CE Advanced Network Security Wireless Security
|
|
|
- Dylan Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CE Advanced Network Security Wireless Security Lecture 23 Mehdi Kharrazi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Acknowledgments: Some of the slides are fully or partially obtained from other sources. Reference is noted on the bottom of each slide, when the content is fully obtained from another source. Otherwise a full list of references is provided on the last slide.
2 Wireless Security What is Wireless Security? The usual: confidentiality, integrity, availability? 2
3 Confidentiality Obvious danger it s easy to intercept traffic Obvious countermeasure cryptography 3
4 Integrity At first glance, integrity seems ok This is radio how can an attacker change messages in mid-packet? Solution: the Evil Twin (or Sybil ) attack 4
5 Wireless Architecture The obvious architecture is pure peer-to-peer each machine has a radio, and talks directly to any other machine In fact, (WiFi) can work that way, but rarely does More common scenario: base stations (also known as access points) IBSS (ad hoc) mode BSS (infrastructure) mode [Bellovin06, Shmatikov] 5
6 Access Points An ordinary wireless node associates with an access point (AP) More precisely, it associates with the AP having a matching network name (if specified) and the strongest signal If another AP starts sending a stronger signal (probably because the wireless node has moved), it will re-associate with the new access point All transmissions from the laptop go to the access point All transmissions to the laptop come from the access point 6
7 Access Point SSID Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name of the access point By default, access point broadcasts its SSID in plaintext beacon frames every few seconds Default SSIDs are easily guessable Linksys defaults to linksys, Cisco to tsunami, etc. This gives away the fact that access point is active Access point settings can be changed to prevent it from announcing its presence in beacon frames and from using an easily guessable SSID But then every user must know SSID in advance [Shmatikov] 7
8 Example You could find defaults easily: Netgear DS products, ME102 and MA401 Default SSID: Wireless Default Channel: 6 Default IP address: Default WEP: Disabled Default WEP KEY1: Default WEP KEY2: Default WEP KEY3: Default WEP KEY4: Default MAC: 00:30:ab:xx:xx:xx [ 8
9 Which AP? Which AP is your laptop associated with? Which network (SSID)? Many people know neither My ISP is Linksys Those who specify anything specify the SSID 9
10 The Evil Twin Attack Simplest way: carry an access point with you Simpler solution: many laptops can emulate access points On Linux, use: iwconfig eth0 mode Master Force others to associate with your laptop, and send you all their traffic... 10
11 Why This Works Conventionally, we worry about authenticating the client to the server Here, we need to authenticate the server to the client The infrastructure wasn t designed for that; more important, users don t expect to check for it (and have no way to do so in any event) 11
12 Integrity Attacks We now see how to do integrity attacks We don t tinker with the packet in the air, we attract it to our attack node You don t go through strong security, you go around it 12
13 Availability Simple version: black-hole evil twin Sophisticated version: battery exhaustion 13
14 Black Holes Emulate an access point Hand out IP addresses Do nothing with received packets More subtly, drop 10-15% of them connections will work, but very slowly 14
15 Battery Exhaustion Wi-Fi is also a power-hungry technology that can cause phone batteries to die quickly in some cases, within an hour or two of talk time. When you turn on the Wi-Fi it does bring the battery life down, said Mike Hendrick, director of product development for T-Mobile. New York Times, 27 November
16 Battery Exhaustion Send your enemy large ping packets The reply packets will be just as big and transmitting such packets uses a lot of power The more you transmit, the more power often battery power you use up 16
17 WEP
18 WEP Using a Flawed Cipher in a Bad Way for the Wrong Application It was obvious from the start that some crypto was needed Choice: WEP Wireline Equivalent Privacy for networks Many different mistakes Case study in bad crypto design 18
19 Datagrams and Stream Ciphers WEP uses RC4 because RC4 is very efficient But is datagram-oriented --> Must rekey for every packet But you can t reuse a stream cipher key on different packets... 19
20 Key Setup 20
21 Key Setup for WEP Each WEP node keeps a 24-bit packet counter (the IV) Actual cipher key is configured key concatenated with counter Two different flaws... 2^24 packets isn t that many you still get key reuse when the packet counter overflows RC4 has a cryptanalytic flaw But it s worse than that 21
22 Cryptanalysis of RC4 In 2001, Fluhrer, Mantin and Shamir showed that RC4 could be cryptanalyzed if the keys were close to each other a related key attack Because of the IV algorithm, they are close in WEP Key recovery attacks are feasible and have been implemented 22
23 IV Replay Suppose you recover the complete plaintext of a single packet You can generate new packets that use the same counter Receiving nodes don t and can t check for rapid counter reuse Indefinite forgery! 23
24 Packet Redirection Suppose you know (or can guess) the destination IP address of a packet Because RC4 is a stream cipher, you can make controlled changes to the plaintext by flipping ciphertext bits Flip the proper bits to send the packet to you instead, and reinject it 24
25 Checksums WEP does use a checksum However, it s a CRC rather than a cryptographic hash It s also unkeyed Result: it s feasible to compensate for plaintext changes without disturbing the checksum 25
