Requirements Engineering. Contents. Functional requirements. What is a requirement?
|
|
|
- Emil Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents Ø Introduction 4 Ø Engineering Ø Project Management Ø Software Design Ø Detailed Design and Coding Ø Quality Assurance Engineering Ø What is a Requirement? Ø RE Activities Ø Documentation Ø RE Methods and Notations Ø Examples Analysis Design Coding Testing Specification Installation Planning Operation and Maintenance PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 1 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 2 What is a requirement? Functional requirements q A Requirement is something that the product must do or a quality that the product must have. q Three kinds of requirements: o those that absolutely must be met o those that are highly desirable but not necessary o those that are possible but could be eliminated Describe what the system should do o What inputs the system should accept o What outputs the system should produce o What data the system should store that other systems might use o What computations the system should perform o The timing and synchronization of the above PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 3 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 4
2 Non-Functional Non functional requirements are properties or qualities the product must have. q Product qualities: o Usability o Efficiency Performance Space o Reliability o Portability o Cultural and political o Legal requirements o... Constraints q Constraints are global issues that shape the requirements q Examples: Programming languages Operating system The users of the product... PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 5 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 6 Examples 1. System shall communicate with external system X. 2. The product shall run on the company s existing Unix machines. 3. The system must have a file containing a complete list of students that is accessible only by the teacher. 4. The product should be user friendly......new users should be able to add buttons within 30 minutes of their first attempt at Functional Constraint Functional and 2 non functional Non Functional RE Activities q Acquire and identify requirements o Study the system / organisation o Study available documents o Ask users / domain experts Questionnaires Interviews q Analyse and evaluate requirements o Domain analysis o Prototyping o JAD o Scenario modelling q Document requirements q Review and validate requirements using the product. 7 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 8
3 Definition Definition Definition Definition x x x x x x Specification x x Specification xx Specification xx xx Specification xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx Definition Definition Definition Definition x x x x x x x x Specification xx Specification xx Specification xx Specification xx xx xx xx xx x xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx Purpose of the Document q Describe external system behaviour o Functional requirements o User interface o Acceptable responses to undesired events q Describe system properties o Non-functional requirements o Acceptance criteria Ł Implementation independent reference Ł Specifies the WHAT and not the HOW guide design guide analysis Ł Part of the contract between customer and developer PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 9 Types of Document Two extremes: An informal outline of the requirements using a few paragraphs or simple diagrams requirements definition A long list of specifications that contain thousands of pages of intricate detail requirements specification o documents for large systems are normally arranged in a hierarchy x x xx xx subsystem 1 subsystem 2 x Definition x x xx x Specification xx xx xx x xx sub-subsystems xx sub-subsystems PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 10 xx Format of a Document A. Problem B. Background information C. Operational Environment D. Functional E. Non-functional requirements F. Constraints Volere Specification Template PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 11 Writing Style Do not use vague terms or verbs like some, obviously, usually, often, it follows that, Make sure that uncompleted lists are understood completely (e.g. etc., and so on,,...) Make sure that ranges are clearly understood, e.g. what means in the range of 1 to 100 Ask for clear definitions of terms like always, never, almost, etc. Use pictures and examples to aid in understanding Explain all of your terminology Use shall, must, should, consistently PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 12
4 review q Review goals and objectives of system. q Compare requirements with goals and objectives. q Describe operational environment. q Check for omissions, incompleteness, inconsistency. q Document risks. q Discuss how system will be tested. Engineering Ø What is a Requirement? 4 Ø RE Activities 4 Ø Documentation 4 Ø RE Methods and Notations Ø Examples 13 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 14 Classical Approaches to RE q Problems: o Coping with size Structured approach Stepwise refinement Hierarchical organisation o Coping with change Logic model Maintainable results o Coping with documentation Simple notation Graphical elements q Solutions: o SA (75/75) Function-oriented o ER (end 70s) Data-oriented o SA/RT (85/87) Control-oriented o Integrated approaches SA/ER/RT (end 80s) OO/RT (early/mid 90s)??? Systematic approaches to requirements analysis and definition PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 15 Structured Analysis (SA) q Developed 1975/76 o DeMarco/Yourdon o Gane/Sarson q System = Process transforming input into output q Hierarchical, logical system model o Processes o Data flows o Data stores o Terminators q Notation: o Data flow diagrams (DFDs) o Data dictionary (DD) o Process specifications (PSpecs) 16
5 Gane/Sarson data item(s) Data Flow Diagrams Terminator: Source or destination of data/information. Outside the system boundaries. Data flow: Flow of data. Process: Transforms input data flow(s) into output data flow(s). Data store: Data repository. DeMarco/Yourdon data item(s) PVK DFD Development q Start with a context diagram q Successively refine processes q Describe all data in the data dictionary q Describe all atomic processes by PSpecs q Example: Order processing Customer order invoice package data process orders credit status customer data refine Customer order package data verify if order is valid credit status customer data assemble available and invoice packages order invoice PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 18 DFDs--Managing Complexity DFD hierarchy + numbering/naming rules + balancing rules Level n Leveled DFDs - Example structure Level n+1 Data Storage Level n+2 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 20
