ethernet 0/3 Permanent All 00D0.588F.B604 FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All 00E0.1E5D.AE2B FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All 00D C4 FastEthernet 0/27 Dynamic All 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-57
58 Setting Restricted Static MAC Address wg_sw_a(config)# mac-address-table restricted static {mac-address type module/port src-if-list} 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-58
59 Setting Restricted Static MAC Address wg_sw_a(config)# mac-address-table restricted static {mac-address type module/port src-if-list} wg_sw_a(config)#mac-address-table restricted static e0/4 e0/1 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-59
60 Setting Restricted Static MAC Address wg_sw_a(config)# mac-address-table restricted static {mac-address type module/port src-if-list} wg_sw_a(config)#mac-address-table restricted static e0/4 e0/1 wg_sw_a#sh mac-address-table Number of permanent addresses : 1 Number of restricted static addresses : 1 Number of dynamic addresses : 4 Address Dest Interface Type Source Interface List Ethernet 0/4 Static Et0/1 00E0.1E5D.AE2F Ethernet 0/2 Dynamic All Ethernet 0/3 Permanent All 00D0.588F.B604 FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All 00E0.1E5D.AE2B FastEthernet 0/26 Dynamic All 00D C4 FastEthernet 0/27 Dynamic All 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-60
61 Configuring Port Security wg_sw_a(config-if)# port secure [max-mac-count count] Configures an interface to be a secured port Define a maximum number of mac addresses allowed in the address table for this port Count can be from 1 to 132 Default is , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-61
62 Configuring Port Security wg_sw_a(config-if)# port secure [max-mac-count count] Configures an interface to be a secured port Define a maximum number of mac addresses allowed in the address table for this port Count can be from 1 to 132 Default is 132 wg_sw_a(config)#interface e0/4 wg_sw_a(config-if)#port secure wg_sw_a(config-if)#port secure max-mac-count , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-62
63 Configuring Port Security wg_sw_a#show mac-address-table security wg_sw_a#show mac-address-table security Action upon address violation : Suspend Interface Addressing Security Address Table Size Ethernet 0/1 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/2 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/3 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/4 Enabled 1 Ethernet 0/5 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/6 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/7 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/8 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/9 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/10 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/11 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/12 Disabled N/A 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-63
64 Configuring Port Security wg_sw_a#show mac-address-table security wg_sw_a#show mac-address-table security Action upon address violation : Suspend Interface Addressing Security Address Table Size Ethernet 0/1 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/2 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/3 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/4 Enabled 1 Ethernet 0/5 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/6 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/7 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/8 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/9 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/10 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/11 Disabled N/A Ethernet 0/12 Disabled N/A wg_sw_a(config)#address-violation {suspend disable ignore} 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-64
65 Show Version wg _sw_a#show version Cisco Catalyst 1900/2820 Enterprise Edi tion Software Version V Copyright (c) Cisco Systems, Inc ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 3.03 wg _sw_d uptime is 8day(s) 17hour(s) 53minute(s) 25second(s) cisco Catalyst 1900 (486sxl) processor with 2048K/1024K bytes of memory Hardware board revision is 1 Upgrade Status: No upgrade currently in progress. Config File Status: File wgswd.cfg downloaded from Fi xed Ethernet/IEEE interface(s) Base Ethernet Address: wg _sw_a# 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-65
66 Managing Configuration File To send the configuration to a TFTP server: wg_sw_a# copy nvram tftp://host/dst_file 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-66
67 Managing Configuration File To send the configuration to a TFTP server: wg_sw_a# copy nvram tftp://host/dst_file To download the configuration from a TFTP server: wg_sw_a# copy tftp://host/src_file nvram 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-67
68 Managing Configuration File To send the configuration to a TFTP server: wg_sw_a# copy nvram tftp://host/dst_file To download the configuration from a TFTP server: wg_sw_a# copy tftp://host/src_file nvram wg_sw_a#copy nvram tftp:// /wgswd.cfg Configuration upload is successfully completed wg_sw_a#copy tftp:// /wgswd.cfg nvram TFTP successfully downloaded configuration file 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-68
69 Clear NVRAM wg_sw_d#delete nvram Resets the system configuration to factory defaults. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-69