26 The Biggest Flaw in WEP There s no key management; all users at a site always share the same WEP key. --> You can t rekey when the counter overflows --> Everyone shares the same key; if it s cryptanalyzed or stolen or betrayed, everyone is at risk --> It s all but impossible to rekey a site of any size, since everyone has to change their keys simultaneously and you don t have a secure way to provide the new keys 26
27 What WEP Should Have Been Use a block cipher in CBC mode Use a separate key per user, plus a key identifier like the SPI Provide dynamic key management WPA WiFi Protected Access is better than WEP; forthcoming wireless security standards will use AES. 27
28 War-Driving
29 War-Driving Put a laptop in network (SSID) scanning mode Drive around a neighborhood looking for access points Perhaps include a GPS receiver to log locations Detect presence or absence of WEP 29
30 Unprotected Networks! Statistics show that only O(1/3) use even WEP The rest tend to be wide open Many people don t change or hide the SSID 30
31 The Consequences Some incidence of theft of service (Is it war-driving a crime? Unclear under US law) Sometimes done to hide criminal activity 31
32 Network Access Control
33 No Perimeter The fundamental difference: there s no physical boundary On a wired net, physical access control can compensate for lack of technical security Most of the attacks are the same, for wired or wireless nets 33
34 Tracing Attacks With wired networks, you can trace an attack to a given switch port With wireless networks, you can trace an attack to a given AP, but the AP might serve hundreds or thousands of square meters No good way to trace all you can do is log and block MAC addresses 34
35 MAC Address Filtering Can allow or block endpoints based on MAC address However MAC address spoofing is pretty easy Evade blocks and/or impersonate accepted hosts What s accepted? Look for machines that receive non-syn TCP packets 35
36 Clayton s Spoofing Attack Impersonate a known-good IP and MAC address TCP replies will go to the real owner and the fake one The real one will send out a TCP RST packet Build a circuit that listens for the bit pattern of the RST and sends a jam signal instead 36
37 Windows XP SP2 and Spoofing With SP2, the built-in firewall blocks most inbound packets In particular, it only allows in replies to outbound packets The TCP reply packets don t match any outbound connections TCP never sees the reply, and hence doesn t generate RST No need for Clayton s attack 37
38 Network Access Control Fundamentally, the problem is network access control We have none with wireless Usual solution: let people onto your network, but require some sort of Webbased login 38
39 Evil Twin Redux Set up your evil twin in a hotspot Intercept the login session and/or the registration Registration often involves a credit card... 39
40 Living with Wireless For residential use, turn off SSID broadcast (Hard to do in an enterprise) Put your wireless net outside the firewall Use WEP it s still (marginally) better than nothing Better yet, use WPA Use end-to-end crypto Check the certificate on registration or login pages 40
41 Acknowledgments/References COMS W4180 Network Security Class Columbia University, Steven Bellovin, [Shmatikov] CS Network Security and Privacy, Vitaly Shmatikov, University of Texas at Austin, Fall
Overview of Security
 Overview of 802.11 Security Bingdong Li Present for CPE 601 2/9/2011 Sources: 1 Jesse Walker (Intel) & 2. WinLab 1 Agenda Introduction 802.11 Basic Security Mechanisms What s Wrong? Major Risks Recommendations
Overview of 802.11 Security Bingdong Li Present for CPE 601 2/9/2011 Sources: 1 Jesse Walker (Intel) & 2. WinLab 1 Agenda Introduction 802.11 Basic Security Mechanisms What s Wrong? Major Risks Recommendations
CS-435 spring semester Network Technology & Programming Laboratory. Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis
 CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
CE Advanced Network Security
 CE 817 - Advanced Network Security Lecture 3 Mehdi Kharrazi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Acknowledgments: Some of the slides are fully or partially obtained from other
CE 817 - Advanced Network Security Lecture 3 Mehdi Kharrazi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Acknowledgments: Some of the slides are fully or partially obtained from other
2013 Summer Camp: Wireless LAN Security Exercises JMU Cyber Defense Boot Camp
 2013 Summer Camp: Wireless LAN Security Exercises 2013 JMU Cyber Defense Boot Camp Questions Have you used a wireless local area network before? At home? At work? Have you configured a wireless AP before?
2013 Summer Camp: Wireless LAN Security Exercises 2013 JMU Cyber Defense Boot Camp Questions Have you used a wireless local area network before? At home? At work? Have you configured a wireless AP before?
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: WIRELESS ATTACKS
 CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: WIRELESS ATTACKS Wireless networks are everywhere, from the home to corporate data centres. They make our lives easier by avoiding bulky cables and related problems. But with these
CYBER ATTACKS EXPLAINED: WIRELESS ATTACKS Wireless networks are everywhere, from the home to corporate data centres. They make our lives easier by avoiding bulky cables and related problems. But with these
Analysis of Security or Wired Equivalent Privacy Isn t. Nikita Borisov, Ian Goldberg, and David Wagner
 Analysis of 802.11 Security or Wired Equivalent Privacy Isn t Nikita Borisov, Ian Goldberg, and David Wagner WEP Protocol Wired Equivalent Privacy Part of the 802.11 Link-layer security protocol Security
Analysis of 802.11 Security or Wired Equivalent Privacy Isn t Nikita Borisov, Ian Goldberg, and David Wagner WEP Protocol Wired Equivalent Privacy Part of the 802.11 Link-layer security protocol Security
Outline : Wireless Networks Lecture 10: Management. Management and Control Services : Infrastructure Reminder.
 Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures
 Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design. Artoré & Bizollon : Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design
 Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
Network Security - ISA 656 IPsec IPsec Key Management (IKE)
 Network Security - ISA 656 IPsec IPsec (IKE) Angelos Stavrou September 28, 2008 What is IPsec, and Why? What is IPsec, and Why? History IPsec Structure Packet Layout Header (AH) AH Layout Encapsulating
Network Security - ISA 656 IPsec IPsec (IKE) Angelos Stavrou September 28, 2008 What is IPsec, and Why? What is IPsec, and Why? History IPsec Structure Packet Layout Header (AH) AH Layout Encapsulating
Managing and Securing Computer Networks. Guy Leduc. Chapter 7: Securing LANs. Chapter goals: security in practice: Security in the data link layer
 Managing and Securing Computer Networks Guy Leduc Chapter 7: Securing LANs Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 7 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2016. (section 8.8) Also
Managing and Securing Computer Networks Guy Leduc Chapter 7: Securing LANs Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 7 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2016. (section 8.8) Also
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536)
 Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks
 A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
RC4. Invented by Ron Rivest. A stream cipher Generate keystream byte at a step
 RC4 RC4 1 RC4 Invented by Ron Rivest o RC is Ron s Code or Rivest Cipher A stream cipher Generate keystream byte at a step o Efficient in software o Simple and elegant o Diffie: RC4 is too good to be true
RC4 RC4 1 RC4 Invented by Ron Rivest o RC is Ron s Code or Rivest Cipher A stream cipher Generate keystream byte at a step o Efficient in software o Simple and elegant o Diffie: RC4 is too good to be true
Lecture 33. Firewalls. Firewall Locations in the Network. Castle and Moat Analogy. Firewall Types. Firewall: Illustration. Security April 15, 2005
 Firewalls Lecture 33 Security April 15, 2005 Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Intranet Firewall DMZ Router Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks
Firewalls Lecture 33 Security April 15, 2005 Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Intranet Firewall DMZ Router Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks
Wireless Security. Comp Sci 3600 Security. Attacks WEP WPA/WPA2. Authentication Encryption Vulnerabilities
 Wireless Security Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline 1 2 3 Wired versus wireless Endpoint Access point Figure 24.1 Wireless Networking Components Locations and types of attack Outline 1 2 3 Wired Equivalent
Wireless Security Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline 1 2 3 Wired versus wireless Endpoint Access point Figure 24.1 Wireless Networking Components Locations and types of attack Outline 1 2 3 Wired Equivalent
Wireless Security Security problems in Wireless Networks
 Wireless Security Security problems in Wireless Networks Security of Wireless Networks Wireless networks are everywhere more and more electronic devices are becoming wireless However, ensuring security
Wireless Security Security problems in Wireless Networks Security of Wireless Networks Wireless networks are everywhere more and more electronic devices are becoming wireless However, ensuring security
What is a Wireless LAN? The wireless telegraph is not difficult to understand. The ordinary telegraph is like a very long cat. You pull the tail in Ne
 Introduction to Wireless Networking and Security Chino Information Technology Center Steve Siedschlag, Associate Professor What is a Wireless LAN? The wireless telegraph is not difficult to understand.
Introduction to Wireless Networking and Security Chino Information Technology Center Steve Siedschlag, Associate Professor What is a Wireless LAN? The wireless telegraph is not difficult to understand.
How Insecure is Wireless LAN?
 Page 1 of 7 How Insecure is Wireless LAN? Abstract Wireless LAN has gained popularity in the last few years due to its enormous benefits such as scalability, mobile access of the network, and reduced cost
Page 1 of 7 How Insecure is Wireless LAN? Abstract Wireless LAN has gained popularity in the last few years due to its enormous benefits such as scalability, mobile access of the network, and reduced cost
Analyzing Wireless Security in Columbia, Missouri
 Analyzing Wireless Security in Columbia, Missouri Matthew Chittum Clayton Harper John Mixon Johnathan Walton Abstract The current state of wireless security in most areas can be estimated based on trends
Analyzing Wireless Security in Columbia, Missouri Matthew Chittum Clayton Harper John Mixon Johnathan Walton Abstract The current state of wireless security in most areas can be estimated based on trends
How crypto fails in practice? CSS, WEP, MIFARE classic. *Slides borrowed from Vitaly Shmatikov
 How crypto fails in practice? CSS, WEP, MIFARE classic *Slides borrowed from Vitaly Shmatikov Stream Ciphers One-time pad: Ciphertext(Key,Message)=Message Key Key must be a random bit sequence as long
How crypto fails in practice? CSS, WEP, MIFARE classic *Slides borrowed from Vitaly Shmatikov Stream Ciphers One-time pad: Ciphertext(Key,Message)=Message Key Key must be a random bit sequence as long
Security in IEEE Networks
 Security in IEEE 802.11 Networks Mário Nunes, Rui Silva, António Grilo March 2013 Sumário 1 Introduction to the Security Services 2 Basic security mechanisms in IEEE 802.11 2.1 Hidden SSID (Service Set
Security in IEEE 802.11 Networks Mário Nunes, Rui Silva, António Grilo March 2013 Sumário 1 Introduction to the Security Services 2 Basic security mechanisms in IEEE 802.11 2.1 Hidden SSID (Service Set
5 Tips to Fortify your Wireless Network
 Article ID: 5035 5 Tips to Fortify your Wireless Network Objective Although Wi-Fi networks are convenient for you and your employees, there may be unwanted clients using up the bandwidth you pay for. In
Article ID: 5035 5 Tips to Fortify your Wireless Network Objective Although Wi-Fi networks are convenient for you and your employees, there may be unwanted clients using up the bandwidth you pay for. In
Network Security - ISA 656 Review
 Network Security - ISA 656 Review Material Test Conditions 7:20pm - 9:30pm, Thursday, Dec 11th, in the Lab (STI-128) Same style of questions as the midterm I m not asking you to write programs Angelos
Network Security - ISA 656 Review Material Test Conditions 7:20pm - 9:30pm, Thursday, Dec 11th, in the Lab (STI-128) Same style of questions as the midterm I m not asking you to write programs Angelos
HW/Lab 4: IPSec and Wireless Security. CS 336/536: Computer Network Security DUE 11 am on 12/01/2014 (Monday)
 HW/Lab 4: IPSec and Wireless Security CS 336/536: Computer Network Security DUE 11 am on 12/01/2014 (Monday) This HW/Lab assignment covers Lectures 8 (IPSec) and 10 (Wireless Security). Please review these
HW/Lab 4: IPSec and Wireless Security CS 336/536: Computer Network Security DUE 11 am on 12/01/2014 (Monday) This HW/Lab assignment covers Lectures 8 (IPSec) and 10 (Wireless Security). Please review these
Stream Ciphers. Stream Ciphers 1
 Stream Ciphers Stream Ciphers 1 Stream Ciphers Generate a pseudo-random key stream & xor to the plaintext. Key: The seed of the PRNG Traditional PRNGs (e.g. those used for simulations) are not secure.