6 DFDs-- Forbidden Structures The SAnotation is not formally defined Rules are defined by experiences and tool features In-data only Terminator-to-terminator flows DFD Naming and Balancing Context diagram Level 0 Term input System output 0 System Level 1 other data Do Y input Do X output 2 1 data some data Do Z 3 Out-data only Store-to-store flows Cycles Unnamed dataflows (exception: from/to data stores) All names must be unambiguous. Numbering scheme helps to find processes in the hierarchy DoC:3.3 Do Z Level 2 d2 data Do A.1 d1 Do C astore.3 Do B.2 d3 d6 In data dictionary: some data = d5 + d6 (alternatively: some data = d5 d6) d5 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 21 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 22 PSpecs and DD q The format of PSpecs is not restricted o Free text o Pseudocode q PSpecs must be defined for all atomic processes q The format of the DD is semi-formal q Example: selection (or) telephone number = [ local extension outside number ] local extension = 2 + { number } 3 composition (and) outside number = 0 + [ local number long distance number ] local number = prefix + access number optional long distance number = (1) + area code + local number prefix = [ ] access number = { number } 4 repetition number = * any number between 0 and 9 * a comment PVK SA--Summary q Advantages o Simple notation o Supports hierarchical decomposition o Easy to understand o Good communication medium o Supports consistency checks q Disadvantages o Not well defined o No common guidelines o Many dialects o Incomplete Very poor data descriptions No description of control flows PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 24
7 State Transition Diagram (STD) STDvs. DFD start S1 condition action S2 stop 1 X State X signal Activity bubble2 State 1 2 Y Y signal St State Activity bubble3 State 3 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 25 PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 26 Data Modelling q The entity-relationship (ER) model was developed by Chen (late 70s) to support data(base) modelling q Focuses only on the static structure of data q Notation o Entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs) o Attribute dictionary PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 27 ERDNotation q According to Chen + common extensions m Entitytype Relationship type Attribute n Set of real or abstract things about whichdataisstored Set relations between entities with cardinalities m and n. Information that is stored along with entities and relationships. Composition of entities. Classification between entity- and relationship types. PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 28
8 ERD--An Example Name Address Rank Attribute Dictionary Attribute structures TeamMember = Name, Address, Rank; Employee =...;... Attribute types Name = STRING; Address = STRING;... Employee Team Member External n Responsibility h/week Equipment SWProject Documents PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 29 m n Process SA/ER Integration DFDs ProjectTeam ERDs Name Address Rank Data Dictionary Employee Team Member External ProjectTeam = { TeamMember } n TeamMember = Name + Address + Rank... Responsibility n Responsibility 1..3 SWProject PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 30 ERM--Summary q Advantages o Simple notation o Supports hierarchical and structural decomposition o Easy to understand o Good communication medium o Well understood o Widely used o Good tool support Ł Well-suited for DB design Extensions of ERM lead to OO approaches q Disadvantages o No behaviour descriptions o No control descriptions Ł Almost useless for non- DB applications PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 31 Use Case Modelling q Actor: external person, organization, or system communicating with the system (data exchange) q System boundary: Collection of all use cases q Use case: action that is triggered by an actor or produces a result for an actor q Use case description: textual or semi-formalized description of a use case content Actor Use case PVK-02 bella@cs.umu.se 32
9 Use Case Diagram Student Sign on for exams Take exam Student Secretary Administer marks Schedule lectures Prof Dean PVK-02 33
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies
 REQUIREMENTS GATHERING AND ANALYSIS The analyst starts requirement gathering activity by collecting all information that could be useful to develop system. In practice it is very difficult to gather all
REQUIREMENTS GATHERING AND ANALYSIS The analyst starts requirement gathering activity by collecting all information that could be useful to develop system. In practice it is very difficult to gather all
Process Modeling. Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU
 Process Modeling Based on Chapter 9 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU 2 Models: Logical and
Process Modeling Based on Chapter 9 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU 2 Models: Logical and
Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS. PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall Bühnová, Sochor, Ráček
 Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall 2015 1 Outline ² Yourdon Modern Structured Analysis (YMSA) Context diagram (CD) Data flow diagram
Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall 2015 1 Outline ² Yourdon Modern Structured Analysis (YMSA) Context diagram (CD) Data flow diagram
Administrivia. Wednesday: Requirements and Specification. CS169 Lecture 4. We assign teams and you start on Monday. Determining Stakeholders and Needs
 Administrivia Requirements and Specification CS169 Lecture 4 Wednesday: Groups and one-sentence idea(s) due at class One per group If you have a small group, still submit so that you will be kept together.
Administrivia Requirements and Specification CS169 Lecture 4 Wednesday: Groups and one-sentence idea(s) due at class One per group If you have a small group, still submit so that you will be kept together.
Methods for requirements engineering
 Methods for requirements engineering Objectives To explain the role of methods and techniques in requirements engineering To introduce data-flow modelling To introduce semantic data modelling To introduce
Methods for requirements engineering Objectives To explain the role of methods and techniques in requirements engineering To introduce data-flow modelling To introduce semantic data modelling To introduce
06. Analysis Modeling
 06. Analysis Modeling Division of Computer Science, College of Computing Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2017 Overview of Analysis Modeling 1 Requirement Analysis 2 Analysis Modeling Approaches
06. Analysis Modeling Division of Computer Science, College of Computing Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2017 Overview of Analysis Modeling 1 Requirement Analysis 2 Analysis Modeling Approaches
PPSC Competitive Exam for the Post of System Analyst
 PPSC Competitive Exam for the Post of System Analyst Question Paper Along with Answer Key Date: 21 st June, 2014 Time: 09: 00 AM to 11:00 AM Total Number of Questions: 100 Q 1. Which of the following is
PPSC Competitive Exam for the Post of System Analyst Question Paper Along with Answer Key Date: 21 st June, 2014 Time: 09: 00 AM to 11:00 AM Total Number of Questions: 100 Q 1. Which of the following is
Software Design Document (SDD) Template (summarized from IEEE STD 1016)
 Software Design Document (SDD) Template (summarized from IEEE STD 1016) Software design is a process by which the software requirements are translated into a representation of software components, interfaces,
