Survey on Location Based Routing Protocols in MANET
|
|
|
- Reynard Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Survey on Location Based Routing Protocols in MANET Vivek Nikam, Prof. G.T. Chavan Sinhgad College of engineering, University of Pune Abstract- Due to the infrastructure less and dynamic nature of mobile ad hoc networks it becomes challenging to establish and maintain a connection between two end points. Therefore designing a routing protocol for MANET is now became a broad area of research. While establishing and maintaining a end to end connection or route in a MANET many routing parameters like routing overhead, end to end delay, packet delivery fraction can get affected. So the routing protocols are designed in such a way that optimizing these parameters. In routing protocols like AODV, DSR etc. routing overhead is a big concern as route request floods in all direction in these protocols. In location based routing, the nodes location information is used to route the packets. In LAR the route request is forwarded in the direction of destination node. This selective flooding reduces the routing overhead in the network. This paper gives the study and comparison of some location based routing protocols. Keywords: MANET, LAR, Routing parameters. I. INTRODUCTION Mobile ad hoc network is a self configuring dynamic network in which any node can leave or join the network at any time. Due to these features routing in MANET became a big challenge. Any node which is part of communication link may move away so the connection may break down. In this condition many times network has to re-establish the connection. To establish a connection between two end points, the routing path has to be found out between these two points. This task is done by routing protocols. There are many routing protocols like AODV, DSDV, DSR are available. The major drawback of these protocols is routing overhead. It is the total number of packets or messages sent over a network to establish a path between end points. In these protocols the routing packets are sent or flooded in all directions. Location based routing protocols are specially designed for reduction of routing overhead. In location based routing protocols the flooding area of routing messages is reduced by using location information of destination node. That area of flooding is called as request zone. They also work well in packet delivery fraction and end to end delay. But there are many problems to it as location estimation, holes in request zone etc. To get location information is a very critical problem in MANET because there are some limitations on using GPS. We can t use GPS to get location information of nodes within the MANET in some cases. For indoor network GPS can t be used because there is a problem of GPS range inside the houses or offices. For smaller wireless devices or sensor node it is difficult to install GPS hardware and antenna over it. GPS is very expensive for such small devices or networks. In standard GPS there is location error up to meters. For MANET such error can t be tolerated. If MANET is highly dense, that means nodes are very close to each other within network then GPS can t be used in such cases [9][10]. II. STUDY OF LOCATION BASED ROUTING PROTOCOLS A. Location Aided Routing One of geographical-based routing protocol is locationaided routing (LAR). The main objective of LAR is to limit flooding of routing request packets in a small group of nodes which belong to a request zone. Compared with other routing protocols such as AODV or DSR, in which routing packets are flooded throughout the network, LAR saves considerable bandwidth and leaves those mobile nodes that are not between the source and destination untouched. The area of network in which current location of destination is expected to be is known as expected zone and the area through which request packet has to travel is called as request zone. By using location information, the Location-Aided Routing (LAR) protocols limit the search for a new route to a smaller request zone of the ad hoc network. This results in a significant reduction in the number of routing messages. There are two schemes which decide the request zone in LAR. To construct the request zone, the expected zone of the destination needs to be obtained first. Suppose both the average speed (say v) and the location of the destination at time t0 (say L) are known to the source, the expected zone of the destination at time t1 is the circle with center at L and radius of v(t1 - t0). Two different schemes are brought to construct the request zone: (1) a rectangular request zone which contains the location of source and the expected zone of the destination; or (2) the group of the nodes closer to the destination than the source. Variations to request zone As shown in figure 1 it is alternative definition to the request zone in LAR scheme1. In this figure it is seen that request zone includes only expected zone circle. But in LAR scheme1 it considers the whole rectangle containing source node coordinates as one end of diagonal of rectangle
2 and other end encompassing expected zone. In figure 1, rectangular request zone shown is the request zone considered in LAR scheme1. If we compare these two request zones then it can be seen that the area of alternative request zone is less than rectangular request zone in LAR scheme1. That means the routing overhead in alternative request zone is less than the rectangular request zone. Fig 1 Alternative definitions of request zone for LAR scheme 1 [5]. As shown in figure 2 it is alternative definition to the request zone in LAR scheme2. In this figure it is seen that request zone (outer circle) includes expected zone circle and source node on the circle of request zone. But in LAR scheme2 it considers the whole circle containing source node coordinates as on it and encompassing expected zone as request zone. In figure 2 initial circular request zone shown is the request zone considered in LAR scheme2. But in alternative request zone the request zone is adaptively considered. That means when request comes to inner node I then to forward request by I it considers the request zone calculated by node I that means inner circle shown in figure 2. That means request zone adaptively changing while request is moving towards destination. Also the area of request zones is going decreasing. If we compare these two request zones then it can be seen that the area of alternative request zone is less than initial request zone in LAR scheme2. That means the routing overhead in alternative request zone is less than the initial request zone. Fig 2 Alternative definitions of request zone for LAR scheme 2 [5]. B. IHLAR In reactive routing end-to-end delay is more because of the route discovery phase for long path takes much of time. In this IHLAR protocol, reactive protocol AODV is integrated with a geographic protocol. For long path geographical routing works better. Topology-based routing usually finds the shortest path, in number of hops. So the path length of hybrid protocol is correspondingly shorter than geographic protocol. This IHLAR protocol integrates two type of routing schemes as follows. a. Topology-based routing (Intra-Zone-Routing) In this algorithm, each node maintains a table of neighbors within specified numbers of hops (ρ-radius). Using this information zone is formed. When a source node or a forwarding node wants to send or forward a packet to a destination node, then first of all it checks whether the node is in the table. If the destination node resides within zone of the source node or the intermediate node, then the node will route the packet using AODV protocol, as shown in Fig. 3. If source node S wants to send a packet to D1, D1 is within the zone, then AODV is used to route the packet. For highly mobile networks it s better to keep zone radius shorter because for high mobility topology based routing does not work well. [1] Fig.3 Routing in IHLAR [1] b. Geographical routing (Inter-Zone-Routing) If the destination node is not within the zone of source node then the greedy forwarding is used. It means that the next node is geographically closer to the current node. As shown in Fig.4 S needs to communicate with D2, but D2 is out of the zone. Thus S forwards packet to the closest node towards to the destination until packet reaches to the zone of destination. Once it reached to the zone of destination then topology based routing is used to forward the packet. But packet may be stuck at a dead-end node during greedy forwarding. In this case no node is closer to the destination than the source node itself. In this situation, ARP is used in this case to detour around voids. In angular routing protocol, each node maintains a neighbor table containing location-information of its one hop nodes. Nodes send a packet, which includes its location and speed information, non-periodically at a rate proportional to their speeds. The angles of neighbors are calculated with respect to