Stream Ciphers Stream Ciphers 1 Stream Ciphers Generate a pseudo-random key stream & xor to the plaintext. Key: The seed of the PRNG Traditional PRNGs (e.g. those used for simulations) are not secure.
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security
 Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
Wireless Network Security
 Wireless Network Security Why wireless? Wifi, which is short for wireless fi something, allows your computer to connect to the Internet using magic. -Motel 6 commercial 2 but it comes at a price Wireless
Wireless Network Security Why wireless? Wifi, which is short for wireless fi something, allows your computer to connect to the Internet using magic. -Motel 6 commercial 2 but it comes at a price Wireless
TinySec: A Link Layer Security Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks. Presented by Paul Ruggieri
 TinySec: A Link Layer Security Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks Chris Karlof, Naveen Sastry,, David Wagner Presented by Paul Ruggieri 1 Introduction What is TinySec? Link-layer security architecture
TinySec: A Link Layer Security Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks Chris Karlof, Naveen Sastry,, David Wagner Presented by Paul Ruggieri 1 Introduction What is TinySec? Link-layer security architecture
05 - WLAN Encryption and Data Integrity Protocols
 05 - WLAN Encryption and Data Integrity Protocols Introduction 802.11i adds new encryption and data integrity methods. includes encryption algorithms to protect the data, cryptographic integrity checks
05 - WLAN Encryption and Data Integrity Protocols Introduction 802.11i adds new encryption and data integrity methods. includes encryption algorithms to protect the data, cryptographic integrity checks
Network Encryption 3 4/20/17
 The Network Layer Network Encryption 3 CSC362, Information Security most of the security mechanisms we have surveyed were developed for application- specific needs electronic mail: PGP, S/MIME client/server
The Network Layer Network Encryption 3 CSC362, Information Security most of the security mechanisms we have surveyed were developed for application- specific needs electronic mail: PGP, S/MIME client/server
Configuring WEP and WEP Features
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Message Integrity Check (MIC), and Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). This chapter contains these sections: Understanding
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Message Integrity Check (MIC), and Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). This chapter contains these sections: Understanding
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Security Protocols (2)
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Security Protocols (2) Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message Integrity 8.4 End point Authentication
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Security Protocols (2) Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message Integrity 8.4 End point Authentication
CSE 3461/5461: Introduction to Computer Networking and Internet Technologies. Network Security. Presentation L
 CS 3461/5461: Introduction to Computer Networking and Internet Technologies Network Security Study: 21.1 21.5 Kannan Srinivasan 11-27-2012 Security Attacks, Services and Mechanisms Security Attack: Any
CS 3461/5461: Introduction to Computer Networking and Internet Technologies Network Security Study: 21.1 21.5 Kannan Srinivasan 11-27-2012 Security Attacks, Services and Mechanisms Security Attack: Any
NETWORK SECURITY. Ch. 3: Network Attacks
 NETWORK SECURITY Ch. 3: Network Attacks Contents 3.1 Network Vulnerabilities 3.1.1 Media-Based 3.1.2 Network Device 3.2 Categories of Attacks 3.3 Methods of Network Attacks 03 NETWORK ATTACKS 2 3.1 Network
NETWORK SECURITY Ch. 3: Network Attacks Contents 3.1 Network Vulnerabilities 3.1.1 Media-Based 3.1.2 Network Device 3.2 Categories of Attacks 3.3 Methods of Network Attacks 03 NETWORK ATTACKS 2 3.1 Network
LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY
 LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY Raúl Siles raul@taddong.com Founder and Security Analyst at Taddong Introduction to Wi Fi Network Security Wireless networks or Wi Fi networks IEEE 802.11 Standards Information
LESSON 12: WI FI NETWORKS SECURITY Raúl Siles raul@taddong.com Founder and Security Analyst at Taddong Introduction to Wi Fi Network Security Wireless networks or Wi Fi networks IEEE 802.11 Standards Information
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security. Spring 2007 Lecture 8
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 8 Announcements Reminder: Project 1 is due on tonight by midnight. Midterm 1 will be held next Thursday, Feb. 8th. Example midterms
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 8 Announcements Reminder: Project 1 is due on tonight by midnight. Midterm 1 will be held next Thursday, Feb. 8th. Example midterms
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Security in Data Link Protocols
 Security in 802.11 Data Link Protocols Gianluca Dini Dept. of Ingegneria dell Informazione University of Pisa, Italy Via Diotisalvi 2, 56100 Pisa gianluca.dini@ing.unipi.it If you believe that any security
Security in 802.11 Data Link Protocols Gianluca Dini Dept. of Ingegneria dell Informazione University of Pisa, Italy Via Diotisalvi 2, 56100 Pisa gianluca.dini@ing.unipi.it If you believe that any security
Wireless Security Algorithms
 (NOTE: If you are using a virtual lab to run your attacks you will need an external Wi Fi attachment. The other option is to have a direct install on your computer. Virtual labs cannot access your wireless
(NOTE: If you are using a virtual lab to run your attacks you will need an external Wi Fi attachment. The other option is to have a direct install on your computer. Virtual labs cannot access your wireless
CS 161 Computer Security
 Paxson Spring 2017 CS 161 Computer Security Midterm 2 Print your name:, (last) (first) I am aware of the Berkeley Campus Code of Student Conduct and acknowledge that any academic misconduct will be reported
