hp calculators HP 9g Probability Random Numbers Random Numbers Simulation Practice Using Random Numbers for Simulations
|
|
|
- Helena Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Random Numbers Simulation Practice Using Random Numbers for Simulations
2 Random numbers Strictly speaking, random numbers are those numbers the digits of which are chosen with replacement so that it is one of a set of numbers that can be chosen, all of which are equally likely. Chosen with replacement means that once a digit has been chosen it may be chosen again with the same probability as the other digits. When it is a computer or calculator that generates the random numbers, they are also known as pseudo-random numbers or quasi-random numbers because they are not exactly random, but can be treated as if they were random for all practical purposes. The HP 9g provides two commands to generate random numbers, namely RAND (Y1) and RANDI (Y2). The former returns a random number between 0 and 1, and the latter takes two integers A and B and returns a random integer n such as A n B (assuming A B). Random numbers are internally generated using the previous random number generated, and the first one is generated using a seed for each seed, a different series of numbers is generated. On the HP 9g, there is no way of changing this seed, but it is based on the value of the internal clock, so it changes at every reset. Among the most important uses of random numbers are games and simulations: they are used to decide what the next piece will be in the Tetris game we are playing, as well as in stock market simulations. Simulation In mathematics, a simulation is a mathematical model of a system or a process which often involves the element of chance. Simulations help to explain some physical behavior (e.g., the motion of waves, the flip of a coin, etc.). This is certainly an extensive topic and the following examples cannot be exhaustive, but they show a few ways random numbers can be used on your HP 9g. Note. The values returned by RAND and RANDI on your HP 9g will probably be different than the ones in these examples because a new series of random numbers is created for each seed. Practice using random numbers for simulations Example 1: Simulate flipping a coin four times. When a coin is flipped, there are only two possible events: the probability of heads is 0.5 and of tails also 0.5. Let the number 0 equate to observing a heads and 1 equate to observing a tails. Therefore, RANDI(0,1) is a suitable simulation of the flip of a coin, since it returns either 0 or, and both results are equally likely. On your HP 9g, press: Y20W01= Notice that to separate the two arguments, you have to use the comma, which is entered by W0. It returns 1 (tails). To simulate the other three flips, you have to repeat the calculation, which is as easy as pressing =three times: 1, 1, and 0 are returned which means that heads happened only once. The result of flipping the coin four times is three tails and a heads. hp calculators Version 1.0
3 Example 2: Simulate rolling 2 dice. When a die is rolled, the result is equally likely to be a 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. Since these are all integer numbers, we can use the RANDI command for this purpose: RANDI(1,6). Press Y21W06= jot down the result and press =again to simulate the second dice. The value of the first die was a 6 and the second was a 5, for a total on the two dice of 11. Example 3: Vladimir s Newstand sells newspapers and has experienced demand for newspapers as follows over the last 50 days: 10 newspapers on 5 of the days; 15 newspapers on 20 of the days; 20 newspapers on 15 of the days; and 25 newspapers on 10 of the days. Using random numbers simulate demand for the next 5 days. The first step will be to translate the past demand into ranges for our random numbers for the simulation. Out of past 50 days, demand was 10 on 5 of these days, or 10% of the time. Out of the past 50 days, demand was 15 on 20 of these days, or 40% of the time. Out of the past 50 days, demand was 20 on 15 of these days, or 30% of the time. Finally, out of the past 50 days, demand was 25 on 10 of the days, or 20% of the time. This information can be summarized in a table as shown below. Demand Probability Next, we need to assign a range for each level of demand that corresponds to the relative probability for that demand. It is this range that will be used to classify each random number as a specific simulated demand. Demand Probability Range < random number < random number < random number < random number < 1.0 Note that each range corresponds to the probability of each outcome (the range between 0.1 and 0.5 is 40% of the possible outcomes of the random numbers and therefore reflects the 40% chance that a demand of 15 will occur). We can now generate the five random numbers. Let s evaluate each random number as it is generated. On your HP 9g, press Y1=The number returned is: This corresponds to a demand of 15 newspapers. To repeat the calculation and generate a new random number, press =: the number displayed is now , which also corresponds to a demand of 15 newspapers. We have to repeat this calculation three times more: hp calculators Version 1.0
4 Pressing =returns This corresponds to a demand of 20 newspapers. Pressing =returns This corresponds to a demand of 20 newspapers. Pressing =returns This corresponds to a demand of 20 newspapers. The results were demands of 15, 15, 20, 20 and 20 newspapers. If the simulation were carried out for a longer period (which could be done by writing a program), other levels of demand would be generated. Example 4: Write a program that generates a large number of random digits and returns how many 0 s, 1 s, 2 s,..., 8 s and 9 s have been generated. This is one of the simplest ways of testing a random number generator, it is called the frequency test. The ten digits should occur about 10% each. This is the program: INPUT N FOR ( Z = 1; Z N ; Z++ ) { ++A [RANDI( 0, 9 )] PRINT Z } PRINT PRESS RCL END Line # Command Explanation Keys Line 1 INPUT N Asks for the number of random digits to be generated ~v 0WN= Line 2 The following two ~v3w3w=1 FOR ( Z = 1; Z N ; instructions are done N W3~ÍWN W3 Z++ ) { times ~v 2 = Generates a random digit i ~v Line 3 ++A [RANDI( 0, 9 )] (=0...9). Var A[i] (A...J) is incremented by one 2WAW[Y 20W09 = Line 4 PRINT Z } Displays the loop counter ~v 3W3 = Line 5 PRINT PRESS RCL Once finished, tells the user what to do next. ~v 3~w, 79E//- 9CLW When running for the first time, press ~Ö to clear all the variables, it is not done by the program so that further executions can add their results to the existing values. The program starts by asking the user how many random digits have to be generated, say, 200. Since it takes some time, the program always displays the number of random digits that has generated thus far. At the end, the message PRESS RCL appears meaning that the results can be viewed in the menu of variables displayed by ~a. A contains the number of 0 s generated, in B are the number of 1 s, and so on till J, which contains the number of 9 s. To get the relative frequency instead, divide each variable by N. The above table includes the keystrokes needed to enter the program once you are in Program Edit mode. (Refer to the learning module Writing a Small Program for more information on creating and editing programs). hp calculators Version 1.0
