Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE
|
|
|
- Donald Simon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE
2 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA
3 Two main approaches to the delivery of voice over LTE, both of which can be implemented in two ways The first approach - Treat voice like any other data service - Deliver it using a voice over IP server that lies outside the LTE network - Can be implemented by A third party service provider A separate IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)
4 The second approach - Connect LTE to the circuit switched (CS) domains of 2G and 3G, and to use their existing capabilities for placing voice calls - Can be implemented using two other techniques Circuit switched fallback [ 備 用系統 ] Voice over LTE via generic access (VoLGA) Each of these four techniques can be adapted for the delivery of text messages, using either SMS or a proprietary messaging application
5 1. The Market for Voice and SMS Figure 1.5 Measurements of voice and data traffic in worldwide mobile telecommunication networks, in the period from January 2007 to July 2011.
6 Figure 1.6 Forecasts of voice and data traffic in worldwide mobile telecommunication networks, in the period from 2011 to 2016.
7 Figure 16.1 Revenue earned by network operators in Western Europe from voice, messaging and other data services, with operators data up to 2011 and forecasts thereafter.
8 Data applications supply most of the operators traffic, but voice supplies most of their revenue The imbalance between voice and data traffic is even more extreme in Western Europe than elsewhere, e.g. Data comprised about 90% of Western European traffic in 2011, compared with about 70% worldwide
9 Voice data rates are low (usually 64 kbps in the CS domains of 2G and 3G) and now only make up a small percentage of the total network traffic Voice applications provide many valuable features to the user Notably supplementary services such as voic and call forwarding Communication with fixed phones on PSTN The ability to place emergency calls Because of this, operators can still charge a large premium [ 額外費 用 ] for voice services This premium is falling, but, voice still makes a disproportionate [ 不成比例 ] contribution to operator revenue A similar but more extreme situation applies in the case of messaging services, which make a negligible contribution to network traffic
10 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA
11 2. Third Party Voice over IP The simplest technique is to provide a voice over IP (VoIP) service through a third party supplier such as Skype The following figure shows the generic architecture that might typically be used for a voice service A similar approach can be used for text messages
12 Figure 16.2 Architecture of a generic third party VoIP system.
13 The user sets up a call by Exchanging VoIP signaling messages with an external VoIP server, and ultimately with another fixed or mobile phone During call setup VoIP server can send LTE signaling messages to the Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF), so as to request a dedicated EPS bearer to transport the call
14 By doing this, the system can ensure a good QoS for the user, at least over the path between mobile and P-GW Using media gateways (MGW) The VoIP system can also convert IP packets to and from the data streams that are used by traditional CS networks This allows the user to make a call from a VoIP device to a 2G or 3G phone, or to a land line
15 Some technical issues If the user moves outside the region of LTE coverage, then the system may be able to handle the call using the 2G or 3G PS domains, or may be able to convert it to a traditional CS call - If it does not support either of these approaches, then the call will have to be dropped Skype does not support emergency calls, so cannot yet be used to replace a traditional voice service
16 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA
17 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 3.1 IMS Architecture 3.2 IMS Procedures 3.3 SMS over IMS
18 3.1 IMS Architecture IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) A separate 3GPP network, which communicates with EPC and with the PS domains of UMTS and GSM so as to control real time IP multimedia services such as voice over IP IMS was originally specified in 3GPP Release 5
19 Few 3G operators ever introduced because it is a complex system that requires significant investment from network operator IMS is very suitable for the delivery of voice and SMS over LTE and can be viewed as a sophisticated 3GPP version of the third party VoIP system The use of IMS is being promoted by the Voice over LTE (VoLTE) initiative of the GSM Association (GSMA), based on earlier work by an industrial collaboration known as One Voice It is likely to be the main long term solution for the delivery of voice over LTE
20 A simplified version of IMS and its relationship with LTE The most important components are Call Session Control Functions (CSCFs), of which there are three types Proxy CSCF (P-CSCF) - The mobile s first point of contact with IMS - Compresses the signaling messages that the mobile exchanges with the IMS so as to reduce their load on the LTE transport network - Secures those messages by encryption and integrity protection - Communicates with PCRF over the Rx interface, so as to guarantee the QoS of the IP multimedia streams
21 Serving CSCF (S-CSCF) - Controls the mobile, in a similar way to an MME - Every mobile is registered with a S-CSCF, which sets up calls with other devices on the mobile s behalf and which contacts the mobile if an incoming call arrives Interrogating CSCF (I-CSCF) - The first point of contact for signaling messages that arrive from another IMS
22 Figure 16.3 Basic architecture of the IP multimedia subsystem.
23 IMS Media Gateway (IM-MGW) and Media Gateway Control Function (MGCF) Allow IMS to communicate with traditional CS networks such as PSTN IM-MGW converts VoIP streams to CS streams and back again MGCF carries out the same role for signaling messages, controls the IM- MGW and is itself controlled by S-CSCF Application Servers (ASs) Provide the user with supplementary services such as voic Home Subscriber Server (HSS) A central database that is shared with EPC
24 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) The main IMS signaling protocol An IETF protocol widely used by other VoIP systems IMS network elements use SIP to - Communicate with each other and with the mobile - Carry out tasks such as registering the mobile and setting up a call SIP messages can contain embedded information written using Session Description Protocol (SDP) - SDP defines the properties of the media such as the requested data rate and the supported codecs
25 The mobile Identifies itself to IMS using a private identity, which acts in a similar way to the IMSI Identifies itself to the outside world using one or more public identities, which act like phone numbers or addresses These identities are stored in the IP multimedia services identity module (ISIM), which is a UICC (Universal Integrated Circuit Card) application similar to the USIM
26 3.2 IMS Procedures The two most important IMS procedures are registration and call setup If a mobile supports IMS, then it registers with the IMS after it has completed the attach procedure Network operators typically use a separate Access Point Name (APN) for IMS, so the mobile begins by connecting to that APN using the UE requested PDN connectivity procedure
27 The network responds by setting up a default EPS bearer for signaling communications with the IMS, most likely using QoS class identifier (QCI) 5
28 Using this bearer, the mobile sends a SIP registration request to the P-CSCF, which forwards it to a suitable S-CSCF In the registration procedure that follows, the mobile and S-CSCF authenticate each other, and the mobile registers its public identities with S-CSCF
29 ECM:EPS Connection Management SDP:Session Description Protocol If an incoming call arrives, then the S-CSCF contacts the mobile by sending it a SIP signaling message over the EPS bearer If the mobile is in ECM-IDLE state, then the message triggers the LTE paging procedure The mobile moves back to ECM-CONNECTED by means of a service request and responds
30 ECM:EPS Connection Management SDP:Session Description Protocol During call setup The two mobiles exchange SIP signaling messages with embedded SDP session descriptions, so as to set up the call and negotiate the voice codec that they will use At the same time, the two IMSs negotiate the QoS
31 In each IMS PCRF:Policy and Charging Rules Function P-CSCF asks PCRF to supply a QoS that is appropriate for the selected codec In response The P-GW sets up a dedicated EPS bearer that will carry the call The IMS can also set up a call to a traditional CS network, using the media and signaling conversion functions provided by IM-MGW and MGCF
32 Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) If a mobile moves outside the coverage area of LTE, then the network can use SRVCC technique to transfer the mobile from VoIP communications over IMS to traditional CS communications over GSM, UMTS or cdma2000 1xRTT SRVCC technique is based on inter-system handover procedures, but with extra steps to transfer the call without loss of service IMS offers full support for emergency calls over LTE from Release 9, using features such as null integrity protection algorithm Integrity protection allows a device to detect modifications to the signaling messages that it receives, as a protection against problems such as man-in-the-middle attacks From Release 9, mobiles can use a null integrity protection algorithm for the sole purpose of making emergency voice calls without a UICC (Universal Integrated Circuit Card)
33 3.3 SMS over IMS IMS can also deliver SMS messages using SMS over generic IP access technique The only new component is the IP short message gateway (IP-SM-GW), which acts as an interface between IMS and the network elements that handle SMS messages
