A framework for community safety and resilience
|
|
|
- Delphia Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 11/21/08 1:01 PM Page 1 Red Cross Red Crescent support to the Millenium Development Goals Building community safety and resilience Millenium Development Goals Community safety and resilience Red Cross Red Crescent framework for community safety and resilience Global alliance for disaster risk reduction Other disaster risk reduction efforts/programmes Red Cross Red Crescent global policies and strategies Hyogo Framework for Action Appendix 1: main areas of focus for the core components Risk assessment and identification and the warning and prediction Risk assessment and analysis including VCA Community empowerment for action Information management and dissemination for timely response and for developing medium- to longer-term programming to anticipate future risks Advocacy for community action Construction of databases to inform programme baselines Developing links with preparedness Capacity-building for early warning. Community-based disaster preparedness Building from the priorities of the VCA Developing preparedness at community and household levels Building community infrastructure Contingency planning Community organization through branches Establishing branch disaster response teams Skills training Identification of target groups schools, home, workplace Developing partnerships with knowledge centres Programming to link disaster preparedness with longer-term disaster risk reduction. Strong auxiliary relationships with local and national governments Support institution building the inclusion of National Societies in national policies and plans Representation of National Societies on national platforms for DRR National Societies as advocates for the identification of community level delivery in national policies, strategies, plans and programmes Promotion of inclusive action at the local level with communities, National Societies, local governments and other stakeholders. Nepal Red Cross Society For further information, please contact: International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Community people busy in vulnerability mapping and disaster preparedness training. In the face of disaster risk Partnerships with international, governmental, non-governmental and community-based organizations The promotion of local platforms for DRR The support of multi-stakeholder partnerships in programmes to promote community resilience Capacity development at all levels Knowledge-sharing at all levels Leadership in all aspects of promoting the cause of community resilience Advocacy for the Global Agenda and links with the HFA. Advocacy, education and awareness-raising Knowledge and experience sharing Awareness-raising for community organizations Capacity development for National Society staff and volunteers and the community Focus on schools Developing partnerships with knowledge centres. Disaster policy and preparedness department P.O. Box Geneva 19 - Switzerland secretariat@ifrc.org Web site: A framework for community safety and resilience /2008 E 1, Framework-community-EN:Layout 1 Background Our global commitment Disaster risk reduction (DRR) offers a major contribution to the building of safer, resilient communities. Central to this is the focus on communities and specifically communities that are at risk from regular and new disaster impacts. We know that we have been implementing DRR for some years now, but with the world becoming increasingly unsafe, it is important that we try to build on the foundations of previous endeavours and do more of what works and is effective. We also need to be more systematic in what we do as well as enhancing what we are doing to ensure that the basic objectives of safety and resilience are being addressed. National Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies have been implementing DRR for many years although it might not have been characterized as such. The 1980s saw new directions in programming with development-focused activities being implemented in Africa, Asia and Latin America, including community-based disaster preparedness. We are not necessarily concerned with a lot of new areas of work but rather with building on, enhancing and adapting what National Societies have already been doing and will continue to do in the future, looking for opportunities to make DRR action more effective and relevant to both existing and new disaster risks. Thus, the framework for community safety and resilience is concerned with what contributions the Red Cross Red Crescent can make in building community safety and resilience through a focus on disaster risk and its reduction. This framework has emerged from a widespread consultative process. At the National Society level, the framework was presented at five regional meetings for review and feedback. These regional meetings were held in Johannesburg, Katmandu, Penang, Panama and Rabat and were attended by over 70 National Societies. In 2003, the 28th International Conference of the Red Cross and Red Crescent adopted Final Goal 3.1 of its Agenda for Humanitarian Action which acknowledges the importance of DRR and undertakes measures to minimize the impact of disasters on vulnerable populations. Across the seven zones, a reference group was established to provide ongoing feedback on the framework reflecting National Society concerns. At the secretariat level the framework has been consistently under the scrutiny of a Global Alliance on DRR advisory group set up from among disaster management staff, while the disaster preparedness and risk reduction group of the Participating National Societies has also been regularly consulted. Suggestions and recommendations from all these groups have been incorporated into the framework. This new approach later became enshrined in our global commitments. In 1999, a new disaster preparedness policy recognized disaster preparedness as the link between emergency response, recovery and development. Regional conferences in Algiers, Guayaquil and Singapore reinforced this focus. DRR is identified as a key action in achieving the goals of Strategy 2010, stating particularly that we should scale up our actions with vulnerable communities in health promotion, disease prevention and disaster risk reduction. The 30th International Conference in 2007 adopted the declaration together for humanity which stated the importance of ensuring that environmental degradation and adaptation to climate change are integrated, where relevant, in disaster risk reduction and disaster management policies and plans. The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (International Federation) also supports and resolves to work towards achieving the priorities of the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA), adopted by the global community following the world conference on DRR held in Kobe, Japan in January 2005 (see below).
2 International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Objectives This framework has the following principal goal: To establish a foundation on which all Red Cross Red Crescent programmes, projects and interventions in DRR and all actions which contribute to the building of safe and resilient communities can be created, developed and sustained. The use of this framework in programming for safety, resilience and DRR assumes support to National Societies through the following three strategic objectives: 1 the integration of DRR into policies, planning and longer-term programming 2 targeted disaster prevention, mitigation and preparedness activities and advocacy 3 the focused integration of DRR considerations into humanitarian response and disaster recovery Linking what we do to the HFA All the actions we take in the implementation of DRR projects and programmes will be linked to the five priorities of the HFA. This is important because the HFA is truly global and has been endorsed by most governments, international agencies and non-governmental organizations. We are a part of this global network and it is important, therefore, for us to positively address the HFA priorities which are: 1 To ensure that DRR is a local and national priority with a strong institutional basis for implementation. 2 To identify, assess and monitor disaster risks and enhance early warning. 3 To use knowledge, innovation and education to build a culture of safety and resilience at all levels. 4 To reduce the underlying risk factors. 5 To strengthen disaster preparedness for effective response at all levels. However, the DRR actions that we take are to build safer and resilient communities. Incidentally, it is likely that most of what we do will be consistent with the HFA priorities. The Global Alliance on DRR The Global Alliance will be the principal instrument for increasing our work in DRR over the coming five-year period. The Global Alliance will focus on specific target National Societies and will give them high profile support to achieve agreed DRR goals, implemented according to the framework outlined in this paper and thus contributing to building community safety and resilience. The number of involved National Societies is likely to grow during the course of programme implementation. The Global Alliance, with its objectives emphasizing the importance of implementation at the community level, can help us to promote our DRR, community safety and resilience agendas and bring them to the attention of the international community at regional and global levels, thus mobilizing support to enable us to achieve a major programme outcome. The Global Alliance, as a mechanism for the delivery of scaled-up DRR, will use the framework as its planning and programming guideline, along with all other programmes supporting an increase in our DRR work. Focusing on building community safety and resilience in the face of disaster risk. In the International Federation we are promoting a common consensus around the building of safe and resilient communities. This concept was identified as a key strategic direction at the global meeting on DRR held in Costa Rica in November 2006 and reinforced as the central objective of the Global Alliance on DRR. It helps us to focus on households and communities and assists us in talking directly to the objectives of the Global Agenda. Safe and resilient communities can be identified as having the following key characteristics: They understand the disaster risks that they face, they can assess and monitor these risks and can protect and make themselves safe to minimize losses and damage when a disaster strikes. They are able to do much for themselves and can sustain their basic community functions and structures despite the impact of disasters. They can build back after a disaster and work towards ensuring that vulnerabilities continue to be reduced for the future. More safety and resilience means less vulnerability. They understand that building safety and resilience is a long-term, continuous process that requires ongoing commitment. In the face of such unknown factors as the effects of climate change, or the degree of urban growth or environmental degradation, they understand that there is much that can be done to adapt to future problems and challenges by building on their current knowledge. They appreciate the fact that being safe and disaster resilient means that there is a greater chance of meeting development goals which, in themselves, will greatly add to safety and resilience.
