Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services
|
|
|
- Priscilla Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Network Architecture and Services Telegraph Networks & Message Switching Telephone Networks and Circuit Switching Computer Networks & Packet Switching Future Network Architectures and Services Key Factors in Network Evolution 1
2 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Network Architecture and Services 2
3 Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services & applications are everywhere. server Exchange of text messages via servers 3
4 Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services & applications are everywhere. Web Browsing Web server Retrieval of information from web servers 4
5 Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services & applications are everywhere. Instant Messaging Direct exchange of text messages 5
6 Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services & applications are everywhere. Telephone Real-time bidirectional voice exchange 6
7 Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services & applications are everywhere. Cell phone Real-time voice exchange with mobile users 7
8 Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services & applications are everywhere. Short Message Service Fast delivery of short text messages 8
9 Many other examples! Peer-to-peer applications Napster, Gnutella, Kazaa file exchange Searching for ExtraTerrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Audio & video streaming Network games On-line purchasing Text messaging in PDAs, cell phones (SMS) Voice-over-Internet 9
10 Services & Applications Service: Basic information transfer capability Internet transfer of individual block of information Internet reliable transfer of a stream of bytes Real-time transfer of a voice signal Applications build on communication services & web build on reliable stream service Fax and modems build on basic telephone service New applications build on multiple networks SMS builds on Internet reliable stream service and cellular telephone text messaging 10
11 What is a communication network? Communication Network The equipment (hardware & software) and facilities that provide the basic communication service Virtually invisible to the user; Usually represented by a cloud Equipment Routers, servers, switches, multiplexers, hubs, modems, Facilities Copper wires, coaxial cables, optical fiber Ducts, conduits, telephone poles 11 How are communication networks designed and operated?
12 Communication Network Architecture Network architecture: the plan that specifies how the network is built and operated Architecture is driven by the network services Overall communication process is complex Network architecture partitions overall communication process into separate functional areas called layers Next we will trace evolution of three network architectures: telegraph, telephone, and computer networks 12
13 Network Architecture Evolution Information transfer per second 1.0E E E E E E E E ? Telegraph networks Telephone networks Internet, Optical & Wireless networks Next Generation Internet 13
14 Network Architecture Evolution Telegraph Networks Message switching & digital transmission Telephone Networks Circuit Switching Analog transmission digital transmission Mobile communications Internet Packet switching & computer applications Next-Generation Internet Multiservice packet switching network 14
15 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Telegraph Networks & Message Switching 15
16 Telegraphs & Long-Distance Communications Approaches to long-distance communications Courier: physical transport of the message Messenger pigeons, pony express, FedEx Telegraph: message is transmitted across a network using signals Drums, beacons, mirrors, smoke, flags, semaphores Electricity, light Telegraph delivers message much sooner 16
17 Optical (Visual) Telegraph Claude Chappe invented optical telegraph in the 1790 s Semaphore mimicked a person with outstretched arms with flags in each hand Different angle combinations of arms & hands generated hundreds of possible signals Code for enciphering messages kept secret Signal could propagate 800 km in 3 minutes! 17
18 Message Switching Network nodes were created where several optical telegraph lines met (Paris and other sites) Network Node North line Store-and-Forward Operation: Messages arriving on each line were decoded Next-hop in route determined by destination address of a message Each message was carried by hand to next line, and stored until operator became available for next transmission West line South line East line 18
19 Electric Telegraph William Sturgeon Electro-magnet (1825) Electric current in a wire wrapped around a piece of iron generates a magnetic force Joseph Henry (1830) Current over 1 mile of wire to ring a bell Samuel Morse (1835) Pulses of current deflect electromagnet to generate dots & dashes Experimental telegraph line over 40 miles (1840) Signal propagates at the speed of light!!! Approximately 2 x 10 8 meters/second in cable 19
20 Digital Communications Morse code converts text message into sequence of dots and dashes Use transmission system designed to convey dots and dashes Morse Code Morse Code Morse Code Morse Code A J S 2 B K T 3 C L U 4 D M V 5 E N W 6 F O X 7 G P Y 8 H Q Z 9 I R
21 Electric Telegraph Networks Electric telegraph networks exploded Message switching & Store-and-Forward operation Key elements: Addressing, Routing, Forwarding Optical telegraph networks disappeared Message Message Source Message Message Switches Destination 21
22 Baudot Telegraph Multiplexer Operator words/minute but a wire can carry much more Baudot multiplexer: Combine 4 signals in 1 wire Binary block code (ancestor of ASCII code) A character represented by 5 bits Time division multiplexing Binary codes for characters are interleaved Framing is required to recover characters from the binary sequence in the multiplexed signal Keyboard converts characters to bits 22
23 Baudot Telegraph Multiplexer Keyboard Baudot Multiplexer Baudot Demultiplexer Paper Tape Printer Paper Tape Printer A 2 D 1 C 1 B 1 A 1 Paper Tape Printer 5 bits / character Paper Tape Printer 23
24 Elements of Telegraph Network Architecture Digital transmission Text messages converted into symbols (dots/dashes, zeros/ones) Transmission system designed to convey symbols Multiplexing Framing needed to recover text characters Message Switching Messages contain source & destination addresses Store-and-Forward: Messages forwarded hop-by-hop across network Routing according to destination address 24