Paxson Spring 2017 CS 161 Computer Security Midterm 2 Print your name:, (last) (first) I am aware of the Berkeley Campus Code of Student Conduct and acknowledge that any academic misconduct will be reported
WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you
 Black Hat USA 2010 WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you Leandro Meiners (lmeiners@coresecurity.com / @gmail.com) Diego Sor (dsor@coresecurity.com / diegos@gmail.com) Page 1 WPA Migration Mode:
Black Hat USA 2010 WPA Migration Mode: WEP is back to haunt you Leandro Meiners (lmeiners@coresecurity.com / @gmail.com) Diego Sor (dsor@coresecurity.com / diegos@gmail.com) Page 1 WPA Migration Mode:
Computer and Network Security
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 7 Announcements First project: Due: TOMORROW at 11:59 p.m. http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis551/project1.html Plan for Today: Networks:
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 7 Announcements First project: Due: TOMORROW at 11:59 p.m. http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis551/project1.html Plan for Today: Networks:
Wireless Network Security
 Wireless Network Security Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-11/
Wireless Network Security Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-11/
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics
 Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
Network Security. Thierry Sans
 Network Security Thierry Sans HTTP SMTP DNS BGP The Protocol Stack Application TCP UDP Transport IPv4 IPv6 ICMP Network ARP Link Ethernet WiFi The attacker is capable of confidentiality integrity availability
Network Security Thierry Sans HTTP SMTP DNS BGP The Protocol Stack Application TCP UDP Transport IPv4 IPv6 ICMP Network ARP Link Ethernet WiFi The attacker is capable of confidentiality integrity availability
Wireless Security. Training materials for wireless trainers
 Wireless Security Training materials for wireless trainers This one hour talk covers the essential problems of wireless security, and some techniques to address them. Version 1.2 by Rob, @2009-11-23 Version
Wireless Security Training materials for wireless trainers This one hour talk covers the essential problems of wireless security, and some techniques to address them. Version 1.2 by Rob, @2009-11-23 Version
Csci388. Wireless and Mobile Security Access Control: 802.1X, EAP, and RADIUS. Importance of Access Control. WEP Weakness. Wi-Fi and IEEE 802.
 WEP Weakness Csci388 Wireless and Mobile Security Access Control:, EAP, and Xiuzhen Cheng cheng@gwu.edu 1. IV is too short and not protected from reuse 2. The per packet key is constructed from the IV,
WEP Weakness Csci388 Wireless and Mobile Security Access Control:, EAP, and Xiuzhen Cheng cheng@gwu.edu 1. IV is too short and not protected from reuse 2. The per packet key is constructed from the IV,
The 8 th International Scientific Conference DEFENSE RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN THE 21st CENTURY Braşov, November 14 th 2013
 The 8 th International Scientific Conference DEFENSE RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN THE 21st CENTURY Braşov, November 14 th 2013 Florin OGÎGĂU-NEAMŢIU National Defense University of Romania "Carol I"/ The Regional
The 8 th International Scientific Conference DEFENSE RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN THE 21st CENTURY Braşov, November 14 th 2013 Florin OGÎGĂU-NEAMŢIU National Defense University of Romania "Carol I"/ The Regional
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Expected Outcomes Able to design the network security for the entire network Able to develop and suggest the security plan and policy
 CHAPTER 9 DEVELOPING NETWORK SECURITY STRATEGIES Expected Outcomes Able to design the network security for the entire network Able to develop and suggest the security plan and policy Network Security Design
CHAPTER 9 DEVELOPING NETWORK SECURITY STRATEGIES Expected Outcomes Able to design the network security for the entire network Able to develop and suggest the security plan and policy Network Security Design
Wireless LAN Security. Gabriel Clothier
 Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
Implementing Cryptography: Good Theory vs. Bad Practice
 Implementing Cryptography: Good Theory vs. Bad Practice Viet Pham Information Security Group, Department of Mathematics Royal Holloway, University of London Outline News report What is cryptography? Why
Implementing Cryptography: Good Theory vs. Bad Practice Viet Pham Information Security Group, Department of Mathematics Royal Holloway, University of London Outline News report What is cryptography? Why
Hacking Air Wireless State of the Nation. Presented By Adam Boileau
 Hacking Air Wireless State of the Nation Presented By Adam Boileau Introduction Wireless in 2006 802-dot-what? Threats to Wireless Networks Denial of Service Attacks against Authentication Attacks against
Hacking Air Wireless State of the Nation Presented By Adam Boileau Introduction Wireless in 2006 802-dot-what? Threats to Wireless Networks Denial of Service Attacks against Authentication Attacks against
Wireless Security and Monitoring. Training materials for wireless trainers
 Wireless Security and Monitoring Training materials for wireless trainers Goals to understand which security issues are important to consider when designing WiFi networks to be introduced to encryption,
Wireless Security and Monitoring Training materials for wireless trainers Goals to understand which security issues are important to consider when designing WiFi networks to be introduced to encryption,
Cryptography ThreeB. Ed Crowley. Fall 08
 Cryptography ThreeB Ed Crowley Fall 08 Cryptanalysis History Modern Cryptanalysis Characterization of Cryptanalysis Attacks Attack Types Cryptanalysis. Science of cracking ciphers and codes, decoding secrets,
Cryptography ThreeB Ed Crowley Fall 08 Cryptanalysis History Modern Cryptanalysis Characterization of Cryptanalysis Attacks Attack Types Cryptanalysis. Science of cracking ciphers and codes, decoding secrets,
Multi-Layered Security Framework for Metro-Scale Wi-Fi Networks