3 There may be other characteristics that we should add particularly in a regional or national context but these are offered as a general set of characteristics that help to define community safety and resilience in many communities globally. The key elements of the framework The framework for community safety and resilience in the face of disaster risk is constructed from a number of interrelated components. The essential end result, a safe and resilient community, emerges as an outcome of the achievement of a number of interrelated development goals. This is reinforced by increasingly reduced loss of life, livelihoods and assets following a disaster and the ability to build back stronger afterwards. Reduced loss of life, livelihoods and assets are enabled by a greater awareness of hazards and risks, a greater capacity for disaster response and the establishment and maintenance of safe environments. The ability to build back stronger is enabled by having access to essential services, resolving the provision of basic needs, particularly among the most vulnerable, and the creation of an enabling environment. The elements that identify the Red Cross Red Crescent contribution to DRR as a key action in building community safety and resilience are as follows: 1 Risk-informed humanitarian response. The provision of relief and the satisfaction of immediate needs following a disaster, as well as follow-on recovery activities aimed at getting communities back on their feet, are undertaken in a way that works towards meeting longer-term risk reduction objectives. It is understood that humanitarian response to disaster and recovery following a disaster is the absolute imperative of National Societies. However, this is not an end in itself but a means to an end, with increased safety and resilience and decreased vulnerability as a consequence, implying a diminishing need to respond to disasters in the future. 2 Country-specific mitigation, prevention and adaptation activities. National Societies will be working with their own country-specific hazard profile and within their national socio-economic, environmental and political contexts, and with communities in both rural and urban situations. They will also be working within a mandate agreed to and supported by national governments and civil society generally. Support to community safety and resilience will include mitigation, prevention and adaptation projects targeted towards the reduction of risks from specific hazards. 3 Sector-based programming to build across the disaster management spectrum. National Societies may have ongoing sector-based programmes in, for example, health and care, water and sanitation and shelter. These sectors are important elements of effective community-based DRR programmes. With good coordination these sector-based contributions should work towards DRR objectives and the building of community safety and resilience. It is intended that each of the Red Cross Red Crescent sector-based programmes will offer guidance in supporting programming from response through to DRR and the building of community safety and resilience. Core Red Cross Red Crescent cross-cutting components These are considered to be components that are essential to every National Society in addressing community safety and resilience. We are conscious that there are aspects of our work that we do well and that are consistent with our overall principles and values, goals and objectives. We should seek to encourage all National Societies that commit themselves to community safety and resilience to demonstrate their commitment through the implementation of these core components, related to their specific national context and hazard profile and integrated into all activities aimed at building community safety and resilience. The core components are: 1 Risk assessment and identification and the warning and prediction. Activities that may grow from a vulnerability and capacity assessment (VCA) or from other assessment processes that may help communities to identify the risks that they have to face, building early warning for the short-term and predictive capacity in the medium to long-term particularly in the context of climate change. 2 Community-based disaster preparedness. Support activities aimed at building the capacities of communities in enabling them to organize and address specific disaster risks. 3 Advocacy, education and awareness-raising. Activities across the spectrum of Red Cross Red Crescent work that aim to build a greater consciousness of the risk factors faced by communities and the ways in which these can be addressed within a range of different programmes. Advocacy, education and awareness-raising can be aimed at communities, local and national governments, other organizations at different levels, the private sector and, of course, the staff
4 A framework for community safety and resilience In the face of disaster risk and volunteers of the National Societies themselves. 4 A strong auxiliary relationship with local and national governments. One of the unique positions of the Red Cross Red Crescent is its auxiliary relationship with governments. This relationship is important in the context of ensuring increasingly that government at all levels is focused on strengthening community safety and resilience in the face of disaster risk and that this is reflected within national laws, policies, strategies and programmes. In particular, National Societies should be encouraging their governments to develop and implement laws, policies and plans that promote DRR at the community level. 5 Partnerships with international, governmental, non-governmental and communitybased organizations. It is important to recognize that the building of community safety and resilience in the face of disaster risk cannot be achieved by the Red Cross Red Crescent alone. We can certainly make our contribution but the systematic and ongoing building of safety and resilience can only be built upon strong working partnerships between all stakeholders from the communities themselves, to local and national governments, governmental and nongovernmental organizations and the private sector. A list of possible areas of focus for each of these five core components is given in Appendix 1. These five core components, integrated across the programme areas of Red Cross Red Crescent activity, help to identify our brand in DRR and support the building of community safety and resilience. They help us to focus on activity areas within which we have the capacity and competence to deliver, which reflect our comparative advantages and which are consistent with the priorities of the Global Agenda. The focus on these core components as a central part of our work in DRR recognizes the importance of our considerable network of volunteers who will have a key role in the delivery of DRR as a contribution to building community safety and resilience, coming as many of our volunteers do from the vulnerable communities themselves. In addition, the capacity development that is a key part of the process of increasing the scale and scope of our DRR activities must have a heavy emphasis on building the capacity of branches as a major element of organizational development. To truly identify the Red Cross Red Crescent approach to promoting community safety and resilience, we should look for National Societies that are implementing or supporting the core components integrated across their major programme or thematic areas, particularly those that relate to addressing country or hazard-specific DRR. It is likely that many National Societies will be involved with these areas already; therefore, we should concentrate on scaling up and expanding or enhancing existing programmes. This does not preclude support to new areas of work, provided that the National Society can demonstrate clearly the capacity to undertake such activity. In each case, National Societies should be encouraged to ensure that their planning and programming is integrated, seeking the linkages between the different core and country-specific components to promote common safety and resilience goals. The tools in implementing programmes Our National Societies already have many of the tools they need in implementing programmes to support community safety and resilience and DRR. However, they may not be oriented towards the achievement of community safety and resilience goals and there may be gaps that are identified as we continue to scale-up DRR action. To achieve community safety and resilience goals we will need to ensure that our National Societies have: The ability and capacity to identify strengths and weaknesses with communities and to respond to communitydriven priorities The ability to effectively use community knowledge and experience More robust and DRR focused VCA processes (VCA needs to provide input for assessing needs for effective DRR interventions) More exchanges of good practice and experience Better understanding of key legal and policy issues in DRR to strengthen humanitarian and development advocacy More developed skills in working with communities Better linkages and partnerships with others Better and more consistent technical support Consistent training opportunities Adequate financial and human resources to support sustainability A greater capacity to deliver DRR An active youth strategy A strong working relationship with local and national governments.
5 11/21/08 1:01 PM Page 1 Red Cross Red Crescent support to the Millenium Development Goals Building community safety and resilience Millenium Development Goals Community safety and resilience Red Cross Red Crescent framework for community safety and resilience Global alliance for disaster risk reduction Other disaster risk reduction efforts/programmes Red Cross Red Crescent global policies and strategies Hyogo Framework for Action Appendix 1: main areas of focus for the core components Risk assessment and identification and the warning and prediction Risk assessment and analysis including VCA Community empowerment for action Information management and dissemination for timely response and for developing medium- to longer-term programming to anticipate future risks Advocacy for community action Construction of databases to inform programme baselines Developing links with preparedness Capacity-building for early warning. Community-based disaster preparedness Building from the priorities of the VCA Developing preparedness at community and household levels Building community infrastructure Contingency planning Community organization through branches Establishing branch disaster response teams Skills training Identification of target groups schools, home, workplace Developing partnerships with knowledge centres Programming to link disaster preparedness with longer-term disaster risk reduction. Strong auxiliary relationships with local and national governments Support institution building the inclusion of National Societies in national policies and plans Representation of National Societies on national platforms for DRR National Societies as advocates for the identification of community level delivery in national policies, strategies, plans and programmes Promotion of inclusive action at the local level with communities, National Societies, local governments and other stakeholders. Nepal Red Cross Society For further information, please contact: International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Community people busy in vulnerability mapping and disaster preparedness training. In the face of disaster risk Partnerships with international, governmental, non-governmental and community-based organizations The promotion of local platforms for DRR The support of multi-stakeholder partnerships in programmes to promote community resilience Capacity development at all levels Knowledge-sharing at all levels Leadership in all aspects of promoting the cause of community resilience Advocacy for the Global Agenda and links with the HFA. Advocacy, education and awareness-raising Knowledge and experience sharing Awareness-raising for community organizations Capacity development for National Society staff and volunteers and the community Focus on schools Developing partnerships with knowledge centres. Disaster policy and preparedness department P.O. Box Geneva 19 - Switzerland secretariat@ifrc.org Web site: A framework for community safety and resilience /2008 E 1, Framework-community-EN:Layout 1 Background Our global commitment Disaster risk reduction (DRR) offers a major contribution to the building of safer, resilient communities. Central to this is the focus on communities and specifically communities that are at risk from regular and new disaster impacts. We know that we have been implementing DRR for some years now, but with the world becoming increasingly unsafe, it is important that we try to build on the foundations of previous endeavours and do more of what works and is effective. We also need to be more systematic in what we do as well as enhancing what we are doing to ensure that the basic objectives of safety and resilience are being addressed. National Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies have been implementing DRR for many years although it might not have been characterized as such. The 1980s saw new directions in programming with development-focused activities being implemented in Africa, Asia and Latin America, including community-based disaster preparedness. We are not necessarily concerned with a lot of new areas of work but rather with building on, enhancing and adapting what National Societies have already been doing and will continue to do in the future, looking for opportunities to make DRR action more effective and relevant to both existing and new disaster risks. Thus, the framework for community safety and resilience is concerned with what contributions the Red Cross Red Crescent can make in building community safety and resilience through a focus on disaster risk and its reduction. This framework has emerged from a widespread consultative process. At the National Society level, the framework was presented at five regional meetings for review and feedback. These regional meetings were held in Johannesburg, Katmandu, Penang, Panama and Rabat and were attended by over 70 National Societies. In 2003, the 28th International Conference of the Red Cross and Red Crescent adopted Final Goal 3.1 of its Agenda for Humanitarian Action which acknowledges the importance of DRR and undertakes measures to minimize the impact of disasters on vulnerable populations. Across the seven zones, a reference group was established to provide ongoing feedback on the framework reflecting National Society concerns. At the secretariat level the framework has been consistently under the scrutiny of a Global Alliance on DRR advisory group set up from among disaster management staff, while the disaster preparedness and risk reduction group of the Participating National Societies has also been regularly consulted. Suggestions and recommendations from all these groups have been incorporated into the framework. This new approach later became enshrined in our global commitments. In 1999, a new disaster preparedness policy recognized disaster preparedness as the link between emergency response, recovery and development. Regional conferences in Algiers, Guayaquil and Singapore reinforced this focus. DRR is identified as a key action in achieving the goals of Strategy 2010, stating particularly that we should scale up our actions with vulnerable communities in health promotion, disease prevention and disaster risk reduction. The 30th International Conference in 2007 adopted the declaration together for humanity which stated the importance of ensuring that environmental degradation and adaptation to climate change are integrated, where relevant, in disaster risk reduction and disaster management policies and plans. The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (International Federation) also supports and resolves to work towards achieving the priorities of the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA), adopted by the global community following the world conference on DRR held in Kobe, Japan in January 2005 (see below).