25 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Telephone Networks and Circuit Switching 25
26 Bell s Telephone Alexander Graham Bell (1875) working on harmonic telegraph to multiplex telegraph signals Discovered voice signals can be transmitted directly Microphone converts voice pressure variation (sound) into analogous electrical signal Loudspeaker converts electrical signal back into sound Telephone patent granted in 1876 Bell Telephone Company founded in 1877 Signal for ae as in cat Microphone Loudspeaker analog electrical sound signal sound 26
27 Bell s Sketch of Telephone 27
28 Signaling Signaling required to establish a call Flashing light and ringing devices to alert the called party of incoming call Called party information to operator to establish calls Signaling + voice signal transfer 28
29 The N 2 Problem For N users to be fully connected directly Requires N(N 1)/2 connections Requires too much space for cables Inefficient & costly since connections not always on 1 N 2 N = 1000 N(N 1)/2 =
30 Telephone Pole Congestion 30
31 Circuit Switching Patchcord panel switch invented in 1877 Operators connect users on demand Establish circuit to allow electrical current to flow from inlet to outlet Only N connections required to central office N 1 N
32 Manual Switching 32
33 Strowger Switch Human operators intelligent & flexible But expensive and not always discreet Strowger invented automated switch in 1888 Each current pulse advances wiper by 1 position User dialing controls connection setup Decimal telephone numbering system Hierarchical network structure simplifies routing Area code, exchange (CO), station number 1 st digit 2 nd digit
34 Strowger Switch 34
35 Hierarchical Network Structure CO = central office Toll Tandem CO Tandem CO CO CO CO Telephone subscribers connected to local CO (central office) Tandem & Toll switches connect CO s 35
36 Three Phases of a Connection 1. Telephone network Pick up phone 2. Telephone network Dial tone. Connection set up 3. Telephone network Dial number Network selects route; 4. Telephone network Sets up connection; Called party alerted Information transfer 5. Telephone network Exchange voice signals Connection release 6. Telephone network Hang up. 36
37 Computer Connection Control A computer controls connection in telephone switch Computers exchange signaling messages to: Coordinate set up of telephone connections To implement new services such as caller ID, voice mail,... To enable mobility and roaming in cellular networks Intelligence inside the network A separate signaling network is required Computer Signaling... Switch connects Inlets to Outlets... Voice 37
38 Digitization of Telephone Network Pulse Code Modulation digital voice signal Voice gives 8 bits/sample x 8000 samples/sec = 64x10 3 bps Time Division Multiplexing for digital voice T-1 multiplexing (1961): 24 voice signals = 1.544x10 6 bps Digital Switching (1980s) Switch TDM signals without conversion to analog form Digital Cellular Telephony (1990s) Optical Digital Transmission (1990s) One OC-192 optical signal = 10x10 9 bps One optical fiber carries 160 OC-192 signals = 1.6x10 12 bps! All digital transmission, switching, and control 38
39 Digital Transmission Evolution 1.0E+14 Wavelength Division Multiplexing? Information transfer per second 1.0E E E E E E+02 Baudot T-1 Carrier SONET Optical Carrier 1.0E Morse 39
40 Elements of Telephone Network Architecture Digital transmission & switching Digital voice; Time Division Multiplexing Circuit switching User signals for call setup and tear-down Route selected during connection setup End-to-end connection across network Signaling coordinates connection setup Hierarchical Network Decimal numbering system Hierarchical structure; simplified routing; scalability Signaling Network Intelligence inside the network 40
41 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Computer Networks & Packet Switching 41
42 Computer Network Evolution Overview 1950s: Telegraph technology adapted to computers 1960s: Dumb terminals access shared host computer SABRE airline reservation system 1970s: Computers connect directly to each other ARPANET packet switching network TCP/IP internet protocols Ethernet local area network 1980s & 1990s: New applications and Internet growth Commercialization of Internet , file transfer, web, P2P,... Internet traffic surpasses voice traffic 42
43 What is a protocol? Communications between computers requires very specific unambiguous rules A protocol is a set of rules that governs how two or more communicating parties are to interact Internet Protocol (IP) Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) 43
44 A familiar protocol Caller Caller replies Caller replies Caller waits Caller replies Caller waits Caller dials Dials 411 What city? Springfield What name? Simpson Thank you, please hold Do you have a first name or street? Evergreen Terrace Thank you, please hold System replies System replies System replies Operator replies Operator replies System replies with number 44
45 Terminal-Oriented Networks Early computer systems very expensive Time-sharing methods allowed multiple terminals to share local computer Remote access via telephone modems Terminal... Terminal Modem Telephone Network Modem Terminal Host computer 45
46 Medium Access Control Dedicated communication lines were expensive Terminals generated messages sporadically Frames carried messages to/from attached terminals Address in frame header identified terminal Medium Access Controls for sharing a line were developed Example: Polling protocol on a multidrop line Polling frames & output frames input frames Terminal Terminal... Terminal Host computer Terminals at different locations in a city Must avoid collisions on inbound line 46
47 Statistical Multiplexing Statistical multiplexer allows a line to carry frames that contain messages to/from multiple terminals Frames are buffered at multiplexer until line becomes available, i.e. store-and-forward Address in frame header identifies terminal Header carries other control information Frame CRC Information Header Terminal Terminal Header Information CRC... Terminal Host computer Multiplexer 47
48 Error Control Protocol Communication lines introduced errors Error checking codes used on frames Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) calculated based on frame header and information payload, and appended Header also carries ACK/NAK control information Retransmission requested when errors detected CRC Information Header Header Information CRC Terminal 48