5 Running the program for N=100,000 returns these values: (remember that your calculator may generate different random numbers) 0 s (A) 1 s (B) 2 s (C) 3 s (D) 4 s (E) 5 s (F) 6 s (G) 7 s (H) 8 s (I) 9 s (J) Freq. 9,936 10,003 10,042 9,994 9,962 10,043 10,036 10,045 9,886 10,053 All these values are quite close to the ideal value a perfect generator would return, i.e. 10,000. Below is a frequency histogram of the generated digits. Number 8 was the least frequent digit and 9 the most frequent. Try increasing the number of random digits generated in order to get more meaningful results Frequency of the numbers generated by the RANDI function hp calculators Version 1.0
Topic 3: Fractions. Topic 1 Integers. Topic 2 Decimals. Topic 3 Fractions. Topic 4 Ratios. Topic 5 Percentages. Topic 6 Algebra
 Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
You ve already read basics of simulation now I will be taking up method of simulation, that is Random Number Generation
 Unit 5 SIMULATION THEORY Lesson 39 Learning objective: To learn random number generation. Methods of simulation. Monte Carlo method of simulation You ve already read basics of simulation now I will be
Unit 5 SIMULATION THEORY Lesson 39 Learning objective: To learn random number generation. Methods of simulation. Monte Carlo method of simulation You ve already read basics of simulation now I will be
TI-84 GRAPHING CALCULATOR
 TI-84 GRAPHING CALCULATOR Table of Contents Set Up & Troubleshooting... 3 TI-84: Resetting the Calculator... 4 TI-84: Mode Settings... 5 Entering Data... 7 TI-84: Entering & Editing Lists of Data... 8
TI-84 GRAPHING CALCULATOR Table of Contents Set Up & Troubleshooting... 3 TI-84: Resetting the Calculator... 4 TI-84: Mode Settings... 5 Entering Data... 7 TI-84: Entering & Editing Lists of Data... 8
Heads Up! (Continued)
 . Name Date A c t i v i t y 6 Heads Up! (Continued) In this activity, you will do more experiments with simulations and use a calculator program that will quickly simulate multiple coin tosses. The Problem
. Name Date A c t i v i t y 6 Heads Up! (Continued) In this activity, you will do more experiments with simulations and use a calculator program that will quickly simulate multiple coin tosses. The Problem
Functions in C++ Problem-Solving Procedure With Modular Design C ++ Function Definition: a single
 Functions in C++ Problem-Solving Procedure With Modular Design: Program development steps: Analyze the problem Develop a solution Code the solution Test/Debug the program C ++ Function Definition: A module
Functions in C++ Problem-Solving Procedure With Modular Design: Program development steps: Analyze the problem Develop a solution Code the solution Test/Debug the program C ++ Function Definition: A module
C Functions. 5.2 Program Modules in C
 1 5 C Functions 5.2 Program Modules in C 2 Functions Modules in C Programs combine user-defined functions with library functions - C standard library has a wide variety of functions Function calls Invoking
1 5 C Functions 5.2 Program Modules in C 2 Functions Modules in C Programs combine user-defined functions with library functions - C standard library has a wide variety of functions Function calls Invoking
COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps
 COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps Craps is a game of chance played by rolling two dice for a series of rolls and placing bets on the outcomes. The background on probability,
COMP 110 Programming Exercise: Simulation of the Game of Craps Craps is a game of chance played by rolling two dice for a series of rolls and placing bets on the outcomes. The background on probability,
Function Call Stack and Activation Records
 71 Function Call Stack and Activation Records To understand how C performs function calls, we first need to consider a data structure (i.e., collection of related data items) known as a stack. Students
71 Function Call Stack and Activation Records To understand how C performs function calls, we first need to consider a data structure (i.e., collection of related data items) known as a stack. Students
MODIFIED VERSION OF: An introduction to Matlab for dynamic modeling ***PART 3 ***
 MODIFIED VERSION OF: An introduction to Matlab for dynamic modeling ***PART 3 *** Stephen P. Ellner 1 and John Guckenheimer 2 1 Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, and 2 Department of Mathematics
MODIFIED VERSION OF: An introduction to Matlab for dynamic modeling ***PART 3 *** Stephen P. Ellner 1 and John Guckenheimer 2 1 Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, and 2 Department of Mathematics
More About WHILE Loops
 More About WHILE Loops http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/isc/week04 lecture 07.pdf... ISC3313: Introduction to Scientific Computing with C++ Summer Semester 2011... John Burkardt Department of Scientific
More About WHILE Loops http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/isc/week04 lecture 07.pdf... ISC3313: Introduction to Scientific Computing with C++ Summer Semester 2011... John Burkardt Department of Scientific
Functions and Recursion
 Functions and Recursion 1 Outline Introduction Program Components in C++ Math Library Functions Functions Function Definitions Function Prototypes Header Files Random Number Generation Example: A Game
Functions and Recursion 1 Outline Introduction Program Components in C++ Math Library Functions Functions Function Definitions Function Prototypes Header Files Random Number Generation Example: A Game
Statistical Computing
 SERIES I ARTICLE Statistical Computing 1. Understanding Randomness and Random Numbers Sudhakar Kunte Elements of statistical computing are discussed in this series. We begin with the notion of random numbers