3 destination position. When node encounters a void condition, then the node selects a neighboring node that makes minimum angle, among available neighbors as shown in fig 4. Here node A is a dead-end node, no neighbor node is closer to the destination than the node A. Then node N1 is selected as forwarder because it makes least angle with the destination. [1] C. ARZAODV Fig. 4 Node selection in void [1] In Adaptive Request Zone, request zones are based on the variation of distance between source node and destination node while both nodes are mobile. The request zones are adaptively chosen depending on the distance between source node and destination node and radius of expected zone as shown in the Fig 5 Fig 5 adaptive request zones in ARZAODV [2] As shown in fig 5, the area of 1,000 X 1,000 meters is considered. If distance between source node and destination node is larger than or equal to three fourth of the diagonal line (S->D4), the maximum of radius R4 =250 m is taken for calculating the expected zone and also increase the request zone respectively. If the distance between source node and destination node is larger than or equal to a half of the diagonal line (S->D3), the maximum of radius R3 =187.5 m is taken. If the distance between source node and destination node is larger than or equal to one fourth of the diagonal line (S->D2), the minimum of radius R2 = 125 m is taken. If source node and destination node locates very close like node S and node Dl, the minimum of radius Rl = 65 m will be taken. It divides the variation of the distance to adapt the radius of expected zone four parts based on the diagonal line. [2] D. LAROD LoDiS In this scheme geographical routing protocol LAROD integrated with a location service. a. LAROD LAROD is a geographical routing protocol that uses geographical routing with the store carry forward principle. It uses greedy packet forwarding when possible. To forward a message toward the destination, a custodian simply broadcasts the message. All nodes within a predefined forwarding area are eligible to forward the packet and are called tentative custodians. All tentative custodians set a delay timer td specific for each node, and the node whose delay timer expires first is the selected as new custodian. Upon becoming a custodian, the node forwards the message in the same manner as the previous custodian. The current custodian repeats the broadcast of the message until a new custodian becomes available due to node mobility. The rebroadcast time is randomly chosen for each transmission between two configured values. The values should be chosen so that forwarding opportunities are not missed as well as to avoid wasting bandwidth. It is possible that not all nodes in the forwarding area will overhear the broadcast made by the new custodian, thereby producing packet duplicates. This case will not only increase the load in the system but will enable the exploration of multiple paths to the destination as well. When the paths of two copies cross, only one copy will continue to be forwarded. To prevent a packet from indefinitely trying to find a path to its destination, all packets have a time to live expressed as duration. When the TTL expires, a packet is deleted by its custodian. [3] b. LoDiS In LoDiS, every node acts as a location server, and location data are updated by data exchange between nodes. The reason that all nodes are location servers is to avoid delaying the packet at the source node. If only a limited set of nodes were location servers, then the response time of location servers increases. Due to the disconnected nature of IC MANETs, this response may be long. But maintaining such information at every node should not increase a problem of memory and extra overhead. When the routing protocol requests a location from LoDiS, one thing that it should consider is that the location may be wrong, but if the provided location points the packet in the right direction, it should be best solution for the routing. To reduce the location error, the geographical routing protocol should update the location data in a packet for each node that the packet traverses. This approach is done by inquiring that node s local LoDiS server whether it has more accurate information about the destination. Because nodes closer to the destination should have better
4 information on the destination s location, the accuracy of the destination position is incrementally increased. [3] E. ALERT In this routing it is considered that network area is rectangle. Each node knows the bottom-right and upper left boundary of the network area. This information enables a node to locate the positions of nodes in the entire network for zone partitions in ALERT. ALERT features a dynamic and unpredictable routing path, which consists of a number of dynamically determined intermediate relay nodes. Fig. 6 Routing in ALERT [4] Fig. 6 shows an example of routing in ALERT. The shaded zone is the destination zone. Specifically, in the ALERT routing, each data source or forwarder executes the hierarchical zone partition process. First of all it checks whether source node itself and destination are in the same zone. If not so, it divides the zone alternatively in the horizontal and vertical directions. This process is repeated until source node itself and destination node are not in the same zone. It then randomly chooses a position in the other zone called temporary destination (TD), and uses the GPSR routing algorithm to send the data to the node closest to TD. This node is called as a random forwarder (RF). At the last step, the data are broadcasted to k nodes in destination zone ZD, providing k-anonymity to the destination. Given an S-D pair, the partition pattern in ALERT varies depending on the randomly selected TDs and the order of horizontal and vertical partitions, which provides a better anonymity protection. ALERT sets the partition in the alternative horizontal and vertical manner in order to ensure that a packet approaches D in each step. As GPSR, it assumes that the destination node will not move far away from its position during the data transmission, so it can successfully receive the data. In this design, the tradeoff is the anonymity protection degree and transmission delay. A larger number of hierarchies generate more routing hops, which increases anonymity degree but also increases the delay. To ensure the delivery of packets, the destination sends a confirmation to the source upon receiving the packets as acknowledgement. If the source has not received the ack during a predefined time period, it will resend the packets. [4] III. COMPARISION The comparison of location based routing protocols is done based on literature survey given in table 1. The given methods are compared based on routing overhead, end to end delay, packet delivery ratio and security provided in the protocol. In IHLAR use of topology-based routing and geographical routing for intrazone and inter-zone communication respectively results in reduced end to end delay. In ARZAODV due to the adaptive request zone, routing overhead is reduced