49 Tree Topology Networks National & international terminal-oriented networks Routing was very simple (to/from host) Each network typically handled a single application San Francisco T T New York City Chicago T Atlanta 49
50 Computer-to-Computer Networks As cost of computing dropped, terminal-oriented networks viewed as too inflexible and costly Need to develop flexible computer networks Interconnect computers as required Support many applications Application Examples File transfer between arbitrary computers Execution of a program on another computer Multiprocess operation over multiple computers 50
51 Packet Switching Network should support multiple applications Transfer arbitrary message size Low delay for interactive applications But in store-and-forward operation, long messages induce high delay on interactive messages Packet switching introduced Network transfers packets using store-and-forward Packets have maximum length Break long messages into multiple packets ARPANET testbed led to many innovations 51
52 ARPANET Packet Switching Host generates message Source packet switch converts message to packet(s) Packets transferred independently across network Destination packet switch reasembles message Destination packet switch delivers message Message Packet 2 Packet Switch Packet 2 Message Packet Switch Packet Switch Packet 1 Packet Switch Packet 1 Packet Switch Packet 1 52
53 ARPANET Routing Routing is highly nontrivial in mesh networks No connection setup prior to packet transmission Packets header includes source & destination addresses Packet switches have table with next hop per destination Routing tables calculated by packet switches using distributed algorithm Packet Switch Hdr Packet Packet Switch Packet Switch Packet Switch Packet Switch Dest: Next Hop: xyz abc wvr edf 53
54 Other ARPANET Protocols Error control between adjacent packet switches Congestion control between source & destination packet switches limit number of packets in transit Flow control between host computers prevents buffer overflow Packet Switch Error Control Packet Switch Congestion Control Packet Switch Packet Switch Packet Switch Flow Control 54
55 ARPANET Applications ARPANET introduced many new applications , remote login, file transfer, Intelligence at the edge AMES McCLELLAN UTAH BOULDER GWC CASE RADC AMES USC ILL LINC CARN UCSB MIT MITRE STAN SCD ETAC UCLA RAND TINKER BBN HARV NBS 55
56 Ethernet Local Area Network In 1980s, affordable workstations available Need for low-cost, high-speed networks To interconnect local workstations To access local shared resources (printers, storage, servers) Low cost, high-speed communications with low error rate possible using coaxial cable Ethernet is the standard for high-speed wired access to computer networks 56
57 Ethernet Medium Access Control Network interface card (NIC) connects workstation to LAN Each NIC has globally unique address Frames are broadcast into coaxial cable NICs listen to medium for frames with their address Transmitting NICs listen for collisions with other stations, and abort and reschedule retransmissions Transceivers 57
58 The Internet Different network types emerged for data transfer between computers ARPA also explored packet switching using satellite and packet radio networks Each network has its protocols and is possibly built on different technologies Internetworking protocols required to enable communications between computers attached to different networks Internet: a network of networks 58
59 Internet Protocol (IP) Routers (gateways) interconnect different networks Host computers prepare IP packets and transmit them over their attached network Routers forward IP packets across networks Best-effort IP transfer service, no retransmission Net 1 Net 2 Router 59
60 Addressing & Routing Hierarchical address: Net ID + Host ID IP packets routed according to Net ID Routers compute routing tables using distributed algorithm H H Net 1 G G Net 3 G G Net 5 H Net 2 G Net 4 G H 60
61 Transport Protocols Host computers run two transport protocols on top of IP to enable process-to-process communications User Datagram Protocol (UDP) enables best-effort transfer of individual block of information Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) enables reliable transfer of a stream of bytes Transport Protocol Internet 61
62 Names and IP Addresses Routing is done based on 32-bit IP addresses Dotted-decimal notation Hosts are also identified by name Easier to remember Hierarchical name structure tesla.comm.utoronto.edu Domain Name System (DNS) provided conversion between names and addresses 62
63 Internet Applications All Internet applications run on TCP or UDP TCP: HTTP (web); SMTP ( ); FTP (file transfer; telnet (remote terminal) UDP: DNS, RTP (voice & multimedia) TCP & UDP incorporated into computer operating systems Any application designed to operate over TCP or UDP will run over the Internet!!! 63
64 Elements of Computer Network Architecture Digital transmission Exchange of frames between adjacent equipment Framing and error control Medium access control regulates sharing of broadcast medium. Addresses identify attachment to network or internet. Transfer of packets across a packet network Distributed calculation of routing tables 64
65 Elements of Computer Network Architecture Congestion control inside the network Internetworking across multiple networks using routers Segmentation and reassembly of messages into packets at the ingress to and egress from a network or internetwork End-to-end transport protocols for process-to-process communications Applications that build on the transfer of messages between computers. Intelligence is at the edge of the network. 65
Chapter 1 Communication
 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Network Architecture and Services Telegraph Networks & Message Switching Telephone Networks and Circuit Switching Computer Networks & Packet Switching Future
Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Network Architecture and Services Telegraph Networks & Message Switching Telephone Networks and Circuit Switching Computer Networks & Packet Switching Future
Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services
 Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services
Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services Communication Services & Applications A communication service enables the exchange of information between users at different locations. Communication services
Computer-to-Computer Networks (cont.)