6 11/21/08 1:01 PM Page 1 Red Cross Red Crescent support to the Millenium Development Goals Building community safety and resilience Millenium Development Goals Community safety and resilience Red Cross Red Crescent framework for community safety and resilience Global alliance for disaster risk reduction Other disaster risk reduction efforts/programmes Red Cross Red Crescent global policies and strategies Hyogo Framework for Action Appendix 1: main areas of focus for the core components Risk assessment and identification and the warning and prediction Risk assessment and analysis including VCA Community empowerment for action Information management and dissemination for timely response and for developing medium- to longer-term programming to anticipate future risks Advocacy for community action Construction of databases to inform programme baselines Developing links with preparedness Capacity-building for early warning. Community-based disaster preparedness Building from the priorities of the VCA Developing preparedness at community and household levels Building community infrastructure Contingency planning Community organization through branches Establishing branch disaster response teams Skills training Identification of target groups schools, home, workplace Developing partnerships with knowledge centres Programming to link disaster preparedness with longer-term disaster risk reduction. Strong auxiliary relationships with local and national governments Support institution building the inclusion of National Societies in national policies and plans Representation of National Societies on national platforms for DRR National Societies as advocates for the identification of community level delivery in national policies, strategies, plans and programmes Promotion of inclusive action at the local level with communities, National Societies, local governments and other stakeholders. Nepal Red Cross Society For further information, please contact: International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies Community people busy in vulnerability mapping and disaster preparedness training. In the face of disaster risk Partnerships with international, governmental, non-governmental and community-based organizations The promotion of local platforms for DRR The support of multi-stakeholder partnerships in programmes to promote community resilience Capacity development at all levels Knowledge-sharing at all levels Leadership in all aspects of promoting the cause of community resilience Advocacy for the Global Agenda and links with the HFA. Advocacy, education and awareness-raising Knowledge and experience sharing Awareness-raising for community organizations Capacity development for National Society staff and volunteers and the community Focus on schools Developing partnerships with knowledge centres. Disaster policy and preparedness department P.O. Box Geneva 19 - Switzerland secretariat@ifrc.org Web site: A framework for community safety and resilience /2008 E 1, Framework-community-EN:Layout 1 Background Our global commitment Disaster risk reduction (DRR) offers a major contribution to the building of safer, resilient communities. Central to this is the focus on communities and specifically communities that are at risk from regular and new disaster impacts. We know that we have been implementing DRR for some years now, but with the world becoming increasingly unsafe, it is important that we try to build on the foundations of previous endeavours and do more of what works and is effective. We also need to be more systematic in what we do as well as enhancing what we are doing to ensure that the basic objectives of safety and resilience are being addressed. National Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies have been implementing DRR for many years although it might not have been characterized as such. The 1980s saw new directions in programming with development-focused activities being implemented in Africa, Asia and Latin America, including community-based disaster preparedness. We are not necessarily concerned with a lot of new areas of work but rather with building on, enhancing and adapting what National Societies have already been doing and will continue to do in the future, looking for opportunities to make DRR action more effective and relevant to both existing and new disaster risks. Thus, the framework for community safety and resilience is concerned with what contributions the Red Cross Red Crescent can make in building community safety and resilience through a focus on disaster risk and its reduction. This framework has emerged from a widespread consultative process. At the National Society level, the framework was presented at five regional meetings for review and feedback. These regional meetings were held in Johannesburg, Katmandu, Penang, Panama and Rabat and were attended by over 70 National Societies. In 2003, the 28th International Conference of the Red Cross and Red Crescent adopted Final Goal 3.1 of its Agenda for Humanitarian Action which acknowledges the importance of DRR and undertakes measures to minimize the impact of disasters on vulnerable populations. Across the seven zones, a reference group was established to provide ongoing feedback on the framework reflecting National Society concerns. At the secretariat level the framework has been consistently under the scrutiny of a Global Alliance on DRR advisory group set up from among disaster management staff, while the disaster preparedness and risk reduction group of the Participating National Societies has also been regularly consulted. Suggestions and recommendations from all these groups have been incorporated into the framework. This new approach later became enshrined in our global commitments. In 1999, a new disaster preparedness policy recognized disaster preparedness as the link between emergency response, recovery and development. Regional conferences in Algiers, Guayaquil and Singapore reinforced this focus. DRR is identified as a key action in achieving the goals of Strategy 2010, stating particularly that we should scale up our actions with vulnerable communities in health promotion, disease prevention and disaster risk reduction. The 30th International Conference in 2007 adopted the declaration together for humanity which stated the importance of ensuring that environmental degradation and adaptation to climate change are integrated, where relevant, in disaster risk reduction and disaster management policies and plans. The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (International Federation) also supports and resolves to work towards achieving the priorities of the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA), adopted by the global community following the world conference on DRR held in Kobe, Japan in January 2005 (see below).