to the great extent. LAROD-LoDiS gives a much higher delivery rate than topological routing. ALERT strengthens the anonymity protection of source and destination by hiding the data initiator/receiver among a number of data initiators/ receivers. IV. CONCLUSION From the study of these location based routing protocols it can be concluded that they works best for the routing overhead as nodes know their physical positions in a network. Also the packet delivery ratio is relatively high and as compared to pure reactive routing protocol end to end delay is also lower. Location based routing protocols works best in the case of given performance parameters if the location information is known. Getting updated location information is very critical task as there are limitations on using GPS in MANET. The routing overhead can be reduced to a great level if exact location of destination is known. Also the security can be provided in these protocols for their use for military purposes. Table1 Comparison of existing methods Protocol\Parameter Routing overhead End to end delay Packet delivery ratio Security Location based Proactive/Reactive ARZAODV Low Low High No Yes Reactive IHLAR High Low High No Partially Reactive LAROD-LoDiS Low High High No Yes Hybrid ALERT High Low High Yes Yes Reactive
5 REFERENCES [1]. Dan Luo,Jipeng Zhou An Improved Hybrid Location-Based Routing Protocol for Ad Hoc Networks 2011 IEEE. [2]. S. Thipchaksurat and P. Kirdpipat, Position-based routing protocol by reducing routing overhead with adaptive request zone for mobile ad hoc networks., ECTI Association of Thailand - Conference [3]. Erik Kuiper and Simin Nadjm-Tehrani, Geographical Routing With Location Service in Intermittently Connected MANETs. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 60, NO. 2, FEBRUARY [4]. Haiying Shen and Lianyu Zhao, ALERT: An Anonymous Location- Based Efficient Routing Protocol in MANETs IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTING, VOL. 12, NO. 6, JUNE 2013 [5]. Young-Bae Ko and Nitin H. Vaidya, Location-Aided Routing (LAR) in mobile ad hoc networks, Wireless Networks vol. 6, no. 4, pp , (2000) [6]. Putthiphong Kirdpipat, Sakchai Thipchaksurat, Impact of Mobility on Location-based Routing with Adaptive Request Zone in MANET IEEE. [7]. Tzay-Farn Shih Hsu-Chun Yen, Location-aware routing protocol with dynamic adaptation of request zone for mobile ad hoc networks, Springer Science Wireless Netw(2008). [8]. R. Plestys, R. Zakarevicius, Request and Response Zone Control for Routing in MANET th Biennial Baltic Electronics Conference (BEC2010). [9]. Kazuyuki Ishii, Naoshi Sato GPS-free host approaching in mobile ad-hoc networks Seventh International Conference on Innovative Mobile and Internet Services in Ubiquitous Computing. [10]. Kei Itoh, Hiroaki Higaki, Estimation of Ad-Hoc Network Topology Preserving Neighbor Relations among Nodes International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications. [11]. Farah Mourad, Hichem Snoussi, Interval-Based Localization using RSSI Comparison in MANET IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AEROSPACE AND ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS VOL. 47, NO. 4 OCTOBER
Location Awareness in Ad Hoc Wireless Mobile Neworks
 Location Awareness in Ad Hoc Wireless Mobile Neworks Lijuan Ai Wenyu Wang Yi Zhou 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing, Fall 2001 1 PART I INTRODUCTION TO MANET & LOCATION-AWARE COMPONENTS 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing,
Location Awareness in Ad Hoc Wireless Mobile Neworks Lijuan Ai Wenyu Wang Yi Zhou 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing, Fall 2001 1 PART I INTRODUCTION TO MANET & LOCATION-AWARE COMPONENTS 11/14/2001 Mobile Computing,
Energy Aware and Anonymous Location Based Efficient Routing Protocol
 Energy Aware and Anonymous Location Based Efficient Routing Protocol N.Nivethitha 1, G.Balaji 2 1 PG student, 2 Asst.Professor Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Angel College of Engineering
Energy Aware and Anonymous Location Based Efficient Routing Protocol N.Nivethitha 1, G.Balaji 2 1 PG student, 2 Asst.Professor Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Angel College of Engineering
Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
 International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
Location Oriented Networking
 Location Oriented Networking Daniel Alves University of California Santa Cruz dalves@ucsc.edu Suppose you want to send a message to everyone in this room Use location information on the network Message
Location Oriented Networking Daniel Alves University of California Santa Cruz dalves@ucsc.edu Suppose you want to send a message to everyone in this room Use location information on the network Message
Routing in Ad Hoc Wireless Networks PROF. MICHAEL TSAI / DR. KATE LIN 2014/05/14
 Routing in Ad Hoc Wireless Networks PROF. MICHAEL TSAI / DR. KATE LIN 2014/05/14 Routing Algorithms Link- State algorithm Each node maintains a view of the whole network topology Find the shortest path
Routing in Ad Hoc Wireless Networks PROF. MICHAEL TSAI / DR. KATE LIN 2014/05/14 Routing Algorithms Link- State algorithm Each node maintains a view of the whole network topology Find the shortest path
EZR: Enhanced Zone Based Routing In Manet
 EZR: Enhanced Zone Based Routing In Manet Bency Wilson 1, Geethu Bastian 2, Vinitha Ann Regi 3, Arun Soman 4 Department of Information Technology, Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology, Rajagiri
EZR: Enhanced Zone Based Routing In Manet Bency Wilson 1, Geethu Bastian 2, Vinitha Ann Regi 3, Arun Soman 4 Department of Information Technology, Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology, Rajagiri
Content. 1. Introduction. 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm. 3. Simulation and Results. 4. Future Work. 5.
 Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads
 Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads Aye Zarchi Minn 1, May Zin Oo 2, Mazliza Othman 3 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University, Myanmar
Analysis of GPS and Zone Based Vehicular Routing on Urban City Roads Aye Zarchi Minn 1, May Zin Oo 2, Mazliza Othman 3 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Mandalay Technological University, Myanmar
QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET
 2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET Ashwini V. Biradar
2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET Ashwini V. Biradar
Kapitel 5: Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Characteristics. Applications of Ad Hoc Networks. Wireless Communication. Wireless communication networks types
 Kapitel 5: Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Mobilkommunikation 2 WS 08/09 Wireless Communication Wireless communication networks types Infrastructure-based networks Infrastructureless networks Ad hoc networks Prof.
Kapitel 5: Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Mobilkommunikation 2 WS 08/09 Wireless Communication Wireless communication networks types Infrastructure-based networks Infrastructureless networks Ad hoc networks Prof.
A Survey - Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in MANET
 , pp. 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2016.9.5.16 A Survey - Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in MANET Jyoti Upadhyaya and Nitin Manjhi Department of Computer Science, RGPV University Shriram
, pp. 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2016.9.5.16 A Survey - Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in MANET Jyoti Upadhyaya and Nitin Manjhi Department of Computer Science, RGPV University Shriram
CLASSIFICATION OF ROUTING Routing. Fig.1 Types of routing
 Volume 5, Issue 5, MAY 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey on Unicast
Volume 5, Issue 5, MAY 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey on Unicast
Example of TORA operations. From last time, this was the DAG that was built. A was the source and X was the destination.