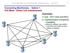 Computer-to-Computer Networks (cont.) 1 Connecting Mainframes - Option 1: Full Mesh / Direct Link Infrastructure Downsides: 1) cost - O(n 2 ) links and NICs 2) implementation complexity / scalability [
Computer-to-Computer Networks (cont.) 1 Connecting Mainframes - Option 1: Full Mesh / Direct Link Infrastructure Downsides: 1) cost - O(n 2 ) links and NICs 2) implementation complexity / scalability [
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I
 COSC 3213: Computer Networks I Course Instructor: Teaching Assistant: Amir Asif TBA Contact Information: Instructor: Section M Teaching Assistant: Office: CSE 3028 TBA asif@cs.yorku.ca (416) 736-2100 X70128
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I Course Instructor: Teaching Assistant: Amir Asif TBA Contact Information: Instructor: Section M Teaching Assistant: Office: CSE 3028 TBA asif@cs.yorku.ca (416) 736-2100 X70128
COSC 3213: Communication Networks
 COSC 3213: Communication Networks Course Instructor: Marvin Mandelbaum Contact Information: Instructor: Section E Teaching Assistant: Office: CSE 3012 TBA mandel@cse.yorku.ca (416) 736-2100 X40630 URL:
COSC 3213: Communication Networks Course Instructor: Marvin Mandelbaum Contact Information: Instructor: Section E Teaching Assistant: Office: CSE 3012 TBA mandel@cse.yorku.ca (416) 736-2100 X40630 URL:
Chapter 1 Introduction. COSC 3213 Summer 2003
 Chapter 1 Introduction COSC 3213 Summer 2003 5/7/2003 Course Objectives Introduce communication networks and understand how different components work including the underlying technology including hardware
Chapter 1 Introduction COSC 3213 Summer 2003 5/7/2003 Course Objectives Introduce communication networks and understand how different components work including the underlying technology including hardware
Introduction. Computer Networks: Introduction 1
 Introduction Computer Networks: Introduction 1 Network Definitions and Classification Preliminary definitions and network terminology Sample application paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology
Introduction Computer Networks: Introduction 1 Network Definitions and Classification Preliminary definitions and network terminology Sample application paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology
Introduction. Computer Networks Term B10
 Introduction Computer Networks Term B10 Introduction Outline Preliminary Definitions Internet Components Network Application Paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology by size/scale by topology
Introduction Computer Networks Term B10 Introduction Outline Preliminary Definitions Internet Components Network Application Paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology by size/scale by topology
Communication Networks - 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols
 Communication Networks - Overview CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 7 September 2011 Course Content 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital communications
Communication Networks - Overview CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 7 September 2011 Course Content 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital communications
Introduction to CSE 3213
 Introduction to CSE 3213 CSE 3213 Fall 2007 12:15 PM 1 Course Contents 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital it communications including
Introduction to CSE 3213 CSE 3213 Fall 2007 12:15 PM 1 Course Contents 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital it communications including
L1: Introduction to Communication Networks (Telegraph & Telephone) Outline
 EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L1: Introduction to Communication Networks (Telegraph & ) Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Course texts, mark breakdown, topics Telegraph A connectionless message-switching
EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L1: Introduction to Communication Networks (Telegraph & ) Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Course texts, mark breakdown, topics Telegraph A connectionless message-switching
CS4514 Computer Networks
 CS4514 Computer Networks Term B07 Professor Bob Kinicki Networks: Introduction 1 Course Objectives Networks: Introduction 2 Course Objectives 1. To develop an understanding of modern network architectures
CS4514 Computer Networks Term B07 Professor Bob Kinicki Networks: Introduction 1 Course Objectives Networks: Introduction 2 Course Objectives 1. To develop an understanding of modern network architectures
Overview of Networks
 CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
TCOM 370 NOTES 99-1 NETWORKING AND COMMUNICATIONS
 TCOM 370 NOTES 99-1 NETWORKING AND COMMUNICATIONS Communication Networks Allow Exchange of Information between Users telephone network for voice communication interconnected computers and peripherals,
TCOM 370 NOTES 99-1 NETWORKING AND COMMUNICATIONS Communication Networks Allow Exchange of Information between Users telephone network for voice communication interconnected computers and peripherals,
L1: Introduction to Communication Networks. Outline
 SC/CSE 3213 Winter 2014 L1: Introduction to Communication Networks Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Course texts, mark breakdown, topics Telegraph A connectionless message-switching network
SC/CSE 3213 Winter 2014 L1: Introduction to Communication Networks Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Course texts, mark breakdown, topics Telegraph A connectionless message-switching network
L2: Introduction to Communication Networks: Internet. Outline
 EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L2: Introduction to Communication Networks: Internet Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline ARPANET A connectionless datagram network Internet A connectionless/connection-oriented
EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L2: Introduction to Communication Networks: Internet Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline ARPANET A connectionless datagram network Internet A connectionless/connection-oriented
Internet A Brief Tutorial. Jean Walrand EECS U.C. Berkeley
 Internet A Brief Tutorial Jean Walrand EECS U.C. Berkeley Contents History Key Ideas Protocols Technology Research History 1962 L. Kleinrock proposes Packet Switching 1966 L. Roberts proposes architecture
Internet A Brief Tutorial Jean Walrand EECS U.C. Berkeley Contents History Key Ideas Protocols Technology Research History 1962 L. Kleinrock proposes Packet Switching 1966 L. Roberts proposes architecture
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications. Communication and Networks. What will we learn?
 Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
Session 1. Introduction to Communication Networks
 Session 1. Introduction to Communication Networks Networks 1 Network Services The Traditional Networks Postal mail Water supply networks Electricity power networks Transportation networks Cable and television
Session 1. Introduction to Communication Networks Networks 1 Network Services The Traditional Networks Postal mail Water supply networks Electricity power networks Transportation networks Cable and television
Lecture 2: Internet Structure
 Lecture 2: Internet Structure COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Lecture 2: Internet Structure COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Outline: Connecting Many Computers
 Outline: Connecting Many Computers Last lecture: sending data between two computers This lecture: link-level network protocols (from last lecture) sending data among many computers 1 Review: A simple point-to-point
Outline: Connecting Many Computers Last lecture: sending data between two computers This lecture: link-level network protocols (from last lecture) sending data among many computers 1 Review: A simple point-to-point
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Part I: Introduction. 1: Introduction 1
 Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks. Jean Walrand
 EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks Jean Walrand www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~wlr Fall 2002 Course Information Instructor: Jean Walrand n Office Hours: M-Tu 1:00-2:00 Time/Place: MW 2:00-3:30 in 285 Cory
EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks Jean Walrand www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~wlr Fall 2002 Course Information Instructor: Jean Walrand n Office Hours: M-Tu 1:00-2:00 Time/Place: MW 2:00-3:30 in 285 Cory
CSE3213 Computer Network I
 CSE3213 Computer Network I Introduction Course page: http://www.cse.yorku.ca/course/3213 1 Course Contents 3 general areas: data communications, networking, and protocols 1. Data communications: basic
CSE3213 Computer Network I Introduction Course page: http://www.cse.yorku.ca/course/3213 1 Course Contents 3 general areas: data communications, networking, and protocols 1. Data communications: basic
COMPONENTS OF DATA COMMUNICATION
 COMPONENTS OF DATA COMMUNICATION ANALOG AND DIGITAL TRANSMISSION An analog signal is one that is continuous with respect to time and may take on any value within a given range of values. Eg Human voice.
COMPONENTS OF DATA COMMUNICATION ANALOG AND DIGITAL TRANSMISSION An analog signal is one that is continuous with respect to time and may take on any value within a given range of values. Eg Human voice.
DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS
 DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS A/L Guide TERAN SUBASINGHE Data Communication What is data communication? Data Communication is a process of exchanging data or information between two or more devices along
DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS A/L Guide TERAN SUBASINGHE Data Communication What is data communication? Data Communication is a process of exchanging data or information between two or more devices along
# DEFINITIONS TERMS. 5) A set of devices interconnected by media links. Network
 CHAPTER 21 INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) Information that is stored in digital form. Information that has been processed, organized and stored. Data 2) Knowledge
CHAPTER 21 INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) Information that is stored in digital form. Information that has been processed, organized and stored. Data 2) Knowledge
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION TELECOMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM COMPONENTS 1/28/2015. Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com
 INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
Computer Communication Networks
 Contents ELL 785 Computer Communication Networks Introduction Lecture 1 Taxonomy of communication works Computer Communication Networks Building a work ed work architecture 1-1 Introduction PC server wireless
Contents ELL 785 Computer Communication Networks Introduction Lecture 1 Taxonomy of communication works Computer Communication Networks Building a work ed work architecture 1-1 Introduction PC server wireless
Networking Applications
 Networking Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport 1 Outline Internet Layers Internet Data Packet transmission
Networking Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid College of Computing and Information Technology Arab Academy for Science & Technology and Maritime Transport 1 Outline Internet Layers Internet Data Packet transmission
ELC 537 Communication Networks
 Modern Academy for Engineering and Technology Electronics Engineering and Communication Technology Dpt. ELC 537 Communication Networks Prepared by: Dr. Nelly Muhammad Hussein Sections & Objectives Principles
Modern Academy for Engineering and Technology Electronics Engineering and Communication Technology Dpt. ELC 537 Communication Networks Prepared by: Dr. Nelly Muhammad Hussein Sections & Objectives Principles
Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network
 Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network Elements of Communication Communicating the Messages Continuous stream of bits 00101010100101010101010101010101010 I have to wait Single communications (e.g. video,
Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network Elements of Communication Communicating the Messages Continuous stream of bits 00101010100101010101010101010101010 I have to wait Single communications (e.g. video,
Raj Jain. The Ohio State University Columbus, OH
 Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@CIS.Ohio-State.Edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 3-1 Overview ISO/OSI Reference Model TCP/IP Reference Model Differences between ISO and TCP Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 LANs Interconnecting
Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@CIS.Ohio-State.Edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 3-1 Overview ISO/OSI Reference Model TCP/IP Reference Model Differences between ISO and TCP Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 LANs Interconnecting
A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet. A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet Overview
 CPSC 852 Intering A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu http://www.cs.clemson.edu/~mweigle/courses/cpsc852 1 A
CPSC 852 Intering A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu http://www.cs.clemson.edu/~mweigle/courses/cpsc852 1 A
Computer Networks. Computer Networks. Telecommunication Links. CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Spring Chapter 12: Computer Networks 1
 Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Layering in Networked computing. OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer
 Layering in Networked computing OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer Learning outcomes Understand the need of layering in Networked computing Understand the OSI model and the tcp/ip model Understand
Layering in Networked computing OSI Model TCP/IP Model Protocols at each layer Learning outcomes Understand the need of layering in Networked computing Understand the OSI model and the tcp/ip model Understand
Session 3 Networks I
 15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 3 Networks I Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas, Stuart Madnick Acknowledgments: Slides marked SM are adapted from Stuart Madnick, MIT. Slides
15.561 Information Technology Essentials Session 3 Networks I Copyright 2005 Thomas Malone, Chris Dellarocas, Stuart Madnick Acknowledgments: Slides marked SM are adapted from Stuart Madnick, MIT. Slides
Chapter 2 - Part 1. The TCP/IP Protocol: The Language of the Internet
 Chapter 2 - Part 1 The TCP/IP Protocol: The Language of the Internet Protocols A protocol is a language or set of rules that two or more computers use to communicate 2 Protocol Analogy: Phone Call Parties
Chapter 2 - Part 1 The TCP/IP Protocol: The Language of the Internet Protocols A protocol is a language or set of rules that two or more computers use to communicate 2 Protocol Analogy: Phone Call Parties
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering. Spring 2018
 ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Networking Introduction Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Computer Networking A background of important areas
ECE 650 Systems Programming & Engineering Spring 2018 Networking Introduction Tyler Bletsch Duke University Slides are adapted from Brian Rogers (Duke) Computer Networking A background of important areas
Introduction to computer networking
 edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
Communicating over the Network
 Communicating over the Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Version 4.0 1 Network Structure The elements of communication 3 common elements of communication Message source people/electronic devices need
Communicating over the Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Version 4.0 1 Network Structure The elements of communication 3 common elements of communication Message source people/electronic devices need
IP Packet Switching. Goals of Todayʼs Lecture. Simple Network: Nodes and a Link. Connectivity Links and nodes Circuit switching Packet switching
 IP Packet Switching CS 375: Computer Networks Dr. Thomas C. Bressoud Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Connectivity Links and nodes Circuit switching Packet switching IP service model Best-effort packet delivery
IP Packet Switching CS 375: Computer Networks Dr. Thomas C. Bressoud Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Connectivity Links and nodes Circuit switching Packet switching IP service model Best-effort packet delivery
Data Communication. Introduction of Communication. Data Communication. Elements of Data Communication (Communication Model)
 Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Computer Networks
 15-441 Computer s Lecture 3 Professor Hui Zhang Wean Hall 7126 hzhang@cs.cmu.edu 1 Review of Lecture 1 How long does it take to move 1GB data from campus to your home? 56Kbps modem 2Mbps DSL Other possibilities?
15-441 Computer s Lecture 3 Professor Hui Zhang Wean Hall 7126 hzhang@cs.cmu.edu 1 Review of Lecture 1 How long does it take to move 1GB data from campus to your home? 56Kbps modem 2Mbps DSL Other possibilities?