34 Figure 16.4 Architecture used to deliver SMS messages over the IP multimedia subsystem.
35 To transmit an SMS message The mobile embeds it into a SIP signaling message and sends it to IMS The IP-SM-GW extracts the embedded SMS message and sends it to SMS interworking MSC (SMS-IWMSC) This device then forwards the message to the SMS service centre (SC), which stores the message for delivery to its destination The same sequence is used in reverse to deliver a message, except that the SMS-IWMSC is replaced by SMS gateway MSC (SMS-GMSC)
36 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA
37 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 4.1 Architecture 4.2 Combined EPS/IMSI Attach Procedure 4.3 Voice Call Setup 4.4 SMS over SGs 4.5 Circuit Switched Fallback to cdma2000 1xRTT
38 4.1 Architecture Many network operators are rolling out [ 推出 ] LTE before they roll out IMS Because of this, users may wish to place voice calls from LTE devices in the absence of IMS To deal with this possibility, 3GPP has standardized circuit switched (CS) fallback as a possible interim approach
39 Using CS fallback, a user can make voice calls by reverting [ 回復 ] to traditional CS communications over UMTS or GSM The architecture builds on the architecture for inter-operation with the 2G/3G PS domain, by supporting the CS domain as well
40 Figure 16.5 Circuit switched fallback architecture.
41 In this architecture An MME can communicate with a MSC server that supports CS fallback, across SGs interface The signaling messages are written using the SGs application protocol (SGsAP) Using these messages, a mobile can - Register with an MSC server - Set up a CS voice call - Send or receive an SMS message using SMS over SGs technique
42 4.2 Combined EPS/IMSI Attach Procedure When a mobile switches on It registers with a serving MME using the attach procedure This procedure is modified for mobiles that support CS fallback, so as to register the mobile with an MSC server as well
43 Figure 11.4 Overview of the attach procedure.
44 Figure 16.6 Combined EPS/IMSI attach procedure.
45 Step (1) In its attach request, the mobile uses EPS attach type to request a combined EPS/IMSI attach This indicates that it is configured for CS fallback and/or SMS over SGs and would like to register with an MSC server
46 Step (2) The MME runs steps 3 to 16 of the attach procedure, which cover the steps required for identification and security, location updates and default bearer creation Step (3) The MME then identifies a suitable MSC server and sends it an SGsAP Location Update Request
47 Step (4) In response, MSC server creates an association between mobile and MME and runs a location update procedure, in which it registers the mobile and updates the CS domain s copy of the mobile s location Step (5-6) The MSC server then acknowledges the original request from the MME and the MME runs the remaining steps of the attach procedure In its attach accept, the MME indicates whether the result was a combined EPS/IMSI attach, or an EPS only attach
48 4.3 Voice Call Setup The figure shows the procedure for a mobile originated voice call using CS fallback Assumptions The mobile has previously registered with the CS domain using the combined EPS/IMSI attach and that the mobile is starting in RRC_IDLE state The network can hand over the mobile s PS services to the 2G/3G PS domain
49 Figure 16.7 Procedure for mobile originated call setup using circuit switched fallback, with the packet switched services handed over.
50 The mobile starts with the usual procedures for random access and RRC connection establishment, and then writes an Extended Service Request This indicates that the mobile would like to place a voice call using CS fallback and includes the reason for the request, namely Step (1-2) - Mobile originated call - Mobile terminated call - Emergency call The mobile sends the message to BS as part of its RRC Connection Setup Complete The BS forwards the message to MME
51 Step (3) The MME tells the BS to set up a signaling connection for the mobile in the usual way, but also sets a CS fallback indicator that requests a handover to the CS domain Step (4-5) The BS activates Access Stratum (AS) security and tells the mobile to move into ECM_CONNECTED state Step (6-7) The mobile s response triggers an acknowledgement from BS to MME
52 Step (8) As part of step 5, the BS also tells the mobile to measure the signals that it can receive from nearby UMTS and GSM cells The mobile makes the measurements and transmits a measurement report Step (9) Using the measurement report, the BS starts the procedure for handover from LTE to UMTS or GSM
53 Step (10) Once the mobile is communicating with the target radio access network, it can contact the MSC server using a Connection Management (CM) Service Request that is written using the CS domain s mobility management (MM) protocol Step (11) The mobile can then initiate the 2G/ 3G procedure for establishing a CS voice call Step (12) At the same time, the network can complete the handover by transferring the mobile s EPS bearers to the 2G/3G PS domain, so that the user can continue any previous data sessions On completion of the call, the network can hand the mobile back to LTE
54 If the network or mobile does not support PS handovers, then CS fallback is implemented using a different procedure, in which the BS releases the mobile s S1 connection and tells the mobile to carry out a cell reselection to 2G or 3G As a result, the mobile s PS services are suspended for the duration of the call
55 If a mobile terminated call arrives for the mobile, then the incoming signaling message arrives at the MSC server This notices that the mobile is registered with an MME and sends the MME an SGsAP paging request The MME runs the paging procedure and the mobile responds with an extended service request as before The call setup procedure then continues in a similar way
56 If a mobile terminated call arrives while idle mode signaling reduction (ISR) is active, then the MSC server sends an SGsAP paging request to the MME in the same manner as before The MME contacts the SGSN, both devices page the mobile and the mobile responds in the usual way There are no direct communications between MSC server and SGSN, so the MSC server remains unaware of the use of ISR Idle Mode Signaling Reduction (ISR) * If the mobile is near the edge of the LTE coverage area, then it can easily bounce back and forth between cells that are using LTE and cells that are using UMTS or GSM. There is then a risk that the mobile will execute a large number of routing and tracking area updates, leading to excessive signaling. * ISR technique behaves very like the registration of a mobile in multiple tracking areas. When using ISR, the network can simultaneously register the mobile in a routing area that is served by an S3-based SGSN and in one or more tracking areas that are served by an MME. The mobile can then freely reselect between cells that are using the three radio access technologies and only has to inform the network if it moves into a routing or tracking area in which it is not currently registered.
57 CS fallback only requires a few enhancements to the system and is likely to be the main interim [ 過渡時期 ] solution for the delivery of voice over LTE Several drawbacks Firstly, the mobile can only use the technique if it is simultaneously in the coverage area of LTE and a 2G or 3G cell Secondly, the procedure involves delays of a few seconds while the mobile makes its measurements and the network hands it over Thirdly, inter-system handovers have traditionally been one of the least reliable aspects of a mobile telecommunication system - If this unreliability is repeated in the case of LTE, then CS fallback will result in many dropped calls Overall, the resulting service degradation makes it doubtful whether CS fallback is actually an acceptable solution
58 4.4 SMS over SGs Similar ideas for the delivery of SMS messages The mobile does not have to hand over to a 2G or 3G network before sending or receiving a message Instead, the network uses SMS over SGs technique to deliver SMS messages by embedding them into signaling messages between MME and MSC server SGs
59 Figure 16.8 Architecture for SMS over SGs.
60 SMS over SGs technique The mobile registers with the CS domain using the combined EPS/IMSI attach procedure It can then send an SMS message to MME, by embedding it into an Uplink NAS transport message The MME can then forward the SMS message to the MSC server, by embedding it into an SGsAP Uplink Unitdata message From there, the SMS message is passed to the SMS interworking MSC and the service center in the usual way NAS:Non Access Stratum
61 If a mobile terminated SMS reaches the MSC server while the mobile is in ECM-IDLE state Then the MSC server alerts the MME using an SGsAP Paging Request This triggers the paging procedure and the mobile replies by initiating a service request MME can then retrieve the SMS message from the MSC server and can deliver it to the mobile ECM:EPS Connection Management SGsAP:SGs Application Protocol
62 4.5 Circuit Switched Fallback to cdma2000 1xRTT The 3GPP specifications also support CS fallback to cdma2000 1xRTT networks