70 Visual Objective pod sw ro s e0 A B C D E F G H I J K L wg_sw_a wg_sw_l wg_pc_a fa0/26 e0/1 (port A) e0/2 fa0/26 (port A) e0/1 wg_pc_l e0/2 e0 e0 wg_ro_a wg_ro_l fa0/1 fa0/12 core_ server (tftp server) fa0/24 core_sw_a , Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-70
71 Summary After completing this chapter, you should be able to perform the following tasks: Describe Layer 2 switching (bridging) operations Describe the Catalyst 1900 switch operations Describe the Catalyst 1900 switch s default configuration Configure Catalyst 1900 switch Use show commands to verify Catalyst 1900 switch configuration and operations 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. ICND v1.0a 6-71
Operating and Configuring a Cisco Catalyst Switch. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 4-1
 Operating and Configuring a Cisco Catalyst Switch 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 4-1 Objectives On completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Start up the Catalyst switch and
Operating and Configuring a Cisco Catalyst Switch 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 4-1 Objectives On completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Start up the Catalyst switch and
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1
 Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
CCNA Layer 2 switching. Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03
 CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
Configuring and Monitoring from the Switch Manager
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring and Monitoring from the Switch Manager This chapter explains how to use the switch manager to change the configuration settings and to monitor the switch. This chapter assumes that
CHAPTER 3 Configuring and Monitoring from the Switch Manager This chapter explains how to use the switch manager to change the configuration settings and to monitor the switch. This chapter assumes that
Chapter 2. Switch Concepts and Configuration. Part I
 Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to
 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
Section 3 Understanding Ethernet and Switch Operations
 Section 3 Understanding Ethernet and Switch Operations Ethernet is the technology of choice for today s LANs. It is fast, has low costs, and is easy to maintain. Today s Ethernet standards support speeds
Section 3 Understanding Ethernet and Switch Operations Ethernet is the technology of choice for today s LANs. It is fast, has low costs, and is easy to maintain. Today s Ethernet standards support speeds
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Lab Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
Chapter. Managed Switch Software Monitoring. In This Chapter...
 Managed Switch Software Monitoring Chapter 23 In This Chapter... System Information...3 2 Port and Power Status...3 4 Network Statistics...3 5 Spanning Tree Status...3 8 Real-Time Ring Status...3 10 Multicast
Managed Switch Software Monitoring Chapter 23 In This Chapter... System Information...3 2 Port and Power Status...3 4 Network Statistics...3 5 Spanning Tree Status...3 8 Real-Time Ring Status...3 10 Multicast
3. What could you use if you wanted to reduce unnecessary broadcast, multicast, and flooded unicast packets?
 Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Configuring Interfaces and Circuits
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure the CSS interfaces and circuits and how to bridge interfaces to Virtual LANs (VLANs). Information in this chapter applies to all CSS models, except where
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure the CSS interfaces and circuits and how to bridge interfaces to Virtual LANs (VLANs). Information in this chapter applies to all CSS models, except where
Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol
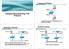 Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0)
 200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트
 PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching
 Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Catalyst 1900 Series and Catalyst 2820 Series Enterprise Edition Software Configuration Guide
 INDEX A allowed list, VLAN 2-28 to 2-29 ATM 2-5 firmware upgrade B-5 to B-7 LANE trunk connections 1-4 module 2-9, 2-13, 2-23 networks 2-5 trunk 2-4, 2-14 B bridge groups 3-15 bridge number 2-10 Bridge
INDEX A allowed list, VLAN 2-28 to 2-29 ATM 2-5 firmware upgrade B-5 to B-7 LANE trunk connections 1-4 module 2-9, 2-13, 2-23 networks 2-5 trunk 2-4, 2-14 B bridge groups 3-15 bridge number 2-10 Bridge
Packet Switching on L2 (LAN Level)
 Packet Switching on L2 (LAN Level) Transparent Bridging (TB), Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid STP, L2 Bridging versus L3 Routing Agenda Introduction Transparent Bridging Basics Spanning Tree Protocol
Packet Switching on L2 (LAN Level) Transparent Bridging (TB), Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid STP, L2 Bridging versus L3 Routing Agenda Introduction Transparent Bridging Basics Spanning Tree Protocol
Switched Ethernet Virtual LANs
 Switched Ethernet Virtual LANs Computer Networks Lecture 4 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Switched Ethernet 2 LAN Switches Behave as bridges (operates in the logical tree topology) Switching is implemented by hardware
Switched Ethernet Virtual LANs Computer Networks Lecture 4 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Switched Ethernet 2 LAN Switches Behave as bridges (operates in the logical tree topology) Switching is implemented by hardware