Software Design Document (SDD) Template (summarized from IEEE STD 1016) Software design is a process by which the software requirements are translated into a representation of software components, interfaces,
Introduction to Software Specifications and Data Flow Diagrams. Neelam Gupta The University of Arizona
 Introduction to Software Specifications and Data Flow Diagrams Neelam Gupta The University of Arizona Specification A broad term that means definition Used at different stages of software development for
Introduction to Software Specifications and Data Flow Diagrams Neelam Gupta The University of Arizona Specification A broad term that means definition Used at different stages of software development for
Marking Guidelines for MVK Projects. MVK12. Version 6.2 (PPD, URD, RURD, ADD and software demo)
 Marking Guidelines for MVK Projects. MVK12 Version 6.2 (PPD, URD, RURD, ADD and software demo) 2013-02- 13 Final Grade formulas: MVK DD1365 Grade = 33% PPD + 66% URD. Bachelor s Thesis DD143X Grade = ADD
Marking Guidelines for MVK Projects. MVK12 Version 6.2 (PPD, URD, RURD, ADD and software demo) 2013-02- 13 Final Grade formulas: MVK DD1365 Grade = 33% PPD + 66% URD. Bachelor s Thesis DD143X Grade = ADD
SE 1: Software Requirements Specification and Analysis
 SE 1: Software Requirements Specification and Analysis Lecture 4: Basic Notations Nancy Day, Davor Svetinović http://www.student.cs.uwaterloo.ca/ cs445/winter2006 uw.cs.cs445 U Waterloo SE1 (Winter 2006)
SE 1: Software Requirements Specification and Analysis Lecture 4: Basic Notations Nancy Day, Davor Svetinović http://www.student.cs.uwaterloo.ca/ cs445/winter2006 uw.cs.cs445 U Waterloo SE1 (Winter 2006)
Chapter 9. Process Modeling. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Process Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives Define systems modeling and differentiate logical and physical models. Define
Chapter 9 Process Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives Define systems modeling and differentiate logical and physical models. Define
Requirements. Chapter Learning objectives of this chapter. 2.2 Definition and syntax
 Chapter 2 Requirements A requirement is a textual description of system behaviour. A requirement describes in plain text, usually English, what a system is expected to do. This is a basic technique much
Chapter 2 Requirements A requirement is a textual description of system behaviour. A requirement describes in plain text, usually English, what a system is expected to do. This is a basic technique much
(Team Name) (Project Title) Software Design Document. Student Name (s):
 (Team Name) (Project Title) Software Design Document Student Name (s): TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2 1.1Purpose 2 1.2Scope 2 1.3Overview 2 1.4Reference Material 2 1.5Definitions and Acronyms 2 2.
(Team Name) (Project Title) Software Design Document Student Name (s): TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2 1.1Purpose 2 1.2Scope 2 1.3Overview 2 1.4Reference Material 2 1.5Definitions and Acronyms 2 2.
Requirements. Requirements. Types of Requirement. What Is a Requirement?
 Beatrice Åkerblom beatrice@dsv.su.se Everything else in software development depends on the requirements. If you cannot get stable requirements you cannot get a predictable plan... What Is a Requirement?!
Beatrice Åkerblom beatrice@dsv.su.se Everything else in software development depends on the requirements. If you cannot get stable requirements you cannot get a predictable plan... What Is a Requirement?!
Basics : the Requirements Engineering Process
 SEG3101 (Fall 2010) Basics : the Requirements Engineering Process Gregor v. Bochmann, University of Ottawa Based on Powerpoint slides prepared by Gunter Mussbacher with material from: Sommerville & Kotonya
SEG3101 (Fall 2010) Basics : the Requirements Engineering Process Gregor v. Bochmann, University of Ottawa Based on Powerpoint slides prepared by Gunter Mussbacher with material from: Sommerville & Kotonya
Structured Analysis and Design
 1 st Cut - Creating... 14:10 A Actors... 2:11 Additional Notations... 11:17 Alternative Names for the System... 13:15 Analysis - Overview... 1:9 Analysis and Design - Goals... 1:6 Analysis and Design -
1 st Cut - Creating... 14:10 A Actors... 2:11 Additional Notations... 11:17 Alternative Names for the System... 13:15 Analysis - Overview... 1:9 Analysis and Design - Goals... 1:6 Analysis and Design -
Requirements Analysis. SE 555 Software Requirements & Specification
 Requirements Analysis Goals of Requirements Analysis Create requirements containing sufficient detail and of high enough quality to allow realistic project planning as well as successful design and implementation.
Requirements Analysis Goals of Requirements Analysis Create requirements containing sufficient detail and of high enough quality to allow realistic project planning as well as successful design and implementation.
Session 2b: structured specifications Purpose and criteria Structured specification components Introduction to dataflow diagrams
 Session 2b: structured specifications Purpose and criteria Structured specification components Introduction to dataflow diagrams COMP 320 / 420, Spring, 2018 Conrad Weisert Criteria for the ESD (from session
Session 2b: structured specifications Purpose and criteria Structured specification components Introduction to dataflow diagrams COMP 320 / 420, Spring, 2018 Conrad Weisert Criteria for the ESD (from session
Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design
 Oracle University Contact Us: +632 976 8896, 1800 16516277 Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design Duration: 4 Days What you will learn This Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design
Oracle University Contact Us: +632 976 8896, 1800 16516277 Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design Duration: 4 Days What you will learn This Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design
Ch 4: Requirements Engineering. What are requirements?
 Ch 4: Engineering What are? Functional and non-functional The software document specification engineering processes elicitation and analysis validation management The descriptions of what the system should
Ch 4: Engineering What are? Functional and non-functional The software document specification engineering processes elicitation and analysis validation management The descriptions of what the system should
Requirement Analysis
 Requirement Analysis Requirements Analysis & Specification Objective: determine what the system must do to solve the problem (without describing how) Done by Analyst (also called Requirements Analyst)
Requirement Analysis Requirements Analysis & Specification Objective: determine what the system must do to solve the problem (without describing how) Done by Analyst (also called Requirements Analyst)
Non-overlappingoverlapping. Final outcome of the worked example On pages R&C pages R&C page 157 Fig 3.52
 Objectives Computer Science 202 Database Systems: Entity Relation Modelling To learn what a conceptual model is and what its purpose is. To learn the difference between internal models and external models.
Objectives Computer Science 202 Database Systems: Entity Relation Modelling To learn what a conceptual model is and what its purpose is. To learn the difference between internal models and external models.