 Multi-Layered Security Framework for Metro-Scale Wi-Fi Networks A Security Whitepaper January, 2004 Photo courtesy of NASA Image exchange. Image use in no way implies endorsement by NASA of any of the
Multi-Layered Security Framework for Metro-Scale Wi-Fi Networks A Security Whitepaper January, 2004 Photo courtesy of NASA Image exchange. Image use in no way implies endorsement by NASA of any of the
network security s642 computer security adam everspaugh
 network security s642 adam everspaugh ace@cs.wisc.edu computer security today Announcement: HW3 to be released WiFi IP, TCP DoS, DDoS, prevention 802.11 (wifi) STA = station AP = access point BSS = basic
network security s642 adam everspaugh ace@cs.wisc.edu computer security today Announcement: HW3 to be released WiFi IP, TCP DoS, DDoS, prevention 802.11 (wifi) STA = station AP = access point BSS = basic
Wireless Network Security Spring 2011
 Wireless Network Security 14-814 Spring 2011 Patrick Tague Feb 8, 2011 Class #9 Link/MAC layer security Announcements HW #1 is due on Thursday 2/10 If anyone would like Android phones for their course
Wireless Network Security 14-814 Spring 2011 Patrick Tague Feb 8, 2011 Class #9 Link/MAC layer security Announcements HW #1 is due on Thursday 2/10 If anyone would like Android phones for their course
Security and Authentication for Wireless Networks
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 5-21-2004 Security and Authentication for 802.11 Wireless Networks Michel Getraide
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 5-21-2004 Security and Authentication for 802.11 Wireless Networks Michel Getraide
Wireless Networking. Chapter The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
COSC4377. Chapter 8 roadmap
 Lecture 28 Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity 8.4 Securing e mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections: SSL 8.6 Network layer security: IPsec 8.7
Lecture 28 Chapter 8 roadmap 8.1 What is network security? 8.2 Principles of cryptography 8.3 Message integrity 8.4 Securing e mail 8.5 Securing TCP connections: SSL 8.6 Network layer security: IPsec 8.7
Internet Security in my Crystal Ball
 Steven M. Bellovin June 21, 2001 1 Florham Park, NJ 07932 AT&T Labs Research +1 973-360-8656 http://www.research.att.com/ smb Steven M. Bellovin Internet Security in my Crystal Ball security speculation
Steven M. Bellovin June 21, 2001 1 Florham Park, NJ 07932 AT&T Labs Research +1 973-360-8656 http://www.research.att.com/ smb Steven M. Bellovin Internet Security in my Crystal Ball security speculation
Today s challenge on Wireless Networking. David Leung, CISM Solution Consultant, Security Datacraft China/Hong Kong Ltd.
 Today s challenge on Wireless Networking David Leung, CISM Solution Consultant, Security Datacraft China/Hong Kong Ltd. Agenda How Popular is Wireless Network? Threats Associated with Wireless Networking
Today s challenge on Wireless Networking David Leung, CISM Solution Consultant, Security Datacraft China/Hong Kong Ltd. Agenda How Popular is Wireless Network? Threats Associated with Wireless Networking
WarDriving. related fixed line attacks war dialing port scanning
 WarDriving slide 1 related fixed line attacks war dialing port scanning war driving drive through a metropolitan area looking for wireless access points software logs, latidute/longitude runs software
WarDriving slide 1 related fixed line attacks war dialing port scanning war driving drive through a metropolitan area looking for wireless access points software logs, latidute/longitude runs software
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol: TKIP. Tim Fielder University of Tulsa Tulsa, Oklahoma
 Temporal Key Integrity Protocol: TKIP Tim Fielder University of Tulsa Tulsa, Oklahoma History IEEE released the first 802.11 specification back in 1997 The Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) authentication/encryption
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol: TKIP Tim Fielder University of Tulsa Tulsa, Oklahoma History IEEE released the first 802.11 specification back in 1997 The Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) authentication/encryption
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. PCI Adapter with SRX 400. User Guide WIRELESS WMP54GX4. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SRX 400 User Guide Model No. WMP54GX4 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SRX 400 User Guide Model No. WMP54GX4 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
SIP and VoIP What is SIP? What s a Control Channel? History of Signaling Channels
 Network Security - ISA 656 Voice Over IP (VoIP) Security Simple SIP ing Alice s Bob Session Initiation Protocol Control channel for Voice over IP (Other control channel protocols exist, notably H.323 and
Network Security - ISA 656 Voice Over IP (VoIP) Security Simple SIP ing Alice s Bob Session Initiation Protocol Control channel for Voice over IP (Other control channel protocols exist, notably H.323 and
Cryptanalysis. Ed Crowley
 Cryptanalysis Ed Crowley 1 Topics Cryptanalysis History Modern Cryptanalysis Characterization of Cryptanalysis Attacks Attack Types 2 Cryptanalysis Science of cracking ciphers and codes, decoding secrets,
Cryptanalysis Ed Crowley 1 Topics Cryptanalysis History Modern Cryptanalysis Characterization of Cryptanalysis Attacks Attack Types 2 Cryptanalysis Science of cracking ciphers and codes, decoding secrets,
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking. Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology
 CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
Introduction to Computer Security
 Introduction to Computer Security Instructor: Mahadevan Gomathisankaran mgomathi@unt.edu CSCE 4550/5550, Fall 2009 Lecture 10 1 Announcements Project Group Due today Attendance Mandatory Ave. 85% ( 4 absentees
Introduction to Computer Security Instructor: Mahadevan Gomathisankaran mgomathi@unt.edu CSCE 4550/5550, Fall 2009 Lecture 10 1 Announcements Project Group Due today Attendance Mandatory Ave. 85% ( 4 absentees