63 Figure 16.9 Architecture for circuit switched fallback to cdma2000 1xRTT.
64 After attaching to LTE The mobile preregisters with a cdma2000 1xRTT MSC, using 1xRTT signaling messages that are transported across the S102 interface If the user wishes to place a voice call later on The mobile sends an extended service request to the MME MME tells the BS to initiate a handover to cdma2000 1xRTT If an incoming call arrives for the mobile The 1xRTT MSC sends the mobile a paging message across the S102 interface This triggers an extended service request from the mobile and the call setup procedure The mobile can also send and receive SMS messages, by tunneling them to and from the 1xRTT MSC over S102
65 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA
66 5. VoLGA Voice over LTE via generic access (VoLGA) Another technique for delivering voice calls to LTE devices using the existing capabilities of the 2G/3G CS domain Through VoLGA, a mobile can reach the 2G/3G core network through a generic access network such as a WLAN VoLGA architecture connects P-GW to 2G/3G CS domain through a VoLGA Access Network Controller (VANC)
67 From the viewpoint of P-GW, VANC looks like any other server in the outside world From the viewpoint of CS domain, VANC looks like a generic radio access network As a result, LTE system can impersonate [ 模仿 ] the behavior of a generic radio access network and can give the mobile access to the services of the 2G/3G CS domain VoLGA has found less support from the industry than the other approaches, and appears unlikely to be widely adopted
68 Figure VoLGA architecture.
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 13 年 5 月 27 日星期 一
 Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a data
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a data
SRVCC Ensuring voice service continuity in VoLTE/IMS
 SRVCC Ensuring voice service continuity in VoLTE/IMS White Paper 2013 Author : Binu K G 1 Wireless service has turned a full circle and voice remains the most popular and killer application for any mobile
SRVCC Ensuring voice service continuity in VoLTE/IMS White Paper 2013 Author : Binu K G 1 Wireless service has turned a full circle and voice remains the most popular and killer application for any mobile
System Architecture Evolution
 System Architecture Evolution Contents 2.1 Architecture of LTE 2.2 Communication Protocols 2.3 Example Information Flows 2.4 Bearer Management 2.5 State Diagrams 2.6 Spectrum Allocation 2.1 Architecture
System Architecture Evolution Contents 2.1 Architecture of LTE 2.2 Communication Protocols 2.3 Example Information Flows 2.4 Bearer Management 2.5 State Diagrams 2.6 Spectrum Allocation 2.1 Architecture
DAY 2. HSPA Systems Architecture and Protocols
 DAY 2 HSPA Systems Architecture and Protocols 1 LTE Basic Reference Model UE: User Equipment S-GW: Serving Gateway P-GW: PDN Gateway MME : Mobility Management Entity enb: evolved Node B HSS: Home Subscriber
DAY 2 HSPA Systems Architecture and Protocols 1 LTE Basic Reference Model UE: User Equipment S-GW: Serving Gateway P-GW: PDN Gateway MME : Mobility Management Entity enb: evolved Node B HSS: Home Subscriber
Quality of Service, Policy and Charging
 Quality of Service, Policy and Charging Contents 1. Policy and Charging Control! 2. Session Management Procedures! 3. Charging and Billing 1. Policy and Charging Control 1.1 Introduction! 1.2 Quality of
Quality of Service, Policy and Charging Contents 1. Policy and Charging Control! 2. Session Management Procedures! 3. Charging and Billing 1. Policy and Charging Control 1.1 Introduction! 1.2 Quality of
Timmins Training Consulting
 VoLTE Core Network Course Outline Short Description VoLTE stands for voice over Long-Term Evolution. It is a combination of LTE and IMS technology which enables processing of digital packet voice service
VoLTE Core Network Course Outline Short Description VoLTE stands for voice over Long-Term Evolution. It is a combination of LTE and IMS technology which enables processing of digital packet voice service
Basic SAE Management Technology for Realizing All-IP Network
 LTE SAE EPC Special Articles on SAE Standardization Technology Basic SAE Management Technology for Realizing All-IP Network The standardization of 3GPP Release 8 brings new provisions for All-IP networks
LTE SAE EPC Special Articles on SAE Standardization Technology Basic SAE Management Technology for Realizing All-IP Network The standardization of 3GPP Release 8 brings new provisions for All-IP networks
Spirent Landslide VoLTE
 /IMS Node and SIP UE Emulation Voice over LTE () is the combination of IMS-based voice, messaging and video services over the 4G mobile network. To ensure a successful transition, mobile carriers and equipment
/IMS Node and SIP UE Emulation Voice over LTE () is the combination of IMS-based voice, messaging and video services over the 4G mobile network. To ensure a successful transition, mobile carriers and equipment
NG40 IMS Emulator. Key features: IMS Registration VoLTE Basic SRVCC (one-way HO of single active speech session from 4G PS to 3G CS)
 NG40 IMS Emulator IMS Emulation for LTE has been added to the ng4t portfolio. The NG40 IMS Emulator is an extension to the NG40 eutran and to the NG40 EPC Emulator. The NG40 eutran Emulator simulates the
NG40 IMS Emulator IMS Emulation for LTE has been added to the ng4t portfolio. The NG40 IMS Emulator is an extension to the NG40 eutran and to the NG40 EPC Emulator. The NG40 eutran Emulator simulates the
VoLTE is the mainstream solution
 Expert's Forum Top 10 E2E VoLTE considerations By Wang Yachen VoLTE is unprecedented in its complexity and a great challenge to carrier networks and telco business transformation. This article details
Expert's Forum Top 10 E2E VoLTE considerations By Wang Yachen VoLTE is unprecedented in its complexity and a great challenge to carrier networks and telco business transformation. This article details
VoIP and Voice over LTE
 VoIP and Voice over LTE Sridevi Assistant Professor, Department of computer Science, Karnatak University, Dharwad. Abstract: The LTE system was optimised for high data rates and high quality voice services
VoIP and Voice over LTE Sridevi Assistant Professor, Department of computer Science, Karnatak University, Dharwad. Abstract: The LTE system was optimised for high data rates and high quality voice services
CSFB and SMS over SGs Interface
 Circuit Switched Fallback (CSFB) provides an interim solution for enabling telephony and short message service (SMS) for LTE operators that do not plan to deploy IMS packet switched services at initial
Circuit Switched Fallback (CSFB) provides an interim solution for enabling telephony and short message service (SMS) for LTE operators that do not plan to deploy IMS packet switched services at initial
Voice over LTE via Generic Access (VoLGA) A Whitepaper - August 2009
 Voice over LTE via Generic (VoLGA) A Whitepaper - August 2009 V 1.0 Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...2 2 VoLGA Overview...3 3 Handover...7 4 Quality of Service...8 5 International Roaming...9 6
Voice over LTE via Generic (VoLGA) A Whitepaper - August 2009 V 1.0 Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...2 2 VoLGA Overview...3 3 Handover...7 4 Quality of Service...8 5 International Roaming...9 6
POWER-ON AND POWER-OFF PROCEDURES
 POWER-ON AND POWER-OFF PROCEDURES TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Power-On Sequence 2. Network and Cell Selection 3. RRC Connection Establishment 4. Attach Procedure 5. Detach Procedure 1. POWER-ON SEQUENCE The following
POWER-ON AND POWER-OFF PROCEDURES TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Power-On Sequence 2. Network and Cell Selection 3. RRC Connection Establishment 4. Attach Procedure 5. Detach Procedure 1. POWER-ON SEQUENCE The following
LTE. over. Voice. ericsson white paper Uen December Voice over LTE a step towards future telephony
 ericsson white paper 284 23-3145 Uen December 2010 Voice over Voice over a step towards future telephony Which voice over solution offers the most advantages for operators and satisfies user expectations?
ericsson white paper 284 23-3145 Uen December 2010 Voice over Voice over a step towards future telephony Which voice over solution offers the most advantages for operators and satisfies user expectations?