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.30 and Add.1)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.30 and Add.1)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.30 and Add.1)]](/thumbs/87/95227437.jpg) United Nations A/RES/62/91 General Assembly Distr.: General 8 February 2008 Sixty-second session Agenda item 71 (a) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.30
United Nations A/RES/62/91 General Assembly Distr.: General 8 February 2008 Sixty-second session Agenda item 71 (a) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.30
From Hyogo to Sendai. Anoja Seneviratne Disaster Management Centre
 From Hyogo to Sendai Anoja Seneviratne Disaster Management Centre Milestone Event in the Year 2015 New York in September 2015 to World Conference define voluntary on Disaster Risk Sustainable Reduction
From Hyogo to Sendai Anoja Seneviratne Disaster Management Centre Milestone Event in the Year 2015 New York in September 2015 to World Conference define voluntary on Disaster Risk Sustainable Reduction
UPU UNIVERSAL POSTAL UNION. CA C 4 SDPG AHG DRM Doc 3. Original: English COUNCIL OF ADMINISTRATION. Committee 4 Development Cooperation
 UPU UNIVERSAL POSTAL UNION CA C 4 SDPG AHG DRM 2014.1-Doc 3 Original: English COUNCIL OF ADMINISTRATION Committee 4 Development Cooperation Sustainable Development Project Group Ad hoc group on Disaster
UPU UNIVERSAL POSTAL UNION CA C 4 SDPG AHG DRM 2014.1-Doc 3 Original: English COUNCIL OF ADMINISTRATION Committee 4 Development Cooperation Sustainable Development Project Group Ad hoc group on Disaster
Plan of action for Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction in Central Asia and South Caucasus Region
 Plan of action for Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 in Central Asia and South Caucasus Region I. Background All governments in the Central Asia and South Caucasus
Plan of action for Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 in Central Asia and South Caucasus Region I. Background All governments in the Central Asia and South Caucasus
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 14 December [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.44 and Add.1)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 14 December [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.44 and Add.1)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 14 December [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.44 and Add.1)]](/thumbs/83/87224038.jpg) United Nations A/RES/61/132 General Assembly Distr.: General 1 March 2007 Sixty-first session Agenda item 69 (a) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 14 December 2006 [without reference to a Main
United Nations A/RES/61/132 General Assembly Distr.: General 1 March 2007 Sixty-first session Agenda item 69 (a) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 14 December 2006 [without reference to a Main
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/60/488/Add.3)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/60/488/Add.3)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/60/488/Add.3)]](/thumbs/90/103086719.jpg) United Nations A/RES/60/195 General Assembly Distr.: General 2 March 2006 Sixtieth session Agenda item 52 (c) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [on the report of the Second Committee (A/60/488/Add.3)]
United Nations A/RES/60/195 General Assembly Distr.: General 2 March 2006 Sixtieth session Agenda item 52 (c) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [on the report of the Second Committee (A/60/488/Add.3)]
The Hyogo Framework for Action: an instrument to reduce the impact of disasters
 1 22 February 2007 The Hyogo Framework for Action: an instrument to reduce the impact of disasters Dialogue on Private-Public Partnerships in Disaster Risk Reduction Global Facility for Disaster Reduction
1 22 February 2007 The Hyogo Framework for Action: an instrument to reduce the impact of disasters Dialogue on Private-Public Partnerships in Disaster Risk Reduction Global Facility for Disaster Reduction
ISDR National Platforms for DRR - Guidelines
 1 ISDR National Platforms for DRR - Guidelines Multi-stakeholder meeting on Disaster Risk Reduction Bishkek 27 July 2009 Lars Bernd, Programme Officer National Platforms, UNISDR secretariat Geneva, bernd@un.org
1 ISDR National Platforms for DRR - Guidelines Multi-stakeholder meeting on Disaster Risk Reduction Bishkek 27 July 2009 Lars Bernd, Programme Officer National Platforms, UNISDR secretariat Geneva, bernd@un.org
International Workshop on Flood Risk Management Tsukuba, January 2006
 International Workshop on Flood Risk Management Tsukuba, 24 26 January 2006 Implementation of Hyogo Framework for Actions in the area of Water-related disasters Yuichi ONO International Strategy for Disaster
International Workshop on Flood Risk Management Tsukuba, 24 26 January 2006 Implementation of Hyogo Framework for Actions in the area of Water-related disasters Yuichi ONO International Strategy for Disaster
Building Resilience to Disasters for Sustainable Development: Visakhapatnam Declaration and Plan of Action
 Building Resilience to Disasters for Sustainable Development: Visakhapatnam Declaration and Plan of Action Adopted at the Third World Congress on Disaster Management Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India
Building Resilience to Disasters for Sustainable Development: Visakhapatnam Declaration and Plan of Action Adopted at the Third World Congress on Disaster Management Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India
The Science and Technology Roadmap to Support the Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
 29 February 2016 The Science and Technology Roadmap to Support the Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030
29 February 2016 The Science and Technology Roadmap to Support the Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/56/561/Add.2)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/56/561/Add.2)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/56/561/Add.2)]](/thumbs/85/92603079.jpg) United Nations A/RES/56/195 General Assembly Distr.: General 21 January 2002 Fifty-sixth session Agenda item 98 (b) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [on the report of the Second Committee (A/56/561/Add.2)]
United Nations A/RES/56/195 General Assembly Distr.: General 21 January 2002 Fifty-sixth session Agenda item 98 (b) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [on the report of the Second Committee (A/56/561/Add.2)]
Outcomes of the Sendai Framework of Disaster Risk Reduction and the 3rd World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction
 Outcomes of the Sendai Framework of Disaster Risk Reduction and the 3rd World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Kiyoshi NATORI Executive Director of Asian Disaster Reduction Center The Third UN World
Outcomes of the Sendai Framework of Disaster Risk Reduction and the 3rd World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Kiyoshi NATORI Executive Director of Asian Disaster Reduction Center The Third UN World
Local Action for Building Resilience at Nations and Communities
 Local Action for Building Resilience at Nations and Communities Yongkyun Kim Institute Coordinator UNISDR Northeast Asia Office and Global Education and Training Institute for DRR Incheon Sister Friendly
Local Action for Building Resilience at Nations and Communities Yongkyun Kim Institute Coordinator UNISDR Northeast Asia Office and Global Education and Training Institute for DRR Incheon Sister Friendly
TURNING STRATEGIES INTO ACTION DISASTER MANAGEMENT BUREAU STRATEGIC PLAN
 DISASTER MANAGEMENT BUREAU STRATEGIC PLAN 2005-2006 PREFACE Historical statistics would suggest that Bangladesh is one of the most disaster prone countries in the world with the greatest negative consequences
DISASTER MANAGEMENT BUREAU STRATEGIC PLAN 2005-2006 PREFACE Historical statistics would suggest that Bangladesh is one of the most disaster prone countries in the world with the greatest negative consequences
BACKGROUND PAPER. Sub-Regional Platform on Disaster Risk Reduction
 BACKGROUND PAPER Sub-Regional Platform on Disaster Risk Reduction Niamey, Niger 11-14 November 2013 1 BACKGROUND The ECOWAS Policy on Disaster Risk Reduction adopted by West African Heads of State and
BACKGROUND PAPER Sub-Regional Platform on Disaster Risk Reduction Niamey, Niger 11-14 November 2013 1 BACKGROUND The ECOWAS Policy on Disaster Risk Reduction adopted by West African Heads of State and
Disaster risk reduction Summary of the Oslo conference, February 2009
 Disaster risk reduction Summary of the Oslo conference, February 2009 Building safer, resilient communities Introduction As a result of an increasing number of disasters triggered by natural hazards, the
Disaster risk reduction Summary of the Oslo conference, February 2009 Building safer, resilient communities Introduction As a result of an increasing number of disasters triggered by natural hazards, the
The UNISDR Private Sector Alliance for Disaster Resilient Societies
 The UNISDR Private Sector Alliance for Disaster Resilient Societies Sandra Amlang United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR) Regional Office- the Americas. 24 August 2017 Increase in Frequency
The UNISDR Private Sector Alliance for Disaster Resilient Societies Sandra Amlang United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR) Regional Office- the Americas. 24 August 2017 Increase in Frequency
Post Disaster Needs Assessment Guide and
 Post Disaster Needs Assessment Guide and Framework Guide International Platform Forum 2014 January 21, 2014 Kobe, Japan Post Disaster Needs Assessment Agreement between EU, UN and World Bank to collaborate
Post Disaster Needs Assessment Guide and Framework Guide International Platform Forum 2014 January 21, 2014 Kobe, Japan Post Disaster Needs Assessment Agreement between EU, UN and World Bank to collaborate
Common Framework for Preparedness
 INTER-AGENCY STANDING COMMITTEE Common Framework for Preparedness I Summary 18 October 2013 A range of actors assists member states and communities towards achieving resilience, including through enhancing