Architectural Blueprint
 IMPORTANT NOTICE TO STUDENTS These slides are NOT to be used as a replacement for student notes. These slides are sometimes vague and incomplete on purpose to spark a class discussion Architectural Blueprint
IMPORTANT NOTICE TO STUDENTS These slides are NOT to be used as a replacement for student notes. These slides are sometimes vague and incomplete on purpose to spark a class discussion Architectural Blueprint
Chapter : Analysis Modeling
 Chapter : Analysis Modeling Requirements Analysis Requirements analysis Specifies software s operational characteristics Indicates software's interface with other system elements Establishes constraints
Chapter : Analysis Modeling Requirements Analysis Requirements analysis Specifies software s operational characteristics Indicates software's interface with other system elements Establishes constraints
Lecture 8 Requirements Engineering
 Lecture 8 Requirements Engineering Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 18, 2008 Lecture Overview
Lecture 8 Requirements Engineering Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 18, 2008 Lecture Overview
Scenario-Based Analysis. Scenario-Based Analysis (example) Form analysis
 Scenario-Based Analysis Scenario-Based Analysis (example) Provides a more user-oriented view perspective on the design and development of an interactive system. The defining property of a scenario is that
Scenario-Based Analysis Scenario-Based Analysis (example) Provides a more user-oriented view perspective on the design and development of an interactive system. The defining property of a scenario is that
Enterprise Architect Training Courses
 On-site training from as little as 135 per delegate per day! Enterprise Architect Training Courses Tassc trainers are expert practitioners in Enterprise Architect with over 10 years experience in object
On-site training from as little as 135 per delegate per day! Enterprise Architect Training Courses Tassc trainers are expert practitioners in Enterprise Architect with over 10 years experience in object
Marking Guidelines for MVK Projects. MVK11. Version 6.2 (PPD, URD, ADD, revised URD+ADD, and software demo)
 Marking Guidelines for MVK Projects. MVK11 Version 6.2 (PPD, URD, ADD, revised URD+ADD, and software demo) 2012-05- 03 Final Grade formulas: MVK DD1365 Grade = PPD + URD. Bachelor s Thesis DD143X Grade
Marking Guidelines for MVK Projects. MVK11 Version 6.2 (PPD, URD, ADD, revised URD+ADD, and software demo) 2012-05- 03 Final Grade formulas: MVK DD1365 Grade = PPD + URD. Bachelor s Thesis DD143X Grade
A l Ain University Of Science and Technology
 A l Ain University Of Science and Technology 4 Handout(4) Database Management Principles and Applications The Entity Relationship (ER) Model http://alainauh.webs.com/ 1 In this chapter, you will learn:
A l Ain University Of Science and Technology 4 Handout(4) Database Management Principles and Applications The Entity Relationship (ER) Model http://alainauh.webs.com/ 1 In this chapter, you will learn:
Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18
 Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~pbell/comp201.html Lecture 13 Design
Lecturer: Sebastian Coope Ashton Building, Room G.18 E-mail: coopes@liverpool.ac.uk COMP 201 web-page: http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~coopes/comp201 http://www.csc.liv.ac.uk/~pbell/comp201.html Lecture 13 Design
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR
 SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : M.Sc-CST Semester / Year : Even / II Subject Name
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : M.Sc-CST Semester / Year : Even / II Subject Name
Lecture 9 Requirements Engineering II
 Lecture 9 Requirements Engineering II Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 23, 2008 Announcements
Lecture 9 Requirements Engineering II Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 23, 2008 Announcements
Structured Analysis and Structured Design
 Structured Analysis and Structured Design - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis - Structured Design Ver. 1.5 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr References Modern
Structured Analysis and Structured Design - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis - Structured Design Ver. 1.5 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr References Modern
CS350 Lecture 2 Requirements Engineering. Doo-Hwan Bae
 CS350 Lecture 2 Requirements Engineering Doo-Hwan Bae bae@se.kaist.ac.kr Contents Overview of Requirements Engineering OO Analysis: Domain modeling, Use-case, sequence, class Structured Analysis: Dataflow
CS350 Lecture 2 Requirements Engineering Doo-Hwan Bae bae@se.kaist.ac.kr Contents Overview of Requirements Engineering OO Analysis: Domain modeling, Use-case, sequence, class Structured Analysis: Dataflow
Software Development Chapter 1
 Software Development Chapter 1 1. Introduction Software Applications are increasingly used to tackle problems that concern everyday life : Automatic Bank tellers Airline reservation systems Air traffic
Software Development Chapter 1 1. Introduction Software Applications are increasingly used to tackle problems that concern everyday life : Automatic Bank tellers Airline reservation systems Air traffic
Data. Entities. Accounting Information Systems. Chapter 4: Data Management
 Accounting Information Systems Chapter 4: Data Management Data Data may be defined broadly to include two interrelated components: Data Models that provide structure to data File Orientation Data-base
Accounting Information Systems Chapter 4: Data Management Data Data may be defined broadly to include two interrelated components: Data Models that provide structure to data File Orientation Data-base
Vragen. Use case analysis. Use-Cases: describing how the user will Use cases
 Vragen Use case analysis Welke problemen kunnen optreden bij het expliciet maken van het impliciete model bij conceptueel modelleren? Wat is het doel van elicitatie? Noem een aantal elicitatie technieken?
Vragen Use case analysis Welke problemen kunnen optreden bij het expliciet maken van het impliciete model bij conceptueel modelleren? Wat is het doel van elicitatie? Noem een aantal elicitatie technieken?
Overview. What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies
 Overview What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies Information Systems What is a system? Why do systems fail? What is systems analysis and design? How do we do systems analysis?
Overview What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies Information Systems What is a system? Why do systems fail? What is systems analysis and design? How do we do systems analysis?