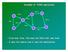 Example of TORA operations A Link 2 D Link 6 Y Link 1 Link 3 C Link 4 Link 8 B Link 5 E Link 7 X From last time, this was the DAG that was built. A was the source and X was the destination. Link 1 A B
Example of TORA operations A Link 2 D Link 6 Y Link 1 Link 3 C Link 4 Link 8 B Link 5 E Link 7 X From last time, this was the DAG that was built. A was the source and X was the destination. Link 1 A B
A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
 Journal homepage: www.mjret.in ISSN:2348-6953 A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Ms. Amruta Kodole 1, Prof. P. M. Agarkar 2 Computer Engineering Dr. D. Y. Patil School Of Engineering
Journal homepage: www.mjret.in ISSN:2348-6953 A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Ms. Amruta Kodole 1, Prof. P. M. Agarkar 2 Computer Engineering Dr. D. Y. Patil School Of Engineering
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. WI-7 Ad hoc networks. Wireless Internet Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione WI-7 Ad hoc networks Wireless Internet Prof. Antonio Capone Acknowlegments o This class notes are mostly based on the teaching material of:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione WI-7 Ad hoc networks Wireless Internet Prof. Antonio Capone Acknowlegments o This class notes are mostly based on the teaching material of:
Zone-based Proactive Source Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Networks
 2014 IJSRSET Volume i Issue i Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Science Zone-based Proactive Source Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Networks Dr.Sangheethaa.S 1, Dr. Arun Korath
2014 IJSRSET Volume i Issue i Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Science Zone-based Proactive Source Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Networks Dr.Sangheethaa.S 1, Dr. Arun Korath
Comparative Analysis of Throughput and Dropped rate for Location-Aided Routing Protocol
 Comparative Analysis of Throughput and Dropped rate for Location-Aided Routing Protocol Neelima Parsendia, Amit Sinhal Dept. of I.T., Technocrats Institute of Technology, Bhopal Abstract A wireless LAN
Comparative Analysis of Throughput and Dropped rate for Location-Aided Routing Protocol Neelima Parsendia, Amit Sinhal Dept. of I.T., Technocrats Institute of Technology, Bhopal Abstract A wireless LAN
A Location-based Directional Route Discovery (LDRD) Protocol in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks
 A Location-based Directional Route Discovery (LDRD) Protocol in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks Stephen S. Yau, Wei Gao, and Dazhi Huang Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State University Tempe,
A Location-based Directional Route Discovery (LDRD) Protocol in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks Stephen S. Yau, Wei Gao, and Dazhi Huang Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State University Tempe,
Vaibhav Jain 2, Pawan kumar 3 2,3 Assistant Professor, ECE Deptt. Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, India. Rohtak, India
 Volume 3, Issue 8, August 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Improved OLSR
Volume 3, Issue 8, August 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Improved OLSR
A COMPARISON OF IMPROVED AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL BASED ON IEEE AND IEEE
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 2 (2009) 132-141 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College A COMPARISON OF IMPROVED AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL BASED ON IEEE 802.11 AND IEEE
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 2 (2009) 132-141 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College A COMPARISON OF IMPROVED AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL BASED ON IEEE 802.11 AND IEEE
Middle in Forwarding Movement (MFM): An efficient greedy forwarding approach in location aided routing for MANET
 Middle in Forwarding Movement (MFM): An efficient greedy forwarding approach in location aided routing for MANET 1 Prashant Dixit* Department of CSE FET, Manavrachna international institute of research
Middle in Forwarding Movement (MFM): An efficient greedy forwarding approach in location aided routing for MANET 1 Prashant Dixit* Department of CSE FET, Manavrachna international institute of research
Performance Evaluation of DSDV, DSR AND ZRP Protocol in MANET
 Performance Evaluation of, AND Protocol in MANET Zaiba Ishrat IIMT Engg college,meerut Meerut, India Pankaj singh Sidhi vinayak Group of College,Alwar Alwar,Rajasthan Rehan Ahmad IIMT Engg college,meerut
Performance Evaluation of, AND Protocol in MANET Zaiba Ishrat IIMT Engg college,meerut Meerut, India Pankaj singh Sidhi vinayak Group of College,Alwar Alwar,Rajasthan Rehan Ahmad IIMT Engg college,meerut
A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh
 A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India Abstract MANET is a dynamic topology wireless network in which
A Topology Based Routing Protocols Comparative Analysis for MANETs Girish Paliwal, Swapnesh Taterh Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India Abstract MANET is a dynamic topology wireless network in which
Mitigating Superfluous Flooding of Control Packets MANET
 Mitigating Superfluous Flooding of Control Packets MANET B.Shanmugha Priya 1 PG Student, Department of Computer Science, Park College of Engineering and Technology, Kaniyur, Coimbatore, India 1 Abstract:
Mitigating Superfluous Flooding of Control Packets MANET B.Shanmugha Priya 1 PG Student, Department of Computer Science, Park College of Engineering and Technology, Kaniyur, Coimbatore, India 1 Abstract:
A Hybrid Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Wireless Network Based on Proactive and Reactive Routing Schemes
 A Hybrid Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Wireless Network Based on Proactive and Reactive Routing Schemes Chetana K. Kamate, Dr. Santosh L. Deshpande Department P.G. Studies in Computer Network and Engineering,
A Hybrid Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Wireless Network Based on Proactive and Reactive Routing Schemes Chetana K. Kamate, Dr. Santosh L. Deshpande Department P.G. Studies in Computer Network and Engineering,
Recent Researches in Communications, Information Science and Education
 AODV Based Multi-path Local Repairing Scheme for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Eman Shaaban, PhD Computer Systems Dept. Faculty of computer and information science Ain-Shams university, Cairo, Egypt Eman.shaaban@cis.asu.edu.eg
AODV Based Multi-path Local Repairing Scheme for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Eman Shaaban, PhD Computer Systems Dept. Faculty of computer and information science Ain-Shams university, Cairo, Egypt Eman.shaaban@cis.asu.edu.eg
Routing Protocols in MANET: Comparative Study
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 7, July 2014, pg.119
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 7, July 2014, pg.119
Performance Analysis of Wireless Mobile ad Hoc Network with Varying Transmission Power
 , pp.1-6 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsacs.2015.3.1.01 Performance Analysis of Wireless Mobile ad Hoc Network with Varying Transmission Power Surabhi Shrivastava, Laxmi Shrivastava and Sarita Singh Bhadauria
, pp.1-6 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsacs.2015.3.1.01 Performance Analysis of Wireless Mobile ad Hoc Network with Varying Transmission Power Surabhi Shrivastava, Laxmi Shrivastava and Sarita Singh Bhadauria
Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking. Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT
 Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT GPS & navigation system On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) systems DVD player Satellite communication 2 Internet
Lecture 6: Vehicular Computing and Networking Cristian Borcea Department of Computer Science NJIT GPS & navigation system On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) systems DVD player Satellite communication 2 Internet
Gateway Discovery Approaches Implementation and Performance Analysis in the Integrated Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET)-Internet Scenario
 Gateway Discovery Approaches Implementation and Performance Analysis in the Integrated Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET)-Internet Scenario K.Gautham 1, Nagajothi A 2 Student, Computer Science and Engineering,
Gateway Discovery Approaches Implementation and Performance Analysis in the Integrated Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET)-Internet Scenario K.Gautham 1, Nagajothi A 2 Student, Computer Science and Engineering,
Performance Evaluation of MANET through NS2 Simulation
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 1 (2014), pp. 25-30 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 1 (2014), pp. 25-30 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
Performance of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols in Different Network Sizes
 Performance of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols in Different Network Sizes Sudheer Kumar 1, Akhilesh Yadav 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Kanpur Institute of Technology, Kanpur sudheerkr21@gmail.co
Performance of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols in Different Network Sizes Sudheer Kumar 1, Akhilesh Yadav 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Kanpur Institute of Technology, Kanpur sudheerkr21@gmail.co
LOCATION-AIDED ROUTING PROTOCOL IN HYBRID WIRED-WIRELESS NETWORKS. WU MINTAO (B.Eng.(Hons.), NTU)
 LOCATION-AIDED ROUTING PROTOCOL IN HYBRID WIRED-WIRELESS NETWORKS WU MINTAO (B.Eng.(Hons.), NTU) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING
LOCATION-AIDED ROUTING PROTOCOL IN HYBRID WIRED-WIRELESS NETWORKS WU MINTAO (B.Eng.(Hons.), NTU) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING
White Paper. Mobile Ad hoc Networking (MANET) with AODV. Revision 1.0
 White Paper Mobile Ad hoc Networking (MANET) with AODV Revision 1.0 This page is intentionally blank, or rather nearly blank. Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS...3 TABLE OF FIGURES...4 WHAT IS MANET?...5
White Paper Mobile Ad hoc Networking (MANET) with AODV Revision 1.0 This page is intentionally blank, or rather nearly blank. Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS...3 TABLE OF FIGURES...4 WHAT IS MANET?...5
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
DYNAMIC DATA ROUTING IN MANET USING POSITION BASED OPPORTUNISTIC ROUTING PROTOCOL
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 DYNAMIC DATA ROUTING IN MANET USING POSITION BASED OPPORTUNISTIC ROUTING PROTOCOL P. Kalaivani 1, G. Sathya 2, N.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 DYNAMIC DATA ROUTING IN MANET USING POSITION BASED OPPORTUNISTIC ROUTING PROTOCOL P. Kalaivani 1, G. Sathya 2, N.