6 Computer Networks 6.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
6 Computer Networks 6.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
Objectives. Learn how computers are connected. Become familiar with different types of transmission media
 Objectives Learn how computers are connected Become familiar with different types of transmission media Learn the differences between guided and unguided media Learn how protocols enable networking 2 Objectives
Objectives Learn how computers are connected Become familiar with different types of transmission media Learn the differences between guided and unguided media Learn how protocols enable networking 2 Objectives
Digital Communication Networks
 Digital Communication Networks MIT PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE, 6.20s July 25-29, 2005 Professor Muriel Medard, MIT Professor, MIT Slide 1 Digital Communication Networks Introduction Slide 2 Course syllabus
Digital Communication Networks MIT PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE, 6.20s July 25-29, 2005 Professor Muriel Medard, MIT Professor, MIT Slide 1 Digital Communication Networks Introduction Slide 2 Course syllabus
The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Integrating Information Systems: Technology, Strategy, and Organizational Factors
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SLOAN SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT 15.565 Integrating Information Systems: Technology, Strategy, and Organizational Factors 15.578 Global Information Systems: Communications
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SLOAN SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT 15.565 Integrating Information Systems: Technology, Strategy, and Organizational Factors 15.578 Global Information Systems: Communications
Chapter 2 Network Architectures A global view
 Chapter 2 Architectures A global view Professor Dongning uo Architecture Architecture, n. 2a: formation or construction as or as if as the result of conscious act, 2b: a unifying or coherent form or structure.
Chapter 2 Architectures A global view Professor Dongning uo Architecture Architecture, n. 2a: formation or construction as or as if as the result of conscious act, 2b: a unifying or coherent form or structure.
precise rules that govern communication between two parties TCP/IP: the basic Internet protocols IP: Internet protocol (bottom level)
 Protocols precise rules that govern communication between two parties TCP/IP: the basic Internet protocols IP: Internet protocol (bottom level) all packets shipped from network to network as IP packets
Protocols precise rules that govern communication between two parties TCP/IP: the basic Internet protocols IP: Internet protocol (bottom level) all packets shipped from network to network as IP packets
Designing the Future Internet
 Designing the Future Internet Dr. Arjan Durresi Computer Science Department Louisiana State University durresi@acm.org Designing the Future Internet - 1 Overview Short history of Communications Evolution
Designing the Future Internet Dr. Arjan Durresi Computer Science Department Louisiana State University durresi@acm.org Designing the Future Internet - 1 Overview Short history of Communications Evolution
VoIP Dictionary, Glossary and Terminology
 VoIP Dictionary, Glossary and Terminology The following provides a glossary of terms and definitions that are commonly used in VoIP Solutions. We hope this will provide a good reference for you during
VoIP Dictionary, Glossary and Terminology The following provides a glossary of terms and definitions that are commonly used in VoIP Solutions. We hope this will provide a good reference for you during
Internet Architecture & Performance. What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view
 Internet Architecture & Performance Internet, Connection, Protocols, Performance measurements What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end systems pc s workstations,
Internet Architecture & Performance Internet, Connection, Protocols, Performance measurements What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end systems pc s workstations,
Networks 15.2 Multiplexing Technologies Access Networks 15.5 Common Peripheral Interfaces
 Chapter 15 Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.11 Basics of Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.2 Multiplexing Technologies 15.3 LAN and WAN 15.4 Access Networks 15.5 Common Peripheral Interfaces 15.6
Chapter 15 Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.11 Basics of Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.2 Multiplexing Technologies 15.3 LAN and WAN 15.4 Access Networks 15.5 Common Peripheral Interfaces 15.6
Networking. Networking and Communication Trends Convergence (Accessibility) Speed Stability Simplicity* Embeddedness
 Networking and Communication Trends Convergence (Accessibility) Speed Stability Simplicity* Embeddedness What is a Computer Network General definition Related hardware Network Interface Card Network Operating
Networking and Communication Trends Convergence (Accessibility) Speed Stability Simplicity* Embeddedness What is a Computer Network General definition Related hardware Network Interface Card Network Operating
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks
 EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 2 Wenbing Zhao wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Misc. Interested in research? Secure
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 2 Wenbing Zhao wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Misc. Interested in research? Secure
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies. Networks
 ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
Communication Networks
 Communication Networks Nicholas Honeth (nicholash@ics.kth.se) Contents of the series Lecture 10 - Recap of the networks we ve seen so far - OSI model - Circuit and packet switching - Physical media Lecture
Communication Networks Nicholas Honeth (nicholash@ics.kth.se) Contents of the series Lecture 10 - Recap of the networks we ve seen so far - OSI model - Circuit and packet switching - Physical media Lecture
Applications/Design. Example. Locating Resource. End-to-end. Connection UCB. Applications EECS 122
 /Design Web Browsing Web Browsing Telephone Call Multiplexing Protocols IETF Summary Example Locating Resource: DNS Connection End-to-end Packets Bits Points to remember TOC TOC Web Browsing Example Click
/Design Web Browsing Web Browsing Telephone Call Multiplexing Protocols IETF Summary Example Locating Resource: DNS Connection End-to-end Packets Bits Points to remember TOC TOC Web Browsing Example Click
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Applications
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based s 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve complex procedures better if task broken into subtasks
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based s 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve complex procedures better if task broken into subtasks
Introduction to Networking
 Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
INTRODUCTION TO ICT.