SERIES I ARTICLE Statistical Computing 1. Understanding Randomness and Random Numbers Sudhakar Kunte Elements of statistical computing are discussed in this series. We begin with the notion of random numbers
UNIT 9A Randomness in Computation: Random Number Generators
 UNIT 9A Randomness in Computation: Random Number Generators 1 Last Unit Computer organization: what s under the hood 3 This Unit Random number generation Using pseudorandom numbers 4 Overview The concept
UNIT 9A Randomness in Computation: Random Number Generators 1 Last Unit Computer organization: what s under the hood 3 This Unit Random number generation Using pseudorandom numbers 4 Overview The concept
Biostatistics & SAS programming. Kevin Zhang
 Biostatistics & SAS programming Kevin Zhang February 27, 2017 Random variables and distributions 1 Data analysis Simulation study Apply existing methodologies to your collected samples, with the hope to
Biostatistics & SAS programming Kevin Zhang February 27, 2017 Random variables and distributions 1 Data analysis Simulation study Apply existing methodologies to your collected samples, with the hope to
CME 112- Programming Languages II. Week 1 Introduction, Scope Rules and Generating Random Numbers
 1 CME 112- Programming Languages II Week 1 Introduction, Scope Rules and Generating Random Numbers Assist. Prof. Dr. Caner Özcan You have two options at any given moment. You can either: Step forward into
1 CME 112- Programming Languages II Week 1 Introduction, Scope Rules and Generating Random Numbers Assist. Prof. Dr. Caner Özcan You have two options at any given moment. You can either: Step forward into
Distributions of Continuous Data
 C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
Anatomy of a Function. Pick a Name. Parameters. Definition. Chapter 20: Thinking Big: Programming Functions
 Chapter 20: Thinking Big: Programming Functions Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Anatomy of a Function Functions are packages for algorithms 3 parts Name Parameters
Chapter 20: Thinking Big: Programming Functions Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Anatomy of a Function Functions are packages for algorithms 3 parts Name Parameters
Random numbers program
 Fundamentals of Computer Science 2010-2011 Laboratory 11 Vectors (1) Objectives: Acquire abilities in the use of vectors (one-dimensional arrays) Get to know the generation of pseudo-random numbers Lower
Fundamentals of Computer Science 2010-2011 Laboratory 11 Vectors (1) Objectives: Acquire abilities in the use of vectors (one-dimensional arrays) Get to know the generation of pseudo-random numbers Lower
Functions. Computer System and programming in C Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Functions In general, functions are blocks of code that perform a number of pre-defined commands to accomplish something productive. You can either use the built-in library functions or you can create
Functions In general, functions are blocks of code that perform a number of pre-defined commands to accomplish something productive. You can either use the built-in library functions or you can create
Random Simulation Simulation Modeling
 Random Simulation 5.1 86 Simulation Modeling Goal: Use probabilistic methods to analyze deterministic and probabilistic models. Example. Determine the best elevator delivery scheme. The wait is too long,
Random Simulation 5.1 86 Simulation Modeling Goal: Use probabilistic methods to analyze deterministic and probabilistic models. Example. Determine the best elevator delivery scheme. The wait is too long,
Programming Assignment #3 Event Driven Simulation
 CS-2303, System Programming Concepts, A-term 2012 Project 3 (45 points) Assigned: Friday, September 7, 2012 Due: Friday, September 14, 2012, 11:59 PM Abstract Programming Assignment #3 Event Driven Simulation
CS-2303, System Programming Concepts, A-term 2012 Project 3 (45 points) Assigned: Friday, September 7, 2012 Due: Friday, September 14, 2012, 11:59 PM Abstract Programming Assignment #3 Event Driven Simulation
Programming Assignment #4 Arrays and Pointers
 CS-2301, System Programming for Non-majors, B-term 2013 Project 4 (30 points) Assigned: Tuesday, November 19, 2013 Due: Tuesday, November 26, Noon Abstract Programming Assignment #4 Arrays and Pointers
CS-2301, System Programming for Non-majors, B-term 2013 Project 4 (30 points) Assigned: Tuesday, November 19, 2013 Due: Tuesday, November 26, Noon Abstract Programming Assignment #4 Arrays and Pointers
Dr M Kasim A Jalil. Faculty of Mechanical Engineering UTM (source: Deitel Associates & Pearson)
 Lecture 9 Functions Dr M Kasim A Jalil Faculty of Mechanical Engineering UTM (source: Deitel Associates & Pearson) Objectives In this chapter, you will learn: To understand how to construct programs modularly
Lecture 9 Functions Dr M Kasim A Jalil Faculty of Mechanical Engineering UTM (source: Deitel Associates & Pearson) Objectives In this chapter, you will learn: To understand how to construct programs modularly
Solution: It may be helpful to list out exactly what is in each of these events:
 MATH 5010(002) Fall 2017 Homework 1 Solutions Please inform your instructor if you find any errors in the solutions. 1. You ask a friend to choose an integer N between 0 and 9. Let A = {N 5}, B = {3 N
MATH 5010(002) Fall 2017 Homework 1 Solutions Please inform your instructor if you find any errors in the solutions. 1. You ask a friend to choose an integer N between 0 and 9. Let A = {N 5}, B = {3 N
Programming for Engineers Functions
 Programming for Engineers Functions ICEN 200 Spring 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Introduction Real world problems are larger, more complex Top down approach Modularize divide and control Easier to track smaller
Programming for Engineers Functions ICEN 200 Spring 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Introduction Real world problems are larger, more complex Top down approach Modularize divide and control Easier to track smaller
Building on the foundation. Now that we know a little about cout cin math operators boolean operators making decisions using if statements
 Chapter 5 Looping Building on the foundation Now that we know a little about cout cin math operators boolean operators making decisions using if statements Advantages of Computers Computers are really
Chapter 5 Looping Building on the foundation Now that we know a little about cout cin math operators boolean operators making decisions using if statements Advantages of Computers Computers are really
Mat 2170 Week 9. Spring Mat 2170 Week 9. Objects and Classes. Week 9. Review. Random. Overloading. Craps. Clients. Packages. Randomness.