Analysis of Black-Hole Attack in MANET using AODV Routing Protocol
 Analysis of Black-Hole Attack in MANET using Routing Protocol Ms Neha Choudhary Electronics and Communication Truba College of Engineering, Indore India Dr Sudhir Agrawal Electronics and Communication
Analysis of Black-Hole Attack in MANET using Routing Protocol Ms Neha Choudhary Electronics and Communication Truba College of Engineering, Indore India Dr Sudhir Agrawal Electronics and Communication
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK COMPARISON OF MANET REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS USING OPNET SIMULATOR SANGEETA MONGA
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK COMPARISON OF MANET REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS USING OPNET SIMULATOR SANGEETA MONGA
LERP: A Secure Location Based Efficient Routing Protocol
 LERP: A Secure Location Based Efficient Routing Protocol Rajan Gandhi #1, Prof Prasanna Joeg * 2 # PG Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science Engineering Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune
LERP: A Secure Location Based Efficient Routing Protocol Rajan Gandhi #1, Prof Prasanna Joeg * 2 # PG Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science Engineering Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune
Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model
 Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model 1 R. Jeevitha, 2 M. Chandra Kumar 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer
Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model 1 R. Jeevitha, 2 M. Chandra Kumar 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer
Performance Comparison of DSDV, AODV, DSR, Routing protocols for MANETs
 2012 International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Systems (CNCS 2012) IPCSIT vol.35(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Comparison of DSDV, AODV, DSR, Routing protocols
2012 International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Systems (CNCS 2012) IPCSIT vol.35(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Comparison of DSDV, AODV, DSR, Routing protocols
A Review Paper on Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks
 A Review Paper on Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks Seema Pahal 1, Kusum Dalal 2 1,2 ECE Department, DCRUST MURTHAL, Haryana Abstract- This paper presents a literature review on WSN networks,
A Review Paper on Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks Seema Pahal 1, Kusum Dalal 2 1,2 ECE Department, DCRUST MURTHAL, Haryana Abstract- This paper presents a literature review on WSN networks,
Experiment and Evaluation of a Mobile Ad Hoc Network with AODV Routing Protocol
 Experiment and Evaluation of a Mobile Ad Hoc Network with AODV Routing Protocol Kalyan Kalepu, Shiv Mehra and Chansu Yu, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University 2121
Experiment and Evaluation of a Mobile Ad Hoc Network with AODV Routing Protocol Kalyan Kalepu, Shiv Mehra and Chansu Yu, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University 2121
DYNAMIC RESPONSE ZONE ROUTING FOR MANET
 DYNAMIC REPONE ZONE ROUTING FOR MANET Rimantas Plestys, Rokas Zakarevicius Kaunas University of Technology, Department of Computer Networks, tudentu str. 50-4, Kaunas, Lithuania, rimantas.plestys@ktu.lt,
DYNAMIC REPONE ZONE ROUTING FOR MANET Rimantas Plestys, Rokas Zakarevicius Kaunas University of Technology, Department of Computer Networks, tudentu str. 50-4, Kaunas, Lithuania, rimantas.plestys@ktu.lt,
The General Analysis of Proactive Protocols DSDV, FSR and WRP
 Volume 116 No. 10 2017, 375-380 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu The General Analysis of Proactive Protocols DSDV, FSR and WRP 1 Dr.
Volume 116 No. 10 2017, 375-380 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu The General Analysis of Proactive Protocols DSDV, FSR and WRP 1 Dr.
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSR USING A NOVEL APPROACH
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSR USING A NOVEL APPROACH 1. Prof.S.P. Setti 2. Narasimha Raju K 3. Naresh Kumar K CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., AU College of Engineering, AU College of Engineering,
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSR USING A NOVEL APPROACH 1. Prof.S.P. Setti 2. Narasimha Raju K 3. Naresh Kumar K CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., AU College of Engineering, AU College of Engineering,
II. CLASSIFICATION OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS MANET routing protocols are classified into three major categories: proactive, reactive and hybrid.
 A COMPLETE STUDY ON POWER AWARE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MOBILE ADHOC NETWORK A. Kumaravel 1, Dr. M.Chandrasekaran 2 1 (Electronics and Communication Engineering, Paavai Engineering College,India) 2 (Electronics
A COMPLETE STUDY ON POWER AWARE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MOBILE ADHOC NETWORK A. Kumaravel 1, Dr. M.Chandrasekaran 2 1 (Electronics and Communication Engineering, Paavai Engineering College,India) 2 (Electronics
Ad Hoc Routing Protocols and Issues
 Ad Hoc Routing Protocols and Issues Stefano Basagni ECE Dept Northeastern University Boston, Jan 2003 Ad hoc (AD-HAHK or AD-HOKE)-Adjective a) Concerned with a particular end or purpose, and b) formed
Ad Hoc Routing Protocols and Issues Stefano Basagni ECE Dept Northeastern University Boston, Jan 2003 Ad hoc (AD-HAHK or AD-HOKE)-Adjective a) Concerned with a particular end or purpose, and b) formed
An Efficient Routing Approach and Improvement Of AODV Protocol In Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks
 An Efficient Routing Approach and Improvement Of AODV Protocol In Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks Tejomayee Nath #1 & Suneeta Mohanty *2 # School of Computer Engineering, KIIT University Bhubaneswar,, India Abstract
An Efficient Routing Approach and Improvement Of AODV Protocol In Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks Tejomayee Nath #1 & Suneeta Mohanty *2 # School of Computer Engineering, KIIT University Bhubaneswar,, India Abstract
Appointed BrOadcast (ABO): Reducing Routing Overhead in. IEEE Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
 Appointed BrOadcast (ABO): Reducing Routing Overhead in IEEE 802.11 Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Chun-Yen Hsu and Shun-Te Wang Computer Network Lab., Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University
Appointed BrOadcast (ABO): Reducing Routing Overhead in IEEE 802.11 Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Chun-Yen Hsu and Shun-Te Wang Computer Network Lab., Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University
Geographical routing 1
 Geographical routing 1 Routing in ad hoc networks Obtain route information between pairs of nodes wishing to communicate. Proactive protocols: maintain routing tables at each node that is updated as changes