VoLTE: The Next Generation of Voice
 VoLTE: The Next Generation of Voice Introduction Voice over LTE (VoLTE) is no longer just a buzz word in the telecom community but is quickly becoming reality, with implementations appearing around the
VoLTE: The Next Generation of Voice Introduction Voice over LTE (VoLTE) is no longer just a buzz word in the telecom community but is quickly becoming reality, with implementations appearing around the
Voice over Long Term Evolution Migration Strategies
 White Paper Voice over Long Term Evolution Migration Strategies What You Will Learn The evolution of mobile networks to the Voice over Long Term Evolution (VoLTE) all-ip technology standard has generated
White Paper Voice over Long Term Evolution Migration Strategies What You Will Learn The evolution of mobile networks to the Voice over Long Term Evolution (VoLTE) all-ip technology standard has generated
Improvement of VoLTE Domain HO with Operators Vision
 TS-A3 (Technical Session): Mobile Access and Network - #4 Improvement of VoLTE Domain HO with Operators Vision NW Strategy Group, Global Standardization Team Network Development Department NTT DOCOMO R&D
TS-A3 (Technical Session): Mobile Access and Network - #4 Improvement of VoLTE Domain HO with Operators Vision NW Strategy Group, Global Standardization Team Network Development Department NTT DOCOMO R&D
IP multimedia in 3G. Structure. Author: MartinHarris Orange. Understanding IP multimedia in 3G. Developments in 3GPP. IP multimedia services
 IP multimedia in 3G Author: MartinHarris Orange slide 1 Structure Understanding IP multimedia in 3G Developments in 3GPP IP multimedia services IMS challenges and open issues IP multimedia roadmap slide
IP multimedia in 3G Author: MartinHarris Orange slide 1 Structure Understanding IP multimedia in 3G Developments in 3GPP IP multimedia services IMS challenges and open issues IP multimedia roadmap slide
Communication and Distributed Systems Seminar on : LTE Security. By Anukriti Shrimal May 09, 2016
 Communication and Distributed Systems Seminar on : LTE Security By Anukriti Shrimal May 09, 2016 LTE network with interfaces LTE Security 2 Contents LTE Security : Why, What, How EPS Architecture Design
Communication and Distributed Systems Seminar on : LTE Security By Anukriti Shrimal May 09, 2016 LTE network with interfaces LTE Security 2 Contents LTE Security : Why, What, How EPS Architecture Design
Requirement Plan Plan Name: LTE_Data_Retry Plan Id: LTEDATARETRY Version Number: 31 Release Date: June 2018
 Requirement Plan Requirement Plan Plan Name: Plan Id: LTEDATARETRY Version Number: 31 Release Date: June 2018 This document provides initial information related to Verizon Wireless Long Term Evolution
Requirement Plan Requirement Plan Plan Name: Plan Id: LTEDATARETRY Version Number: 31 Release Date: June 2018 This document provides initial information related to Verizon Wireless Long Term Evolution
3GPP TS V8.7.0 ( )
 TS 23.237 V8.7.0 (2010-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Service Continuity; Stage
TS 23.237 V8.7.0 (2010-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Service Continuity; Stage
Sh Gy. Ro Gx. Cx Ici. Mr Mj
 Sh Ro Cx Ici SIP UT IMS Sv LTE Mr Mj Mi Mg ISC Mw LTE / VoLTE IMS Protocols Interfaces LTE Protocol Stack IMS Protocol Stack LTE (4G) IMS PSTN / LTE Ex : S1, S5, SGi LTE Control Plane Ex : S1, S10, S11,
Sh Ro Cx Ici SIP UT IMS Sv LTE Mr Mj Mi Mg ISC Mw LTE / VoLTE IMS Protocols Interfaces LTE Protocol Stack IMS Protocol Stack LTE (4G) IMS PSTN / LTE Ex : S1, S5, SGi LTE Control Plane Ex : S1, S10, S11,
5G voice network evolution aspects. Voice over NR in a 5G System and migration from Evolved Packet System Fallback. Paper 3
 5G voice network evolution aspects Voice over NR in a 5G System and migration from Evolved Packet System Fallback Paper 3 2 Ericsson 5G voice network evolution aspects Abstract This document is part of
5G voice network evolution aspects Voice over NR in a 5G System and migration from Evolved Packet System Fallback Paper 3 2 Ericsson 5G voice network evolution aspects Abstract This document is part of
Primebit Solution EXPERT DIPLOMA IN PROTOCOL TESTING COURSE CONTENT
 EXPERT DIPLOMA IN PROTOCOL TESTING COURSE CONTENT MODULE 1 : UMTS (3G) AND GSM (2G) BASIC 2G and 3G Network Architecture - CS & PS domain. RAT- FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, WCDMA, DFDMA, SCFDMA. SDU,PDU,UMTS N/W
EXPERT DIPLOMA IN PROTOCOL TESTING COURSE CONTENT MODULE 1 : UMTS (3G) AND GSM (2G) BASIC 2G and 3G Network Architecture - CS & PS domain. RAT- FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, WCDMA, DFDMA, SCFDMA. SDU,PDU,UMTS N/W
INTRODUCTION TO LTE. ECE MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018
 INTRODUCTION TO LTE ECE 2526 - MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018 1 WHAT IS LTE? 1. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and it was started as a project in 2004 by the Third Generation Partnership
INTRODUCTION TO LTE ECE 2526 - MOBILE COMMUNICATION Monday, 25 June 2018 1 WHAT IS LTE? 1. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and it was started as a project in 2004 by the Third Generation Partnership
Version LTE Emulators v10.2 Release Notes - Page 1 of 16 - Release Date: Aug 28, Resolved Issues
 Version 10.2.0.15 Release Date: Aug 28, 2015 Resolved Issues LTE Emulators v10.2 Release Notes - Page 1 of 16-11336 MME does not release previous S1 association when UE Context Release Request procedure
Version 10.2.0.15 Release Date: Aug 28, 2015 Resolved Issues LTE Emulators v10.2 Release Notes - Page 1 of 16-11336 MME does not release previous S1 association when UE Context Release Request procedure
ITU-T Q Signalling architecture and requirements for IP-based short message service over ITU-T defined NGN
 I n t e r n a t i o n a l T e l e c o m m u n i c a t i o n U n i o n ITU-T Q.3053 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (03/2017) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING, AND ASSOCIATED MEASUREMENTS
I n t e r n a t i o n a l T e l e c o m m u n i c a t i o n U n i o n ITU-T Q.3053 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (03/2017) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING, AND ASSOCIATED MEASUREMENTS
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations. Mobile Telephony Networks
 Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations Mobile Telephony Networks 1 The Evolution of Mobile Telephony 1st Generation 2nd 3rd 4th Analogue Voice
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations Mobile Telephony Networks 1 The Evolution of Mobile Telephony 1st Generation 2nd 3rd 4th Analogue Voice
Next Generation Core Networks Summit 2011 Standardisation and Developments within SAE
 Next Generation Core Networks Summit 2011 Standardisation and Developments within SAE Frédéric Firmin (frederic.firmin@3gpp.org) 3GPP Technical Officer Mobile World Congress, 19 th February 2009 1 Terminology
Next Generation Core Networks Summit 2011 Standardisation and Developments within SAE Frédéric Firmin (frederic.firmin@3gpp.org) 3GPP Technical Officer Mobile World Congress, 19 th February 2009 1 Terminology
Implementing Cisco Service Provider Mobility LTE Networks ( )
 Implementing Cisco Service Provider Mobility LTE Networks (600-212) Exam Description: The Implementing Cisco LTE Packet Core Networks (600-212 SPLTE) exam is a 90- minute, 65 75 question assessment within
Implementing Cisco Service Provider Mobility LTE Networks (600-212) Exam Description: The Implementing Cisco LTE Packet Core Networks (600-212 SPLTE) exam is a 90- minute, 65 75 question assessment within