ECHONET Lite SPECIFICATION. ECHONET Lite System Design Guidelines 2011 (2012) ECHONET CONSORTIUM ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 Part V ECHONET Lite System Design Guidelines i 2011 (2012) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED The specifications published by the ECHONET Consortium are established without regard to industrial property rights (e.g.,
Part V ECHONET Lite System Design Guidelines i 2011 (2012) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED The specifications published by the ECHONET Consortium are established without regard to industrial property rights (e.g.,
Wireless Network Security Spring 2015
 Wireless Network Security Spring 2015 Patrick Tague Class #7 More WiFi Security 2015 Patrick Tague 1 Class #7 Continuation of WiFi security 2015 Patrick Tague 2 Device Private WiFi Networks AP Local AAA
Wireless Network Security Spring 2015 Patrick Tague Class #7 More WiFi Security 2015 Patrick Tague 1 Class #7 Continuation of WiFi security 2015 Patrick Tague 2 Device Private WiFi Networks AP Local AAA
KRACKing WPA2 by Forcing Nonce Reuse. Mathy Chaos Communication Congress (CCC), 27 December 2017
 KRACKing WPA2 by Forcing Nonce Reuse Mathy Vanhoef @vanhoefm Chaos Communication Congress (CCC), 27 December 2017 Introduction PhD Defense, July 2016: You recommend WPA2 with AES, but are you sure that
KRACKing WPA2 by Forcing Nonce Reuse Mathy Vanhoef @vanhoefm Chaos Communication Congress (CCC), 27 December 2017 Introduction PhD Defense, July 2016: You recommend WPA2 with AES, but are you sure that
Lecture 13 Page 1. Lecture 13 Page 3
 IPsec Network Security: IPsec CS 239 Computer Software March 2, 2005 Until recently, the IP protocol had no standards for how to apply security Encryption and authentication layered on top Or provided
IPsec Network Security: IPsec CS 239 Computer Software March 2, 2005 Until recently, the IP protocol had no standards for how to apply security Encryption and authentication layered on top Or provided
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking
 CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
0/41. Alice Who? Authentication Protocols. Andreas Zeller/Stephan Neuhaus. Lehrstuhl Softwaretechnik Universität des Saarlandes, Saarbrücken
 0/41 Alice Who? Authentication Protocols Andreas Zeller/Stephan Neuhaus Lehrstuhl Softwaretechnik Universität des Saarlandes, Saarbrücken The Menu 1/41 Simple Authentication Protocols The Menu 1/41 Simple
0/41 Alice Who? Authentication Protocols Andreas Zeller/Stephan Neuhaus Lehrstuhl Softwaretechnik Universität des Saarlandes, Saarbrücken The Menu 1/41 Simple Authentication Protocols The Menu 1/41 Simple
IPSec. Slides by Vitaly Shmatikov UT Austin. slide 1
 IPSec Slides by Vitaly Shmatikov UT Austin slide 1 TCP/IP Example slide 2 IP Security Issues Eavesdropping Modification of packets in transit Identity spoofing (forged source IP addresses) Denial of service
IPSec Slides by Vitaly Shmatikov UT Austin slide 1 TCP/IP Example slide 2 IP Security Issues Eavesdropping Modification of packets in transit Identity spoofing (forged source IP addresses) Denial of service
KRACKing WPA2 by Forcing Nonce Reuse. Mathy Nullcon, 2 March 2018
 KRACKing WPA2 by Forcing Nonce Reuse Mathy Vanhoef @vanhoefm Nullcon, 2 March 2018 Introduction PhD Defense, July 2016: You recommend WPA2 with AES, but are you sure that s secure? Seems so! No attacks
KRACKing WPA2 by Forcing Nonce Reuse Mathy Vanhoef @vanhoefm Nullcon, 2 March 2018 Introduction PhD Defense, July 2016: You recommend WPA2 with AES, but are you sure that s secure? Seems so! No attacks
 Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
What is Eavedropping?
 WLAN Security What is Eavedropping? War Driving War Driving refers to someone driving around with a laptop and an 802.11 client card looking for an 802.11 system to exploit. War Walking Someone walks
WLAN Security What is Eavedropping? War Driving War Driving refers to someone driving around with a laptop and an 802.11 client card looking for an 802.11 system to exploit. War Walking Someone walks
Network Security. Security in local-area networks. Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Autumn 2014
 Network Security Security in local-area networks Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Autumn 2014 Announcement Exercise class (werkcollege) time and room changed: Friday, 15:30-17:30, in LIN 8
Network Security Security in local-area networks Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Autumn 2014 Announcement Exercise class (werkcollege) time and room changed: Friday, 15:30-17:30, in LIN 8
U S E R M A N U A L b/g PC CARD
 U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
Internet Layers. Physical Layer. Application. Application. Transport. Transport. Network. Network. Network. Network. Link. Link. Link.
 Internet Layers Application Application Transport Transport Network Network Network Network Link Link Link Link Ethernet Fiber Optics Physical Layer Wi-Fi ARP requests and responses IP: 192.168.1.1 MAC:
Internet Layers Application Application Transport Transport Network Network Network Network Link Link Link Link Ethernet Fiber Optics Physical Layer Wi-Fi ARP requests and responses IP: 192.168.1.1 MAC:
Integrating Wireless into Campus Networks
 Integrating Wireless into Campus Networks This document is a result of work by the Network Startup Resource Center (NSRC at http://www.nsrc.org). This document may be freely copied, modified, and otherwise
Integrating Wireless into Campus Networks This document is a result of work by the Network Startup Resource Center (NSRC at http://www.nsrc.org). This document may be freely copied, modified, and otherwise
Review. Error Detection: CRC Multiple access protocols. LAN addresses and ARP Ethernet. Slotted ALOHA CSMA/CD
 Review Error Detection: CRC Multiple access protocols Slotted ALOHA CSMA/CD LAN addresses and ARP Ethernet Some slides are in courtesy of J. Kurose and K. Ross Overview Ethernet Hubs, bridges, and switches
Review Error Detection: CRC Multiple access protocols Slotted ALOHA CSMA/CD LAN addresses and ARP Ethernet Some slides are in courtesy of J. Kurose and K. Ross Overview Ethernet Hubs, bridges, and switches
Wireless-N. User Guide. USB Network Adapter WUSB300N WIRELESS. Model No.