Geographical routing 1 Routing in ad hoc networks Obtain route information between pairs of nodes wishing to communicate. Proactive protocols: maintain routing tables at each node that is updated as changes
Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 04 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 1
 Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 04 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 1 Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Ad-hoc networks deployment For routing, target detection,
Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 04 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 1 Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Ad-hoc networks deployment For routing, target detection,
PNR: New Position based Routing Algorithm for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
 PNR: New Position based Routing Algorithm for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Hossein Ashtiani, Shahpour Alirezaee, seyed mohsen mir hosseini, HamidKhosravi Abstract An ad hoc network (MANET) has no fixed networking
PNR: New Position based Routing Algorithm for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Hossein Ashtiani, Shahpour Alirezaee, seyed mohsen mir hosseini, HamidKhosravi Abstract An ad hoc network (MANET) has no fixed networking
Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency
 Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency JIRI HOSEK 1, KAROL MOLNAR 2 Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Purkynova
Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency JIRI HOSEK 1, KAROL MOLNAR 2 Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Purkynova
Impact of Pause Time on the Performance of DSR, LAR1 and FSR Routing Protocols in Wireless Ad hoc Network
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 2, February 2015,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 2, February 2015,
A Survey of Vehicular Ad hoc Networks Routing Protocols
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 3 July 2013, pp. 829-846 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ A Survey
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 3 July 2013, pp. 829-846 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ A Survey
Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET
 208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2
 An Implemented approach of VANET using Location Information based Technique for safe city and vehicle Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2 #1. M.Tech Scholor,ECE,Krukshetra University, *2. A.P.ECE Department,
An Implemented approach of VANET using Location Information based Technique for safe city and vehicle Aanchal Walia #1, Pushparaj Pal *2 #1. M.Tech Scholor,ECE,Krukshetra University, *2. A.P.ECE Department,
ENERGY-AWARE FOR DH-AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORK
 ENERGY-AWARE FOR DH-AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORK Yousif Ali Saadi, Rosilah Hassan and Dahlila Putri Dahnil Network Communication Lab Research, Centre for Software Technology and Management
ENERGY-AWARE FOR DH-AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORK Yousif Ali Saadi, Rosilah Hassan and Dahlila Putri Dahnil Network Communication Lab Research, Centre for Software Technology and Management
Nearest Neighbor Query in Location- Aware Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 3, March 2015,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 3, March 2015,
ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT REACTIVE, PROACTIVE & HYBRID ROUTING PROTOCOLS: A REVIEW
 ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT REACTIVE, PROACTIVE & HYBRID ROUTING PROTOCOLS: A REVIEW Kirandeep Kaur 1, Mr.Pawan Luthra 2, Er.Gagandeep 3 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shaheed Bhagat Singh
ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT REACTIVE, PROACTIVE & HYBRID ROUTING PROTOCOLS: A REVIEW Kirandeep Kaur 1, Mr.Pawan Luthra 2, Er.Gagandeep 3 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shaheed Bhagat Singh
Scalability Performance of AODV, TORA and OLSR with Reference to Variable Network Size
 Lovekesh Kumar / International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: Scalability Performance of AODV, TORA and OLSR with Reference to Variable Network Size Lovekesh Kumar* *(Department
Lovekesh Kumar / International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: Scalability Performance of AODV, TORA and OLSR with Reference to Variable Network Size Lovekesh Kumar* *(Department
STUDY AND COMPARISION OF PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK
 STUDY AND COMPARISION OF PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK 1 Arpita Singh, 2 Navendu Nitin, 3 Neelesh Agrawal, 4 Arvind Kumar Jaiswal 1 PG student, SHIATS-DU,
STUDY AND COMPARISION OF PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK 1 Arpita Singh, 2 Navendu Nitin, 3 Neelesh Agrawal, 4 Arvind Kumar Jaiswal 1 PG student, SHIATS-DU,
[Kamboj* et al., 5(9): September, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116
![[Kamboj* et al., 5(9): September, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116 [Kamboj* et al., 5(9): September, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/92/109489555.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY NOVEL REVIEW OF MANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS Nippun Kamboj*, Dr. Munishwar Rai Department of Computer Applications Maharishi Markandeshwar
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY NOVEL REVIEW OF MANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS Nippun Kamboj*, Dr. Munishwar Rai Department of Computer Applications Maharishi Markandeshwar
A New Approach for Energy Efficient Routing in MANETs Using Multi Objective Genetic Algorithm
 A New Approach for Energy Efficient in MANETs Using Multi Objective Genetic Algorithm Neha Agarwal, Neeraj Manglani Abstract Mobile ad hoc networks (MANET) are selfcreating networks They contain short
A New Approach for Energy Efficient in MANETs Using Multi Objective Genetic Algorithm Neha Agarwal, Neeraj Manglani Abstract Mobile ad hoc networks (MANET) are selfcreating networks They contain short
MANET is considered a collection of wireless mobile nodes that are capable of communicating with each other. Research Article 2014
 Throughput Analysis of Proactive and Reactive MANET Routing Protocols Kiranveer Kaur 1 Surinderjit Kaur 2 Vikramjit Singh 3 Department of Computer Science, University College of Engineering, Department
Throughput Analysis of Proactive and Reactive MANET Routing Protocols Kiranveer Kaur 1 Surinderjit Kaur 2 Vikramjit Singh 3 Department of Computer Science, University College of Engineering, Department
MANET TECHNOLOGY. Keywords: MANET, Wireless Nodes, Ad-Hoc Network, Mobile Nodes, Routes Protocols.