 INTRODUCTION TO ICT. (Introducing Basic Network Concepts) Lecture # 24-25 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1 INTRODUCTION TO
INTRODUCTION TO ICT. (Introducing Basic Network Concepts) Lecture # 24-25 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1 INTRODUCTION TO
Data Networks. Lecture 1: Introduction. September 4, 2008
 Data Networks Lecture 1: Introduction September 4, 2008 Slide 1 Learning Objectives Fundamental aspects of network Design and Analysis: Architecture: layering, topology design, switching mechanisms Protocols:
Data Networks Lecture 1: Introduction September 4, 2008 Slide 1 Learning Objectives Fundamental aspects of network Design and Analysis: Architecture: layering, topology design, switching mechanisms Protocols:
Network Architecture
 Unit 7 Network Architecture Acknowledgments: These slides were originally developed by Prof. Jean Walrand for EE122. The past and current EE122 instructors including Kevin Fall, Abhay Parekh, Shyam Parekh,
Unit 7 Network Architecture Acknowledgments: These slides were originally developed by Prof. Jean Walrand for EE122. The past and current EE122 instructors including Kevin Fall, Abhay Parekh, Shyam Parekh,
CS1302 / Computer Networks
 CS1302 / Computer Networks Year/Sem : III/VI UNIT I- DATA COMMUNICATIONS 1. Define Data communication 2. List out the characteristics of data communication 3. What are the components of data communication?
CS1302 / Computer Networks Year/Sem : III/VI UNIT I- DATA COMMUNICATIONS 1. Define Data communication 2. List out the characteristics of data communication 3. What are the components of data communication?
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 37 Networks. No Machine is an Island!
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 37 Networks April 24, 2006 John Wawrzynek Page 1 No Machine is an Island! Computer Processor (active) Control ( brain ) Datapath ( brawn ) Memory (passive) (where programs,
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 37 Networks April 24, 2006 John Wawrzynek Page 1 No Machine is an Island! Computer Processor (active) Control ( brain ) Datapath ( brawn ) Memory (passive) (where programs,
Computer Network Fundamentals (IT 221)
 Computer Network Fundamentals (IT 221) أساسيات شبكات الحاسب Business Applications: Lecture 1: Computer network: collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. Goals: sharing
Computer Network Fundamentals (IT 221) أساسيات شبكات الحاسب Business Applications: Lecture 1: Computer network: collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. Goals: sharing
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks
 Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Module 2 Overview of. Computer Networks
 Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Reti di Calcolatori I
 Reti di Calcolatori I Prof. Roberto Canonico Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e delle Tecnologie dell Informazione Corso di Laurea in Ingegneria delle Telecomunicazioni Corso di Laurea in Ingegneria
Reti di Calcolatori I Prof. Roberto Canonico Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e delle Tecnologie dell Informazione Corso di Laurea in Ingegneria delle Telecomunicazioni Corso di Laurea in Ingegneria
Area Covered is small Area covered is large. Data transfer rate is high Data transfer rate is low
 Chapter 15 Networking Concepts 1. Define networking. It is the interconnection of independent computing devices for sharing of information over shared medium. 2. What is the need for networking? / What
Chapter 15 Networking Concepts 1. Define networking. It is the interconnection of independent computing devices for sharing of information over shared medium. 2. What is the need for networking? / What
COMMUNICATION NETWORK EVOLUTION OF NETWORK ARCHITECTURE AND SERVICES
 COMMUNICATION NETWORK A communication network, consists of a set of equipment and facilities that provide a service, the transfer of information between users located at various geographical points. For
COMMUNICATION NETWORK A communication network, consists of a set of equipment and facilities that provide a service, the transfer of information between users located at various geographical points. For
APPENDIX F THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE
 APPENDIX F THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE William Stallings F.1 TCP/IP LAYERS... 2 F.2 TCP AND UDP... 4 F.3 OPERATION OF TCP/IP... 6 F.4 TCP/IP APPLICATIONS... 10 Copyright 2014 Supplement to Computer
APPENDIX F THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE William Stallings F.1 TCP/IP LAYERS... 2 F.2 TCP AND UDP... 4 F.3 OPERATION OF TCP/IP... 6 F.4 TCP/IP APPLICATIONS... 10 Copyright 2014 Supplement to Computer
end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core
 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Network Architecture. TOC Architecture
 Network Architecture Introduction Layering Example Internet Layers First Look Layering Step by Step Downside of Layering Interconnecting Networks The Internet TOC Architecture Introduction Issues: Inter-operability
Network Architecture Introduction Layering Example Internet Layers First Look Layering Step by Step Downside of Layering Interconnecting Networks The Internet TOC Architecture Introduction Issues: Inter-operability
Chapter 15 Networks. Chapter Goals. Networking. Chapter Goals. Networking. Networking. Computer network. Node (host) Any device on a network
 Chapter Goals Chapter 15 Networks Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
Chapter Goals Chapter 15 Networks Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
Computer Networks and the internet. Daniel Graham Ph.D
 Computer Networks and the internet Daniel Graham Ph.D 1.1 What Is the Internet? The Internet is a computer network that interconnects hundreds of millions of computing devices throughout the world. As
Computer Networks and the internet Daniel Graham Ph.D 1.1 What Is the Internet? The Internet is a computer network that interconnects hundreds of millions of computing devices throughout the world. As
Access to the Web. Coverage. Basic Communication Technology. CMPT 165: Review
 Access to the Web CMPT 165: Review Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University December 5, 2011 Access to the Web requires: a computer (of some kind) a connection
Access to the Web CMPT 165: Review Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University December 5, 2011 Access to the Web requires: a computer (of some kind) a connection
Computer Communication & Networks / Data Communication & Computer Networks Week # 03
 Computer Communication & Networks / Data Communication & Computer Networks Week # 03 M.Nadeem Akhtar CS & IT Department The University of Lahore Email: nadeem.akhtar@cs.uol.edu.pk URL-https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemuolcsccn/home