Long Term Evolution - Evolved Packet Core S1 Interface Conformance Test Plan
 Long Term Evolution - Evolved Packet Core S1 Interface Conformance Test Plan Table of Contents 1 SCOPE... 10 2 REFERENCES... 10 3 ABBREVIATIONS... 11 4 OVERVIEW... 14 5 TEST CONFIGURATION... 16 5.1 NETWORK
Long Term Evolution - Evolved Packet Core S1 Interface Conformance Test Plan Table of Contents 1 SCOPE... 10 2 REFERENCES... 10 3 ABBREVIATIONS... 11 4 OVERVIEW... 14 5 TEST CONFIGURATION... 16 5.1 NETWORK
TECHNICAL REPORT Speech and multimedia Transmission Quality (STQ); Quality of Service aspects of voice communication in an LTE environment
 TR 103 219 V1.1.1 (2015-04) TECHNICAL REPORT Speech and multimedia Transmission Quality (STQ); Quality of Service aspects of voice communication in an LTE environment 2 TR 103 219 V1.1.1 (2015-04) Reference
TR 103 219 V1.1.1 (2015-04) TECHNICAL REPORT Speech and multimedia Transmission Quality (STQ); Quality of Service aspects of voice communication in an LTE environment 2 TR 103 219 V1.1.1 (2015-04) Reference
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 24.341 V12.6.0 (2014-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage 3 (Release 12) The
TS 24.341 V12.6.0 (2014-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage 3 (Release 12) The
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. 1 Short Message Service and IP Network Integration 1. 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS 39
 Acknowledgments Introduction xv xvii 1 Short Message Service and IP Network Integration 1 1.1 SMS-IP Integration with SM-SC 3 1.1.1 NCTU Short Message System 4 1.1.2 Statistics for SMS Delivery 7 1.2 isms
Acknowledgments Introduction xv xvii 1 Short Message Service and IP Network Integration 1 1.1 SMS-IP Integration with SM-SC 3 1.1.1 NCTU Short Message System 4 1.1.2 Statistics for SMS Delivery 7 1.2 isms
Timmins Training Consulting Sdn. Bhd. VoLTE Core Network
 Timmins Training Consulting Sdn. Bhd. VoLTE Core Network Timmins Training Consulting Our Training Profile About Us - was established in 2015. We are an HRDF registered training provider and our courses
Timmins Training Consulting Sdn. Bhd. VoLTE Core Network Timmins Training Consulting Our Training Profile About Us - was established in 2015. We are an HRDF registered training provider and our courses
The Evolution of Diameter Signaling
 The Evolution of Diameter Signaling A Whitepaper July 2012 By Chris Knight Product/Solution Engineering Abstract: The network architecture of the mobile core has evolved to be more complex with many more
The Evolution of Diameter Signaling A Whitepaper July 2012 By Chris Knight Product/Solution Engineering Abstract: The network architecture of the mobile core has evolved to be more complex with many more
Seamless Interoperability Across LTE And WiMAX Using Vertical Handover Mechanism
 Seamless Interoperability Across LTE And WiMAX Using Vertical Handover Mechanism Bharatesh Chakravarthi S. B M.Tech. Dept of ISE The Oxford College of Engineering Bangalore, India Prof. D. Jayaramaiah
Seamless Interoperability Across LTE And WiMAX Using Vertical Handover Mechanism Bharatesh Chakravarthi S. B M.Tech. Dept of ISE The Oxford College of Engineering Bangalore, India Prof. D. Jayaramaiah
ETSI TS V8.3.0 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 124 301 V8.3.0 (2009-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for Evolved Packet System (EPS); Stage 3 (3GPP TS 24.301 version
TS 124 301 V8.3.0 (2009-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for Evolved Packet System (EPS); Stage 3 (3GPP TS 24.301 version
3GPP TR V ( )
 TR 23.885 V11.0.0 (2011-09) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Feasibility Study of Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC)
TR 23.885 V11.0.0 (2011-09) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Feasibility Study of Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC)
3GPP TR V9.0.0 ( )
 TR 23.869 V9.0.0 (2009-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support for Internet Protocol (IP) based IP Multimedia
TR 23.869 V9.0.0 (2009-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support for Internet Protocol (IP) based IP Multimedia
2. enodeb Emulator: Simulation of emtc and NB-IoT UE and enodeb conforming to 3GPP Release 13 enhancements for Cellular IoT.
 Version 13.0.0.2 Release Date: Feb 17, 2017 NetTest v13.0 Release Notes Page 1 of 12 1. C-SGN Emulator: Includes the MME, SGW and PGW Emulators with new interfaces and functions for testing CIoT base stations
Version 13.0.0.2 Release Date: Feb 17, 2017 NetTest v13.0 Release Notes Page 1 of 12 1. C-SGN Emulator: Includes the MME, SGW and PGW Emulators with new interfaces and functions for testing CIoT base stations
End-to-end IP Service Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 -
 End-to-end IP Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
End-to-end IP Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
I DOCUMENTS ISSUED FOR ONE STEP APPROVAL PROCEDURE (OAP)
 FT ETSI STANDARDS FOR PUBLIC COMMENT The following ETSI documents are issued under the Public Enquiry PE20111027. Comments are welcome and should be addressed to the named contact to arrive by 22 September
FT ETSI STANDARDS FOR PUBLIC COMMENT The following ETSI documents are issued under the Public Enquiry PE20111027. Comments are welcome and should be addressed to the named contact to arrive by 22 September
COURSE DESCRIPTION VOICE OVER LTE (VOLTE) Format: Face to Face, Live on Web. Duration: 2 Days, 4 x 3 Hours
 COURSE DESCRIPTION VOICE OVER LTE (VOLTE) Format: Face to Face, Live on Web Duration: 2 Days, 4 x 3 Hours COURSE SUMMARY HIGHLIGHTS Highly focused and in-depth training from the experts - including relevant
COURSE DESCRIPTION VOICE OVER LTE (VOLTE) Format: Face to Face, Live on Web Duration: 2 Days, 4 x 3 Hours COURSE SUMMARY HIGHLIGHTS Highly focused and in-depth training from the experts - including relevant
GTP-based S2b Interface Support on the P-GW and SAEGW
 GTP-based S2b Interface Support on the P-GW and SAEGW This chapter describes the GTP-based S2b interface support feature on the standalone P-GW and the SAEGW. Feature, page 1 How the S2b Architecture Works,
GTP-based S2b Interface Support on the P-GW and SAEGW This chapter describes the GTP-based S2b interface support feature on the standalone P-GW and the SAEGW. Feature, page 1 How the S2b Architecture Works,
Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING NOVEMBER 17, 2017
 Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING NOVEMBER 17, 2017 Motivation Volume of data to be transported in across a mobile network keeps increasing Proprietary
Virtual Mobile Core Placement for Metro Area BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING NOVEMBER 17, 2017 Motivation Volume of data to be transported in across a mobile network keeps increasing Proprietary
Agenda. Introduction Roaming Scenarios. Other considerations. Data SMS Voice IMS
 LTE Roaming Agenda Introduction Roaming Scenarios Data SMS Voice IMS Other considerations LTE Roaming Situation None of Verizon LTE subscribers can roam on another LTE network, not even on other 700 MHz
LTE Roaming Agenda Introduction Roaming Scenarios Data SMS Voice IMS Other considerations LTE Roaming Situation None of Verizon LTE subscribers can roam on another LTE network, not even on other 700 MHz
David Williams. Next Generation ecall
 David Williams Next Generation ecall 1 Background ecall standardisation began in 2004 A GSM & UMTS world The chosen solution was in-band modem and circuit switched 112 call The in-band modem was optimised