 MANET TECHNOLOGY Dharna 1, Varsha Saroha 2, R. B. Dubey 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Hindu College of Engineering, Sonepat, Haryana,(India) ABSTRACT Wireless technology
MANET TECHNOLOGY Dharna 1, Varsha Saroha 2, R. B. Dubey 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Hindu College of Engineering, Sonepat, Haryana,(India) ABSTRACT Wireless technology
Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario
 Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario Uttara Vyas 1, Prof. Kamlesh Chopra 2, Prof. Prashant Lakkadwala 3 1 Computer Science and Engineering,Acropolis Technical
Performance Enhancement of Routing Protocols for VANET With Variable Traffic Scenario Uttara Vyas 1, Prof. Kamlesh Chopra 2, Prof. Prashant Lakkadwala 3 1 Computer Science and Engineering,Acropolis Technical
Geographic Routing Without Location Information. AP, Sylvia, Ion, Scott and Christos
 Geographic Routing Without Location Information AP, Sylvia, Ion, Scott and Christos Routing in Wireless Networks Distance vector DSDV On-demand DSR, TORA, AODV Discovers and caches routes on demand Geographic
Geographic Routing Without Location Information AP, Sylvia, Ion, Scott and Christos Routing in Wireless Networks Distance vector DSDV On-demand DSR, TORA, AODV Discovers and caches routes on demand Geographic
Energy aware geographic routing in wireless sensor networks with anchor nodes. Mircea Cretu Stancu Utrecht University Computing Science May 2013
 Energy aware geographic routing in wireless sensor networks with anchor nodes Mircea Cretu Stancu Utrecht University Computing Science May 2013 Overview Introduction Current paradigm EAGR preliminaries
Energy aware geographic routing in wireless sensor networks with anchor nodes Mircea Cretu Stancu Utrecht University Computing Science May 2013 Overview Introduction Current paradigm EAGR preliminaries
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 10: Mobile Transport Layer & Ad Hoc Networks. [Schiller, Section 8.3 & Section 9] [Reader, Part 8]
![Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 10: Mobile Transport Layer & Ad Hoc Networks. [Schiller, Section 8.3 & Section 9] [Reader, Part 8] Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 10: Mobile Transport Layer & Ad Hoc Networks. [Schiller, Section 8.3 & Section 9] [Reader, Part 8]](/thumbs/92/110300020.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 10: Mobile Transport Layer & Ad Hoc Networks [Schiller, Section 8.3 & Section 9] [Reader, Part 8] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 10 Mobile transport layer
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 10: Mobile Transport Layer & Ad Hoc Networks [Schiller, Section 8.3 & Section 9] [Reader, Part 8] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 10 Mobile transport layer
ROUTING ALGORITHMS Part 1: Data centric and hierarchical protocols
 ROUTING ALGORITHMS Part 1: Data centric and hierarchical protocols 1 Why can t we use conventional routing algorithms here?? A sensor node does not have an identity (address) Content based and data centric
ROUTING ALGORITHMS Part 1: Data centric and hierarchical protocols 1 Why can t we use conventional routing algorithms here?? A sensor node does not have an identity (address) Content based and data centric
Packet Estimation with CBDS Approach to secure MANET
 Packet Estimation with CBDS Approach to secure MANET Mr. Virendra P. Patil 1 and Mr. Rajendra V. Patil 2 1 PG Student, SSVPS COE, Dhule, Maharashtra, India 2 Assistance Professor, SSVPS COE, Dhule, Maharashtra,
Packet Estimation with CBDS Approach to secure MANET Mr. Virendra P. Patil 1 and Mr. Rajendra V. Patil 2 1 PG Student, SSVPS COE, Dhule, Maharashtra, India 2 Assistance Professor, SSVPS COE, Dhule, Maharashtra,
Hybrid gateway advertisement scheme for connecting mobile ad hoc networks to the Internet
 * gateway advertisement scheme for connecting mobile ad hoc networks to the Internet Jeongkeun Lee (), Dongkyun Kim (2), J.J.Garcia-Luna-Aceves (3), Yanghee Choi (), Jihyuk Choi (4), Sangwoo Nam (4) ()
* gateway advertisement scheme for connecting mobile ad hoc networks to the Internet Jeongkeun Lee (), Dongkyun Kim (2), J.J.Garcia-Luna-Aceves (3), Yanghee Choi (), Jihyuk Choi (4), Sangwoo Nam (4) ()
Performance Analysis of MANET Routing Protocols OLSR and AODV
 VOL. 2, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 211 Performance Analysis of MANET Routing Protocols OLSR and AODV Jiri Hosek Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Email: hosek@feec.vutbr.cz
VOL. 2, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 211 Performance Analysis of MANET Routing Protocols OLSR and AODV Jiri Hosek Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Email: hosek@feec.vutbr.cz
A COMPARISON OF REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS DSR, AODV AND TORA IN MANET
 ISSN: 2278 1323 All Rights Reserved 2016 IJARCET 296 A COMPARISON OF REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS DSR, AODV AND TORA IN MANET Dr. R. Shanmugavadivu 1, B. Chitra 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer
ISSN: 2278 1323 All Rights Reserved 2016 IJARCET 296 A COMPARISON OF REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS DSR, AODV AND TORA IN MANET Dr. R. Shanmugavadivu 1, B. Chitra 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer
A Position-Based Connectionless Routing Algorithm for MANET and WiMAX under High Mobility and Various Node Densities
 Information Technology Journal 7 (3): 458-465, 08 ISSN 1812-5638 08 Asian Network for Scientific Information A Position-Based Connectionless Routing Algorithm for MANET and WiMAX under High Mobility and
Information Technology Journal 7 (3): 458-465, 08 ISSN 1812-5638 08 Asian Network for Scientific Information A Position-Based Connectionless Routing Algorithm for MANET and WiMAX under High Mobility and
A Literature survey on Improving AODV protocol through cross layer design in MANET
 A Literature survey on Improving AODV protocol through cross layer design in MANET Nidhishkumar P. Modi 1, Krunal J. Panchal 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, LJIET, Gujarat, India 2 Asst.Professor,
A Literature survey on Improving AODV protocol through cross layer design in MANET Nidhishkumar P. Modi 1, Krunal J. Panchal 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, LJIET, Gujarat, India 2 Asst.Professor,
COMPARITIVE ANALYSIS OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS
 COMPARITIVE ANALYSIS OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS Er. Upasana garg 1, Dr. Vikram Singh 2 1 Student, Computer Science and Application Deptt, CDLU, Sirsa, Haryana, India,upasna.garg44@gmail.com
COMPARITIVE ANALYSIS OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS Er. Upasana garg 1, Dr. Vikram Singh 2 1 Student, Computer Science and Application Deptt, CDLU, Sirsa, Haryana, India,upasna.garg44@gmail.com
A Neighbor Coverage Based Probabilistic Rebroadcast Reducing Routing Overhead in MANETs
 A Neighbor Coverage Based Probabilistic Rebroadcast Reducing Routing Overhead in MANETs Ankita G. Rathi #1, Mrs. J. H. Patil #2, Mr. S. A. Hashmi #3 # Computer Science-Information Technology Department,
A Neighbor Coverage Based Probabilistic Rebroadcast Reducing Routing Overhead in MANETs Ankita G. Rathi #1, Mrs. J. H. Patil #2, Mr. S. A. Hashmi #3 # Computer Science-Information Technology Department,
Multipath Routing Protocol for Congestion Control in Mobile Ad-hoc Network
 1 Multipath Routing Protocol for Congestion Control in Mobile Ad-hoc Network Nilima Walde, Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology, Army Institute of Technology, Pune, India Dhananjay
1 Multipath Routing Protocol for Congestion Control in Mobile Ad-hoc Network Nilima Walde, Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology, Army Institute of Technology, Pune, India Dhananjay
The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security
 The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security Parveen Kumar Research Scholar, CMJ University, Shillong, Meghalaya (India) Abstract In VANET, or Intelligent Vehicular
The Study of Routing Strategies in Vehicular Ad- Hoc Network to Enhance Security Parveen Kumar Research Scholar, CMJ University, Shillong, Meghalaya (India) Abstract In VANET, or Intelligent Vehicular