 Spring 2014 Student Responsibilities Reading: Textbook, Sections 6.1 6.3 Attendance Recall: Writing Methods Decomposition: break a problem down into smaller subproblems Use methods whenever you can in
Spring 2014 Student Responsibilities Reading: Textbook, Sections 6.1 6.3 Attendance Recall: Writing Methods Decomposition: break a problem down into smaller subproblems Use methods whenever you can in
function [A,V,a] = spherical cap(r,h) % Returns the area, volume and radius of a spherical cap % cut from a sphere of radius r, and cap height h
![function [A,V,a] = spherical cap(r,h) % Returns the area, volume and radius of a spherical cap % cut from a sphere of radius r, and cap height h function [A,V,a] = spherical cap(r,h) % Returns the area, volume and radius of a spherical cap % cut from a sphere of radius r, and cap height h](/thumbs/80/81585938.jpg) 1 Spherical Cap 1.a Area and Volume In this part all you have to do is to transfer the given mathematical formulas into assignments using arithmetic operators in MATLAB. When you run the script file, test
1 Spherical Cap 1.a Area and Volume In this part all you have to do is to transfer the given mathematical formulas into assignments using arithmetic operators in MATLAB. When you run the script file, test
Chapter Four: Loops. Slides by Evan Gallagher. C++ for Everyone by Cay Horstmann Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved
 Chapter Four: Loops Slides by Evan Gallagher The Three Loops in C++ C++ has these three looping statements: while for do The while Loop while (condition) { statements } The condition is some kind of test
Chapter Four: Loops Slides by Evan Gallagher The Three Loops in C++ C++ has these three looping statements: while for do The while Loop while (condition) { statements } The condition is some kind of test
hp calculators HP 35s Using Algebraic Mode Calculation modes Functions of a single number in algebraic A simple example in algebraic
 Calculation modes Functions of a single number in algebraic A simple example in algebraic Arithmetic calculations with two numbers Another example - the area of a piece of carpet Algebraic mode in detail
Calculation modes Functions of a single number in algebraic A simple example in algebraic Arithmetic calculations with two numbers Another example - the area of a piece of carpet Algebraic mode in detail
Student Responsibilities. Mat 2170 Week 9. Notes About Using Methods. Recall: Writing Methods. Chapter Six: Objects and Classes
 Student Responsibilities Mat 2170 Week 9 Objects and Classes Spring 2014 Reading: Textbook, Sections 6.1 6.3 Lab 9 Attendance 1 2 Recall: Writing Methods 3 Decomposition: break a problem down into smaller
Student Responsibilities Mat 2170 Week 9 Objects and Classes Spring 2014 Reading: Textbook, Sections 6.1 6.3 Lab 9 Attendance 1 2 Recall: Writing Methods 3 Decomposition: break a problem down into smaller
Assignment #3 Answers
 Assignment #3 Answers Introductory C Programming UW Experimental College Assignment #3 ANSWERS Question 1. How many elements does the array int a[5] contain? Which is the first element? The last? The array
Assignment #3 Answers Introductory C Programming UW Experimental College Assignment #3 ANSWERS Question 1. How many elements does the array int a[5] contain? Which is the first element? The last? The array
CC INTEGRATED II ETOOLS
 CC INTEGRATED II ETOOLS Table of Contents General etools... 4 Algebra Tiles (CPM)... 5 Pattern Tile & Dot Tool (CPM)... 8 Similarity Toolkit (CPM)...10 Probability Tools (CPM)...12 Desmos Graphing Calculator...16
CC INTEGRATED II ETOOLS Table of Contents General etools... 4 Algebra Tiles (CPM)... 5 Pattern Tile & Dot Tool (CPM)... 8 Similarity Toolkit (CPM)...10 Probability Tools (CPM)...12 Desmos Graphing Calculator...16
Chapter 2 Random Number Generators
 Chapter 2 Random Number Generators Introduction For many past years, numerous applications of randomness have led to a wide variety of methods for generating random data of various type, like rolling dice,
Chapter 2 Random Number Generators Introduction For many past years, numerous applications of randomness have led to a wide variety of methods for generating random data of various type, like rolling dice,
8. DEALING WITH RANDOMNESS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 8.1 GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS... 3 ACTIVITY 1... 4 ACTIVITY 2... 4 8.2 TRANSFORMING RANDOM NUMBERS... 6 ACTIVITY 3... 6 ACTIVITY 4... 7 ACTIVITY 5... 8 8.3 DISPLAYING RANDOMNESS... 10
TABLE OF CONTENTS 8.1 GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS... 3 ACTIVITY 1... 4 ACTIVITY 2... 4 8.2 TRANSFORMING RANDOM NUMBERS... 6 ACTIVITY 3... 6 ACTIVITY 4... 7 ACTIVITY 5... 8 8.3 DISPLAYING RANDOMNESS... 10
STEP Support Programme. Assignment 13
 STEP Support Programme Assignment 13 Warm-up You probably already know that for a graph with gradient dy : if dy > 0 then the graph is increasing ; if dy < 0 then the graph is decreasing. The sign of the
STEP Support Programme Assignment 13 Warm-up You probably already know that for a graph with gradient dy : if dy > 0 then the graph is increasing ; if dy < 0 then the graph is decreasing. The sign of the
Chapter 1 Histograms, Scatterplots, and Graphs of Functions
 Chapter 1 Histograms, Scatterplots, and Graphs of Functions 1.1 Using Lists for Data Entry To enter data into the calculator you use the statistics menu. You can store data into lists labeled L1 through
Chapter 1 Histograms, Scatterplots, and Graphs of Functions 1.1 Using Lists for Data Entry To enter data into the calculator you use the statistics menu. You can store data into lists labeled L1 through
If statements and For loops
 Advanced Random Simulation 5.1 89 If statements and For loops In order to incorporate more complex aspects into the model, use If statements and For loops. If[condition,t,f] Advanced Random Simulation
Advanced Random Simulation 5.1 89 If statements and For loops In order to incorporate more complex aspects into the model, use If statements and For loops. If[condition,t,f] Advanced Random Simulation
Section 3.1 Shapes of Distributions MDM4U Jensen
 Section 3.1 Shapes of Distributions MDM4U Jensen Part 1: Histogram Review Example 1: Earthquakes are measured on a scale known as the Richter Scale. There data are a sample of earthquake magnitudes in
Section 3.1 Shapes of Distributions MDM4U Jensen Part 1: Histogram Review Example 1: Earthquakes are measured on a scale known as the Richter Scale. There data are a sample of earthquake magnitudes in
Functions. Angela Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan.
 Functions Angela Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan 2009 Fall Outline 5.1 Introduction 5.3 Math Library Functions 5.4 Functions 5.5
Functions Angela Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan 2009 Fall Outline 5.1 Introduction 5.3 Math Library Functions 5.4 Functions 5.5
CS112 Lecture: Repetition Statements
 CS112 Lecture: Repetition Statements Objectives: Last revised 2/18/05 1. To explain the general form of the java while loop 2. To introduce and motivate the java do.. while loop 3. To explain the general
CS112 Lecture: Repetition Statements Objectives: Last revised 2/18/05 1. To explain the general form of the java while loop 2. To introduce and motivate the java do.. while loop 3. To explain the general
hp calculators HP 50g Calculator Modes and Customization Choosing how to use your Calculator Examples Selecting Radians Mode
 Choosing how to use your Calculator Examples Selecting Radians Mode Displaying the Time and Date Selecting Exact or Approximate Mode Changing the Display Font Customization with Menus Using Flags and Menus
Choosing how to use your Calculator Examples Selecting Radians Mode Displaying the Time and Date Selecting Exact or Approximate Mode Changing the Display Font Customization with Menus Using Flags and Menus
3.4. FOR-LOOPS 65. for <v a r i a b l e > in < sequence >:
 3.4. FOR-LOOPS 65 3.4 For-loops In the previous section we looked at while-loops, Python s basic looping structure. There is a second loop construct in Python called a for-loop. This is more specialized.