David Williams Next Generation ecall 1 Background ecall standardisation began in 2004 A GSM & UMTS world The chosen solution was in-band modem and circuit switched 112 call The in-band modem was optimised
Primebit Solution MASTERED DIPLOMA IN PROTOCOL DEVELOPMENT COURSE CONTENT
 MASTERED DIPLOMA IN PROTOCOL DEVELOPMENT COURSE CONTENT MODULE 1 : UMTS (3G) AND GSM (2G) BASIC 2G and 3G Network Architecture - CS & PS domain. RAT- FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, WCDMA, DFDMA, SCFDMA. SDU,PDU,UMTS
MASTERED DIPLOMA IN PROTOCOL DEVELOPMENT COURSE CONTENT MODULE 1 : UMTS (3G) AND GSM (2G) BASIC 2G and 3G Network Architecture - CS & PS domain. RAT- FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, WCDMA, DFDMA, SCFDMA. SDU,PDU,UMTS
Evolution from GSM to UMTS
 2 Evolution from GSM to UMTS Evolution is one of the most common terms used in the context of UMTS. Generally it is understood to mean the technical evolution, i.e. how and what kind of equipment and in
2 Evolution from GSM to UMTS Evolution is one of the most common terms used in the context of UMTS. Generally it is understood to mean the technical evolution, i.e. how and what kind of equipment and in
VOLTE and the IP/MPLS Cell Site Evolution
 AVIAT NETWORKS VOLTE and the IP/MPLS Cell Site Evolution By Eduardo J. Sánchez, Aviat Networks Technical Marketing TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 PROBLEM: DEPLOYING VOLTE FOR RELIABLE VOICE AND VIDEO...3
AVIAT NETWORKS VOLTE and the IP/MPLS Cell Site Evolution By Eduardo J. Sánchez, Aviat Networks Technical Marketing TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 PROBLEM: DEPLOYING VOLTE FOR RELIABLE VOICE AND VIDEO...3
MSF Architecture for 3GPP Evolved Packet System (EPS) Access MSF-LTE-ARCH-EPS-002.FINAL
 MSF Architecture for 3GPP Evolved Packet System (EPS) Access MSF-LTE-ARCH-EPS-002.FINAL MultiService Forum Architecture Agreement Contribution Number: Document Filename: Working Group: Title: Editor: Contact
MSF Architecture for 3GPP Evolved Packet System (EPS) Access MSF-LTE-ARCH-EPS-002.FINAL MultiService Forum Architecture Agreement Contribution Number: Document Filename: Working Group: Title: Editor: Contact
xavier[dot]mila[at]upf[dot]edu Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF)
![xavier[dot]mila[at]upf[dot]edu Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) xavier[dot]mila[at]upf[dot]edu Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF)](/thumbs/85/91532160.jpg) Evaluation of Signaling Loads in 3GPP Networks Journal Club 2007 08 Session 4 Xavier Milà xavier[dot]mila[at]upf[dot]edu April, 4 th 2008 Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) Article Reference Title: Evaluation
Evaluation of Signaling Loads in 3GPP Networks Journal Club 2007 08 Session 4 Xavier Milà xavier[dot]mila[at]upf[dot]edu April, 4 th 2008 Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) Article Reference Title: Evaluation
INICTEL-UNI 15/11/2010. Tecnología de Banda Ancha Inalámbrica LTE
 INICTEL-UNI 15/11/2010 Tecnología de Banda Ancha Inalámbrica LTE 1 2Market Overview 2 LTE Presentation / Alcatel-Lucent. Title January 2008 Market Trends iphone (Apple) and G1 (Google) are bandwidth drivers
INICTEL-UNI 15/11/2010 Tecnología de Banda Ancha Inalámbrica LTE 1 2Market Overview 2 LTE Presentation / Alcatel-Lucent. Title January 2008 Market Trends iphone (Apple) and G1 (Google) are bandwidth drivers
IxLoad EPC Diameter Testing
 IxLoad EPC Diameter Testing IxLoad is a full-featured layer 4-7 test application that provides real-world traffic emulation testing of voice, video, and data networks and components. IxLoad simultaneously
IxLoad EPC Diameter Testing IxLoad is a full-featured layer 4-7 test application that provides real-world traffic emulation testing of voice, video, and data networks and components. IxLoad simultaneously
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 124 341 V12.6.0 (2015-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage
TS 124 341 V12.6.0 (2015-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage
Leveraging Wi-Fi Calling To Reduced Operator Costs and Improve the Customer Experience
 Leveraging Wi-Fi Calling To Reduced Operator Costs and Improve the Customer Experience Steve Northridge Email: Steve.Northridge@Oracle.com Twitter: @stevenorthridge 3 Photo Source: Boston Public Library
Leveraging Wi-Fi Calling To Reduced Operator Costs and Improve the Customer Experience Steve Northridge Email: Steve.Northridge@Oracle.com Twitter: @stevenorthridge 3 Photo Source: Boston Public Library
UNIK4230: Mobile Communications Spring Semester, Per Hj. Lehne
 UNIK4230: Mobile Communications Spring Semester, 2015 Per Hj. Lehne per-hjalmar.lehne@telenor.com 916 94 909 Network Architecture and Functionality 5 February 2015 Contents Network Architecture Protocol
UNIK4230: Mobile Communications Spring Semester, 2015 Per Hj. Lehne per-hjalmar.lehne@telenor.com 916 94 909 Network Architecture and Functionality 5 February 2015 Contents Network Architecture Protocol
3GPP TS V9.4.0 ( )
 TS 23.221 V9.4.0 (2010-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Architectural requirements (Release 9) The present document
TS 23.221 V9.4.0 (2010-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Architectural requirements (Release 9) The present document
VoLTE Security in NG PRDs
 Background A number of different audits and security analysis of various VoLTE networks have been performed. - See also FSAG WP VoLTE Security Threats and Attacks The observation from the audits were in
Background A number of different audits and security analysis of various VoLTE networks have been performed. - See also FSAG WP VoLTE Security Threats and Attacks The observation from the audits were in
LTE Training LTE (Long Term Evolution) Training Bootcamp, Crash Course
 LTE Training LTE (Long Term Evolution) Training Bootcamp, Crash Course Why should you choose LTE Training? LTE Training is an intensive learning experience that cover the essential elements of Long Term
LTE Training LTE (Long Term Evolution) Training Bootcamp, Crash Course Why should you choose LTE Training? LTE Training is an intensive learning experience that cover the essential elements of Long Term
Nexus8610 Traffic Simulation System. Intersystem Handover Simulation. White Paper
 Traffic Simulation System Intersystem Handover Simulation White Paper Notice Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document was accurate at the time of printing. However, the
Traffic Simulation System Intersystem Handover Simulation White Paper Notice Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document was accurate at the time of printing. However, the
Voice Over LTE (VoLTE) - A Core Perspective Comprehensive hands-on workshop
 DISCOVER new ideas SHARE expertise EXPLORE new solutions 2017 6-8 December 9.00 AM - 5.00 PM Bangalore India Timmins Training and Consulting Voice Over LTE (VoLTE) - A Core Perspective Comprehensive hands-on
DISCOVER new ideas SHARE expertise EXPLORE new solutions 2017 6-8 December 9.00 AM - 5.00 PM Bangalore India Timmins Training and Consulting Voice Over LTE (VoLTE) - A Core Perspective Comprehensive hands-on
8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look
 8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look 243 The anchoring of the media in TrGW also has an implicit topology-hiding effect. Without anchoring, the SDP answer provided to the other network would contain
8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look 243 The anchoring of the media in TrGW also has an implicit topology-hiding effect. Without anchoring, the SDP answer provided to the other network would contain
Location Services. Location Services - Feature Description