Out-of-Band Management
 CHAPTER 4 Out-of-Band Management Note Out-of-band management requires the optional Cisco network management module (NMM). This chapter describes how to manage your hub or hub stack using the management
CHAPTER 4 Out-of-Band Management Note Out-of-band management requires the optional Cisco network management module (NMM). This chapter describes how to manage your hub or hub stack using the management
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
Managing Your Switches
 CHAPTER 3 Managing Your Switches You can use the IOS Release 12.0(5)XP software to manage a single switch, a stack of switches that are managed individually, or a cluster of switches that is managed through
CHAPTER 3 Managing Your Switches You can use the IOS Release 12.0(5)XP software to manage a single switch, a stack of switches that are managed individually, or a cluster of switches that is managed through
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
Overview. About the Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 Switches CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 Overview This chapter describes the Enterprise Edition software features for Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 switches. It also describes the feature default settings and shows the management
CHAPTER 1 Overview This chapter describes the Enterprise Edition software features for Catalyst 2820 and Catalyst 1900 switches. It also describes the feature default settings and shows the management
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP)
 3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP) 3.1. STP Operation In an extended Ethernet network (a large network, including many switches) multipath propagation may exist
3. INTERCONNECTING NETWORKS WITH SWITCHES. THE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (STP) 3.1. STP Operation In an extended Ethernet network (a large network, including many switches) multipath propagation may exist
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP. 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch. User s Manual
 SWP-0208G 1 SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch User s Manual Version: 3.4 April 1, 2008 2 TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 MAIN FEATURES...4 1.2 START TO MANAGE THIS SWITCH...6
SWP-0208G 1 SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch User s Manual Version: 3.4 April 1, 2008 2 TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 MAIN FEATURES...4 1.2 START TO MANAGE THIS SWITCH...6
Spanning-Tree Protocol
 Spanning-Tree Protocol Agenda» What Problem is Solved by STP?» Understanding STP Root Bridge Election» BPDU Details and Pathcost» Understanding STP Root and Designated Port Election» Understanding and
Spanning-Tree Protocol Agenda» What Problem is Solved by STP?» Understanding STP Root Bridge Election» BPDU Details and Pathcost» Understanding STP Root and Designated Port Election» Understanding and
VLANs Level 3 Unit 9 Computer Networks
 VLANs Some Requirements of LANs Need to split up broadcast domains to make good use of bandwidth People in different departments may need to be grouped together for access to servers Security: restrict
VLANs Some Requirements of LANs Need to split up broadcast domains to make good use of bandwidth People in different departments may need to be grouped together for access to servers Security: restrict
Packet Switching on L2 (LAN Level)
 Packet Switching on L2 (LAN Level) Transparent Bridging (TB), Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid STP, L2 Bridging versus L3 Routing Agenda Introduction Transparent Bridging Basics Principles Broadcast
Packet Switching on L2 (LAN Level) Transparent Bridging (TB), Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid STP, L2 Bridging versus L3 Routing Agenda Introduction Transparent Bridging Basics Principles Broadcast
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Configuring and Monitoring from the Hub Manager
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring and Monitoring from the Hub Manager This chapter explains how to use the FastHub 400 series Hub Manager on the FastHub 400M models to change the configuration settings and to monitor
CHAPTER 3 Configuring and Monitoring from the Hub Manager This chapter explains how to use the FastHub 400 series Hub Manager on the FastHub 400M models to change the configuration settings and to monitor
Chapter 5 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
 Chapter 5 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the operation of the Ethernet sublayers. Identify the major fields of the Ethernet frame. Describe the purpose
Chapter 5 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the operation of the Ethernet sublayers. Identify the major fields of the Ethernet frame. Describe the purpose
Exam Questions
 Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Exam Questions 200-105 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ 1.At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops? A. physical
Index. Numerics. Index p priority (QoS) definition Q VLAN standard w as a region 5-54
 Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) 802.1Q VLAN standard 5-7 802.1w as a region 5-54 A active path 5-5 address IP 7-8 advertisement 3-3 applicable products 1-ii ARP age setting 7-10 cache 7-4 cache table
Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) 802.1Q VLAN standard 5-7 802.1w as a region 5-54 A active path 5-5 address IP 7-8 advertisement 3-3 applicable products 1-ii ARP age setting 7-10 cache 7-4 cache table
Exam E1 Copyright 2010 Thaar AL_Taiey
 Exam E1 2 Exam E1 E1-1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the internetwork shown in Figure E1-1? (Select all that apply) Figure E1-1 A Sample Internetwork A. The link number 15 uses a
Exam E1 2 Exam E1 E1-1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the internetwork shown in Figure E1-1? (Select all that apply) Figure E1-1 A Sample Internetwork A. The link number 15 uses a
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Exam : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Title : Version : DEMO
 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Version : DEMO 1.Refer to the exhibit. What could be possible causes for the "Serial0/0 is down" interface status? (Choose two.) A. A Layer
Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Version : DEMO 1.Refer to the exhibit. What could be possible causes for the "Serial0/0 is down" interface status? (Choose two.) A. A Layer
Imi :... Data:... Nazwisko:... Stron:...
 Imi :.................................................... Data:....................... Nazwisko:............................................... Stron:...................... 1. Which of the following protocols
Imi :.................................................... Data:....................... Nazwisko:............................................... Stron:...................... 1. Which of the following protocols
Introduction to LAN Protocols
 CHAPTER 2 Chapter Goals Learn about different LAN protocols. Understand the different methods used to deal with media contention. Learn about different LAN topologies. This chapter introduces the various
CHAPTER 2 Chapter Goals Learn about different LAN protocols. Understand the different methods used to deal with media contention. Learn about different LAN topologies. This chapter introduces the various
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols
 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end
Semester 3 Switch CLI labs Basic switch management S1 (DTE) net net net net
 Lab 2.3.10.2cli Switch port options Semester 3 Switch CLI labs 192.5.5.0 net C 201.100.11.0 net B 199.6.13.0 net 204.204.7.0 ne t D E A 205.7.5.0 net 223.8.151.0 net 210.93. 105.0 net 219.17.100.0 net
Lab 2.3.10.2cli Switch port options Semester 3 Switch CLI labs 192.5.5.0 net C 201.100.11.0 net B 199.6.13.0 net 204.204.7.0 ne t D E A 205.7.5.0 net 223.8.151.0 net 210.93. 105.0 net 219.17.100.0 net
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging
 Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
Understanding Issues Related to Inter VLAN Bridging Document ID: 11072 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Spanning Tree Topology Concerns Recommended Use of Hierarchical
Transparent Bridging and VLAN
 Transparent Bridging and VLAN Plug and Play Networking (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 Algorhyme I think that I shall never see a graph more lovely than a tree a graph whose crucial property is loop-free connectivity.
Transparent Bridging and VLAN Plug and Play Networking (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 Algorhyme I think that I shall never see a graph more lovely than a tree a graph whose crucial property is loop-free connectivity.
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B)
 CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B) 1. Identify the factors that contribute to congestion on an Ethernet LAN. (Choose three.) improper placement of enterprise level servers addition of hosts to a physical segment
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B) 1. Identify the factors that contribute to congestion on an Ethernet LAN. (Choose three.) improper placement of enterprise level servers addition of hosts to a physical segment
Configuring the Catalyst 3920
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Catalyst 3920 You might not have to configure the Catalyst 3920 for it to work in your network; it is shipped with default configuration parameters and can function with these
CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Catalyst 3920 You might not have to configure the Catalyst 3920 for it to work in your network; it is shipped with default configuration parameters and can function with these
CS IT. Lecture (06) STP (I) Problem statement. By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee
 Lecture (06) STP (I) By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Problem statement If your network consists of layer 2 switches that allow computers connect and exchange data, you will need to consider the design that
Lecture (06) STP (I) By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Problem statement If your network consists of layer 2 switches that allow computers connect and exchange data, you will need to consider the design that
Cisco - Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations
 Page 1 of 19 Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations Document ID: 10556 This document contains Flash animation. Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco
Page 1 of 19 Spanning Tree Protocol Problems and Related Design Considerations Document ID: 10556 This document contains Flash animation. Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco
The following graphic shows a single switch VLAN configuration.