R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only
 Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, 6/e Chapter 10 Architectural Design copyright 1996, 2001, 2005 R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only May be reproduced ONLY for student
Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, 6/e Chapter 10 Architectural Design copyright 1996, 2001, 2005 R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only May be reproduced ONLY for student
Work with design rules that can be applied to check and enforce the integrity and consistency of your
 Oracle - Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design Code: Lengt h: URL: D56497GC20 4 days View Online This Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design training covers the Data Modeling
Oracle - Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design Code: Lengt h: URL: D56497GC20 4 days View Online This Oracle Data Modeling and Relational Database Design training covers the Data Modeling
1: Specifying Requirements with Use Case Diagrams
 Outline UML Design Supplement 1: Specifying Requirements with Use Case Diagrams Introduction Use Case Diagrams Writing Use Cases Guidelines for Effective Use Cases Slide adapted from Eran Toch s lecture
Outline UML Design Supplement 1: Specifying Requirements with Use Case Diagrams Introduction Use Case Diagrams Writing Use Cases Guidelines for Effective Use Cases Slide adapted from Eran Toch s lecture
Meltem Özturan
 Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 1 1 The systems development life cycle (SDLC) provides an overall framework for the process of system development, but the developer relies on many more
Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 1 1 The systems development life cycle (SDLC) provides an overall framework for the process of system development, but the developer relies on many more
Unit 1 Introduction to Software Engineering
 Unit 1 Introduction to Software Engineering João M. Fernandes Universidade do Minho Portugal Contents 1. Software Engineering 2. Software Requirements 3. Software Design 2/50 Software Engineering Engineering
Unit 1 Introduction to Software Engineering João M. Fernandes Universidade do Minho Portugal Contents 1. Software Engineering 2. Software Requirements 3. Software Design 2/50 Software Engineering Engineering
A l Ain University Of Science and Technology
 A l Ain University Of Science and Technology 4 Handout(4) Database Management Principles and Applications The Entity Relationship (ER) Model http://alainauh.webs.com/ http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~lingt
A l Ain University Of Science and Technology 4 Handout(4) Database Management Principles and Applications The Entity Relationship (ER) Model http://alainauh.webs.com/ http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~lingt
Lesson 06. Requirement Engineering Processes
 Lesson 06 Requirement Engineering Processes W.C.Uduwela Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Objectives To describe the principal requirements engineering activities and their relationships To
Lesson 06 Requirement Engineering Processes W.C.Uduwela Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Objectives To describe the principal requirements engineering activities and their relationships To
SEG3201 Basics of the Requirements Process
 SEG3201 Basics of the Requirements Process Based on material from: I Bray: An introduction to Requirements Engineering Gerald Kotonya and Ian Sommerville: Requirements Engineering Processes and Techniques,
SEG3201 Basics of the Requirements Process Based on material from: I Bray: An introduction to Requirements Engineering Gerald Kotonya and Ian Sommerville: Requirements Engineering Processes and Techniques,
INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design
 INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design Session 13 Systems Analysis and Construction Tools Lecturer: Prof. Ellis Edwin Badu, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eebadu@ug.edu.gh College of Education
INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design Session 13 Systems Analysis and Construction Tools Lecturer: Prof. Ellis Edwin Badu, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eebadu@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Lab # 1. Structuring System Requirements: Diagrams
 Lab # 1 Structuring System Requirements: Diagrams Objectives 1. Use Case diagrams 2. Class Objects (CO) diagrams 3. Context Data Flow Diagrams (Context DFDs) 4. Level-0 Data Flow Diagrams (Level-0 DFDs)
Lab # 1 Structuring System Requirements: Diagrams Objectives 1. Use Case diagrams 2. Class Objects (CO) diagrams 3. Context Data Flow Diagrams (Context DFDs) 4. Level-0 Data Flow Diagrams (Level-0 DFDs)
JOURNAL OF OBJECT TECHNOLOGY
 JOURNAL OF OBJECT TECHNOLOGY Online at www.jot.fm. Published by ETH Zurich, Chair of Software Engineering JOT, 2002 Vol. 1, no. 4, September-October 2002 Requirements Engineering Donald G. Firesmith, Firesmith
JOURNAL OF OBJECT TECHNOLOGY Online at www.jot.fm. Published by ETH Zurich, Chair of Software Engineering JOT, 2002 Vol. 1, no. 4, September-October 2002 Requirements Engineering Donald G. Firesmith, Firesmith
Object Oriented Programming
 Binnur Kurt kurt@ce.itu.edu.tr Istanbul Technical University Computer Engineering Department 1 Version 0.1.2 About the Lecturer BSc İTÜ, Computer Engineering Department, 1995 MSc İTÜ, Computer Engineering
Binnur Kurt kurt@ce.itu.edu.tr Istanbul Technical University Computer Engineering Department 1 Version 0.1.2 About the Lecturer BSc İTÜ, Computer Engineering Department, 1995 MSc İTÜ, Computer Engineering
<Project Name> Use Case Specification: <Use-Case Name> Version <1.0>
 1 z 5 2007-02-26 15:57 Use Case Specification: Version [Note: The following template is provided for use with the Rational Unified Process. Text enclosed in square
1 z 5 2007-02-26 15:57 Use Case Specification: Version [Note: The following template is provided for use with the Rational Unified Process. Text enclosed in square
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS 6403 - SOFTWARE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK TWO MARKS UNIT I SOFTWARE PROCESS AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT 1. What is software engineering? Software engineering
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS 6403 - SOFTWARE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK TWO MARKS UNIT I SOFTWARE PROCESS AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT 1. What is software engineering? Software engineering
13/11/2017. Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515
 Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Represent entities and relations with diagrams
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define data modeling terms Describe E-R Model Identify entities and relations Represent entities and relations with diagrams WHAT IS DATA MODELING? A data model is a collection of concepts
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define data modeling terms Describe E-R Model Identify entities and relations Represent entities and relations with diagrams WHAT IS DATA MODELING? A data model is a collection of concepts
Requirements Engineering Process
 Requirements Engineering Process Requirement A description of a service that the system is expected to provide and the constraints under which it must operate. 1 Requirement Types Functional Requirement
Requirements Engineering Process Requirement A description of a service that the system is expected to provide and the constraints under which it must operate. 1 Requirement Types Functional Requirement
Requirements Elicitation
 Requirements Elicitation Introduction into Software Engineering Lecture 4 25. April 2007 Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen 1 Outline Motivation: Software Lifecycle
Requirements Elicitation Introduction into Software Engineering Lecture 4 25. April 2007 Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen 1 Outline Motivation: Software Lifecycle
System Analysis & design
 Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) Copyright 2014 Dr. Hossam Ragab 6 data model describes the data that flow through
Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) Copyright 2014 Dr. Hossam Ragab 6 data model describes the data that flow through
SIF8035. Events and System Requirements
 SIF8035 Lecture 4 DFD and PrM Events and System Requirements Events Occurrences at a specific time and place Trigger all system processing Requirement definition Determine relevant events External events
SIF8035 Lecture 4 DFD and PrM Events and System Requirements Events Occurrences at a specific time and place Trigger all system processing Requirement definition Determine relevant events External events
Chapter 4: Data Management
 Accounting Information Systems: Essential Concepts and Applications Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-Wing Chapter 4: Data Management Slides Authored by Somnath Bhattacharya, Ph.D.