 2.4 GHz WIRELESS Wireless-N USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB300N Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark
2.4 GHz WIRELESS Wireless-N USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB300N Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark
Network Security - ISA 656 Routing Security
 What is? Network Security - ISA 656 Angelos Stavrou What is Routing Security? History of Routing Security Why So Little Work? How is it Different? Bad guys play games with routing protocols. Traffic is
What is? Network Security - ISA 656 Angelos Stavrou What is Routing Security? History of Routing Security Why So Little Work? How is it Different? Bad guys play games with routing protocols. Traffic is
Steven M. Bellovin AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ 07932
 Steven M. Bellovin! " $#"##%& '( ) * 973-360-8656 AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ 07932 Steven M. Bellovin June 13, 2003 1 What is? Bad guys play games with routing protocols. Traffic is diverted.
Steven M. Bellovin! " $#"##%& '( ) * 973-360-8656 AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ 07932 Steven M. Bellovin June 13, 2003 1 What is? Bad guys play games with routing protocols. Traffic is diverted.
Wireless Router at Home
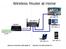 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Best Practice - Protect Against TCP SYN Flooding Attacks with TCP Accept Policies
 Best Practice - Protect Against TCP SYN Flooding Attacks with TCP Accept Policies In order to establish a TCP connection, the TCP three-way handshake must be completed. You can use different accept policies
Best Practice - Protect Against TCP SYN Flooding Attacks with TCP Accept Policies In order to establish a TCP connection, the TCP three-way handshake must be completed. You can use different accept policies
Wireless Network Security Spring 2016
 Wireless Network Security Spring 2016 Patrick Tague Class #7 WiFi Security 1 Announcements Please do HW#2 in using the stable OMNET++ 4.6, not the beta version. Porting has proven difficult... Form project
Wireless Network Security Spring 2016 Patrick Tague Class #7 WiFi Security 1 Announcements Please do HW#2 in using the stable OMNET++ 4.6, not the beta version. Porting has proven difficult... Form project
An introduction to wireless security at home, on the road and on campus. Sherry Callahan and Kyle Crane
 Out of Thin Air! An introduction to wireless security at home, on the road and on campus Sherry Callahan and Kyle Crane University of Kansas Medical Center October 5, 2009 Wireless Networking at Home Sherry
Out of Thin Air! An introduction to wireless security at home, on the road and on campus Sherry Callahan and Kyle Crane University of Kansas Medical Center October 5, 2009 Wireless Networking at Home Sherry
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems. Network Security Concepts
 CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Network Security Concepts Topics 1. Protocols and Layers 2. Layer 2 Network Concepts 3. MAC Spoofing 4. ARP 5. ARP Spoofing 6. Network Sniffing Protocols A protocol defines
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Network Security Concepts Topics 1. Protocols and Layers 2. Layer 2 Network Concepts 3. MAC Spoofing 4. ARP 5. ARP Spoofing 6. Network Sniffing Protocols A protocol defines
Network Security. Security in local-area networks. Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Autumn 2014
 Network Security Security in local-area networks Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Autumn 2014 Announcement Exercise class (werkcollege) time and room changed: Friday, 15:30-17:30, in LIN 8
Network Security Security in local-area networks Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands Autumn 2014 Announcement Exercise class (werkcollege) time and room changed: Friday, 15:30-17:30, in LIN 8
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. USB Network Adapter. User Guide WIRELESS WUSB54G. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
Securing Wireless Networks by By Joe Klemencic Mon. Apr
 http://www.cymru.com/ Securing Wireless Networks by By Joe Klemencic (faz@home.com) Mon. Apr 30 2001 Many companies make attempts to embrace new technologies, but unfortunately, many of these new technologies
http://www.cymru.com/ Securing Wireless Networks by By Joe Klemencic (faz@home.com) Mon. Apr 30 2001 Many companies make attempts to embrace new technologies, but unfortunately, many of these new technologies
Security in Data Link Protocols
 Security in 802.11 Data Link Protocols Gianluca Dini!"#$%&'(&)*+"+*",-.&/"001)*(',2.3-'*" University of Pisa, Italy Via Diotisalvi 2, 56100 Pisa gianluca.dini@ing.unipi.it!"#$%&#'()*(+(#,-.,#./$#0(1&2*,$#32%')(4#1./#
Security in 802.11 Data Link Protocols Gianluca Dini!"#$%&'(&)*+"+*",-.&/"001)*(',2.3-'*" University of Pisa, Italy Via Diotisalvi 2, 56100 Pisa gianluca.dini@ing.unipi.it!"#$%&#'()*(+(#,-.,#./$#0(1&2*,$#32%')(4#1./#
Secure Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks: Attacks and Countermeasures
 Secure Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks: Attacks and Countermeasures By Chris Karlof and David Wagner Lukas Wirne Anton Widera 23.11.2017 Table of content 1. Background 2. Sensor Networks vs. Ad-hoc
Secure Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks: Attacks and Countermeasures By Chris Karlof and David Wagner Lukas Wirne Anton Widera 23.11.2017 Table of content 1. Background 2. Sensor Networks vs. Ad-hoc
Wireless MAXg Technology
 Wireless MAXg Technology MAXimizing range, performance, security and simplicity for 802.11g networks Technology Note Wireless technology has undoubtedly become a ubiquitous presence in our computing environment,
Wireless MAXg Technology MAXimizing range, performance, security and simplicity for 802.11g networks Technology Note Wireless technology has undoubtedly become a ubiquitous presence in our computing environment,