 7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
- Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers -
 1 Layered Communication - Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers - Network communication models are generally organized into layers. The OSI model specifically consists of seven layers, with each layer representing
1 Layered Communication - Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers - Network communication models are generally organized into layers. The OSI model specifically consists of seven layers, with each layer representing
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior
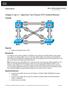 Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Computer Networking. December 2004 CEN CN
 Computer Networking CEN CN 1 Layer 2 - Bridge Frame Header Data Bridge Trailer Data Link Layer Physical Layer More complex than repeat, it requires hardware and software Bridges have diminished because
Computer Networking CEN CN 1 Layer 2 - Bridge Frame Header Data Bridge Trailer Data Link Layer Physical Layer More complex than repeat, it requires hardware and software Bridges have diminished because
Switches Chapter 2 1
 Switches Chapter 2 1 Topics Operation of 100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Switches and how they forward frames Configure a switch Basic security on a switch 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts Wireless
Switches Chapter 2 1 Topics Operation of 100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Switches and how they forward frames Configure a switch Basic security on a switch 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts Wireless
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
CCNA Practice test. 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage? A. NTP B. WCCP C. Telnet D. SNMP Answer: D
 1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
A. ARPANET was an early packet switched network initially connecting 4 sites (Stanford, UC Santa Barbara, UCLA, and U of Utah).
 Volume: 245 Questions Question No: 1 Which of the following statements best describes ARPANET? A. ARPANET was an early packet switched network initially connecting 4 sites (Stanford, UC Santa Barbara,
Volume: 245 Questions Question No: 1 Which of the following statements best describes ARPANET? A. ARPANET was an early packet switched network initially connecting 4 sites (Stanford, UC Santa Barbara,
Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching
 Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching 1 Converged Networks Growing Complexity of Networks Our digital world is changing Information must be accessed from anywhere in the world Networks
Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching 1 Converged Networks Growing Complexity of Networks Our digital world is changing Information must be accessed from anywhere in the world Networks
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Objectives. Hexadecimal Numbering and Addressing. Ethernet / IEEE LAN Technology. Ethernet
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Ethernet Network Fundamentals Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 1 Introduce Hexadecimal number system Describe the features of various
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Ethernet Network Fundamentals Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 1 Introduce Hexadecimal number system Describe the features of various
Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks
 10 Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks Contents Overview..................................................... 10-3 Transmitting Non-IP Traffic..................................
10 Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks Contents Overview..................................................... 10-3 Transmitting Non-IP Traffic..................................
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Catalyst Switches for Microsoft Network Load Balancing Configuration Example
 Catalyst Switches for Microsoft Network Load Balancing Configuration Example Document ID: 107995 Contributed by Shashank Singh, Cisco TAC Engineer. Dec 19, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Catalyst Switches for Microsoft Network Load Balancing Configuration Example Document ID: 107995 Contributed by Shashank Singh, Cisco TAC Engineer. Dec 19, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
AT-S41 Version 1.1.7C Management Software for the AT-8326GB and AT-8350GB Series Fast Ethernet Switches. Software Release Notes
 AT-S41 Version 1.1.7C Management Software for the AT-8326GB and AT-8350GB Series Fast Ethernet Switches Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S41 management software.
AT-S41 Version 1.1.7C Management Software for the AT-8326GB and AT-8350GB Series Fast Ethernet Switches Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S41 management software.
Switch configuration. By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch.