INTER-AGENCY STANDING COMMITTEE Common Framework for Preparedness I Summary 18 October 2013 A range of actors assists member states and communities towards achieving resilience, including through enhancing
Common Framework for Preparedness
 I Summary INTER-AGENCY STANDING COMMITTEE Common Framework for Preparedness 18 October 2013 A range of actors assists member states and communities towards achieving resilience, including through enhancing
I Summary INTER-AGENCY STANDING COMMITTEE Common Framework for Preparedness 18 October 2013 A range of actors assists member states and communities towards achieving resilience, including through enhancing
RESOLUTION ADOPTED BY THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/54/588/Add.2)]
![RESOLUTION ADOPTED BY THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/54/588/Add.2)] RESOLUTION ADOPTED BY THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/54/588/Add.2)]](/thumbs/87/97255893.jpg) UNITED NATIONS A General Assembly Distr. GENERAL A/RES/54/219 3 February 2000 Fifty-fourth session Agenda item 100 (b) RESOLUTION ADOPTED BY THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY [on the report of the Second Committee
UNITED NATIONS A General Assembly Distr. GENERAL A/RES/54/219 3 February 2000 Fifty-fourth session Agenda item 100 (b) RESOLUTION ADOPTED BY THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY [on the report of the Second Committee
Prioritized Action Plan of the Arab Strategy for Disaster Risk Reduction 2030
 Prioritized Action Plan 2018-2020 of the Arab Strategy for Disaster Risk Reduction 2030 1. Preamble to implement the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 1.1. The Sendai Framework for
Prioritized Action Plan 2018-2020 of the Arab Strategy for Disaster Risk Reduction 2030 1. Preamble to implement the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 1.1. The Sendai Framework for
Private sector s engagement in the implementation of the Sendai Framework
 Private sector s engagement in the implementation of the Sendai Framework Palais des Nations, Geneva, 2 May 2017 Oz Ozturk, PricewaterhouseCoopers Content: Introduction Key messages Sendai Framework and
Private sector s engagement in the implementation of the Sendai Framework Palais des Nations, Geneva, 2 May 2017 Oz Ozturk, PricewaterhouseCoopers Content: Introduction Key messages Sendai Framework and
New International Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
 New International Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Yuichi Ono Assistant Director and Professor International Research Institute of Disaster Science Tohoku University 1 Promote International Movement
New International Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Yuichi Ono Assistant Director and Professor International Research Institute of Disaster Science Tohoku University 1 Promote International Movement
Caribbean Private Sector Network meeting 24 August 2017, Ministry of Trade, Port-of-Spain, Trinidad and Tobago
 Caribbean Private Sector Network meeting 24 August 2017, Ministry of Trade, Port-of-Spain, Trinidad and Tobago Background The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 1 was adopted by United
Caribbean Private Sector Network meeting 24 August 2017, Ministry of Trade, Port-of-Spain, Trinidad and Tobago Background The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 1 was adopted by United
ASEAN COOPERATION ON DISASTER MANAGEMENT. Disaster Management & Humanitarian Assistance Division, ASEAN Secretariat
 ASEAN COOPERATION ON DISASTER MANAGEMENT Disaster Management & Humanitarian Assistance Division, ASEAN Secretariat AADMER - FOR A MORE UNITED AND COORDINATED RESPONSE TOWARD DISASTERS WITHIN THE REGION
ASEAN COOPERATION ON DISASTER MANAGEMENT Disaster Management & Humanitarian Assistance Division, ASEAN Secretariat AADMER - FOR A MORE UNITED AND COORDINATED RESPONSE TOWARD DISASTERS WITHIN THE REGION
Progress in Disaster Risk Reduction through Multi-National Cooperation in Asia
 Progress in Disaster Risk Reduction through Multi-National Cooperation in Asia Koji SUZUKI Asian Disaster Reduction Center() Establishment & Expansion of Network Establishment 1994 World Conference on
Progress in Disaster Risk Reduction through Multi-National Cooperation in Asia Koji SUZUKI Asian Disaster Reduction Center() Establishment & Expansion of Network Establishment 1994 World Conference on
United Nations Conference on the Human Environment (Stockholm)
 1972 1982 1992 2000 United Nations Conference on the Human Environment (Stockholm) àonly One Earth Session of a Special Character' (SSC) of the Governing Council of the United Nations Environment Programme
1972 1982 1992 2000 United Nations Conference on the Human Environment (Stockholm) àonly One Earth Session of a Special Character' (SSC) of the Governing Council of the United Nations Environment Programme
Hyogo Framework for Action:
 Hyogo Framework for Action: Building the capacity and resilience of the community against the disasters 2005-2015 Regional workshop on Disaster Communications Organized by :ITU/ ESCAP 12-15 December 06,
Hyogo Framework for Action: Building the capacity and resilience of the community against the disasters 2005-2015 Regional workshop on Disaster Communications Organized by :ITU/ ESCAP 12-15 December 06,
Progress of Regional Cooperation in the Field of Disaster Risk Reduction in Asia
 Asian Conference on Disaster Reduction 2007 25-27 June 2007, Astana, Republic of Kazakhstan Progress of Regional Cooperation in the Field of Disaster Risk Reduction in Asia Going forward with Hyogo Framework
Asian Conference on Disaster Reduction 2007 25-27 June 2007, Astana, Republic of Kazakhstan Progress of Regional Cooperation in the Field of Disaster Risk Reduction in Asia Going forward with Hyogo Framework
UAE National Space Policy Agenda Item 11; LSC April By: Space Policy and Regulations Directory
 UAE National Space Policy Agenda Item 11; LSC 2017 06 April 2017 By: Space Policy and Regulations Directory 1 Federal Decree Law No.1 of 2014 establishes the UAE Space Agency UAE Space Agency Objectives
UAE National Space Policy Agenda Item 11; LSC 2017 06 April 2017 By: Space Policy and Regulations Directory 1 Federal Decree Law No.1 of 2014 establishes the UAE Space Agency UAE Space Agency Objectives
About the Asia-Pacific Regional Coordination Mechanism
 2017 Dr. Shamshad Akhtar Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations and Executive Secretary, United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific The role of the Regional Coordination
2017 Dr. Shamshad Akhtar Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations and Executive Secretary, United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific The role of the Regional Coordination
TERMS OF REFERENCE URBAN RAILWAY DEVELOPMENT GUIDEBOOK SUPPORT TO DEVELOP CHAPTER 15 CLIMATE AND NATURAL DISASTER RESILIENCE IN URBAN RAIL PROJECTS
 TERMS OF REFERENCE URBAN RAILWAY DEVELOPMENT GUIDEBOOK SUPPORT TO DEVELOP CHAPTER 15 CLIMATE AND NATURAL DISASTER RESILIENCE IN URBAN RAIL PROJECTS CONSULTANT Contents Background on the Knowledge Product...
TERMS OF REFERENCE URBAN RAILWAY DEVELOPMENT GUIDEBOOK SUPPORT TO DEVELOP CHAPTER 15 CLIMATE AND NATURAL DISASTER RESILIENCE IN URBAN RAIL PROJECTS CONSULTANT Contents Background on the Knowledge Product...
SAINT PETERSBURG DECLARATION Building Confidence and Security in the Use of ICT to Promote Economic Growth and Prosperity
 SAINT PETERSBURG DECLARATION Building Confidence and Security in the Use of ICT to Promote Economic Growth and Prosperity 1. We, APEC Ministers responsible for the Telecommunications and Information Industry,
SAINT PETERSBURG DECLARATION Building Confidence and Security in the Use of ICT to Promote Economic Growth and Prosperity 1. We, APEC Ministers responsible for the Telecommunications and Information Industry,
General Assembly UNITED NATIONS. Distr. GENERAL. A/CONF.206/PC(II)/4 13 August 2004 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION
 UNITED NATIONS A General Assembly Distr. GENERAL 13 August 2004 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION Preparatory Committee Second Session Geneva, 11-12 October 2004 Item 10 of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS A General Assembly Distr. GENERAL 13 August 2004 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION Preparatory Committee Second Session Geneva, 11-12 October 2004 Item 10 of the provisional
National Policy and Guiding Principles
 National Policy and Guiding Principles National Policy, Principles, and Organization This section describes the national policy that shapes the National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace and the basic framework
National Policy and Guiding Principles National Policy, Principles, and Organization This section describes the national policy that shapes the National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace and the basic framework
3 rd World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction
 2015/SOM1/EPWG/008 Agenda Item: 11 1.2 3 rd World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Purpose: Information Submitted by: Japan 7 th Emergency Preparedness Working Group Meeting Subic, Philippines 28-29
2015/SOM1/EPWG/008 Agenda Item: 11 1.2 3 rd World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Purpose: Information Submitted by: Japan 7 th Emergency Preparedness Working Group Meeting Subic, Philippines 28-29
Regional Development Forum For the Arab States(RDF-ARB) 2018
 Regional Development Forum For the Arab States(RDF-ARB) 2018 ICT4SDGs: Towards the implementation of WTDC17 outcomes Algiers, Algeria 12, 13 February 2018 Background Concept Note In the framework of the
Regional Development Forum For the Arab States(RDF-ARB) 2018 ICT4SDGs: Towards the implementation of WTDC17 outcomes Algiers, Algeria 12, 13 February 2018 Background Concept Note In the framework of the
UNISDR Strategic Framework
 UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Pages // 4 Pages // 5 THE ROLE OF THE UNITED NATIONS OFFICE FOR DISASTER
UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Pages // 4 Pages // 5 THE ROLE OF THE UNITED NATIONS OFFICE FOR DISASTER
UNISDR Strategic Framework
 UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Pages // 4 THE ROLE OF THE UNITED NATIONS OFFICE FOR DISASTER RISK REDUCTION: A THEORY OF CHANGE Introduction The UNISDR Strategic
UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 UNISDR Strategic Framework 2016-2021 Pages // 4 THE ROLE OF THE UNITED NATIONS OFFICE FOR DISASTER RISK REDUCTION: A THEORY OF CHANGE Introduction The UNISDR Strategic
Provisional Annotated Agenda
 Tel. : +41 22 017 8828 Fax : +41 22 917 8964 globalplatform@un.org International Environment House II 7-9 Chemin de Balexert CH 1219 Châtelaine Geneva, Switzerland Invest today for a safer tomorrow The
Tel. : +41 22 017 8828 Fax : +41 22 917 8964 globalplatform@un.org International Environment House II 7-9 Chemin de Balexert CH 1219 Châtelaine Geneva, Switzerland Invest today for a safer tomorrow The
The Africa Programme of Action for Disaster Risk Reduction
 The Africa Programme of Action for Disaster Risk Reduction Inception Workshop Drought Cycle Management in the Great Horn of Africa Nairobi, 12-13 October 2010 Dr. Pedro Basabe Head, UNISDR Regional Office
The Africa Programme of Action for Disaster Risk Reduction Inception Workshop Drought Cycle Management in the Great Horn of Africa Nairobi, 12-13 October 2010 Dr. Pedro Basabe Head, UNISDR Regional Office
Guatemala Mid-Year Report 2012
 Guatemala Mid-Year Report 2012 MAAGT002 29 July 2013 This report covers the period 01 January 2012 to 31June 2012. Photo caption and credits Communication Department Guatemala Red Cross In Brief To follow
Guatemala Mid-Year Report 2012 MAAGT002 29 July 2013 This report covers the period 01 January 2012 to 31June 2012. Photo caption and credits Communication Department Guatemala Red Cross In Brief To follow
World Meteorological Organization Working together in weather, climate and water
 WMO World Meteorological Organization Working together in weather, climate and water Workshop on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems for Urban Areas Dr Maryam Golnaraghi Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction
WMO World Meteorological Organization Working together in weather, climate and water Workshop on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems for Urban Areas Dr Maryam Golnaraghi Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction
Hazard Management Cayman Islands
 Hazard Management Cayman Islands Strategic Plan 2012 2016 Executive Summary HMCI strategic plan outlines the agency s outlook in the next five years and illustrates the main strategies as goals that will
Hazard Management Cayman Islands Strategic Plan 2012 2016 Executive Summary HMCI strategic plan outlines the agency s outlook in the next five years and illustrates the main strategies as goals that will
The World Conference on Disaster Reduction: Serious commitments and clearer priorities for the next decade
 The World Conference on Disaster Reduction: Serious commitments and clearer priorities for the next decade Yuichi Ono, UN/ISDR Platform for the Promotion of Early Warning, Bonn, Germany Presentation to
The World Conference on Disaster Reduction: Serious commitments and clearer priorities for the next decade Yuichi Ono, UN/ISDR Platform for the Promotion of Early Warning, Bonn, Germany Presentation to
Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Preparedness, Response & Early Warning
 Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Preparedness, Response & Early Warning Regional Office for Middle East and North Africa (ROMENA) & Emergency Preparedness and Environmental Section (EPES)
Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Preparedness, Response & Early Warning Regional Office for Middle East and North Africa (ROMENA) & Emergency Preparedness and Environmental Section (EPES)
How Sendai Framework will affect future Resilience for Business & Consumers
 How Sendai Framework will affect future Resilience for Business & Consumers Aris Papadopoulos Resilience Action Fund FIU Extreme Events Institute FLASH National Disaster Resilience Conference October 26,
How Sendai Framework will affect future Resilience for Business & Consumers Aris Papadopoulos Resilience Action Fund FIU Extreme Events Institute FLASH National Disaster Resilience Conference October 26,
National Coordinator - DRR & Disaster Management
 National Coordinator - DRR & Disaster Management Location: [Africa] [Kenya] [Nairobi] Category: Food Security & Livelihood Purpose of the Position: This position is responsible for coordinating and managing
National Coordinator - DRR & Disaster Management Location: [Africa] [Kenya] [Nairobi] Category: Food Security & Livelihood Purpose of the Position: This position is responsible for coordinating and managing
Promoting accountability and transparency of multistakeholder partnerships for the implementation of the 2030 Agenda
 2016 PARTNERSHIP FORUM Promoting accountability and transparency of multistakeholder partnerships for the implementation of the 2030 Agenda 31 March 2016 Dialogue Two (3:00 p.m. 5:45 p.m.) ECOSOC CHAMBER,
2016 PARTNERSHIP FORUM Promoting accountability and transparency of multistakeholder partnerships for the implementation of the 2030 Agenda 31 March 2016 Dialogue Two (3:00 p.m. 5:45 p.m.) ECOSOC CHAMBER,
UN-ISDR AMADORA LOCAL CAMPAIGN
 Comando Distrital de Operações de Socorro de Lisboa STAKEHOLDERS: Associação Cultural Moinho da Juventude UN-ISDR 2010-2015 AMADORA LOCAL CAMPAIGN INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY FOR DISASTER REDUCTION Making Cities
Comando Distrital de Operações de Socorro de Lisboa STAKEHOLDERS: Associação Cultural Moinho da Juventude UN-ISDR 2010-2015 AMADORA LOCAL CAMPAIGN INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY FOR DISASTER REDUCTION Making Cities
STRATEGY ATIONAL. National Strategy. for Critical Infrastructure. Government
 ATIONAL STRATEGY National Strategy for Critical Infrastructure Government Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2009 Cat. No.: PS4-65/2009E-PDF ISBN: 978-1-100-11248-0 Printed in Canada Table of contents
ATIONAL STRATEGY National Strategy for Critical Infrastructure Government Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2009 Cat. No.: PS4-65/2009E-PDF ISBN: 978-1-100-11248-0 Printed in Canada Table of contents
Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (SFDRR) and IFRC
 SFDRR and and Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (SFDRR) and Expected Outcome The substantial reduction of disaster risk and losses in lives, livelihoods and health and in the economic, physical,
SFDRR and and Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (SFDRR) and Expected Outcome The substantial reduction of disaster risk and losses in lives, livelihoods and health and in the economic, physical,
2009/7 Assessment of the progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit on the Information Society
 Resolutions 2009/7 Assessment of the progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit on the Information Society The Economic and Social Council, Recalling the outcome
Resolutions 2009/7 Assessment of the progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit on the Information Society The Economic and Social Council, Recalling the outcome
Strengthening Early Recovery and Preparedness Coordination Mechanisms in Kenya. Final Narrative Report
 Strengthening Early Recovery and Preparedness Coordination Mechanisms in Kenya Final Narrative Report January June 2012 0 Summary To respond to the impacts of 2011 drought defined as one of the worst droughts
Strengthening Early Recovery and Preparedness Coordination Mechanisms in Kenya Final Narrative Report January June 2012 0 Summary To respond to the impacts of 2011 drought defined as one of the worst droughts
National Disaster Risk Management Plan Disaster Management Centre Ministry of Disaster Management
 National Disaster Risk Management Plan 2018-2030 Disaster Management Centre Ministry of Disaster Management 1 CHAPTER CONTENT VOLUME I Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter
National Disaster Risk Management Plan 2018-2030 Disaster Management Centre Ministry of Disaster Management 1 CHAPTER CONTENT VOLUME I Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter
Implementation of Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) in Indonesia
 Implementation of Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) in Indonesia Sugeng Triutomo Director for Disaster Mitigation National Coordinating Board for Disaster Management (BAKORNAS PB) Five Priorities of Hyogo
Implementation of Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) in Indonesia Sugeng Triutomo Director for Disaster Mitigation National Coordinating Board for Disaster Management (BAKORNAS PB) Five Priorities of Hyogo
Assessment of the progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit on the Information Society
 ECOSOC Resolution 2008/3 Assessment of the progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit on the Information Society The Economic and Social Council, Recalling
ECOSOC Resolution 2008/3 Assessment of the progress made in the implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the World Summit on the Information Society The Economic and Social Council, Recalling
STRATEGIC PLAN. USF Emergency Management
 2016-2020 STRATEGIC PLAN USF Emergency Management This page intentionally left blank. Organization Overview The Department of Emergency Management (EM) is a USF System-wide function based out of the Tampa
2016-2020 STRATEGIC PLAN USF Emergency Management This page intentionally left blank. Organization Overview The Department of Emergency Management (EM) is a USF System-wide function based out of the Tampa
and resilient societies: The 2030 Space Agenda
 DLR Climate Change Conference Cologne, Germany 17 19 April 2018 Space technology for lowemission and resilient societies: The 2030 Space Agenda Juan Carlos Villagran de Leon United Nations Office for Outer
DLR Climate Change Conference Cologne, Germany 17 19 April 2018 Space technology for lowemission and resilient societies: The 2030 Space Agenda Juan Carlos Villagran de Leon United Nations Office for Outer
Security. The total budget is CHF 0.8m (USD 0.8m and EUR 0.5m) (Click here to go directly to the summary budget of the plan).