Accounting Information Systems: Essential Concepts and Applications Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-Wing Chapter 4: Data Management Slides Authored by Somnath Bhattacharya, Ph.D.
Natural Language Specification
 REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2017/2018 Dr. Jörg Dörr Natural Language Specification Most Requirements are Described in Natural Language Free Text (Prose) In Word In Excel (Tabular) In RM-Tools In Sys-ML
REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2017/2018 Dr. Jörg Dörr Natural Language Specification Most Requirements are Described in Natural Language Free Text (Prose) In Word In Excel (Tabular) In RM-Tools In Sys-ML
Modeling. Slides by: Ms. Shree Jaswal. Slides by:ms. Shree Jaswal 1
 Modeling Slides by: Ms. Shree Jaswal Slides by:ms. Shree Jaswal 1 Model What is a model? a model is a simplification of reality Why do we model? we build models so that we can better understand the system
Modeling Slides by: Ms. Shree Jaswal Slides by:ms. Shree Jaswal 1 Model What is a model? a model is a simplification of reality Why do we model? we build models so that we can better understand the system
Data about data is database Select correct option: True False Partially True None of the Above
 Within a table, each primary key value. is a minimal super key is always the first field in each table must be numeric must be unique Foreign Key is A field in a table that matches a key field in another
Within a table, each primary key value. is a minimal super key is always the first field in each table must be numeric must be unique Foreign Key is A field in a table that matches a key field in another
*ANSWERS * **********************************
 CS/183/17/SS07 UNIVERSITY OF SURREY BSc Programmes in Computing Level 1 Examination CS183: Systems Analysis and Design Time allowed: 2 hours Spring Semester 2007 Answer ALL questions in Section A and TWO
CS/183/17/SS07 UNIVERSITY OF SURREY BSc Programmes in Computing Level 1 Examination CS183: Systems Analysis and Design Time allowed: 2 hours Spring Semester 2007 Answer ALL questions in Section A and TWO
Business Process Modelling
 CS565 - Business Process & Workflow Management Systems Business Process Modelling CS 565 - Lecture 2 20/2/17 1 Business Process Lifecycle Enactment: Operation Monitoring Maintenance Evaluation: Process
CS565 - Business Process & Workflow Management Systems Business Process Modelling CS 565 - Lecture 2 20/2/17 1 Business Process Lifecycle Enactment: Operation Monitoring Maintenance Evaluation: Process
Identify the guidelines for system development. Discuss the purpose of the activities performed in the analysis phase
 Discovering Computers 2010 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Define system development and list the system development phases Identify the guidelines for system development Discuss the importance
Discovering Computers 2010 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Define system development and list the system development phases Identify the guidelines for system development Discuss the importance
Object Oriented Modeling
 Overview UML Unified Modeling Language What is Modeling? What is UML? A brief history of UML Understanding the basics of UML UML diagrams UML Modeling tools 2 Modeling Object Oriented Modeling Describing
Overview UML Unified Modeling Language What is Modeling? What is UML? A brief history of UML Understanding the basics of UML UML diagrams UML Modeling tools 2 Modeling Object Oriented Modeling Describing
Requirements engineering
 engineering Chapter 4 1 Engineering in the textbook 4.1 Functional and non-functional 4.2 The software document 4.4 engineering processes 4.5 elicitation and analysis 4.3 specification 4.6 validation 4.7
engineering Chapter 4 1 Engineering in the textbook 4.1 Functional and non-functional 4.2 The software document 4.4 engineering processes 4.5 elicitation and analysis 4.3 specification 4.6 validation 4.7
Chapter 4 Objectives
 Chapter 4 Objectives Eliciting requirements from the customers Modeling requirements Reviewing requirements to ensure their quality Documenting requirements for use by the design and test teams 4.1 The
Chapter 4 Objectives Eliciting requirements from the customers Modeling requirements Reviewing requirements to ensure their quality Documenting requirements for use by the design and test teams 4.1 The
Requirements Analysis. Requirement analysis. Requirements analysis 3/11/14. Advanced Programming
 Requirements Analysis Advanced Programming 11 March 2014 Barbara Russo 11 Requirement analysis Understanding which services are required from the system and identifying the constraints on the system s
Requirements Analysis Advanced Programming 11 March 2014 Barbara Russo 11 Requirement analysis Understanding which services are required from the system and identifying the constraints on the system s
Lecture Notes. Structured Systems Analysis
 Lecture Notes Structured Systems Analysis Lecture 3 Structured Analysis & Data Flow Diagrams Written by Dr. Fred Grossman Copyright 1999 Fred Grossman All Rights Reserved Structured Systems Analysis Structured
Lecture Notes Structured Systems Analysis Lecture 3 Structured Analysis & Data Flow Diagrams Written by Dr. Fred Grossman Copyright 1999 Fred Grossman All Rights Reserved Structured Systems Analysis Structured
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Rajkot Unit-1
 Failure Rate Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Rajkot Unit-1 SOFTWARE (What is Software? Explain characteristics of Software. OR How the software product is differing than
Failure Rate Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Rajkot Unit-1 SOFTWARE (What is Software? Explain characteristics of Software. OR How the software product is differing than
SEEKING THE ACTUAL REASONS FOR THE "NEW PARADIGM" IN THE AREA OF IS ANALYSIS 2. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE "STRUCTURED APPROACH" IN IS DEVELOPMENT
 SEEKING THE ACTUAL REASONS FOR THE "NEW PARADIGM" IN THE AREA OF IS ANALYSIS Václav Řepa Prague University of Economics, W.Churchill sq. 4, 130 00 Praha 3, Czech Republic E-mail: REPA@VSE.CZ 1. INTRODUCTION
SEEKING THE ACTUAL REASONS FOR THE "NEW PARADIGM" IN THE AREA OF IS ANALYSIS Václav Řepa Prague University of Economics, W.Churchill sq. 4, 130 00 Praha 3, Czech Republic E-mail: REPA@VSE.CZ 1. INTRODUCTION