Computer Communication & Networks / Data Communication & Computer Networks Week # 03 M.Nadeem Akhtar CS & IT Department The University of Lahore Email: nadeem.akhtar@cs.uol.edu.pk URL-https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemuolcsccn/home
CSE 3461 / 5461: Computer Networking & Internet Technologies
 CSE 3461 / 5461: Computer Networking & Internet Technologies Instructor: Prof. Kannan Srinivasan The fundamental problem of communication is that of reproducing at one point either exactly or approximately
CSE 3461 / 5461: Computer Networking & Internet Technologies Instructor: Prof. Kannan Srinivasan The fundamental problem of communication is that of reproducing at one point either exactly or approximately
Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Modified by Tony Chen 05/20/2008
 Communicating Over the Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Modified by Tony Chen 05/20/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Drippy Sweet Pancakes
Communicating Over the Network Network Fundamentals Chapter 2 Modified by Tony Chen 05/20/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Drippy Sweet Pancakes
Part 1: Introduction. Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview
 Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
 1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
Data & Computer Communication
 Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
Computer Networks Medium Access Control. Mostafa Salehi Fall 2008
 Computer Networks Medium Access Control Mostafa Salehi Fall 2008 2008 1 Outline Issues ALOHA Network Ethernet Token Ring Wireless 2 Main Issues Local Area Network (LAN) : Three or more machines are physically
Computer Networks Medium Access Control Mostafa Salehi Fall 2008 2008 1 Outline Issues ALOHA Network Ethernet Token Ring Wireless 2 Main Issues Local Area Network (LAN) : Three or more machines are physically
Chapter 12. Network Organization and Architecture
 Chapter 12 Network Organization and Architecture Chapter 12 Objectives Learn the basic physical components of networks. Become familiar with routing protocols. 2 Computer networks are often classified
Chapter 12 Network Organization and Architecture Chapter 12 Objectives Learn the basic physical components of networks. Become familiar with routing protocols. 2 Computer networks are often classified
Next Steps Spring 2011 Lecture #18. Multi-hop Networks. Network Reliability. Have: digital point-to-point. Want: many interconnected points
 Next Steps Have: digital point-to-point We ve worked on link signaling, reliability, sharing Want: many interconnected points 6.02 Spring 2011 Lecture #18 multi-hop networks: design criteria network topologies
Next Steps Have: digital point-to-point We ve worked on link signaling, reliability, sharing Want: many interconnected points 6.02 Spring 2011 Lecture #18 multi-hop networks: design criteria network topologies
This PDF document is a sample chapter from the book...
 This PDF document is a sample chapter from the book... To order this book, print the last page of this document. Copyright 2001 Society of Manufacturing Engineers Chapter 37 Manufacturing Networks 37.1
This PDF document is a sample chapter from the book... To order this book, print the last page of this document. Copyright 2001 Society of Manufacturing Engineers Chapter 37 Manufacturing Networks 37.1
Announcements. TAs office hours: Mohamed Grissa: Mohamed Alkalbani:
 Announcements TAs office hours: Mohamed Grissa: grissam@oregonstate.edu Tuesday: 4-5 Friday: 11-12 Mohamed Alkalbani: alkalbmo@oregonstate.edu Wednesday: 11-12 Thursday: 11-12 Lecture slides: Will be posted
Announcements TAs office hours: Mohamed Grissa: grissam@oregonstate.edu Tuesday: 4-5 Friday: 11-12 Mohamed Alkalbani: alkalbmo@oregonstate.edu Wednesday: 11-12 Thursday: 11-12 Lecture slides: Will be posted
CMSC 611: Advanced. Interconnection Networks
 CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Interconnection Networks Interconnection Networks Massively parallel processor networks (MPP) Thousands of nodes Short distance (
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Interconnection Networks Interconnection Networks Massively parallel processor networks (MPP) Thousands of nodes Short distance (
PART X. Internetworking Part 1. (Concept, IP Addressing, IP Routing, IP Datagrams, Address Resolution)
 PART X Internetworking Part 1 (Concept, IP Addressing, IP Routing, IP Datagrams, Address Resolution) CS422 Part 10 1 Spring 1999 Motivation For Internetworking LANs Low cost Limited distance WANs High
PART X Internetworking Part 1 (Concept, IP Addressing, IP Routing, IP Datagrams, Address Resolution) CS422 Part 10 1 Spring 1999 Motivation For Internetworking LANs Low cost Limited distance WANs High
Computer Networks and the Internet. CMPS 4750/6750: Computer Networks
 Computer Networks and the Inter CMPS 4750/6750: Computer Networks Outline What Is the Inter? Access Networks Packet Switching and Circuit Switching A closer look at delay, loss, and throughput Interconnection
Computer Networks and the Inter CMPS 4750/6750: Computer Networks Outline What Is the Inter? Access Networks Packet Switching and Circuit Switching A closer look at delay, loss, and throughput Interconnection
5105: BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARMPALLI UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS AND LINK LAYER PART A
 5105: BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARMPALLI 635 854. NAME OF THE STAFF : R.ANBARASAN DESIGNATION & DEPARTMENT : AP/CSE SUBJECT CODE : CS 6551 SUBJECT NAME : COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS
5105: BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARMPALLI 635 854. NAME OF THE STAFF : R.ANBARASAN DESIGNATION & DEPARTMENT : AP/CSE SUBJECT CODE : CS 6551 SUBJECT NAME : COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS By Syed Bakhtawar Shah Abid Lecturer in Computer Science 1 Public Switched Telephone Network Structure The Local Loop Trunks and Multiplexing Switching 2 Network Structure Minimize
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS By Syed Bakhtawar Shah Abid Lecturer in Computer Science 1 Public Switched Telephone Network Structure The Local Loop Trunks and Multiplexing Switching 2 Network Structure Minimize
Networking interview questions
 Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Local Area Networks (LANs): Packets, Frames and Technologies Gail Hopkins. Part 3: Packet Switching and. Network Technologies.
 Part 3: Packet Switching and Gail Hopkins Local Area Networks (LANs): Packets, Frames and Technologies Gail Hopkins Introduction Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching LANs and shared media Star, bus and
Part 3: Packet Switching and Gail Hopkins Local Area Networks (LANs): Packets, Frames and Technologies Gail Hopkins Introduction Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching LANs and shared media Star, bus and