 By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
Spanning Tree Protocol
 For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Chapter 5. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I
 Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 5-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series ISR
 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
 Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
Introducing Campus Networks
 Cisco Enterprise Architecture Introducing Campus Networks 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. BCMSN v2.0 2-2 Campus Data Center Combines switching
Cisco Enterprise Architecture Introducing Campus Networks 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. BCMSN v2.0 2-2 Campus Data Center Combines switching
Answers to the Do I Know This Already? Quizzes
 Appendix C Answers to the Do I Know This Already? Quizzes Chapter 1 1. D and F. Of the remaining answers, Ethernet defines both physical and data link protocols, PPP is a data link protocol, IP is a network
Appendix C Answers to the Do I Know This Already? Quizzes Chapter 1 1. D and F. Of the remaining answers, Ethernet defines both physical and data link protocols, PPP is a data link protocol, IP is a network
Powered by Accton. ES Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch. Management Guide.
 Powered by Accton ES4324 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch Management Guide www.edge-core.com Management Guide 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch with 24 1000BASE-T (RJ-45) Ports, and 4 Combination (RJ-45/SFP)
Powered by Accton ES4324 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch Management Guide www.edge-core.com Management Guide 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch with 24 1000BASE-T (RJ-45) Ports, and 4 Combination (RJ-45/SFP)
EIGRP Features and Operation
 EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
Why Packet Switching on LAN? Packet Switching on L2 (LAN Level) Bridge / Router. Agenda
 Why Packet Switching on LN? Packet Switching on L2 (LN Level) Transparent Bridging (TB), Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid STP, L2 Bridging versus L3 Routing LN was primarily designed for shared media
Why Packet Switching on LN? Packet Switching on L2 (LN Level) Transparent Bridging (TB), Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid STP, L2 Bridging versus L3 Routing LN was primarily designed for shared media
Overview. Switch Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 Overview The 2900 XL series switches are workgroup Ethernet switches that supply autosensing 10BaseT or 100BaseT connections on all ports. Expansion slots on Catalyst 2912MF XL and 2924M XL switches
CHAPTER 1 Overview The 2900 XL series switches are workgroup Ethernet switches that supply autosensing 10BaseT or 100BaseT connections on all ports. Expansion slots on Catalyst 2912MF XL and 2924M XL switches
Cisco EXAM CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate. Buy Full Product.
 Cisco EXAM - 200-120 CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/200-120.html Examskey Cisco 200-120 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product.
Cisco EXAM - 200-120 CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/200-120.html Examskey Cisco 200-120 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product.
Chapter 5: Ethernet. Introduction to Networks - R&S 6.0. Cisco Networking Academy. Mind Wide Open
 Chapter 5: Ethernet Introduction to Networks - R&S 6.0 Cisco Networking Academy Mind Wide Open Chapter 5 - Sections 5.1 Ethernet Protocol Describe the Ethernet MAC address and frame fields 5.2 LAN Switches
Chapter 5: Ethernet Introduction to Networks - R&S 6.0 Cisco Networking Academy Mind Wide Open Chapter 5 - Sections 5.1 Ethernet Protocol Describe the Ethernet MAC address and frame fields 5.2 LAN Switches
The following steps should be used when configuring a VLAN on the EdgeXOS platform:
 EdgeXOS VLANs VLAN Overview This document provides an overview of what a VLAN is and how it is configured on the EdgeXOS platform. Use the step-by-step guide below to configure a VLAN on the Edge appliance
EdgeXOS VLANs VLAN Overview This document provides an overview of what a VLAN is and how it is configured on the EdgeXOS platform. Use the step-by-step guide below to configure a VLAN on the Edge appliance
Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols
 CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end stations might
CHAPTER 4 Token Ring VLANs and Related Protocols A VLAN is a logical group of LAN segments, independent of physical location, with a common set of requirements. For example, several end stations might
Configuring Interfaces on the ML-Series Card
 5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
Establishing a Frame Relay PVC Connection Cisco Systems, Inc. 14-1
 Establishing a Frame Relay PVC Connection 2000 Cisco Systems, Inc. 14-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Determine how Frame Relay operates Configure
Establishing a Frame Relay PVC Connection 2000 Cisco Systems, Inc. 14-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Determine how Frame Relay operates Configure