Requests Charges. Librarian. University affiliated patrons students, faculty, staff. Media Center Staff
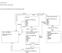 Catherine Rutan INFO 530-901 Dr. Valerie Yonker Circulation of Media Materials from University Media Center: Requests Charges Librarian Circulation Desk Attendant Inquires University ID # (Primary Key)
Catherine Rutan INFO 530-901 Dr. Valerie Yonker Circulation of Media Materials from University Media Center: Requests Charges Librarian Circulation Desk Attendant Inquires University ID # (Primary Key)
From Analysis to Design. LTOOD/OOAD Verified Software Systems
 From Analysis to Design 1 Use Cases: Notation Overview Actor Use case System X System boundary UCBase «extend» UCExt Actor A UCVar1 UCVar2 Extending case Generalization «include» Actor B UCIncl Included
From Analysis to Design 1 Use Cases: Notation Overview Actor Use case System X System boundary UCBase «extend» UCExt Actor A UCVar1 UCVar2 Extending case Generalization «include» Actor B UCIncl Included
Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications (IEEE)
 Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications (IEEE) Author: John Doe Revision: 29/Dec/11 Abstract: The content and qualities of a good software requirements specification (SRS) are described
Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications (IEEE) Author: John Doe Revision: 29/Dec/11 Abstract: The content and qualities of a good software requirements specification (SRS) are described
Action-Oriented Design Methods
 Action-Oriented Design Methods Prof. Dr. U. Aßmann Technische Universität Dresden Institut für Software- und Multimediatechnik Gruppe Softwaretechnologie http://www-st.inf.tu-dresden.de Softwaretechnologie
Action-Oriented Design Methods Prof. Dr. U. Aßmann Technische Universität Dresden Institut für Software- und Multimediatechnik Gruppe Softwaretechnologie http://www-st.inf.tu-dresden.de Softwaretechnologie
(Murlidhar Group of Institutions,Bhavnagar Road, Rajkot) by:-assit. Prof. Vijay Vora (SOOADM) MCA-III
 Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Design. Introduction
 Design Introduction a meaningful engineering representation of some software product that is to be built. can be traced to the customer's requirements. can be assessed for quality against predefined criteria.
Design Introduction a meaningful engineering representation of some software product that is to be built. can be traced to the customer's requirements. can be assessed for quality against predefined criteria.
Systems Analysis and Design
 Systems Analysis and Design Michael Brydon Summer 2003 Slide 1 Introduction to the Course Course structure Lectures: material from the Dennis text Labs: in-lab assignments, demonstrations, and consulting
Systems Analysis and Design Michael Brydon Summer 2003 Slide 1 Introduction to the Course Course structure Lectures: material from the Dennis text Labs: in-lab assignments, demonstrations, and consulting
2. Introduction to UML & Discussion of Related S.E.
 2. Introduction to UML & Discussion of Related S.E. 2. Introduction to UML...1 2.1 Context of UML...2 2.1.1 A classical view of specification & design, & how they are related...2 2.1.2 Examples of requirement
2. Introduction to UML & Discussion of Related S.E. 2. Introduction to UML...1 2.1 Context of UML...2 2.1.1 A classical view of specification & design, & how they are related...2 2.1.2 Examples of requirement
Software Modeling & Analysis. - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis. Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO
 Software Modeling & Analysis - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr References Modern Structured Analysis, Edward Yourdon, 1989. Introduction to System Analysis
Software Modeling & Analysis - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr References Modern Structured Analysis, Edward Yourdon, 1989. Introduction to System Analysis
THE ENTITY- RELATIONSHIP (ER) MODEL CHAPTER 7 (6/E) CHAPTER 3 (5/E)
 THE ENTITY- RELATIONSHIP (ER) MODEL CHAPTER 7 (6/E) CHAPTER 3 (5/E) 2 CHAPTER 7 OUTLINE Using High-Level, Conceptual Data Models for Database Design Entity-Relationship (ER) model Popular high-level conceptual
THE ENTITY- RELATIONSHIP (ER) MODEL CHAPTER 7 (6/E) CHAPTER 3 (5/E) 2 CHAPTER 7 OUTLINE Using High-Level, Conceptual Data Models for Database Design Entity-Relationship (ER) model Popular high-level conceptual
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay. Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II)
 Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
The software lifecycle and its documents
 The software lifecycle and its documents Supplementary material for Software Architecture course B. Meyer, May 2006 Lifecycle models Origin: Royce, 1970, Waterfall model Scope: describe the set of processes
The software lifecycle and its documents Supplementary material for Software Architecture course B. Meyer, May 2006 Lifecycle models Origin: Royce, 1970, Waterfall model Scope: describe the set of processes
Requirements Specifications & Standards
 REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2014/2015 Dr. Jörg Dörr Requirements Specifications & Standards AGENDA Standards & Templates Natural Language Requirements Specification with Conceptual Models Suitable
REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2014/2015 Dr. Jörg Dörr Requirements Specifications & Standards AGENDA Standards & Templates Natural Language Requirements Specification with Conceptual Models Suitable
Lecture 6: Requirements Engineering
 Lecture 6: Requirements Engineering Software System Design and Implementation ITCS/ITIS 6112/8112 001 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte
Lecture 6: Requirements Engineering Software System Design and Implementation ITCS/ITIS 6112/8112 001 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte
EXAM PREPARATION GUIDE
 EXAM PREPARATION GUIDE PECB Certified ISO 21500 Lead Project Manager The objective of the PECB Certified ISO 21500 Lead Project Manager examination is to ensure that the candidate has the knowledge and
EXAM PREPARATION GUIDE PECB Certified ISO 21500 Lead Project Manager The objective of the PECB Certified ISO 21500 Lead Project Manager examination is to ensure that the candidate has the knowledge and
1.2 Building the Right System. Identifying Needs & Expectations. Where to look for needs & expectations? or Who are the stakeholders?