 Executive summary The unit will continue to focus on developing a security culture within the International Federation and our RC/RC Societies through security training and education, security assessments,
Executive summary The unit will continue to focus on developing a security culture within the International Federation and our RC/RC Societies through security training and education, security assessments,
OCHA POLICY & RESEARCH CONFERENCE
 ASSOCIATION OF SOUTHEAST ASIAN NATIONS OCHA POLICY & RESEARCH CONFERENCE Session 2: Adaptation and innovation in humanitarian action Larry Maramis, Director (CSC) ASEAN Secretariat one vision one identity
ASSOCIATION OF SOUTHEAST ASIAN NATIONS OCHA POLICY & RESEARCH CONFERENCE Session 2: Adaptation and innovation in humanitarian action Larry Maramis, Director (CSC) ASEAN Secretariat one vision one identity
INFORMATION NOTE. United Nations/Germany International Conference
 INFORMATION NOTE United Nations/Germany International Conference Earth Observation: Global solutions for the challenges of sustainable development in societies at risk Organized by The United Nations Office
INFORMATION NOTE United Nations/Germany International Conference Earth Observation: Global solutions for the challenges of sustainable development in societies at risk Organized by The United Nations Office
Submission from the United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction
 SAICM/ICCM.3/INF/33 Distr.: General 9 August 2012 English only International Conference on Chemicals Management Third session Nairobi, 17 21 September 2012 Item 6 of the provisional agenda Cooperation
SAICM/ICCM.3/INF/33 Distr.: General 9 August 2012 English only International Conference on Chemicals Management Third session Nairobi, 17 21 September 2012 Item 6 of the provisional agenda Cooperation
Asian Disaster Preparedness Center
 Asian Disaster Preparedness Center ASIAN DISASTER PREPAREDNESS CENTER (ADPC) ADPC IS A LEADING REGIONAL, NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION BASED IN BANGKOK, THAILAND, MANDATED TO PROMOTE SAFER COMMUNITIES AND SUSTAINABLE
Asian Disaster Preparedness Center ASIAN DISASTER PREPAREDNESS CENTER (ADPC) ADPC IS A LEADING REGIONAL, NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION BASED IN BANGKOK, THAILAND, MANDATED TO PROMOTE SAFER COMMUNITIES AND SUSTAINABLE
Ministry of Food and Disaster Management. Comprehensive Disaster Management Programme (CDMP) October 5, 2005
 Ministry of Food and Disaster Management Comprehensive Disaster Management Programme (CDMP) October 5, 2005 GoB Vision on Disaster Management: to reduce the vulnerability of people, especially the poor,
Ministry of Food and Disaster Management Comprehensive Disaster Management Programme (CDMP) October 5, 2005 GoB Vision on Disaster Management: to reduce the vulnerability of people, especially the poor,
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 Chapter 4 CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS UNDP and the Special Unit have considerable experience in South-South cooperation and are well positioned to play a more active and effective role in supporting
Chapter 4 CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS UNDP and the Special Unit have considerable experience in South-South cooperation and are well positioned to play a more active and effective role in supporting
GUIDING PRINCIPLES I. BACKGROUND. 1 P a g e
 GUIDING PRINCIPLES I. BACKGROUND At the Summit of the Americas held in Port-of-Spain, Trinidad and Tobago, in April 2009, the leaders of the Western Hemisphere noted that energy challenges are among the
GUIDING PRINCIPLES I. BACKGROUND At the Summit of the Americas held in Port-of-Spain, Trinidad and Tobago, in April 2009, the leaders of the Western Hemisphere noted that energy challenges are among the
DEVELOPMENT OF A DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT NATIONAL ACTION PLAN
 DEVELOPMENT OF A DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT NATIONAL ACTION PLAN The RMI Experience Presented by Jorelik Tibon Disaster Risk Management Task Force Office of the Chef Secretary, Republic of the Marshall Islands
DEVELOPMENT OF A DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT NATIONAL ACTION PLAN The RMI Experience Presented by Jorelik Tibon Disaster Risk Management Task Force Office of the Chef Secretary, Republic of the Marshall Islands
Hyogo Framework for Action. United States of America. National Progress Report on the
 National Progress Report on the Hyogo Framework for Action United States of America 2008 This report was prepared within the framework of the HFA-Monitor, the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction
National Progress Report on the Hyogo Framework for Action United States of America 2008 This report was prepared within the framework of the HFA-Monitor, the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction
RESOLUTION 179 (REV. BUSAN, 2014) ITU's role in child online protection
 402 Res. 179 RESOLUTION 179 (REV. BUSAN, 2014) ITU's role in child online protection The Plenipotentiary Conference of the International Telecommunication Union (Busan, 2014), recognizing a) Resolution
402 Res. 179 RESOLUTION 179 (REV. BUSAN, 2014) ITU's role in child online protection The Plenipotentiary Conference of the International Telecommunication Union (Busan, 2014), recognizing a) Resolution
RESOLUTION 67 (Rev. Buenos Aires, 2017)
 524 Res. 67 RESOLUTION 67 (Rev. Buenos Aires, 2017) The role of the ITU Telecommunication Development Sector in child online protection The World Telecommunication Development Conference (Buenos Aires,
524 Res. 67 RESOLUTION 67 (Rev. Buenos Aires, 2017) The role of the ITU Telecommunication Development Sector in child online protection The World Telecommunication Development Conference (Buenos Aires,
RESOLUTION 45 (Rev. Hyderabad, 2010)
 212 RESOLUTION 45 (Rev. Hyderabad, 2010) The World Telecommunication Development Conference (Hyderabad, 2010), recalling a) Resolution 45 (Doha, 2006) of the World Telecommunication Development Conference
212 RESOLUTION 45 (Rev. Hyderabad, 2010) The World Telecommunication Development Conference (Hyderabad, 2010), recalling a) Resolution 45 (Doha, 2006) of the World Telecommunication Development Conference
RESOLUTION 179 (REV. BUSAN, 2014) ITU's role in child online protection
 RESOLUTION 179 (REV. BUSAN, 2014) ITU's role in child online protection The Plenipotentiary Conference of the International Telecommunication Union (Busan, 2014), recognizing a) Resolution 67 (Rev. Dubai,
RESOLUTION 179 (REV. BUSAN, 2014) ITU's role in child online protection The Plenipotentiary Conference of the International Telecommunication Union (Busan, 2014), recognizing a) Resolution 67 (Rev. Dubai,
Training Workshop on Multi Hazard Early Warning Systems
 Training Workshop on Multi Hazard Early Warning Systems with focus on Institutional Coordination and Cooperation Website: http://www.wmo.int/pages/prog/drr/events/pula/index_en.html 1 3 October 2009 Pula,
Training Workshop on Multi Hazard Early Warning Systems with focus on Institutional Coordination and Cooperation Website: http://www.wmo.int/pages/prog/drr/events/pula/index_en.html 1 3 October 2009 Pula,
Localization in Climate Fragility
 Localization in Climate Fragility @ ISAP 2017 Takeshi Komino General Secretary, CWS Japan Secretariat, Japan CSO Coalition for Disaster Risk Reduction SG/Executive Committee, Asian Disaster Reduction and
Localization in Climate Fragility @ ISAP 2017 Takeshi Komino General Secretary, CWS Japan Secretariat, Japan CSO Coalition for Disaster Risk Reduction SG/Executive Committee, Asian Disaster Reduction and
Member of the County or municipal emergency management organization
 EMERGENCY OPERATIONS PLAN SUUPPORT ANNEX B PRIVATE-SECTOR COORDINATION Coordinating Agency: Cooperating Agencies: Chatham Emergency Management Agency All Introduction Purpose This annex describes the policies,
EMERGENCY OPERATIONS PLAN SUUPPORT ANNEX B PRIVATE-SECTOR COORDINATION Coordinating Agency: Cooperating Agencies: Chatham Emergency Management Agency All Introduction Purpose This annex describes the policies,
Earthquake Preparedness
 Ministry of State for Emergency Preparedness Emergency Management BC Earthquake Preparedness UBCM September 22, 2015 2014 OAG AUDIT CATASTROPHIC EARTHQUAKE AN OPPORTUNITY Build capacity Develop strategic
Ministry of State for Emergency Preparedness Emergency Management BC Earthquake Preparedness UBCM September 22, 2015 2014 OAG AUDIT CATASTROPHIC EARTHQUAKE AN OPPORTUNITY Build capacity Develop strategic
WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION
 UNITED NATIONS A General Assembly ADVANCE COPY Distr. GENERAL A/CONF.206/PC(II)/9 24 September 2004 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION Preparatory Committee Second Session Geneva,
UNITED NATIONS A General Assembly ADVANCE COPY Distr. GENERAL A/CONF.206/PC(II)/9 24 September 2004 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION Preparatory Committee Second Session Geneva,
Forecast-based Action. by the DREF
 Forecast-based Action by the DREF About Forecast-based Financing (FbF) FbF is a programme that enables access to humanitarian funding for early action based on in-depth forecast information and risk analysis.
Forecast-based Action by the DREF About Forecast-based Financing (FbF) FbF is a programme that enables access to humanitarian funding for early action based on in-depth forecast information and risk analysis.
CO-CHAIRS NON-PAPER. Chapter Paragraphs Page. Understanding disaster risk
 Explanation Note 1. The present document is the pre-zero draft of the post-2015 framework for disaster risk reduction. It will serve as the basis for the open-ended informal consultative meetings which
Explanation Note 1. The present document is the pre-zero draft of the post-2015 framework for disaster risk reduction. It will serve as the basis for the open-ended informal consultative meetings which
--- International Forum on Geospatial Information and Services for Disasters Session 3. Bridgetown, Barbados 4-5 September ggim.un.