3.4. FOR-LOOPS 65 3.4 For-loops In the previous section we looked at while-loops, Python s basic looping structure. There is a second loop construct in Python called a for-loop. This is more specialized.
Applications. 72 Variables and Patterns
 Applications. Sean bought a DVD player and a receiver. The store offered him an interest-free payment plan with weekly installments. Sean figured out that after n weeks of payments, he would still owe
Applications. Sean bought a DVD player and a receiver. The store offered him an interest-free payment plan with weekly installments. Sean figured out that after n weeks of payments, he would still owe
Modeling RNA/DNA with Matlab - Chemistry Summer 2007
 Modeling RNA/DNA with Matlab - Chemistry 694 - Summer 2007 If you haven t already, download MatlabPrograms.zip from the course Blackboard site and extract all the files into a folder on your disk. Be careful
Modeling RNA/DNA with Matlab - Chemistry 694 - Summer 2007 If you haven t already, download MatlabPrograms.zip from the course Blackboard site and extract all the files into a folder on your disk. Be careful
adjacent angles Two angles in a plane which share a common vertex and a common side, but do not overlap. Angles 1 and 2 are adjacent angles.
 Angle 1 Angle 2 Angles 1 and 2 are adjacent angles. Two angles in a plane which share a common vertex and a common side, but do not overlap. adjacent angles 2 5 8 11 This arithmetic sequence has a constant
Angle 1 Angle 2 Angles 1 and 2 are adjacent angles. Two angles in a plane which share a common vertex and a common side, but do not overlap. adjacent angles 2 5 8 11 This arithmetic sequence has a constant
LAB: WHILE LOOPS IN C++
 LAB: WHILE LOOPS IN C++ MODULE 2 JEFFREY A. STONE and TRICIA K. CLARK COPYRIGHT 2014 VERSION 4.0 PALMS MODULE 2 LAB: WHILE LOOPS IN C++ 2 Introduction This lab will provide students with an introduction
LAB: WHILE LOOPS IN C++ MODULE 2 JEFFREY A. STONE and TRICIA K. CLARK COPYRIGHT 2014 VERSION 4.0 PALMS MODULE 2 LAB: WHILE LOOPS IN C++ 2 Introduction This lab will provide students with an introduction
UNC Charlotte 2010 Comprehensive
 00 Comprehensive March 8, 00. A cubic equation x 4x x + a = 0 has three roots, x, x, x. If x = x + x, what is a? (A) 4 (B) 8 (C) 0 (D) (E) 6. For which value of a is the polynomial P (x) = x 000 +ax+9
00 Comprehensive March 8, 00. A cubic equation x 4x x + a = 0 has three roots, x, x, x. If x = x + x, what is a? (A) 4 (B) 8 (C) 0 (D) (E) 6. For which value of a is the polynomial P (x) = x 000 +ax+9
Three Types of Probability
 CHAPTER Three Types of Probability This article is not so much about particular problems or problem solving tactics as it is about labels. If you think about it, labels are a big key to the way we organize
CHAPTER Three Types of Probability This article is not so much about particular problems or problem solving tactics as it is about labels. If you think about it, labels are a big key to the way we organize
Computational modeling
 Computational modeling Lecture 3 : Random variables Theory: 1 Random variables Programming: 1 Implicit none statement 2 Modules 3 Outputs 4 Functions 5 Conditional statement Instructor : Cedric Weber Course
Computational modeling Lecture 3 : Random variables Theory: 1 Random variables Programming: 1 Implicit none statement 2 Modules 3 Outputs 4 Functions 5 Conditional statement Instructor : Cedric Weber Course
Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements
 Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Basics of Programming with Python
 Basics of Programming with Python A gentle guide to writing simple programs Robert Montante 1 Topics Part 3 Obtaining Python Interactive use Variables Programs in files Data types Decision-making Functions
Basics of Programming with Python A gentle guide to writing simple programs Robert Montante 1 Topics Part 3 Obtaining Python Interactive use Variables Programs in files Data types Decision-making Functions
CSC 1351: Quiz 6: Sort and Search
 CSC 1351: Quiz 6: Sort and Search Name: 0.1 You want to implement combat within a role playing game on a computer. Specifically, the game rules for damage inflicted by a hit are: In order to figure out
CSC 1351: Quiz 6: Sort and Search Name: 0.1 You want to implement combat within a role playing game on a computer. Specifically, the game rules for damage inflicted by a hit are: In order to figure out
Problem Dice program
 Activity 1 Problem Dice program Aim: Based on the Maths 00 activity Problem Dice, Introduce the Program app to simulate 100 rolls of the dice. Creating a program automates a sequence of instructions we
Activity 1 Problem Dice program Aim: Based on the Maths 00 activity Problem Dice, Introduce the Program app to simulate 100 rolls of the dice. Creating a program automates a sequence of instructions we
Lecture VII : Random systems and random walk
 Lecture VII : Random systems and random walk I. RANDOM PROCESSES In nature, no processes are truly deterministic. However, while dealing with many physical processes such as calculating trajectories of
Lecture VII : Random systems and random walk I. RANDOM PROCESSES In nature, no processes are truly deterministic. However, while dealing with many physical processes such as calculating trajectories of
More about Loops and Decisions
 More about Loops and Decisions 5 In this chapter, we continue to explore the topic of repetition structures. We will discuss how loops are used in conjunction with the other control structures sequence
More about Loops and Decisions 5 In this chapter, we continue to explore the topic of repetition structures. We will discuss how loops are used in conjunction with the other control structures sequence
INITIALIZE CLEAR beneath COUNT
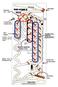 INITIALIZE Strictly speaking, the Digi-Comp II does not have an "INITIALIZE" function- it is a task that the human operator must perform, before most computations, to prepare the wooden "circuitry" for
INITIALIZE Strictly speaking, the Digi-Comp II does not have an "INITIALIZE" function- it is a task that the human operator must perform, before most computations, to prepare the wooden "circuitry" for
Loops. Repeat after me
 Loops Repeat after me 1 Loops A loop is a control structure in which a statement or set of statements execute repeatedly How many times the statements repeat is determined by the value of a control variable,
Loops Repeat after me 1 Loops A loop is a control structure in which a statement or set of statements execute repeatedly How many times the statements repeat is determined by the value of a control variable,
Is the result of multiplying 2 positive numbers positive or negative? Is the result of multiplying 2 negative numbers positive or negative?