 These slides are designed for presentation, not for stand-alone reading. 1.2 Building the Right System Elizabeth Bjarnason elizabeth@cs.lth.se Department Of Computer Science Lund University Identifying
These slides are designed for presentation, not for stand-alone reading. 1.2 Building the Right System Elizabeth Bjarnason elizabeth@cs.lth.se Department Of Computer Science Lund University Identifying
Process Modelling. Data flow Diagrams. Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams. CSE Information Systems 1
 CSE104 - Information s 1 Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams Process Modelling Process modelling aims to graphically represent the processes which capture, manipulate, store and distribute data. data
CSE104 - Information s 1 Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams Process Modelling Process modelling aims to graphically represent the processes which capture, manipulate, store and distribute data. data
Functional Design of Web Applications. (partially, Chapter 7)
 Functional Design of Web Applications (partially, Chapter 7) Functional Design: An Overview Users of modern WebApps expect that robust content will be coupled with sophisticated functionality The advanced
Functional Design of Web Applications (partially, Chapter 7) Functional Design: An Overview Users of modern WebApps expect that robust content will be coupled with sophisticated functionality The advanced
MTAT Introduction to Databases
 MTAT.03.105 Introduction to Databases Lecture #4 Entity-Relationship Modelling Ljubov Jaanuska (ljubov.jaanuska@ut.ee) Lecture 3. Summary So far we have been dealing with a relational database (PCA.db)
MTAT.03.105 Introduction to Databases Lecture #4 Entity-Relationship Modelling Ljubov Jaanuska (ljubov.jaanuska@ut.ee) Lecture 3. Summary So far we have been dealing with a relational database (PCA.db)
1. i. What are the 3 major components of a information system and show their relationship input output
 Higher National Diploma in Information Technology First Year, Second semesterexamination-2011 IT2005: System Analysis and Design Answer Script No. of pages: 11 1. i. What are the 3 major components of
Higher National Diploma in Information Technology First Year, Second semesterexamination-2011 IT2005: System Analysis and Design Answer Script No. of pages: 11 1. i. What are the 3 major components of
Requirements Validation and Negotiation
 REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2015/2016 Eddy Groen Requirements Validation and Negotiation AGENDA Fundamentals of Requirements Validation Fundamentals of Requirements Negotiation Quality Aspects of
REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE 2015/2016 Eddy Groen Requirements Validation and Negotiation AGENDA Fundamentals of Requirements Validation Fundamentals of Requirements Negotiation Quality Aspects of
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS6403 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING II year/ IV sem CSE (Regulation 2013) UNIT 1- SOFTWARE PROCESS AND PROJECT
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS6403 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING II year/ IV sem CSE (Regulation 2013) UNIT 1- SOFTWARE PROCESS AND PROJECT
COIT20248: Information Systems Analysis and Design Term 2, 2015 Assignment 2. Lecturer: Dr. Meena Jha Tutor: Aries Tao
 COIT20248: Information Systems Analysis and Design Term 2, 2015 Assignment 2 Lecturer: Dr. Meena Jha Tutor: Aries Tao Prepared by: AXXXX XXXX: S0XXXXXX AXXXX MXXXXX: BisXXXXX BaXXXX: S0XXXXX S02XXXX SXXXXX
COIT20248: Information Systems Analysis and Design Term 2, 2015 Assignment 2 Lecturer: Dr. Meena Jha Tutor: Aries Tao Prepared by: AXXXX XXXX: S0XXXXXX AXXXX MXXXXX: BisXXXXX BaXXXX: S0XXXXX S02XXXX SXXXXX
CS487 Midterm Exam Summer 2005
 1. (4 Points) How does software differ from the artifacts produced by other engineering disciplines? 2. (10 Points) The waterfall model is appropriate for projects with what Characteristics? Page 1 of
1. (4 Points) How does software differ from the artifacts produced by other engineering disciplines? 2. (10 Points) The waterfall model is appropriate for projects with what Characteristics? Page 1 of
T52-Software Engineering
 T52-Software Engineering UNIT II System Engineering: Requirements elicitation - Need for SRS - Requirement Process- Problem Analysis Informal Approach - Cardinality and modality Entity / Relationship diagram
T52-Software Engineering UNIT II System Engineering: Requirements elicitation - Need for SRS - Requirement Process- Problem Analysis Informal Approach - Cardinality and modality Entity / Relationship diagram
What is a Data Model?
 What is a Data Model? Overview What is a Data Model? Review of some Basic Concepts in Data Modeling Benefits of Data Modeling Overview What is a Data Model? Review of some Basic Concepts in Data Modeling
What is a Data Model? Overview What is a Data Model? Review of some Basic Concepts in Data Modeling Benefits of Data Modeling Overview What is a Data Model? Review of some Basic Concepts in Data Modeling
Oracle Data Modelling & Database Design Course Content:35-40hours
 Oracle Data Modelling & Database Design Course Content:35-40hours Course Outline Introduction to Modeling List the reasons why modeling is important Describe the phases of the Database and Application
Oracle Data Modelling & Database Design Course Content:35-40hours Course Outline Introduction to Modeling List the reasons why modeling is important Describe the phases of the Database and Application