On the Scalability of Hierarchical Ad Hoc Wireless Networks
 On the Scalability of Hierarchical Ad Hoc Wireless Networks Suli Zhao and Dipankar Raychaudhuri Fall 2006 IAB 11/15/2006 Outline Motivation Ad hoc wireless network architecture Three-tier hierarchical
On the Scalability of Hierarchical Ad Hoc Wireless Networks Suli Zhao and Dipankar Raychaudhuri Fall 2006 IAB 11/15/2006 Outline Motivation Ad hoc wireless network architecture Three-tier hierarchical
6367(Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March April (2013), IAEME & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET)
 INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
A NOVEL CLUSTER BASED WORMHOLE AVOIDANCE ALGORITHM FOR MOBILE AD- HOC NETWORKS
 A NOVEL CLUSTER BASED WORMHOLE AVOIDANCE ALGORITHM FOR MOBILE AD- HOC NETWORKS Subhashis Banerjee 1 and Koushik Majumder 2 1 Department of Computer Science & Engineering, West Bengal University of Technology,
A NOVEL CLUSTER BASED WORMHOLE AVOIDANCE ALGORITHM FOR MOBILE AD- HOC NETWORKS Subhashis Banerjee 1 and Koushik Majumder 2 1 Department of Computer Science & Engineering, West Bengal University of Technology,
BOND: Unifying Mobile Networks with Named Data. Michael Meisel
 BOND: Unifying Mobile Networks with Named Data Michael Meisel Ph.D. Dissertation Defense March 16, 2011 Freeform Wireless Networks Multi-hop Unpredictable mobility Can be connected or disconnected Examples:
BOND: Unifying Mobile Networks with Named Data Michael Meisel Ph.D. Dissertation Defense March 16, 2011 Freeform Wireless Networks Multi-hop Unpredictable mobility Can be connected or disconnected Examples:
CASER Protocol Using DCFN Mechanism in Wireless Sensor Network
 Volume 118 No. 7 2018, 501-505 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu CASER Protocol Using DCFN Mechanism in Wireless Sensor Network A.Shirly
Volume 118 No. 7 2018, 501-505 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu CASER Protocol Using DCFN Mechanism in Wireless Sensor Network A.Shirly
A Survey on Geographic Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Networks
 A Survey on Geographic Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Networks Atekeh Maghsoudlou, Marc St-Hilaire, and Thomas Kunz Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, Ottawa, ON,
A Survey on Geographic Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Networks Atekeh Maghsoudlou, Marc St-Hilaire, and Thomas Kunz Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, Ottawa, ON,
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSDV, AODV ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSDV, AODV ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET K. Venkateswarlu 1, G. Murali 2 1 M. Tech, CSE, JNTUA College of Engineering (Pulivendula), Andhra Pradesh, India 2 Asst.Prof (HOD), CSE,
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSDV, AODV ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN VANET K. Venkateswarlu 1, G. Murali 2 1 M. Tech, CSE, JNTUA College of Engineering (Pulivendula), Andhra Pradesh, India 2 Asst.Prof (HOD), CSE,
CHAPTER 5 MULTICAST GEOGRAPHY BASED ROUTING IN AD HOC NETWORKS
 89 CHAPTER 5 MULTICAST GEOGRAPHY BASED ROUTING IN AD HOC NETWORKS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Efficient routing in MANET is a tough task due to their highly dynamic network topology, bandwidth controlled links and
89 CHAPTER 5 MULTICAST GEOGRAPHY BASED ROUTING IN AD HOC NETWORKS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Efficient routing in MANET is a tough task due to their highly dynamic network topology, bandwidth controlled links and
Performance Comparison of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR MANET Routing Protocols
 Performance Comparison of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR MANET Routing Protocols Akshay Shankar, Lavanya Chelle Information Science Engineering RNS Institute of Technology Bangalore, India Abstract- A Mobile
Performance Comparison of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR MANET Routing Protocols Akshay Shankar, Lavanya Chelle Information Science Engineering RNS Institute of Technology Bangalore, India Abstract- A Mobile
Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs
 Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs Rajneesh Gujral Associate Proffesor (CSE Deptt.) Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Mullana, Ambala Sanjeev Rana Associate
Study and Comparison of Mesh and Tree- Based Multicast Routing Protocols for MANETs Rajneesh Gujral Associate Proffesor (CSE Deptt.) Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Mullana, Ambala Sanjeev Rana Associate
A Comparative Analysis of Energy Preservation Performance Metric for ERAODV, RAODV, AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in MANET
 A Comparative Analysis of Energy Preservation Performance Metric for ERAODV, RAODV, AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in MANET Bhabani Sankar Gouda Department of Computer Science & Engineering National Institute
A Comparative Analysis of Energy Preservation Performance Metric for ERAODV, RAODV, AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in MANET Bhabani Sankar Gouda Department of Computer Science & Engineering National Institute
ECS-087: Mobile Computing
 ECS-087: Mobile Computing Mobile Adhoc Networks and Routing in MANETS (most of the slides borrowed from Prof. Sridhar Iyer) Diwakar Yagyasen 1 Index Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET) MAC in MANET MANET routing
ECS-087: Mobile Computing Mobile Adhoc Networks and Routing in MANETS (most of the slides borrowed from Prof. Sridhar Iyer) Diwakar Yagyasen 1 Index Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET) MAC in MANET MANET routing
Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths
 Chapter 5 Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths 5.1 Introduction In recent years, on demand routing protocols have attained more attention in mobile Ad Hoc networks as compared to other routing schemes
Chapter 5 Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths 5.1 Introduction In recent years, on demand routing protocols have attained more attention in mobile Ad Hoc networks as compared to other routing schemes
GSM Based Comparative Investigation of Hybrid Routing Protocols in MANETS
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 3, Ver. II (May - Jun. 214), PP 82-86 GSM Based Comparative Investigation of Hybrid
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 3, Ver. II (May - Jun. 214), PP 82-86 GSM Based Comparative Investigation of Hybrid
15-441: Computer Networking. Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks
 15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Scenarios and Roadmap Point to point wireless networks (last lecture) Example: your laptop to CMU wireless Challenges: Poor and variable
15-441: Computer Networking Lecture 24: Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks Scenarios and Roadmap Point to point wireless networks (last lecture) Example: your laptop to CMU wireless Challenges: Poor and variable
2. LITERATURE REVIEW. Performance Evaluation of Ad Hoc Networking Protocol with QoS (Quality of Service)
 2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
Networking Sensors, I
 Networking Sensors, I Sensing Networking Leonidas Guibas Stanford University Computation CS428 Networking Sensors Networking is a crucial capability for sensor networks -- networking allows: Placement
Networking Sensors, I Sensing Networking Leonidas Guibas Stanford University Computation CS428 Networking Sensors Networking is a crucial capability for sensor networks -- networking allows: Placement
1 Multipath Node-Disjoint Routing with Backup List Based on the AODV Protocol
 1 Multipath Node-Disjoint Routing with Backup List Based on the AODV Protocol Vahid Zangeneh i and Shahriar Mohammadi ii * ABSTRACT In recent years, routing has been the most focused area in ad hoc networks
1 Multipath Node-Disjoint Routing with Backup List Based on the AODV Protocol Vahid Zangeneh i and Shahriar Mohammadi ii * ABSTRACT In recent years, routing has been the most focused area in ad hoc networks