 Write down all the work necessary for the problem, this is a part of your class notes that you can use to study from. You will not be able to use notes on quizzes or tests. DO NOT simply write it and toss
Write down all the work necessary for the problem, this is a part of your class notes that you can use to study from. You will not be able to use notes on quizzes or tests. DO NOT simply write it and toss
12/22/11. } Rolling a Six-Sided Die. } Fig 6.7: Rolling a Six-Sided Die 6,000,000 Times
 } Rolling a Six-Sided Die face = 1 + randomnumbers.nextint( 6 ); The argument 6 called the scaling factor represents the number of unique values that nextint should produce (0 5) This is called scaling
} Rolling a Six-Sided Die face = 1 + randomnumbers.nextint( 6 ); The argument 6 called the scaling factor represents the number of unique values that nextint should produce (0 5) This is called scaling
Chapter 9 Reduction Variables
 Chapter 9 Reduction Variables Part I. Preliminaries Part II. Tightly Coupled Multicore Chapter 6. Parallel Loops Chapter 7. Parallel Loop Schedules Chapter 8. Parallel Reduction Chapter 9. Reduction Variables
Chapter 9 Reduction Variables Part I. Preliminaries Part II. Tightly Coupled Multicore Chapter 6. Parallel Loops Chapter 7. Parallel Loop Schedules Chapter 8. Parallel Reduction Chapter 9. Reduction Variables
Chapter 4 - Arrays. 4.1 Introduction. Arrays Structures of related data items Static entity (same size throughout program)
 Chapter - Arrays 1.1 Introduction 2.1 Introduction.2 Arrays.3 Declaring Arrays. Examples Using Arrays.5 Passing Arrays to Functions.6 Sorting Arrays. Case Study: Computing Mean, Median and Mode Using Arrays.8
Chapter - Arrays 1.1 Introduction 2.1 Introduction.2 Arrays.3 Declaring Arrays. Examples Using Arrays.5 Passing Arrays to Functions.6 Sorting Arrays. Case Study: Computing Mean, Median and Mode Using Arrays.8
LAB: FOR LOOPS IN C++
 LAB: FOR LOOPS IN C++ MODULE 2 JEFFREY A. STONE and TRICIA K. CLARK COPYRIGHT 2014 VERSION 4.0 PALMS MODULE 2 LAB: FOR LOOPS IN C++ 2 Introduction This lab will provide students with an introduction to
LAB: FOR LOOPS IN C++ MODULE 2 JEFFREY A. STONE and TRICIA K. CLARK COPYRIGHT 2014 VERSION 4.0 PALMS MODULE 2 LAB: FOR LOOPS IN C++ 2 Introduction This lab will provide students with an introduction to
Chapter 4 - Arrays. 4.1 Introduction. Arrays Structures of related data items Static entity (same size throughout program) A few types
 Chapter 4 - Arrays 1 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Arrays 4.3 Declaring Arrays 4.4 Examples Using Arrays 4.5 Passing Arrays to Functions 4.6 Sorting Arrays 4.7 Case Study: Computing Mean, Median and Mode Using
Chapter 4 - Arrays 1 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Arrays 4.3 Declaring Arrays 4.4 Examples Using Arrays 4.5 Passing Arrays to Functions 4.6 Sorting Arrays 4.7 Case Study: Computing Mean, Median and Mode Using
Warm-Up If last month was July, then what month will it be 22 months from now?
 Warm-Up. If last month was July, then what month will it be months from now?. The maximum slope for handicap ramps was changed from to. What is the positive difference of these slopes? Express your answer
Warm-Up. If last month was July, then what month will it be months from now?. The maximum slope for handicap ramps was changed from to. What is the positive difference of these slopes? Express your answer
IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures
 IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures Module 2.5: Methods A Deeper Look Xianrong (Shawn) Zheng Spring 2017 1 Outline static Methods, static Variables, and Class Math Methods with Multiple
IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures Module 2.5: Methods A Deeper Look Xianrong (Shawn) Zheng Spring 2017 1 Outline static Methods, static Variables, and Class Math Methods with Multiple
Activity 7. Modeling Exponential Decay with a Look at Asymptotes. Objectives. Introduction. Modeling the Experiment: Casting Out Sixes
 Objectives Activity 7 Modeling Exponential Decay with a Look at Asymptotes Define parameters A and B in the exponential equation y = ab x Understand asymptotes, particularly non-zero asymptotes Identify
Objectives Activity 7 Modeling Exponential Decay with a Look at Asymptotes Define parameters A and B in the exponential equation y = ab x Understand asymptotes, particularly non-zero asymptotes Identify
Programming. Why is programming fun?
 Why is programming fun? Programming First is the sheer joy of making things. As the child delights in his mud pie, so the adult enjoys building things, especially things of his own design. I think this
Why is programming fun? Programming First is the sheer joy of making things. As the child delights in his mud pie, so the adult enjoys building things, especially things of his own design. I think this
Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE. CCM Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date:
 Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6+ 2015-16 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and 3-6 label Reflect
Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6+ 2015-16 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and 3-6 label Reflect
Computer Applications for Engineers ET 601
 Computer Applications for Engineers ET 601 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Random Variables 1 Office Hours: (BKD 3601-7) Wednesday 9:30-11:30 Wednesday 16:00-17:00 Thursday 14:40-16:00
Computer Applications for Engineers ET 601 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Random Variables 1 Office Hours: (BKD 3601-7) Wednesday 9:30-11:30 Wednesday 16:00-17:00 Thursday 14:40-16:00
Chapter 4. Procedural Abstraction and Functions That Return a Value. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4 Procedural Abstraction and Functions That Return a Value Overview 4.1 Top-Down Design 4.2 Predefined Functions 4.3 Programmer-Defined Functions 4.4 Procedural Abstraction 4.5 Local Variables
Chapter 4 Procedural Abstraction and Functions That Return a Value Overview 4.1 Top-Down Design 4.2 Predefined Functions 4.3 Programmer-Defined Functions 4.4 Procedural Abstraction 4.5 Local Variables
Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS
 Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS 1 Motivations Divide hug tasks to blocks: divide programs up into sets of cooperating functions. Define new functions with function calls and parameter passing. Use functions
Lecture 04 FUNCTIONS AND ARRAYS 1 Motivations Divide hug tasks to blocks: divide programs up into sets of cooperating functions. Define new functions with function calls and parameter passing. Use functions
Plug the USB interface of KAMKBMXBRNA gaming keyboard onto the free USB port of the computer. The
 System Requirements: 1. Windows XP / Windows Vista / Windows 7 / Windows8 Operation System 2. Free USB 2.0 Port 3. CD-ROM Driver 4. 50 Mb available memory Windows XP / Windows Vista / Windows 7 / Windows
System Requirements: 1. Windows XP / Windows Vista / Windows 7 / Windows8 Operation System 2. Free USB 2.0 Port 3. CD-ROM Driver 4. 50 Mb available memory Windows XP / Windows Vista / Windows 7 / Windows
troduction to Algebra Section 8.1
 Chapter Eight Graphing and Introduction to Statistics Section 8.1 Reading Pictographs, Bar Graphs, Histograms, and Line Graphs Pictographs A pictograph is a graph in which pictures or symbols are used.