 LoCation Services (LCS) on the MME and SGSN is a 3GPP standards-compliant feature that enables the system (MME or SGSN) to collect and use or share location (geographical position) information for connected
LoCation Services (LCS) on the MME and SGSN is a 3GPP standards-compliant feature that enables the system (MME or SGSN) to collect and use or share location (geographical position) information for connected
Simulation of LTE Signaling
 Simulation of LTE Signaling 1 Florin SANDU, 2 Szilárd CSEREY, 3 Eugen MILE-CIOBANU 1 "Transilvania University of Brasov Bd Eroilor nr. 29A RO-500036 Brasov sandu@unitbv.ro, 2,3 SIEMENS Program and System
Simulation of LTE Signaling 1 Florin SANDU, 2 Szilárd CSEREY, 3 Eugen MILE-CIOBANU 1 "Transilvania University of Brasov Bd Eroilor nr. 29A RO-500036 Brasov sandu@unitbv.ro, 2,3 SIEMENS Program and System
Modeling Voice over LTE
 Modeling Voice over LTE Ahmed Amou El Arby and Ousmane Thiare University Gaston Berger, Saint Louis, Senegal E-mail: elarby.amou@gmail.com; othiare@ugb.edu.sn Received 15 September 2016; Accepted 11 October
Modeling Voice over LTE Ahmed Amou El Arby and Ousmane Thiare University Gaston Berger, Saint Louis, Senegal E-mail: elarby.amou@gmail.com; othiare@ugb.edu.sn Received 15 September 2016; Accepted 11 October
P-GW Service Configuration Mode Commands
 Service Configuration Mode Commands The (PDN Gateway) Service Configuration Mode is used to create and manage the relationship between specified services used for either GTP or PMIP network traffic. Exec
Service Configuration Mode Commands The (PDN Gateway) Service Configuration Mode is used to create and manage the relationship between specified services used for either GTP or PMIP network traffic. Exec
ETSI documents published or circulated for vote/comment in January 2019
 ETSI documents published or circulated for vote/comment in January 2019 ETSI documents issued under AP20190409. Comments should be sent to the named contact by 10/03/2019 ETSI identifier Title Committee
ETSI documents published or circulated for vote/comment in January 2019 ETSI documents issued under AP20190409. Comments should be sent to the named contact by 10/03/2019 ETSI identifier Title Committee
IxLoad LTE Evolved Packet Core Network Testing: enodeb simulation on the S1-MME and S1-U interfaces
 IxLoad LTE Evolved Packet Core Network Testing: enodeb simulation on the S1-MME and S1-U interfaces IxLoad is a full-featured layer 4-7 test application that provides realworld traffic emulation testing
IxLoad LTE Evolved Packet Core Network Testing: enodeb simulation on the S1-MME and S1-U interfaces IxLoad is a full-featured layer 4-7 test application that provides realworld traffic emulation testing
E1-E2 UPGRADATION COURSE CONSUMER MOBILITY. 3G Concept
 E1-E2 UPGRADATION COURSE CONSUMER MOBILITY 3G Concept Page 1 CHAPTER-TWO 3 G CONCEPT UMTS and the information society Rapid advancements in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) have already
E1-E2 UPGRADATION COURSE CONSUMER MOBILITY 3G Concept Page 1 CHAPTER-TWO 3 G CONCEPT UMTS and the information society Rapid advancements in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) have already
LTE EPC Emulators v10.0 Release Notes - Page 1 of 15 -
 LTE EPC Emulators v10.0 Release Notes - Page 1 of 15 - Version 10.0.0.7 Release Date: Feb 24, 2014 Components 1. LTE Emulators : MME (with internal HSS), SGW and PGW (with internal PCRF) 1. LTE Emulators
LTE EPC Emulators v10.0 Release Notes - Page 1 of 15 - Version 10.0.0.7 Release Date: Feb 24, 2014 Components 1. LTE Emulators : MME (with internal HSS), SGW and PGW (with internal PCRF) 1. LTE Emulators
ETSI TR V (201
 TR 124 980 V13.1.0 (201 16-07) TECHNICAL REPORT LTE; Minimum Requirements for support of MCPTT Servicee over the Gm reference point (3GPP TR 24.980 version 13.1.0 Release 13) 1 TR 124 980 V13.1.0 (2016-07)
TR 124 980 V13.1.0 (201 16-07) TECHNICAL REPORT LTE; Minimum Requirements for support of MCPTT Servicee over the Gm reference point (3GPP TR 24.980 version 13.1.0 Release 13) 1 TR 124 980 V13.1.0 (2016-07)
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 129 118 V14.2.0 (2018-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Mobility Management Entity (MME) - Visitor Location Register (VLR) SGs interface specification
TS 129 118 V14.2.0 (2018-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Mobility Management Entity (MME) - Visitor Location Register (VLR) SGs interface specification
Mobile Network Evolution Part 2
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 2 From UMTS to LTE or How to Further Increase Network Capacity and QoS Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Advanced Mobile Communication Networks 1 Outline Evolution from Circuit Switching
Mobile Network Evolution Part 2 From UMTS to LTE or How to Further Increase Network Capacity and QoS Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Advanced Mobile Communication Networks 1 Outline Evolution from Circuit Switching
NetHawk EAST EPC for Evolved Packet-Core Testing
 for Evolved Packet-Core Testing This test tool enables wrap-around-testing of the core network elements in LTE MME, S-GW and PDN-GW. SPEC SHEET KEY FEATURES Effective functional and load testing of signaling
for Evolved Packet-Core Testing This test tool enables wrap-around-testing of the core network elements in LTE MME, S-GW and PDN-GW. SPEC SHEET KEY FEATURES Effective functional and load testing of signaling
CRITICAL ISSUES FOR ROAMING IN 3G ANDERS ROOS, MAGNUS HARTMAN, AND STEPHEN DUTNALL, NORTHSTREAM AB
 3G MOBILE N ETWORK T ECHNOLOGIES AND E XPERIENCES CRITICAL ISSUES FOR ROAMING IN 3G ANDERS ROOS, MAGNUS HARTMAN, AND STEPHEN DUTNALL, NORTHSTREAM AB UE Applications and services Node B RNC UTRAN (PS) SCP
3G MOBILE N ETWORK T ECHNOLOGIES AND E XPERIENCES CRITICAL ISSUES FOR ROAMING IN 3G ANDERS ROOS, MAGNUS HARTMAN, AND STEPHEN DUTNALL, NORTHSTREAM AB UE Applications and services Node B RNC UTRAN (PS) SCP
3G TS V2.0.0 ( )
 Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem - Stage 2 (3G TS 23.228 version 2.0.0) The present document
Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem - Stage 2 (3G TS 23.228 version 2.0.0) The present document
3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status
 3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status 2 nd SDO Emergency Services Coordination Workshop (ESW07) Library of Congress, Washington, DC, USA April 10-12, 2007 Stephen Edge, Qualcomm,
3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status 2 nd SDO Emergency Services Coordination Workshop (ESW07) Library of Congress, Washington, DC, USA April 10-12, 2007 Stephen Edge, Qualcomm,
Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks. Presenter: S. Vasudevan, Technical Manager, Advanced Technology Standards
 Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Presenter: S. Vasudevan, Technical Manager, Advanced Technology Standards What are Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Integrated Networks supporting a range of cell sizes
Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Presenter: S. Vasudevan, Technical Manager, Advanced Technology Standards What are Multi-RAT Heterogeneous Networks Integrated Networks supporting a range of cell sizes
Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence
 Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence Prepared for: WOCC 2007 Fuchun Joseph Lin Chief Scientist fjlin@research.telcordia.com Telcordia Technologies, Inc. April 28, 2007
Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence Prepared for: WOCC 2007 Fuchun Joseph Lin Chief Scientist fjlin@research.telcordia.com Telcordia Technologies, Inc. April 28, 2007