 Potential Areas for Collaboration 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 Strategic Framework for GISD 2016-2030 --- International Forum on Geospatial
Potential Areas for Collaboration 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 Strategic Framework for GISD 2016-2030 --- International Forum on Geospatial
J.Enhancing energy security and improving access to energy services through development of public-private renewable energy partnerships
 J.Enhancing energy security and improving access to energy services through development of public-private renewable energy partnerships Background ESCAP, jointly with the ECLAC, the ECA, the ECE, and the
J.Enhancing energy security and improving access to energy services through development of public-private renewable energy partnerships Background ESCAP, jointly with the ECLAC, the ECA, the ECE, and the
Flagship Programme for Disaster Risk Management as proposed by the Nepal Risk Reduction. Outcomes
 Flagship Programme for Disaster Risk Management as proposed by the Nepal Risk Reduction Consortium: a Concepts, Outlines & Expected Outcomes Prepared by UNDP DRM Unit on behalf of the Nepal Risk Reduction
Flagship Programme for Disaster Risk Management as proposed by the Nepal Risk Reduction Consortium: a Concepts, Outlines & Expected Outcomes Prepared by UNDP DRM Unit on behalf of the Nepal Risk Reduction
On Urban Risk Reduction
 Asia Regional Task Force On Urban Risk Reduction Yuki Matsuoka UNISDR Hyogo Office RTF-URR Coordinator At Special Event on Urban Risk Reduction by RTF-URR 17 June 2009 1 The Asia Regional Task Force on
Asia Regional Task Force On Urban Risk Reduction Yuki Matsuoka UNISDR Hyogo Office RTF-URR Coordinator At Special Event on Urban Risk Reduction by RTF-URR 17 June 2009 1 The Asia Regional Task Force on
Private Sector Engagement in Disaster Risk Reduction
 Private Sector Engagement in Disaster Risk Reduction Asian Disaster Preparedness Center, Bangkok Repeated Calls for Private Sector Engagement in Disaster Risk Reduction Support local communities to have
Private Sector Engagement in Disaster Risk Reduction Asian Disaster Preparedness Center, Bangkok Repeated Calls for Private Sector Engagement in Disaster Risk Reduction Support local communities to have
Institutional Arrangements for Natural Disaster Management A Review of National Implementation of Priority 1 of the Hyogo Framework for Action
 1 Institutional Arrangements for Natural Disaster Management A Review of National Implementation of Priority 1 of the Hyogo Framework for Action Managing Vulnerability in East Asia World Bank June 25-26,
1 Institutional Arrangements for Natural Disaster Management A Review of National Implementation of Priority 1 of the Hyogo Framework for Action Managing Vulnerability in East Asia World Bank June 25-26,
Liberia ICT Policy
 Liberia ICT Policy 2017-2021 Initial Stakeholders Consultation Eleanor Sarpong Head of Policy and Advocacy November 23, 2016 a4ai.org Goals of consultation To convene under the auspices of the GoL (MoPT
Liberia ICT Policy 2017-2021 Initial Stakeholders Consultation Eleanor Sarpong Head of Policy and Advocacy November 23, 2016 a4ai.org Goals of consultation To convene under the auspices of the GoL (MoPT
Review of the WMO DRR Programme activities in the area of MHEWS as a contribution to the WMO DRR Priority (2005 to present)
 Review of the WMO DRR Programme activities in the area of MHEWS as a contribution to the WMO DRR Priority (2005 to present) Session 2: Background UI-EAG MHEWS, 19-21 April 2016, Geneva James Douris Project
Review of the WMO DRR Programme activities in the area of MHEWS as a contribution to the WMO DRR Priority (2005 to present) Session 2: Background UI-EAG MHEWS, 19-21 April 2016, Geneva James Douris Project
Asian Disaster Preparedness Center
 Asian Disaster Preparedness Center Presentation by Loy Rego At the ProVention Consortium Forum February 2007 Historical Overview Established in 1986, at the initiatives of 3 UN organizations: WMO, UNDP
Asian Disaster Preparedness Center Presentation by Loy Rego At the ProVention Consortium Forum February 2007 Historical Overview Established in 1986, at the initiatives of 3 UN organizations: WMO, UNDP
MARCH 2016 ONE BILLION COALITION FOR RESILIENCE
 MARCH 2016 ONE BILLION COALITION FOR RESILIENCE AN URGENT CHALLENGE DISASTERS AND COMPLEX EMERGENCIES are becoming more frequent and more severe ASKING FOR MORE MONEY to respond to more crises is not the
MARCH 2016 ONE BILLION COALITION FOR RESILIENCE AN URGENT CHALLENGE DISASTERS AND COMPLEX EMERGENCIES are becoming more frequent and more severe ASKING FOR MORE MONEY to respond to more crises is not the
HFA Implementation Review Simplified Version for ACDR2010
 HFA Implementation Review Simplified Version for ACDR2010 Country: Republic of Korea Date of data filled out: Nov. 25, 2009 Name of the respondent: Dugkeun Park 1 Priority for action 1: Ensure that disaster
HFA Implementation Review Simplified Version for ACDR2010 Country: Republic of Korea Date of data filled out: Nov. 25, 2009 Name of the respondent: Dugkeun Park 1 Priority for action 1: Ensure that disaster
UN/Germany Conference November 2017 Thematic Priority 6: International cooperation towards low-emission and resilient societies
 UN/Germany Conference 22-24 November 2017 Thematic Priority 6: International cooperation towards low-emission and resilient societies United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs United Nations Office
UN/Germany Conference 22-24 November 2017 Thematic Priority 6: International cooperation towards low-emission and resilient societies United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs United Nations Office
Early Warning > Early Action: why it matters! and why we need each other!
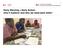 Early Warning > Early Action: why it matters! and why we need each other! 1 Red Cross in the Pacific OUR LINK BETWEEN PACIFIC POLICY AND COMMUNITY ACTIONS Pacific Resilience Partnership National level
Early Warning > Early Action: why it matters! and why we need each other! 1 Red Cross in the Pacific OUR LINK BETWEEN PACIFIC POLICY AND COMMUNITY ACTIONS Pacific Resilience Partnership National level
UAE Space Policy Efforts Towards Long Term Sustainability of Space Activities Agenda Item 4; COPUOS June 2017 By: Space Policy and
 UAE Space Policy Efforts Towards Long Term Sustainability of Space Activities Agenda Item 4; COPUOS 2017 07-16 June 2017 By: Space Policy and Regulations Directory 1 The UAE will build the first city on
UAE Space Policy Efforts Towards Long Term Sustainability of Space Activities Agenda Item 4; COPUOS 2017 07-16 June 2017 By: Space Policy and Regulations Directory 1 The UAE will build the first city on
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 21 December [on the report of the Second Committee (A/64/422/Add.3)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 21 December [on the report of the Second Committee (A/64/422/Add.3)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 21 December [on the report of the Second Committee (A/64/422/Add.3)]](/thumbs/81/84531605.jpg) United Nations A/RES/64/211 General Assembly Distr.: General 17 March 2010 Sixty-fourth session Agenda item 55 (c) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 21 December 2009 [on the report of the Second
United Nations A/RES/64/211 General Assembly Distr.: General 17 March 2010 Sixty-fourth session Agenda item 55 (c) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 21 December 2009 [on the report of the Second
Metadata Framework for Resource Discovery
 Submitted by: Metadata Strategy Catalytic Initiative 2006-05-01 Page 1 Section 1 Metadata Framework for Resource Discovery Overview We must find new ways to organize and describe our extraordinary information
Submitted by: Metadata Strategy Catalytic Initiative 2006-05-01 Page 1 Section 1 Metadata Framework for Resource Discovery Overview We must find new ways to organize and describe our extraordinary information
Global Infrastructure Connectivity Alliance Initiative
 Global Infrastructure Connectivity Alliance Initiative 1. Background on Global Infrastructure Connectivity Global Infrastructure Connectivity refers to the linkages of communities, economies and nations
Global Infrastructure Connectivity Alliance Initiative 1. Background on Global Infrastructure Connectivity Global Infrastructure Connectivity refers to the linkages of communities, economies and nations
Disaster Planning and Preparedness
 Disaster Planning and Preparedness Appeal No. MAA00021 19/08/2008 This report covers the period 01/01/2008 to 01/07/2008. Shahidul Islam, a member of the Community Disaster Preparedness committee, takes
Disaster Planning and Preparedness Appeal No. MAA00021 19/08/2008 This report covers the period 01/01/2008 to 01/07/2008. Shahidul Islam, a member of the Community Disaster Preparedness committee, takes