Chapter Eight Graphing and Introduction to Statistics Section 8.1 Reading Pictographs, Bar Graphs, Histograms, and Line Graphs Pictographs A pictograph is a graph in which pictures or symbols are used.
Discrete Mathematics Exam File Fall Exam #1
 Discrete Mathematics Exam File Fall 2015 Exam #1 1.) Which of the following quantified predicate statements are true? Justify your answers. a.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 b.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 2.) Prove that
Discrete Mathematics Exam File Fall 2015 Exam #1 1.) Which of the following quantified predicate statements are true? Justify your answers. a.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 b.) n Z, k Z, n + k = 0 2.) Prove that
Probability and Statistics for Final Year Engineering Students
 Probability and Statistics for Final Year Engineering Students By Yoni Nazarathy, Last Updated: April 11, 2011. Lecture 1: Introduction and Basic Terms Welcome to the course, time table, assessment, etc..
Probability and Statistics for Final Year Engineering Students By Yoni Nazarathy, Last Updated: April 11, 2011. Lecture 1: Introduction and Basic Terms Welcome to the course, time table, assessment, etc..
Splitting Algorithms
 Splitting Algorithms We have seen that slotted Aloha has maximal throughput 1/e Now we will look at more sophisticated collision resolution techniques which have higher achievable throughput These techniques
Splitting Algorithms We have seen that slotted Aloha has maximal throughput 1/e Now we will look at more sophisticated collision resolution techniques which have higher achievable throughput These techniques
Chapter Four: Loops II
 Chapter Four: Loops II Slides by Evan Gallagher & Nikolay Kirov Chapter Goals To understand nested loops To implement programs that read and process data sets To use a computer for simulations Processing
Chapter Four: Loops II Slides by Evan Gallagher & Nikolay Kirov Chapter Goals To understand nested loops To implement programs that read and process data sets To use a computer for simulations Processing
Tutorial 12 Craps Game Application: Introducing Random Number Generation and Enumerations
 Tutorial 12 Craps Game Application: Introducing Random Number Generation and Enumerations Outline 12.1 Test-Driving the Craps Game Application 12.2 Random Number Generation 12.3 Using an enum in the Craps
Tutorial 12 Craps Game Application: Introducing Random Number Generation and Enumerations Outline 12.1 Test-Driving the Craps Game Application 12.2 Random Number Generation 12.3 Using an enum in the Craps
EECS 140 Laboratory Exercise 4 3-to-11 Counter Implementation
 EECS 140 Laboratory Exercise 4 3-to-11 Counter Implementation 1. Objectives A. To apply knowledge of combinatorial design. B. Gain expertise in designing and building a simple combinatorial circuit This
EECS 140 Laboratory Exercise 4 3-to-11 Counter Implementation 1. Objectives A. To apply knowledge of combinatorial design. B. Gain expertise in designing and building a simple combinatorial circuit This
Last Time: Rolling a Weighted Die
 Last Time: Rolling a Weighted Die import math/rand func DieRoll() int { return rand.intn(6) + 1 Multiple Rolls When we run this program 100 times, we get the same outcome! func main() int { fmt.println(dieroll())
Last Time: Rolling a Weighted Die import math/rand func DieRoll() int { return rand.intn(6) + 1 Multiple Rolls When we run this program 100 times, we get the same outcome! func main() int { fmt.println(dieroll())
absolute value- the absolute value of a number is the distance between that number and 0 on a number line. Absolute value is shown 7 = 7-16 = 16
 Grade Six MATH GLOSSARY absolute value- the absolute value of a number is the distance between that number and 0 on a number line. Absolute value is shown 7 = 7-16 = 16 abundant number: A number whose
Grade Six MATH GLOSSARY absolute value- the absolute value of a number is the distance between that number and 0 on a number line. Absolute value is shown 7 = 7-16 = 16 abundant number: A number whose
Lecture #2 January 30, 2004 The 6502 Architecture
 Lecture #2 January 30, 2004 The 6502 Architecture In order to understand the more modern computer architectures, it is helpful to examine an older but quite successful processor architecture, the MOS-6502.
Lecture #2 January 30, 2004 The 6502 Architecture In order to understand the more modern computer architectures, it is helpful to examine an older but quite successful processor architecture, the MOS-6502.
LSP 121. LSP 121 Math and Tech Literacy II. Topics. Loops. Loops. Loops
 LSP 121 Math and Tech Literacy II Greg Brewster DePaul University Topics The FOR loop Repeats a set of statements a fixed number of times The WHILE loop Repeats a set of statements until a condition is
LSP 121 Math and Tech Literacy II Greg Brewster DePaul University Topics The FOR loop Repeats a set of statements a fixed number of times The WHILE loop Repeats a set of statements until a condition is
Reading Assignment. Lazy Evaluation
 Reading Assignment Lazy Evaluation MULTILISP: a language for concurrent symbolic computation, by Robert H. Halstead (linked from class web page Lazy evaluation is sometimes called call by need. We do an
Reading Assignment Lazy Evaluation MULTILISP: a language for concurrent symbolic computation, by Robert H. Halstead (linked from class web page Lazy evaluation is sometimes called call by need. We do an
Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page
 Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page image pre-image transformation translation image pre-image reflection clockwise counterclockwise origin rotate 180 degrees rotate 270 degrees rotate
Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page image pre-image transformation translation image pre-image reflection clockwise counterclockwise origin rotate 180 degrees rotate 270 degrees rotate
Islamic University of Gaza Computer Engineering Dept. C++ Programming. For Industrial And Electrical Engineering By Instructor: Ruba A.