Outline. Wireless Technology Evolution GPRS Overview 3GPP All IP Network 3GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem
 3GPP All IP Network Outline Wireless Technology Evolution GPRS Overview 3GPP All IP Network 3GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem Vision of Comm. System 3G/4G/ Source: DoCoMo 3 Wireless Technology Evolution 1G
3GPP All IP Network Outline Wireless Technology Evolution GPRS Overview 3GPP All IP Network 3GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem Vision of Comm. System 3G/4G/ Source: DoCoMo 3 Wireless Technology Evolution 1G
High-Touch Delivery Learning Services
 Data Sheet High-Touch Delivery Learning Services Implementing Cisco Service Provider Mobility LTE Networks The Implementing Cisco LTE Packet Core Networks (SPLTE) Version 1.0 is an instructor-led course
Data Sheet High-Touch Delivery Learning Services Implementing Cisco Service Provider Mobility LTE Networks The Implementing Cisco LTE Packet Core Networks (SPLTE) Version 1.0 is an instructor-led course
3GPP. 3GPP Roadmap. Release 99 Release 4 Release 5 Release 6 Release 7 Release 8. Khaled Alutaibi
 3GPP Release 99 Release 4 Release 5 Release 6 Release 7 Release 8 Khaled Alutaibi LOGO 976452 3GPP Roadmap Radio Access Air Interface Principles Release99 The main improvement of UMTS compared to GSM in
3GPP Release 99 Release 4 Release 5 Release 6 Release 7 Release 8 Khaled Alutaibi LOGO 976452 3GPP Roadmap Radio Access Air Interface Principles Release99 The main improvement of UMTS compared to GSM in
GPRS and UMTS T
 GPRS and UMTS T-110.2100 Global Packet Radio Service GPRS uses the time slots not used for circuit switched services Data rate depends on the availability of free time slots GPRS uses the multislot technique,
GPRS and UMTS T-110.2100 Global Packet Radio Service GPRS uses the time slots not used for circuit switched services Data rate depends on the availability of free time slots GPRS uses the multislot technique,
Cisco Converged Services Platform
 Data Sheet Cisco Converged Services Platform Mobile subscribers are demanding the same type of services that are provided over the Internet on their mobile phones including messaging, social networking,
Data Sheet Cisco Converged Services Platform Mobile subscribers are demanding the same type of services that are provided over the Internet on their mobile phones including messaging, social networking,
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 123 221 V12.0.0 (2014-10) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Architectural requirements (3GPP TS 23.221
TS 123 221 V12.0.0 (2014-10) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Architectural requirements (3GPP TS 23.221
Mobile Network Evolution Part 2
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 2 From UMTS to LTE or How to Further Increase Network Capacity and QoS Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Advanced Mobile Communication Networks 1 Outline Evolution from Circuit Switching
Mobile Network Evolution Part 2 From UMTS to LTE or How to Further Increase Network Capacity and QoS Andreas Mitschele-Thiel Advanced Mobile Communication Networks 1 Outline Evolution from Circuit Switching
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 129 118 V8.11.0 (2012-10) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Mobility Management Entity (MME) - Visitor Location Register (VLR) SGs interface specification
TS 129 118 V8.11.0 (2012-10) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Mobility Management Entity (MME) - Visitor Location Register (VLR) SGs interface specification
Testing Voice over LTE (VoLTE) on your device. January 2016 Sandy Fraser
 Testing Voice over LTE (VoLTE) on your device January 2016 Sandy Fraser Agenda Page 2 Intro: a very brief history of IMS, Legacy (CS) vs. LTE (PS) domain considerations Architecture of IMS, components
Testing Voice over LTE (VoLTE) on your device January 2016 Sandy Fraser Agenda Page 2 Intro: a very brief history of IMS, Legacy (CS) vs. LTE (PS) domain considerations Architecture of IMS, components
Temporary Document Page 2 - switches off, the allocated resources and PCC rules information of PDN GWs used by the UE in non- network will not be dele
 Temporary Document Page 1 - TSG SA WG2 Architecture S2#58 S2-072558 25-29 June 2007 Orlando, FL, USA Source: Huawei Title: Attach Type in attach procedure Document for: Discussion / Approval Agenda Item:
Temporary Document Page 1 - TSG SA WG2 Architecture S2#58 S2-072558 25-29 June 2007 Orlando, FL, USA Source: Huawei Title: Attach Type in attach procedure Document for: Discussion / Approval Agenda Item:
EPC-SIM for enb/henb/ HeNB-GW Testing VERSION 5.0
 EPC-SIM for enb/henb/ HeNB-GW Testing VERSION 5.0 Flexible, functional load testing tool for LTE RAN SPEC SHEET KEY FEATURES Simulation of EPC, IMS and enb in a single unit for validation of S1 and X2
EPC-SIM for enb/henb/ HeNB-GW Testing VERSION 5.0 Flexible, functional load testing tool for LTE RAN SPEC SHEET KEY FEATURES Simulation of EPC, IMS and enb in a single unit for validation of S1 and X2
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (
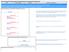 This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side bearer termination. When
This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side bearer termination. When
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 23.204 V12.4.0 (2013-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
TS 23.204 V12.4.0 (2013-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 23.204 V11.5.0 (2013-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
TS 23.204 V11.5.0 (2013-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
LTE RAN Operation (ARI0001) Course Outline
 (ARI0001) Course Outline LTE RAN Operation This four day course focuses on LTE RAN operations. ariesogeo exercises will enhance LTE/ VoLTE theory. Section 1 E-UTRA Introduction E-UTRA Features: Radio Access,
(ARI0001) Course Outline LTE RAN Operation This four day course focuses on LTE RAN operations. ariesogeo exercises will enhance LTE/ VoLTE theory. Section 1 E-UTRA Introduction E-UTRA Features: Radio Access,
REFERENCE ARCHITECTURE FOR END-TO-END QOS IN HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORK ENVIRONMENTS
 REFERENCE ARCHITECTURE FOR END-TO-END QOS IN HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORK ENVIRONMENTS Sandra Frei 1, 2, Woldemar Fuhrmann 3, Andreas Rinkel 2 and Bogdan Ghita 1 1 Centre for Information Security and
REFERENCE ARCHITECTURE FOR END-TO-END QOS IN HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORK ENVIRONMENTS Sandra Frei 1, 2, Woldemar Fuhrmann 3, Andreas Rinkel 2 and Bogdan Ghita 1 1 Centre for Information Security and
on QoS/QoE measurements
 ITU Workshop on Performance, Quality of Service and Quality of Experience of Emerging Networks and Services (Athens, Greece, 7-8 September 2015) Impact of LTE/VoLTE network architecture on QoS/QoE measurements
ITU Workshop on Performance, Quality of Service and Quality of Experience of Emerging Networks and Services (Athens, Greece, 7-8 September 2015) Impact of LTE/VoLTE network architecture on QoS/QoE measurements
UMTS Addresses and Identities Mobility and Session Management
 UMTS Addresses and Identities Mobility and Session Management - Numbering, addressing and location identities - UE modes - Mobility management - Session management and QoS Numbering, Addressing and Location
UMTS Addresses and Identities Mobility and Session Management - Numbering, addressing and location identities - UE modes - Mobility management - Session management and QoS Numbering, Addressing and Location