 Islamic University of Gaza Computer Engineering Dept. C++ Programming For Industrial And Electrical Engineering By Instructor: Ruba A. Salamh Chapter Four: Loops 2 Chapter Goals To implement while, for
Islamic University of Gaza Computer Engineering Dept. C++ Programming For Industrial And Electrical Engineering By Instructor: Ruba A. Salamh Chapter Four: Loops 2 Chapter Goals To implement while, for
At this time we have all the pieces necessary to allocate memory for an array dynamically. Following our example, we allocate N integers as follows:
 Pointers and Arrays Part II We will continue with our discussion on the relationship between pointers and arrays, and in particular, discuss how arrays with dynamical length can be created at run-time
Pointers and Arrays Part II We will continue with our discussion on the relationship between pointers and arrays, and in particular, discuss how arrays with dynamical length can be created at run-time
An Introduction to Stata By Mike Anderson
 An Introduction to Stata By Mike Anderson Installation and Start Up A 50-user licensed copy of Intercooled Stata 8.0 for Solaris is accessible on any Athena workstation. To use it, simply type add stata
An Introduction to Stata By Mike Anderson Installation and Start Up A 50-user licensed copy of Intercooled Stata 8.0 for Solaris is accessible on any Athena workstation. To use it, simply type add stata
Math INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB L. J. Gross - August 1995
 Math 151-2 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB L. J. Gross - August 1995 This is a very basic introduction to the elements of MATLAB that will be used in the early part of this course. A much more complete description
Math 151-2 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB L. J. Gross - August 1995 This is a very basic introduction to the elements of MATLAB that will be used in the early part of this course. A much more complete description
Objectivities. Experiment 1. Lab6 Array I. Description of the Problem. Problem-Solving Tips
 Lab6 Array I Objectivities 1. Using rand to generate random numbers and using srand to seed the random-number generator. 2. Declaring, initializing and referencing arrays. 3. The follow-up questions and
Lab6 Array I Objectivities 1. Using rand to generate random numbers and using srand to seed the random-number generator. 2. Declaring, initializing and referencing arrays. 3. The follow-up questions and
Prentice Hall. Connected Mathematics 2, 7th Grade Units Mississippi Mathematics Framework 2007 Revised, Grade 7
 Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 2, 7th Grade Units 2006 C O R R E L A T E D T O Mississippi Mathematics Framework 2007 Revised, Grade 7 NUMBER AND OPERATIONS 1. Apply concepts of rational numbers and
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 2, 7th Grade Units 2006 C O R R E L A T E D T O Mississippi Mathematics Framework 2007 Revised, Grade 7 NUMBER AND OPERATIONS 1. Apply concepts of rational numbers and
Fundamentals of Operations Research. Prof. G. Srinivasan. Department of Management Studies. Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture No.
 Fundamentals of Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 13 Transportation Problem, Methods for Initial Basic Feasible
Fundamentals of Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 13 Transportation Problem, Methods for Initial Basic Feasible
The benefits of understanding RPN stack operations. Understanding the HP12C RPN stack operation. Viewing and reordering stack-register contents
 HP 12C Using the RPN stack to solve problems efficiently The benefits of understanding RPN stack operations Understanding the HP12C RPN stack operation Viewing and reordering stack-register contents Using
HP 12C Using the RPN stack to solve problems efficiently The benefits of understanding RPN stack operations Understanding the HP12C RPN stack operation Viewing and reordering stack-register contents Using
The Command Shell, Libraries and Clients, Formatted Printing. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 The Command Shell, Libraries and Clients, Formatted Printing Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Graphical User Interface vs. Command Shell Starting the Command Shell Commands Compiling and Running
The Command Shell, Libraries and Clients, Formatted Printing Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Graphical User Interface vs. Command Shell Starting the Command Shell Commands Compiling and Running
Chapter 3. Finding Sums. This chapter covers procedures for obtaining many of the summed values that are
 1 Chapter 3 Finding Sums This chapter covers procedures for obtaining many of the summed values that are commonly used in statistical calculations. These procedures will produce values that are identical
1 Chapter 3 Finding Sums This chapter covers procedures for obtaining many of the summed values that are commonly used in statistical calculations. These procedures will produce values that are identical
Programming Basics and Practice GEDB029 Decision Making, Branching and Looping. Prof. Dr. Mannan Saeed Muhammad bit.ly/gedb029
 Programming Basics and Practice GEDB029 Decision Making, Branching and Looping Prof. Dr. Mannan Saeed Muhammad bit.ly/gedb029 Decision Making and Branching C language possesses such decision-making capabilities
Programming Basics and Practice GEDB029 Decision Making, Branching and Looping Prof. Dr. Mannan Saeed Muhammad bit.ly/gedb029 Decision Making and Branching C language possesses such decision-making capabilities
EE 231 Fall EE 231 Homework 8 Due October 20, 2010
 EE 231 Homework 8 Due October 20, 20 1. Consider the circuit below. It has three inputs (x and clock), and one output (z). At reset, the circuit starts with the outputs of all flip-flops at 0. x z J Q
EE 231 Homework 8 Due October 20, 20 1. Consider the circuit below. It has three inputs (x and clock), and one output (z). At reset, the circuit starts with the outputs of all flip-flops at 0. x z J Q
Math 574 Review Exam #1
 Math 574 Review Exam 1 1. How many 8-card hands, dealt from a standard deck of 5, consist of: (a). 5 of one suit and 3 of another suit? (b). 4 each of two suits. (c). 3 of one suit, 3 of a second suit,
Math 574 Review Exam 1 1. How many 8-card hands, dealt from a standard deck of 5, consist of: (a). 5 of one suit and 3 of another suit? (b). 4 each of two suits. (c). 3 of one suit, 3 of a second suit,
We will give examples for each of the following commonly used algorithm design techniques:
 Review This set of notes provides a quick review about what should have been learned in the prerequisite courses. The review is helpful to those who have come from a different background; or to those who
Review This set of notes provides a quick review about what should have been learned in the prerequisite courses. The review is helpful to those who have come from a different background; or to those who
